Abstract
This paper described an improved method for high-throughput and sensitive determination of zearalenone and its five metabolites (zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, α-zearalanol and β-zearalanol) in human serum. Serum samples were measured both before and after enzyme hydrolysis to assess the free and total amount of each compound by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) in multi reaction monitoring (MRM) mode following off-line 96-well μElution solid-phase extraction (SPE). All the analytes were completely separated on a C18 column within 6 min. It enabled multi-sample preparation at the same time eliminating tedious evaporation and reconstitution steps, allowing 96 (one plate) samples to be processed and analyzed within 24 h. Using an isotope labelled internal standard (13C-ZEN), high recoveries were achieved for all the compounds in the range 91.6%–119.5%, with intra-day and inter-day relative standard deviations (RSDs) of less than 8%. The limits of detection (LOD) and the limits of quantification (LOQ) were 0.02–0.06 ng mL−1 (0.6–2 fmol) and 0.1–0.2 ng mL−1 (3–6 fmol), respectively, demonstrating a notable enhancement in sensitivity compared to the existing methods. The validated method was applied to the analysis of paired urine and serum samples collected from 125 healthy individuals in Henan Province, locating in the middle area of China. ZEN metabolites in human serum were significantly lower than those in urine. Only one serum sample was positive for ZEN after enzyme digestion, whereas at least one of ZEN biomarkers was detected in 75.2% of the paired urine samples. Some comparison and discussion were also included in this paper.
1. Introduction
Zearalenone (ZEN) is a naturally occurring mycotoxin produced by several species of Fusarium molds [1,2]. Many crops can be easily infested by these molds and thereby contaminated by ZEN. Hence, humans and animals could be at high risk of being exposed to ZEN through the intake of contaminated food or feed. ZEN showed adverse effects on reproductive systems of mammalian species [2,3,4,5], despite its relatively low acute toxicity. According to some reports regarding blood parameters, ZEN was also evidenced to be haematotoxic and hepatotoxic [3,6,7].
After ingestion, ZEN is primarily metabolized to two hydroxyl isomers α-zearalenol (α-ZOL) and β-zearalenol (β-ZOL) [1,8,9], which can be subsequently reduced to α-zearalanol (α-ZAL) and β-zearalanol (β-ZAL), respectively [10,11]. A small portion of the α-ZAL is also found to be converted to β-ZAL and zearalanone (ZAN) [12]. Besides, these metabolites as well as ZEN itself can be partially conjugated with glucuronic acid and substantially excreted in bile. The glucuronide of ZEN may also be re-absorbed and metabolized further by intestinal mucosal cells, ultimately entering the liver and the systemic circulation via the portal blood supply [13].
Humans are easily exposed to ZEN through the food consumption [14]. For the past decades, exposure assessment of mycotoxins was conventionally performed by combining the occurrence data with the food consumption data [15,16,17,18]. However, due to the heterogeneous distribution of mycotoxins in food and variability of individual toxicokinetics, this approach is considered to be not quite reliable. Hence, an internal exposure strategy directly detecting mycotoxin biomarkers in biological fluids could be more accurate and reliable for assessment purpose [3]. It seems important to develop a method to satisfy the current need.
A number of approaches to quantify ZEN and its metabolites have been proposed for biological samples in last decade, which are commonly performed with gas or liquid chromatography coupled to mass or tandem mass spectrometry [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Among these methods, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) gradually became a prior technique for mycotoxin analysis in biological samples for its high selectivity and sensitivity. However, since the scarcity of human serum or plasma samples, some of the methods was applied to analyze animal serum or plasma [28,29]. And some of the applications limited their detection to ZEN and one (ZAN) [30] or two (α-ZOL, β-ZOL) [31] metabolites. Furthermore, ZEN and its metabolites were easy to form conjugates, such as ZEN-14-glucuronic acid (ZEN-14-GlcA), ZEN-74-GlcA and α/β–ZOL-14-GlcA in vivo. Some works published previously [20,27] failed to monitor the conjugated forms. A strategy involving enzymatic hydrolysis was then developed and applied to chicken and pig serum [24]. However, the defects of labor-intensive and time-consuming operation (liquid–liquid extractions, solid phase extraction, evaporation and reconstitution) restricted its further application in large-scale sample analysis. Recently, a method has been successfully established to determine the total (free + conjugated) amount of ZEN and its metabolites in human serum, involving enzymatic digestion, sample cleanup and UPLC-MS/MS analysis [32]. This method achieved higher sensitivity but still had drawback of time-consuming due to the step of evaporation and reconstitution. To address such an issue, a material (96-well μElution plate) for high-throughput sample preparation was employed in this work, allowing for the simultaneous preparation of multiple samples, avoiding evaporation step and meanwhile reducing the time and labor consumed.
The aim of this work was to develop a high-throughput and sensitive method for the quantitation of ZEN and its biomarkers (both total and free) in serum, using UPLC-MS/MS technique combined with 96-well μElution plate. The method provided the capability of simultaneous multi-sample processing and chromatographic baseline separation of all target analytes, highly improving the efficiency of human biomonitoring. The proposed method was applied to the analysis of 125 human serum samples from healthy volunteers whose paired urine samples are also available.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
The certificated standard solutions of ZEN, ZAN, α-ZAL, β-ZAL, α-ZOL, β-ZOL and isotope labeled internal standard (IS) 13C18-ZEN (25 μg mL−1) were from Romer Labs (Tulln, Austria). Beta-glucuronidase (produced from E.coli) used for enzyme digestion was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (MO, USA). Acetonitrile and methanol were of LC-MS grade. Formic acid, acetic acid and ammonia acetate (HPLC grade) were supplied by Fisher Scientific (Leicestershire, United Kingdom). Potassium phosphate dibasic and potassium phosphate monobasic (analytical grade) were supplied by Sinopharm (Beijing, China). A Milli-Q system (Millipore Corp., Bedford, MA) provided deionized water (18.2 MΩ cm) for all study. A mixed standard solution was prepared with concentration of 1 μg mL−1 for each analyte and stored at 4 °C. The working solutions of mixed standard were prepared in initial mobile phase at the beginning of each batch of measurement. The enzyme solution was freshly prepared by dissolving 14.4 mg β-glucuronidase (694300 U g solid−1) in 10 mL of 0.075 mol L−1 phosphate buffer (pH 6.8, prepared with potassium phosphate monobasic and potassium phosphate dibasic) according to the instruction of supplier on the day of use. The Oasis® PRiME HLB 96-well μElution plate (3 mg sorbent per well) were purchased from Waters (Milford, MA, USA).
2.2. Sample Collection and Storage
Serum samples were collected from 125 healthy volunteers in Henan province, China. A written and approved informed consent was given from all the participants; and the proposal was approved by the ethics committee of CFSA. Samples were numbered and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Since the lack of commercial blank serum matrix, samples with undetected levels of the analytes were selected as blank matrices in method evaluation and quality control (QC).
2.3. Standard Solution and QC Samples
The calibration standard solutions at levels of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 ng mL−1 for each analyte were made by serial dilutions of the mixed standard solution. Each calibration standard solution contained 25 μg mL−1 of 13C18-ZEN as internal standard. QC samples were prepared at low, medium and high concentrations (0.5, 1 and 5 ng mL−1) by spiking blank serum matrix with standard mixture.
2.4. Sample Preparation
For the free analyte.
After thawed at room temperature, serum samples were centrifuged at 8000×g for 20 min at 4 °C. 13C18-ZEN was added to 100 μL supernatant as internal standards with final concentration of 25 μg mL-1, followed by a dilution with 100 μL of phosphate buffer (pH 6.8, 0.075 mol L−1). Under appropriate vacuum conditions, Oasis® PRiME HLB μElution plate was pretreated by methanol and water (500 μL of each) for conditioning and then loaded with the diluted samples which was allowed to slowly flow through the cartridge at a rate about 0.5 mL min−1. Subsequently, the wells were washed with 500 μL of water and then 500 μL of methanol/water (1/1, v/v) to remove interferences. Finally, the analytes absorbed to the cartridge were eluted twice with 50 μL of methanol each and collected. After a 1:1 dilution with water, the solution was injected for UPLC-MS/MS analysis.
For the total (free + conjugate) analyte.
After being thawed, centrifuged and spiked with internal standards, 500 μL of the serum sample was mixed with 500 μL enzyme solution containing 500 units of β-glucuronidase and shaken in a water-bath at 37 °C over night. Then the resulted solution was centrifuged (8000×g; 20 min; 4 °C); and 200 μL of the supernatant was loaded onto the preconditioned (as mentioned above) PRiME HLB μElution plate. The following steps were exactly the same as described above.
2.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
An ACQUITY UPLC™ I-Class system (Waters, MA, USA) combined with Xevo® TQ-S tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer (Waters, MA, USA) was used for the analysis. Instrument control and data collecting and processing were carried out using Masslynx software (version 4.1).
The target compounds were separated on a UPLC column (CORTECS™ C18 Column, 2.1×100 mm, 1.6 μm) in combination with a guard column of the same type under a gradient program. Water (solvet A) and acetonitrile/methanol (20/80, v/v, solvent B) were used as mobile phase, with a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. A gradient elution started with 50% B and then was performed as following: 0–4 min (linear gradient to 66% B), 4–4.1 min (immediately increased to 90%), 4.1–6.0 min (90% B), 6.0–6.1 min (returned to 50% B), 6.1–8.0 min (50% B). The column was maintained at a constant temperature of 40 °C and the injection volume was 10 μL.
The detection was performed on a Xevo® TQ-S tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with ESI source. The instrument parameters were optimized by infusing standard solution of each analyte in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Ion spray voltage was set to −2.8 kV in negative mode. Optimum cone voltages (CV) and collision energies (CE) for a scheduled MRM transition were shown in Table 1. The source temperature was set to 150 °C. Nitrogen was used as the cone gas and desolvation gas at settings of 150 L h−1 and 900 L h−1, respectively. Argon was used as the collision gas (0.15 mL/min).

Table 1.
MS/MS transitions of ZEN and its metabolites.
2.6. Method Validation
The linearity, selectivity, accuracy, precision, sensitivity and carry over were evaluated refer to the guideline for bioanalytical assay validation defined by the US Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) [13]. The method recovery (RM) which served as accuracy was evaluated at three spiking levels (0.5 ng/mL, 1.0 ng/mL and 5.0 ng/mL) in blank serum with internal standard correction of 13C18-ZEN. To determine the apparent recovery (RA), extraction recovery (RE) and matrix effects (signal suppression/enhancement, SSE), three types of calibration curves were established as follows: standard calibration curve prepared in neat solvent as Set I, matrix-matched standard curve using blank serum matrices fortified before and after sample preparation as Set II and Set III, respectively. The RA, RE and SSE were determined by dividing the slope of Set II by the slope of Set I, the slope of Set II by the slope of Set III and the slope of Set III by the slope of Set I, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Mass Conditions
The MS/MS condition was optimized on a Xevo® TQ-S by individual infusion of each compound. To obtain the most intensive response of precursor ions, ionization mode, cone gas flow, desolvation gas flow and temperature, source temperature, capillary voltage and cone voltage were manually optimized in steps. Negative mode with capillary voltage set at −2.8 kV was adopted for all the analytes; other parameters were recommended in the method section. After that, the collision energy (CE) for each compound was tuned up individually to generate the most intensive and stable product ions. Two product ions were selected and optimized for each compound in MRM mode, one for quantification and another for identification, as listed in Table 1.
3.2. Chromatographic Separation
The main factors that affect chromatographic behavior were investigated aiming for a sufficient chromatographic separation, including UPLC columns, mobile phase, additives and gradient program. Waters CORTECS™ C18 UPLC column provided the optimal resolution and stability for all compounds and was chosen for further studies. Several combinations of mobile phase were separately evaluated, that is, the additives (formic acid, acetic acid, ammonium formate or ammonium acetate) in water, the organic modifier (methanol or acetonitrile) and the gradient elution program. Common additives like formic acid, ammonium formate, acetic acid and ammonium acetate gave slight influence on intensity and no contribution for separation. However, the organic modifier considerably helped the separation. ZEN, ZAN and α-ZOL were hardly separated completely while using methanol or acetonitrile alone as the organic modifier, which was also discussed previously [33]. Eventually, a mixture of acetonitrile and methanol (20/80, v/v) was employed and provided a complete baseline separation of all compounds within an 8-min run time. A chromatogram of standards mixture of all analytes was presented in Figure 1.
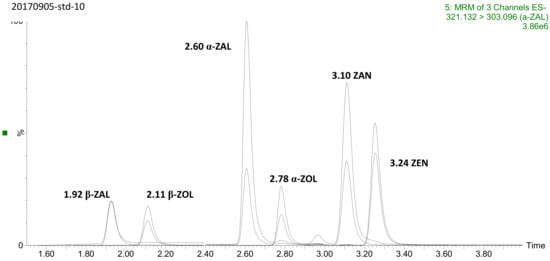
Figure 1.
The overlaid chromatography of standard solution (10 ng mL-1 of each analyte).
3.3. Sample Preparation
As an accepted extraction method, solid-phase extraction (SPE) was widely used in the field of ZEN analysis. However, high labor-intensity and time-consuming limited the further application in large-scale analysis. To address such issues, a high-throughput sample preparation method using a 96-well μElution plate was introduced to extract ZEN and its derivatives from human serum samples. The main parameters that affect extraction procedure were optimized including loading, washing and elution conditions.
Phospholipids, carbohydrates, mineral salts and other metabolites in the serum may cause the endogenous interferences or the risk of cartridge clogging. Hence, all samples were 2-fold diluted with phosphate buffer or β-glucuronidase solvent before loading onto the plate.
The washing and elution buffer directly affected the matrix effect and recovery. Spiked serum samples (both before and after enzymatic digestion) with the concentration of 10 ng mL−1 for each analyte were used in the test of selection. To remove the salts and other polar interferences in serum, the plate was washed with 500 μL of water after loading as a weak wash step. For further cleanup, a selection of strong wash solvent was performed by washing the cartridge with methanol/water buffer (ranged from 5% to 100% methanol, v/v) and the effluent were collected for analysis of target compounds. All the analytes started to flow out at 50% methanol and were completely eluted by pure methanol. Hence, an additional wash with 500 μL of 50% methanol as a strong wash step was adopted before the final elution with 100% methanol. Varying elution volumes of 25, 50, 75, 100, 150 and 200 μL were evaluated as well to obtain high recoveries and less interference. The maximum recoveries were achieved for all analytes with the elution volume of 100 μL. To avoid the solvent effect and achieve sharp peaks, the collected eluent needed to be diluted with 100 μL of water before instrumental analysis. Finally, the optimized extraction procedure was obtained as described in the method section.
To determine the total amount of each analyte including the conjugated forms, enzymatic hydrolysis is necessary. Since ZEN biomarkers in body fluids commonly occurred in the low ng mL−1 range, there was no need to worry about the adequacy of enzyme. On the other hand, the enzyme amount might should be optimized to minimize the exogenous interferences that influence analyte extraction and matrix effect. Spiked serum samples (10 ng mL−1 for each analyte) together with varying levels of enzyme (100, 200, 500, 1000, 2000 and 5000 U mL−1) were incubated at 37 °C for 18 h. The recoveries of five analytes, except for β–ZAL, reduced in different degree while the enzyme concentration up to 2000 U mL−1, as shown in Figure 2. Therefore, the concentration of 1000 U mL−1 was chosen in further study.
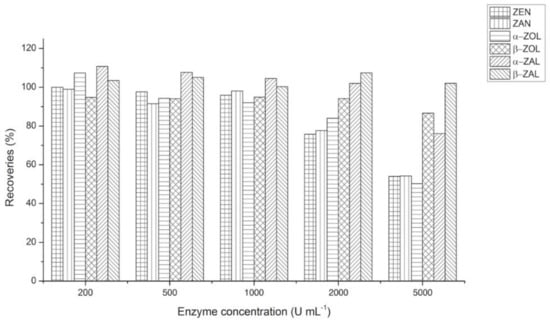
Figure 2.
Optimization of enzyme concentration.
The sample preparation with the PRiME HLB μElution plate eliminated laborious steps of evaporation and reconstitution. Under the optimized condition, this method drastically improved the efficiency, allowing 96 samples to be processed in 1 h with good recoveries and well controlled matrix interference.
3.4. Method Validation
The validation in terms of linearity, selectivity, accuracy (RM), precision (intra- and inter-day variability), sensitivity (LOD and LOQ) and carry over was conducted according to the guidelines.
The linearity was tested by a calibration curve including eight levels of 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 and 50 ng mL−1. The calibration curve was built by plotting the peak area ratio of each analyte to IS versus the concentration ratio of analyte to IS with a linear regression weighting factor of 1/concentration. Regression coefficients (R2) of the calibration curves were greater than 0.9978 with deviations less than 12% for all concentrations, indicating a good linearity within the ranges defined.
The mothed should be able to differentiate the target analyte and endogenous components in matrices. The selectivity was proved using 8 individual blank serum samples, which were analyzed before and after fortified with target analytes at levels close to the LOQs. No obvious interferences from endogenous components were observed at the retention time of each analyte, as shown in Figure 3. In addition, the complete chromatographic separation of all the target compounds provided further evidence for the high specificity of the method.
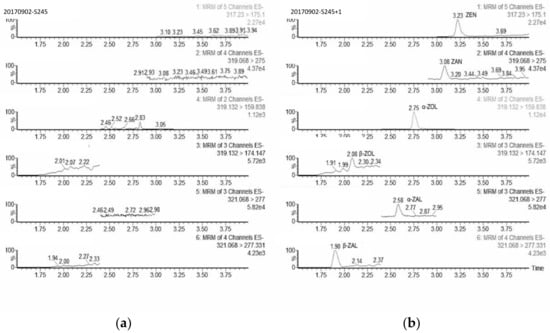
Figure 3.
The chromatograms of blank serum sample (a) and spiked sample at 0.1 ng mL-1 (b).
The Sensitivity (LOD/LOQ) of the assay were obtained by analyzing spiked serum samples at low levels. The LOD and LOQ for each analyte were determined as signal to noise ratio (S/N) greater than 3 and 10, which ranged 0.02–0.06 ng mL−1 and 0.1 and 0.2 ng mL−1 respectively for all target compounds, as given in Table 2. The values demonstrated a high improvement in sensitivity [24,27,28,29,30].

Table 2.
Extraction recovery, matrix effect, accuracy, precision and sensitivity of the method.
The accuracy and precision were investigated from six replicates of fortified serum samples at three levels (0.5, 1.0 and 5.0 ng/ mL) once a day on three consecutive days. Method recovery (RM) which had been corrected by IS were from 91.6% to 123.6% for all the analytes at three concentrations (Table 2). The relative standard deviation (RSD) of intra-day and inter-day, representing the precision of the method, were ranged 2.53%–5.99% and 3.62%–8.22%, respectively. Besides, extraction recovery (RE) of sample preparation step and the matrix effect (signal suppression/enhancement, SSE) of instrument analysis step showed great results, meaning that acceptable accuracy can also be achieved even without IS compensation.
No carry-over was observed within the assay which was performed by injecting three blank solvents after injection of a high concentration standard at 100 ng mL−1.
3.5. Method Application to Real Samples
Using the proposed method, 125 serum samples collected from healthy volunteers in Henan Province were measured. For each volunteer, the paired serum and urine samples were collected and the 125 urine samples have already been tested and included in our recent study on ZEN internal exposure assessment that was based on a total of 301 urine samples [33].
For the paired urine samples, ZEN, α-ZOL, β-ZOL and ZAN were detected. ZEN showed the highest detection rate of 75.2%, followed by β-ZOL (21.6%), α-ZOL (5.6%) and ZAN (1.6%). Alpha-ZAL and β-ZAL were absent in all these urine samples. The mean concentration and range of each analyte were as following: ZEN (mean 0.31 ng/mL, range ND~3.68 ng/mL), β-ZOL (mean 0.084 ng/mL, range ND~1.32 ng/mL), α-ZOL (mean 0.051 ng/mL, range ND~2.64 ng/mL) and ZAN (mean 0.019 ng/mL, range ND~0.518 ng/mL). The results were comparable with those reported for other countries, normally with the mean concentration between 0.009~1.82 ng/mL [22,23,26,32,33,34,35,36,37].
On the contrary, among the serum samples, only one was found to be positive for ZEN after enzyme digestion, whose chromatogram was presented in Figure 4. ZAN, α-ZOL, β-ZOL, α-ZAL and β-ZAL were all absent. It can be attributed to the rapid clearance and excretion of ZEN from blood after oral intake.
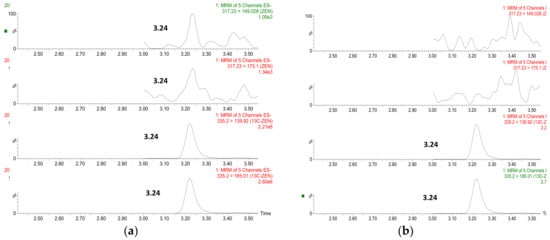
Figure 4.
Chromatograms of a positive sample (a) and a negative sample (b).
Up to now, very limited data are available in this area as collected in Table 3. ZEN and its metabolites were hardly detected in human serum or plasma [32,38], except for some patients [39,40]. They were commonly detected in animal serum/plasma after oral administration of high amount of ZEN [4,24,28,29]. Compared to theses previously reported works, the method developed here possessed a higher sensitivity for ZEN and its derivatives in blood, which can be applicable for disease research and toxicokinetic study. Additionally, the results of paired serum-urine samples in this study suggested that for ZEN biomonitoring and internal exposure study for healthy people, urine would be a preferred medium because of the higher concentration and longer lifetime.

Table 3.
Occurrence of ZEN biomarkers in human serum/plasma.
4. Conclusions
A sensitive and high-throughput LC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for the analysis of ZEN and its five metabolites in serum samples using 96-well PRiME HLB μElution plate. It provided a simple and concurrent multiple sample treatment strategy without evaporation and reconstitution steps. The developed method significantly improved sensitivity and selectivity and reduced the labor-intensity, time consumption and waste generated at the same time. Although high sensitivity and good recoveries were achieved for all the analytes, ZEN and its derivatives were hardly detected in serum samples from healthy subjects due to their fast clearance and excretion from blood. The timing of sampling after oral intake may strongly affect the residue levels of ZEN biomarkers in serum.
Author Contributions
Methodology, D.S., C.L. and S.Z.; validation, Z.G.; formal analysis, D.S. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S. and C.L.; writing—review and editing, S.Z. and Y.Y.G.; supervision, Y.Z.; project administration, Y.Y.G. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, S.Z. and Y.W.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1602600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871723) and CFSA “523” High Level Talents Development Project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Scott, P.M.; Watanabe, H. Risk assessment of the mycotoxin zearalenone. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1987, 7, 253–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañés, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulation and intake of zearalen-one: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, S.; Dänicke, S.; Schnurrbusch, U. The effect of increasing concentrations of Fusarium toxins in the diets for piglets on histological parameters of the uterus. Mycotoxin Res. 2003, 19, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minervini, F.; Giannoccaro, A.; Cavallini, A.; Visconti, A. Investigations on cellular proliferation induced by zearalenone and its derivatives in relation to the estrogenic parameters. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 159, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, K.; Chekir, L.; Creppy, E.E.; Ellouz, F.; Bacha, H. Zearalenone induces modifications in haematological and biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicon 1996, 34, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concová, E.; Laciaková, A.; Pástorová, B.; Seidel, H.; Kovác, G. The effect of zearalenone on some enzymatic parameters in rabbits. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 121, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, M.L.; Prelusky, D.B.; Koritz, G.D.; Hartin, K.E.; Buck, W.B.; Trenholm, H.L. Biliary excretion and enterohepatic cycling of zearalenone in immature pigs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1993, 121, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmuson, A.E.; Scahill, B.G.; West, D.M. Natural zeranol (α-Zearalanol) in the urine of pasture-fed animals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videmann, B.; Mazallon, M.; Tep, J.; Lecoeur, S. Metabolism and transfer of the mycotoxin zearalenone in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.G.; McEvoy, J.D.G.; Hewitt, S.A.; Cannavan, A.; Blanchflower, W.J.; Elliott, C.T. Zeranol is formed from Fusarium spp. toxins in cattle in vivo. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migdalof, B.H.; Dugger, H.A.; Heider, J.G.; Coombs, R.A.; Terry, M.K. Biotransformation of zeranol: Disposition and metabolism in the female rat, rabbit, dog, monkey and man. Xenobiotica 1983, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001.
- Peraica, M.; Rasic, D.; Milicevic, D. Principles of Risk Assessment of Mycotoxins in Food and Feed. In Proceedings of the International 57th Meat Industry Conference—Meat and Meat Products—Perspectives of Sustainable Production, Belgrade, Serbia, 10–12 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.Y.; De Saeger, S. (Eds.) Determining Mycotoxins and Mycotoxigenic Fungi in Food and Feed; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Portolés, T.; Ripollés, C.; Sancho, J.V.; Yusà, V.; Marín, S.; Hernández, F. Development of sensitive and rapid analytical methodology for food analysis of 18 mycotoxins included in a total diet study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 783, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, F.; Nasreddine, L.; Hilan, C.; Bartosik, M.; Parent-Massin, D. Dietary exposure to aflatoxins, ochratoxin A and deoxynivalenol from a total diet study in an adult urban Lebanese population. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 73, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirot, V.; Fremy, J.M.; Leblanc, J.C. Dietary exposure to mycotoxins and health risk assessment in the second French total diet study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blokland, M.H.; Sterk, S.S.; Stephany, R.W.; Launay, E.M.; Kennedy, D.G.; Van Ginkel, L.A. Determination of resorcylic acid lactones in biological samples by GC-MS. Discrimination between illegal use and contamination with fusarium toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songsermsakul, P.; Sontag, G.; Cichna-Markl, M.; Zentek, J.; Razzazi-FaZOLi, E. Determination of zearalenone and its metabolites in urine, plasma and faeces of horses by HPLC-APCI-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 843, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Ediage, E.N.; Wu, A.; DeSaeger, S. Development and application of salting-out assisted liquid/liquid extraction for multi-mycotoxin biomarkers analysis in pig urine with high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matraszek-Zuchowska, I.; Wozniak, B.; Zmudzki, J. Determination of zeranol, taleranol, zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol and zearalenone in urine by LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. 2013, 30, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhassen, H.; Jiménez-Díaz, I.; Ghali, R.; Ghorbel, H.; Molina-Molina, J.M. Validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of zearalenone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, α-zearalanol, β-zearalanol and zearalanone in human urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 962, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baerea, S.; Osselaere, A.; Devreese, M.; Vanhaeckeb, L.; De Backera, P.; Croubels, S. Development of a liquid–chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry method for the quantitative determination of zearalenone and its major metabolites in chicken and pig plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 756, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandera, E.V.; Chandran, U.; Buckley, B.; Lin, Y.; Isukapalli, S.; Marshal, I.; King, M.; Zarbl, H. Urinary mycoestrogens, body size and breast development in New Jersey girls. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5221–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediagea, E.N.; Di Mavungua, J.D.; Song, S.Q. A direct assessment of mycotoxin biomarkers in human urine samples by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2012, 741, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezina, U.; Valenta, H.; Rempe, I.; Kersten, S.; Humpf, H.U.; Dänicke, S. Development of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of zearalenone, deoxynivalenol and their metabolites in pig serum. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devreese, M.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Quantitative determination of several toxicological important mycotoxins in pig plasma using multi-mycotoxin and analyte-specific high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1257, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osselaere, A.; Devreese, M.; Goossens, J.; Vandenbroucke, V.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Toxicokinetic study and absolute oral bioavailability of deoxynivalenol, T-2 toxin and zearalenone in broiler chickens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.S.; Hong, S.H.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.B.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Yoo, S.D. Determination of zearalenone by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, D.; Chuturgoon, A.A.; Nevines, E.; Manickum, T.; Deppe, W.; Dutton, M.F. The quantitative analysis of zearalenone and its derivatives in plasma of patients with breast and cervical cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, S.C.; Churchwell, M.I.; Doerge, D.R.; Teeguarden, J.G. Urine and serum biomonitoring of exposure to environmental estrogens II: Soy isoflavones and zearalenone in pregnant women. Food Chem. Toxicl. 2016, 95, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Deng, C.L.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.D.; Gong, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.N. High-throughput and sensitive determination of urinary zearalenone and metabolites by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a human exposure study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meky, F.A.; Turner, P.C.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Miller, J.D.; Qiao, Y.L.; Roth, M.J.; Wild, C.P. Development of a urinary biomarker of human exposure to deoxynivalenol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.C.; Rothwell, J.A.; White, K.L.; Gong, Y.Y.; Cade, J.E.; Wild, C.P. Urinary deoxynivalenol is correlated with cereal intake in individuals from the United Kingdom. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzo, M.; Gambacorta, L.; Lattanzio, V.M.; Powers, S.; Visconti, A. Simultaneous LC-MS/MS determination of aflatoxin M1, ochratox- in A, deoxynivalenol, de-epoxydeoxynivalenol, alpha and beta-zearalenols and fumonisin B1 in urine as a multi-biomarker method to assess exposure to mycotoxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Sulyok, M.; Fruhmann, P.; Mikula, H.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Hametner, C.; Abia, W.A.; Adam, G.; Froehlich, J.; et al. Development and validation of a rapid multi-biomarker liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method to assess human exposure to mycotoxins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteresch, B.; Viegas, S.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.U. Multi-mycotoxin analysis using dried blood spots and dried serum spots. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3369–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, B.; Raggi, M.E.; Moretti, G.; Facchiano, F.; Mezzelani, A.; Villa, L.; Bonfanti, A.; Campioni, A.; Rossi, S.; Camposeo, S.; et al. Study on the association among mycotoxins and other variables in children with autism. Toxins 2017, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massart, F.; Meucci, V.; Saggese, G.; Soldani, G. High growth rate of girls with precocious puberty exposed to estrogenic mycotoxins. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).