Featured Application
This work will serve as a valuable resource for the research on APS.
Abstract
The Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) are important bioactive components of Astragali Radix, the dry root of Astragalus membranaceus, which has been used in traditional Chinese medicine. In this review, the extraction conditions and extraction rates of APS are first compared for water, microwave-assisted, ultrasonic wave, and enzymatic hydrolysis extraction methods. Some studies have also shown that different methods can be combined to improve the extraction rate of APS. Subsequently, the chemical composition and structure of APS are discussed, as related to the extraction and purification method. Most studies have shown that APS is mainly composed of glucose, in addition to rhamnose, galactose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucuronic acid, and galacturonic acid. We also reviewed studies on the modification of APS using chemical methods, including sulfated modification using the chlorosulfonic acid–pyridine method, which is commonly used for chemical modification of APS. Finally, the pharmacological activities and mechanisms of action of APS are summarized, with a special focus on its immunoregulatory, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects. This review will serve as a valuable resource for the research on APS.
1. Introduction
Astragali Radix (Huangqi) is the dry root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. and A. membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. It is a traditional Chinese medicine, which is described in the 2015 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia [1]. The use of Astragali Radix dates back to more than 2000 years ago, and it was recorded in Shen Nong’s Materia Medica, written during the Han dynasty. Astragali Radix growing in the Inner Mongolia area is considered a genuine medicinal material and is famous for its high quality [2]. Since there is a substantial demand for Astragali Radix and its wild resources have been nearly exhausted, Astragali Radix for commercial purposes is currently mainly obtained by artificial cultivation. Astragali Radix produced in Inner Mongolia ranks first in China and is mainly produced in Chifeng, Baotou, Ulanchabu, Bayannaoer, Alxa League, and Hohhot [3,4].
Studies conducted in the last two decades have provided significant insights into the pharmacological activities of different components of Astragali Radix, especially its polysaccharide fraction [5]. The Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) are important bioactive components of Astragali Radix, which has important pharmacological activities both in vivo and in vitro, such as immunomodulation, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-aging, and cardiovascular protection activities [6,7,8]. Its chemical composition and structure play an important role in the pharmacological activities of APS. Numerous studies have found that the structural modification of polysaccharides greatly enhances their biological activities. To further develop and utilize APS, studies have focused on the extraction process of APS since the 1980s. Currently, the commonly used methods include water, microwave-assisted, ultrasonic wave, and enzymatic hydrolysis extraction. In addition, several studies have suggested that a combination of these methods can increase the extraction rate of APS. At present, studies on the modification of APS mainly use chemical methods, including sulfation, phosphorylation, selenation, carboxymethylation, acetylation, alkylation, etc. In this paper, extraction, purification, the chemical composition, structural modification, and pharmacological functions of APS are reviewed to provide the basis for the development and clinical application of APS.
2. Extraction of Astragalus Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are polar macromolecules, and different kinds of polysaccharides are obtained with different extraction methods. Most of the methods involve extraction with water or diluted alkali solutions as solvents. In recent years, the extraction of APS has been studied extensively, and some of the commonly used extraction methods are described below.
2.1. Water Extraction Methods
These methods are simple and easy to operate. Moreover, they are the most traditional extraction method for APS. The main factors affecting the extraction process are ranked in the following decreasing order of their effects: extraction temperature > material/liquid ratio > extraction time [9]. Zhu et al. [10] concentrated a crude water extract of APS to a certain volume using a rotary evaporator, then added absolute ethanol, allowed the mixture to stay overnight, and finally precipitated and centrifuged the extract. The results showed that the best solid-to-liquid ratio was 1:10, and the best extraction temperature and time were 80 °C and 2 h, respectively; under these conditions, the extraction rate reached 9.77%. Aqueous solutions of CaO and Na2CO3 have also been used to prepare APS crude extracts, and the results showed that the extraction yield was the highest (11.7%) with a CaO aqueous solution, which was 3.25 and 2.05 times higher than that obtained with water (3.6%) and a Na2CO3 aqueous solution (5.7%), respectively [11]. However, the temperature of boiling water is usually 100 °C, leading to two major disadvantages. The first one is the poor selectivity of the extraction method so that components such as flavonoids and saponins cannot subsequently be separated from APS. The second disadvantage is the waste of energy and resources, leading to low economic returns.
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Extraction Methods
Microwaves are characterized by strong penetration, high selectivity, and a high heating efficiency. The thermal effect of microwaves can break the cell wall and inactivate enzymes in the cell membrane; therefore, polysaccharides can be easily extracted from cells, and the yield can be effectively improved. Thus, microwaves can be employed in the extraction of APS. The following have been reported as the optimal extraction conditions for microwave-assisted extraction: the water/material ratio, 12:1; pH, regulated by saturated limewater, 9; and two doses of microwave radiation (300 W) for 10 min each. Under these conditions, the yield of the crude APS product was 14.6%, and the purity was 88.1% [12]. In another study using a microwave-assisted extraction method, the extraction rate of APS was 4.50%, with the APS content of 31.25%, indicating that this method was time and energy saving and highly efficient [13]. Dong et al. [14] have reported the optimum enzymatic-microwave extraction conditions as follows: the liquid/solid ratio, 10:1; enzyme ratio, 57.6 U/g; and cellulase reaction time, 60 min, followed by 8 min of microwave irradiation (480 W). Under these conditions, the maximum extraction rate reached 16.07%, and the purity was up to 88.40%, which were considerably higher than those achieved by other extraction methods. Although microwave-assisted extraction methods can improve the extraction rate of polysaccharides, the effects of microwaves on the chemical structure and pharmacological activities of polysaccharides are still unclear and require further studies.
2.3. Ultrasonic Wave Extraction Methods
The cavitation effect of ultrasound leads to the rupture of the plant cell wall, thereby increasing the yield of polysaccharides. Ultrasonic extraction methods have been used to extract APS since they can shorten the extraction time and improve the extraction efficiency. A study on ultrasonic-assisted extraction of APS has reported the following as the optimal extraction conditions: the extraction time, 90 min; ultrasonic power, 250 W; and extraction temperature, 80 °C [15]. The effects of these factors on ultrasonic extraction were shown to decrease in the following order: ultrasonic power > extraction temperature > extraction time. The extraction of APS using ultrasonic waves in combination with microwaves resulted in an extraction rate as high as 4.25% under the following optimal extraction conditions: the extraction time, 150 s; microwave power, 120 W; and solid/liquid ratio, 1:25 [16]. When ultrasonic extraction was combined with cellulase hydrolysis to extract APS, the effects of the factors influencing the extraction rate were shown to decrease in the following order: ultrasonic time > ultrasonic temperature > enzyme amount > material/liquid ratio. The extraction rate was 24.12% under the following optimal conditions: the ultrasound time, 30 min; ultrasound temperature, 40 °C; solid/liquid ratio, 1:20; and enzyme amount, 10 mg [17]. Overall, an ultrasonic wave extraction method can be an important supplement to other methods.
2.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis Extraction Methods
Cellulase can break down the plant cell wall, thereby releasing polysaccharides from cells without destroying the structure of polysaccharides. For APS extraction with cellulase, the optimum enzymatic hydrolysis time was 120 min, the ratio of the enzyme was 0.8%, and the hydrolysis temperature was 75 °C. Under these conditions, the extraction rate of APS was 9.78%, and that of total sugar was 50.2% [18]. After pretreatment with three different cellulase concentrations (0.3%, 0.4%, and 0.5%), the yield of APS obtained by a water extraction method increased by 314.8%, 392.6%, and 342.6%, respectively, compared with that obtained by the water extraction method alone [19]. When enzymatic hydrolysis was combined with a microwave method, the maximum extraction rate of APS reached 16.07%, and the purity was 88.40% under the following optimum extraction conditions: the liquid/solid ratio, 10:1; enzyme ratio, 57.6 U/g; and cellulase reaction time, 60 min, followed by 8 min of microwave irradiation (480 W) [14]. In conclusion, enzymatic hydrolysis of plant material can be employed as a pretreatment to improve the yield of APS.
3. Purification of Astragalus Polysaccharides
The purity of the extracts obtained with the above extraction methods is not sufficient for APS to be used for chemical composition and structure analyses. The extracted APS usually contains oligosaccharides, pigments, proteins, flavonoids, and other impurities. Therefore, purification must be carried out. The common purification methods employed are as follows: enzyme-Sevag, diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex A-25, and Sephadex G-100 [10]; a polyamide column and an AB-8 macroporous resin column [9,20]; X-5 macroporous resin [21]; chitosan flocculation [22]; and a type II ZTC1+1 natural clarifier [23]. The purified APS obtained by these methods can be used for subsequent chemical composition and structural analyses.
4. Chemical Composition and Structure of Astragalus Polysaccharides
The monosaccharide compositions of APS obtained from different plant varieties and habitats and using different methods are different. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), mass spectrometry (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) are commonly used to analyze the chemical composition and structure of APS. Most studies have shown that APS is mainly composed of glucose, in addition to rhamnose, galactose, arabinose, and other monosaccharides (Figure 1). The main chain contains linked α-(1→4) glucose residues. The relative molecular mass of APS is 5.6 × 103–106 Da (Table 1). Monosaccharide composition analysis of an APS sample by HPLC revealed that it was composed of rhamnose, glucose, galacturonic acid, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 1.19:72.01:5.85:20.95 [24]. Hydrolysis of another APS sample with trifluoroacetic acid to monosaccharides and analysis of the monosaccharide composition by HPLC revealed that this polysaccharide was composed of mannose, rhamnose, galacturonic acid, glucose, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 0.02:0.05:0.17:1.00:0.18 [25]. Yao et al. [26] determined the monosaccharide composition of APS by capillary GC, and the results showed that it was composed of arabinose, fructose, glucose, and mannose in a molar ratio of 1.00:3.24:7.00:0.46.
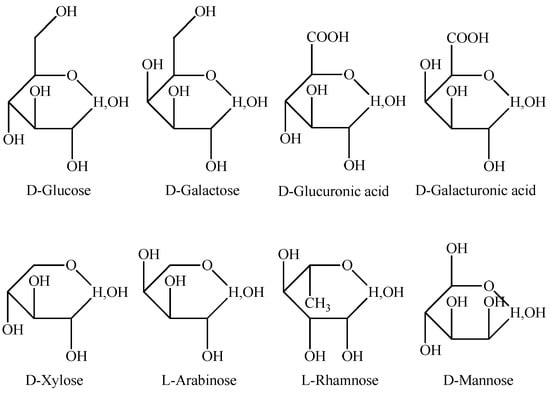
Figure 1.
The monosaccharide structure of Astragalus polysaccharides.

Table 1.
The chemical composition of Astragalus Polysaccharides.
The structures of APS isolated from different varieties of Astragali Radix are also different. Moreover, the chemical structure of polysaccharides influences their biological activities. Thus, Chen et al. [27] analyzed monosaccharides in APS by GC-MS, and the results revealed that the polysaccharide was mainly composed of L-rhamnose, L-arabinose, D-xylose, L-xylose, D-ribose, L-ribose, D-galactose, D-glucose, and D-mannose. Furthermore, monosaccharides extracted from a different A. membranaceus variety were different. The structure of APS was determined by GC-MS and infrared spectroscopy (IR), and the results showed that the main chain was mainly composed of glucose, xylose, and galactose, and the side chains were composed of glucose, arabinose, and galactose [28]. Furthermore, the branching point was composed of glucose, galactose, and arabinose, and the terminal residue was glucose. The APS powder for injection, developed by Panhua Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., is mainly used as a chemotherapy or adjuvant therapy after radiotherapy in cancer patients. It has been reported that the main components of APS are alpha-1,4(1,6)-glucan, arabinose–galactose, rhamnose–galacturonic acid polysaccharide, and arabinose–galactoprotein polysaccharide [29]. These studies have laid a foundation for further analysis of the mechanisms of pharmacological activities of APS.
5. Structural Modification of Astragalus Polysaccharides
Pharmacological activities of polysaccharides are closely related to their structures. Several studies have shown that structural modification of polysaccharides can change their pharmacological activities. Structural modification is usually performed using chemical, physical, enzymatic, and other effective methods for the improvement of nutraceutical and therapeutic functions of polysaccharides. Currently, studies on the modification of APS mainly employ chemical methods, including sulfation, phosphorylation, selenation, and carboxymethylation.
Sulfation of APS is a commonly used chemical modification method. It involves the reaction of polysaccharides, dissolved in a specific solvent, with corresponding sulfating reagents under certain conditions, leading to the introduction of sulfate groups into hydroxyl groups of side chains of polysaccharides (Figure 2). Sulfated polysaccharides can be obtained using the chlorosulfonic acid–pyridine (CSA–Pyr), sulfuric acid, and sulfur trioxide–dimethylacetamide or pyridine methods [43,44,45]. The CSA–Pyr method is the most popular, owing to its convenience, high yield, and high degree of sulfation. The sulfated APS obtained by the CSA–Pyr method had a better anti-inflammatory activity than did unmodified APS, in vitro and in vivo [46,47]. Sulfation of APS by the CSA–Pyr method also enhanced its antiviral effect [48]. Huang et al. [49] have found that compared with non-sulfated APS, sulfated APS could significantly increase the antibody titer and promote lymphocyte proliferation. Therefore, sulfated APS can be a candidate for a new immune adjuvant [50,51].
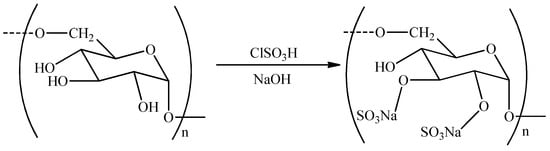
Figure 2.
The reaction of APS sulfate by the chlorosulfonic acid–pyridine (CSA–Pyr) method.
Phosphorylation is a covalent modification of hydroxyl groups in side chains of polysaccharides with phosphate groups. Studies have shown that phosphorylation of polysaccharides can enhance their bioactivities. Phosphorylation of APS using the sodium tripolyphosphate–sodium trimetaphosphate method enhanced its antiviral effect against duck viral hepatitis [52]. Reaction with polyphosphoric acid under alkaline conditions resulted in a good antiviral activity of APS against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus [53].
Natural Se-containing polysaccharides have been found in several animals, plants, and microorganisms. As organic Se compounds, polysaccharides modified with Se can exhibit the physiological activities of both Se and polysaccharides. Moreover, the bioavailability of Se and its physiological functions as an essential trace element are effectively improved, while its toxicity and side effects are considerably lower than those of inorganic Se. Gong et al. [54] have reacted APS with a SeOCl2 reagent and obtained a Se-containing APS, with a Se content of 16.820 mg/g. It has been reported that the inhibitory rate of tumor growth was 51.14% in the Se–APS group compared with 23.66% in the water control group, suggesting that combining APS with Se might enhance not only the tumor inhibitory effects of APS but also the antioxidant effect of Se [55,56]. It has been reported that a high Se content in Se-modified APS increases the antioxidant effect of APS [57].
Carboxymethyl groups are introduced into polysaccharide chains for complete carboxymethylation of polysaccharides. Carboxymethylation increases the negative charge of polysaccharide chains and their solubility in water. In addition, carboxymethylation has a strong effect on the bioactivity of polysaccharides. Yang et al. [58] prepared carboxymethyl-modified APS in the reaction with NaOH and C2H3ClO2. The optimum reaction conditions were as follows: the reaction temperature, 65 °C; NaOH/C2H3ClO2 ratio, 16:1; and reaction time, 3.5 h. The results showed that the carboxymethyl-modified APS had the highest growth-promotion for microwave and immunological activities.
6. Pharmacological Activities of Astragalus Polysaccharides
Astragali Radix enhances immunity, as well as antioxidation, antiradiation, antitumor, antibacterial, and antiviral effects, and protects the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems, as well as the liver, kidneys, and lungs [59]. The Astragalus polysaccharides are important chemical components of Astragali Radix. Recent studies have indicated that APS has immunoregulatory, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-aging, and other biological activities.
6.1. Immunoregulatory Effects
The Astragalus polysaccharides not only enhance the function of immune organs and cells but also stimulate the release of cytokines, affect the nervous–endocrine–immune system network, and promote the expression of related genes. APS can enhance the immune function by increasing the weight of immune organs. It has been reported that APS administration (220 mg/kg) in feed could significantly increase the relative weight of immune organs, as well as the number of lactobacilli and Bacillus cereus in the intestinal microbiota of chicks [60]. Furthermore, APS could increase the weights of the thymus and spleen, as well as the number of peritoneal macrophages in mice [40], and enhance the function of macrophages. It has been reported that APS at a concentration of 300 μg/mL could significantly increase the nitric oxide (NO), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels in the human monocyte/macrophage strain TPH-1, indicating that APS can activate macrophages [61]. Astragalus polysaccharides showed an impact on the functional status and phenotype of T cells during polymicrobial sepsis. Treatment of mice with APS at a dose of 400 mg/kg on day one after cecal ligation and puncture could increase the T helper (Th) cell population and also the percentage of Th17 cells in the blood. Consequently, APS could attenuate immunosuppression in polymicrobial sepsis [62]. In tilapia fish, it has been shown that 1500 mg/kg APS supplementation could upregulate the phagocytic activity, as well as the superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and amylase activities. However, APS had no effect on the serum NO and malondialdehyde levels [63]. In addition, APS can be used as an immunomodulator of vaccines. At a dose of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, APS could markedly increase the titer of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV)-specific antibodies in a dose-dependent manner and upregulate the mRNA expression of interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-6, indicating that APS can protect against FMDV [64]. In summary, APS can be used as an immunopotentiator, affecting the non-specific and specific immune systems.
6.2. Antitumor Effects
Studies have suggested that the antitumor mechanism of APS may be related to its immune enhancement effect. The polysaccharide could enhance the proliferation of spleen lymphocytes, which explained the stimulation of immune activities observed in rats with stomach cancer [65]. It has been reported that bladder cancer was significantly reduced in mice treated with 50 mg/mL APS, compared with that in the controls, because APS could enhance the innate immune response of bladder epithelial cells by increasing the Toll-like receptor 4 expression [66]. It has also been reported that APS could reduce the telomerase activity and induce the apoptosis of human leukemic HL-60 cells, thus exerting an antitumor effect [67]. Xu et al. [68] have reported that APS showed no direct antitumor effect; however, an antitumor effect was achieved by promoting the production of TNF-α in macrophages and INF-γ in splenocytes. Additionally, APS could inhibit the invasion of HepG2 hepatoma cells by regulating the tumor growth factor-β/Smad signal transduction pathway [69]. In vitro studies do not fully reflect the in vivo antitumor activity of APS. However, the effects of APS on the tumor cell cycle, angiogenesis, telomerase activity, signal transduction, and immune function can all contribute to its antitumor activity.
6.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is closely associated with immunity, and the inflammatory response mostly involves the immune mechanism. Early symptoms of inflammation, such as increased vascular permeability, inflammatory exudation, and tissue swelling, accompanied by increased levels of inflammatory transmitters, indicate that the immune function of relevant cells has been affected. The Astragalus polysaccharides can regulate the signal transduction of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and secretion of anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory factors, ultimately balancing the immune response [70]. Zhang et al. [71] have reported that inhibition of adhesion between inflammatory cells and microvascular endothelial cells by downregulating the expression of CD34 on the surface of microvascular endothelial cells may be one of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of APS. It has been reported that APS could significantly reduce the serum NO level and improve chronic inflammation caused by NO metabolic disorder [72]. At a dose of 200 mg/kg, APS could significantly improve 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats by downregulating the expression of TNF-α and IL-1β at both mRNA and protein levels, and upregulating the expression of nuclear factor of activated T cells 4 mRNA and protein [73]. Thus, APS can interfere with various inflammatory diseases and affect several pathways and mediators of inflammation. Although research on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of APS has been conducted at the cellular and molecular levels, in-depth studies on its targets are still lacking.
6.4. Antiviral Effects
The Astragalus polysaccharides can protect the body against viruses, induce, to a certain extent, the production of IFN, and inhibit the viral reproduction. It can also induce CD4+ T cells to produce IL-4, IL-2, and IFN-γ, suggesting that APS can be a potent adjuvant for a hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA vaccine [74]. It has been reported that 0.5 mg of APS can significantly enhance the efficacy of FMDV vaccine by significantly enhancing the phagocytic capacity of peritoneal macrophages, proliferation of splenic lymphocytes, the titer of serum antibodies, and the production of IL-4 and IL-10. The Astragalus polysaccharides can maintain the health of livestock and poultry by inhibiting the propagation of the virus [75]. Moreover, APS could significantly increase the resistance of 15-day-old chickens to H5N1 avian influenza virus [76], and prevent porcine circovirus infection by decreasing the oxidative stress and activating the NF-κB signaling pathway [77]. Furthermore, APS at a concentration of 30 μg/mL could inhibit the reproductive capacity of herpes virus, thereby reducing the incidence of tumor [78]. Briefly, the antiviral activity of APS is generally closely related to cytotoxic T lymphocytes, induced T lymphocytes (CD3+ and CD4+), and NF-κB.
6.5. Other Activities
Recent studies on the pharmacological activities of APS have reported that, besides immunomodulatory, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects, it also exerts antioxidant, anti-aging, cardiovascular protective, antidiabetic, and intestinal protective effects. These pharmacological activities and mechanisms of action of APS are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pharmacological activities and mechanisms of Astragalus Polysaccharides.
7. Conclusions
After several decades of extensive research, great progress has been made in the study of APS. The extraction methods and extraction rate of APS have been continuously improved. It has been found that water, microwave-assisted, ultrasonic wave, enzymatic hydrolysis, and other extraction methods can be combined to improve the extraction rate of APS. Depending on the extraction method and the degree of purification, the chemical composition and structure of APS can be confirmed by HPLC, GC, MS, and NMR. The chemical composition of APS mainly includes glucose, rhamnose, galactose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucuronic acid, and galacturonic acid. However, the monosaccharide composition and the structure of sugar chains of APS, obtained by different extraction and purification methods, are different. Therefore, the extraction and purification methods of APS need to be improved continuously.
As an important bioactive component of Astragali Radix, APS shows important pharmacological activities, including immunoregulatory, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and other activities. Currently, studies on the modification of APS mainly employ chemical methods, including sulfation, phosphorylation, selenation, and carboxymethylation, and suggest that structural modification can change the pharmacological activity of APS. However, studies on pharmacological activities of APS usually use crude polysaccharides, which does not allow the establishment of the structure–activity relationship. In addition, the molecular mechanisms of pharmacological activities of APS are still unclear, which also limits its further development and application. Therefore, separation and purification of APS should be improved. Subsequently, the structure–activity relationship of APS should be elucidated at the primary and secondary structure levels. Finally, the pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of APS should be studied with homogeneously purified APS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W., J.J., and M.L.; investigation, J.W., L.S., and X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W., X.G., and J.X.; writing—review and editing, J.W., M.Y., and M.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Innovation Guidance Project, Inner Mongolia (No. KCBJ2018040); National Nonprofit Industry Research (No. 201507002); the Fourth National Traditional Chinese Medicine Resources Survey Project (No. Caishe [2017] 66); the China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-21); the Science and Technology Planning Project of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China (No. 201701040); the Standardization Project of Mongolian Medicine in Inner Mongolia (No. 2018-[008]); the Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 2018LH03028); the Baotou Science and Technology Project (No. CX-2016-17); and the Scientific Research Foundation Project of Baotou Medical College (No. BYJJ-DF 2017-01).
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Na Zhang from Baotou Medical College, who taught us how to use the ChemDraw software.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 1, p. 302. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, B.M.; Xu, W.; Dai, H.; Tu, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.M. A study on the immune receptors for polysaccharides from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus, a Chinese medicinal herb. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 4, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zhang, D.Z.; Hao, X.X.; Niu, L.L.; Ren-Gaowa, S.A.; Wang, L. Survey on Astragalus in Inner Mongolia. J. Dis. Monit. Control 2013, 3, 165–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, D.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Jian, Y.; Hu, Z.L. Study on Genetic Diversity of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus Populations in Inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Grassl. 2018, 1, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, R.T.; He, J.C.; Wang, B.E.; Zhang, F.K.; Chen, G.Y.; Yin, S.S.; Shen, H. Suppressive effect of Astragalus membranaceus Bunge on chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2003, 51, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, J.H.; Bo, G.; Li, H.D.; Song, S.; Yang, L.X. Advances on Immunoregulation Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2017, 2, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.Z.; Liu, D.W.; Tian, Y.X.; Huang, L.F. Research Progress on Chemical Structure and Pharmacological Activity of Astragalus Polysaccharide. North. Hortic. 2015, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.Z.; Dong, F.; Tang, W.T.; Chen, X. Study on Process of Pharmacology of Astragalus Polysaccharide. Heilongjiang Med. J. 2014, 1, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.P.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, G.Z. Study on optimization of the technology for extraction and purification polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhou, F.; Li, S.F.; Yuan, J. Extraction and purification of Astragalus polysaccharide and its anti-tumor activity. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 376–379. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.M.; Huang, R.Q.; Wang, Y.Z. A technological study on enhancing the extraction rate of Astragalus polysaccharids. J. Northwest. Univ. 2000, 6, 509–510. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.Z.; Yang, Z.R. Investigation into the Microwave-assisted Extraction Technology for Astragalus Polysaccharide. J. South China Univ. Technol. 2004, 8, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Lin, F.; Mo, J.; Du, X.D. Comparison of two extraction methods of Astragalus polysaccharide. Res. Explor. Lab. 2015, 3, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.L.; Huang, X.; Qi, Y.G.; Feng, H. Study on the enzymatic-microwave extraction of Astragalus polysaccharides. J. Zhejiang Univ. Technol. 2011, 3, 220–232. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.C.; Zhou, S.T.; Zhang, D.B. Study on Extraction of Astragalus membranaceus Polysaccharides by Optimized Ultrasonic Method with Uniform Design. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 12, 5498–5499. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.F.; Cai, Z.H.; Wang, G.; Dai, B.; He, L. Study on Extraction of Astragalus Polysaccharide by Ultrasonic-Microwave Synergistically Assisted Technique. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2012, s1, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.G.; Wu, Z.C. Factors analysis of ultrasound combined with cellulose enzymatic extraction of total Astragalus polysaccharides. J. Guangdong Pharm. College 2010, 2, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.W.; Ma, S.L. Extraction of Astragalus Iepsensis by Cellulase Degradation. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2005, 1, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Wei, Y.M.; Chen, L. Extraction of effective component from Radix astragli with cellulase. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2005, 1, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.P.; Jia, C.Z.; Xue, Y.P.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, H.Q. Purification and Sulfating of Radix Astragali Polysacharides and Analysis with Infrared Spectroscopy. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2015, 1, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.C. Extraction, separation and purification of polysaccharides from Astragalus. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, G.Z.; Fan, K.F.; Zhu, Z.H. Study on the technologies for extraction and purification of Astragalus polysaccharides. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2010, 3, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.G.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, G.S.; Xu, X.H. Study on Methods of Astragalus Polysaccharides Extraction and Purification. Henan Sci. 2008, 6, 662–664. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Zhao, W.G.; Lv, X.H. Analysis on chemical components and structure of Astraglus polysaccharides. J. Tradition. Chin. Vet. Med. 2008, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Gong, S.X.; Zhang, T.J. Determination of monosaccharide compositions in Astragalus mongholicus var. mongholicus polysaccharides by pre-column derivatization-HPLC. Drugs Clin. 2012, 5, 468–470. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, D.; Wang, H.J. Monosaccharide composition in Radix Astragali polysaccharides by gas chromatography. Med. Plant 2012, 5, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.R.; Mao, X.Y.; Jin, W.W.; Luo, H.J.; Li, T. Study on Astragalus Polysaccharide Structure and Monosaccharide Constituents by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 2011, s1, 4632–4635. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J. The Isolation, Purification and Structural Characterization of Low molecular Polysaccharide Purified from Radix Astragali. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide (APS-P) on the proliferation and mobilization of murine hematopoietic stem cells. Basic Med. Sci. Clin. 2003, 6, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.h.; Chen, S.L. Structural features of a polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 6, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.G.; Wang, H.Y.; Xie, Z.H.; Whent, M.; Gao, X.D.; Zhang, X.; Zou, S.; Yao, W.B.; Yu, L.L. Structural analysis and bioactivity of a polysaccharide from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch) Bge. var mongolicus (Bge.) Hsiao. Food Chem. 2011, 3, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Chan, C.L.; Yu, H.; Lau, Y.K.; Han, X.Q.; Cheng, S.W.; Wong, C.K.; Lau, B.S.; Xie, M.Y.; Fung, K.P.; et al. Separation, structure characterization, conformation and immunomodulating effect of a hyperbranched heteroglycan from Radix Astragali. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 1, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Tomoda, M.; Kanari, M.; Gonda, R. An acidic polysaccharide having activity on the reticuloendothelial system from the root of Astragalus mongholicus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 11, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.F.; Qiao, S.Y.; Qi, C.H.; Zhang, Y.X. Isolation and structure elucidation of novel glucan from Astragalus mongholicus. Chin. Tradition. Herbal Drugs 2001, 11, 962–964. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Q.; Zhao, W.G.; Lv, X.H.; Li, X.H. Physical and Chemical Analysis of a New Heteropolysaccharide from Radix Astragalus. Chin. Pharma. J. 2009, 9, 654–657. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.G.; Yang, Y.F.; Xu, H.Y. Chemical structure of Astragalus Polysaccharides MAPS-5 and its proliferative activity in vitro. Chin. Herbal Med. 2009, 12, 1865–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Q. Structural Analysis of Polysaccharide from Astragalus and its Anti-tumor Activity. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Wu, H.S.; Zhao, X.F.; Li, H. studies on isolation of astragalan and its immunological activities. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 1994, 1, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.; Zhang, Y.Q. Characterization and renal protective effect of a polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 2, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Weng, Y.Q.; Xie, C.Y.; Liu, D.; Hu, Z.B. Comparing compositions and immunoactivities of polysaccharide in hair root of Astragalus membranaceus and cultivated A. membranaceus. Chin. Tradition. Herbal Drugs 2002, 12, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, W.P.; Chen, H.C.; Liao, S.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Rui, W. Structure Characterization of Honey-Processed Astragalus Polysaccharides and Its Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Vitro. Molecules 2018, 23, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.Y.; Ma, X.L.; Lu, L.; Jing, R.; Li, H.B.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W.J.; Fan, W.B. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharides from Angelica and Astragalus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Mo, X.Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.L. Sulfation modification and anticoagulant activity of the polysaccharides obtained from persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.) fruits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 5, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F. Study on anti-inflammatory activities of Astragalus polysaccharides and their sulphation modification products in vitro and in vivo. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, R.; Nagai, T.; Wu, X.F.; Wu, X.Y.; Huy, N.T.; Kamei, K.; Hara, S. Sulfation of Polysaccharides using Monomethyl Sulfate. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2000, 9, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.J.H.; Yao, J. Sulfated Astragalus polysaccharide can regulate the inflammatory reaction induced by LPS in Caco2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 6, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Shen, J.; Li, S.Z.; Zhi, L.H.; Yang, X.J.; Yao, J.H. Sulfated Astragalus polysaccharide regulates the inflammatory reaction in LPS-infected broiler chicks. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 8, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Jin, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Effects of Eight polysaccharides in Chinese herbal and sulfated polysaccharides on ND. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2012, 8, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.H. Sulfated modification can enhance the adjuvant activity of Astragalus polysaccharide for ND vaccine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 2, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Li, D.P.; Sun, J.L.; Ju, Y.; Hu, Y.L. Effects of sulfated Astragalus polysaccharides on immune responses of chickens inoculated with IBD vaccine. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2009, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.Y.; Bae, I.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.G. Effect of the degree of sulfation on the physicochemical and biological properties of Pleurotus eryngii polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 5, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, D.Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.L. Phosphorylation Molecular Modification of Astragalus Polysaccharide against Duck Viral Hepatitis. CN Patent CN105560352A, 11 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Z.; Liang, J.P.; Tao, L.; Chu, G.P.; Zhao, F.W.; Jia, Z.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, M. A preparation method of Astragalus Polysaccharide phosphate. CN Patent CN104877036A, 2 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.Z.; Ouyang, Z. Investigation of selenoastragalans preparation conditions and structure determination. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 1998, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, F.L. Inhibitory Effects of Se-Astragalus Membranaceus Polysaccharide on Tumor in Mice. Chin. J. Public Health 1997, 4, 229–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, F.L.; Zhang, M.Z. Interaction between Vitamin E and Se-Astragalus Membranaceus Polysaccharide on the effects of tumor inhibition on S180 in mice. Chin. J. Cancer 1996, 6, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H. Selenium modification of Astragalus polysaccharide and its antioxidant acticitu in vitro. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Yao, J.H.; Wang, X.F. Preparation of Astragalus Polysaccharide by Carboxymethylation Molecular Modification. CN Patent CN103030704A, 10 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.P.; Luo, Y.M. Anti-Aging Implications of Astragalus membranaceus (Astragali Radix): A Well-Known Chinese Tonic. Aging Dis. 2017, 6, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Zhao, X.J.; Wang, J.Y. Synergy of Astragalus polysaccharides and probiotics (Lactobacillus and Bacillus cereus) on immunity and intestinal microbiota in chicks. Poult. Sci. 2009, 3, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Wang, Z.X.; Long, T.T.; Zhou, X.; Bao, Y.X. Roles of Astragalus polysaccharides in coculture system of breast cancer cells and macrophages in vitro. Immunol. J. 2017, 6, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.C.; Wu, J.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Wu, M.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Yeh, S.L.; Lin, M.T. Modulatory Effects of Astragalus Polysaccharides on T-Cell Polarization in Mice with Polymicrobial Sepsis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahran, E.; Risha, E.; Abdelhamid, F.; Mahgoub, H.A.; Ibrahim, T. Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on growth performance, immunological parameters, digestive enzymes, and intestinal morphology of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 1, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Zhong, Y.G.; Li, H.R.; Zhang, N.W.; Ma, W.R.; Cheng, G.L.; Liu, F.Q.; Liu, F.H.; Xu, J.Q. Enhancement of Astragalus polysaccharide on the immune responses in pigs inoculated with foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 3, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, W.C.; Wang, W.P.; Tian, W.Y.; Zhang, X.G. Extraction, characterization of Astragalus polysaccharides and its immune modulating activities in rats with gastric cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 4, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Ma, C.Q.; Yao, Z.Y.; Yang, L.J.; Wei, L.; Li, M.Y. Enhancement of the innate immune response of bladder epithelial cells by Astragalus polysaccharides through upregulation of TLR4 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 2, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.F.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, H.X.; Zhang, R.F. Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide on Telomerase of HL-60 Cell. Henan J. Oncol. 2005, 4, 247–248. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.J.; Chen, M.Z. Antitumor activity of APS and its mechanism of action. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2005, 10, 923–925. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Xu, S.X.; He, S.F.; Huang, W.J.; Roberts, M.S. Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract inhibits cell invasion by modulating transforming growth factor-beta/Smad in HepG2 cell. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Dong, J.C.; Zhao, J.X.; Jin, S.Z.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.Y. Effects of different molecule weight Astragalus polysacharin isolated from annual Astragalus membra-neaceus on experssions of inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 cells. J. Jilin Univ. (Med. Ed.) 2011, 6, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Teng, K.D.; Wang, A.R.; Yu, Y.F.; Zhang, H. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide powder injection on the density of microvessels and mast cells in ovalbulmin-sensitized rat skin. J. China Agric. Univ. 2010, 1, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.T.; Liu, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Su, W.; Yan, C.L.; Nie, L. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on immune balance and the expression of nitric oxide in pulmonary fibrosis rats. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2009, 10, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Lin, H.B.; Gong, S.T.; Chen, P.Y.; Geng, L.L.; Zeng, Y.M.; Li, D.Y. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and NFATc4 in a rat model of experimental colitis. Cytokine 2014, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.G.; Zhao, B.; Li, J.Y.; Cao, X.H.; Diao, M.K.; Feng, H.B.; Chen, X.B.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zeng, X.Y. Astragalus polysaccharides enhance immune responses of HBV DNA vaccination via promoting the dendritic cell maturation and suppressing Treg frequency in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 4, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.W.; Li, J.F.; Hu, Y.X.; Cheng, G.L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Liu, F.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.J.; Xu, J.Q. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on the immune response to foot-and-mouth disease vaccine in mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 3, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löndt, B.Z.; Brookes, S.M.; Kelly, M.D.; Nash, B.J.; Brown, I.H. Failure to infect pigs co-housed with ducks or chickens infected experimentally with A/turkey/Turkey/1/2005 (H5N1) highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 2–4, 944–948. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.X.; Gan, F.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Hu, J.F.; Chen, X.X.; Huang, K.H. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits PCV2 replication by inhibiting oxidative stress and blocking NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 7, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.W.; Sun, X.S.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, L.; Yao, G.; Li, F.; Yang, X.; Song, L.; Jiang, G. The effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on the Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle. Acta Virol. 2014, 1, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Xia, P.Y. Protective Effects of Astragali Radix Polysaccharides Combined with Astragaloside IV against Radiation Injury Model Mice. China Pharm. 2014, 3, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R.; Cao, L.P.; Xu, P.; Jeney, G.; Yin, G.J. In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Astragalus polysaccharides against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte damage in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 3, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, J.Y.; Chen, Z.S.; Xing, K.C.; Sun, B. Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses palmitate-induced apoptosis in human cardiac myocytes: The role of Nrf1 and antioxidant response. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 3, 2515–2524. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Chen, W.C.; Wang, W.P.; Tian, W.Y.; Zhang, X.G. Antioxidant activity of Astragalus polysaccharides and antitumour activity of the polysaccharides and siRNA. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 2, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.M.; Liang, Y.Q.; Tang, L.J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.H. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on EA.hy926 cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 1, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.T.; Zhang, Y.K.; Kuang, H.X.; Jin, F.X.; Liu, D.W.; Gao, M.B.; Liu, Z.; Xin, X.J. Mitochondrial protection and anti-aging activity of Astragalus polysaccharides and their potential mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.F.; Wen, D.J. Study on anti-aging effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 4, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.W.; Ou, Q.; Wei, X.D.; Wang, M.F. Study on the Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide on the Activity of Aging HDF-β-galactosidase. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2006, 10, 1361–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Shen, T.; Huang, X.Q.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, B.D.; Pang, J.; Li, G.P.; Wang, Q.; Zohrabian, S.; Duan, C.; et al. Astragalus polysaccharide restores autophagic flux and improves cardiomyocyte function in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Oncotarget 2017, 3, 4837–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.G.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, K.; Shi, S.W.; Li, S. Protection of Astragalus polysaccharides in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Cardiol. 2012, 2, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.X.; Yang, J.; Lu, M.L.; Li, S.T.; Yu, X.C. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibites cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by isoproterenol via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway. Chin. J. Hypertens. 2014, 2, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhu, L.Q.; Xie, L.D.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in Human Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells after Hypoxia and Reoxygenation. Liaoning J. Tradition. Chin. Med. 2008, 27, 5382–5386. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Wu, K.; Mao, X.Q.; Wu, Y.; Ouyang, J.P. Astragalus polysaccharide improves insulin sensitivity in KKAy mice: Regulation of PKB/GLUT4 signaling in skeletal muscle. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 1, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, D.L.; Mao, X.Q.; Zou, F.; Jin, H.; Ouyang, J.P. Astragalus polysaccharides decreased the expression of PTP1B through relieving ER stress induced activation of ATF6 in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 1–2, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, Y.M.; Yu, M.H. Astragalus Polysaccharides: An Effective Treatment for Diabetes Prevention in NOD Mice. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 8, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.H.; Zheng, K.W.; Sun, L.Q. Explore the Regulative Action of Astragalus Polysaccharide for Intestinal Dysbacteriosis in Ulcerative Colitis Rat Models. Stud. Trace Elements Health 2013, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Xu, R.; Yue, H.Y.; Zhou, B.G.; Huang, H.Y.; Sun, Q.M.; Liu, D.Y. Astragalus polysaccharide attenuates rat experimental colitis by inducing regulatory T cells in intestinal Peyer’s patches. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 11, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhao, H.Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, B.; Yu, C.Y.; Zhang, G.; Bian, Z.X.; Lu, A.P.; He, X.J. Regulatory Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharides on Intestinal Intraepithelial γδT Cells of Tumor Bearing Mice. Molecules 2014, 19, 15224–15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jiao, L.; Han, T.; Zhang, H.; Qin, L.P.; Khalid, R. Synergistic hepatoprotective effect of Schisandrae lignans with Astragalus polysaccharides on chronic liver injury in rats. Phytomed. Int. 2009, 9, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, F.F.; Li, Q.; Lv, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P.C.; Xiang, Q.M.; Wei, L. Protective Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharideson Liver Injury Induced with Different Chemotherapeutics in Mice. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 23, 10413–10420. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.Y.; Fan, W.B.; Yu, S.; Li, Y..; Ma, X.L.; Liu, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, W.J. Polysaccharides from Angelica and Astragalus exert hepatoprotective effects against carbon-tetrachloride-induced intoxication in mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).