Abstract
This work presents a robust visual localization technique based on an omnidirectional monocular sensor for mobile robotics applications. We intend to overcome the non-linearities and instabilities that the camera projection systems typically introduce, which are especially relevant in catadioptric sensors. In this paper, we come up with several contributions. First, a novel strategy for the uncertainty management is developed, which accounts for a realistic visual localization technique, since it dynamically encodes the instantaneous variations and drifts on the uncertainty, by defining an information metric of the system. Secondly, an epipolar constraint adaption to the omnidirectional geometry reference is devised. Thirdly, Bayesian considerations are also implemented, in order to produce a final global metric for a consistent feature matching between images. The resulting outcomes are supported by real data experiments performed with publicly-available datasets, in order to assess the suitability of the approach and to confirm the reliability of the main contributions. Besides localization results, real visual SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) comparison experiments with acknowledged methods are also presented, by using a public dataset and benchmark framework.
1. Introduction
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) represents an essential task to be dealt with in mobile robotics. This paradigm comprises a simultaneous estimation of the map and the localization of the robot. This fact implies a real challenge when it comes to complexity, due to the incremental nature of this process, which is very sensitive to the non-linear effects that normally affect the systems in the form of added noise to the input or just in terms of coupled external noise. Both definitely compromise the convergence of the system estimation gravely [1,2].
Under this context, different research lines have been conducted in the field of mobile robotics. It is worth highlighting the evolution of the sensors to acquire information from the environment. Originally, laser [3,4,5] and sonar [6,7] were widely acknowledged. Despite the fact that these sensors are still strongly accepted nowadays [8,9,10], they are being slightly relegated as secondary sensory data to the detriment of visual sensors, which have been experienced an growing use recently. Digital cameras have had a great success, being one of the most feasible tools for acquiring information from the environment. They represent a promising alternative due to their low cost, lightness, low consumption, precision and efficiency to process visual data. They also become an encouraging option for complementing other sensors. In this sense, recent research lines rely on a more extensive combination of visual data with multiple light-computation sensory data, such as IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) [11], RGB-D [12,13] and GPS [14], which are especially oriented to the wide diversity of UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) applications that are deployed these days [15,16,17].
Amongst other visual sensors, omnidirectional cameras are remarkable for their capability to acquire a wide field of view with a unique snapshot. Different approaches have focused on computer vision techniques by using single cameras with visual encoding of 3D landmarks [18,19], stereo-structure [20,21,22] and omnidirectional cameras [23,24,25,26]. In particular, many approaches support matching systems that take advantage of the image side [27,28], but also the mapping side [29].
In this paper, we also rely on the potentials of the matching in order to associate visual information. This association represents the basis for an advanced feature matching, in contrast to generally known approaches [30,31]. Consequently, we are able to extend the localization developments to a wider field of application: visual SLAM. Such context implies that huge efforts have to be addressed in order to assure convergence for the estimation and uncertainty control [1,32]. The core of the approach is sustained by a previous work, in which a view-based monocular EKF was devised [33] under a design that focused on a compact view-map with a reduced set of omnidirectional frames, which are mutually seen as image and landmark at once. This allows us to re-estimate images and also the entire map at a single step for each t, being then more efficient in contrast to large 3D-landmark maps’ re-estimation [19,34]. Besides this, neither parametrization nor tracking are required. Its performance was evaluated [32,35] within a comparison framework under the cover of the original fundamentals for such a SLAM basis [36,37,38], which established the initial foundations for the improved implementations and contributions of the present paper.
Nonetheless, the aim of this approach pursues the specific improvement of the localization by considering the mentioned casuistry in terms of convergence and uncertainty control, rather than further developments or analysis of the SLAM core. Certain approaches also exploit the catadioptric reference for localization tasks [39]; however, our proposal loosens the unified projection model to a panoramic conversion, without estimating any specific parametrized landmarks, but the entire omnidirectional image instead, since it inherently encodes visual landmarks inside. To that aim, several contributions are devised so as to produce robust feedback and to reinforce the matching, which ultimately impacts the localization of the robot. Moreover, straightforward visual SLAM results are also presented as a further final application. The basis is on a dynamic adaption of the current uncertainty of the system, with an associated propagation to the system state. Fusing this information with a Bayesian regression technique [40] permits obtaining a sensor data distribution [41], in order to extract the probability of matching occurrence, which becomes potentially useful for weighting robust features and avoiding false positives. In this context, EKF priors represent a fundamental tool for the developments. Similarly, some works focus on prior inputs in the EKF for a wide scope of modeling, such as deformable environment modeling with FEM (Finite Element Method) [42,43], motion as a visual odometry [44], with systematic parameters [45] or through robot kinematics [46]. In general terms, they all succeed in relaxing the dimensionality of the EKF estimation. However, here, we take most of the filter-based prior stage in the opposite direction, as in [47], where these data are taken as a posterior output to be propagated for inference purposes in the matching. That is, no parametrization for the map of the environment, for the robot, neither for the camera motion is input into the EKF.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 presents the general characteristics of the monocular omnidirectional system and the developments to adapt the epipolar constraint to the omnidirectional geometry. Section 3 comprises the implementation of the robust visual localization, where the dynamic uncertainty management and the Bayesian regression inference are also devised. Section 4 provides a brief explanation of the omnidirectional SLAM approach, as the target application with which the robust localization is aimed to be fused. Section 5 presents the real experimental setup so as to assess the suitability and the benefits of the approach with comparison results under publicly-available real datasets. Section 6 establishes a discussion on the previous results. Section 7 states the main conclusions extracted from this research work.
2. Monocular Omnidirectional System
This monocular vision system consists of an omnidirectional camera, that is a catadioptric set conformed by a hyperbolic mirror jointly assembled with a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, as depicted in Figure 1. The entire real mobile robotic equipment is also presented. The omnidirectional image generation may be expressed in terms of a central sphere unification, according to the projection model detailed in [48].

Figure 1.
Real equipment: (a) Pioneer P3-AT with omnidirectional camera mounted, internal odometer and SICK-LMS200 laser range finder. Omron Adept Technology, Inc. 10 Columbia Drive, Amherst, NH 03031, USA; (b) CCD FireWire DMK21BF04. The Imaging Source Europe GmbH, Uberseetor 18, 28217 Bremen, Germany; (c) Eizho Wide 70 Mirror. Eizho Laboratory Ltd. Suminoue, Osaka, 559-0034, Japan.
2.1. Epipolarity Adaption Definitions
The epipolar constraint [48] becomes a fundamental tool so as to design a localization technique, due to the fact that it represents a motion recovery tool. The nature of our omnidirectional system made us redesign the standard planar epipolar constraint to adapt it to the geometry of our catadioptric system. This allows us to gather visual information from a more reliable point of view, since an advanced feature detection and matching procedure between two omnidirectional images can be designed, in order to localize the robot in terms of poses. To that aim, it is necessary to introduce the essential matrix, [49], and its relation with two matched points between images, x and . Given a particular calibration, the corresponding points may be normalized to and :
The terms in E encode a decomposition: and , as a general rotation and translation, associated with the skew symmetric [48]. Then, a 2D movement ∈ , and angular movement , between two poses of the robot can be recovered up to the scale factor, from:
This adaption to the omnidirectional geometry is represented in Figure 2. The projection of the point X on two image references, x and , is determined by the epipolar plane, , and both camera centers C and . An essential aspect is related to l and , as the epipolar lines that determine the geometric location where feature points should be matched. This is a key aspect for us in order to implement an advanced visual matching, which ultimately returns potential data for a robust localization.
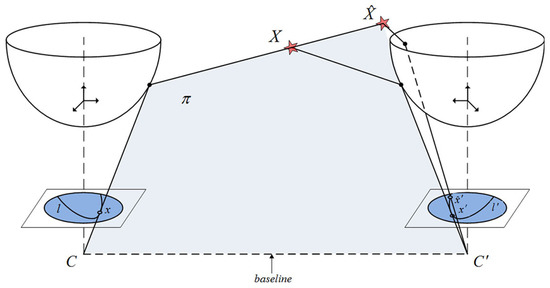
Figure 2.
Epipolar constraint adaption to the omnidirectional geometry of the camera.
In contrast to traditional stereo-planar applications [50,51], here epipolar lines transform into ellipses as they are the intersection of the plane with the surface of the hyperboloid of the mirror. Then, using this adaption for a consistent matching process, some contributions are presented in the following sections, so as to come up with a robust visual localization, sustained by a dynamic uncertainty management and Bayesian techniques, on the grounds of this epipolar adaption.
Finally, it is worth mentioning a last processing step on the image projection. In particular, we obtained better feature point detection with a post-processed projection conversion to a panoramic view. As mentioned above, omnidirectional cameras are very sensitive to non-linearities, due to the nature of the mirror, and this effect is especially evident at top areas of its surface, which consequently reflect 3D points on a pixel area over the image frame with lower resolution. These are the main reasons for computing such a planar conversion, together with a Gaussian filter over the top areas of the image:
being and the panoramic and omnidirectional image frames in pixels, for which () represent the center of the omnidirectional image and is a Gaussian filter applied between heights – in the panoramic view. Angular and radius variables for the omnidirectional view are expressed by ∈ [0, 2] and [, + , ⋯, + (), ], so that the dimensions of the panoramic view can be tuned in order to get the desired areas of the scene, with the final image of (r × ) in pixels.
Figure 3 presents a real example for this projection conversion, with feature points indicated. Figure 3a depicts the conversion seen on the rays’ model side. Omnidirectional projection rays are backprojected from the mirror to lie on the Cartesian panoramic reference system, as denoted in Equation (3). Figure 3b,c represents the same image in its omnidirectional and panoramic projection, after conversion. It may be noticed that the angular variable in the omnidirectional reference, , transfers into the u coordinate in the panoramic reference, highlighted as a blue line. Likewise, the radius r and v are represented in red. Finally, Figure 3d presents a sample image set for evaluating the benefits of the panoramic conversion when extracting feature points. Along 858 real images, the number of feature points detected on the panoramic projection is on average ∼14% higher. In addition, they are only concentrated on bottom areas of the image, thus considering only points between , with a final length of 445 in the v coordinate, leading thus to avoiding features at top pixel areas, where the mirror induces significant non-linearities. This fact implies a valuable aid in the robustness of the feature extraction. A proper calibration is crucial when dealing with backprojections. In this respect, the calibration toolbox presented in [52], was used.
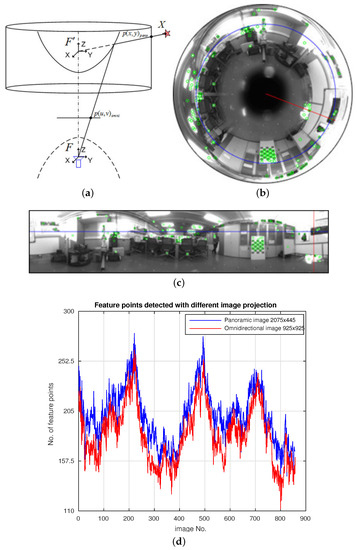
Figure 3.
Projection conversion from omnidirectional to panoramic view. (a) Conversion over the rays’ model side; (b) omnidirectional image with angular and radius variables indicated (,r); (c) same image in its panoramic projection, transferred to (u,v) coordinates; (d) comparison of the number of feature points found on omnidirectional and panoramic images, respectively.
3. Robust Visual Localization
This robust visual localization technique relies on the epipolarity adaption presented above. As observed in Equation (2), two poses of the robot can be univocally related by feature matching points in two omnidirectional images acquired from such poses; that is, a motion relation that is determined by an angular transformation. Figure 4 expresses such image-to-pose equivalence in terms of motion for comparison purposes. Therefore, this can be also deduced from Equation (1). Thus, localization between poses, as observed in Figure 4a, can be transformed into a visual problem, as shown in Figure 4b.
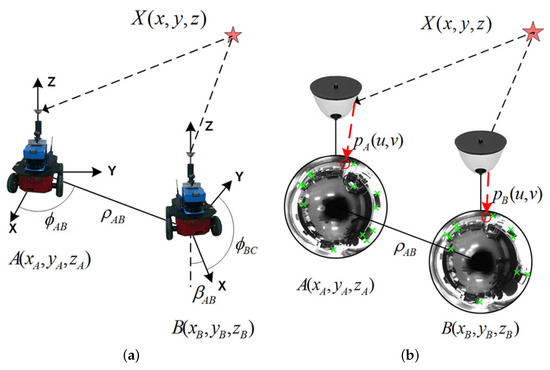
Figure 4.
Omnidirectional visual localization between poses A and B. (a) Robot reference system; (b) camera reference system. Projections and are indicated.
Analytically, Equation (1) can be expressed as a linear system with:
and being the two corresponding points between image poses and represent the composing elements in E, which encode the localization values (, ). Notice that only a reduced amount of matching points is required, , for retrieving a localization, due the dimensions of .
Finally, [48] describes the basis for a Single Value Decomposition (SVD) of Equation (2), which returns a quaternion set of solutions (, ), as two rotations and translations:
3.1. Dynamic Uncertainty Management
After introducing the definition of the fundamentals of the proposed omnidirectional robust localization, now a detailed description for one of the main contributions of this work is addressed: the dynamic uncertainty management. The final goal is to improve the matching by allowing this procedure to adapt dynamically to the instantaneous uncertainties of the system. That is the main reason for considering the instantaneous uncertainty of the system, at each t, being a magnitude closely related to those non-linear effects associated with noise, which is ultimately by the uncertainty matrix, as follows.
The final outcome implies a reduction of the search area for matching points on the pixel side. For that purpose, the epipolar constraint is again evaluated from Equation (1). In such a context, the current inconsistencies in the system (mainly non-linear noise), represented by uncertainty, are propagated through such a constraint, which now accepts a dynamic threshold, :
Note that this threshold depends on a predicted variable, denoted as the observation movement, , which is extracted from the stages of a general filter-based SLAM approach, and it is implicitly associated with the uncertainty of the system. More specifically, Table 1 comprises all the interdependencies extracted from the stage structure of the filter-based SLAM. Then, we can take advantage of the innovation measured between consecutive states of the visual SLAM system, , in order to define a powerful tool to establish predicted values for and, thus, for a rotation and translation, R and T, respectively:

Table 1.
Filter-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) stages.
This aspect entails a predicted matching, which can be found on the second image reference, even when no feature detection is previously run on the second image at current t. Then, a Gaussian multi-scale distribution, , is generated on the first image frame and next propagated on the second, , by introducing the current uncertainty in Equation (7) and also applying the predicted movement in Equation (8).
In this sense, Figure 5 breaks down the complete procedure for this advanced matching, which finally returns a reduced search area where candidate matching points are expected, rather than a global search over the entire image. The construction of this new search area comes from the reformulation of the epipolar constraint, which now transforms into an elliptical surface due to the effects of the omnidirectional adoption and to the drifts induced by . The final stage includes a visual descriptor comparison, and being the visual descriptors of two candidate matching points in the first and second image, respectively. In the end, a Mahalanobis metric [53], (), is evaluated over them, so as to get an acceptable visual distance in order to assume two feature points as a valid pair of matching points:
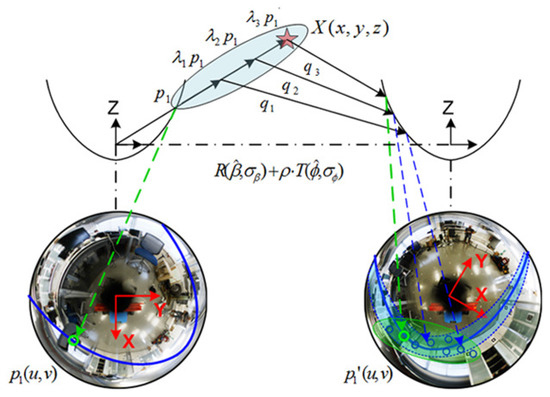
Figure 5.
Dynamic uncertainty management: advanced matching results. represents a multi-scaled distribution, . projects onto the second image as per R∼N() and T∼N(), in Equation (8). A reduced search area is obtained (green). Epipolarity transforms into an elliptic area (blue) due to the uncertainty propagation on Equation (7).
Notice the dynamic adaptive nature of this procedure, which always depends on the current uncertainty, thus adapting to the changing conditions of the system. It is closely related to inconsistencies and instabilities, which are normally caused by non-linear noise. Therefore, this contribution assures a reliable control for the uncertainty management, which implicitly performs false positive avoidance and, thus, non-linear effects reduction. A corresponding analysis of the results will be presented in Section 5 for further validation.
3.2. Bayesian Regression
The dynamic uncertainty management strategy presented in the previous subsection is based on an advanced matching with uncertainty propagation. Now, a further contribution to the robustness of the procedure is presented: a Bayesian regression technique, that is mainly comprised by Gaussian Processes (GP) [40]. We pursue the development of a sensor data distribution for the feature matching on the omnidirectional frame. GP is a powerful regression technique since it does not require the extraction of conventional associations between inputs and outputs, in comparison to traditional inference techniques. We have customized the implementation of a GP in order to return a matching data distribution in terms of probability, which can be mapped onto a global reference system. This information is advantageous in order to refine the search area for matching points. A GP, denoted as , is constituted by its mean, , covariance , and training and test input vectors, x and , respectively.
Considering that the implemented GP provides a probability distribution for our matching, now we can exploit the fusion of this probability with an information metric, in order to reduce even more the search area for matching, thus to enhance the overall system operation and its robustness. This represents valuable feedback data for refinement, which basically represents a second weighting stage before the final match is returned. As far as the selected metric is concerned, we adapted the information-based Kullback–Leibler divergence (KL) [54]:
where is the entropy [55] of the information distribution of the current feature point set at time t. represents the probability of the existence of the current i-th feature points at time t (system step time), that is on the image acquired at the current robot’s pose at t, and also for the previous i-feature points detected at a previous image at .
We seek the evaluation of the variations and fluctuations in the appearance of the matching points and their location. In these terms, KL allows one to determine such variations between matching points detected on a pair of images, , and the next matching points on the following pair . Then, KL encodes substantial variations on the matching points’ location while the robot navigates. Higher values for KL imply newer visual information observed by the robot. Such values can be used for determining a specific metric that finally specifies the weighting coefficients to get robust candidate matchings. This ultimately establishes the probability areas where a corresponding point is more likely to be found, that is distribution sensor data.
An illustrative example may be observed in Figure 6. Here, the robot navigates through a scenario passing through three different poses (A, B and C). Likewise, Figure 7a,b presents the motion transformation between these poses and the same relation expressed in terms of the image reference. Finally, Figure 8a–c shows the returned probability data for the feature points found at each pose, fused with an accumulated probability, while the robot moves and discovers new scenes within this scenario. Notice that the third image at pose C presents newer feature points (in blue), in addition to previous feature points already seen in A and B (green). That is the reason why the probability data for C differ substantially. This is a key aspect in order to apply specific weighting factors within the matching, with the purpose of encoding this visual change on the scene and also avoiding possible false positive.
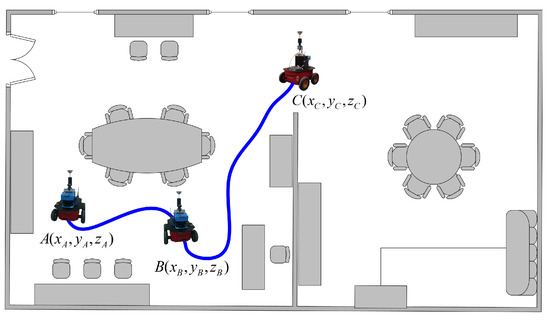
Figure 6.
Navigation example along three different poses within an office-like scenario. The robot sequentially traverses poses A, B and C, respectively. Omnidirectional images are acquired at each pose, and feature matching and Bayesian regression are computed as per Equations (10)–(13). Motion transformations at both the pose reference and image reference are depicted in Figure 7a,b.
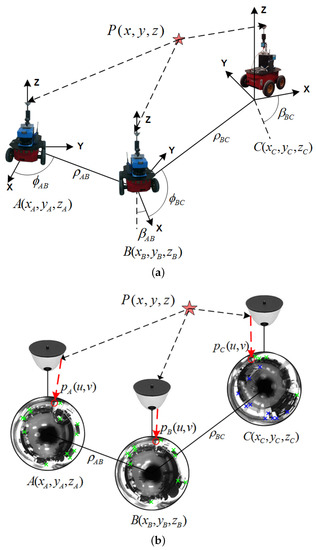
Figure 7.
Description of the example presented in Figure 6, where the following subfigures correspond all to traversed poses A, B and C. (a) motion transformation between poses, on the robot reference system; (b) motion transformation on the image reference system. The projection of is indicated as , and respectively on each image. Repeated matches and new matches are indicated in green and blue, respectively.
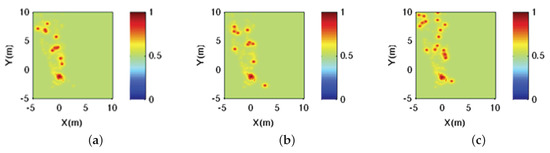
Figure 8.
Evolution of the sensor data information distribution along poses, expressed in terms of the probability of existence, for example in Figure 6. (a): pose A; (b) pose B; (c) pose C.
Overall, this strategy stores the information of the points’ distribution, which is then transferred as a KL value in its accumulative format. Then, this information is used for obtaining new weighting coefficients for the matching:
thus evaluating this metric in an accumulative manner allows one to obtain a global data distribution for the feature points along the navigation, in terms of probability.
3.3. System Workflow
The complete system operation comprises all the introduced contributions, as denoted in Figure 9, where the workflow is:
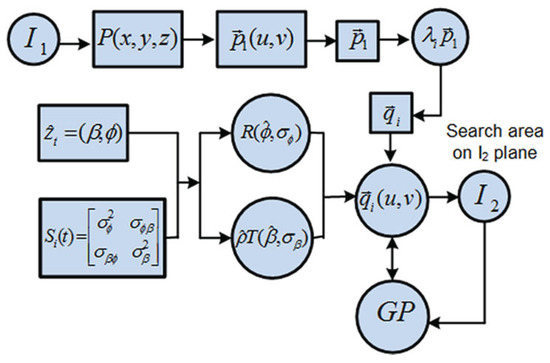
Figure 9.
Complete workflow for the system operation, as detailed in Section 3.3.
- (i)
- omnidirectional image acquisition, .
- (ii)
- multi-scaled distribution: projection of a 3D point, , establishes the seed for a multi-scaled distribution, .
- (iii)
- EKF prior extracted for motion prediction, hence point appearance prediction on the second image according to . Dynamic uncertainty management by propagating R∼N() and T∼N(), thus accounting for the current innovation , as the uncertainty metric.
- (iv)
- Bayesian regression computed as per Equations (10)–(13), to produce weighting coefficients for the final matching over a predicted epipolar search area on the next image, .
4. Robust Localization within Omnidirectional SLAM
Visual SLAM symbolizes a widely-acknowledged final navigation application in mobile robotics. According to this, we fused the proposed robust localization into an omnidirectional SLAM system [33]. Hence, this section condenses the fundamentals of such a system [56], under the cover of the essentials of a verified EKF-SLAM method [19,36], with the proposed robust localization now embedded.
This omnidirectional SLAM approach entails an improved view-based map model with respect to former works, as may be noted in Figure 10. The estimated map is composed of a reduced set of omnidirectional images, or views, , acquired from different poses along the traversed path. Each n-view encodes visual information in terms of SURF feature points [57]. The pose of the robot at t is denoted as . Thus, the definition for a state vector considers and , with the following 2D structure:
each view being . Then, the state vector encodes a map constituted by a total number of N views. It is also worth noticing that each accounts for the visual encoding of a specific area of the environment, so that the robot can always localize itself.
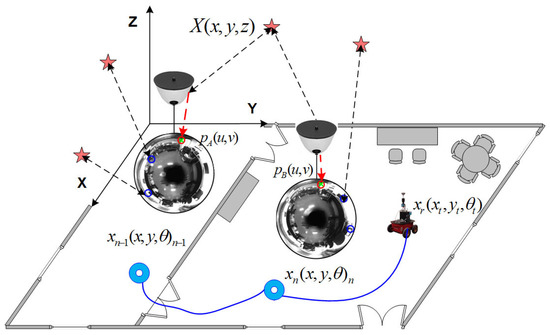
Figure 10.
Dual 2D-3D map model composed by omnidirectional views, . Information is encoded on the 2D image plane by feature points over each view, being able to be recovered on the 3D reference by estimating a scale factor. The re-estimation of implies the whole re-estimation of the map at once, contrary to former 3D-landmark maps.
It is essential to notice the duality characteristic of this mapping approach. It presents a capability of producing both 2D and 3D results, despite the fact that the robot has a monocular camera mounted, and thus, the images are accordingly acquired in a 2D reference. Certainly, the visual information is compressed on the 2D image frame by feature points. However, they express the same information as 3D landmark-based approaches [36,58]. As explained in Section 3, by using a motion prediction together with uncertainty propagation, the lack of scale may be retrieved, and so 3D information. As a result, and contrary to previous 3D landmark models, the re-estimation of the 3D pose of every landmark in the environment is no longer needed. Now, with this approach, a single re-estimation of a view (position), as part of , inherently implies the whole re-estimation of the visual feature points inside it and, at the same time, the re-estimation of the complete map itself, since it is composed by views as a whole. This is a simpler procedure, which allows one to re-estimate at once all the views with all the visual information contained, represented by the set of feature points encoded at each view. Finally, it produces a single and complete map re-estimation. In order to get a clearer picture of this omnidirectional SLAM structure, its workflow may be divided into: (i) view initialization in the map; (ii) observation measurement; (iii) data association. Dealing with localization tasks leads us to concentrate on Stage (ii), which is consequently presented in the following subsection.
Observation Model
The observation model provides measurements that express a motion transformation from the robot’s pose to a specific landmark, in terms of SLAM nomenclature. In this approach, and similarly to the explanation introduced in Section 2, the motion transformation can be referred to the comparison between two images, in angular terms (, ). Thus, the motion between two poses of the robot may be recovered in the same manner. Transferring this localization relation into the robot’s reference system leads to the following notation, where encodes such observation measurements, which already comprises all the presented contributions to come up with a robust localization proposal, as depicted in Section 3.
The terms in correspond to those associated with the different poses of the observed views in the map, , and the current pose of the robot, . It is worth noting that such variables are iteratively re-estimated as part of the state vector of the system, , in Equation (14).
5. Results
This section aims to present real experiment results in order to provide a further understanding of the contributions proposed in this work. The experimental setup has been conducted under the publicly-available datasets [59,60], so as to analyze the positive outcomes and benefits of the robust localization proposal. Additionally, further experiments have also been configured to test the performance of the combined approach: robust localization within an omnidirectional SLAM system. Besides this, a public benchmark toolkit and dataset [61,62] have also been used for comparative purposes with well-acknowledged methods [19,47,63].
The real equipment (CPU: 2 × 1.7 GHz; RAM: 2 GB) was already introduced in Section 2 and Figure 1, and it is set to acquire 1280 × 980 omnidirectional images at a variable [0.25–1.5] fps. Therefore, for the final application, for which this equipment is oriented, such frame rates are acceptable to work in real time. The SICK-LMS200 laser data are processed in order to get a ground truth for error comparison. The software was initially developed in MATLAB 2017 for preprocessing and debugging purposes. Next, the implementation was optimized in the robot operating platform, ROS [64], with the same specified computation resources. The real dataset comprises several subsets [59,60] within indoor office and laboratory-like spaces, from which different sub-datasets have been extracted. Note that Dataset 1 is an appended area of Dataset 2. A third additional sub-dataset, Dataset 3, is extracted from [62]. Its associated benchmark toolkit provides a wide set of solutions [61,65], obtained by verified and reliable methods on different sub-datasets within the same project. For the selected sub-dataset, Bovisa 2008-10-04, a solution computed by an inverse depth parametrization method is provided [47,63]. This solution will be compared to our approach. The main characteristics of these datasets are synthesized in Table 2, and their layouts may be observed in Figure 11 and Figure 12, respectively.

Table 2.
Dataset characteristics.
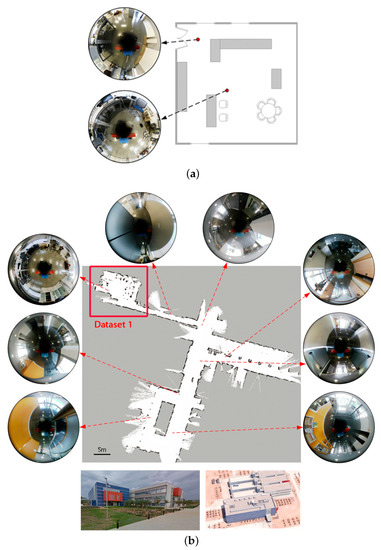
Figure 11.
Main details for the large scenario where the two sub-datasets were acquired. (a) Layout for Dataset 1; (b) layout for Dataset 2.
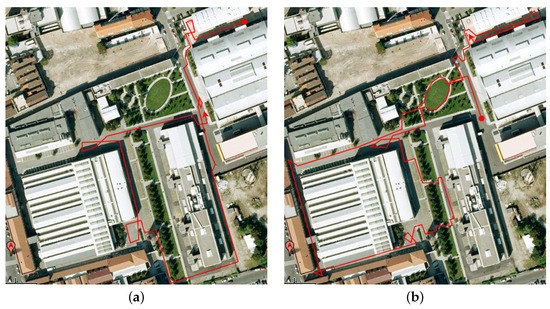
Figure 12.
Main details for Dataset 3 Bovisa 2008-10-04, which is used for comparison purposes. (a) Layout for Part 1; (b) layout for Part 2.
5.1. Robust Localization Results
Initially, we produced localization results only focusing on the proposed robust localization, aiming at validation. Firstly, Figure 13 compares performance results between a general localization technique based on our former approach [33] (‘standard’) and with the proposed robust localization presented here. It is worth mentioning that the experiments are run under Dataset 1, for a 100-times execution setup, in order to get consistent average results to model the error. Poses and associated images are randomly extracted from the dataset for localization computation, so that no specific localization structure is presented rather than a sample, as shown in Figure 13.
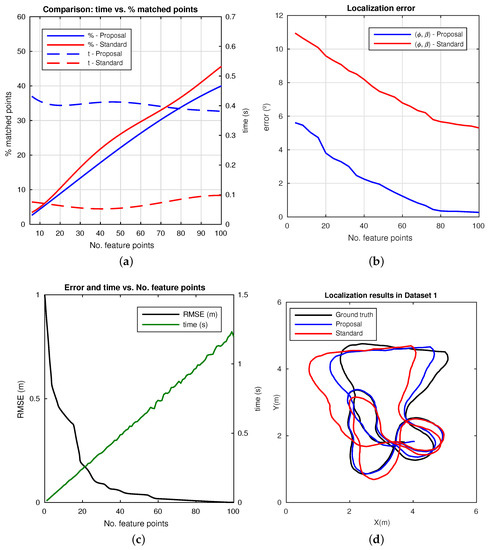
Figure 13.
Omnidirectional localization results. (a) % matched points and time consumption with total number of matched points; (b) localization error in angular terms; (c) Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and time consumption with the number of feature points in a localization experiment; (d) localization results for a sample path in Dataset 1.
Figure 13a presents a comparison between the % of matched points out of the total number of feature points detected in two images (Y-left-axis), with the time consumed in the process (Y-right-axis) and with the total number of matched points (X-axis). The proposed localization technique provides a ∼30% average increase of feature points matched, with respect to the standard. This implies that larger numbers of feature points are now matched correctly, and it increases the probability of obtaining a robust localization. It also produces a considerable reduction of false positives due to the delimited search area on the image. Obviously, this comes at the cost of computation. Notwithstanding that, the time results are proven to keep a stable and bounded solution for real-time purposes, regardless of the number of matchings.
Secondly, Figure 13b presents accuracy results in angular terms for the localization. The robust localization proposal is demonstrated to outperform the standard localization technique ∼40% on average. Note that these results show the average error on the estimated localization (, ), in Equation (15). In general, this is a desirable output, especially when dealing with the parallax effect associated with angular measurements. Then, subtle improvements of the angular localization suffice to ensure convergence on a generic visual SLAM application.
Finally, Figure 13c presents the RMSE (Root Mean Square Error) in the final pose and the time consumption with the total number of feature points detected in two images. It is worth highlighting that an acceptable tradeoff solution is also fulfilled in order to assure real-time operation with a sufficient precision, considering the requirements of the final application. Figure 13d presents an example of the estimated localization structure from a sample path in Dataset 1.
5.2. Omnidirectional SLAM Results
In this subsection, a number of tests is performed to evaluate the overall omnidirectional SLAM system, with the robust localization embedded. Notice that the redesign of the observation model, , in Equation (15), now implements the proposed robust localization. In this sense, Figure 14 shows real data results for such omnidirectional SLAM approach, using Dataset 2. In particular, Figure 14a confirms the suitability of the approach to produce a reliable estimation under a real application operation. Moreover, it is demonstrated to outperform the accuracy of a general SLAM approach, with standard localization, as presented in previous works [33]. This confirms the robustness of the estimation, which remains stable, whereas the estimation of the standard model tends to diverge in the presence of subtle error drifts on the localization. In addition to this, Figure 14b presents the average RMS results for the computed error, when the number of matchings is modified. Likewise, Figure 14c presents the same results for the standard localization. Again, these results confirm that a tradeoff setup with a low number of matching points still produces a well-balanced and feasible estimation.
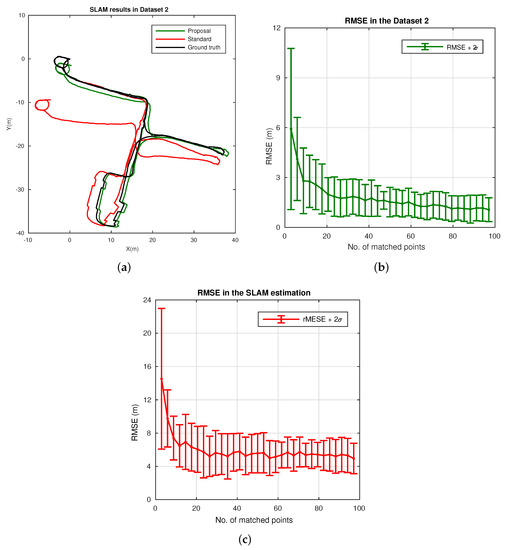
Figure 14.
Omnidirectional Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) results in Dataset 2. (a) SLAM estimation with the proposed localization approach (green), standard (red) and ground truth (black); (b) RMSE (m) with the number of matchings for the localization proposal; (c) RMSE (m) with the number of matchings for the standard localization.
Next, Figure 15 presents more real data results regarding the error-time implications, which refer to the experiment shown in Figure 14. Figure 15a,b shows the behavior of the error on the estimated pose with the time step. In particular, Figure 15a expresses the evolution on the error for each coordinate in the omnidirectional SLAM approach, with the robust localization proposal embedded. Likewise, Figure 15b presents the error for the standard SLAM system, with the standard localization technique. It may be observed that the presented proposal outperforms the standard one.
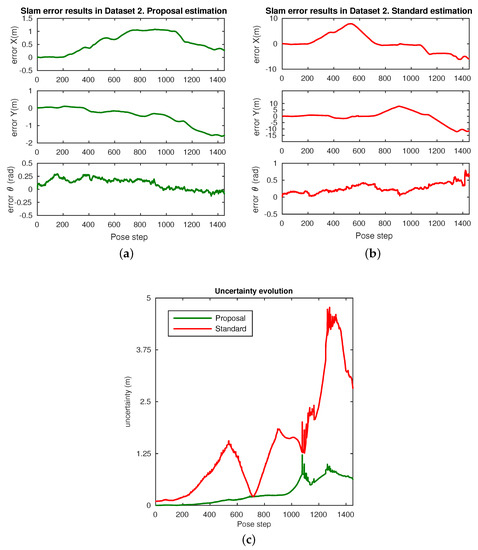
Figure 15.
Omnidirectional SLAM error results in Dataset 2: (a) error in the SLAM estimation for the robot’s pose along each time step with the proposed localization approach (X, Y and ); (b) error in the standard SLAM approach with standard localization; (c) uncertainty evolution (m) at each time step: proposed SLAM approach with robust localization (green); standard SLAM approach (red).
Having tested the validity and suitability of the approach in terms of the estimation accuracy, then it is worth evaluating the behavior of the uncertainty. To that end, Figure 15c assesses the evolution of the current uncertainty of the system at each time step. As described in Section 3, a dynamic uncertanty management was devised, together with Bayesian regression. According to this, the same experimental parameters for the weighting coefficients in the advanced matching, as defined in Equation (13), are here considered. Then, Figure 15c proves that the implemented approach provides a robust and feasible management of the uncertainty, which is significantly improved in contrast to that obtained by the standard SLAM system. The uncertainty metric is computed from the covariance matrix , as presented in Table 1:
5.3. Comparison Results
Finally, in this section, we compare the proposed approach with an extensively verified method, such as the inverse depth parametrization with EKF [19]. Specifically, we run the benchmark toolkit that is provided with Dataset 3, Bovisa 2008-10-04, both publicly-available [62]. The results obtained with the inverse EKF parametrization method were originally discussed in [47,63]. Figure 16 presents the comparison results. Figure 16a represents the estimated solution for both methods. The proposed approach is represented in blue, the inverse parametrization method in red and the available GPS-ground data in black. Next, Figure 16b represents the same comparison, divided into X and Y coordinates.
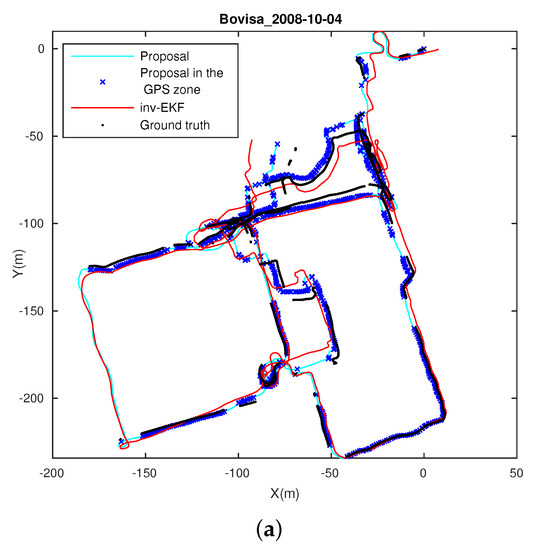
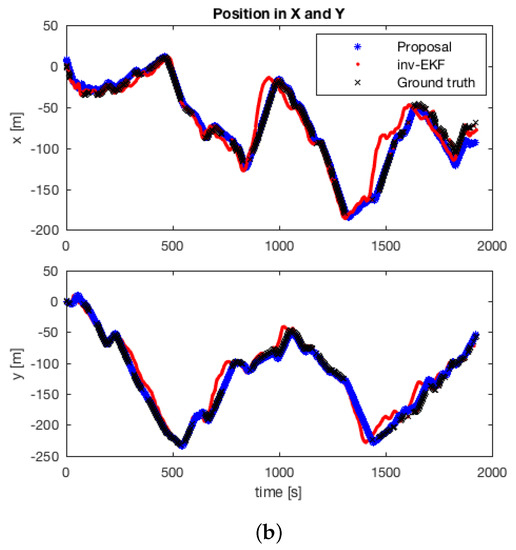
Figure 16.
Estimation results in Dataset 3: (a) position estimation, (m). The proposed solution is presented in blue (dark blue: GPS areas; light blue: rest); the inverse EKF solution in red; the GPS-ground truth in black; (b) evolution in X(m) and Y(m).
It is worth noting that this toolkit computes a transformation alignment for the estimated solution. As explained in [63], the inverse depth method does not estimate the scale factor. This is the reason why the authors compute a transformation alignment by means of an offline Levenberg–Marquardt optimizer. Under these conditions, the presented approach confirms a valid estimation for a proper scale, by introducing the first prior of the odometry into the filter. Then, a robust scale factor estimate is maintained. Consequently, the main outcome can be inferred from Figure 17, where error histograms are presented for the absolute position error. Both results are presented: with the alignment optimization enabled and disabled, in the toolkit options. Figure 17a,c represents the error histograms for the proposed approach for each case. Likewise, Figure 17b,d represents the error histograms for the inverse depth parametrization method, under the same conditions. It may be observed that our approach produces improved accuracy results, with average values under 3 m, independently of the alignment setup.
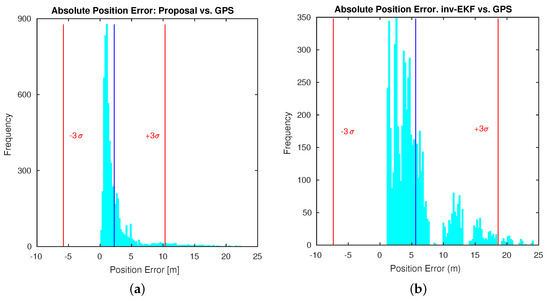
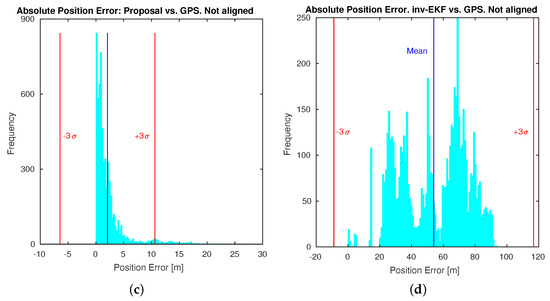
Figure 17.
Histograms for the absolute position error (m) in Dataset 3: (a) proposed approach with alignment optimization; (b) inverse EKF approach with alignment optimization; (c) proposed approach without alignment optimization; (d) inverse EKF approach without alignment optimization.
6. Discussion
Once the results have been presented, in this section, we provide a further insight into the key facts deduced from the real data results.
As an initial outline, Figure 13 demonstrates the reliability and consistency of the proposed robust localization. The results confirm the enhancement of the localization angles and (∼40%), in comparison to the standard visual localization technique. Besides this, a relevant increase of the number of matching points is produced (∼30%), a fact that implies a better final estimate for the pose, since the number of false positives is also reduced. This is an important outcome, as it allows us to get enough visual data to keep producing estimates even under some specific circumstances in which the standard localization technique may be compromised.
Next, the evaluation of the robust localization proposal has been analyzed under real operation conditions within a novel omnidirectional SLAM approach. Figure 14 shows the performance of the approach in a dynamic and challenging scenario. These results highlight the capability to produce an acceptable performance, as a balanced tradeoff, for the final application requirements.
Regarding the error assessment, the results presented in Figure 15 prove the ability of the proposal to keep the estimation error stable, the convergence of the SLAM system and also the uncertainty of the system.
Finally, Figure 16 and Figure 17 present comparison results with a well-acknowledged technique, such as the inverse EKF parametrization method. Here, the proposed approach confirms its validity to deal with large outdoor scenarios, but also to improve the final estimation accuracy and the scale estimate.
Overall, the following aspects should be highlighted:
- (i)
- Robust visual localization technique in terms of accuracy and performance.
- (ii)
- Significant increase of usable visual data (matchings) when standard techniques fail to gather reliable visual data.
- (iii)
- Acceptable tradeoff solution to produce real-time localization.
- (iv)
- Consistent SLAM estimation with the proposed robust localization technique for real-time-oriented tasks.
The most straightforward future improvements are oriented towards the 6DOF extension outdoors, but also towards the computation enhancement. Regarding the uncertainty management, some other developments may be tackled in order to confer the ability to feature entire regions on the image, which would permit accounting for specific area-tracking and also for the associated uncertainty. This would also be interesting for discovering unexplored areas.
7. Conclusions
This article has presented a robust visual localization technique for mobile robotics applications, achieved with a monocular omnidirectional sensor system, constituted by a hyperbolic mirror and a digital camera. Several contributions have been designed and implemented in order to deal with inconsistencies and non-linearities, which especially affect visual sensors. A dynamic uncertainty management control has been devised so as to adaptively conform to the instant variations on the uncertainty of the system. These variations are principally induced by the noise input associated with the changing scene conditions. Moreover, Bayesian regression has also been introduced in order to take most of the sensor data distribution, which ultimately is used to define an informative metric that permits designing robust weighting coefficients for the visual matching block. The adaption of the epipolar geometry towards the omnidirectional nature of the omnidirectional sensor system was also implemented.
The contributions presented herein have been tested in terms of validity and reliability. The results obtained with real datasets have proven the suitability of this realistic robust localization proposal. A tradeoff configuration can be selected in order to operate in real time with sufficient accuracy, considering the specific requirements of the visual SLAM equipment. Besides this, the utilization of visual data has also been improved, since more matching points are detected, in contrast with standard approaches, which tend to fail to gather trustworthy information. Finally, the ultimate SLAM results have confirmed the robustness of the localization proposal when it is embedded in such a real visual system. The final estimations demonstrate consistency in keeping stability and convergence in the system, besides a good tradeoff balance between accuracy and performance. Moreover, the additional comparison results reinforce the validity of this approach.
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by the Spanish government through the project DPI2016-78361-R (AEI/FEDER, UE). In addition, part of the developments has been achieved during a post-doctoral grant for a research stay at the Technical University of Madrid, under a collaboration framework established by the post-doctoral grant APOSTD/2017/028, held by D.Valiente, funded by the Valencian Education Council and the European Social Fund.
Author Contributions
This work emerged under a collaboration framework established between all the authors. D.V., J.M.S. and Ó.R. conceived of the target and research line. D.V., Ó.R. and A.G. defined the software programming planning. D.V. implemented the main software contributions and algorithms. D.V. and L.P. acquired the real dataset and established the experimental benchmark. D.V. performed the experimental tests. D.V. conducted the data processing, and J.M.S. collaborated in the data analysis within the experimental section.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| CCD | Charge Coupled Device |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler divergence |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| SVD | Single Value Decomposition |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
References
- Huang, S.; Dissanayake, G. Convergence and Consistency Analysis for Extended Kalman Filter Based SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Newman, P. Consistent, convergent, and constant-time SLAM. In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Acapulco, Mexico, 9–15 August 2003; pp. 1143–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.; Huang, S.; Dissanayake, G. Active SLAM in structured environments. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1898–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, D.; Newman, P. Using laser range data for 3D SLAM in outdoor environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 1556–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.; Liang, J.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Q. Analysis and Experimental Kinematics of a Skid-Steering Wheeled Robot Based on a Laser Scanner Sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 9681–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Song, J.B. A new sonar salient feature structure for EKF-based SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 5966–5971. [Google Scholar]
- Guadarrama, S.; Ruiz-Mayor, A. Approximate robotic mapping from sonar data by modeling perceptions with antonyms. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 4164–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Tong, Y.; Tang, J.; Chang, L. An Online Solution of LiDAR Scan Matching Aided Inertial Navigation System for Indoor Mobile Mapping. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 4802159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, C.; Leonessa, A. FastSLAM Using Compressed Occupancy Grids. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 3891865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhong, R.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. Feature-Based Laser Scan Matching and Its Application for Indoor Mapping. Sensors 2016, 16, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Şekercioğlu, Y.A.; Drummond, T. Vision-Based Cooperative Pose Estimation for Localization in Multi-Robot Systems Equipped with RGB-D Cameras. Robotics 2015, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Aragón, A.; Macknojia, R.; Payeur, P.; Laganiere, R. Rapid 3D Modeling and Parts Recognition on Automotive Vehicles Using a Network of RGB-D Sensors for Robot Guidance. J. Sens. 2013, 2013, 832963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Lichti, D.D.; Hol, J.D.; Bellusci, G.; Luinge, H. IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Robotics 2014, 3, 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Gankhuyag, G.; Chong, K. Navigation System Heading and Position Accuracy Improvement through GPS and INS Data Fusion. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 7942963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.; García, S.; Barea, R.; Bergasa, L.M.; Molinos, E.J.; Arroyo, R.; Romera, E.; Pardo, S. A Multi-Sensorial Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) System for Low-Cost Micro Aerial Vehicles in GPS-Denied Environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 802. [Google Scholar]
- Munguia, R.; Urzua, S.; Bolea, Y.; Grau, A. Vision-Based SLAM System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Sensors 2016, 16, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recoskie, S.; Lanteigne, E.; Gueaieb, W. A High-Fidelity Energy Efficient Path Planner for Unmanned Airships. Robotics 2017, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, C.; Rives, P. Bearing-only SAM using a minimal inverse depth parametrization. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Madeira, Portugal, 15–18 June 2010; Volume 2, pp. 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Civera, J.; Davison, A.J.; Martínez Montiel, J.M. Inverse Depth Parametrization for Monocular SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Stuckler, J.; Cremers, D. Large-scale direct SLAM with stereo cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1935–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, E.; Munguia, R.; Grau, A. Monocular SLAM for Autonomous Robots with Enhanced Features Initialization. Sensors 2014, 14, 6317–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Nuske, S.; Scherer, S. A Multi-Sensor Fusion MAV State Estimation from Long-Range Stereo, IMU, GPS and Barometric Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Engel, J.; Cremers, D. Large-scale direct SLAM for omnidirectional cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Paya, L.; Amoros, F.; Fernandez, L.; Reinoso, O. Performance of Global-Appearance Descriptors in Map Building and Localization Using Omnidirectional Vision. Sensors 2014, 14, 3033–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paya, L.; Reinoso, O.; Jimenez, L.M.; Julia, M. Estimating the position and orientation of a mobile robot with respect to a trajectory using omnidirectional imaging and global appearance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0175938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Xiang, Z. Design and analysis of a novel omnidirectional stereovision system. In Proceedings of the 2017 Fifteenth IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Nagoya, Japan, 8–12 May 2017; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shuang, Y.; Baoyuan, C.; Lei, Z.; Xiaoyang, Y.; Haibin, W.; Jixun, Z.; Deyun, C. Encoded light image active feature matching approach in binocular stereo vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Forum on Strategic Technology (IFOST), Novosibirsk, Russia, 1–3 June 2016; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Yaojun, L.; Quan, P.; Chunhui, Z.; Feng, Y. Scene matching based EKF-SLAM visual navigation. In Proceedings of the 31st Chinese Control Conference, Hefei, China, 25–27 July 2012; pp. 5094–5099. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, C.; Schuster, M.J.; Hirschmuller, H.; Suppa, M. Submap matching for stereo-vision based indoor/outdoor SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 5670–5677. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, D.; Gil, A.; Fernandez, L.; Reinoso, O. A modified stochastic gradient descent algorithm for view-based SLAM using omnidirectional images. Inf. Sci. 2014, 279, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, D.; Gil, A.; Fernández, L.; Reinoso, Ó. Visual SLAM Based on Single Omnidirectional Views. In Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference, ICINCO 2012, Rome, Italy, 28–31 July 2012; Revised Selected Papers; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.J.; Gonzalez Cid, Y.; Kita, N. Real-Time 3D SLAM with Wide-Angle Vision. In Proceedings of the 5th IFAC/EURON Symposium on Intelligent Autonomous Vehicles, Lisbon, Portugal, 5–7 July 2004; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Valiente, D.; Gil, A.; Fernandez, L.; Reinoso, O. A comparison of EKF and SGD applied to a view-based SLAM approach with omnidirectional images. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.J. Real-Time Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping with a Single Camera. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1403–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, D.; Leonard, J.; Teller, S. Fast Iterative Optimization of Pose Graphs with Poor Initial Estimates. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 2262–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Grisetti, G.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. Non-linear Constraint Network Optimization for Efficient Map Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2009, 10, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rituerto, A.; Puig, L.; Guerrero, J.J. Visual SLAM with an Omnidirectional Camera. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning series, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; University Press Group Ltd.: Bognor Regis, UK, 2006; pp. 1–266. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffari Jadidi, M.; Valls Miro, J.; Valencia, R.; Andrade-Cetto, J. Exploration on Continuous Gaussian Process Frontier Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 6077–6082. [Google Scholar]
- Agudo, A.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Calvo, B.; Montiel, J.M.M. Sequential Non-Rigid Structure from Motion Using Physical Priors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudo, A.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Calvo, B.; Montiel, J. Real-time 3D reconstruction of non-rigid shapes with a single moving camera. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 153, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantarilla, P.F.; Bergasa, L.M.; Dellaert, F. Visual odometry priors for robust EKF-SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 3501–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.G.; Choi, W.S.; An, S.Y.; Oh, S.Y. Augmented EKF based SLAM method for improving the accuracy of the feature map. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 3725–3731. [Google Scholar]
- Oriolo, G.; Paolillo, A.; Rosa, L.; Vendittelli, M. Humanoid odometric localization integrating kinematic, inertial and visual information. Auton. Robot. 2016, 40, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civera, J.; Grasa, O.G.; Davison, A.J.; Montiel, J.M.M. 1-point RANSAC for EKF-based Structure from Motion. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 3498–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, H.C. A computer algorithm for reconstructing a scene from two projections. Nature 1985, 293, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servos, J.; Smart, M.; Waslander, S. Underwater stereo SLAM with refraction correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 3350–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.Z.; Burschka, D.; Hager, G.D. Advances in computational stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, D.; Martinelli, A.; Siegwart, R. A Toolbox for Easily Calibrating Omnidirectional Cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 5695–5701. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, G. Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition; Wiley Series in Probability an Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kulback, S.; Leiber, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2001, 5, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Valiente, D.; Fernández, L.; Marin, J. Building Visual Maps With a Single Omnidirectional Camera. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 28–31 July 2011; pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded Up Robust Features. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, A.; Reinoso, O.; Ballesta, M.; Juliá, M.; Payá, L. Estimation of Visual Maps with a Robot Network Equipped with Vision Sensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 5209–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARVC: Automation, Robotics and Computer Vision Research Group. Miguel Hernandez University. OMnidiectional Image Dataset in a Laboratory at Innova Building. Available online: http://arvc.umh.es/db/images/lab_trajectory/ (accessed on 1 December 2012).
- ARVC: Automation, Robotics and Computer Vision Research Group. Miguel Hernandez University. Omnidiectional Image dataset at Innova Building. Available online: http://arvc.umh.es/db/images/innova_trajectory/ (accessed on 1 December 2012).
- Fontana, G.; Matteucci, M.; Sorrenti, D.G. Rawseeds: Building a Benchmarking Toolkit for Autonomous Robotics. In Methods and Experimental Techniques in Computer Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- The Rawseeds Project: Public Multisensor Benchmarking Dataset. Available online: http://www.rawseeds.org (accessed on 1 December 2012).
- Civera, J.; Grasa, O.G.; Davison, A.J.; Montiel, J.M.M. 1-Point RANSAC for extended Kalman filtering: Application to real-time structure from motion and visual odometry. J. Field Robot. 2010, 27, 609–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Gerkey, B.; Conley, K.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Berger, E.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A. ROS: An open-source Robot Operating System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Workshop on Open Source Robotics, Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ceriani, S.; Fontana, G.; Giusti, A.; Marzorati, D.; Matteucci, M.; Migliore, D.; Rizzi, D.; Sorrenti, D.G.; Taddei, P. Rawseeds ground truth collection systems for indoor self-localization and mapping. Auton. Robot. 2009, 27, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).