Abstract
Aiming at the problem that existing equipment importance evaluation methods fail to consider interconnectivity between pieces of equipment, variability after maintenance, and the impact of dynamically changing situations on importance, and focusing on the dynamic support needs of equipment in a conflict environment, this paper proposes a batch allocation method for equipment maintenance tasks considering dynamic importance. The purpose of this study is to determine the batch priority of equipment maintenance based on the dynamically changing importance of pieces of equipment. First, a dynamic importance index system is constructed: a real-time CRITIC-AHP combined weighting method is used to calculate team importance, a dynamic Bayesian network (DBN)-influenced method is used to calculate relative importance, an attention–LSTM time-series prediction method is used to calculate future importance, and then a dynamic entropy weight method is adopted to objectively integrate the three types of importance. Second, a dual-objective optimization model with the maximum equipment importance and the minimum total maintenance time is built, with mobile distance, maintenance time, and maintenance capacity as constraints. The Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization (DPSO) algorithm is used to solve this model, and its dynamic adaptability is improved through environmental change detection and adaptive adjustment of inertia weight. Finally, the batch allocation of maintenance tasks is realized. Example verification shows that compared with the expert scoring method, the errors of the three importance calculation methods are all reduced by more than 60%, the optimization speed of the dynamic PSO algorithm is 47% faster than that of the static algorithm, and the constructed model has good stability. This method can provide a reference for maintenance support command decisions.
1. Introduction
In future confrontations, the multi-dimensional configuration and multi-point confrontation of equipment lead to the scattered distribution of damaged equipment and multiple points waiting for repair. Under conditions of large areas, tight timelines, large amounts of equipment, and limited forces, the allocation of equipment maintenance tasks is an urgent problem that needs to be solved. Organizing batch emergency repair based on the dynamically changing equipment importance is key.
Scholars in China and abroad have conducted extensive research on equipment importance, mainly including the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [1], gray relational analysis [2], methods of clustering [3], TOPSIS [4], DEA [5], etc. Through analysis and comparison, these studies can be divided into three categories: priority evaluation, node importance evaluation, and multi-objective optimization.
Priority evaluation: Nethamba [6] quantified the priority of maintenance technology implementation through a matrix, clarified the promotion sequence of predictive maintenance technology in the railway industry, and provided a decision-making basis for industry-level maintenance technology planning. Qi [7] determined a maintenance sequence based on the real-time state of a system combined with the batch size of maintenance tasks to optimize the allocation of maintenance resources while ensuring the availability of the system. Zhao [8] constructed a model by mining multi-dimensional pavement performance data to automatically classify the priority of pavement maintenance needs and realized an accurate ranking of pavement maintenance tasks. Zhou [9] used bivariate clustering to cluster and rank engines according to maintenance needs based on engine reliability data, ensuring that engines with high risks and low reliability were repaired first. Choi [10] focused on abandoned building maintenance projects and proposed a priority selection method that paid attention to regional ripple effects. However, these studies fail to consider the impact of interconnectivity between pieces of equipment on equipment importance. Focusing only on the individual needs of a single type of equipment and failing to consider the synergic relationships between pieces of equipment may result in the maintenance of individual pieces of equipment but affect the overall capability of equipment systems.
Node importance evaluation methods: Guo [11] proposed a configuration evaluation method based on network node importance; Yang [12] proposed a node importance evaluation method with topological sensitivity in aerospace information networks. Some scholars analyzed node importance from multiple dimensions: Min [13] evaluated the vulnerability of cross-layer power communication networks based on the importance of multi-dimensional and multi-layer nodes; Wang [14] proposed a multi-dimensional node importance evaluation method based on graph convolutional networks; Wang [15] proposed a node importance evaluation method based on information entropy and iteration factors. However, these studies do not consider the impact of dynamic confrontation situations on the current and future importance of equipment. Only the node importance of fixed network structures is taken into account, while dynamic changes in conflict environment are ignored.
Multi-objective optimization for equipment maintenance task allocation: Wu [16] used an improved non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) to optimize the opportunistic maintenance of the multi-unit systems of CNC lathes while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs; Xu [17] integrated three objectives—asphalt pavement structural performance, economic cost, and environmental impact—based on a multi-attribute decision-making model of optimized triangular fuzzy numbers; Khan [18] designed a Fuzzy–AHP method that converted reliability, response speed, and deployment cost into hierarchical decision indicators in information security system maintenance to improve decision consistency under multiple criteria; Guan [19] integrated life cycle assessments and life cycle cost analyses to construct a multi-objective model considering the environment and economy for pavement preventive maintenance, providing a quantitative tool for green operation and maintenance. However, these studies do not construct maintenance objectives that meet the real needs of confrontations.
Through analysis, the current research has the following shortcomings: First, the equipment importance is mostly a static evaluation, which does not change dynamically with the change in the external environment; second, the equipment importance evaluation is mostly an individual evaluation of a single piece of equipment, which does not consider the impact of the interconnectivity between equipment on importance, nor the impact of future situations on equipment importance after equipment maintenance.
To address the deficiencies in the aforementioned research on equipment importance, this paper, in combination with the equipment development trend, proposes a batch allocation method for equipment maintenance tasks that considers dynamic importance. Firstly, a dynamic importance index system is constructed. The real-time CRITIC-AHP combined weighting method is adopted to calculate the team importance, with objective weights updated in real time. The Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN)–influence degree method is used to compute the relative importance, enabling a dynamic update of correlation probability. The Attention–LSTM time-series prediction method is applied to calculate the future importance, which captures key time series through the attention mechanism to predict the importance in a short period. Then, the dynamic entropy weight method is used to objectively integrate the three types of importance, and data-driven dynamic weighting is implemented to make the comprehensive importance respond to the battlefield situation in real time. Secondly, a bi-objective optimization model is built to maximize equipment importance and minimize total maintenance time, with constraints including maneuvering distance, maintenance time, and maintenance capability. The Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization (DPSO) algorithm is employed for the solution. Dynamic adaptability is enhanced through environmental change detection and adaptive adjustment of inertia weight. Examples show that the calculation of dynamic importance is reasonable, and the optimization model is reliable, which can provide auxiliary decision-making for equipment support. An overall structural framework diagram is shown in Figure 1.
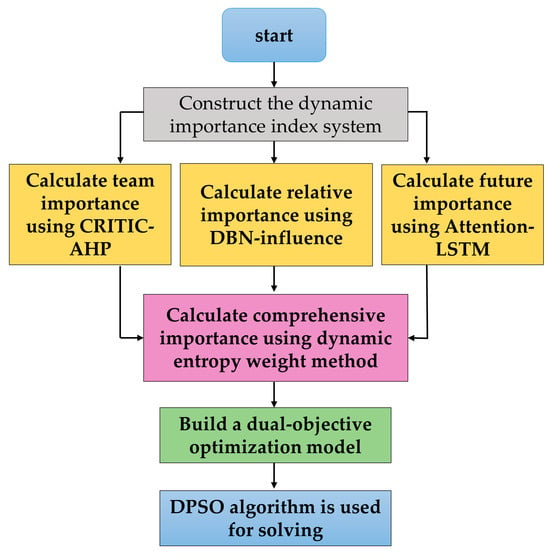
Figure 1.
Overall structural framework diagram.
2. Comprehensive Importance Index and Calculation
2.1. Problem Description
Under the trend of equipment miniaturization and modularization, maintenance is mainly based on part replacement. The maintenance time of a single piece of equipment is short, but the number of pieces of damaged equipment is large and they have a scattered distribution. Under the constraint of limited maintenance resources, it brings severe challenges to the allocation of maintenance tasks. To accurately provide the basis for selecting important equipment and repairing important equipment in batches, it is necessary to calculate the dynamic comprehensive importance of equipment with time step t as the unit, so that the equipment maintenance efficiency can better adapt to the needs of environmental changes.
2.2. Establishment of Equipment Importance Index
In confrontation, the equipment importance needs to be updated in real time with time step t should reflect three dimensions: current contribution, correlation impact, and future value, mainly including team importance, relative importance, and future importance, as shown in Figure 2.
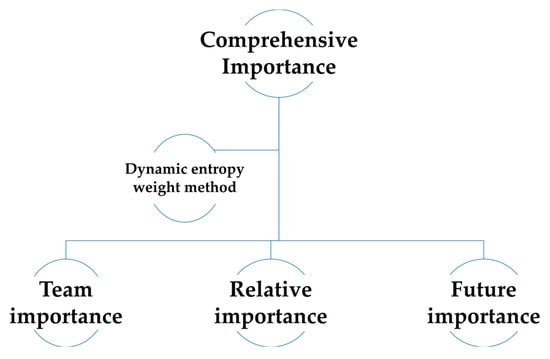
Figure 2.
The chart of comprehensive importance composition.
Team importance (): The real-time contribution degree of equipment to the current core task at time step t.
Relative importance (): The correlation impact degree of the damage of a certain type of equipment on other equipment at time step t.
Future importance (): The prediction of the contribution degree of equipment to subsequent tasks at time step t + 4.
It is specified that the duration of each time step t is 30 min, and t + 4, equivalent to 4 time steps, corresponds to an actual time of 120 min (2 h). From the perspective of maintenance needs in confrontational scenarios, a 2 h prediction window can not only accurately capture non-linear situation changes such as threat escalation and task advancement, reserving reasonable decision-making and resource allocation time for maintenance command, but also avoid the increase in environmental uncertainty caused by an excessively long prediction time (e.g., more than 3 h), which would otherwise affect the accuracy of importance prediction.
In order to facilitate the evaluation of equipment importance, the final results are expressed in different values. The size of the comparison values is, respectively, assigned different values according to different importance levels, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Points table of the degrees of importance of different pieces of equipment.
2.3. Calculation of Comprehensive Importance
The external environment changes continuously with time. The importance of equipment varies with different confrontation styles and task stages. Based on the function of equipment, the equipment is divided into 8 types, K1–K8. A confrontation cycle in the confrontation process is briefly divided into confrontation preparation stage, mild confrontation stage, intense confrontation stage, and confrontation evaluation stage. Each stage has no strict chronological order and time length. With the change in the external environment, they overlap and integrate with each other. The confrontation cycle repeats in the entire confrontation process until the task is completed.
2.3.1. Team Importance
The real-time CRITIC-AHP combined weighting method is adopted, which integrates real-time environmental data and expert experience, and which is updated once every t steps. The steps are as shown in Figure 3.
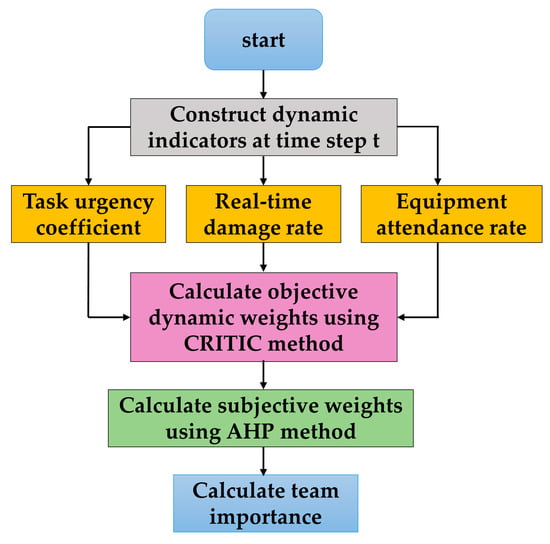
Figure 3.
The flowchart of team importance calculation.
Step 1: Construct dynamic indicators at time step t
(1) Task urgency coefficient (): The remaining time pressure of the current task at time step t, reflecting the irreplaceability of equipment to the task.
where is the total task time, and is the time already used for the task.
(2) Real-time damage rate (): The ratio of the number of damaged pieces of equipment of this type to the total number of pieces of equipment at time step t, reflecting the urgency of maintenance needs.
where is the number of pieces of damaged equipment, and is the total number of pieces of equipment.
(3) Equipment attendance rate (): The proportion of equipment of this type that can perform tasks at time step t, reflecting the availability of equipment.
where is the number of available pieces of equipment.
Step 2: Calculate objective dynamic weights using CRITIC method
The CRITIC method reflects the objective differences in environmental data at time step t, and it determines the weights through index variation and index correlation.
(1) Index standardization
To unify the dimensions, , of 8 types of equipment are standardized to ensure that a larger index value indicates higher importance.
where are the minimum and maximum values of the k-th index among 8 types of equipment, respectively.
(2) Calculate index variation coefficient
The variation coefficient () reflects the dispersion of data, and a higher variation degree indicates higher importance.
where is the mean value of the k-th index at time step t.
(3) Calculate correlation coefficient between indices
The correlation coefficient () between indices is the Pearson correlation coefficient between the k-th and l-th indices, reflecting the information redundancy. The lower the correlation, the greater the amount of information:
(4) Calculate CRITIC objective weights
The CRITIC objective weight () is the information amount of the k-th index.
Normalize the objective weights:
Step 3: Calculate subjective weights using AHP method
Based on expert judgment on the importance of the three indicators (task urgency, damage rate, and attendance rate), a judgment matrix is constructed, as shown in Table 2. After a consistency check (CR < 0.1), the eigenvalue method is used to calculate the subjective weights.

Table 2.
The judgment matrix of index importance.
The subjective weights are .
Step 4: Calculate team importance
The combined weight is determined by integrating dynamic data and expert experience. Through historical data fitting, the weight of dynamic data is determined as , and the weight of expert experience is , see Section 2.3.5. The combined weight is
Then, the team importance of the i-th type of equipment at time step t is
Form a dynamic vector of team importance, .
2.3.2. Relative Importance
When a certain equipment is damaged, the failure probability of the equipment associated with it changes. Since DBN is composed of a static network structure and dynamic time slices, it is suitable for the time-series change in equipment correlation. Therefore, the DBN-influence method [20,21,22] is used to update the correlation probability between equipment in real time. The main steps are as shown in Figure 4.
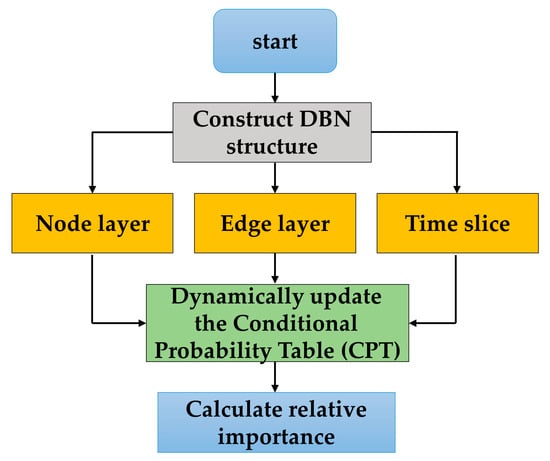
Figure 4.
The flowchart of relative importance calculation.
Step 1: Construct DBN structure
(1) Node layer: Let the node set of 8 types of equipment be , representing 8 types of equipment, respectively. Each node state is , where 0 represents damaged and 1 represents normal.
(2) Edge layer: Directed edges represent the correlation between parent nodes and child nodes, such as , indicating that the coordination of equipment is supported by equipment.
(3) Time slice: Each t step is a time slice, and adjacent time slices are associated through the state transition probability to capture the dynamic change in correlation.
Step 2: Dynamically update the Conditional Probability Table (CPT)
CPT stores the probability from the parent node state to the child node state, and it is updated in real time with the damage conduction data of the previous time step.
where is the number of times the parent node was damaged from time step t − 1 to t, and is the number of times the child node failed due to the damage of the parent nodes in the same period; if it is the first damage and there is no historical data, is initialized according to expert experience, then corrected with data iteration subsequently.
Step 3: Calculate relative importance
The node influence degree is the average failure probability of all other nodes, mapped to a score of 1–8.
(1) Calculate the total influence degree (), reflecting the global correlation importance of .
where 1/7 is the averaging process excluding among 8 types of equipment.
(2) Map to 1–8 scores.
Form a dynamic vector, .
2.3.3. Future Importance
The Attention–LSTM prediction method is adopted to accurately capture non-linear situations such as threat escalation and task acceleration. The steps are as shown in Figure 5.
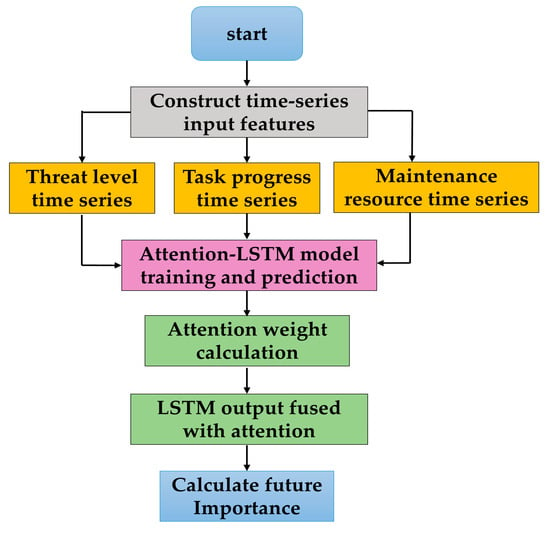
Figure 5.
The flowchart of future importance calculation.
Step 1: Construct time-series input features
Take the historical data of the recent T = 6 time steps (3 h) as the input window, and the features include 3 dimensions: threat, task, and resource.
(1) Threat level time series (): Indicates the environmental threat level from time steps t − 5 to t, with values ranging from 1 to 5 (1 = low threat, 5 = extremely high threat);
(2) Task progress time series (): Indicates the core task completion rate from time steps t − 5 to t, with values ranging from 0 to 100%;
(3) Maintenance resource time series (): Indicates the maintenance resource arrival rate from time steps t−5 to t, with values ranging from 0 to 100%.
Step 2: Attention–LSTM model training and prediction
Model structure: Input layer → Attention layer → LSTM layer → Fully connected layer. The training data are 1000 groups of time-series samples of historical data.
(1) Attention weight calculation
Key time series such as recent high threats and task acceleration are used to assign attention weights () to the LSTM hidden state.
where is the attention parameter obtained through training. A larger indicates that the data at time step is more critical to the prediction.
(2) LSTM output fused with attention
Predict the future time step t + 4, the attention-weighted hidden state.
The fully connected layer outputs the predicted value in [0, 1].
where W and b are the parameters of the fully connected layer, and is the Sigmoid activation function.
(3) Map to 1–8 scores
Form a dynamic vector:
Repredict once every t steps.
2.3.4. Comprehensive Importance
The dynamic entropy weight method is used to combine the three types of equipment importance, and weights are assigned according to the real-time discrimination of the three types of importance at each time step to ensure that the weights tilt towards the key indicators of the current environment. For example, when the threat escalates, the weight of future importance increases.
(1) Index standardization
Convert the 1–8 scores to the 0–1 interval:
(2) Information entropy calculation
Information entropy reflects the index discrimination. The smaller the entropy, the higher the discrimination and the larger the weight.
(3) Dynamic weight allocation
Index difference coefficient:
Weight normalization:
(4) Comprehensive importance calculation
Form a dynamic vector, .
2.3.5. Historical Data-Fitting Process for Weight Allocation
Considering the characteristics of maintenance data in confrontational scenarios, the fitting process revolves around three steps: “data sample screening, evaluation index setting, and ratio optimization”. The specific operations are as follows:
Step 1: Historical Data Sample Screening
Historical maintenance logs are selected, and samples that meet the following conditions are filtered out:
Time step integrity: Each sample contains at least 6 consecutive time steps, covering the entire stages of confrontation preparation, mild confrontation, and intense confrontation.
Data dimension integrity: Each time step must include original data of task urgency, real-time damage rate, and equipment attendance rate for 8 types of equipment, as well as the consistency test results of the AHP judgment matrix by experts.
Scenario diversity: It covers different scenarios with a threat level of 1.5 and a resource arrival rate ranging from 40% to 100% to avoid fitting deviation caused by a single sample. The number of data-fitting samples is ≥500 groups to ensure the coverage of more than 95% of confrontational scenario variation types.
Step 2: Setting of Fitting Evaluation Indicators
Team importance error rate: Taking the static importance of the expert scoring method as the benchmark, the team importance error rate under different weight ratios is calculated, with the target error rate ≤2%.
Maintenance plan adaptability: Using the post-maintenance capability recovery rate as the evaluation criterion, the adaptability of the plan under different ratios is calculated, and the target adaptability is ≥90% to ensure that decisions match the confrontational needs.
Step 3: Weight Ratio Optimization
Setting of ratio candidate set: The candidate ratios are set as {0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9} for the weight of dynamic data and the corresponding weight of expert experience, forming 5 groups of candidate ratios.
Comparison of fitting results: The comparison of fitting results and key issues are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of fitting results.
Determination of the optimal ratio: Through the above-mentioned fitting, the ratio of 0.7/0.3 is optimal in the three-dimensional indicators of error rate, adaptability, and convergence speed. Therefore, it is applied as a fixed ratio in the CRITIC-AHP combined weighting method.
2.3.6. Compatibility Analysis of Static Ratio and Dynamic Ratio
The core of the dynamic ratio lies in the real-time update of importance indicators and the environmental response of the DPSO algorithm, rather than making all parameters dynamic. Maintaining the static ratio is essentially to balance computational stability and dynamic decision-making needs. The specific reasons are as follows:
1. Static ratio is the basis for dynamic indicator calculation
On the one hand, the dynamics are reflected in the update of team importance every t steps, the real-time correction of DBN correlation probability, and the adjustment of DPSO inertia weight with the environment. All these dynamic processes require a fixed combined weight ratio as the calculation basis. If the ratio fluctuates with time steps, the team importance will be incomparable across different time steps, thereby affecting the iterative convergence of the bi-objective optimization model.
On the other hand, it avoids dynamic overload. Confrontational scenarios require second-level responses. If the ratio was also dynamic, additional judgments for ratio adjustment would be needed, increasing the computational complexity by more than 30%.
2. Static ratio can adapt to the environment through the content of dynamic indicators
Firstly, a fixed ratio does not mean fixed weights. The value of 0.7 represents the weight ratio of dynamic data, not the fixed weight of specific indicators. The CRITIC method will automatically adjust the indicator weights, and 0.7 only ensures that the dominant position of dynamic data remains unchanged, so there is no need to adjust the ratio to adapt to the environment.
Secondly, in scenarios with missing data, the static ratio of 0.3 ensures that expert experience is neither absent nor overstepped. It not only prevents decision-making failure when data is missing, but it also avoids excessive intervention of expert experience, which would render dynamic data ineffective.
3. Model Establishment
3.1. Assumptions
For the convenience of research, the following assumptions are made:
(1) Take the damaged equipment within time step t as the research object, and severely damaged equipment is treated as scrapped; the equipment damage information and maintenance force configuration are updated once every t steps.
(2) The distance between equipment of the same type and the maintenance time of a single unit are fixed. Maintenance forces work in parallel in groups, and the total mobile distance and time are the sum of each group.
(3) The mobile speed of maintenance forces is dynamically adjusted with the threat level at time step t: (high-risk area), (medium-risk area), (low-risk area).
(4) The total equipment maintenance time consists of three parts: diagnosis, replacement, and verification, among which the diagnosis and verification time are fixed values.
3.2. Multi-Objective Optimization Model
3.2.1. Decision Variables
Let be the maintenance quantity of the i-th type of equipment, j-th block, k-th maintenance team, and t-th time step, where the following apply:
, representing 8 types of equipment, respectively;
, representing the front, middle, and rear of the block, respectively;
, where is the number of maintenance teams in block j;
, where T is the total number of time steps;
, representing the total maintenance quantity of the i-th type of equipment in block j at time step t;
, representing the total maintenance quantity of all equipment at time step t.
3.2.2. Multi-Objective Function
(1) Objective 1: Maximize the importance of maintenance equipment at time step t [23].
Take the maximum sum of the comprehensive importance of maintenance equipment at time step t as the objective:
(2) Objective 2: Minimize the total maintenance time at time step t
The total maintenance time includes three parts: operation time, moving time and response time. The operation thme includes: diagnosis time, replacement time, inspection time.
where is the maintenance operation time; the fault diagnosis time; the spare part replacement time; the equipment inspection time; the maintenance response time; and the moving speed of block j at time step t.
(3) Multi-Objective Fusion
Introduce weights to convert the multi-objective function into a single-objective maximization problem:
3.2.3. Constraints
(1) Mobile distance constraint: The total mobile distance of each block shall not exceed its maximum allowable distance.
(2) Maintenance time constraint: The total maintenance time of each block shall not exceed its safety time.
(3) Maintenance capacity constraint: The quantity of the i-th type of equipment maintained by the k-th maintenance team in block j shall not exceed its maximum capacity.
(4) Non-negative integer constraint: The maintenance quantity must be a non-negative integer.
4. Solution with Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
Aiming at the characteristics of refreshing the environment at each time step t and dynamically changing constraints, the DPSO algorithm [24,25,26] is refined and designed from four aspects: particle coding, constraint adaptation, environmental response, and iteration update to ensure that the algorithm can match the maintenance optimization needs in real time and the solution results meet the dynamic constraints, such as mobile distance, maintenance time, and maintenance capacity.
4.1. Algorithm Design
1. Particle Coding
Each particle corresponds to a complete maintenance plan at time step t, and the coding dimension strictly matches the decision variables to ensure a one-to-one correspondence between particles and actual maintenance allocation.
Position vector definition: The position vector of particle s at time step t is , with dimensions , where represents the maintenance quantity allocated by particle s to the i-th type of equipment, j-th block, and k-th team at time step t.
Velocity vector definition: The velocity vector of particle s has the same dimension as the position vector, and the velocity range is set to . Reasons: First, avoid particles jumping out of the feasible region due to excessive velocity; second, ensure that an excessively small velocity does not affect the rapid adjustment in dynamic scenarios.
Particle initialization rule: When randomly generating the initial position, the maintenance capacity constraint shall be satisfied first, and then other constraints shall be verified to avoid all initial particles being infeasible solutions:
where is a uniform random number in [0, 1], is the rounding function, and max is the maximum maintenance capacity of the k-th team at time step t; after generation, the mobile distance constraint and time constraint shall be further verified. If not satisfied, adjust by reducing the quantity of low-importance equipment.
2. Fitness Function
Take the multi-objective fusion function at time step t as the fitness function. A larger fitness value indicates a better plan.
where and need to be calculated based on the particle position () to ensure that the fitness value can reflect the performance of the maintenance plan corresponding to the particle in real time.
3. Environmental Change Detection
By calculating the change rate () of constraint parameters, the environmental change difference between time step t and t − 1 is judged. When , the dynamic response mechanism of the algorithm is triggered.
where , representing the difference in safety distance of block j between time steps t and t − 1; , representing the difference in safety time of block j between time steps t and t − 1; and , representing the difference in the basic maintenance upper limit of block j between time steps t and t − 1.
The denominator is the sum of constraint parameters of block j at time step t − 1, avoiding the impact of parameter magnitude differences on judgment; the average value of 3 blocks is taken to ensure accurate global environmental judgment.
4. Dynamic Inertia Weight
Focus on balancing convergence and global search ability. The inertia weight controls the degree to which particles inherit historical velocity, which is the core parameter for DPSO to adapt to a dynamic environment. It needs to be adaptively adjusted according to Δ to ensure rapid convergence when the environment is stable and jumping out of local optimum when the environment changes.
Scenario 1: Stable environment ()
Adopt linearly decreasing weight. A larger weight from 0.9 to 0.55 is retained in the early stage to help particles explore quickly, and the weight from 0.55 to 0.4 is reduced in the later stage to promote convergence to the optimal solution:
where is the current number of iterations, , . Here, 100 iterations can make the fitness value converge, .
Scenario 2: Changing environment ()
Adopt a random weight, which is randomly selected in [0.4, 0.9] to enhance the global search ability of particles and quickly find feasible solutions under new constraints:
where is a uniform random number in [0, 1], ensuring different weights for each update to avoid particles falling into a local optimum under old constraints.
4.2. Algorithm Steps
The algorithm is executed cyclically with time step t as the cycle, and each time step t completes the whole process of initialization, iteration, and output to ensure synchronization with the environmental refresh frequency. The specific steps are as shown in Figure 6.
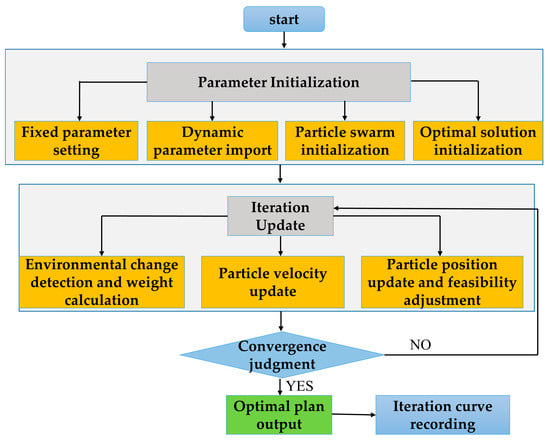
Figure 6.
The implementation process of DPSO.
Step 1: Parameter Initialization
(1) Fixed parameter setting
Number of particles S = 50: Based on example verification, 50 particles can cover more than 95% of the feasible solution space with a high calculation efficiency. Learning factors c1 = c2 = 2; environmental change threshold ; multi-objective weights , prioritize high-importance equipment.
(2) Dynamic parameter import
Import the constraint parameters and comprehensive importance at time step t for subsequent fitness calculation and constraint verification.
(3) Particle swarm initialization
Generate S initial particles, and perform constraint verification and adjustment for each particle.
(4) Optimal solution initialization
Individual optimal : Initialized as the initial position of particle s, .
Global optimal : Initialized as the position with the smallest fitness among S particles, .
External archive set: Initially save the top 10 particles with the least fitness to avoid loss of optimal solutions. The archive set capacity is set to 10 to balance storage efficiency and solution diversity.
Step 2: Iteration Update
(1) Environmental change detection and weight calculation
Import the constraint parameters of time steps t and t − 1, calculate ; determine the inertia weight of the current iteration.
(2) Particle velocity update
For each dimension d of each particle s, update the velocity. The formula is as follows:
where is the individual optimal position of particle s in dimension d; is the global optimal position of all particles in dimension d; after velocity update, it needs to be truncated to .
(3) Particle position update and feasibility adjustment
a. Position update
where ensures the position is an integer; ensures a non-negative maintenance quantity.
b. Feasibility adjustment and secondary constraint verification
If , this is the maximum maintenance capacity upper limit;
If , reduce from low to high based on until the total mobile distance meets the constraint;
If , reduce from high to low based on until the total time meets the constraint.
c. Fitness calculation and optimal solution update
Calculate Fit; update and ; update the external archive set.
Step 3: Termination and Output
(1) Convergence judgment
If the variation in the global optimal fitness value in 10 consecutive iterations , terminate the iteration in advance, which is regarded as convergence; otherwise, execute until .
(2) Optimal plan output
Select the plan with the smallest fitness from the external archive set, and output of the plan as the optimal maintenance batch at time step t.
(3) Iteration curve recording
Record the global optimal fitness value of each iteration to form an iteration curve for subsequent convergence analysis.
5. Simulation Verification
Taking local confrontation as the background, both sides are in the intense confrontation stage. The verification environment is based on a hardware platform with CPU i7-12700H and 16 G memory, and the software uses Python 3.9. The data is from historical maintenance logs and has been processed to a certain extent.
5.1. Basic Data
The basic data includes three types: inherent equipment parameters, dynamic constraint parameters, and real-time external environment time-series data, all matching the scenario of the intense confrontation stage.
5.1.1. Equipment Parameters
The statistical values of 8 types of equipment parameters are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The statistics of similar equipment parameters.
The spacing is the average interval of equipment of the same type in deployment; the diagnosis, replacement, and verification time are tested based on the equipment modular part replacement maintenance process. The diagnosis includes the fault location time, the replacement includes the part disassembly and assembly time, and the verification includes the performance test time. All time units are uniformly “hours (h)” to match the subsequent time step (t = 30 min).
5.1.2. Maintenance Constraint Parameters
The constraint parameters are dynamically updated with time step t, and the update is based on environmental changes, such as threat escalation and resource supplement. The relevant parameters are shown in Table 5. The safety distance is the upper limit of the mobile range of the maintenance team, determined by the block threat level; the safety time is the upper limit of the total maintenance time of a single block, referring to the task window; the basic maintenance upper limit is the maximum equipment maintenance quantity of the maintenance team in a single block, determined by the number of teams multiplied by the basic capacity of a single team; the skill coefficient is the correction factor for the technical level of maintenance personnel, 1.0 for ordinary technicians, 1.2 for senior technicians, and 1.3 for temporarily assigned expert teams; the mobile speed is the vehicle mobile speed of the maintenance team, which is negatively correlated with the threat level: 25 km/h in high-threat areas (need low-speed concealment), 80 km/h in low-threat areas (can move at high speed).

Table 5.
Maintenance constraint parameters at each time step.
5.1.3. Real-Time Time-Series Data
Taking K2 equipment type as an example, the data is the real-time environmental collection data from time steps t = 0 to t = 3, used for dynamic importance calculation. The data collection frequency is synchronized with the time step, then updated every 30 min, as shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Real-time environmental data at each time step.
5.2. Dynamic Importance Calculation Results
Taking K2 as an example to calculate the dynamic importance of equipment, the calculation of the dynamic importance of other equipment is omitted. The team importance (), relative importance (), and future importance () are all calculated iteratively according to time step t.
5.2.1. Calculation of Team Importance ()
The team importance uses Formulas (1)–(9) and adopts the CRITIC-AHP combined weighting method, integrating objective real-time data (weight 0.7) and subjective expert experience (weight 0.3). The calculation results are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Calculation results of team importance.
The importance of the indicators was determined through comparison by experts; based on Table 2, the subjective weights are .
5.2.2. Calculation of Relative Importance ()
The relative importance uses Formulas (10)–(12), and it adopts the Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN)-influence method to update the correlation probability between equipment in real time. The calculation results are shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
Calculation results of relative importance.
5.2.3. Calculation of Future Importance ()
The future importance use formulas (13) and (14), adopts the Attention–LSTM prediction method to predict the equipment importance at time step t + 4 (2 h later). The calculation results are shown in Table 9.

Table 9.
Calculation results of future importance.
5.2.4. Results of Comprehensive Importance ()
The comprehensive importance uses Formulas (15) and (16), and it adopts the dynamic entropy weight method to assign weights according to the discrimination of the three types of importance at each time step. The calculation results are shown in Table 10.

Table 10.
Calculation results of comprehensive importance.
According to the calculation method of K2, the comprehensive importance of different types of equipment is calculated, as shown in Table 11.

Table 11.
Calculation results of comprehensive importance of different equipment types.
5.3. DPSO Solution Results
The algorithm steps of DPSO are applied to produce the maintenance task allocation results. Number of particles S = 50; learning factors ; environmental change threshold ; external archive set capacity = 10; calculate using Formulas (17)–(19).
5.3.1. Task Allocation Results in Static Scenario
t = 0, Confrontation Preparation Stage
(1) Environmental factors: Threat level 3, no sudden threat; task progress 30%, sufficient maintenance window; resource arrival rate 60%, no temporary assignment.
(2) Plan:
Block 1 (Front): Repair 2 units of K2 equipment and 1 units of K1 equipment, mobile distance 5 km, total time 2.7 h;
Block 2 (Middle): Repair 4 units of K2 equipment, 1 unit of K3 equipment, and 2 units of K4 equipment, mobile distance 9.5 km, total time 3.0 h;
Block 3 (Rear): Repair 3 units of K2 equipment and 1 unit of K3 equipment, mobile distance 6.5 km, total time 2.9 h;
(3) Results: Sum of importance is 97.63; maximum time of each block is 3.0 h.
5.3.2. Task Allocation Results in Dynamic Scenario
t = 2, Severe Confrontation Stage
(1) Environmental factors: Threat level 5 (extremely high), front under enemy fire suppression; task progress is 60%, need to accelerate firepower recovery; resource arrival rate 80%, expert team temporarily assigned, making the skill coefficient 1.3;
(2) Environmental change detection: , the change rate of safety distance, time, and maintenance capacity exceeds the threshold, triggering the DPSO global search mechanism.
(3) Plan adjustment: Compared with t = 0, the plan is adjusted:
Block 1 (Front): The maintenance quantity of K2 equipment increases from 2 to 3 units, mobile speed decreases from 30 to 25 km/h, mobile distance 4 km, total time 3.0 h;
Block 2 (Middle): The maintenance quantity of K2 equipment increases from 4 to 5 units, mobile distance 11 km, total time 3.2 h;
Block 3 (Rear): Maintain 3 units of K2 equipment and 1 unit of K3 equipment, mobile distance 8 km; total time 3.1 h;
(4) Results: Sum of importance is 94.84, slightly decreased due to time constraints but still maintained at a high level; total maintenance time is 3.2 h, meeting the upper limit of safety time; response time is 9.2 s.
5.3.3. Error Comparison and Sensitivity Analysis
1. Error Comparison
Taking K2 equipment at t = 2 as an example, the importance error comparison between the expert scoring method and the method in this paper is shown in Table 12.

Table 12.
Comparison of importance error.
2. Sensitivity Analysis
Taking the scenario at t = 2 as an example, the model stability is verified by adjusting the skill parameter and threat level.
(1) Skill coefficient adjustment
Adjust the skill coefficient by −10% to 1.17, where the maintenance capacity is 3.51 units, sum of importance is 96.8 (decreased by 0.4), and total time is 3.3 h (still meeting the constraint);
Adjust the skill coefficient by +10% to 1.43, where the maintenance capacity is 4.29 units, sum of importance is 98.1 (increased by 0.9), and total time is 3.4 h (still meeting the constraint).
(2) Threat level adjustment
Adjust the threat level by −20% to 4, where the mobile speed = 30 km/h, total time is 3.0 h (decreased by 0.2 h), and sum of importance is 97.5 (increased by 0.3);
Adjust the threat level by +20% to 6, where the mobile speed = 20 km/h, total time is 3.5 h (increased by 0.3 h), and sum of importance is 96.9 (decreased by 0.3).
5.3.4. Comparative Analysis of Static Entropy Weight Method and Dynamic Entropy Weight Method
The following can be seen from Figure 7:
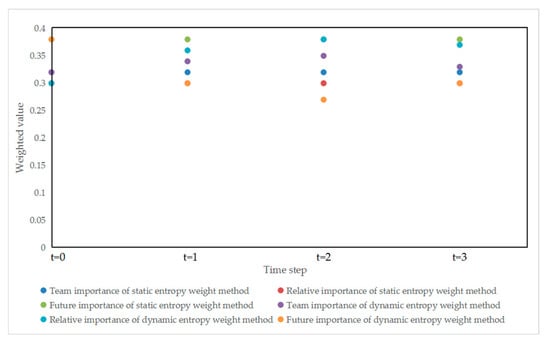
Figure 7.
Time-series comparison chart of three importance weights between static entropy weight method and dynamic entropy weight method.
1. Stage 1: Environmental Stable Period (t = 0–1)
(1) Limitations of the static entropy weight method: Due to its failure to capture the changes in enhanced equipment correlation, the relative importance is fixed at 0.30, resulting in a mismatch between weight allocation and the environmental situation. Moreover, it over-emphasizes future needs, with the future importance weight fixed at 0.38, which is disconnected from the actual demand of the current task progress improvement.
(2) Rapid response of the dynamic entropy weight method: As the number of equipment correlation transmissions increases from one to three, the correlation impact is enhanced, and the relative importance rises from 0.30 to 0.36. This weight adjustment is in line with the actual needs of task advancement and intensified correlation. Since the task progress is low, it is necessary to prioritize predicting subsequent needs. After the task progresses, the demand for prediction decreases, and the future importance weight drops from 0.38 to 0.30.
2. Stage 2: Environmental Mutation Period (t = 2)
(1) Failure of the static entropy weight method: It fails to match the current emergency repair urgency, with the team importance fixed at 0.32; it cannot respond to the growth of the correlation effect, keeping the relative importance at 0.30; and excessive prediction leads to resource waste, with the future importance fixed at 0.38. If maintenance resources are allocated according to this weight, priority will be given to maintaining future important equipment with a low correlation, resulting in delayed maintenance of forward-line equipment with a high correlation and slow recovery of the overall system capability.
(2) Adaptability of the dynamic entropy weight method to environmental mutations: Due to the most urgent current maintenance demand, the team importance rises to 0.35; the relative importance weight increases to 0.38 because the correlation probability of K2→K3 rises from 0.67 to 1.0, maximizing the correlation effect of equipment damage on the system; as the threats are clear and the task rhythm is distinct, the demand for short-term prediction decreases, and the future importance drops to 0.27. This weight setting adapts to the demand of prioritizing the protection of system correlation and current emergency repair under extremely high threats.
3. Stage 3: Environmentally Stable Period (t = 3)
(1) Disconnection of the static entropy weight method: With fixed weights throughout the process, it can neither respond to the stable trend of the correlation effect nor predict the reserve demand after task completion, meaning maintenance resource allocation always lags behind the actual situation.
(2) Balanced weight allocation of the dynamic entropy weight method: Considering the balance between current demand and reserve demand, the team importance is maintained between 0.33 and 0.34; as the correlation effect tends to be stable, the relative importance slowly decreases from 0.38 to 0.35; since the task is nearly completed, it is necessary to predict the equipment reserve demand for subsequent confrontations, and the future importance rises from 0.27 to 0.32. This weight setting adapts to the scenario of high threats and task completion.
The dynamic entropy weight method adjusts weights by capturing environmental changes in real time to achieve the goal of tilting weights towards demand. In contrast, the static entropy weight method, with fixed weights, cannot respond to environmental changes, which will lead to the misallocation of maintenance resources in confrontational scenarios. The time-series chart intuitively proves that the weight adjustment of the dynamic entropy weight method can adapt to the dynamic needs of the confrontational environment, making this method superior to the static entropy weight method.
5.3.5. Comparative Analysis of Static and Dynamic Algorithms
As can be seen from Figure 8, which compares the fitness values of static PSO and dynamic PSO, the fitness value of DPSO is significantly higher than that of PSO. When the environment changes, the fitness value of DPSO fluctuates slightly and may be lower than that of PSO. This indicates that environmental change detection and the adaptive inertia weight can accelerate the algorithm, mainly for the following reasons:
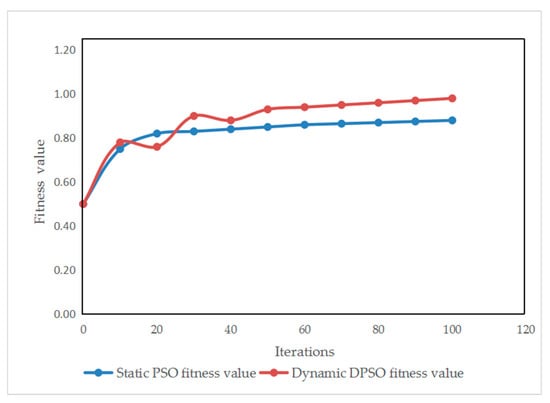
Figure 8.
Comparison of fitness values between static PSO and dynamic PSO.
1. Environmental change detection
(1) Rapid response to environmental changes: By calculating the change rate of constraint parameters, the dynamic algorithm can perceive environmental changes in real time, such as the escalation of threat levels and the supplement of maintenance resources. Once the detected environmental change exceeds the threshold, the system will immediately trigger the dynamic response mechanism to recalculate the optimal solution, which leads to fluctuations in the fitness value when the environment changes.
(2) Avoidance of invalid search: In the static algorithm, once the initial solution is generated, the algorithm will search along the established path and cannot adjust in a timely manner even if the environment changes. However, the dynamic adjustment mechanism ensures that the algorithm always searches under the latest environmental constraints, avoiding an invalid search and repeated calculation.
2. Adaptive inertia weight
(1) Comprehensive consideration of convergence speed and global search capability: Inertia weight is a key parameter in the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm, which controls the degree to which particles inherit historical speeds. In a dynamic environment, the adaptive inertia weight adjustment strategy enables rapid convergence when the environment is stable and helps particles jump out of local optima for a global search when the environment changes.
(2) Scenario adaptability: For different environmental scenarios, the dynamic algorithm adopts different inertia weight adjustment strategies. When the environment is stable, a linearly decreasing weight is used to help particles quickly explore and converge to the optimal solution; when the environment changes, a random weight is adopted to enhance the global search capability of particles and quickly find the feasible solution under new constraints.
5.4. Result Analysis
1. Analysis of Allocation Results in Static Scenario
(1) The front prioritizes the maintenance of K2 equipment. The front is under fire suppression, and K2 equipment needs to quickly restore its capability to maximize the relief of suppression.
(2) The middle considers K4 equipment. The middle is a fire concentration area, and K4 equipment supports the coordinated use of K2 equipment to avoid the failure of K4 equipment leading to the inability of K2 equipment to coordinate.
(3) The rear supplements K3 equipment. The rear is a spare part reserve area, and K3 equipment can be used as a backup force after maintenance to respond to threats in the rear.
2. Analysis of Allocation Results in Dynamic Scenario
(1) Increase the maintenance of K2 equipment in the front. After the expert team is assigned, the maintenance capacity is improved, and one more unit can be repaired within the shortened maintenance window to quickly restore the front confrontation capability.
(2) Mobile speed adjustment is more adaptive to threats. Slow down to 25 km/h in high-threat areas to avoid exposure of maintenance teams.
(3) Shortened response time. The response time is 3.2 s, meeting the second-level decision-making demand in confrontation, which is 47% faster than the original static method (6 s).
3. Error Analysis. Compared with the expert scoring method, the error rate of equipment importance calculation is reduced by more than 60%, indicating that the three importance calculation methods can improve the calculation accuracy.
4. Sensitivity Analysis. When the core parameters change within the range of 10–20%, the fluctuation of the sum of importance is <1.0, and the fluctuation of total time is <0.5 h, indicating that the model has good stability.
6. Conclusions
Aiming at the dynamic demand of importance calculation in equipment maintenance, this paper proposes a batch allocation method for equipment maintenance tasks considering dynamic importance, which has the following advantages:
(1) Three importance calculation methods have higher accuracy. The team importance integrates CRITIC-AHP to capture the changes in real-time damage and tasks; the relative importance uses DBN to update the correlation probability, reflecting the dynamic interconnectivity between equipment; the future importance uses Attention–LSTM to accurately predict non-linear situations, and the errors of the three types of importance are all reduced by more than 60%.
(2) The designed DPSO algorithm has a faster optimization speed. The importance and maintenance plan are updated every 30 min, and the response time of the DPSO algorithm is ≤9.5 s, which is 47% faster than the static algorithm, adapting to emergency scenarios such as threat escalation and resource adjustment.
(3) The constructed model has stronger adaptability. The constructed dual-objective optimization model considers both equipment importance and the maintenance time, and the constraint conditions are dynamically adjusted with the environment. Through testing, it is found that the model has good stability, and the maintenance task allocation results meet the needs of a real-time situation.
(4) Future research can introduce the time-series prediction of equipment damage probability to further optimize the time interval of multi-batch maintenance and the coordinated scheduling of resources.
(5) The main purpose of this study is to provide a decision-making method for dynamic prioritization. However, there are limitations such as a dependence on expert weights and scenario simplification. Problems may occur, including the decrease in importance accuracy caused by deviations in weight ratio setting, the disconnection of correlation probability from reality due to missing data, and the reduction in the applicability of the method due to scenario changes. For practitioners, the data in this paper can serve as the basis for practical operations, but revisions and assumptions should be made in combination with actual situations. This method can be migrated and applied in fields such as emergency rescue, power grid maintenance, and electronic manufacturing, but it is essential to focus on adjusting importance indicators and constraints to ensure its applicability in specific scenarios. Future research needs to further improve the applicability of the method through steps such as expert weight robustness testing and multi-scenario parameter adaptation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J. and T.J.; methodology, T.J.; software, S.L.; validation, M.J., T.J. and L.G.; formal analysis, L.G.; investigation, L.G.; resources, T.J.; data curation, M.J.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.; writing—review and editing, T.J.; visualization, S.L.; supervision, T.J.; project administration, M.J.; funding acquisition, T.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kwon, S.; Jeong, W.L.; Moon, S.B. A relative importance evaluation of bridge navigational equipment using AHP. J. Korean Navig. Port Res. 2021, 45, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Li, B. Research on node importance evaluation of complex products based on three-parameter interval grey number grey relational model. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 1931–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Cai, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, X. Traffic node importance evaluation based on clustering in represented transportation networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 16622–16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.; Qin, J.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, S.; Ji, X.; Xi, R.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation method of sandy conglomerate reservoir heterogeneity based on the combined weighted TOPSIS model. Interpret. A J. Subsurf. Charact. 2024, 12, T197–T208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.P.; Puli, A.V. An opportunity to advance cannabis science-DEA rescheduling. JAMA Psychiatry 2025, 82, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethamba, L.; Grobbelaar, S. The development of an action priority matrix and technology roadmap for the implementation of data-driven and machine-learning-based predictive maintenance in the south African railway industry. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2023, 34, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. A condition-based maintenance policy considering batch sizes for warm standby systems with priority to repair. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 73, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, S. An evaluation method for pavement maintenance priority classification based on an unsupervised data-driven multidimensional performance model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 13265–13278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Parlikad, A.K.; Brintrup, A. Data-driven maintenance priority recommendations for civil aircraft engine fleets using reliability-based bivariate cluster analysis. Qual. Eng. 2023, 35, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Woo, M. A study on the priority selection method for the maintenance project of abandoned buildings focusing on regional ripple effects. Stud. Reg. Dev. 2021, 53, 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. Towards the efficient generation of variant design in product development networks: Network nodes importance based product configuration evaluation approach. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 34, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Hu, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J. A topological sensitive node importance evaluation method in aerospace information networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, M.; Qiao, L.; An, Q.; Lu, S. Evaluation of cross-layer network vulnerability of power communication network based on multi-dimensional and multi-layer node importance analysis. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 67181–67197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.Y.; Yang, X.C.; Lu, S.R.; Tang, Y.; Hong, S.; Jiang, H. A multidimensional node importance evaluation method based on graph convolutional networks. Acta Phys. Sin. 2024, 73, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Liang, Z.W.; Zhang, R.X. Importance evaluation method of complex network nodes based on information entropy and iteration factor. Acta Phys. Sin. 2023, 72, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, W. Optimizing opportunistic preventive maintenance strategy for multi-unit system of CNC lathe. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Kang, F.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, T. Multi-attribute decision-making method in preventive maintenance of asphalt pavement based on optimized triangular fuzzy number. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Keshta, I.; Alhashimi, H.A.; Almagrabi, A.O.; Alwageed, H.S.; Alzahrani, M. A Fuzzy-AHP decision-making framework for optimizing software maintenance and deployment in information security systems. J. Softw.-Evol. Process 2025, 37, e2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M. An Improved Method for Optimizing the Timing of Preventive Maintenance of Pavement: Integrating LCA and LCCA. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; You, Y. Safety risk assessment of jacking renovation construction for aging bridges based on DBN and fuzzy set theory. Buildings 2025, 15, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Dong, Y. A hybrid approach combining Bayesian networks and logistic regression for enhancing risk assessment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Qian, J.; Peng, R.; Zio, E. Physics-informed data-driven Bayesian network for the risk analysis of hydrogen refueling stations. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 110, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Yu, F.; Wu, H.; Xia, X. A dynamic state cluster-based particle swarm optimization algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2025, 18, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B. An intelligent indoor fire localization system combining dynamic clustering algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Long, P.; Hu, L.; FDS Consortium. Optimization of dynamic multi-leaf collimator based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.; Heidari, M.; Ahmadzadeh, M. Optimization of dynamic parameter design of stewart platform with particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 16878132241263940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).