Abstract
Photoacoustic tomography is an innovative non-ionizing imaging technique that combines optical contrast with ultrasound resolution for 3D object characterization. While promising, its broader adoption is limited by challenges such as shallow penetration depth and strong optical scattering. To address these issues, this study introduces a dual illumination and detection photoacoustic tomography method, specifically designed for symmetrical objects like hollow metallic cylinders. The illumination system plays a critical role in determining the quality of photoacoustic signals and, thus, the final image. This approach enhances spatial resolution and contrast by using complementary light delivery and signal detection. In industrial settings, where accurate and efficient non-destructive testing is essential, traditional techniques often lack the precision required. The dual illumination and detection strategy offers significant improvements in effective resolution, contrast, defect detection, and artifact reduction, surpassing the limitations of unidirectional approaches. This technique not only strengthens the characterization of metal structures but also contributes to a deeper understanding of their physical behavior. Applications extend across various fields, including aerospace and biomedical engineering. This paper explores the underlying principles and potential of this advanced imaging modality, highlighting its value in modern diagnostic and inspection technologies.
1. Introduction
Photoacoustic (PA) tomography is an imaging technique that combines optical and ultrasound information, a hybrid imaging modality that continues to evolve, especially for applications of medicine and biology [1]. The integration of high-resolution optical imaging with the depth penetration of ultrasound represents a major advancement in biomedical imaging. Although Rosencwaig reported the first application of PA imaging in solids in 1973 [2,3], subsequent advances in laser technology and instrumentation have established PA imaging as a powerful tool for diagnosis, monitoring, and therapeutic guidance in medicine [4,5], as well as for industrial non-destructive testing (NDT) [6,7,8].
The technique relies on the PA effect, wherein material absorbs pulsed or modulated light and subsequently emits ultrasound waves, thereby enabling the visualization of its structural and functional characteristics. Efficient PA absorbers convert absorbed light into acoustic waves, and wavelength-dependent absorption properties and the efficiency of light energy deposition determine their performance. The nonradiative decay processes and the mechanism of nonradiative energy transfer that plays an important role in the generation of PA signals from solids are discussed in [9]. Quantitative PA imaging techniques aim to extract quantitative information from PA signals to provide precise measurements of various tissue properties. This approach enhances the diagnostic capabilities of PA imaging beyond mere qualitative assessments. A critical component is the illumination of the experimental PA system, as it directly determines the generation of PA signals and influences image quality. Common techniques employ multispectral imaging and structured illumination strategies [10,11]. Those approaches offer microscale resolution and a wide range of contributions but are still limited in the penetration depth [1]. However, challenges such as object geometry, light fluence attenuation, acoustic heterogeneity, and ill-posed inverse problems on image reconstruction necessitate advanced techniques and regularization strategies to improve the image quality, i.e., accuracy and stability. To address this problem, many regularization techniques have been developed [12]. Other studies [13] use contrast agents to improve the image quality.
Despite significant progress in PA tomography for biomedical and industrial applications, substantial challenges persist, particularly in achieving high-resolution imaging of deep internal structures. These limitations are primarily due to the shallow light penetration, optical scattering, and restricted angular coverage inherent in systems that employ unidirectional illumination and detection, like linear sensors arrays in a fixed line, useful for obtaining two-dimensional images, or circular arrays that partially surround the study object and improve angular coverage. In industrial manufacturing, where ensuring product integrity is critical, NDT is essential for identifying defects, discontinuities, or material degradation without compromising the component's usability or structure [4,14,15]. However, commonly used unidirectional NDT techniques—such as contact ultrasound (pulse-echo), direct transmission ultrasound, and laser-induced ultrasound—often suffer from limited contrast, structural artifacts, and incomplete internal visualization [16,17,18]. These shortcomings hinder the accurate detection of subsurface flaws, internal cavities, and weak joints.
The acoustic coupling medium around the sample is crucial for signal fidelity; common detection mechanisms require water, oil, or gel [19]. Cutting-edge research has developed sophisticated methods to circumvent the acoustic impedance mismatch problem and perform PA imaging in air, broadly categorized by laser-induced ultrasound imaging [17], which may also involve optical detection (e.g., optoacoustic interferometry) [20] or electromagnetic induction [21]. Unfortunately, this imaging flexibility can lead to high energies, reaching an ablation regime that may cause damage to the object of interest; hence, it is not convenient for NDT. Furthermore, many current experimental setups rely on contact-based measurements, which can be inadequate in scenarios where preserving structural integrity or avoiding environmental contamination is crucial. These constraints highlight the need for advanced imaging strategies that can deliver high-quality results while minimizing physical interaction.
To overcome these limitations, dual-illumination and dual-detection PA tomography represent a promising alternative [22,23]. By exploiting the axial symmetry of immersed objects and acquiring signals from opposing directions, dual-illumination and detection enhance angular coverage, improve the signal-to-noise ratio, and reduce spatial ambiguities. This approach enables more accurate and robust reconstruction of internal features, effectively addressing many of the deficiencies associated with traditional unidirectional methods.
In PA tomography, image reconstruction plays a crucial role in transforming time-resolved pressure signals into spatially resolved images. Reconstruction algorithms can be broadly categorized into analytical, geometric, and model-based approaches. Among them, geometric algorithms stand out for their simplicity, computational efficiency, and ease of implementation, especially when the speed of sound is assumed to be homogeneous. Commonly used geometric methods include back projection (BP), filtered back projection (FBP), time reversal (TR), and Delay-And-Sum (DAS). These algorithms estimate the location of the initial pressure sources by summing time-shifted signals based on the calculated time-of-flight between each detector and image pixel. To overcome resolution and spatial limitations, the evolution of geometric algorithms follows the trend in the development of adaptive beamforming that dynamically weights signals based on their coherence [24,25] or adopts the superior sidelobe suppression to further enforce the signal-to-noise ratio [26,27,28]. Recent research has also focused on deep learning approaches to emulate or enhance these geometric principles, where convolutional neural networks are trained to learn optimal weighting functions from simulated or experimental data, achieving state-of-the-art results in speed and quality for real-time applications [29,30].
The present work explores how dual illumination and detection of the object of interest can overcome some depth limitations and scattering of PA tomography and offers a special emphasis on industrial applications. In the realm of dual illumination PA tomography, inspired by the progress of Fukutani et al. [11], the mechanisms underpinning signal enhancement are integral to optimizing imaging performance, particularly when applied to metal cylinders. The regularization problem is attained by improving the illumination and extending the amount of data with respect to noise. By exploiting the PA effect, which generates ultrasonic and thermal waves after energy absorption, research can significantly improve an image's spatial resolution and contrast in general. This research is motivated by the need to enhance spatial resolution, improve contrast, and reduce artifacts, thereby enabling more accurate and reliable non-destructive evaluation in 2D photoacoustic tomography of hollow metallic cylinders through a dual illumination and detection approach. In Section 2, we address the relationship between the optical and thermoelastic properties of materials and the generation of the PA signal. In Section 2.1, we resume the theoretical impact of the PA effect on metals. On this background, the studied materials are characterized in Section 2.2. Then, Section 2.3 offers an overview of the experimental setup. The essential reference for validation represents the PATLAB simulation in Section 2.4. Finally, Section 2.5 compares the classic primal approach with the proposed dual PA signal processing on a time sequence detector level. The 2D tomographic reconstruction results are presented and analyzed in Section 3. Here, we employed the basic DAS algorithm due to its widespread use in circular acquisition geometries and its proven ability to reconstruct high-contrast features with relatively low computational cost [21]. We discuss our findings in Section 4 and conclude our work and open problems in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
This study employs an integrated experimental and computational approach to develop and validate a dual illumination and detection strategy for PA tomography of hollow metallic cylinders. The methodology encompasses the characterization of material properties, a custom experimental setup for sequential laser illumination and acoustic detection, and a comprehensive simulation framework using the PATLAB toolbox version 1.0. Signal processing techniques were developed to align primal signals and synthesize dual signals, which were subsequently reconstructed into 2D tomographic images using the Delay-and-Sum (DAS) algorithm. The following sections detail the physical principles, the materials under evaluation, the experimental setup, simulation parameters, and the computational processing workflows that form the basis of this investigation.
2.1. Physical Transport Considerations
We describe PA signal formation in three steps: (i) optical energy deposition and thermoelastic pressure build-up, (ii) heat diffusion and confinement criteria, and (iii) acoustic propagation and linear detection by the sensor.
2.1.1. Optical Deposition and Initial Pressure
For a short pulse, the absorbed power density decays exponentially with depth ,
with [1/cm] as the optical absorption coefficient, H0 as the power density of the pulse and as the pulse profile. Under stress and thermal confinement, the initial pressure measured in Pascals (1 Pa = 1 N/m2) generated by a PA wave is expressed as
where is the temperature-dependent Grüneisen parameter, the absorption coefficient, and F(J/cm2) the optical fluence [31,32]. The Grüneisen parameter contains, in turn, the thermoelastic parameters, as Γ = βKTV/CV; with as the thermal expansivity, KT as the bulk modulus, and CV as the specific heat, with respect to constant temperature and volume [33]. All of these parameters are directly proportional to PA amplitude. The PA effect relies on the photothermal effect to produce sound, although not all photothermal processes necessarily lead to PA signals.
2.1.2. Heat Diffusion and Confinement
The theory of Rosencwaig and Gersho in 1975 predicts the dependence of the PA signal of a solid on the thermal absorption coefficient T of the solid for a specific wavelength [2]. The main source of the acoustic signal of a solid arises from the heat flow. The thermal diffusion equation in the solid can be written in terms of the temperature
where κ = k/ρCV is the thermal diffusivity of the material with thermal conductivity and density ; A = TI0/2k with the incident monochromatic light flux I0, assuming full efficiency of the light to heat conversion.
The incremental pressure of a metal piece under chopped light is
where p0, V0 are the pressure and the volume of the metal piece at ambient temperature, and is the ratio of specific heats; is proportional to the envelope of the sinusoidal pressure variation . For optically opaque solids, as is the case for metals of thickness with optical absorption length , that are thermally thick, i.e., with a thermal diffusion length ,
2.1.3. Acoustic Propagation and Detection
In the thermoelastic regime and under thermal confinement, the time derivative of the temperature field acts as the driving source term of the acoustic field inside solids; this is explicitly illustrated for an aluminum slab (l3 mm thick) [34] and extended to layered media in [35]. Those works also detail how thermal diffusivity couples to the viscous and elastic properties of the medium; the full derivations lie beyond our present scope. Consistent with this framework, under the confinement assumptions the PA field satisfies the driven wave equation
with c as the effective sound speed. Here we adopt a 1-D, normal-incidence description consistent with our geometry, avoiding shear modes and simplifying time-of-flight interpretation. The measured signal S at the sensor face with a pressure spectrum P satisfies
where H() is the pressure-to-output transfer function of the sensor-plus-electronics, which can be obtained by calibration or via a layered transfer-matrix model of the sensor stack and couplant [35].
2.2. Material Characterization
The object of interest is a series of five metallic cylinders (aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, and stainless steel), all with an inner diameter, din mm, and an outer diameter, dout mm, as shown in Figure 1. The density, sound velocity, and acoustic impedance are shown in Table 1. In PA as well as ultrasound imaging, we are concerned about the difference in between two adjacent materials: a small difference implies greater energy transmission, whereas a mismatch induces energy reflection, which typically results in more image artifacts and noise.

Figure 1.
From left to right: aluminum, steel, copper, bronze, and brass (marked with black duct tape for better distinction due to its similarity to bronze) cylinders, viewed from above.

Table 1.
Density, optical absorption coefficient [36] and sound velocity of the five metal cylinders, ordered by acoustic impedance [37]; metal alloys (*) are restricted to higher numerical uncertainty.
The metal sound velocity was obtained experimentally from the arrival time of the PA signal from each of the cylinders, placed in direct contact on the cylinder’s flat, round face with the sensor, and without the beam path passing through the cylinder gap. The arrival time is obtained directly from the signal recorded by the oscilloscope, using the expression of the sound velocity vs = h/ta, with respect to the cylinder's height .
2.3. Experimental Setup
A custom PA tomography setup was designed to implement a dual illumination and detection strategy for the non-destructive evaluation of hollow metallic cylinders. The core configuration, illustrated in Figure 2, essentially utilized two pulsed Nd:YAG lasers for the core challenge to provide sufficient laser fluence F (energy per area). Laser splitters and mirrors could be a viable alternative, but could reduce the pressure spectrum, according to Equation (2). Two acoustic detectors performed in a forward configuration due to optimal signal strength and sensitivity. Also, this method seeks to reach a compromise between linear and circular sensor arrays, placing two sensors in the same plane to obtain simultaneous PA signals in search of symmetry discrepancies in our samples [38,39]. The sequential, multi-angle acquisition was fundamental to synthesizing the enhanced PA tomographic reconstruction. Furthermore, immersing the sensors and samples in water ensures optical coupling for optimal propagation of acoustic waves.
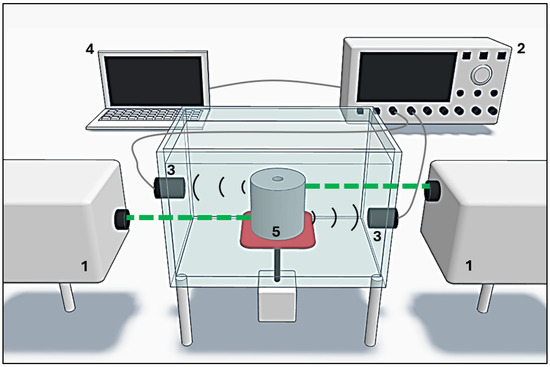
Figure 2.
Schematic of the experimental PA setup. (1) pulsed lasers, (2) oscilloscope, (3) transducers, (4) laptop, and (5) metallic cylinder phantom. Two lasers and two detectors are shown only to illustrate the sequential illumination and detection procedure; however, all measurements were carried out in the same plane. The photodetector is not depicted here to avoid visual saturation of the figure.
The PA experimental setup consisted of: (1) two Quantel Brilliant b pulsed Nd:YAG lasers operating at the second harmonic (532 nm), with a pulse width of 5 ns and a repetition rate of 10 Hz; (2) a Tektronix DPO5204B digital oscilloscope with 2 GHz bandwidth and a 10 GS/s sampling rate; (3) two Olympus A326S-SU of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) immersion transducers with a central frequency of 5 MHz, a bandwidth of 2.57 MHz, and an element diameter of 9.52 mm; (4) a laptop for data acquisition and processing; (5) a set of metallic cylinders with a central hole, used in computed tomography; and (6) a Thorlabs PDA10A amplified silicon detector.
The sample was mounted on a rotating stage, and both were submerged in water inside an acrylic tank. Sequential illumination on a fixed sample position was performed on two diametrically opposite sides of the cylinder, while acoustic detection was carried out in a forward configuration on the same plane, as illustrated in Figure 2. Sequential measurements with an approximate 10 s acquisition time were obtained for each sample, corresponding to the cardinal positions where the laser beam impinged. In order to determine a recommended number of measurements, we consulted the PATLAB simulation of this case in the following subsection.
2.4. PATLAB Simulation
The PA simulation setup offers the important benefit of validating adequate signal processing and noise reduction with respect to the forward problem, as well as the choice of the reconstruction algorithm that solves the inverse problem of tomography.
PATLAB [40] is a specialized software toolbox in MATLAB R2025a for PA tomography simulation and reconstruction, offering a comprehensive interface for 2D and 3D reconstruction, including the k-Wave toolbox for the acoustic wave transport model. It allows the user to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed acquisition techniques in this study. PATLAB consists of four modules: (1) loading/simulating inputs, (2) pre-processing, (3) image reconstruction, and (4) display and save.
The PA simulation images were reconstructed using the Delay-and-Sum (DAS) method [27], one of the most widely adopted beamforming algorithms in ultrasound imaging. Due to its simplicity and ease of implementation, DAS has also been commonly applied in PA tomography [24]. The algorithm calculates the sum of the time points associated with each grid point, assuming that the detectors have omnidirectional sensitivity and that signal acquisition is performed over circular geometry for 2D images [40]. Although the method is fast and straightforward, it provides only an approximate reconstruction of the underlying structures [41]. Consequently, its performance is often limited in terms of resolution and artifact suppression when compared to more advanced model-based or iterative reconstruction techniques [42].
To simulate PA signals and reconstruct 2D images of a metal cylinder with a central cavity, PATLAB was used with the integration of k-Wave to model acoustic wave propagation, supporting both signal simulation (forward problem) and image reconstruction (inverse problem). As a potential drawback of the PATLAB simulation, we identify the exclusive simultaneous illumination possibilities, although wave interferences are likely different, when sequential illumination is implemented. Since the object cannot rotate in the PATLAB framework, the dual detector pair will turn around the metal cylinder, as presented by blue dots in Figure 3 (left).
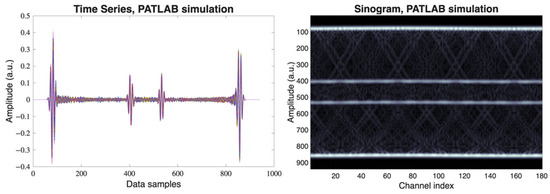
Figure 3.
(Left) All 180 detectors measure as time series data samples. (Right) Acquired sinogram information from the implemented circular detector array.
2.4.1. Dense Sampling
The simulation of acoustic propagation involved defining the four essential components of k-Wave: the computational grid, the acoustic properties of the medium, the sensor configuration, and the acoustic source. A 2D computational domain of 35 × 35 mm2 was used, with a grid spacing of 0.1 mm and centered at (0, 0) mm. The sensor array consisted of 180 equally spaced detectors arranged in a circle of 15.8 mm radius, as dense PA sensing is suggested by the authors of PATLAB [40] for accurate 2D image reconstruction of the internal structure of the object. Two opposite sensor positions are operated 90 times, rotating the cylinder every 2 degrees, and simulated by a 2 × 90 equidistantly distributed circular detector array, respectively. The detector response was modeled with a center frequency of 5 MHz and a 52% bandwidth. The medium was assigned an effective speed of sound of water, without additional attenuation. The acoustic source was defined as a binary image of the object under study, a hollow metal cylinder as described in Section 2.2, assuming omnidirectional illumination and perfect thermoelastic conversion. This concept maximizes the dual illumination strategy. In PATLAB we only locate the light absorber, but not the light sources. A sampling frequency of 50 MHz and a time window of 30 µs were used, consistent with experimental parameters. The simulation generated 2 × 90 almost equal time-series pressure signals, which were arranged into a sinogram of size 180 × , where is the number of time samples, presented as time series and sinogram in Figure 3. The implemented strategy to PA dense sensing provides a robust raw data set to handle the inherent challenges of the imaging system; no additional noise level is implemented. Nonetheless, this concept oversamples the physical space, as geometrical symmetries may be incorporated to optimize the experimental methodology.
2.4.2. Image Reconstruction
The PA signals generated in the simulation were used to reconstruct the 2D cross-sectional image of the metal cylinder. The Delay-And-Sum (DAS) algorithm was applied using the same computational grid and sampling parameters defined during the simulation Section 2.4.1. We assumed a sensor directivity of 30 degrees, along with omnidirectional sensitivity. The resulting image in Figure 4 clearly delineates the inner and outer edges of the cavity as regions of maximum intensity.
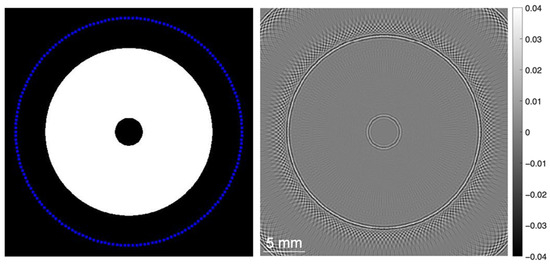
Figure 4.
Designed image of the binary physical section of the cylinder’s geometry with 180 simulated point-like detectors (left) and the DAS 2D reconstruction of this object (right), where gray values indicate amplitude in arbitrary units.
The simulation considered ideal conditions, including uniform acoustic propagation in a non-dispersive, non-attenuating medium and full-field omnidirectional illumination. Although these assumptions do not fully represent real experimental data, appropriate signal processing can help mitigate such limitations. The reconstructed images were normalized and contrast-enhanced to facilitate qualitative and quantitative analysis. Both the preprocessed sinograms and final images were exported for further evaluation using image quality metrics to optimize the reconstruction parameters in future iterations.
2.5. Primal and Dual Experimental PA Signal Processing
Since the object of interest is axisymmetric concerning the centerline of rotation, the experimental setup of Section 2.3 was realized by only four distinct detector positions labeled as “north” (N), “east” (E), “south” (S), and “west” (W) and further implement a reproduction and distribution strategy to fill the physical space densely, see Section 3. Their measurement should give an equivalent amount of information as attained by the simulation 2.4.1 by 180 detectors. By the interpretation that the time sequence reflects the projection of the geometric object of interest, we identify the need to align the time-amplitude signal with the dimensional center of the metal cylinder. Since the time to space projection depends on the acoustic transport velocity, a balance between the sound velocity in water and the corresponding metal is demanded. To attain this balance with an average propagation velocity , the intensity reflection coefficient R2, the squared pressure reflection coefficient R, as contemplated in [32], is taken into account. The intensity reflection coefficient from metal to water equals the intensity from water to metal. The pressure reflection coefficient from the solid metal, where the PA effect initiates, to water, the coupling medium, is calculated by
where Z = ρv describes the characteristic impedance of the penetrating sound wave (see Table 1); hence, for the solid, one calculates Zsolid = ρsolidvsolid, while Zwater = ρwatervwater ≈ 1.481 × 106 (kg/m2s) = 1.481 MRayl. Table 2 contains the evaluation results of the pressure reflection coefficients of the present materials in this study.

Table 2.
Acoustic intensity reflection coefficient and thermal diffusion length.
The effective propagation velocity represents the average speed at which the PA wave travels from the illuminated region of the metal cylinder toward the detector, in forward mode, through alternating layers: metal, water, metal, and water. Since part of the wave is transmitted and part is reflected at each interface, the propagation speed must account for both effects. Inspired by the approach used in layered acoustic media [43,44,45], the effective velocity can be estimated by weighting the sound speeds in the metal and in water according to the acoustic reflection coefficient :
Physically, describes how fast the acoustic energy effectively propagates toward the detector after interacting with several metal–water interfaces. A higher reflection coefficient indicates that most of the wave energy remains in the solid, increasing , while a lower means stronger transmission into water and a reduced effective speed. Incorporating this effective value into the alignment of PA signals allows a more accurate temporal calibration and enhances the fidelity of image reconstruction in heterogeneous or multilayer media. According to this average propagation of the acoustic PA wave in Figure 5, we center the PA time sequence over the metal cylinder.
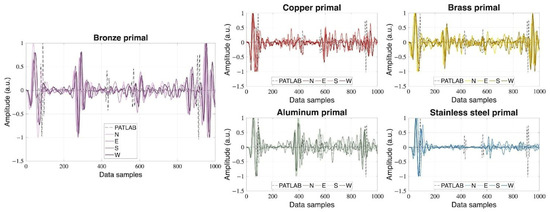
Figure 5.
Primal normalized PA signals, centered over the cylinder according to the average propagation velocity v.
The effective propagation velocity is not merely a physical parameter in PA; it is a critical determinant of image fidelity and quantitative accuracy. Its scientific importance stems from the fact that PA image reconstruction is an inverse problem that relies on knowing the speed of sound to map received signals back to their origin. An incorrect velocity model introduces artifacts, mislocations, and blurring, directly limiting the technology's resolution and functional imaging capabilities.
The experimental setup with two opposing forward PA detection systems will offer temporal sequences each, but the direction of the underlying PA transport is not linked to the spatial coordinates. We propose to interpret one forward PA signal g in the backward direction and register its mirrored time sequence g′ in the temporal system of the other PA signal. Both signals are represented in vectors of the same length, and we look for their element-wise Hadamard product . This way, we realize all possible combinations of detector positions on the circular detector array, evaluated in the experimental setup (labeled by N, E, S, W): (N, E), (N, S), (N, W), (E, S), (E, W), (S, W). Figure 6 shows all dual PA signals.
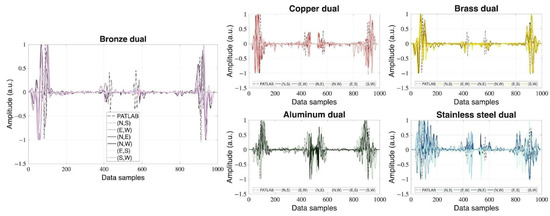
Figure 6.
Dual normalized PA signals of metals.
The derived six dual time sequences of every metal define dual sinogram information that offers 2D tomographic reconstructions. In this regard, we proceed as in the PATLAB simulation of Section 3.3 and obtain dual DAS reconstruction in Figure 7 for the five cylinder sections. Once the 1D PA signals are processed according to the dual illumination methodology, the tomographic section image of the cylinder can be reconstructed according to filtered back projection methods.
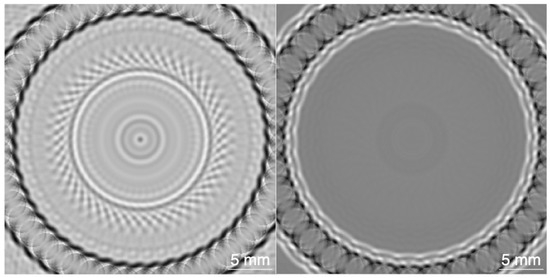
Figure 7.
Primal (left) and dual (right) DAS reconstruction of the bronze cylinder.
3. Results
According to the image reconstruction strategy in Section 2.4.2, we develop 2D PA tomography with the experimental primal and dual signals (Section 2.5) for a total of 180 detectors, equally distributed around a circular array of radius 15.8 mm. We reproduce the four primal signals measured at positions N, E, S, W, 45 times and distribute them equally around the detector array. Equivalently, we replicate the six dual signals (N, E), (N, S), (N, W), (E, S), (E, W), (S, W), 30 times, and again assign them evenly to the 180 detectors in the circle. We compare the results as illustrated in Figure 7, presenting the DAS PA tomographic section image of the bronze cylinder. The primal image contains many artifacts that are likely to result from internal acoustic reflections. The dual image represents a much smoother domain over the metal area but requires further signal enhancement to visualize the internal structure (hollow cylinder).
To prevent loss of information, no filters or pre-processing strategies are implemented in PATLAB or externally. At first sight, the dual reconstruction in Figure 7 resembles more the simulation section image in Figure 4 (right). In order to evaluate the results more objectively with respect to the image reconstruction resolution of the PATLAB simulation, we implement the following to quantify the error between the experimental approach and the simulated study.
3.1. Dissimilarity
Three distance measures are used to evaluate the signal processing approach for PA image reconstruction. The less the difference, the better the match between the experimental performance and the computational simulation. The dissimilarity quantification of the PA results is listed in Figure 8. Excluding the material with the highest acoustic impedance, stainless steel, the dual processing results in a profitable outcome for PA tomographic image reconstruction.
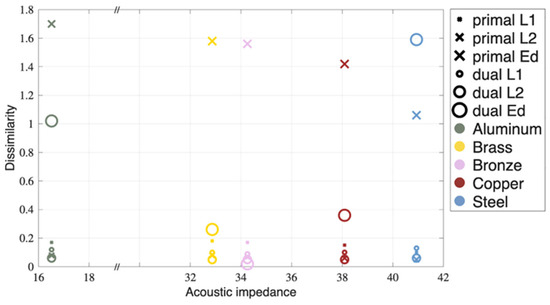
Figure 8.
Dissimilarity evaluation of primal and dual PA time signals with respect to the PATLAB simulation using the three measures L1, L2 and Ed. The smaller the resulting distance, the better the match between experiment and prediction.
The -distance between the PATLAB simulation and an experimental measurement (primal or dual), also known as the Manhattan distance or the mean error performance, is evaluated according to
The -distance between and , or the Euclidean distance or the root mean squared error, is defined by
The entropy of an image is a quantitative measure of its information content [46]. Based on this information, the entropy distance (also known as joint entropy by Shannon [47]) between the simulation image of all PA time sequences and the experimental image for the j-th measurement is calculated following
The MATLAB function entropy is a measure that quantifies the information about the image content, taking into account the histogram information. Its output is a single scalar value that gives a clue about the uncertainty or randomness in the PA data. Higher entropy indicates a richer distribution of pixel intensities, meaning more detail and texture, whereas lower entropy suggests redundancy or loss of information. A high entropy distance means the PA measurements and its simulation are very different and complex when considered together.
3.2. Similarity
In order to quantify how similar the experimental PA information with respect to the PATLAB simulation is, we implement three structural measures. Two of them refer to the space or time domain and offer a direct overall comparison between two images. Images that reveal patterns, textures, and orientations are typically evaluated in the Fourier or frequency domain. By looking at the structure globally, we evaluate a third image measure by incorporating the Fourier transform of the PA information. The similarity quantification of the PA results is listed in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Similarity evaluation of primal and dual PA time signals with respect to the PATLAB simulation using the three measures CCF, SSIM and F-SSIM. The greater the resulting value, the better the match between experiment and prediction.
The CCF evaluation gives a measure of the cross-correlation of two discrete time sequences, as implemented in MATLAB in terms of the function XCORR. The higher the results, the more similar the experimental and simulation time sequences [48,49]. We focus on its maximal element by
Further, the structural similarity is evaluated by MATLAB’s SSIM function, as seen in [50,51]. The same SSIM measure applied to the absolute value of the PA signals in the Fourier domain, |FFT(f)| and |FFT(g)| is also listed in Figure 9 as F-SSIM [52].
3.3. Signal-to-Noise Ratio
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure that compares the level of a desired signal, in this case the simulation data, to the level of background noise, here experimental data, either the primal or the dual case. While the fractional evaluation in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 measures the power of the noise of the experiment, SNR informs about its variance. Figure 10 displays the quantitative evaluation of the results obtained.
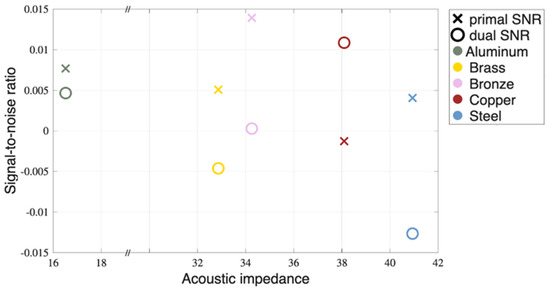
Figure 10.
Signal-to-noise ratio of the PATLAB simulation with respect to the primal and dual PA time signals. The closer the SNR value to one, the better the match between experiment and prediction.
Based on the quantitative analysis in Section 3.1, Section 3.2, and Section 3.3, the results show that dual illumination significantly improves image fidelity, contrast, and noise reduction. The quantitative metrics presented in Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 provide objective evidence of the dual method's superiority. For all metals except stainless steel, the dual processing yielded lower distances to the simulated ideal signal, indicating a closer match to the expected outcome. The increase in cross-correlation and structural similarity values for the dual images further confirms their enhanced fidelity and closer resemblance to the simulated benchmark. Dual signal processing offers a closer approach to SNR = 1, which confirms less variance in noise in experimentally processed data. In summary, the presented results suggest that the dual processing successfully reduced the randomness and uncertainty in the data, resulting in a cleaner, less noisy image that contains more structured information.
4. Discussion
The implementation of a dual illumination and detection strategy in PA tomography for hollow metallic cylinders has demonstrated significant advantages over traditional unidirectional (primal) approaches. The results confirm that this method effectively mitigates several key limitations inherent in conventional PAT systems, particularly those related to artifacts, resolution, and contrast in industrial NDT applications.
The acoustic impedance of the materials plays a critical role in both signal processing and image quality. The high impedance mismatch between the metals and water results in a high pressure reflection coefficient (R > 69.8% for all materials), meaning a large portion of the generated acoustic energy is reflected at the interface. While this strong reflection is needed for the detection principle, it also leads to complex internal reverberations that manifest as artifacts in the primal reconstructions. The dual processing approach appears to compensate for these effects, unless the artifacts dominate the space; stainless steel apparently passes this limit and fails the distance measure under the implemented experimental parameters.
The sound velocity within each metal, which we measured experimentally, is another crucial parameter. The sequence of sound velocities (Aluminum > Stainless steel > Copper > Bronze ≈ Brass) directly influences the time-of-flight of acoustic waves and thus the accuracy of the reconstruction algorithm in the primal mode. The proposed average propagation velocity model for the dual processing, which weights the sound velocity in metal and water by the reflection coefficient, apparently balances this influence.
The thermal properties, specifically the thermal diffusion length, also influence the PA signal generation. Materials with a shorter thermal diffusion length (like bronze) confine heat more effectively (see Section 2.1), leading to a more efficient thermoelastic expansion and a stronger initial PA signal. This may explain why the numerical evaluation of bronze is quantitatively much better than that of brass, although both materials have similar acoustic impedance and sound velocity.
By using a single, simple geometry across five different metals, we intentionally isolated the variables of acoustic impedance, thermal diffusivity, and sound velocity. This controlled approach allowed us to demonstrate that the material properties are a primary source of artifact. Likewise, the reconstructed PA images reflect the combined influence of optical (absorption and scattering) and acoustic (sound propagation) properties, where materials with higher absorption coefficients yield images of greater contrast and edge definition, while those with lower absorption appear less intense and less defined—illustrating the intricate interplay between optical and acoustic behaviors that ultimately determines image quality. Experimentally, this relationship is illustrated in Figure 5 for the primary configuration and in Figure 6 for the dual configuration. In the dual case, where the signals appear cleaner, it can be seen that stainless steel produces the noisiest signals, whereas bronze yields the cleanest ones. Although stainless steel exhibits a high optical absorption coefficient—typically leading to high-intensity signal generation—it also has a very high acoustic reflection coefficient, which can introduce noise due to multiple internal reflections. In contrast, bronze possesses an intermediate acoustic reflection coefficient and a relatively high absorption coefficient, resulting in a better signal-to-noise ratio. Ultimately, the image quality depends on the complex interplay between the optical and acoustic properties of the materials, and determining which effect predominates is not straightforward.
A limitation of this study is the assumption of ideal conditions in the simulation (e.g., uniform illumination, no acoustic attenuation). In practice, dual PA illumination and detection are limited in space and by the sensitivity of the detectors. Future work will focus on denser dual measurement strategies, incorporating different volumes, geometries, and materials, and exploring iterative reconstruction algorithms that can further suppress artifacts and improve quantitative accuracy.
5. Conclusions
This study successfully developed and validated a dual illumination and detection photoacoustic tomography strategy specifically designed for the non-destructive evaluation of hollow metallic cylinders. The dual configuration effectively mitigates artifacts, enhances image contrast and spatial resolution, and compensates for acoustic reflections arising from metal–water impedance mismatches. The results reveal that material properties—specifically acoustic impedance, sound velocity, and thermal diffusion length—play a decisive role in determining signal quality and reconstruction fidelity. The proposed effective propagation velocity model successfully balances transmission and reflection effects, improving the quantitative accuracy of dual-mode reconstructions. Among the analyzed metals, bronze exhibited the most favorable performance due to its optimal optical absorption and acoustic reflection combination.
The key conclusions are enhanced image quality by effective dual signal processing for metals with acoustic impedance < 42 × 106 kg/(m2s) = 42 MRayl, as demonstrated by quantitative PA signal evaluation. This technique addresses the industry's critical limitations of existing NDT methods by offering a non-contact, high-contrast, and high-resolution imaging solution for detecting internal structures and potential defects in symmetric metal components.
Overall, the findings confirm that dual illumination and detection constitute a robust and efficient strategy for improving image quality in PAT-based non-destructive testing, with future work focusing on denser measurement geometries and iterative reconstruction algorithms to further enhance performance.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in the conceptualization, methodology, analysis, and writing of the manuscript, review and editing; software, V.M.M., R.E.C.-L. and M.P.C.-G.; validation and resources, M.P.C.-G., R.E.C.-L., O.E.M.-T. and A.P.-P.; investigation and project administration, V.M.M. and A.P.-P.; data curation and funding acquisition, V.M.M.; visualization, M.P.C.-G.; supervision, A.P.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by DGAPA PAPIIT, grant number IN113824.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The experimental implementation was carried out at the Research and Technological Development Unit (UIDT) of the General Hospital of Mexico (HGM). We are grateful for all the support provided there.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, S.; Miao, J.; Li, L.S. Challenges and Advances in Two-Dimensional Photoacoustic Computed Tomography: A Review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, 70901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosencwaig, A.; Gersho, A. Theory of the Photoacoustic Effect with Solids. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirang Manohar, D.R. Photoacoustics a Historical Review. Adv. Opt. Phot. 2016, 8, 586–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Tian, C. Review Recent Developments in Photoacoustic Imaging and Sensing for Nondestructive Testing and Evaluation. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2021, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Marin, A.; Daeichin, V.; Hunt, A.; Springeling, G.; Beurskens, R.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; van Soest, G. Acoustic Stack for Combined Intravascular Ultrasound and Photoacoustic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2025, 72, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xu, W.; Lai, Y.; Mu, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, P. High-Sensitive Fabry-Perot Cavity-Enhanced Optical Resonator for Photoacoustic Sensing. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 44841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Xue, D.; Cheng, L.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. High-Sensitivity Fiber-Tip Acoustic Sensor with Ultrathin Gold Diaphragm. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 14674–14684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nteroli, G.; Podoleanu, A.; Bradu, A. Combining Photoacoustic and Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for Nondestructive Testing Applications. In Proceedings of the Advances in 3OM: Opto-Mechatronics, Opto-Mechanics, and Optical Metrology, Timisoara, Romania, 13–16 December 2021; Rolland, J.P., Duma, V.-F., Podoleanu, A.G.H., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, V.N.; Thakur, S.N. Physics and Instrumentation of Photothermal and Photoacoustic Spectroscopy of Solids. In Photoacoustic and Photothermal Spectroscopy Principles and Applications; Elasavier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, L.V. Multiscale Functional and Molecular Photoacoustic Tomography. Ultrason. Imaging 2016, 38, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutani, K.; Someda, Y.; Taku, M.; Asao, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Yagi, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Shiina, T.; Sugie, T.; Toi, M. Characterization of Photoacoustic Tomography System with Dual Illumination. In Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing, Proceedings of the SPIE Photonics West 2011, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 January 2011; Oraevsky, A.A., Wang, L.V., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tarvainen, T.; Cox, B. Quantitative Photoacoustic Tomography: Modeling and Inverse Problems. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, S11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, B.; Lim, H.G. Advances in Photoacoustic Imaging Aided by Nano Contrast Agents: Special Focus on Role of Lymphatic System Imaging for Cancer Theranostics. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, J.A. Photothermal Investigations of Solids and Fluids; Academic Press Inc. (London): London, UK, 1989; ISBN 9780126363456. [Google Scholar]
- Hellier, C. Handbook of Nondestructive Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Hellier, C., Ed.; McGraw Hill Professional: Columbus, OH, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780071777148. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, H.; Delgado-Prieto, M.; Trull, J.; Picó, R.; Romeral, L.; Cojocaru, C. Defect Reconstruction by Non-Destructive Testing with Laser Induced Ultrasonic Detection. Ultrasonics 2020, 101, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; Wang, T. Laser-Induced Ultrasound Imaging of Multi Metal Laminate with Complex Interface. Mater. Des. 2023, 232, 112095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiouk, A.B.; Aglyamov, S.R.; Bourgeois, F.; Ben-Yakar, A.; Emelianov, S.Y. Quantitative Ultrasound Method to Detect and Monitor Laser-Induced Cavitation Bubbles. Infrared Phys. 1991, 32, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gamelin, J.; Maurudis, A.; Aguirre, A.; Huang, F.; Guo, P.; Wang, L.V.; Zhu, Q. A Real-Time Photoacoustic Tomography System for Small Animals. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 10489–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberg, M.W.; Hunt, H.K. Hand-Held Optoacoustic Imaging: A Review. Photoacoustics 2018, 11, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughedda, H.; Hacib, T.; Le Bihan, Y.; Chelabi, M.; Acikgoz, H. Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer for Detection and Characterization of Hidden Cracks inside Stainless Steel Material. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 2021, 36, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Maslov, K.I.; Puckett, E.R.; Rowland, K.J.; Warner, B.W.; Wang, L.V. Double-Illumination Photoacoustic Microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liu, C.; Meng, J.; Gong, X.; Lin, R.; Sun, M.; Song, L. Dual-Foci Detection in Photoacoustic Computed Tomography with Coplanar Light Illumination and Acoustic Detection: A Phantom Study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 050501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Thomas, A.; Singh, M.S. Delay-and-Sum-to-Delay-Standard-Deviation Factor: A Promising Adaptive Beamformer. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4662–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaddim, R.A.; Ahmed, R.; Varghese, T. Subaperture Processing-Based Adaptive Beamforming for Photoacoustic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2336–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, R.; Yoshizawa, S.; Umemura, S.-I.; Saijo, Y. Basic Study of Improvement of Axial Resolution and Suppression of Time Side Lobe by Phase-Corrected Wiener Filtering in Photoacoustic Tomography. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 07LD11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarzadeh, M.; Mahloojifar, A.; Orooji, M.; Adabi, S.; Nasiriavanaki, M. Double-Stage Delay Multiply and Sum Beamforming Algorithm: Application to Linear-Array Photoacoustic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Veloz, M.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, G.; Polo-Parada, L.; Cortalezzi, F.; Kline, D.D.; Dantzler, H.A.; Cruz-Alvarez, L.; Castro-Beltrán, R.; Hidalgo-Valadez, C. Image Reconstruction Algorithm for Laser-Induced Ultrasonic Imaging: The Single Sensor Scanning Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, N.; Deán-Ben, X.L.; Razansky, D. Deep Learning Optoacoustic Tomography with Sparse Data. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, N.; Jain, G.; Kalva, S.K.; Pramanik, M.; Yalavarthy, P.K. Deep Neural Network-Based Sinogram Super-Resolution and Bandwidth Enhancement for Limited-Data Photoacoustic Tomography. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 2660–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Jung, U.; Kim, C. Photoacoustic Imaging Platforms for Multimodal Imaging. Ultrasonography 2015, 34, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.V. Tutorial on Photoacoustic Tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 61007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.; Oda, H.; Chopelas, A.; Isaak, D.G. A Thermodynamic Theory of the Grüneisen Ratio at Extreme Conditions: MgO as an Example. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1993, 19, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Reyes, E.; García-Segundo, C.; García-Valenzuela, A.; Ortega, R.; Buj, C.; Filbir, F. Heat Transport Considerations in the Mathematical Analysis of the Photoacoustic and Photothermal Effects. J. Phys. Commun. 2019, 3, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrrez-Reyes, E.; García-Segundo, C.; García-Valenzuela, A.; Reyes-Ramírez, B.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, G.; Guadarrama-Santana, A. Analysis of the Transfer Function for Layered Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Sensors. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 065106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyanskiy, M.N. Refractiveindex.info Database of Optical Constants. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASM International. Nondestructive Evaluation and Quality Control—The Materials Information Company ASM Handbook; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ge, J.; Chen, W.; Qi, L. Advanced Image Post-Processing Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography: A Review. Photonics 2023, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Qiu, J.; Lu, W. Application of Photoacoustic Computed Tomography in Biomedical Imaging: A Literature Review. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidi, P.; Yip, L.C.M.; Rascevska, E.; Diop, M.; Carson, J.J.L. PATLAB: A Graphical Computational Software Package for Photoacoustic Computed Tomography Research. Photoacoustics 2022, 28, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Shen, K.; Dong, W.; Gao, F.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Feng, T.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; et al. Image Reconstruction from Photoacoustic Projections. Photonics Insights 2024, 3, R06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C. Comprehensive Framework of GPU-Accelerated Image Reconstruction for Photoacoustic Computed Tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, 066006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, K., Jr. Propagation of Elastic Waves in Layered Media by Finite Difference Methods. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Treeby, B.E.; Zhang, E.Z.; Cox, B.T. Photoacoustic Tomography in Absorbing Acoustic Media Using Time Reversal. Inverse Probl. 2010, 26, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Romero, M.; Medina-Cázares, O.; García-Rodríguez, F.J.; González-Vega, A.; Martínez-Ponce, G.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, G. Accurate Internal Cavities and Kissing Bond Sizing in Metal Plates by Using the Time-of-Flight of Laser-Induced Ultrasound Waves. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 3641–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E.; Eddins, S.L. Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.T.; Phan, T.T.V.; Bui, N.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Oh, J. A Portable Device with Low-Power Consumption for Monitoring Mouse Vital Signs during In Vivo Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, B.; Kim, L.; Bulthuis, R.F.; Lucka, F.; Manohar, S. Automated Three-Dimensional Image Registration for Longitudinal Photoacoustic Imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, S11515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, E.; Farnia, P.; Lavasani, S.N.; Basij, M.; Yan, Y.; Ghadiri, H.; Ahmadian, A.; Mehrmohammadi, M. Photoacoustic Image Improvement Based on a Combination of Sparse Coding and Filtering. J. Biomed. Opt. 2020, 25, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colín-García, M.P.; Ruiz-Veloz, M.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, G.; Montoya-Ayala, G.; Ramírez-Chavarría, R.G.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Pérez-Pacheco, A. Photoacoustic Tomography in Forward-Detection Mode for Monitoring Structural Changes in an Extracted Wisdom Tooth. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansari, A.; Ranjbaran, S.M.; Zafar, M.; Beirami, M.J.; Avanaki, K. Evaluation of algorithms to decompose signals in MS PAM. Proc. SPIE 2025, 13319, 1331920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).