The Use of Co-Precipitation to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4) from Waste Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Measurement Tools
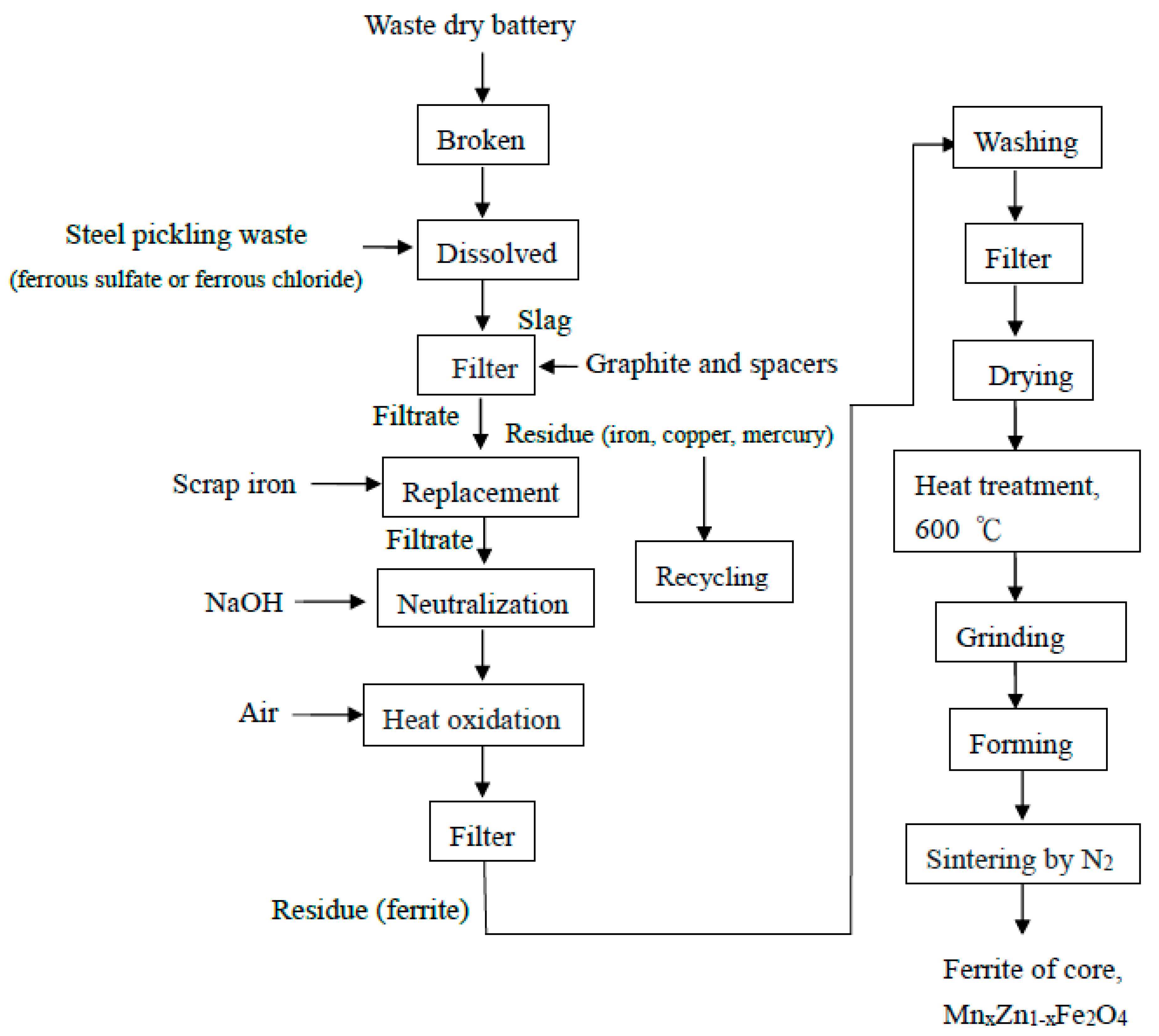
2.2. The Use of Waste Dry Batteries to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4)
2.3. The Chemical Reaction Mechanism and an Analysis of the Use of a Dry Battery to Prepare Ferrite
3. Results and Discussions
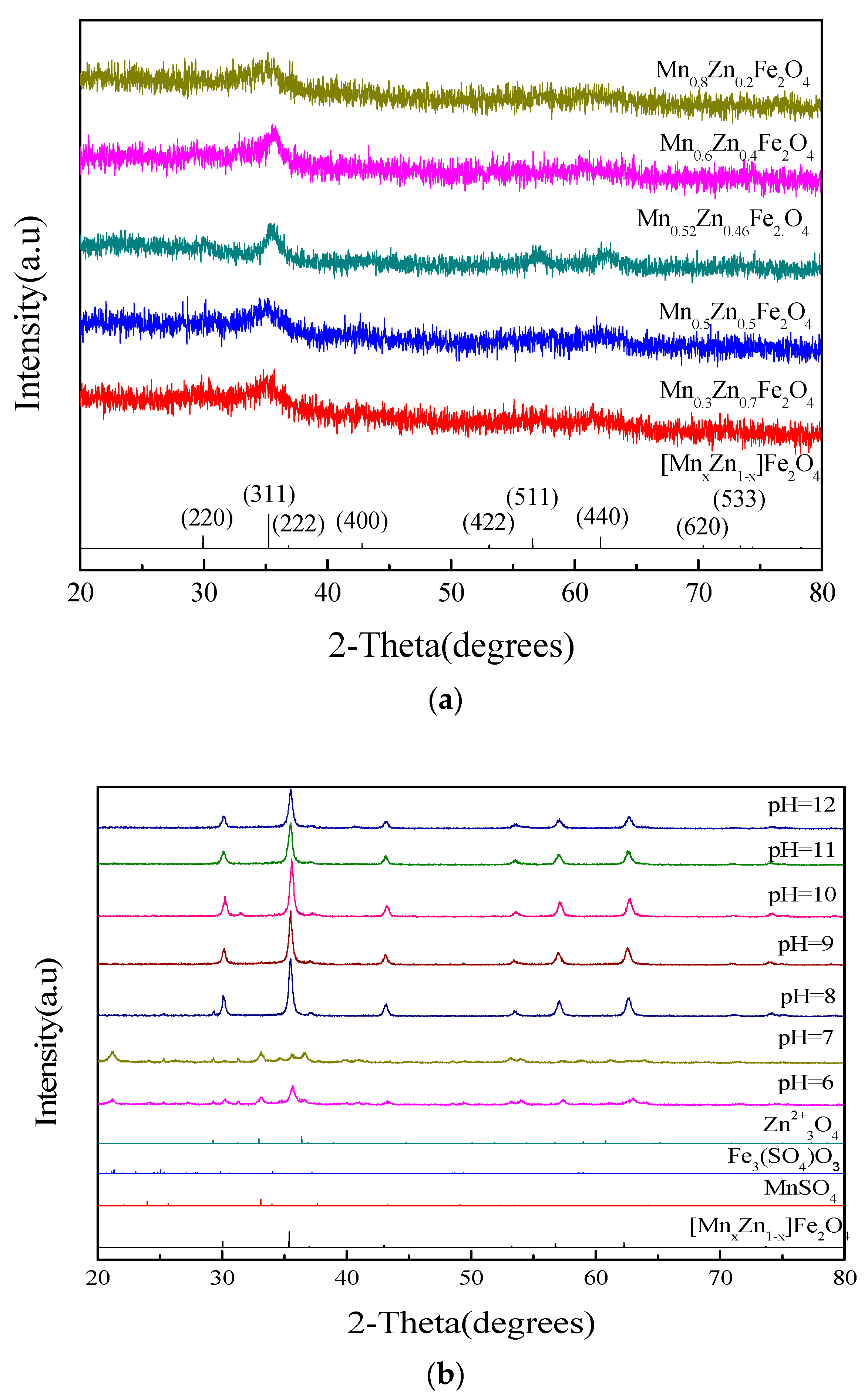
3.1. The Effect of Different Mn and Zn Contents on the Crystal Phase
3.2. The Effect of Different Mn and Zn Contents on the Magnetic Properties
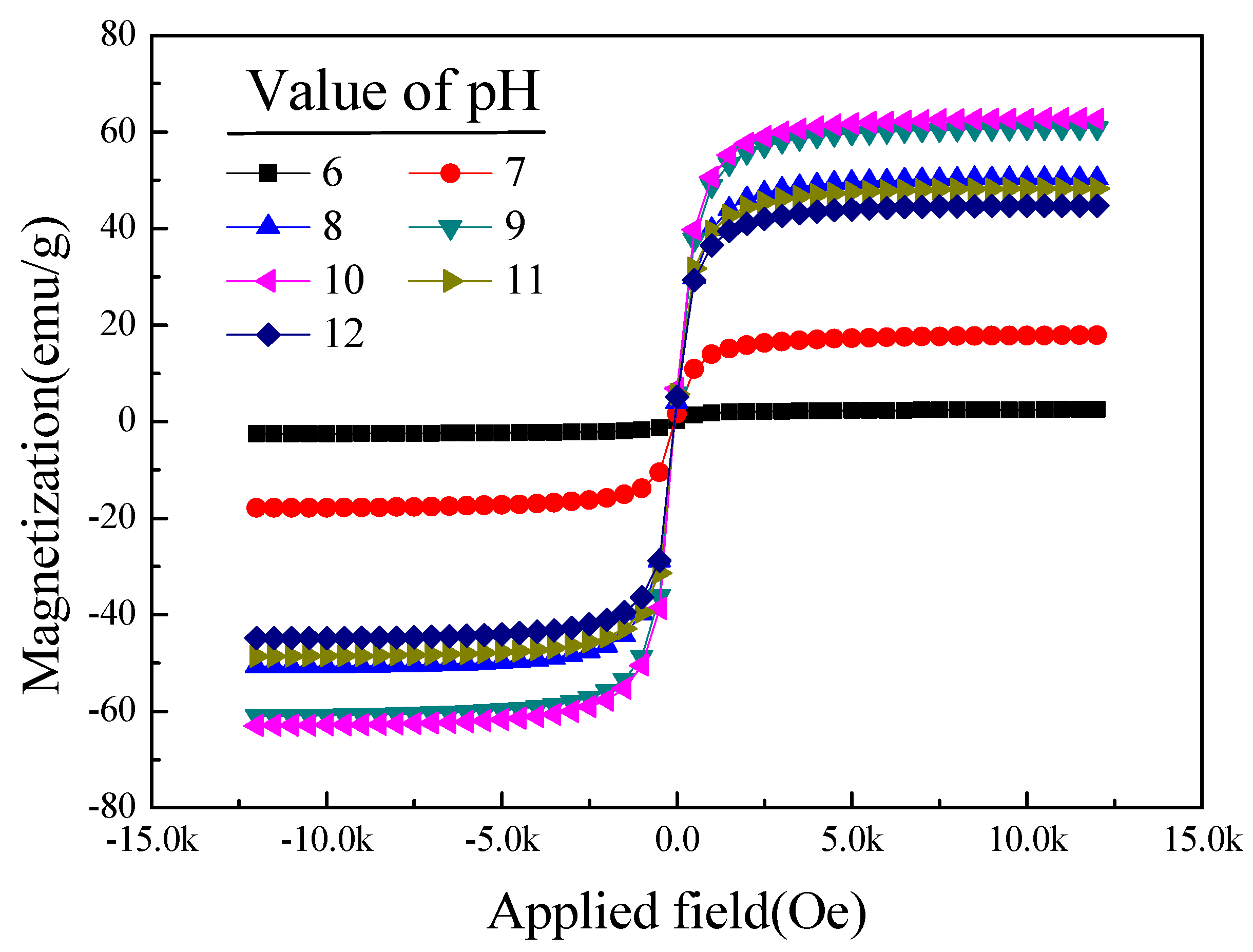
3.3. The Effect of the pH Value on the Magnetic Properties of [Mn0.54Zn0.46]Fe2O4
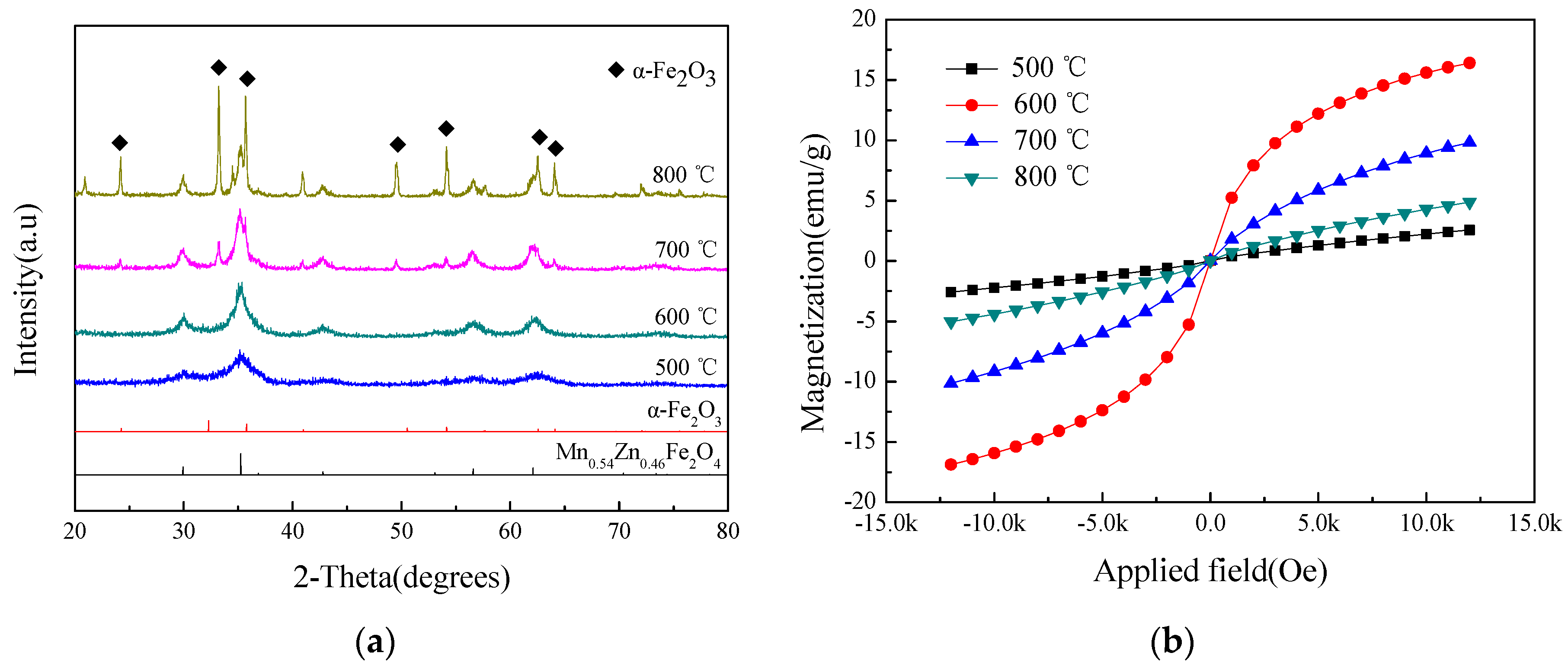
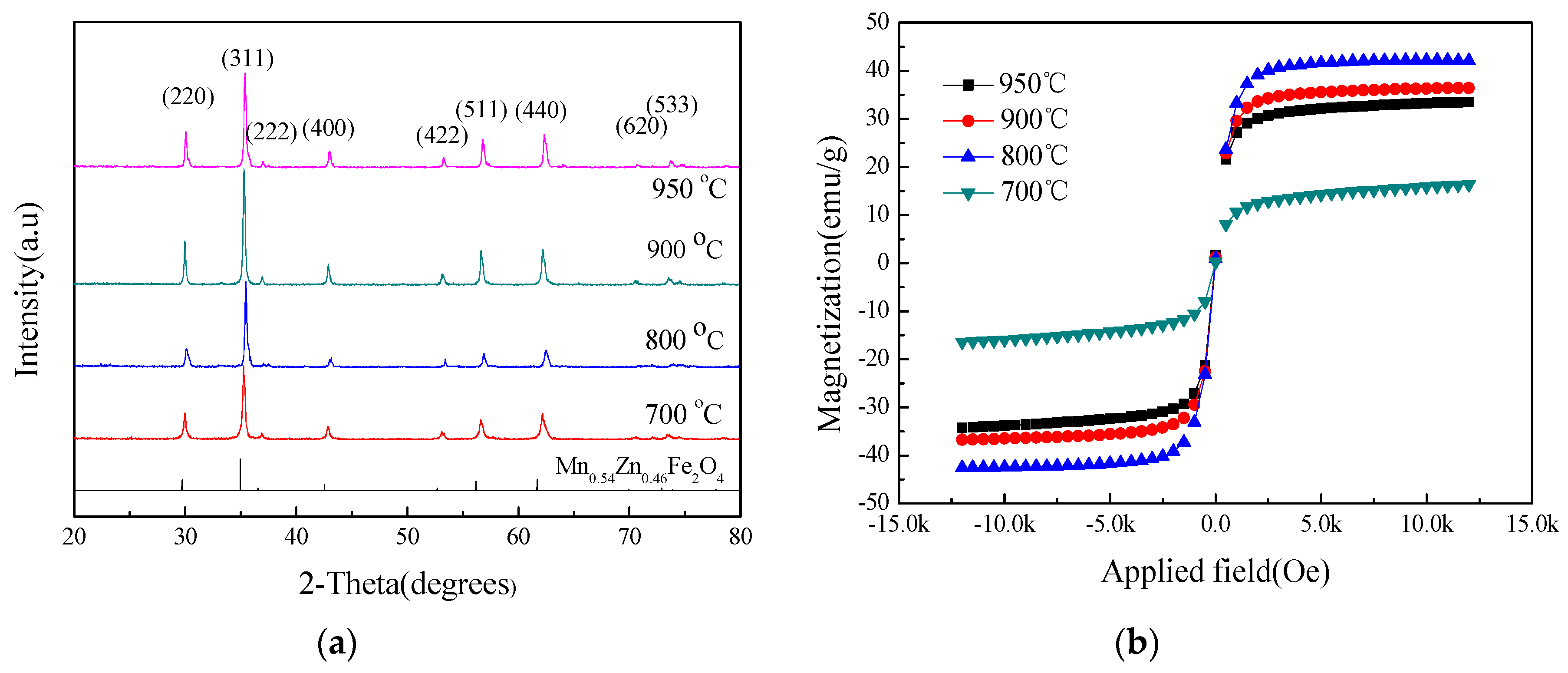
3.4. The Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Crystal Phase and the Magnetic Properties
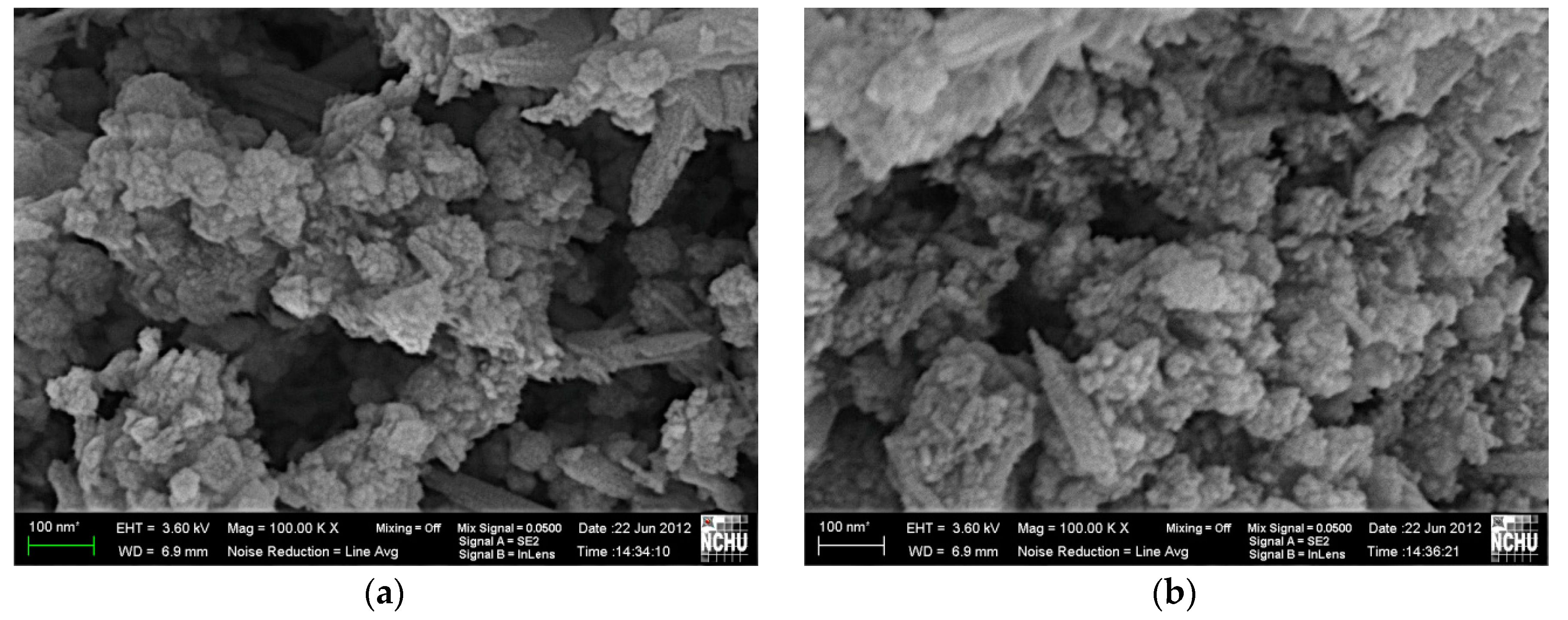
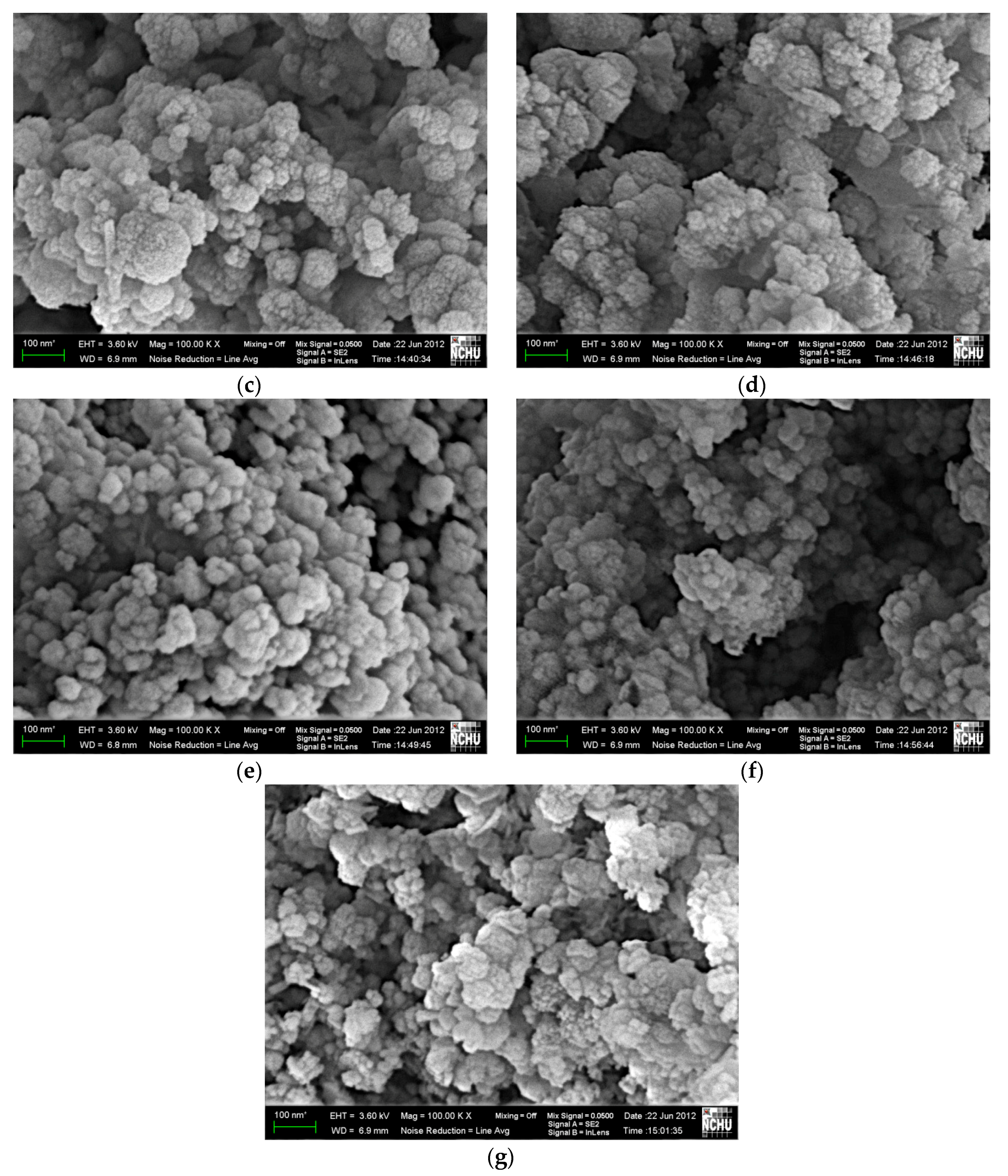
3.5. Surface Morphology and Compositional Analysis of [Mn0.54Zn0.46]Fe2O4
3.6. The Effect of the Sintering Temperature in a N2 Environment on the Crystal Phase and the Magnetic Properties
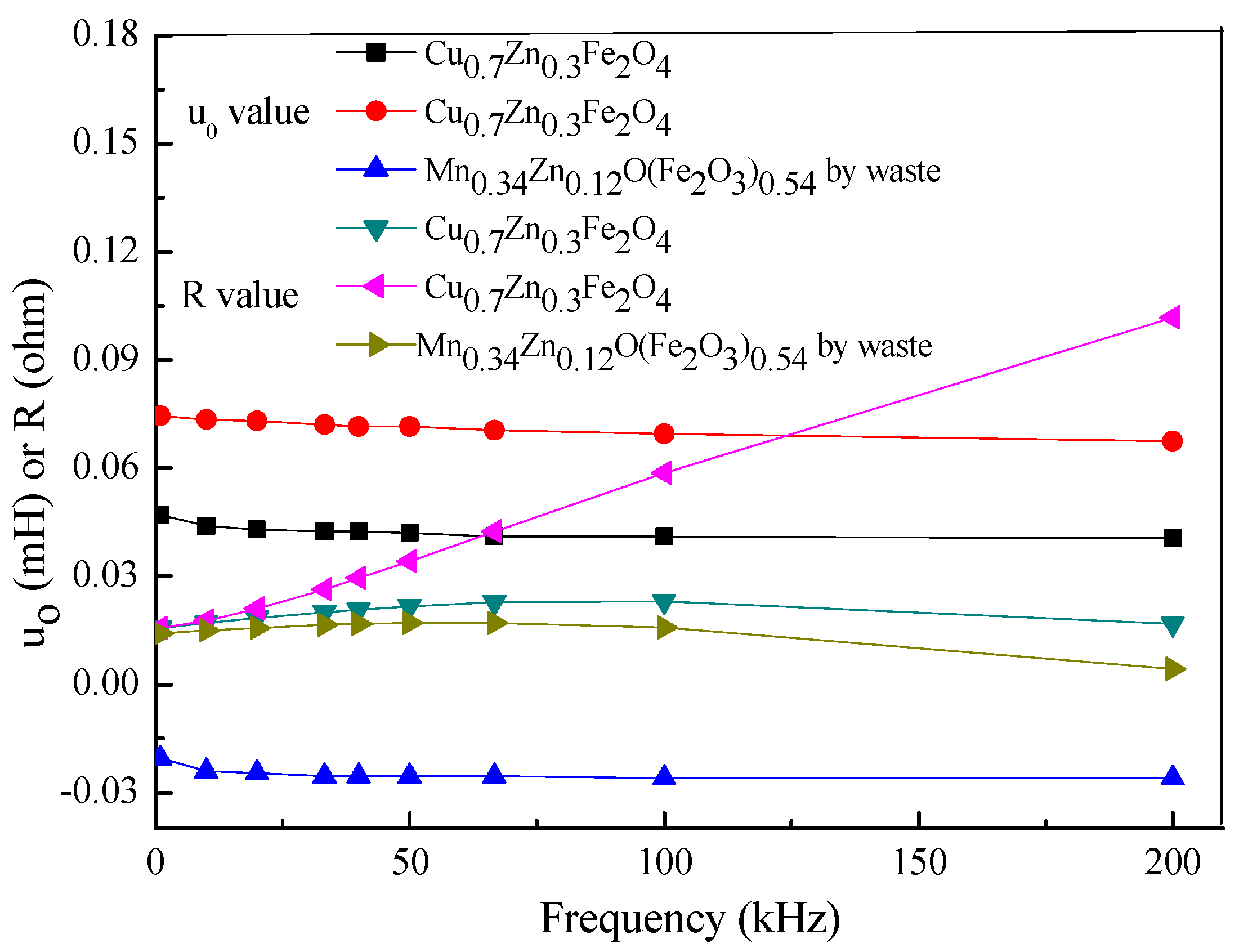
3.7. Measurement of the Electrical Properties for Forming Sintering for Different Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smit, J.; Wijn, H.P.J. Ferrites; Philips Technical Library: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Murdock, E.S.; Simmons, R.F.; Davidson, R. Roadmap for 10 Gbit/in2 Media: Challenges. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1992, 28, 3078–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standley, K.J. Oxide Magnetic Materials, 2nd ed; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Ewais Emad, M.M.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Abdel-Hady, E.A. In-Situ synthesis of Magnetic Mn–Zn Ferrite ceramic object by solid state reaction. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 44, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Topfer, J.; Angermann, A. Nanocrystalline magnetite and Mn–Zn ferrite particiles via the polyol process: Synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Zhong, X.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, H.Y. Synthesis structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ZnxMn1-xFe2O4 prepared by ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 466, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammad, Q.H. The influence of hafnia and impurities (CaO/SiO2) on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 286, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, C.; Verma, H.C.; Rath, C.; Sahu, K.K.; Anand, S.; Das, R.P.; Mishra, N.C. Mossbauer studies of nanosize Mn1-xZnxFe2O4. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 326, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmurugan, R.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Sendhilnathan, S.; Jeyadevan, B. Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for ferrofluid preparation: Study on thermal-magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 298, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, C.; Sahu, K.K.; Anand, S.; Date, S.K.; Mishra, N.C.; Das, R.P. Preparation and characterization of nanosize Mn–Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 202, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, D.R.; Patil, S.; Birajdar, D.D.; Kadam, A.B.; Shirsath, S.E.; Kadam, R.H. Sol–gel synthesis of Cr3+ substituted Li0.5Fe2.5O4:cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Shen, X.; Liu, M.; Xiang, J. Preparation and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19/Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposite ferrite microfibers via sol–gel process. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 126, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klencsár, Z.; Tolnai, G.; Korecz, L.; Sajó, I.; Németh, P.; Osán, J.; Mészáros, S.; Kuzmann, E. Cation distribution and related properties of MnxZn1−xFe2O4 spinel nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 2013, 24, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, I.; Ibraheem, O.A.; Tarek, M.S.; Bahgat, A.A.; Mohamed, M.M. Synthesis of magnetically recyclable spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Zn, Co, Mn) nanocrystals engineered by sol gel-hydrothermal technology: High catalytic performances for nitroarenes reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 181, 389–402. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, T.; Jia, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of Mn–Zn ferrites from spent alkaline Zn–Mn batterie. J. Particuol. 2009, 7, 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Saezpuche, R.; Torralvofernandez, M.J.; Gutierrez, V.B.; Gomez, R.; Marquina, V.; Marquina, M.L.; Perez Mazariego, J.L.; Ridaura, R. Ferrites nanoparticles MFe2O4(M=Ni and Zn): Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties. Boletin de la sociedad Espanola de of Cer’amica y Vidrio 2008, 47, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez-Vilar, S.; Sánchez-Andújar, M.; Gómez-Aguirre, C.; Mira, J.M.A.; Castro-Garcia, S. A simple solvothermal synthes of MFe2O4 (M=Mn, Co and Ni) nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Christina, W.K.; Shinji, H.; Takashi, O.; Toru, I.; Kikuo, O. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, M.; Pedrosa, F.; Margarido, F.; Nogueira, C.A. End-of-life Zn–MnO2 batteries: Electrode materials characterization. Environ. Technol. 2012, 34, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, S.D.B.; Sandra, P.; Luiz, F.R.; Sequeira, C.A.C. Electrodeposition of Zn–Mn alloys from recycling Zn–MnO2 batteries solutions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 13, 3036–3047. [Google Scholar]
- Turek, A.S.; Szczepaniak, W.; Monika, Z.M. Electrochemical evaluation of manganese reducers—Recovery of Mn from Zn–Mn and Zn–C battery waste. J. Power Sources 2014, 270, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobianowska-Turek, A.; Szczepaniak, W.; Maciejewski, P.; Gawlik-Kobylińska, M. Recovery of zinc and manganese, and other metals (Fe, Cu, Ni, Co, Cd, Cr, Na, K) from Zn–MnO2 and Zn-C waste batteries: Hydroxyl and carbonate co-precipitation from solution after reducing acidic leaching with use of oxalic acid. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, A.; Clausell, C.; Jarque, J.C.; Monzo, M. Obtainment of nanoparticulate CuNiZn ferrite powder by high-energy milling. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 120, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raming, T.P.; Winnubst, A.J.A.; van Kats, C.M.; Philipse, A.P. The Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Nanosized Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 249, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, T.; Dragana, M.; Vojislav, S.; Vladan, K.; Maja, R.; Janez, P.; Zvonko, J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of concentrated α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles in a silica. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 441, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Gimenes, R.; Baldissera, M.R.; da Silva, M.R.A.; da Silveira, C.A.; Soares, D.A.W.; Perazolli, L.A.; da Silva, M.R.; Zaghete, M.A. Structural and magnetic characterization of MnxZn1 − xFe2O4 (x = 0.2; 0.35; 0.65; 0.8; 1.0) ferrites obtained by the citrate precursor method. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Property | Hc(Oe) | Ms (emu/g) | Mr (emu/g) | B (gauss/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | |||||
| pH | 6 | 71.30 | 2.52 | 0.20 | 102.95 |
| 7 | 65.81 | 17.90 | 1.59 | 290.63 | |
| 8 | 61.65 | 50.56 | 4.05 | 696.68 | |
| 9 | 69.53 | 60.89 | 5.83 | 834.31 | |
| 10 | 75.08 | 62.85 | 6.84 | 864.48 | |
| 11 | 76.43 | 48.45 | 5.68 | 684.96 | |
| 12 | 74.97 | 44.81 | 5.08 | 637.78 | |
| Temperature (°C) by air | 500 | 34.61 | 4.96 | 0.03 | 96.91 |
| 600 | 2.71 | 16.64 | 0.01 | 211.71 | |
| 700 | 11.45 | 9.97 | 0.02 | 136.67 | |
| 800 | 46.29 | 2.57 | 0.02 | 78.57 | |
| Temperature (°C) by N2 gas | 700 | 17.36 | 16.32 | 0.29 | 222.34 |
| 800 | 16.84 | 42.36 | 0.81 | 548.88 | |
| 900 | 22.54 | 36.58 | 1.06 | 481.98 | |
| 950 | 32.97 | 33.86 | 1.51 | 458.25 |
| Composition/Method | Mn0.54Zn0.46Fe2O4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | XRD | SEM | |
| 6 | 31.10 | 30 | |
| 7 | 32.48 | 35 | |
| 8 | 53.56 | 50 | |
| 9 | 56.45 | 50 | |
| 10 | 59.61 | 58 | |
| 11 | 40.10 | 60 | |
| 12 | 35.03 | 48 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Hsu, J. The Use of Co-Precipitation to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4) from Waste Batteries. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8061005
Liu Y, Hsu J. The Use of Co-Precipitation to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4) from Waste Batteries. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(6):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8061005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yenchun, and Jarnchih Hsu. 2018. "The Use of Co-Precipitation to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4) from Waste Batteries" Applied Sciences 8, no. 6: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8061005
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Hsu, J. (2018). The Use of Co-Precipitation to Produce Nano-Mn–Zn Ferrite ([MnxZn1−x]Fe2O4) from Waste Batteries. Applied Sciences, 8(6), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8061005




