Abstract
Liquefied natural gas plays a crucial role in global energy transitions due to its high efficiency and low emissions, especially in long-distance transportation. However, the thermal management of LNG storage tanks remains a significant challenge due to temperature fluctuations, which impact both efficiency and safety. Traditional methods rely on thermodynamic models or computational fluid dynamics simulations but are computationally expensive and time-consuming. This study proposes a hybrid approach that integrates machine learning techniques with CFD data to predict temperature variations inside LNG storage tanks. Several ML models, including Random Forest, XGBoost, and deep learning-based models like CNN and TCN, were tested. Results indicate that CNN and TCN models offer the best performance in predicting temperature changes, showing superior accuracy and computational efficiency. This approach significantly enhances the real-time prediction capability, offering a promising solution for improving LNG tank thermal management, ensuring both operational safety and efficiency.
1. Introduction
Liquefied natural gas (LNG), as a clean energy source, is playing an increasingly important role in the global energy transition. Characterized by high efficiency and low emissions, LNG serves as an ideal alternative energy, particularly suitable for long-distance transportation, and has gradually become a key energy option [1]. However, thermal management of storage tanks during the design and transportation of LNG remains a significant challenge. Traditional thermal management approaches for LNG tanks typically rely on thermodynamic analysis models or computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. Although these methods offer high accuracy, they are computationally intensive and time-consuming, making them difficult to apply in real-time operational scenarios.
The thermal behavior of high-efficiency LNG storage tanks is influenced by multiple factors, such as the thickness of insulation materials, ambient temperature, and internal pressure [2]. These factors can cause temperature fluctuations within the tank, thereby affecting both transportation efficiency and safety. However, traditional thermal management methods are typically implemented under relatively static conditions, which sometimes limits their ability to predict temperature variations within the tank under varying ambient temperatures [3,4,5]. Therefore, developing a method capable of real-time prediction of internal tank temperature fluctuations is of critical importance. Several recent studies have highlighted the growing interest in the thermal behavior and prediction of LNG tanks. Recently, Jeong et al. applied artificial neural networks to LNG fuel tank operating data and demonstrated the feasibility of data-driven methods for predicting thermodynamics [6]. Marques et al. combined the ideas of traditional data assimilation and multi-environment reinforcement learning to propose a data assimilation method for calibrating the zero-dimensional thermodynamic model of cryogenic fuel tanks [7]. These studies indicate that the application of machine learning to the thermal management of LNG tanks is a timely and promising research direction.
Recently, machine learning (ML) techniques have demonstrated great potential in the optimization of energy systems, especially in time-series forecasting tasks [8]. Compared to conventional approaches, machine learning can process large volumes of data within a shorter time frame while effectively capturing complex nonlinear relationships within the system. Consequently, ML-based temperature prediction models for LNG storage tanks offer a novel approach to enhancing thermal management efficiency and safety. Existing studies have shown that the application of machine learning in thermal prediction—particularly when utilizing CFD simulation and experimental data—can significantly improve both prediction accuracy and computational efficiency.
Nevertheless, current research still faces several challenges, particularly in selecting appropriate machine learning models and handling different types of data. For instance, there is ongoing debate over which ML models are best suited to capture the complex patterns underlying temperature variations in LNG storage tanks, and how to effectively integrate experimental and simulation data to enhance model generalization. To address these issues, this study aims to optimize the temperature prediction process for LNG tanks using machine learning techniques by proposing a hybrid modeling approach that combines CFD simulation data with experimental measurements.
Several machine learning models were investigated, including linear regression, convolutional neural networks (CNN), and temporal convolutional networks (TCN), to evaluate their performance in predicting LNG tank temperatures. The objective is to improve thermal management and tank design. The results show that both CNN and TCN models exhibit superior performance in terms of prediction accuracy and computational efficiency. These models effectively enhance the thermal management capabilities of LNG storage tanks and provide reliable data support for future engineering applications.
In summary, this study leverages machine learning techniques to address the limitations of traditional methods in LNG tank thermal management. By comparing the performance of different models, we offer more scientifically grounded decision-making tools for LNG tank design and operation and propose a novel solution to improve the safety and efficiency of LNG storage during maritime transportation.
2. Literature Review
There are three main types of LNG cargo tanks commonly used in LNG carriers: membrane tanks (Type A), spherical tanks (Type B), and independent tanks (Type C). Among these, Type C tanks are widely used in small- to medium-sized vessels due to their simple structure and high mechanical strength. They can also serve as fuel tanks for main engines, making them highly promising for broader market adoption [9].
However, modeling the thermal behavior of LNG storage tanks still presents numerous technical challenges. While traditional thermodynamic analysis and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations offer high accuracy, their computational cost is substantial, limiting their applicability in real-time scenarios. To reduce computational complexity, many studies have introduced simplifying assumptions—such as constant ambient temperature and other idealized conditions—which compromise the model’s ability to adapt to the complex and dynamic thermal environments encountered during actual marine operations [10,11,12].
In the thermal management of LNG storage tanks, the boil-off gas (BOG) rate is directly influenced by variations in the tank wall temperature, which in turn are closely related to several factors such as insulation thickness, ambient temperature, and internal saturation pressure. Currently, the design of LNG storage tanks primarily relies on empirical formulas, which often tend to overestimate insulation performance. During voyages, it is often difficult for operators to monitor internal temperature changes in real time. This challenge becomes more pronounced under harsh sea conditions, potentially posing safety risks.
To address these challenges—and with the rapid advancement of computing technologies—the academic community has begun exploring hybrid approaches that combine machine learning with CFD simulations. For example, data generated from CFD simulations can be used to train machine learning models to achieve the desired predictive outcomes. This data-driven methodology significantly improves both the accuracy and timeliness of predictions, thereby providing effective support for thermal management in LNG transportation.
In recent years, machine learning (ML) techniques have demonstrated considerable potential in the prediction and control of energy systems. Unlike traditional physics-based modeling methods, machine learning can learn complex nonlinear relationships from limited experimental or simulation data and perform rapid predictions using the trained models. This capability is particularly valuable in edge computing and real-time monitoring systems. Significant advancements have been made in various domains, including energy load forecasting [13,14], fuel consumption modeling [15], and thermal system modeling [6,16], with growing applications in the field of marine engineering.
3. Methodology
This study proposes a machine learning–based predictive model aimed at optimizing the temperature management of liquefied natural gas (LNG) Type C storage tanks. The approach integrates CFD simulation data with experimental measurements and employs machine learning techniques to perform multi-step temperature forecasting. The primary objective of the model is to rapidly predict temperature variations in LNG tanks under various operating conditions, thereby enhancing the efficiency and safety of thermal management during LNG transportation.
As there is currently a lack of research applying machine learning to LNG tank temperature prediction, this study explores a range of algorithmic models, applies targeted optimizations, and performs comparative analyses to identify the most suitable modeling approach.
To further evaluate the generalization ability of the proposed model, we conducted cross-condition validation. In this setting, insulation thickness and boundary conditions were treated as distinct operating conditions. A leave-one-condition-out strategy was adopted: in each round, the model was trained on data from two conditions and tested on the remaining unseen condition. This process ensured that the model’s predictive performance was evaluated under operating scenarios not included in the training phase, providing a robust measure of its adaptability to tank designs with varying insulation thicknesses and thermal design environments.
3.1. Data Acquisition
The data used in this study were obtained from CFD simulation results and experimental measurements. The simulation data were generated using a finite element analysis model, while the experimental data were provided by Jiangsu New Yangzi Shipbuilding Company. These data primarily include temperature variations in LNG tanks with different insulation thicknesses under various environmental conditions. To enhance data applicability, all datasets were preprocessed through interpolation, cleaning, and normalization prior to being fed into the machine learning models.
The CFD dataset consists of 15 simulation cases with varying insulation thicknesses and boundary conditions, covering a total of approximately 17,640 h of thermal behavior. The experimental dataset provided by Jiangsu New Yangzi Shipbuilding contains 24 entries spanning 1176 h of operation (with a sampling frequency of approximately 48 h). Preprocessing steps included interpolation of missing values, removal of outliers, and consistent min-max normalization for all features.
3.2. Machine Learning Algorithm Selection
In terms of model selection, a comprehensive review of existing studies was conducted to compare the application of various machine learning algorithms in temperature prediction. Commonly used algorithms include Random Forest (RF), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN), as well as hybrid models.
Random Forest (RF) is an ensemble learning algorithm that constructs multiple decision trees and aggregates their results through averaging or voting to improve prediction accuracy and model stability. This method performs exceptionally well in handling nonlinear and high-dimensional time-series data and is widely applied in fields such as weather forecasting due to its strong noise resistance and generalization capability [17,18].
XGBoost is an efficient gradient boosting algorithm characterized by powerful nonlinear modeling ability, automatic feature selection, missing value handling, and regularization. It is well-suited for data with complex interactions and has demonstrated excellent performance in energy system forecasting, achieving high accuracy in tasks such as electricity consumption and indoor temperature prediction, as well as power demand modeling [19,20].
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks effectively address the vanishing gradient problem inherent in traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs) by introducing gating mechanisms. This makes LSTM well-suited for handling long-term dependencies in time-series data and widely applicable to temperature prediction tasks. Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) networks are a more streamlined variant of gated recurrent networks, offering higher computational efficiency while similarly capable of modeling long-term dependencies.
The application of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to time-series data has been increasingly prominent. By extracting local features through convolutional layers, CNNs excel in prediction tasks involving both image and sequential data and are extensively used in forecasting scenarios involving time-series and image-type data. Hybrid models, such as CNN-LSTM and CNN-GRU, combine the strengths of CNNs in local feature extraction with the temporal dependency modeling capabilities of LSTM or GRU, thereby further enhancing prediction performance. Studies have shown that these hybrid models perform exceptionally well in spatiotemporal sequence modeling and have been successfully applied to automated weather forecasting and field monitoring tasks, significantly improving the accuracy and stability of temperature predictions [21,22].
In addition, Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs), a deep learning model based on causal and dilated convolutions, excel at modeling long-term dependencies and have achieved remarkable results in various fields, particularly in weather forecasting tasks [23]. Studies have shown that TCNs outperform traditional models such as LSTM in terms of prediction accuracy. In temperature prediction tasks, hybrid models combining TCN and LSTM (TCN-LSTM) have also demonstrated excellent performance. By integrating temporal features extracted by TCN with the time dependency captured by LSTM, the TCN-LSTM model enhances both the efficiency and accuracy of sequence modeling [24]. Another variant, TCN-GRU, which combines TCN’s efficient feature extraction with GRU’s streamlined gating mechanism, has similarly achieved promising prediction results [25].
4. Model Development and Validation
This section describes the training, development, and validation processes of the predictive models applied in this study. As illustrated in Figure 1, the overall predictive simulation framework developed herein is outlined.
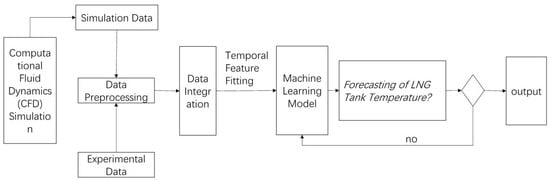
Figure 1.
Predictive Modeling Framework for LNG Tank Temperature.
4.1. Predictive Model Development
Thermodynamic assumptions for modeling [26]: This study assumes liquefied natural gas (LNG) is a single-component fluid, primarily methane, and does not consider the effects of LNG composition, phase separation, or stratification in multicomponent mixtures. While methane is the dominant component, actual LNG compositions can include varying amounts of ethane, propane, and heavier hydrocarbons, which affect heat capacity, density, and latent heat. These compositional variations, along with nonideal behavior during storage and transport, can lead to temperature and density gradients within the tank, potentially challenging model assumptions and affecting heat transfer and boil-off gas (BOG) dynamics.
Furthermore, the model is specific to pressurized LNG tanks and does not directly account for dynamic boil-off rates or their impact on operating conditions. Future work will aim to extend the existing framework to better address these complexities by integrating multicomponent property data, simulating dynamic BOG generation, and optimizing related processing systems, such as reliquefaction and gas utilization.
4.2. Model Training Procedure
To construct a reliable temperature prediction model, input features were standardized prior to training to improve convergence behavior. A time-series window of 30 steps (approximately 6 h) was used for sequence models. Multiple machine learning algorithms were selected for comparative analysis, including Random Forest (RF), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN). Additionally, several hybrid models were employed, such as CNN-LSTM, CNN-GRU, TCN-LSTM, and TCN-GRU. The Adam optimizer was used for training, with hyperparameters such as learning rate tuned to optimize model performance while minimizing manual parameter adjustment efforts.
Considering that temperature variations in LNG tanks are relatively small over short periods, wavelet decomposition was applied to remove trend components from the data. Polynomial fitting was used to eliminate the long-term trends, allowing the models to focus more effectively on the fluctuations rather than on the overall trends. Models were trained using the Adamoptimiser, with early stopping applied based on validation loss stagnation, using a patience value of 70 epochs. Batch sizes of 100 were selected to ensure computational efficiency while preserving generalisability.
In contrast, the linear regression model was trained directly on lagged price data without additional temporal features or sequence windows, allowing for a transparent baseline comparison.
4.3. Model Performance Metrics
To evaluate the performance of the regression models, three commonly used metrics were employed: Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). Lower values of MAE and MSE indicate better predictive accuracy, whereas a higher R2 value denotes a better fit. Their mathematical formulations are given as follows:
Here, denotes the true value, the predicted value, and the mean of the true values. The coefficient of determination theoretically ranges between 0 and 1, where a value of 1 indicates a perfect fit, and 0 implies that the model fails to explain any variability in the data.
4.4. Data Partitioning
To prevent data overfitting, the dataset was split into 80% for training, 10% for validation, and the remaining 10% for testing. The same error metrics were applied to evaluate the hybrid models. Their performance in LNG tank temperature prediction was then assessed and analyzed in comparison with that of individual models.
5. Results and Discussion
This study proposes a method combining CFD simulation with various machine learning models to predict the temperature inside LNG storage tanks. The results indicate significant performance differences among the models in temperature prediction, with each final model exhibiting distinct advantages and limitations in specific application scenarios. This section provides a detailed discussion of the predictive performance of each model, analyzes their strengths and weaknesses, and further explores the potential and limitations of the proposed method and models in practical applications.
5.1. Model Performance Comparison
To comprehensively evaluate the predictive capabilities of various models in engineering applications, Random Forest (RF), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), and Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) were selected. Their prediction performances were compared with those of hybrid models, including CNN-LSTM, CNN-GRU, TCN-LSTM, and TCN-GRU. The evaluation was conducted using metrics such as Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The data presented in Table 1 and further displays them in a radar chart format as shown in Figure 2. Radar charts intuitively display the comprehensive performance of each model across multiple evaluation metrics, making them suitable for presenting the overall model picture and the relative performance of each model on various evaluation metrics.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of ten predictive models.
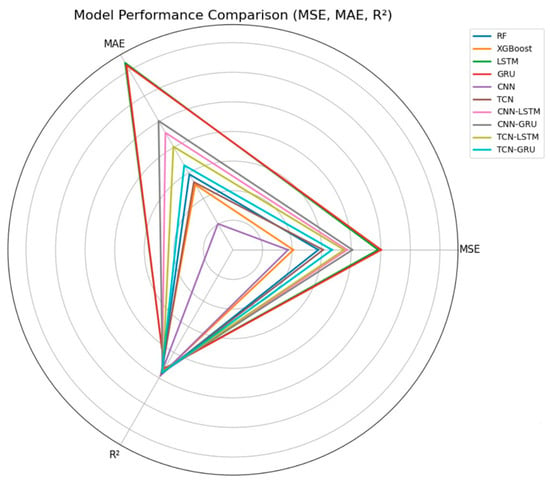
Figure 2.
Comparison of prediction model performance.
Linear regression, used as a baseline model, demonstrated basic predictive performance. Although its MSE and MAE were relatively high, the R2 value was close to 1, indicating that it still possesses a certain predictive capability for LNG tank temperature forecasting. However, due to its simple linear assumptions, linear regression fails to fully capture the complex nonlinear dynamics of temperature variations in LNG storage tanks, resulting in prediction errors. Particularly during periods of rapid temperature changes, its accuracy cannot compete with more sophisticated models.
The Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) exhibited excellent performance in terms of MSE and MAE, achieving the lowest values among all models with an MSE of 0.19138 and an MAE of 0.35005, demonstrating its high precision in LNG tank temperature prediction. Thanks to CNN’s advantage in extracting local features, it effectively captures instantaneous fluctuations in temperature observations, especially when handling time-series data. Consequently, CNN adapts well to temperature volatility. Furthermore, its R2 value of 0.97871, close to 1, indicates strong predictive power, making it suitable for tasks requiring accurate dynamic forecasting.
The Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) model achieved relatively low MSE and MAE values, with an MSE of 0.34385 and an MAE of 0.42624. Although these values are higher than those of the CNN, TCN attained the highest R2 value of 0.98436, indicating excellent predictive performance and generalization capability. TCN efficiently captures long-range dependencies in temporal data and maintains high prediction accuracy amid complex dynamic changes. Compared to traditional LSTM and GRU models, TCN demonstrates better stability and accuracy in handling long-term dependencies in instantaneous data processing, making it well-suited for LNG tank temperature prediction tasks.
XGBoost also performed well in terms of MSE and MAE, with a low MSE and an R2 close to 1, confirming its effectiveness in modeling LNG tank temperature variations. Through its boosted tree approach, XGBoost can handle complex nonlinear relationships within LNG tank temperature data. It maintains high prediction accuracy even under rapid temperature fluctuations and is suitable for use under various operational conditions, especially when the data involve complex interaction effects.
The performance of LSTM and GRU models was moderate: both exhibited reasonable R2 values but had the highest MSE and MAE, indicating larger prediction errors and lower accuracy compared to CNN and XGBoost. Although LSTM and GRU are capable of capturing long-term dependencies, their performance in LNG tank temperature prediction was inferior to that of CNN and XGBoost. The relatively high MSE and MAE for LSTM and GRU suggest that these models struggle to maintain comparable prediction accuracy when faced with complex and dynamic temperature variations.
The hybrid models CNN-LSTM and TCN-LSTM exhibited relatively good performance in terms of R2 values, but their MSE and MAE remained comparatively high. Although these hybrid models combine the strengths of CNN or TCN in local feature extraction with LSTM’s capability in modeling temporal dependencies, the inherent limitations of LSTM in capturing temperature fluctuations restrict the overall performance. Consequently, these hybrid models do not outperform the standalone CNN and TCN models.
The TCN-GRU model showed strong performance across MSE, MAE, and R2 metrics, indicating its stable capability in improving LNG tank temperature prediction. By integrating TCN’s feature extraction proficiency with GRU’s streamlined gating mechanism, TCN-GRU efficiently captures the dynamic characteristics of LNG tank temperature while maintaining low computational complexity. This makes it well-suited for tasks requiring efficient prediction and reduced computational cost.
Based on the comparative analysis of different models, the following conclusions can be drawn:
Best-performing models: CNN and TCN demonstrated superior performance in LNG tank temperature prediction tasks. In particular, CNN exhibited notable advantages in prediction accuracy and generalization capability, making it well-suited for real-time monitoring and temperature forecasting.
Second-best models: XGBoost and TCN-GRU showed stable performance, effectively handling the dynamic fluctuations of LNG tank temperatures. These models are suitable for deployment in environments requiring robust adaptability.
Underperforming models: Although LSTM and GRU can capture long-term dependencies in time series data, their prediction errors increase significantly when faced with temperature fluctuations, resulting in relatively poorer performance. While hybrid models can improve predictive capabilities to some extent, their prediction errors still lag behind those of standalone CNN and TCN models. Next, Figure 3 shows the temperature prediction and actual temperature diagram of CNN as an example to intuitively reflect the performance of the model.
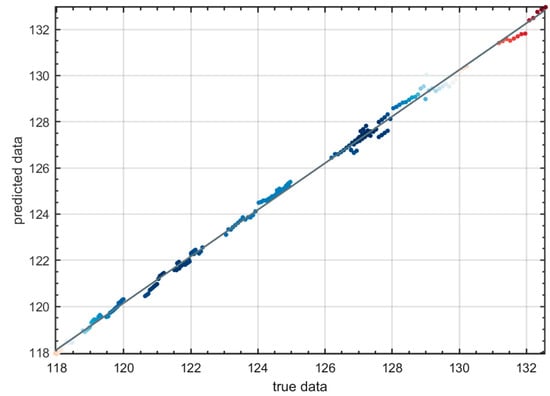
Figure 3.
Temperature prediction and actual temperature.
Based on the above analysis, the best-performing CNN and TCN models were selected for generalization verification. As shown in Table 2, the CNN consistently outperformed the TCN under cross-dataset settings. For example, when trained on datasets B + C and tested on A, the CNN achieved an MSE of 0.0910 and R2 of 0.9883, whereas the TCN suffered a significant degradation (MSE 0.5805, R2 0.9196). These results demonstrate that the CNN model is able to generalize and achieve high prediction accuracy across diverse operating conditions, while the TCN exhibits greater sensitivity to conditional variations. These results confirm the CNN’s robustness in handling unknown design and operating scenarios. These results provide guidance for further model optimization.

Table 2.
Cross-condition validation.
Because this study primarily focuses on the engineering application and feasibility of machine learning in LNG tank thermal management, we primarily rely on error metrics (MSE, MAE, and R2) to compare the various models. These metrics provide clear and sufficient evidence for the superiority of CNN and TCN in practical applications. We will not consider statistical significance testing to verify whether the performance differences between the different models are significant. However, we fully recognize the importance of statistical testing for academic rigor. Therefore, we recommend that future studies include statistical tests such as paired t-tests or Wilcoxon tests to further verify the robustness of the observed differences.
5.2. Advantages and Limitations of the Method
- (1)
- Time Advantage
The traditional CFD-based calculation methods are time-consuming and require substantial computational resources. By integrating machine learning, the time cost is significantly reduced because it is no longer necessary to compute the entire case comprehensively; only partial computations are needed while maintaining accuracy. For example, on a server with a CPU of 7950x and 64 GB of memory, completing a full CFD simulation takes approximately 48 h, whereas the machine learning model requires only 11 s. This integration undoubtedly shortens the computation time and reduces time costs while ensuring accuracy.
- (2)
- Model Advantage
The CNN model achieves optimized accuracy and minimal error in multi-step predictions, making it an ideal choice for short-term LNG tank temperature forecasting. It can provide real-time temperature data for monitoring systems, assisting operators in timely decision-making. Within acceptable error margins, TCN demonstrates the strongest generalization ability and better stability in handling long intermittent sequences in time series data, making it well-suited for LNG tank temperature prediction tasks.
5.3. Limitations
Data and Model Limitations: The model relies on limited CFD and experimental data, which may affect generalization capabilities. Furthermore, its robustness under extreme operating conditions remains to be verified.
Practical Application Complexity: The model does not fully account for the complexities of real-world LNG transportation, such as compositional variations, liquid stratification, sloshing effects, and dynamic boil-off gas (BOG) management.
Simplified Model Assumptions: Current research simplified LNG to pure methane, ignoring the nonideal properties of multicomponent fluids, phase separation, and stratification effects, which can affect prediction accuracy.
5.4. Practical Applications of the Method
Machine learning-based temperature prediction models for LNG tanks have broad application prospects. Through accurate temperature forecasting, the safety and efficiency of LNG tanks during design and transportation processes can be significantly enhanced. The main applications include:
Tank Design Optimization: By predicting temperature variations in LNG tanks under different operating conditions, important reference data can be provided for the insulation design of LNG tanks. Selecting appropriate insulation materials and optimizing the design can improve energy efficiency and economic benefits of the tank.
Real-time Monitoring and Temperature Control Optimization: Utilizing CNN models for real-time temperature prediction can supply data support to LNG tank temperature control systems, helping operators to promptly adjust temperature control measures, thereby avoiding gasification losses or safety hazards caused by excessively low temperatures.
Response and Safety Assurance: Real-time monitoring systems based on temperature prediction can automatically detect abnormal temperature conditions, trigger warnings, and assist operators in implementing emergency response mechanisms to ensure safety during LNG transportation.
6. Future Research and Development Directions
Although the proposed method in this study has achieved good results in LNG tank temperature prediction, future research can be improved and extended in the following directions:
Multimodal Data Fusion: Integrate multimodal sensor data such as temperature, pressure, and humidity by inputting different types of data into the model to further im-prove prediction accuracy and reliability.
Online Learning and Adaptive Adjustment: Introduce online learning mechanisms to allow the model to continuously optimize based on real-time data, thereby adapting to varying environmental changes and consistently improving prediction accuracy.
Optimizing boil-off gas handling: Future research should explore the integration of BOG dynamics into the predictive models, enabling the optimization of BOG management systems. This could include strategies for reliquefaction, fuel gas utilization, and the dynamic interaction between thermal management and BOG generation, ensuring more efficient and cost-effective LNG tanker operations.
Modeling Multi-Component LNG Behavior: Future work should extend the model to consider the effects of phase separation and stratification in multi-component LNG. These effects are crucial for accurately simulating temperature distribution and density gradients in LNG tanks, especially during transportation, where interactions between different components impact prediction accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and J.Q.; Methodology, J.Q.; Software, J.Q.; Validation, J.Q., J.M. and Y.X.; Formal analysis, J.M.; Investigation, B.C.; Resources, H.Z.; Data curation, H.Z.; Writing—original draft preparation, J.Q.; Writing—review and editing, H.Z.; Visualization, Y.L.; Supervision, X.J.; Project administration, J.Q.; Funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and approved the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
APC was funded by the “Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program” of Jiangsu Ocean University (No. Z202411641633004).
Data Availability Statement
Due to privacy and legal restrictions, the data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, H.; Mao, L.; Tao, F. Calculation and Finite Element Analysis of the Independent Tank Structure of Liquefied Natural Gas Carriers. Mech. Manuf. 2018, 56, 43–46+53. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D. Study on Heat Transfer and Evaporation Rate of Independent C-Type LNG Tanks on LNG Carriers. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Temperature Field and Stress Field Analysis of C-Type Independent Cargo Tanks for Small and Medium-Sized LNG Carriers. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, G.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Q. Simulation Experiment on the Steady-State Boil-Off Rate of LNG Storage Tanks Based on ANSYS. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2017, 34, 129–131, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Hu, Y.; Hua, J. Finite Element Analysis of Temperature and Stress Fields in LNG Ship Cargo Tanks. Ship Ocean Eng. 2010, 2, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Park, A.; Chung, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.; Lim, Y. Modeling and simulation of thermodynamic behavior of an LNG fuel tank by using artificial neural network based on operational data. Energy 2025, 314, 134340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.A.; Ahizi, S.; Mendez, M.A. Real-time data assimilation for the thermodynamic modeling of cryogenic storage tanks. Energy 2024, 302, 131739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzelepi, M.; Symeonidis, C.; Nousi, P.; Kakaletsis, E.; Manousis, T.; Tosidis, P.; Nikolaidis, N.; Tefas, A. Deep Learning for Energy Time-Series Analysis and Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.09129. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.09129 (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Qian, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y. A Review of the Temperature Field Research of C-type Liquid Tanks on Small and Medium-sized LNG Ships. Front. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 3, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. A Fluent-Based Method for Predicting LNG Tank Evaporation Parameters. Ship Ocean Eng. 2018, 47, 160–163+167. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, J. Study on the Temperature Distribution of the Hull of Membrane-type Liquefied Natural Gas Carrier. Shipbuild. Technol. 2006, 5, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Zhou, H. Study on the Temperature Field of Membrane-type LNG Carrier. Nat. Gas Ind. 2005, 25, 110–112. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, S.; Aung, P.P.; Rafsanjani, A.S.; Majeed, A.P.A. Machine learning applications in energy systems: Current trends, challenges, and research directions. Energy Inform. 2025, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, S.; Li, Z. Advancing AI-Enabled Techniques in Energy System Modeling: A Review of Data-Driven, Mechanism-Driven, and Hybrid Modeling Approaches. Energies 2025, 18, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Lam, J.S.L.; Xiao, Z. Prediction of harbour vessel fuel consumption based on machine learning approach. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Temperature Prediction of High-pressure Rotor Hazard Points Based on Machine Learning. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 55, 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Dhamodaran, S.; Krishna Chaitanya Varma, C.; Reddy, C.D. Weather Prediction Model Using Random Forest Algorithm and GIS Data Model. In Innovative Data Communication Technologies and Application. ICIDCA 2019; Raj, J., Bashar, A., Ramson, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes on Data Engineering and Communications Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Du, J. Temperature Prediction Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network and Random Forest. Comput. Eng. Des. 2019, 40, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Kang, J.; Ding, Z.; Zhu, H. An XGBoost-Based predictive control strategy for HVAC systems in providing day-aheaddemand response. Build. Environ. 2023, 238, 110350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, N.; Hu, Z.; Magami, D. A metaheuristic approach to model the effect of temperature on urban electricity need utilizing XGBoost and modified boxing match algorithm. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 115318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Lee, C.-H. Deep Learning for Weather Forecasting: A CNN-LSTM Hybrid Model for Predicting Historical Temperature Data. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 99, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilan, T.; Baalamurugan, K.M. Automated weather forecasting and field monitoring usingGRU-CNN model along with IoT to support precision agriculture. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249 Pt A, 123468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewage, P.; Behera, A.; Trovati, M.; Pereira, E.; Ghahremani, M.; Palmieri, F.; Liu, Y. Temporal convolutional neural (TCN) network for an effective weather forecasting using time-series data from the local weather station. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 16453–16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Gui, W. Learning an Enhanced TCN-LSTM Network for Temperature Process Modeling in Rotary Kilns. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 3056–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J. A short-term forecasting method for photovoltaic power generation based on the TCN-ECANet-GRU hybrid model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H. Study on Heat Transfer and Evaporation in Type C LNG Fuel Tank. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).