Featured Application
This work provides an approach to obtaining big data related to lighting. The obtained big data can be used to evaluate lighting performance and impacts on human beings, economics, environment, and ecology.
Abstract
Big lighting data are required for evaluation of lighting performance and impacts on human beings, environment, and ecology for smart urban lighting. However, traditional approaches of measuring road lighting cannot achieve this aim. We propose a rule-of-thumb model approach based on some feature points to reconstruct road lighting in urban areas. We validated the reconstructed illuminance with both software simulated and real road lighting scenes, and the average error is between 6 and 19%. This precision is acceptable in practical applications. Using this approach, we reconstructed the illuminance of three real road lighting environments in a block and further estimated the mesopic luminance and melanopic illuminance performance. In the future, by virtue of Geographic Information System technology, the approach may provide big lighting data for evaluation and analysis, and help build smarter urban lighting.
1. Introduction
Road lighting plays an important role in human life, and many types of light sources, such as the low-pressure sodium lamp (LPS), the high pressure mercury lamp (HPM) [1], the high pressure sodium lamp (HPS) [2], the metal halide lamp (MH) [3], and the light emitting diode (LED) [4], have been used in road lighting. The illuminance of road lighting is of great importance in helping people evaluate efficiency, safety [5,6,7], health [8], and economics issues [9] related to the urban environment. At present, the main approaches of measuring road lighting are illuminance/luminance meters and imaging photometers [10]. The measurement of road lighting is logistically difficult. The measured part of the road should be closed during measurements, which requires cooperation from the local authority. Existing guidance (e.g., British Standards Institution 2016 [11] and CIE 115:2010 [12]) requires approximately 30 measurements to be recorded at equally spaced positions between luminaires, which is a significant undertaking. Extrapolation of the light measurements from the measured section of the road to other parts of the road may not be valid for a number of reasons, such as variations in the distribution of luminaires, the light losses of light sources, and occlusion caused by trees. These issues can cause differences in illuminance distributions in different parts of a road. Existing approaches therefore cannot guarantee a simple measurement of a whole road, without significant resource allocation towards comprehensive measurements of the lighting.
Lighting has a great influence on human beings in many aspects. Prior studies reported that the artificial lighting at night (ALAN) have an impact on human productivity, social activity, accident prevention, health, and safety [13]. Suitable ambient lighting may increase the activities of pedestrians and cyclists at night [14]. There is a strongly held public perception that street lighting contributes directly to the safety [15,16]. Lighting has both positive and negative effects on human health [17]. ALAN is also related to aesthetics, energy, and economic issues. Lighting has been playing important roles in beautifying cities [18], leading to economic benefits. However, energy consumption is also great [19], and several energy performance indicators [20] are proposed for evaluation. The benefits and costs of ALAN should be balanced. Moreover, ALAN may also have an ecology impact and cause light pollution [21]. Most of these related impacts cannot be precisely and clearly evaluated due to a lack of big lighting data.
In terms of the lighting itself, lighting data can provide a range of lighting performance information, with which we can establish a smarter lighting system in the city. With illuminance data, it is possible to evaluate the illuminance levels, uniformity [22], lighting efficiency [23], mesopic luminance [24,25], and melanopic illuminance [26] performance. Most road lighting provides luminances between 0.5 to 2 cd/m2 [27,28] and tends to fall in the mesopic vision of luminance range from 0.005 to 5 cd/m2 [24]. Illuminance/luminance is measured using the spectral sensitivity curve in photopic vision [29], which is the photopic adaptation luminance. A transform to the mesopic luminance provides a more accurate measure of the lighting perceived by an observer at night. The circadian/melanopic illuminance [30,31] is a concept derived from non-visual biological effects relating to health problems. Several models, the Gall model [32], the Rea model [30], and the Lucas work [31], the latter two of which are established considering neuro mechanisms, have been proposed to measure circadian/melanopic illuminance. There is discrepancy between these two works, and none has been formally acknowledged. In this study, we adopt equivalent melanopic lux based on the Lucas work in the calculation.
The existing logistical and resource demands required to measure and characterize lighting on a road means existing lighting big data are very limited. Big data for urban environments in other areas such as crime, traffic safety, air pollution, and travel demand are becoming increasingly available as cities become instrumented with digital devices and infrastructure to make them ‘smart’ [33]. There is no precise big lighting data available for studies and applications at present. Some researchers reported an approach to map artificial lightscapes for ecological studies [34]. However, the approach assumed that street lighting luminaires are hemispherical isotropic point sources emitting at equal intensity in all directions below the horizontal. In the calculation process, information about the location, height above ground level, and bulb type of luminaires is required, and only metal-halide and low-pressure-sodium light sources were included in that study. The proposed model requires many inputs and cannot guarantee precise lighting data. Big lighting data that could provide information about various lighting metrics (e.g., illuminance levels, mesopic luminance, and melanopic illuminance performance) for an entire city can provide insights into the urban environment, particularly through their combination with other big datasets. New approaches are required to obtain such big lighting data. One feasible way is to use remote sensing technology [35]. The pixel resolution of spatial imagery has been increased from 30–100 m [36] to <10 m [37]. Remote sensing of night lights has recently been enhanced, and the threshold of detection of lit areas reached 0.4 W/m2/μm/sr at several different spectral bands ranging from the visual region to the infrared region (0.44 to 2.2 µm) [38]. In other research, images were taken from a plane at a height of 900 m. The imagery reaches 10 cm to 1 m pixel resolution, and was used to estimate a light sources’ category [39].
Remote sensing technology is a promising technology to map lightscapes and obtain big lighting data. However, there are still some technological bottlenecks at present. First, the pixel resolution requires an improvement to around 1–3 m. Second, although the spectral bands cover the visible light region, they are not continuous. Third, it is difficult to precisely transform and correct the detected nighttime light intensities to illuminance or luminance.
In this work, we propose a functional model to reconstruct illuminance distributions of road lighting using a small number feature points. We can obtain more lighting data with very few measured lighting points while reaching the same degree of measurement error as traditional measurements. This technique may be used to obtain big lighting data for lighting performance evaluations and other human-, environment-, and ecology-related impact evaluations.
2. Road Lighting Distributions
2.1. Simulated Road Lighting Scenes
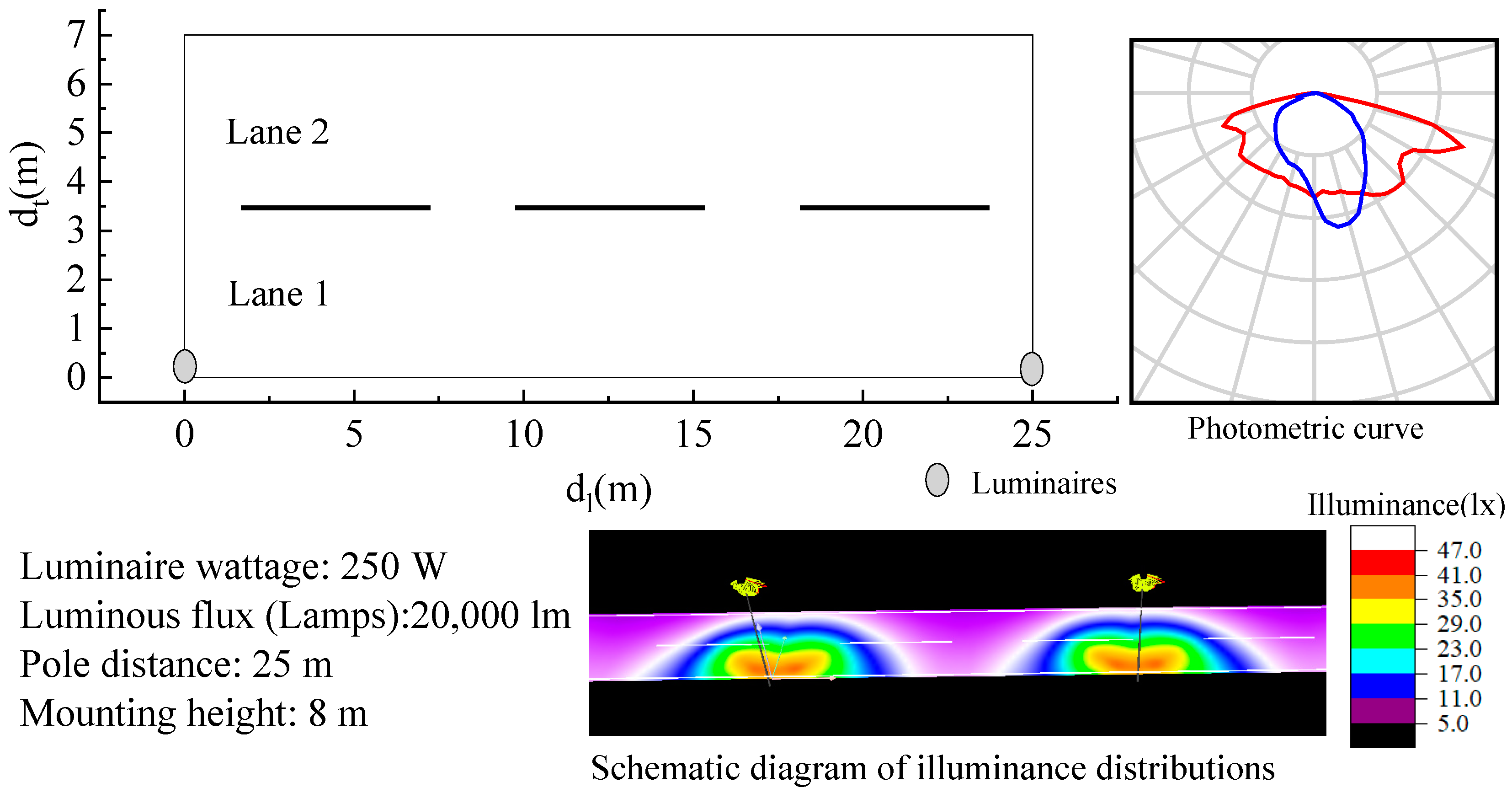
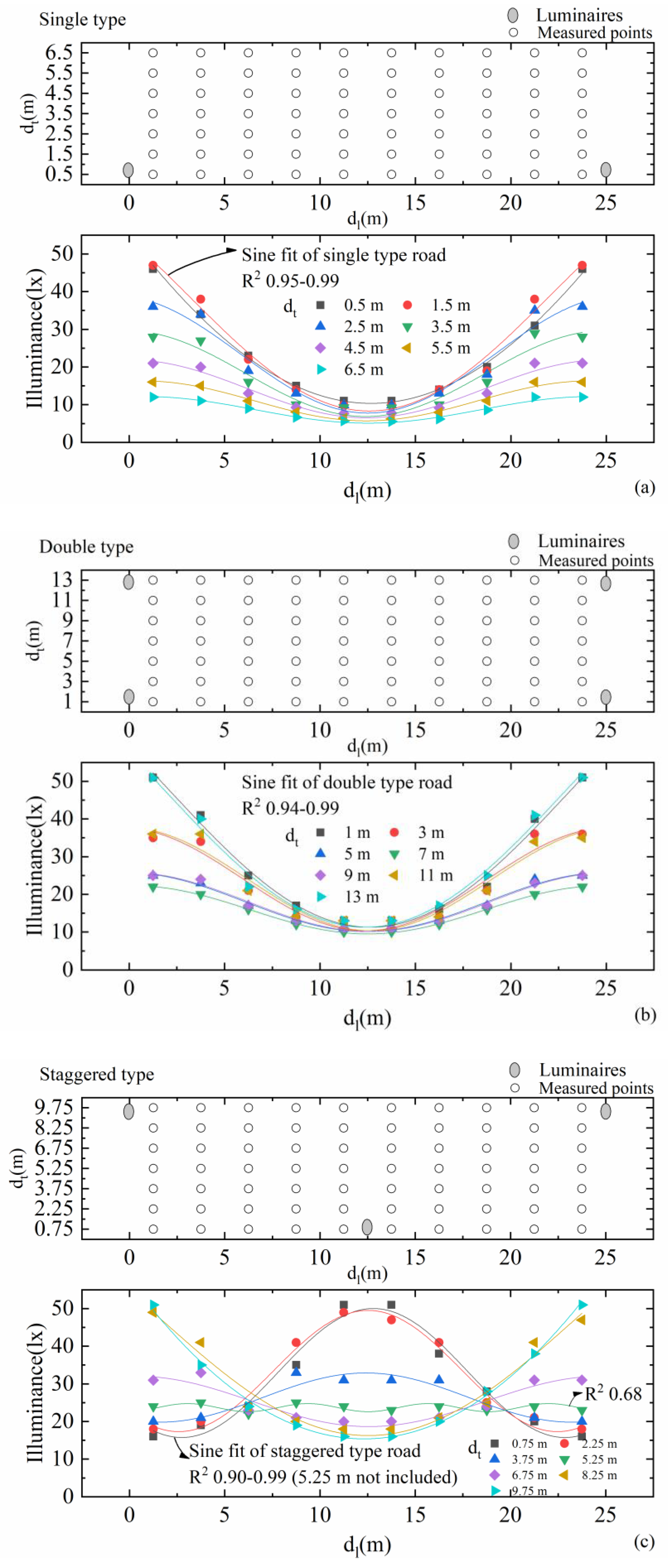
There are three main kinds of road lighting distributions: single (luminaire on one side of road only), double (luminaires on both sides of road, opposite), and staggered types (luminaires alternating between the two sides of the road). We simulate these three types of road lighting distributions in DIALux with various luminaires that differed in their photometric curves, and report a randomly chosen luminaire as an example. These luminaire poles are 8 m in height. The luminaires are of 250 W and 20,000 lm. All three types of simulated roads are 25 m in longitudinal distance (dl) between two luminaires. The single-type road contains two lanes and the transverse distance (dt) is 7 m, the double-type road contains four lanes with dt of 14 m, and the staggered-type road contains three lanes with dt of 10.5 m. The road lighting setups of single type is shown in Figure 1. For each different type of road lighting configuration, 10 × 7 points are measured, as shown in Figure 2, respectively. The illuminance distributions in the longitudinal directions of the three kinds of road types conform to a sine function with high coefficients of determination R2 over 0.90, except for the illuminance distribution of the staggered type at the transverse distance dt = 5.25 m in the center of the road. This is because the illuminances in the center are influenced by luminaires on both sides equally. However, these illuminances in the center are relatively close, and there might not be great errors with sine fitting. The maximum illuminances are likely to appear beneath or around the luminaires, and minimum illuminances at the midpoint between two luminaires. All our simulated illuminance scenes using different luminaires conform to the sine-like illuminance distributions in the longitudinal direction.
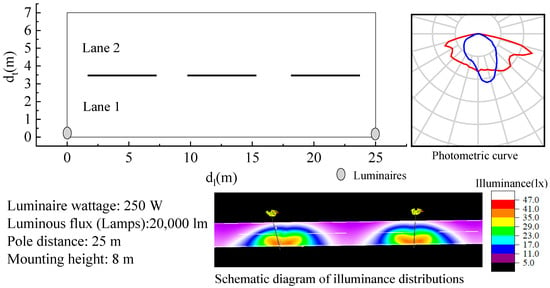
Figure 1.
Road lighting setup taking the single type for example. Most setups, except the number of lanes, for the double and staggered types are the same as the single type.
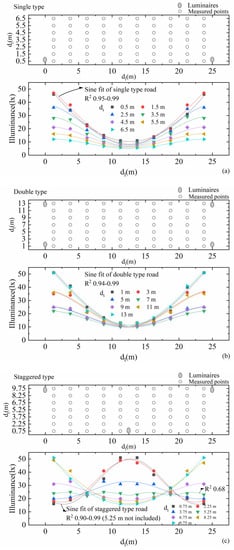
Figure 2.
The illuminance distributions in longitudinal directions at different transverse distance dts of three kinds road types: (a) single type, (b) double type, and (c) staggered type. They are fitted with sine functions at different dts reaching R2 0.95–0.99 for the single type, 0.94–0.99 for the double type, and 0.90–0.99 for the staggered type, excluding the one at dt = 5.25 m of 0.68.
2.2. Real Road Lighting Scenes
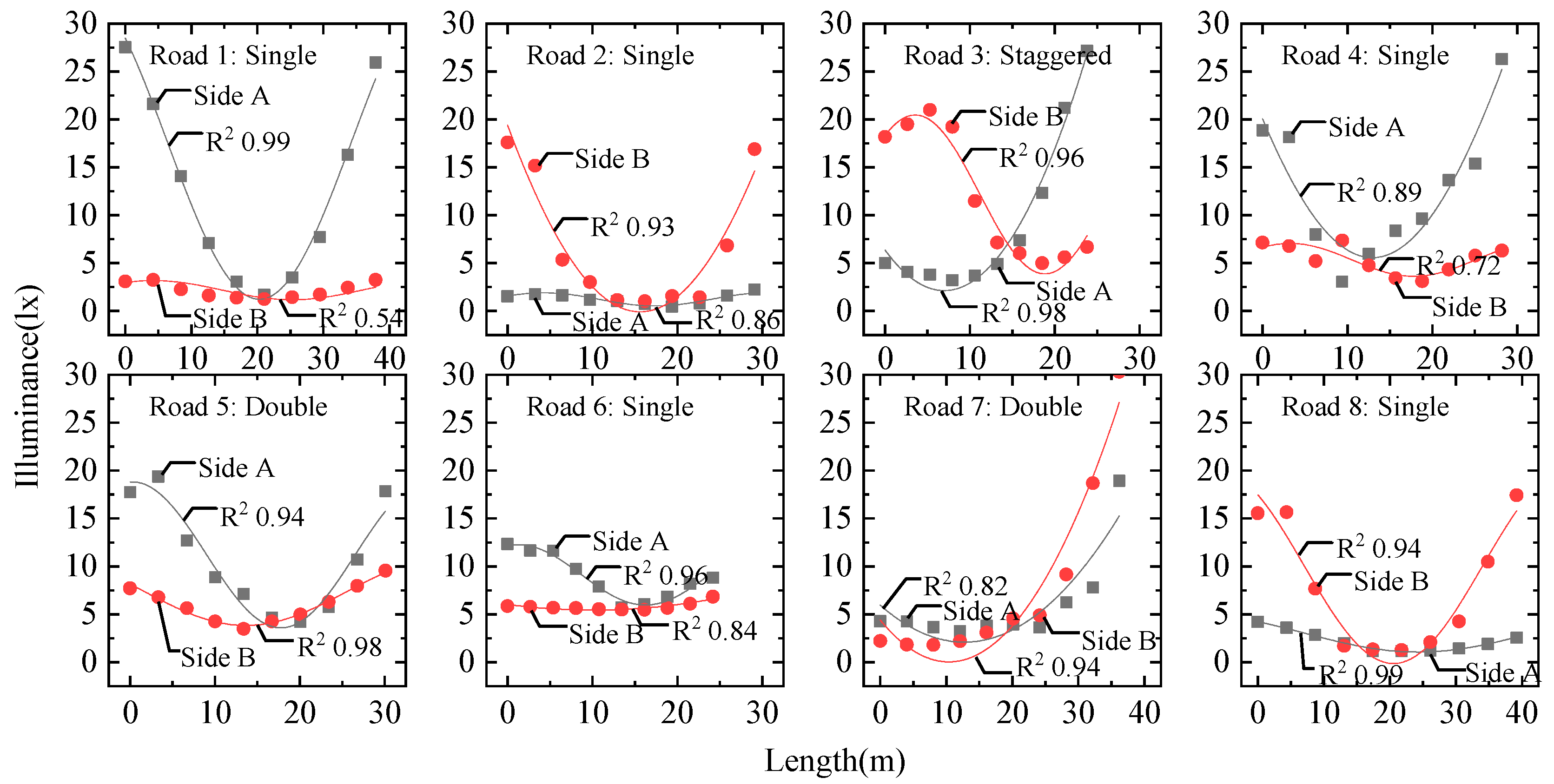
Road lighting on real streets is complicated, due, for example, to suffering light loss, shade block, and obstacles, and such factors may influence illuminance distributions. We measured illuminance distributions at both sides of eight real roads in Sheffield, England [5] and fitted these distributions with sine functions as shown in Figure 3. The illuminance distributions all conform to the sine function well, and most reach very high coefficients of determination R2 over 0.90. Our results show that, although not as ideal as simulated road lighting, real road lighting distributions in the longitudinal direction may also fit well with a sine function.
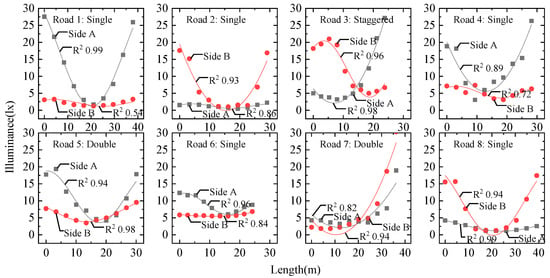
Figure 3.
Illuminance distributions of two sides in the longitudinal direction of eight real road lighting scenes. These roads include the three road types: single, double, and staggered types.
3. A Rule-of-Thumb Model of Road Lighting Illuminance Distributions
3.1. Illuminance Distributions and Modelling in the Longitudinal Direction
As analyzed in Section 2, both illuminance distributions in the longitudinal direction of simulated and real road lighting can be fitted well with sine functions. We tried to establish a sine function model to describe the distribution in Equation (1), where Emax is the illuminance beneath the luminaire, Emin is the illuminance at the midpoint between two luminaires, El is the illuminance along the longitudinal direction, dl is the distance along the longitudinal direction, d0 is the deviation distance to match the values at feature points, and w is the half period equal to distance between two neighbor feature points.
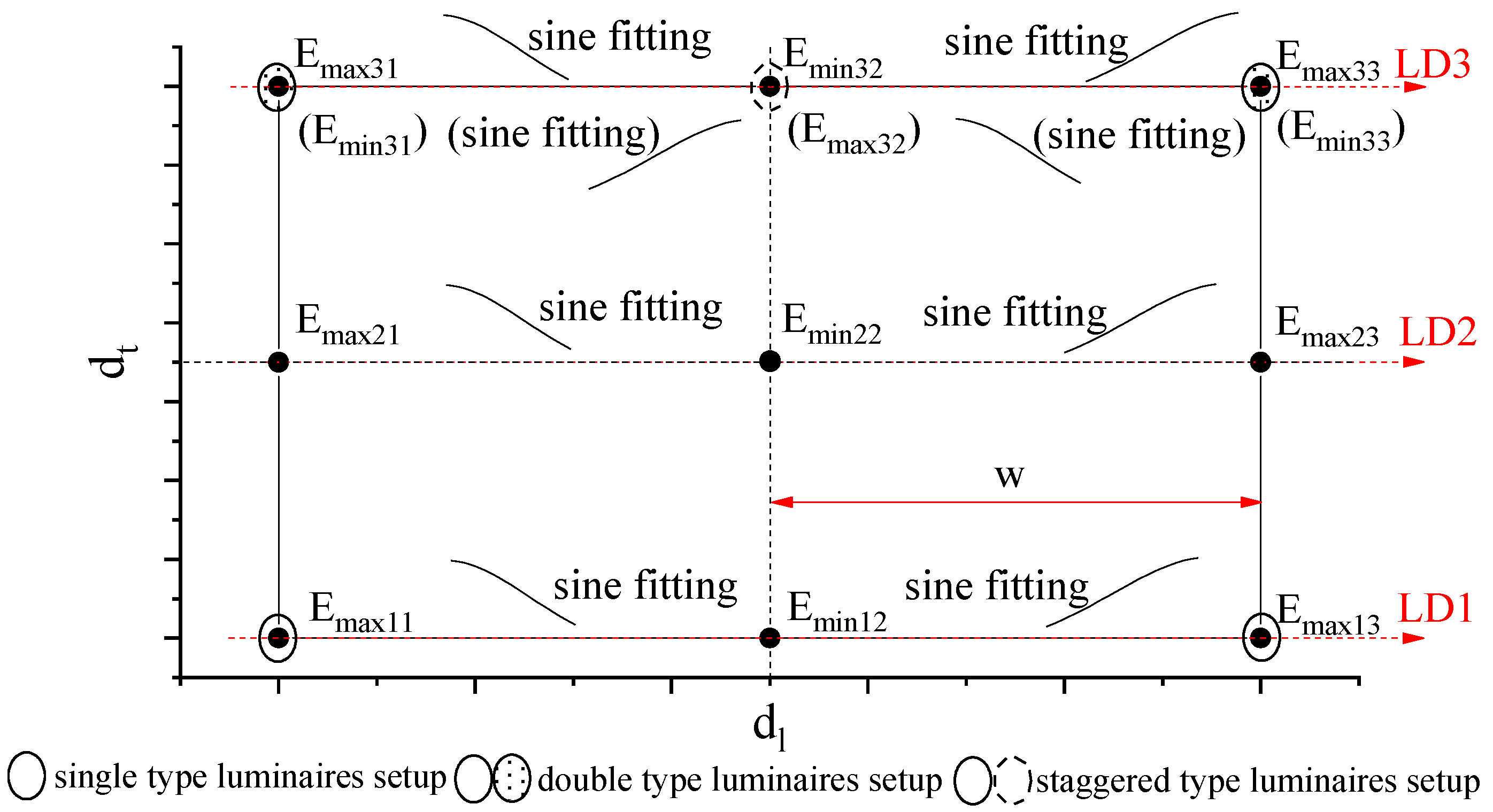
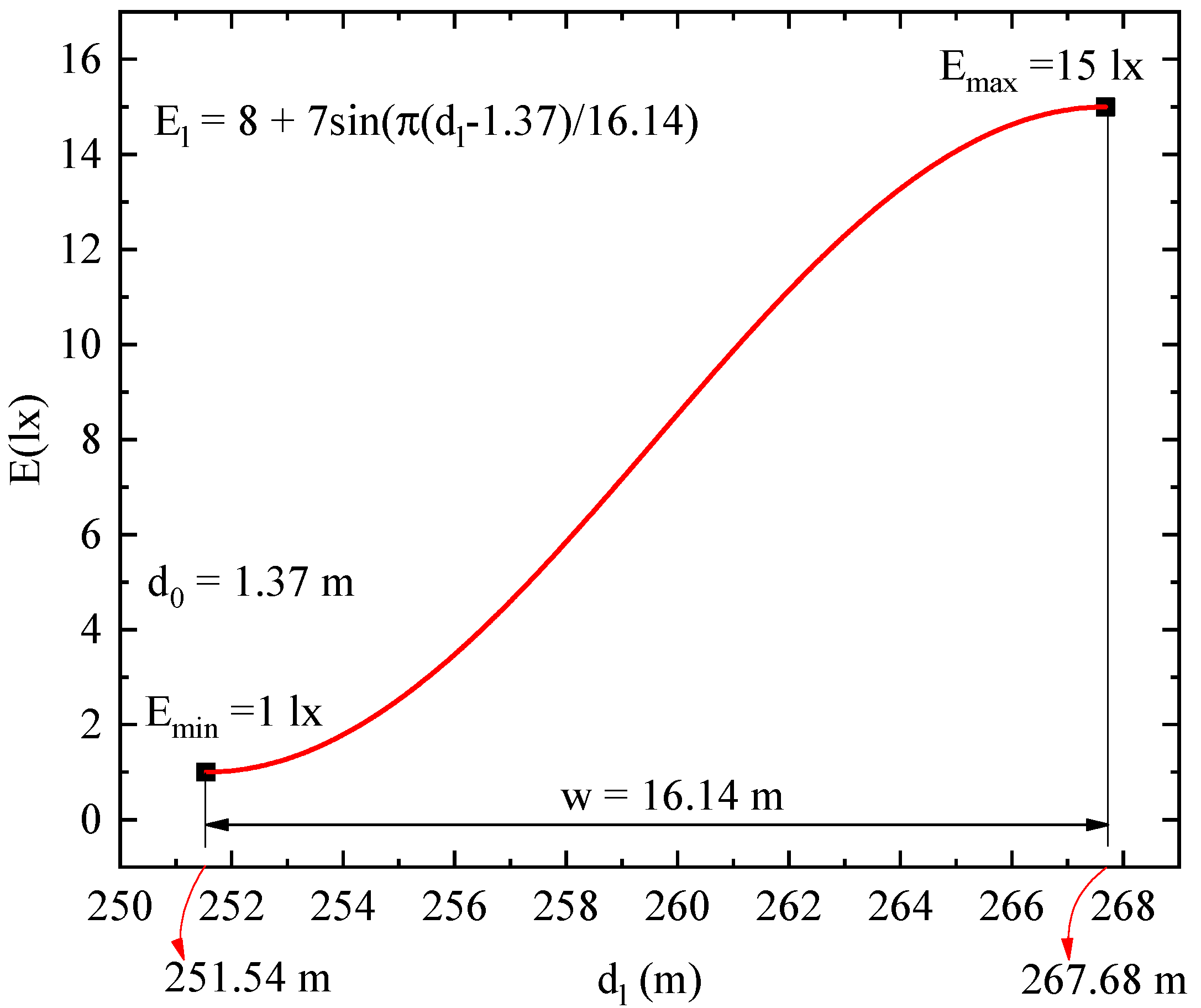
In real lighting, illuminance distributions, which may be influenced by light loss, obstacles, and shade, are not as systematical as simulated ones. The illuminances measured beneath two neighbor luminaires may differ greatly. Therefore, in each lane along the longitudinal direction, we apply two sine functions to reconstruct illuminance between two luminaires. As shown in Figure 4, there are three longitudinal directions LD1 at one side, LD2 in the middle, and LD3 at the other side. The LD1 and LD3 are along the luminaires, and LD2 is in the middle. We measured three points in each longitudinal direction and apply Equation (1) for each two adjacent points, and w is equal to the distance of the two adjacent points. Therefore, we can obtain the illuminance distributions in the longitudinal direction, e.g., and for LD1. For example, we applied the sine function for a part or road from dl = 151.54 m to dl = 267.68 m corresponding to Emin = 1 lx and Emax = 15 lx as shown in Figure 5. We obtained El(Emax, Emin) = 8 + 7sin(π(dl − 1.37)/16.14).
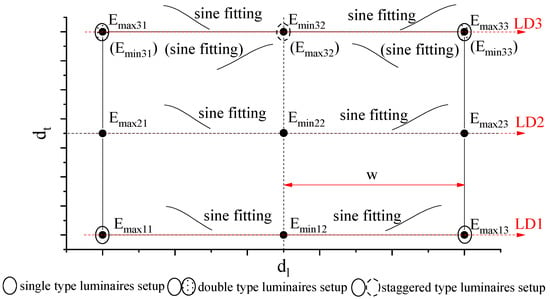
Figure 4.
Illuminance modelling using sine functions with feature points between two luminaires of single type, double type, and staggered type. The illuminances in brackets correspond to the staggered type. LD1: Longitudinal Direction No. 1, LD2: Longitudinal Direction No. 2, and LD3: Longitudinal Direction No. 3.
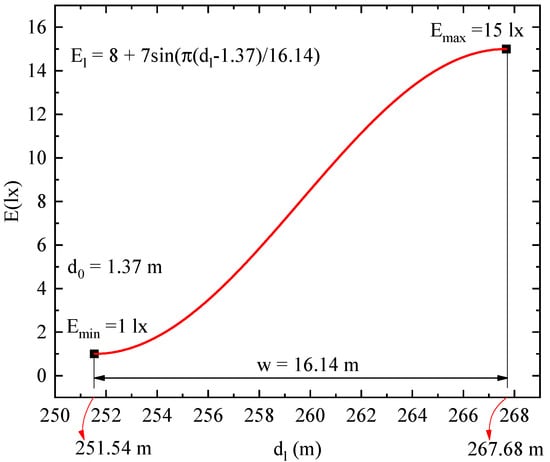
Figure 5.
Example of applying sine model at distances from dl = 151.54 m to 267.68 m in the longitudinal direction of a road. The Emin and Emax corresponding to the two distances are 1 lx and 15 lx, respectively, and w = 16.14 m. All known values, Emin, Emax, w, dl, and El, are used in Equation (1), and d0 is calculated to be 1.37 m.
3.2. Illuminance Distributions and Modelling in the Transverse Direction
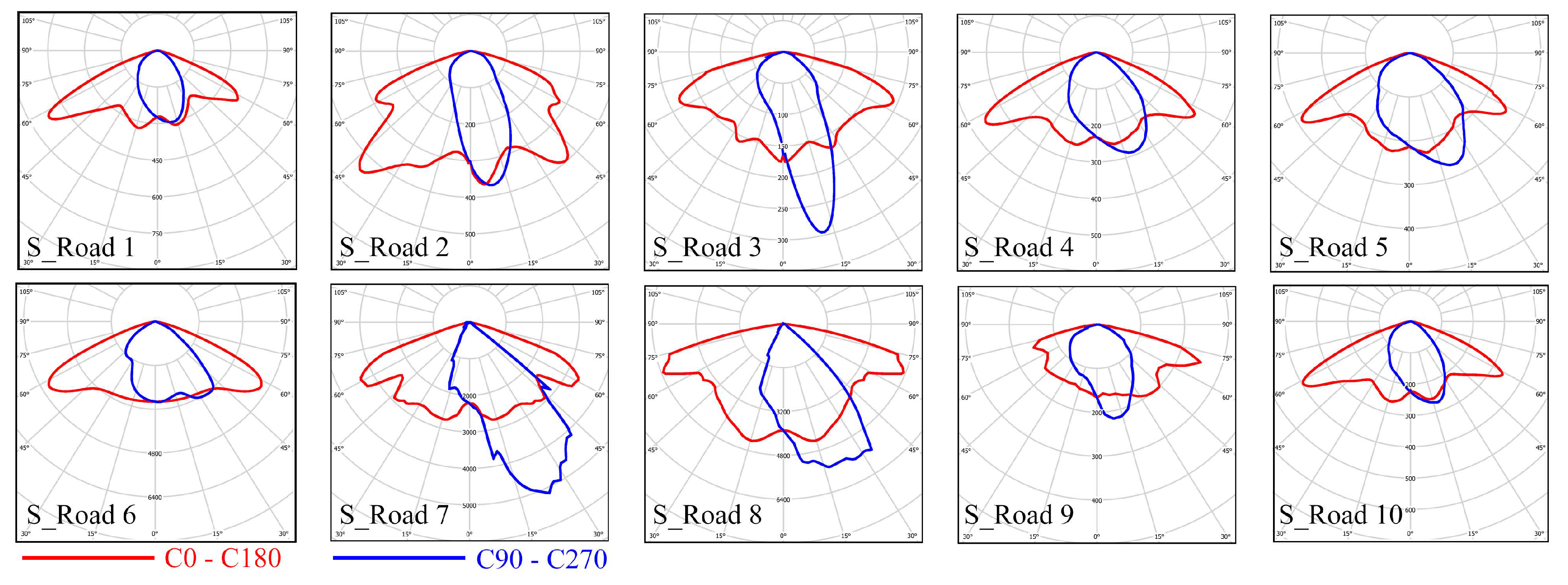
We simulated illuminance distributions in the transverse direction in a four-lane road with 10 kinds of luminaires including high intensity discharge (HID) lamps and LEDs. The road is 14 m in width, and the luminaires are set at a height of 8 m. The 10 luminaires are different in photometric curves, wattages, and lumen outputs as shown in Figure 6, resulting in different illuminance distributions.
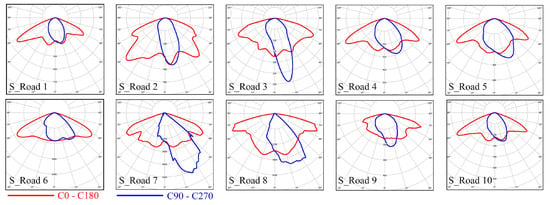
Figure 6.
Photometric curves of the 10 different luminaires. The S_Roads represent the 10 simulated road lighting configurations. S_Roads 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9 and 10 are HID lamps, and S_Roads 6, 7 and 8 are LED luminaires. Wattages and lumen outputs: S_Road 1, 259 W & 27,000 lm; S_Road 2, 261 W & 20,500 lm; S_Road 3, 201 W & 20,500 lm; S_Road 4, 153 W & 14,500 lm; S_Road 5, 149 W & 14,500 lm; S_Road 6, 91 W & 10,280 lm; S_Road 7, 108 W & 11,000 lm; S_Road 8, 105 W & 11,690 lm; S_Road 9, 372 W & 20,000 lm; S_Road 10, 253 W & 20,500 lm.
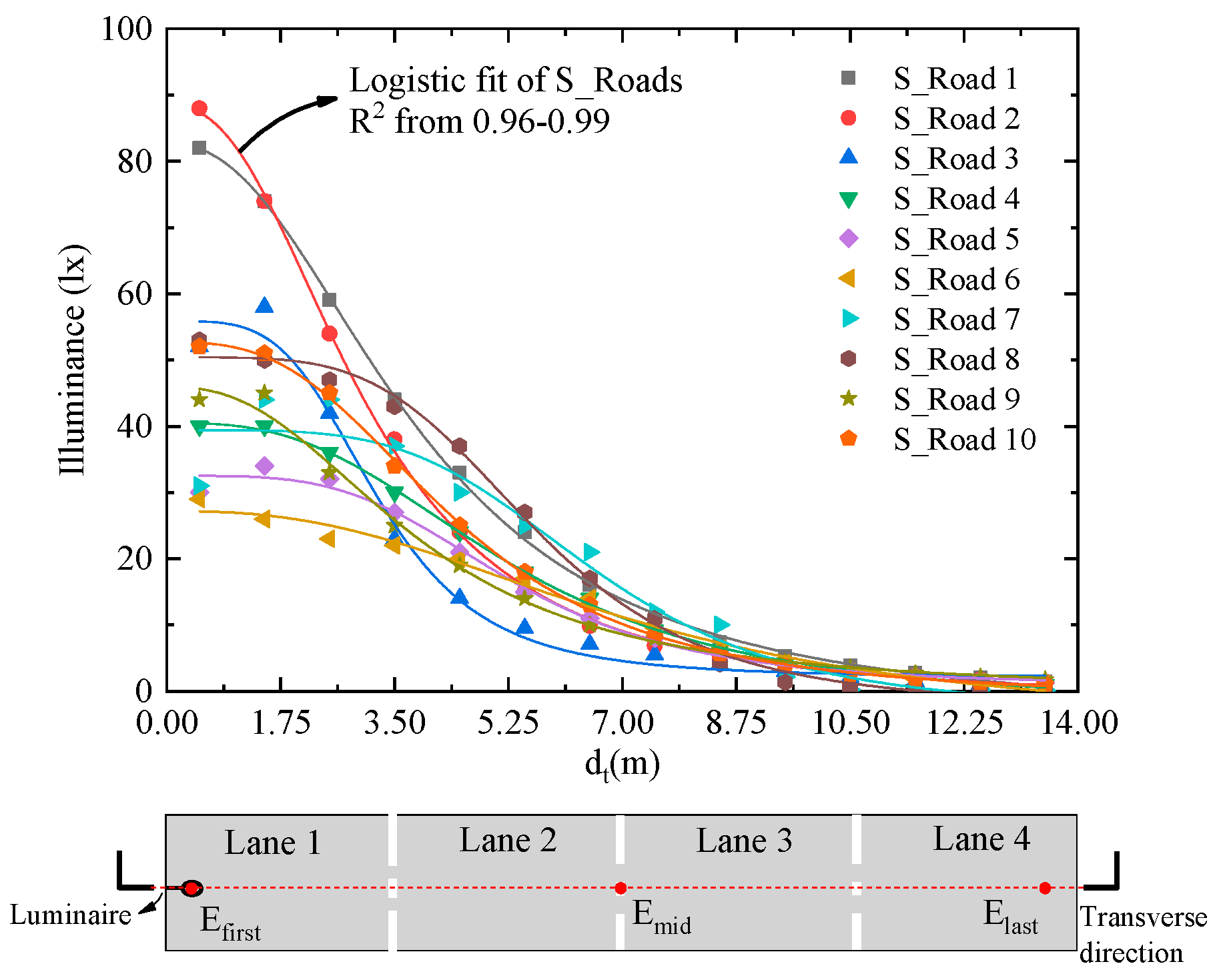
The illuminances, generally decreasing from one side beneath luminaires to the other side, are shown in Figure 7. The maximum illuminances mostly appear beneath the luminaires, and the minimum illuminances on the other side of the road. Although the decreasing rates are different for 10 illuminance distributions, they conform to the logistic fit function in Equation (2) with high R2 from 0.96 to 0.99. The Et is the illuminance in the transverse direction, E1 is the first illuminance, E2 is the last illuminance, dt is the distance in the transverse direction, d′0 is the distance where maximum illuminance of the feature points in the transverse direction decreases to a half, and p is the power. The p value may be varied with decreasing rates of the data. For the 10 logistical fittings in Figure 7, the p values are 3.18 ± 0.80, namely p may be set to 3.0 in default. We can apply the least square method in the curve fitting process to obtain a precise p value by virtue of curve fitting toolbox in MATLAB (Mathworks). However, the logistic function works well in the transverse direction when many points (>3) are measured. If only three feature points are measured, the E1 should be equal to Efirst beneath the luminaire, and the E2 should be equal to Elast at the opposite side in Figure 7. The R2 is decreased.
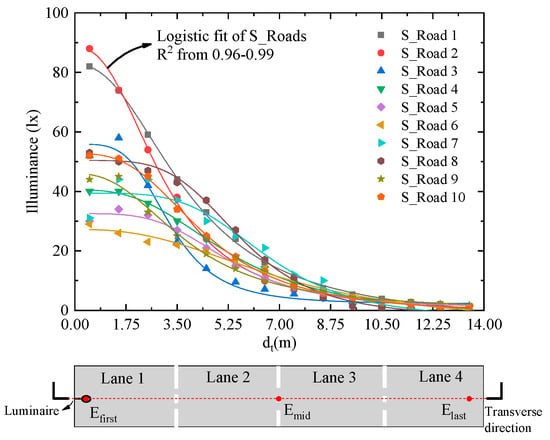
Figure 7.
Illuminance distributions in the transverse direction (red-dashed line) start from the illuminance beneath the luminaire. The S_Roads represent the 10 simulated road lightings.
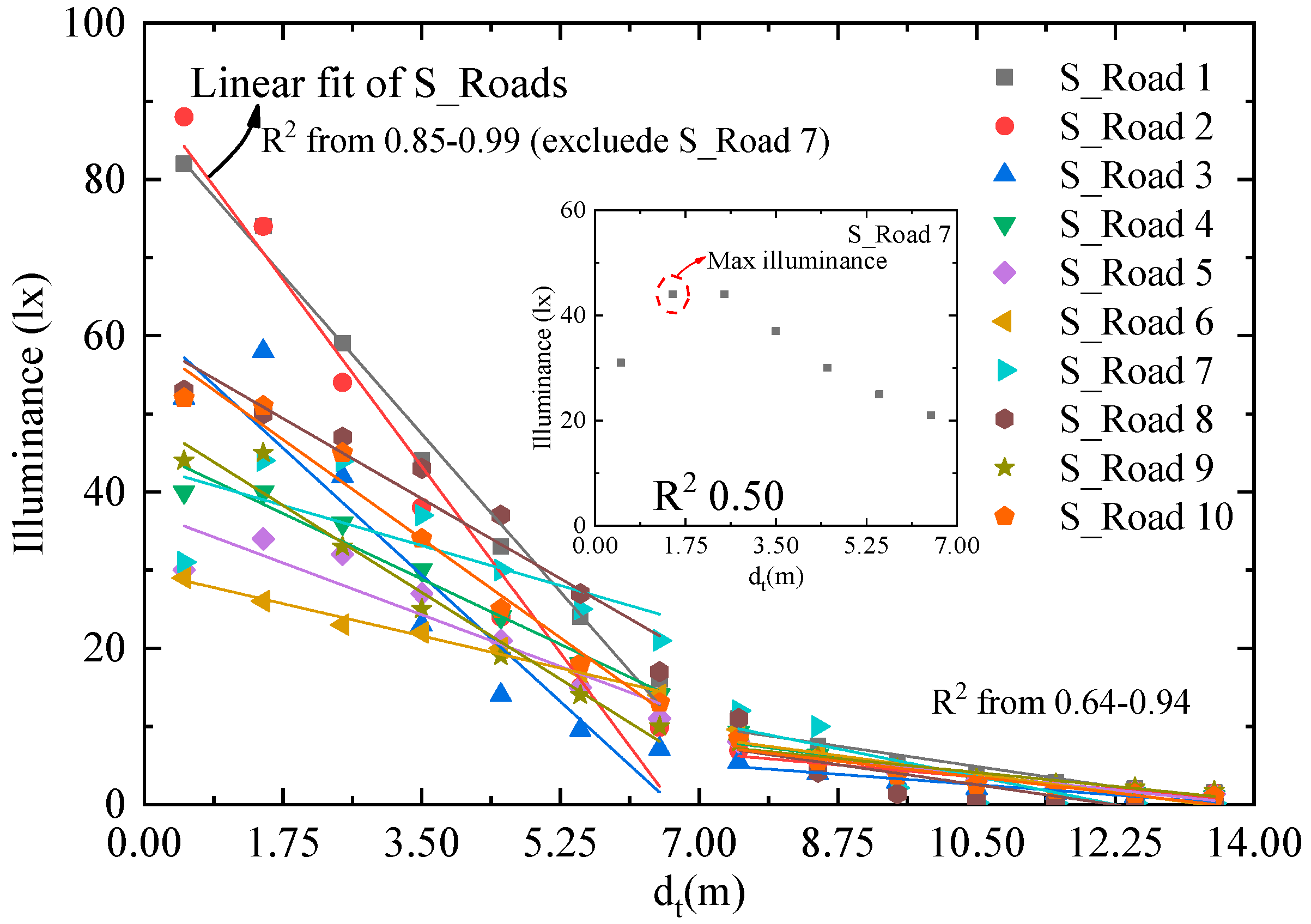
The logistic function is complex, and the fitting precision decreases if three feature points are applied. We therefore also applied two partitional linear fittings in the transverse direction of the 10 illuminance distributions as shown in Figure 8. The fitting also reaches a good level of R2 from 0.85 to 0.99 in the first two lanes of interest, except S_Road 7. For S_Road 7, the maximum illuminance appears at the second point, and the R2 is only 0.50. Although the fitting precision of linear function is not as precise as logistic function, it may not be decreased by fitting with three feature points.
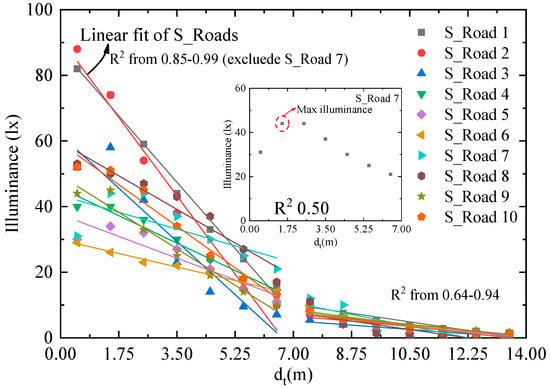
Figure 8.
Illuminance distributions in the transverse direction fitted with linear function.
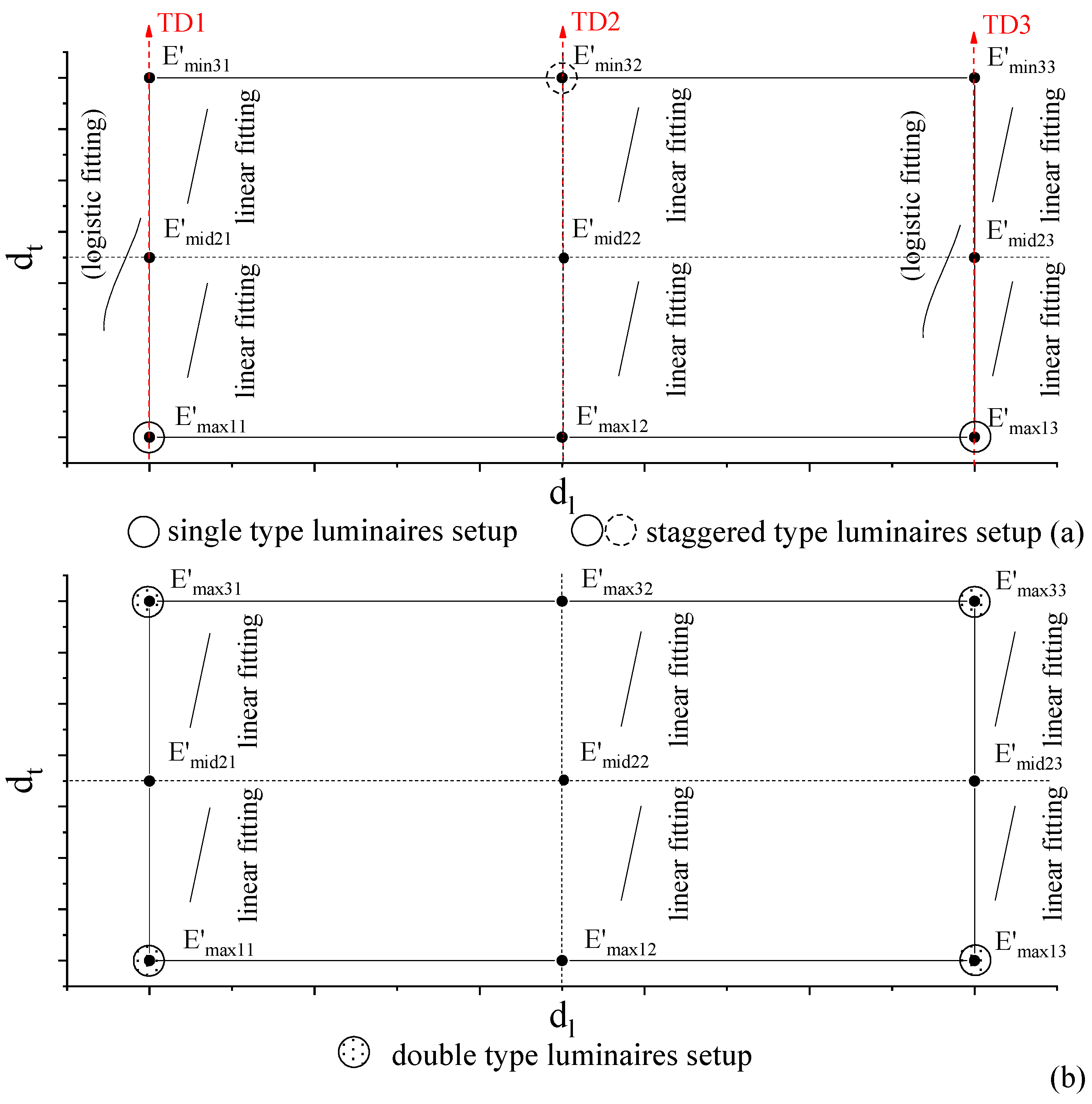
In the transverse direction of road lighting, we applied the logistic/linear model to reconstruct the illuminance. The logistic function can only be applied in the transverse direction along the luminaire, e.g., TD1 and TD3. As shown in Figure 9, we modelled the illuminance distributions in the transverse direction with nine feature points with linear functions. The logistic function can be applied for single- and staggered-type lighting in TD1 and TD3. Although logistic function in Figure 7 shows better fitting than the linear fitting in Figure 8 with many measured points, it does not show better precisions when fitting with three feature points in the transverse direction. Therefore, in this work, we apply linear modelling for each two neighboring feature points in the transverse directions.
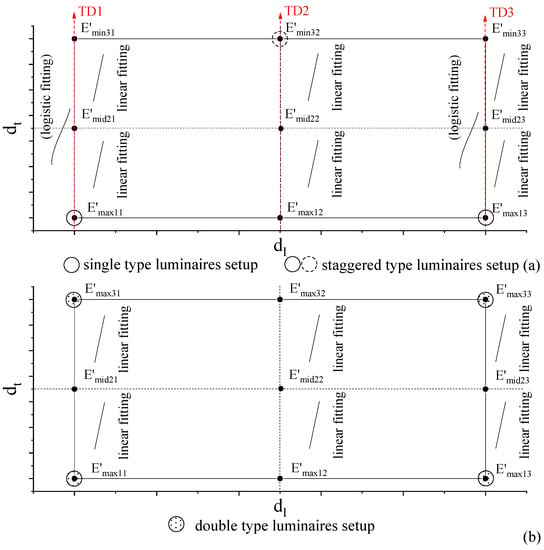
Figure 9.
Illuminance modelling using logistic/linear functions with feature points in the transverse direction of single type, staggered type, and double type. (a) Logistic/linear fittings are applied for single- and staggered-type luminaires setup between two luminaires. (b) Linear fittings are applied for double-type luminaires setup between two luminaires. TD1: Transverse Direction No. 1, TD2: Transverse Direction No. 2, TD3: Transverse Direction No. 3. The feature points with the same rank numbers correspond to those in Figure 4. TD1 and TD3 are perpendicular to the luminaires direction. TD2 is in the middle for the single and double types, and perpendicular to the luminaires for the staggered type.
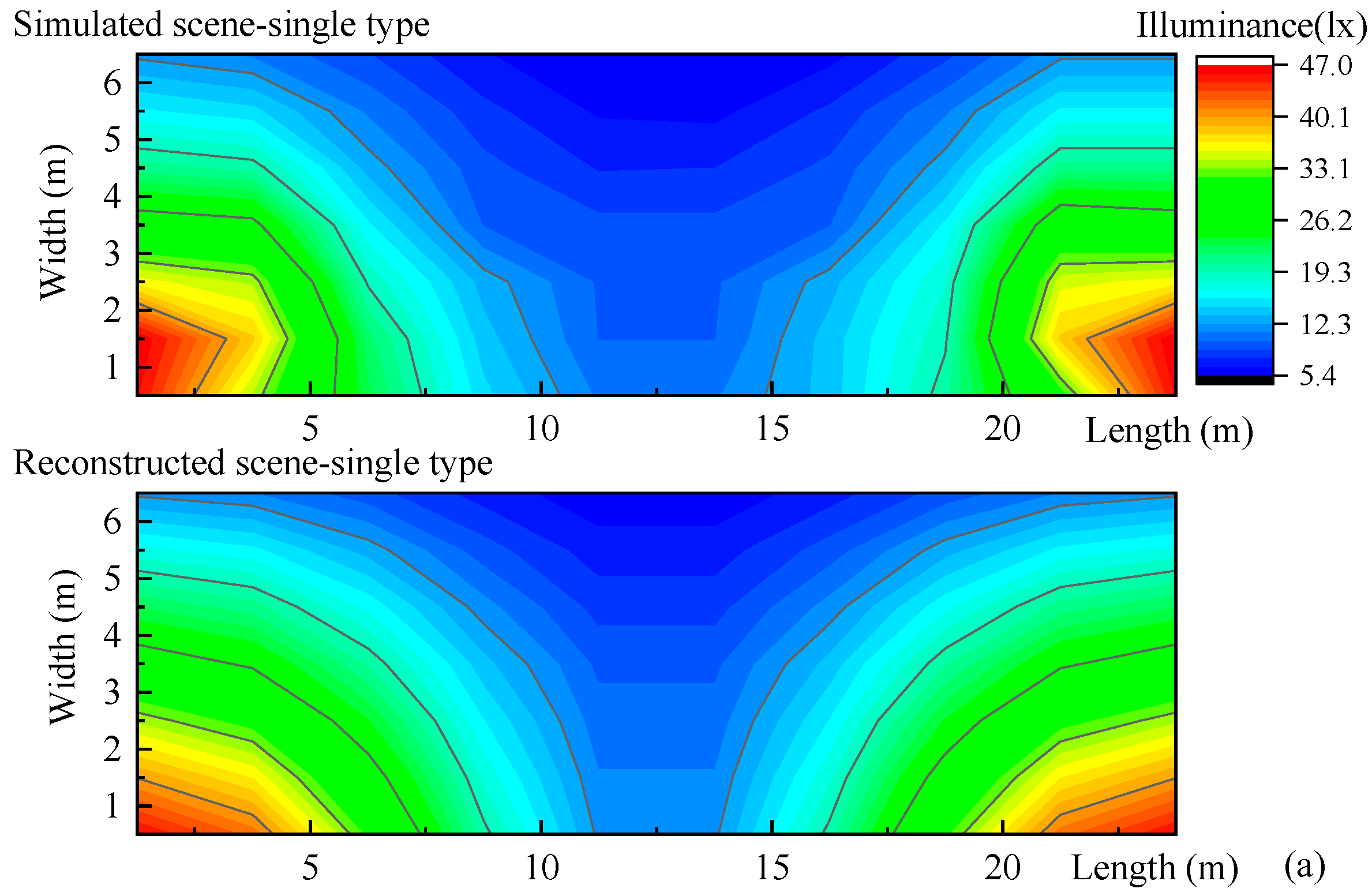
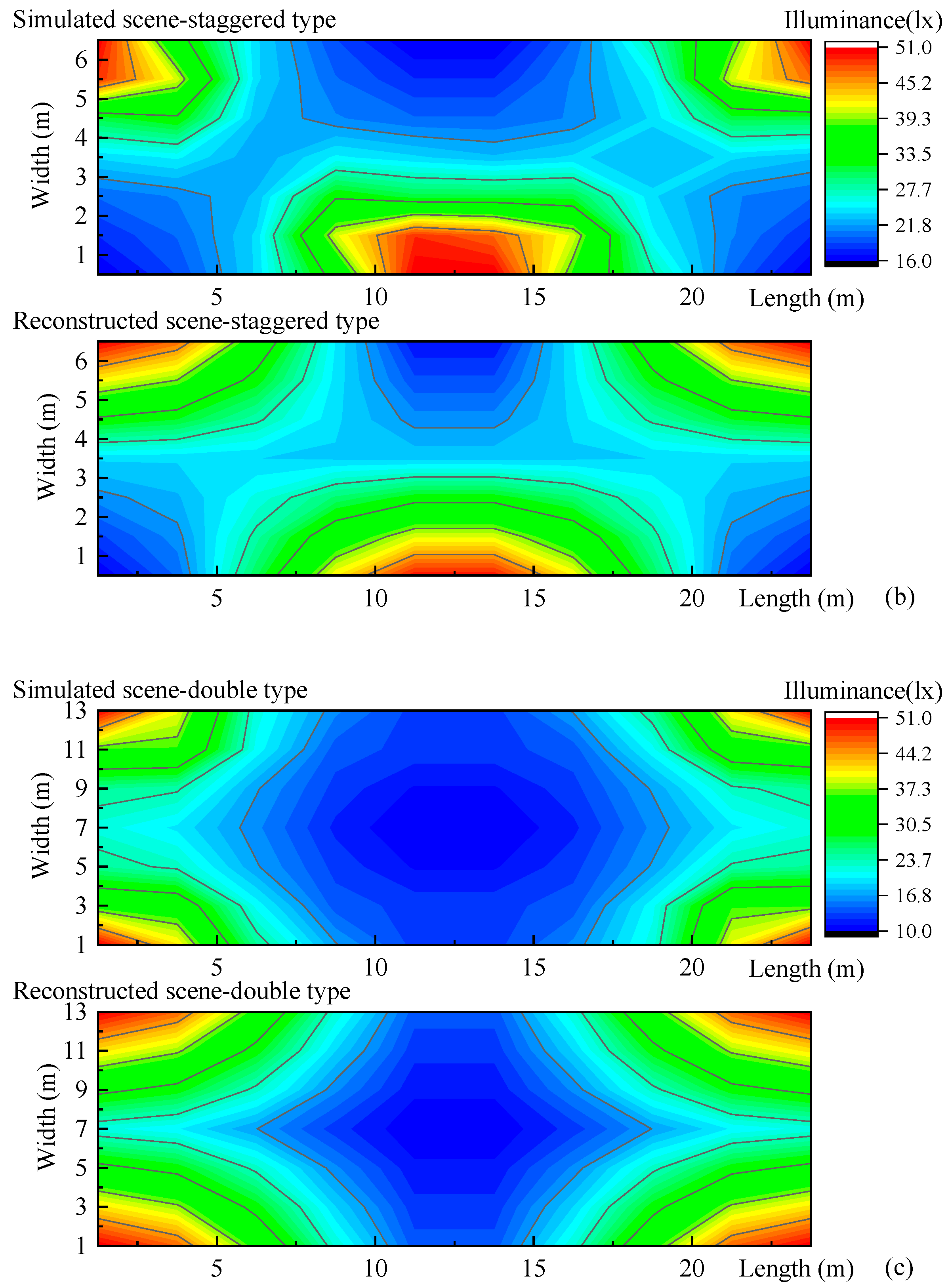
3.3. Illuminance Construction of Simulated Road Lighting Scenes
We reconstructed the illuminances of above-mentioned simulated road lighting scenes (Figure 2), the single-type, staggered-type, and double-type road lighting setups as shown in Figure 10. The results of simulated and reconstructed road lighting formed by 10 × 7 points are shown in Table 1. The differences between reconstructed illuminances, referring to simulated illuminances, are calculated from the 10 × 7 points. The mean difference, calculated from the 70 points, is from 10.5 to 19%. The differences in minimum illuminance and the average illuminance and uniformity tend to be smaller.
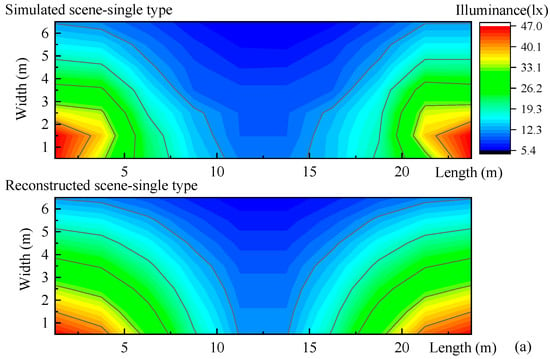
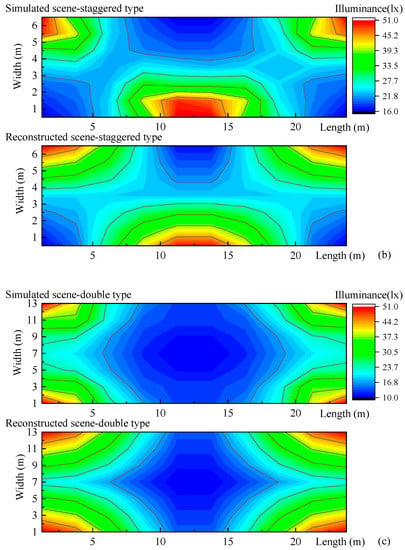
Figure 10.
Illuminance reconstructions of simulated road lighting scenes of (a) single type (b) staggered type, and (c) double type in Section 2.1. The measured illuminance points for these road lighting scenes are 10 × 7. The reconstructed illuminances are based on nine feature points.

Table 1.
Illuminance parameters of simulated and reconstructed road lightings. S represents simulated road lighting, and R represents reconstructed road lighting. The ‘difference’ is the difference of reconstructed and simulated illuminance. The ‘mean difference’ is the mean of difference of reconstructed and simulated illuminance calculated point to point. U0 is the overall uniformity and is calculated by dividing the minimum and average illuminance.
3.4. Verifications with Real Road Lighting Scenes
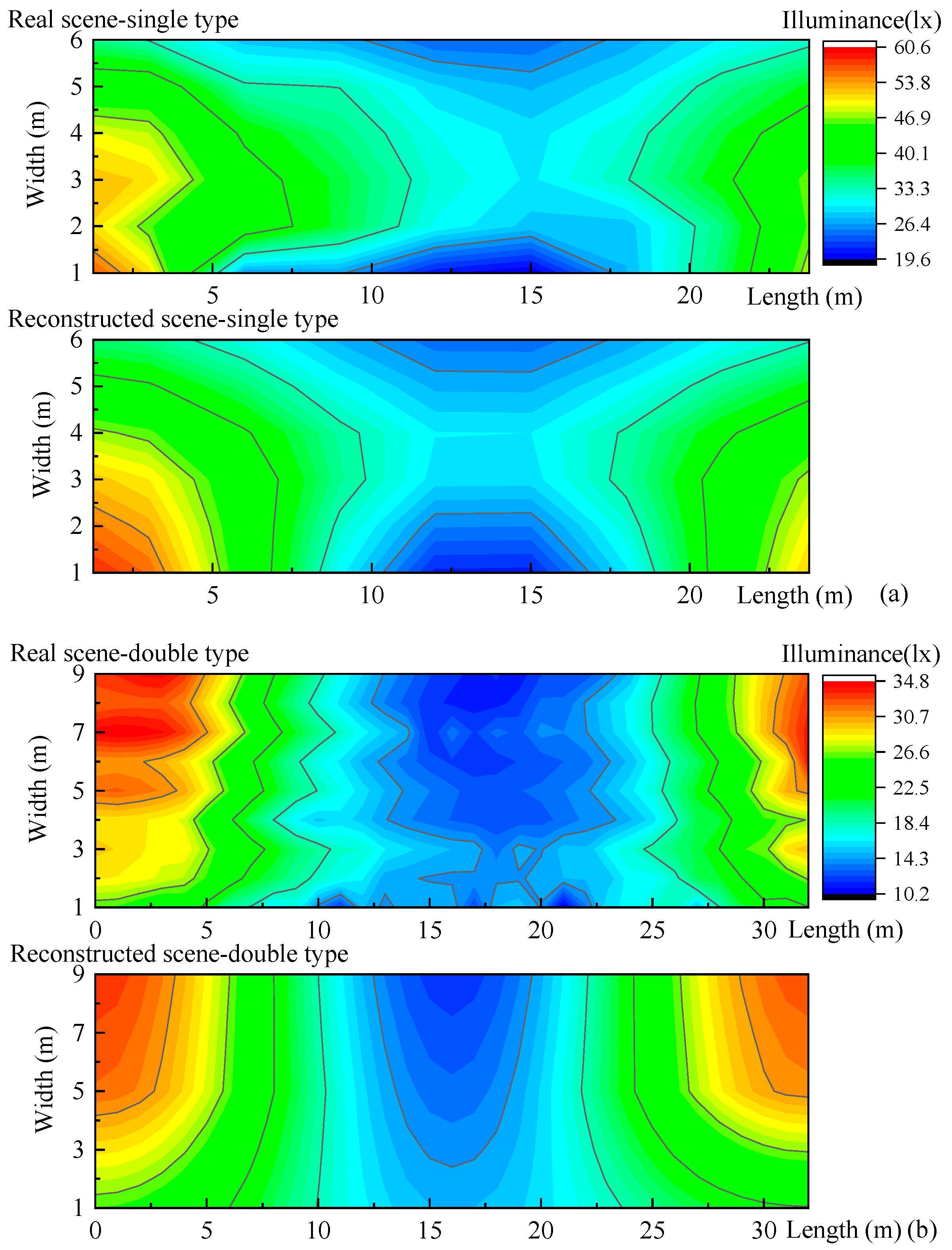
We measured two real road lighting setups in Shenzhen, China: one of single type, 10 × 6 points measured, and one of double type, 33 × 9 points measured, and reconstructed the illuminance with nine feature points as shown in Figure 11. The mean differences, as shown in Table 2, are 6.0 and 11.6%, respectively.
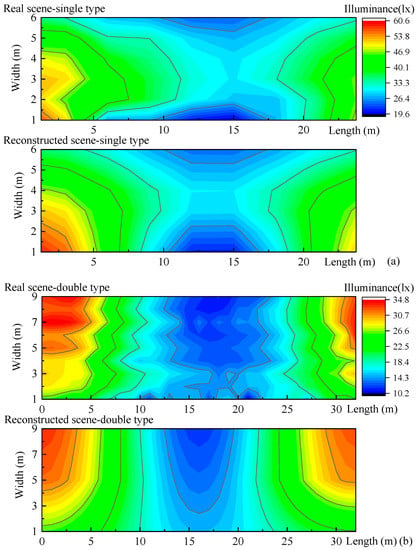
Figure 11.
Illuminance reconstructions of real road light scenes. (a) The real single road lighting, 27 m in length and 7 m in width. The measured points are 10 × 6. (b) The real double road lighting, 32 m in length and 20 m in width, and a half is measured. The measured points are 33 × 9.

Table 2.
Illuminance parameters of simulated and reconstructed road lightings. The ‘Real’ represents real road lighting, and ‘R’ represents reconstructed road lightings.
4. Application
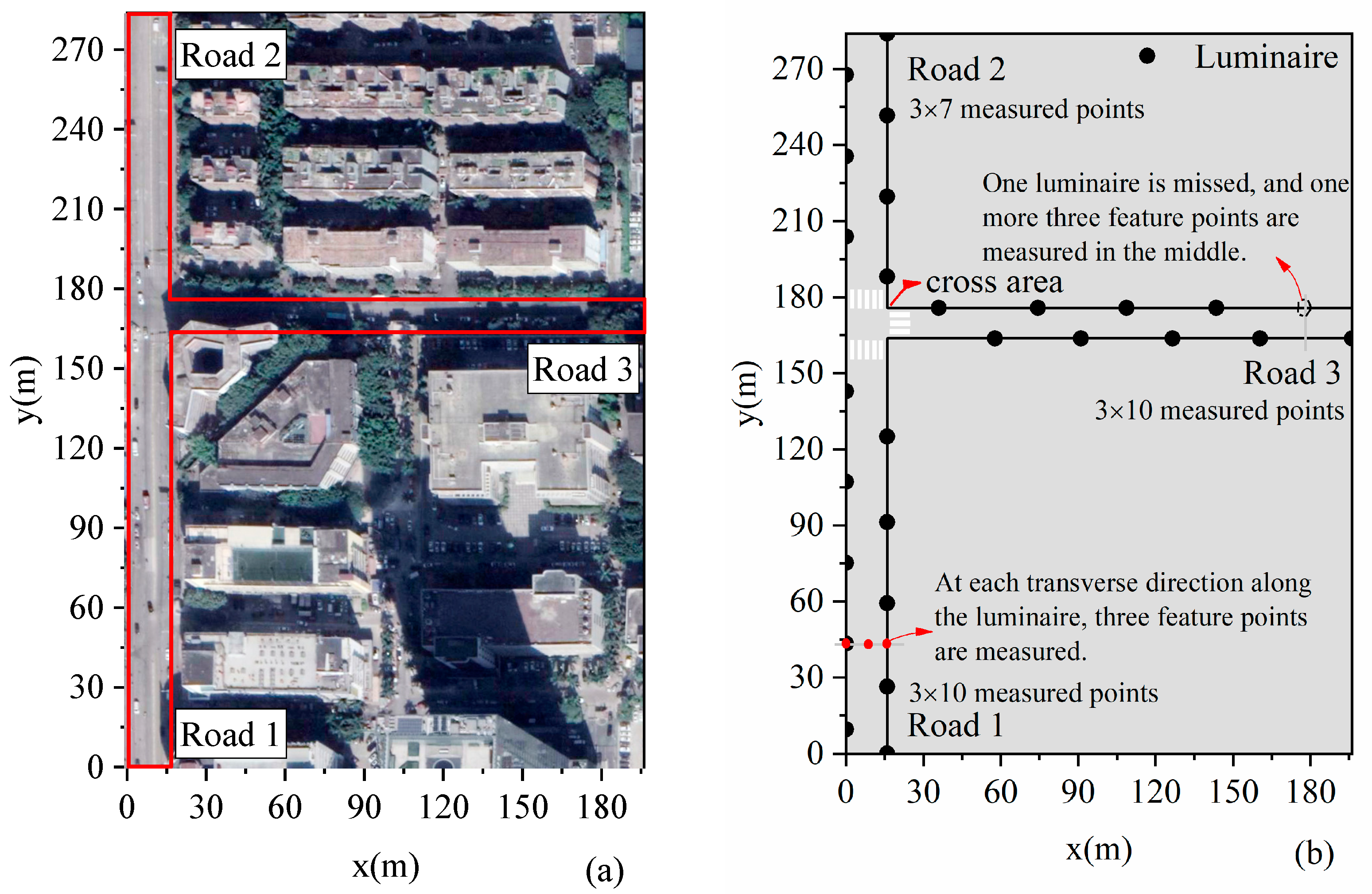
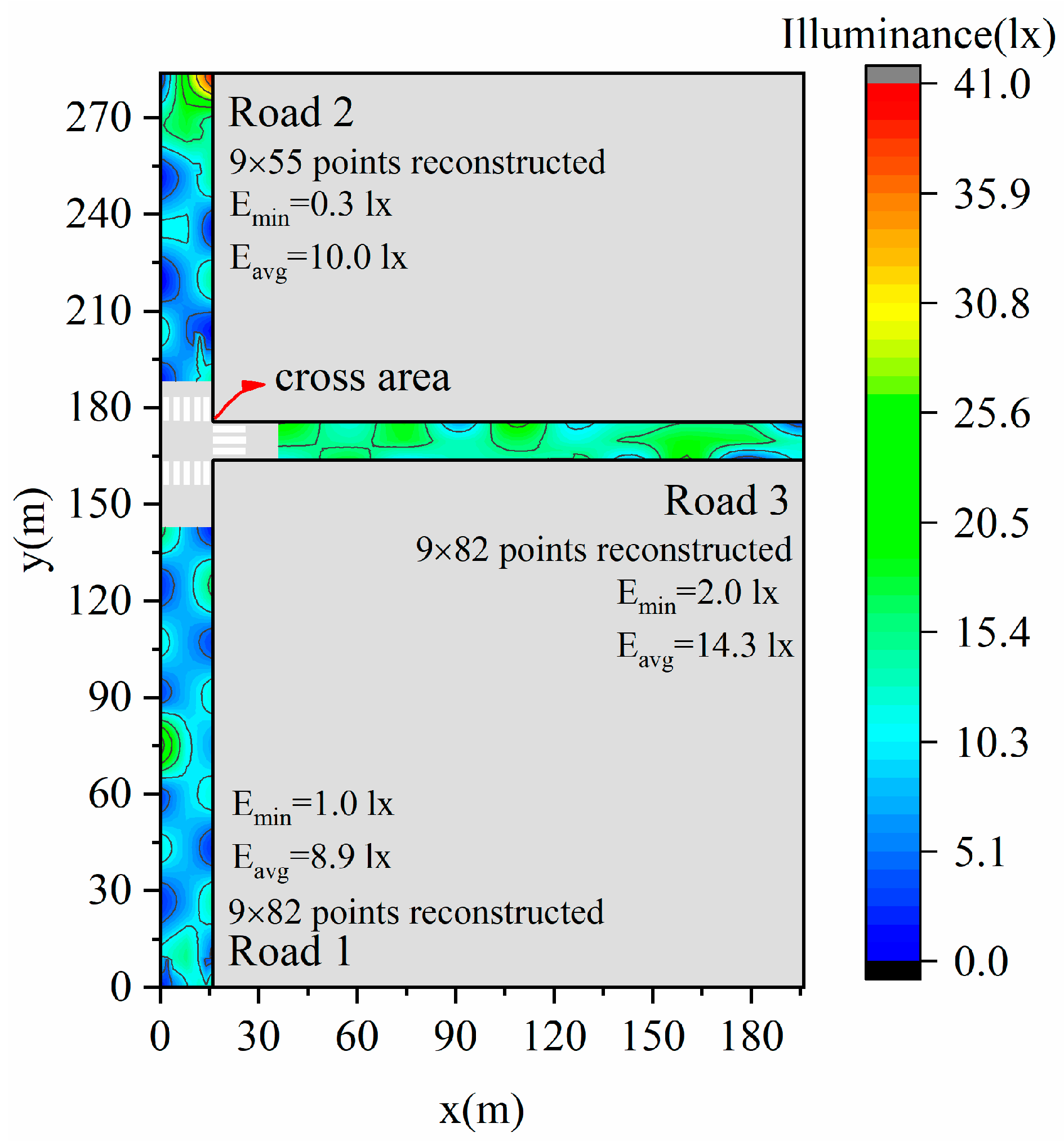
We measured feature points of three road lighting environments in a block in Shenzhen, China, in Figure 12 and reconstructed the illuminance distributions using our proposed approach in Figure 13. The illuminances in the transverse directions of each road are reconstructed with linear functions and longitudinal directions with sine functions. Luminaires may sometimes be missing or not in operation in some parts, and the double-/staggered-type distributions may be regarded as single-type in such situations. The accuracy of reconstruction work is therefore robust when applied to streets with missing luminaires. The average illuminances for the three roads are 8.9, 10.0, and 14.3 lx, respectively. For the three roads, the same type of luminaire is used. The spectral power distribution of the luminaires, namely typical LEDs, is shown in Figure 14.
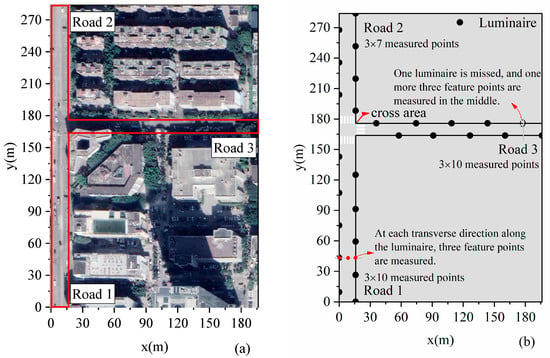
Figure 12.
Road lighting measurements. (a) Three roads, Road 1, 165 m × 16 m, Road 2, 100 m × 16 m, and Road 3, 180 m × 12 m, are measured (b) Luminaire distributions are as follows: for Road 1, 10 luminaires, for Road 2, 7 luminaires, and, for Road 3, 9 luminaires.
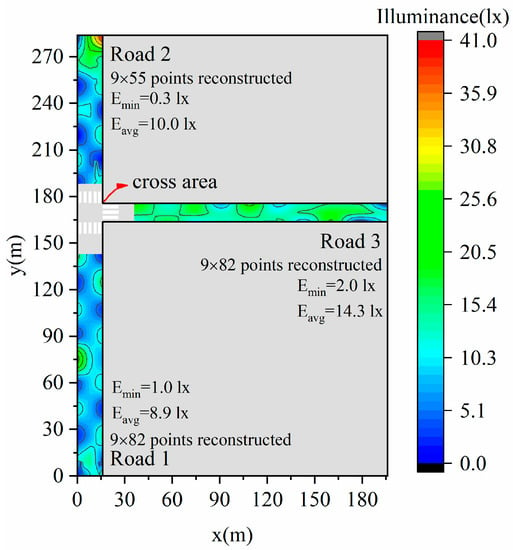
Figure 13.
Illuminance reconstructions of three roads using linear function in the transverse direction and sine function in the longitudinal direction.
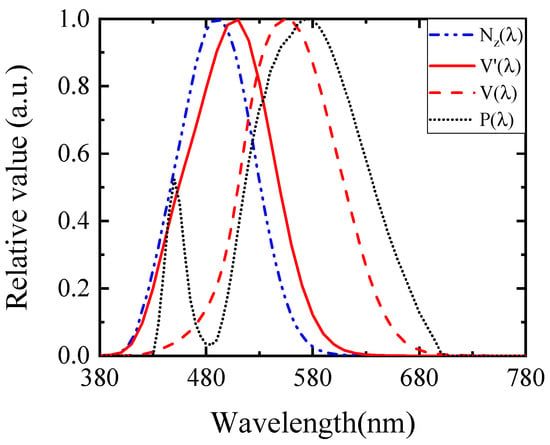
Figure 14.
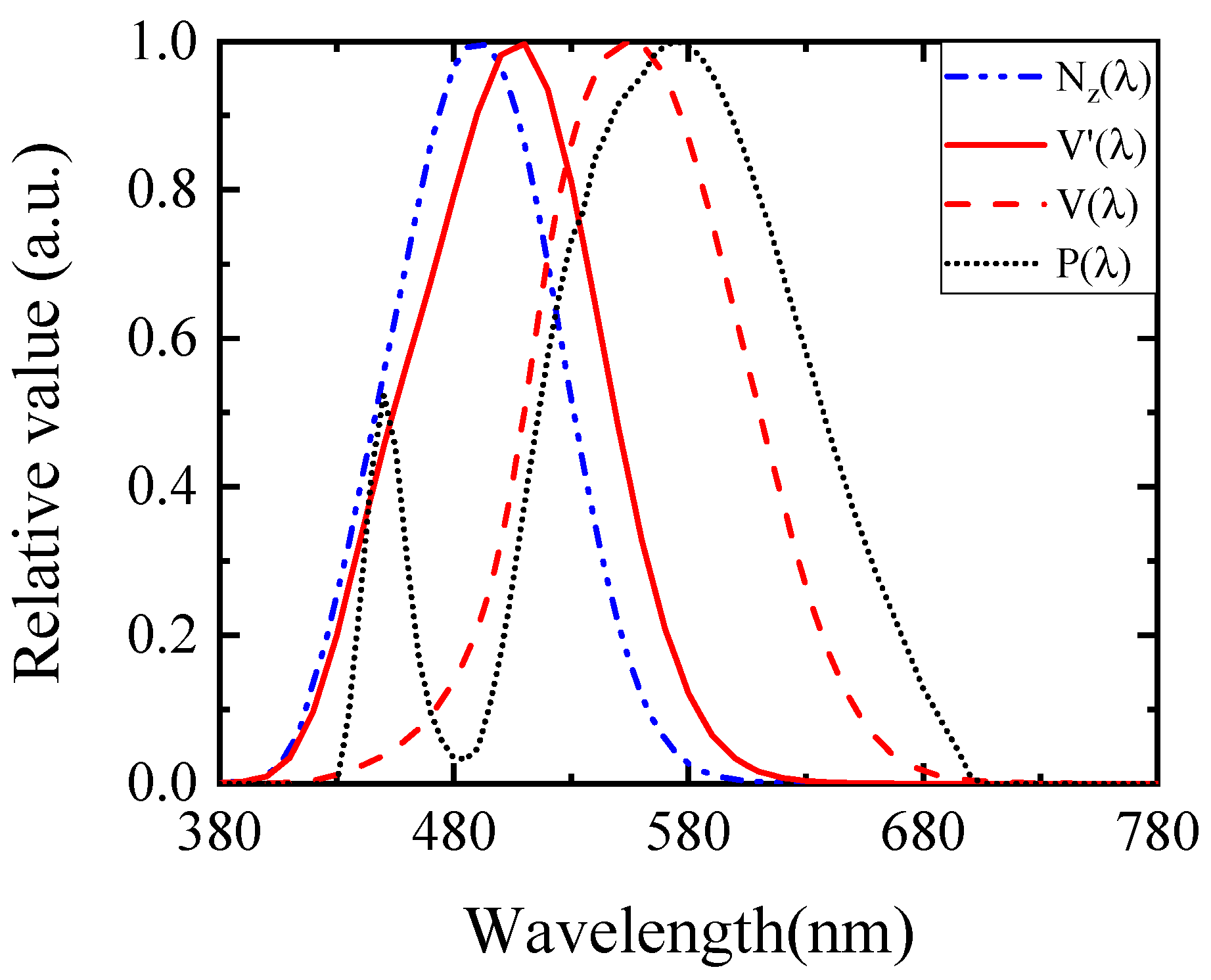
Spectral power distribution P(λ) of the LED luminaires used in the three roads. The V′(λ) and V(λ) are the scotopic and photopic sensitivity functions. The Nz(λ) is the melanopic sensitivity function [31]. Characteristics of the LED luminaires are correlated color temperature 3640 K, chromaticity coordinates (0.42, 0.45), CIE Ra 63, and IES Rf 69 and Rg 85.
To study the mesopic luminance performance, the illuminance should be transformed to photopic luminance using a rule-of-thumb formula [40] in Equation (3), where q0 is the surface luminance coefficient [41] equal to 0.0700 sr−1 for a standard road. S/P ratio [42], the quotient of luminous efficacy in scotopic vision and photopic vision, is necessary information in calculation of mesopic luminance. The corresponding S/P ratio of the LED luminaires is 1.33. In the calculation of mesopic luminance processes, an adaptation field [42] should be applied. However, for a long road, it is difficult to define such an adaptation field. Therefore, we transform the photopic adaptation luminance to mesopic luminance [43] point to point.
For the calculation of equivalent melanopic lux [31], the corneal illuminance or vertical illuminance is required. For commercial roads, the corresponding illuminance ranges are 10–20 lx horizontally and 2–4 lx vertically at a 1.5 m height [1]. The vertical illuminance is about 0.2 times the horizontal illuminance. Some standards [44] recommend lighting classes for pedestrians and pedal cyclists to have average horizontal–vertical illuminance values as follows: 15–5.0 lx for the P1 class, 10–3.0 lx for the P2 class, 7.5–2.5 lx for the P3 class, 5.0–1.5 lx for the P4 class, 3.0–1.0 lx for the P5 class, and 2.0–0.6 lx for the P6 class, respectively. The vertical illuminances are about 0.2–0.33 times the horizontal illuminance. There is no research work studying the relationship between the corneal illuminance and horizontal illuminance, and it is impossible to obtain big data of vertical illuminances with the present technology. Based on the relation of horizontal illuminance and vertical illuminance recommended in standards, we assumed a linear relation between them as shown in Equation (4), where Ec is the corneal illuminance, and α is the coefficient within 0–1.0. In reference to the relation for commercial roads [1], we set the coefficient α as 0.2 in this work. This result can be refined if new research results on horizontal–vertical illuminance are given.
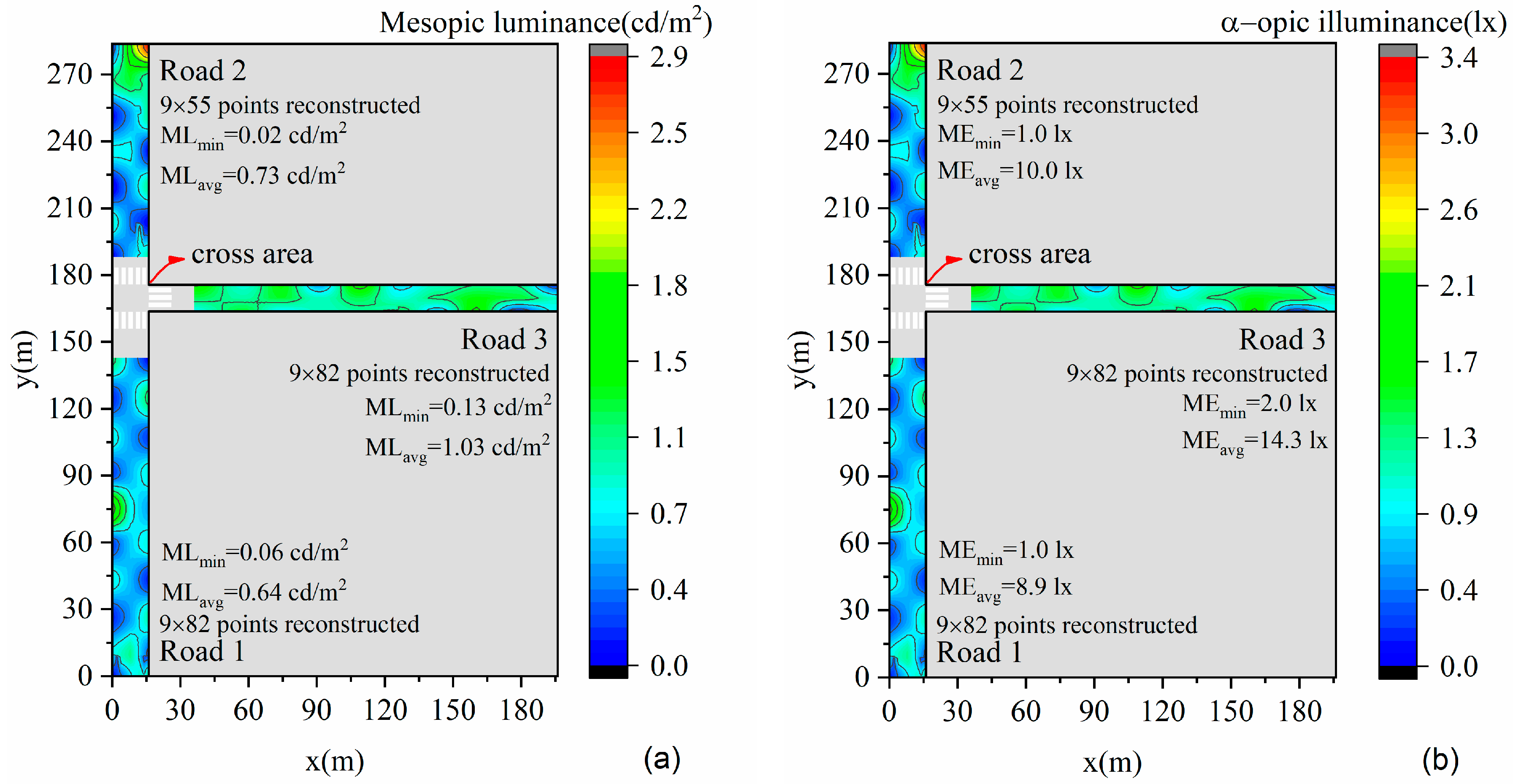
Based on the reconstructed illuminance, the mesopic luminance and equivalent melanopic lux are shown in Figure 15. According to Chinese road lighting standards [28], the three roads are classed as secondary roads, and luminance should reach 1.0 cd/m2. The average mesopic luminance of Road 3 reaches the standard. For the melanopic illuminance, it is better to be small for nighttime applications. However, there are no standards or research providing clear guidance on melanopic illuminance requirements for road lighting at present, and we cannot comment on the melanopic illuminance performance of these three roads. Although equivalent melanopic lux as a metric is gradually being incorporated into research work and applications, there are suggestions [45] that it may be incorrect. Our work just shows the feasibility for evaluating such performance. If more acknowledged research is presented in the future, the calculation on melanopic illuminance could be refined.
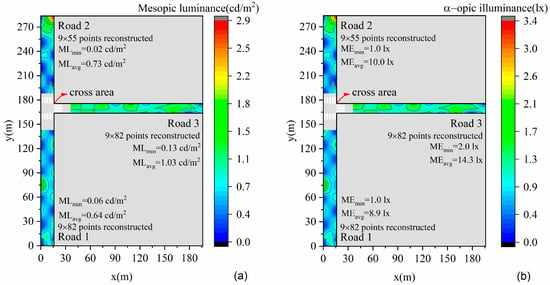
Figure 15.
Lighting performance evaluation. (a) Mesopic luminance calculation based on reconstructed illuminance; (b) equivalent melanopic lux calculation based on reconstructed illuminance. ML represents mesopic luminance, and ME represents equivalent melanopic lux.
5. Discussion
We present an approach to reconstructing horizontal illuminances for three types of road lighting configurations, single-type, double-type, and staggered-type high-pole (≥6 m) road lighting. These types of lighting cover most present road lighting. The basic assumption of applying the sine model and linear model is that local maximum illuminance may appear beneath or around the luminaire. There are three reasons that may explain why local maximum illuminance is likely to appear beneath the luminaire. First, most luminaires’ intensities are relatively strongly downward, except the bat-wing type photometric curves. Second, the relation between illuminance and intensity conforms to the inverse square law, and the place beneath the luminaire is of the smallest distance from the luminaire. Third, two neighbor luminaires in road lighting are about 20–30 m away, and influence from neighboring luminaire is often insufficient to cause the illuminance between two luminaires to exceed the maximum illuminance beneath a single luminaire. Most road lighting may achieve these three conditions, and the proposed models may work well in most situations. The bat-wing photometric curve luminaires are designed for high uniformity, and illuminances at different measured points are close. Conforming to the proposed model or not, few errors may take place for bat-wing-type luminaires. Real road lighting measurements agreed well with the reconstructed illuminance distributions produced by our model, suggesting the model may be useful in providing reasonably accurate estimates of illuminance values for most road lighting situations. Although we did not apply the model to a road lighting setup in which lighting with a long arm that places the lamp over the center of the carriageway is installed, our model may work equally well with such lighting. In the transverse direction, the long arm may lead to the maximum illuminance appear in the middle lane, and minimum illuminances may appear at two sides, which may not influence the sine distribution in the longitudinal direction. In the transverse direction, as a linear function is applied for two neighbored points, and the linear model may still suit for such cases. There might be some special cases for road lighting that may not work, such as luminaires with a low pole height, or neighboring luminaires that are relatively close together.
Lighting has both positive and negative impacts on human beings, the environment, and ecology. Obtaining and using big lighting data can add value to the scientific investigation of these impacts. Remote sensing technology is a promising approach to obtaining big lighting data, but there are some limitations in resolutions, wavelength ranges [38], and intensity transformations at present. These cannot be solved in a short time. As mentioned above, two works have tried to obtain big lighting data. In Hale’s work [39], although they succeed in detecting light source categories with photographs taken from a 900 m height, their illuminance transformations from image pixel intensities reached a 3–10-fold error at different illuminance levels. Bennie’s work [34] made assumptions about hemispherical isotropic point sources emitting at equal intensity in all directions, but this is not true for most luminaires and will lead to large errors. Furthermore, many details about the setup of luminaires are required. Their model is therefore of limited use. Our proposed reconstruction approach is dependent on measured feature points, guaranteeing an error within 20%. It is much more precise than reported approaches to obtain lighting data. A major benefit of our reconstruction point is that only a small number of measurement points are required, making workload and resource allocation more acceptable.
However, there are still some limitations for this work. First, in the longitudinal direction, the sine model reaches a good level of precision in the reconstruction work, but in the transverse direction, there is potential for improvement on the linear reconstruction model. In each transverse direction, if more measured points (more than three feature points) were adopted, the logistic model may be better for single and staggered-type road lighting, and the sine model may be better for double-type road lighting. Second, the reconstructed illuminances were based on a limited number of tests of lighting on real roads. More road lighting should be tested to verify the effectiveness of the reconstructed models. Third, for transformation from horizontal illuminance to luminance or corneal illuminance, rule-of-thumb formulas are applied. These require more refined formulae and precise coefficients in the future.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we reconstructed urban road lighting illuminances with nine feature points between two luminaires. We proposed sine models for reconstruction in longitudinal directions and linear models in transverse directions based on analyses of 10 simulated road lighting setups and 8 real road lighting setups measured in England. We reconstructed illuminance for three simulated roads and two real roads and compared them with reconstructed illuminances based on the nine feature point models we developed. Mean differences between the simulated and reconstructed illuminances were 15.2% for single-type lighting, 10.5% for staggered-type lighting, and 19.0% for double-type lighting, and those between the real and reconstructed illuminances were 6.0% for single-type lighting, and 11.6% for double-type lighting. The overall average illuminance across the whole of each road estimated from the reconstructed illuminances differed from overall averages from the simulated illuminances by 8.9%, 5.0%, and 17.8%, and the real measurements by 2.1% and 6.9%. We believe these margins of error are acceptable in practical applications given the significant logistical savings offered by taking only nine measurements between luminaires, compared with current measurement standards. Although not clearly stated empirically in existing literature, a ± 20% error in illuminance measurements may be acceptable. Existing road lighting guidance 1 specifies recommended average horizontal illuminances for different classifications of roads, such as S-class. The difference between adjacent category levels within a class of road does not exceed 20%, so even an error of ±20% in terms of illuminance reconstruction would not result in a change in the categorization of the road. Based on present results and analysis, it is likely that, for most situations, the average error for reconstructed illuminance using our model may be within 20%.
Further illuminance reconstruction work for three long roads shows that it is feasible to obtain more lighting data with a few measured feature points. Based on the reconstructed illuminance, we also demonstrate that mesopic luminance and equivalent melanopic illuminance can be easily calculated. The illuminance reconstruction work may also therefore help for evaluation of lighting efficiency and healthy performance in urban areas. The obtained illuminance data may also be used to study other impacts of lighting on areas such as the environment, local ecology, and crime, and the precision for the present reconstructed works are adequate.
There are two other major advantages to our approach. First, the approach may work together with remote sensing technology, and requirements on imagery resolution and data storage can be decreased, as only features points are required. Second, the approach can augment manual measurement of an area of interest. In the future, it may not be possible to obtain real-time lighting data for some areas, even if the remote sensing technology is sufficiently advanced, and we are likely to still have to rely on manual measurements. However, as shown from the field measurements in Section 4, the lighting distributions along a single road may vary between significantly depending on the area of the road that is measured. This indicates the traditional way of measuring road lighting using one section of the road to represent its entirety may not be very precise. Our reconstruction method would allow a more accurate estimate to be made of the illuminance distribution along the full length of the road, without the need for additional measurement points.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Y.; Methodology, Q.Y.; Software, Q.Y.; Validation, Q.Y. and J.U.; Formal Analysis, Q.Y.; Investigation, H.W. and X.Z.; Resources, Q.Y., H.W. and X.Z.; Data Curation, Q.Y.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Q.Y.; Writing—Review & Editing, Q.Y. and J.U.; Visualization, Q.Y.; Supervision, Q.Y.; Project Administration, Q.Y.; Funding Acquisition, Q.Y.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant number 61605125 and Shenzhen Knowledge Innovation Program—Basic Research grant number JCYJ20170818141507055.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Steve Fotios and Chris Cheal for their valuable suggestions, the reviewers’ professional comments, and the editors’ immediate processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Boyce, P.R.; Fotios, S.; Richards, M. Road lighting and energy saving. Light. Res. Technol. 2009, 41, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y. Research on Facial Recognition and Color Identification under CMH and HPS Lamps for Road Lighting. LEUKOS 2009, 6, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, M.S.; Bullough, J.D.; Akashi, Y. Several views of metal halide and high-pressure sodium lighting for outdoor applications. Light. Res. Technol. 2009, 41, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, D.; Song, X.; Chen, Y. LEDs: A Promising Energy-Saving Light Source for Road Lighting. APPEEC 2009, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.; Monteiro, A.L.; Uttley, J. Evaluation of pedestrian reassurance gained by higher illuminances in residential streets using the day–dark approach. Light. Res. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanvik, P.O. Effects of road lighting: An analysis based on Dutch accident statistics 1987–2006. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotios, S.; Unwin, J.; Farrall, S. Road lighting and pedestrian reassurance after dark: A review. Light. Res. Technol. 2014, 47, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Bian, Y. Establishing Functional Model of Photometric Performance of Trichromatic Light Sources in Chromaticity Diagrams. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, M.; Djokic, L.; Pojatar, D.; Strbac-Hadzibegovic, N. Technical and economic analysis of road lighting solutions based on mesopic vision. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrias, A.; Eloholma, M.; Halonena, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y. Road lighting and headlights: Luminance measurements and automobile lighting simulations. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 13201-3:2015. Road Lighting, Part 3: Calculation of Performance; BSI: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- CIE 115:2010. Lighting of Roads for Motor and Pedestrian Traffic; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gaston, K.J.; Gaston, S.; Bennie, J.; Hopkins, J. Benefits and costs of artificial nighttime lighting of the environment. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttley, J.; Fotios, S. Using the daylight savings clock change to show ambient light conditions significantly influence active travel. J. Environ. Psychol. 2017, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackett, M.; Frith, W. Quantifying the impact of road lighting on road safety-A New Zealand Study. IATSS Res. 2013, 36, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Highways Agency. Design Manual for Roads and Bridges; Advice Note TA49/07; HMSO: London, UK, 2007.
- Jennifer, V. Light, Lighting, and Health: Issues for Consideration. LEUKOS 2005, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommel, V.W. From road lighting to city beautification. Ingineria iluminatului. Light. Eng. 2007, 9, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, Y.; Saunders, D.; Creighton, R.; Coltrin, E.; Simmons, J. Solid-state lighting: An energy-economics perspective. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leccese, F.; Salvadori, G.; Rocca, M. Critical analysis of the energy performance indicators for road lighting systems in historical towns of central Italy. Energy 2017, 138, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuechly, H.U.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Ruhtz, T.; Lindemann, C.; Christian, W.; Fischer, J.; Hölkera, F. Aerial survey and spatial analysis of sources of light pollution in Berlin, Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 126, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, A.V.; Castillo, J.L.S.; Castillo, A.M.; Gómez, J.M.P.; Gutierrez-Martinez, J.M. An Artificial Neural Network for Analyzing Overall Uniformity in Outdoor Lighting Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccali, M.; Bonomolo, M.; Ciulla, G.; Galatioto, A.; Lo Brano, V. Improvement of energy efficiency and quality of street lighting in South Italy as an action of Sustainable Energy Action Plans. The case study of Comiso (RG). Energy 2015, 92, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE 191:2010. Recommended System for Mesopic Photometry Based on Visual Performance; CIE Central Bureau Kegelgasse: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q. Application-dependent spectrum optimization of four-package LEDs. Light. Res. Technol. 2016, 48, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enezi, J.; Revell, V.; Brown, T.; Wynne, J.; Schlangen, L.; Lucas, R. A ‘Melanopic’ Spectral efficiency function predicts the sensitivity of melanopsin photoreceptors to polychromatic lights. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2011, 26, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BS EN 13201-2:2003. Road Lighting—Part 2: Performance Requirements; BSI: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- CJJ 45-2015. Standard for Lighting Design of Urban Road; China Architecture & Buliding Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Internationale de l’Éclairage. Principales Decisions (6e Session, 1924), CIE Sixième Session, Genève, Juillet, 1924. Recueil des Travaux et Compte Rendu de Séances; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1926; pp. 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rea, M.S.; Figueiro, M.G. Light as a circadian stimulus for architectural lighting. Light. Res. Technol. 2018, 50, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.J.; Peirson, S.N.; Berson, D.M.; Brown, T.M.; Cooper, H.M.; Czeisler, C.A.; Figueiro, M.G.; Gamlin, P.D.; Lockley, S.W.; O’Hagan, J.B.; et al. Measuring and using light in the melanopsin age. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, D.; Bieske, K. Definition and measurement of circadian radiometric quantities, light and health—Non-visual effects. In Proceedings of the CIE symposium, Vienna, Austria, 30 September–2 October 2004; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin, R. The real-time city? Big data and smart urbanism. GeoJournal 2014, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Mapping artificial lightscapes for ecological studies. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, D.P.; Kiser, J.D. Aerial Photography and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.R.; Arvesen, J.; Sutton, P.; Small, C.; Ebener, S. The Nightsat mission concept. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2645–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hong, S.H. Relationship between the reflected brightness of artificial lighting and land-use types: A case study of the University of Arizona campus. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 11, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Phinn, S. Illuminating the capabilities of Landsat 8 for mapping night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.D.; Davies, G.; Fairbrass, A.J.; Matthews, T.J.; Rogers, D.F.; Sadler, J.P. Mapping Lightscapes: Spatial Patterning of Artificial Lighting in an Urban Landscape. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIE TN 007:2017. Interim Recommendation for Practical Application of the CIE System for Mesopic Photometry in Outdoor Lighting; CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CIE 144:2001. Road Surface and Road Marking Reflection Characteristics; CIE Technical Report; CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 2001; 35p. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, T.; Ayama, M.; Akashi, Y.; Hara, N.; Kitano, T.; Kodaira, Y.; Sakai, K. Adaptation luminance simulation for CIE mesopic photometry system implementation. Light. Res. Technol. 2016, 48, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIE TN 004:2016. The Use of Terms and Units in Photometry–Implementation of the CIE System for Mesopic Photometry; CIE Technical Report; CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 2016; 115p. [Google Scholar]
- BS EN 13201-2:2015. Road Lighting; Performance Requirements; BSI: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiro, M.; Rea, M.S. Quantifying Circadian Light and Its Impact. 2017. Available online: https://www.archlighting.com/technology/quantifying-circadian-light-and-its-impact_o (accessed on 18 August 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).