Abstract
The co-occurrence of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and zearalenone (ZEN) in grain-based food and animal feed poses significant health risks to humans and animals due to their potent mutagenic, cytotoxic, and carcinogenic properties. Conventional physical and chemical methods are insufficient for effectively detoxifying multiple mycotoxins present in food and feed. In this study, we evaluated the capability of Bacillus subtilis ZJ-2019-1 (B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1) to simultaneously degrade AFB1 and ZEN while optimizing reaction to enhance degradation efficiency. The localization of active ingredients from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 was determined using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Our findings demonstrated that B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 eliminated 60.88% of AFB1 and 33.18% of ZEN within 72 h at a concentration of 10 mg/L at 37 °C (pH 7.0) and exerted greater activity under alkaline conditions. The autoclaved and boiled supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 exhibited significant enhancement in the degradation of AFB1 and ZEN, achieving degradation rates of 79.85% and 100%, respectively, at a concentration of 1 mg/L within 48 h at 37 °C. Moreover, the crude enzymes from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 showed maximum degradation rates for AFB1 (100%) and ZEN (94.29%) within 72 h at 70 °C. Additionally, divalent cations (such as Co2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, and Ni2+) significantly augmented the activity of crude enzymes from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 towards mycotoxin degradation. Furthermore, when applied to corn gluten meals, B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain effectively detoxify 66.08% of AFB1 and 22.01% of ZEN, surpassing the efficacy of a commercial detoxification agent on the market (34.17% for AFB1 and 2.28% for ZEN). Collectively, these findings indicated that B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 is a promising candidate for the simultaneous removal of multiple mycotoxins in food and feed, while addressing health concerns associated with harmful mycotoxins.
Keywords:
mycotoxins; degradation; aflatoxin; zearalenone; Bacillus subtilis; active components; feed Key Contribution:
The Bacillus subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain exhibits simultaneous degradation of AFB1 and ZEN. In comparison to a commercial mildew removal agent; Bacillus subtilis ZJ-2019-1 demonstrates superior efficacy in detoxifying mycotoxins present in raw feed materials.
1. Introduction
Mycotoxins are naturally occurring metabolites produced by a diverse range of molds, which can induce acute or chronic toxicity in both humans and animals [1,2]. These toxins have the potential to cause damage to vital organs such as the liver, kidney, nervous system, hematopoietic tissue, and skin [3]. Typically characterized by their low molecular weight compounds, mycotoxins possess considerable toxic properties. Moreover, their structural stability enables them to withstand high temperature; however, the extent of toxicity varies depending on their specific structures [4]. It is worth noting that a single mold species may produce one or more secondary metabolites, while different molds can also generate the same mycotoxin. The combined toxicity of mycotoxins is intricate and influenced by various factors including the type, dosage, host response, and duration of exposure. Furthermore, it encompasses synergistic effects as well as additive and antagonistic interactions [5,6,7].
Aflatoxin (AF) is a secondary metabolite produced by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Currently, a total of 18 types of AF have been isolated and identified, including B1, B2, G1, G2, M1, M2, B2a, G2a, BM2a, and GM2a. Among them, aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is the most potent toxin known to be carcinogenic, genotoxic, teratogenic, immune-toxic, and mutagenic to both humans and animals [8,9]. Prolonged exposure to AFB1 can lead to chronic poisoning in animals, resulting in growth retardation, immune dysfunction, as well as tissue and organ damage with potentially fatal consequences [10,11,12]. Moreover, AFB1 residues may also be present in meat, eggs, and dairy products, thereby posing serious threats to food safety, which ultimately jeopardizes human health [13,14,15]. Zearalenone (ZEN) is produced by major members of the Fusarium genus, such as F. graminis, F. roseum, F. transversum, and F. trilineatum. ZEN is one of the most prevalent mycotoxins in cereals and foodstuffs worldwide and poses a significant threat to food/feed security as well as human and animal health [16]. It primarily affects the reproductive system of animals and can elevate estrogen levels [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In cases of acute poisoning, ZEN can have detrimental effects on vital organs including the heart, liver, kidney, lung, and nervous system [23,24].
Both AFB1 and ZEN are commonly co-occurring mycotoxins in cereals, and their widespread contamination and toxicity to animals have made the efficient removal of these compounds prominent research topic for an extended period. Currently, various physical, chemical, and biological methods exist for eliminating mycotoxins. Among them, biodegradation has garnered significant attention due to its high efficiency, strong specificity, minimal environmental pollution, and negligible impact on nutritional value [25]. Notably, Bacillus sp. S62-W has been reported to efficiently degrade ZEN [26], while B. subtilis ANSB01G not only degrades ZEN, but also relieves apoptosis induced by ZEN toxicity and oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Additionally, it reduces the residual amount of ZEN in feces [27]. The optimized fermentation conditions greatly enhanced AFB1 degradation ability of Bacillus subtilis Q125. The optimal fermentation conditions were as follows: a fermentation time of 38.6 h, an inoculum concentration of 5.8%, and a fermentation temperature of 36 °C [28]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that several bacteria (such as Rhodococcus pyridinivorans, Pseudomonas fluorescens1, and Enterococcus faecium) are capable of degrading multiple mycotoxins [29,30,31]. However, only a few bacteria have been reported to simultaneously degrade both AFB1 and ZEN, highlighting the importance of strain screening and reaction condition optimization. Additionally, the degradation mechanisms for many strains remain unclear, which hinders their potential application in food and feed.
In our previous study, we isolated and identified the Bacillus subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain, which was found to effectively degrade ZEN both in vitro and in female gilts [32]. In this work, we aimed to investigate the simultaneous degradation of ZEN and AFB1 by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, followed by optimization of degradation conditions including temperatures, pH values, and time. Furthermore, active fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 were identified and utilized for detoxification of mycotoxins in corn gluten meal.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Source, Chemicals, and Reagents
The B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain was isolated from pig feces collected from three pig houses in Xingtai, Hebei Province [32]. The strain has been stored at the General Microbiology Center of the China Microbiological Culture Preservation and Management Committee (CGMCC No. 23636).
For bacterial culture, Luria–Bertani (LB) medium (containing 10 g/L tryptone, 10 g/L NaCl and 5 g/L yeast extract) was utilized. AFB1 (C17H12O6) and ZEN (C18H22O5) were purchased from Qingdao Prebon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (Qingdao, Shandong). Methanol and acetonitrile (high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade) were purchased from Beijing Maida Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Protease K, metallic, and inorganic salts (including NaCl, MgSO4, FeSO4, FeCl3, NiSO4, MnCl2, ZnCl2, CuSO4, CoCl2 and SDS powder) were obtained from Beijing Soleibao Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Mildew remover-mildew clean-3 was obtained from Hebei Tianyin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Langfang, Hebei). Other reagents were of analytical purity.
2.2. Detection of AFB1 and ZEN by HPLC
The mycotoxin detection was performed using an Agilent SB-C18 (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) analytical column in the HPLC system. The mobile phase consisted of a mixture of methanol, acetonitrile, and water (22:22:56 for AFB1 and 8:46:46 for ZEN), which was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter prior to use. The column temperature was maintained at 40 °C for AFB1 analysis and at 30 °C for ZEN analysis. An injection volume of 10 μL and a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min were employed during the analysis process. For fluorescence detection, the excitation/emission wavelengths were set at 365 nm/430 nm for AFB1 and at 235 nm/460 nm for ZEN.
2.3. Degradation of AFB1 and ZEN by the B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 Strain
The B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain was cultured for 72 h until reaching a stable stage, and then divided into two equal parts. One part of the bacterial culture was centrifuged to collect the supernatants and cells separately. The supernatants were filtered through 0.22 μm filters (cell-free supernatants), followed by the addition of AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L. The cells were washed four times with sterile phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH 7.0) and then treated with an equal volume of sterile PBS containing AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L.
The other part of the bacterial culture was also centrifuged to collect the supernatants and cells separately, which were then subjected to heat treatment by boiling at 100 °C for 3 h or autoclaving at 0.1 MPa, 121 °C for 15 min using a YXQ-S Ⅱ Vertical Steam Sterilizer; afterwards, AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L was added. The blank control group was treated with sterile PBS containing mycotoxins.
The samples were incubated at 37 °C (200 rpm) for 48 h; 1 mL of sample was taken and centrifuged at room temperature for 10 min (12,000 rpm). The supernatants were then analyzed for the presence of AFB1 or ZEN using HPLC [32].
2.4. Effects of Various Factors on the Degradation of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
The B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 strain was cultured until it reached the logarithmic growth phase and then centrifuged at room temperature for 5 min at a speed of 6000 rpm. Subsequently, the bacterial cells were washed with sterile PBS and finally resuspended in PBS to achieve an optical density (OD600) of 0.3–0.5 [33,34].
To investigate the impact of temperature, AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L was added to B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 culture (2% inoculation, pH 7.0), which was incubated for 72 h at temperatures ranging from 22 to 42 °C [33]. Samples were collected and the degradation rate of mycotoxins was determined using HPLC as described above. To examine the effect of different pH values on the degradation rate, AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L was added to the bacterial culture adjusted to various pH values (4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, or 9.0), followed by incubation for 72 h at 37 °C. Regarding incubation time, AFB1 or ZEN (10 mg/L) was added into B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and then incubated at 37 °C for varying time: 0, 6, 12, 24, 36, or 48 h [33]. Additionally, to evaluate the effect of mycotoxin concentration on degradation rate, different concentrations of AFB1 or ZEN (2, 5, 10, 20, or 40 mg/L) were added into B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. Following incubation, samples were collected and analyzed using HPLC. The residual rate and degradation rate of mycotoxins were calculated by the following formulas [35]:
Residual rate (%) = peak area of the experimental group/peak area of the control group × 100%
Degradation rate (%) = (peak area of the control group − peak area of the experimental group)/peak area of the control group × 100%
2.5. Localization of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 Active Substances for Degradation of AFB1 and ZEN
To determine the active ingredients of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 to degrade mycotoxins, the strain was cultured until reaching a stable stage, followed by centrifugation at 4 °C for 20 min (8000 rpm) to obtain the supernatants. These supernatants were then collected and filtered through 0.22 μm filters to obtain cell-free supernatants. The bacterial precipitate was resuspended in sterile PBS and underwent three rounds of centrifugation and washing with sterile PBS. Subsequently, ultrasonication was performed for 5 min (600 W, working 5 s and intermittent 5 s). The resulting bacterial mixture was further centrifuged at 4 °C for 20 min (10,000 rpm, and the sediment obtained was resuspended in sterile PBS as cellular contents [36,37,38].
The cell-free supernatants were autoclaved at 121 °C for 15 min and boiled in a water bath at 100 °C for 3 h following previous studies with slight modifications [35,36,37]. Specifically, the heated supernatants were supplemented with 1 mg/L of AFB1 or ZEN and incubated at 37 °C (200 rpm) for 48 h. To investigate whether the degradation of mycotoxins was enzymatic in nature, the cell-free supernatants were treated with protease K (2 mg/mL), SDS (1%), or both, at a temperature of 58 °C for 3 h [32]. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. The degradation of AFB1 and ZEN was determined using HPLC as described above.
2.6. Effects of Different Factors on the Degradation of AFB1 and ZEN by the Crude Enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
To investigate the impact of temperature on degradation rate, 10 mg/L AFB1 or ZEN was added into the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, followed by incubation at temperatures ranging from 30 to 70 °C for 72 h. Subsequently, samples were collected, and mycotoxin degradation rates were determined using HPLC analysis. For pH effect assessment, 10 mg/L AFB1 or ZEN was added to the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and incubated for 72 h at 37 °C under varying pH conditions (4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, or 9.0) [39]. Similarly, in the metal chelator treatment test, different concentrations of EDTA solutions (10, 20, 30, 40, or 50 mmol/L) were added into the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, followed by incubation at 37 °C for 72 h following previous studies with slight modifications [39].
To evaluate the effect of mycotoxin concentration on degradation rate, different concentrations of AFB1 or ZEN (1, 5, 10, 15, and 20 mg/L) were added into the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1. The resulting mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 72 h. To examine the impact of metal ions on degradation rate, diverse metal ion solutions (such as Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+) were added to the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and incubated at 37 °C for 72 h following previous studies with slight modifications [34]. Each metal ion had a final concentration of 5 mmol/L. Furthermore, regarding reaction time, the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 were subjected to incubation with either AFB1 or ZEN at a concentration of 10 mg/L at 37 °C for 24, 48, 72, 96, or 144 h. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. Following incubation, samples were collected and analyzed using HPLC to determine mycotoxin degradation rates.
2.7. Detoxification of AFB1 and ZEN in Corn Gluten Meal by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
A total of 5 g of corn gluten meal contaminated with AFB1 (0.8 mg/kg) and ZEN (3 mg/kg) was ground and added to a 20 mL culture of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 1–6 days (200 rpm). Subsequently, the supernatant was centrifuged, mixed with 0.5 g of NaCl and 25 mL of the extract (acetonitrile:water = 4:1), and incubated for 1 h (200 rpm/min). After centrifugation and filtration (0.22 μm), the degradation rates of AFB1 and ZEN in the corn gluten meal were determined by HPLC according to Chinese Standard GB/T 28716-2012 [40]. The corresponding corn gluten meal (5 g) was added to sterile PBS (0.01 mM, pH 7.0) in a volume of 20 mL, followed by the addition of an antifungal agent (0.01 g, mold remover) as a control for detoxifying mycotoxins. The same incubation process was carried out at 37 °C for 1–6 days. All experiments were independently repeated three times.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) within 95% confidence intervals, followed by either Student’s test or Duncan’s test, using the statistical software SPSS 28.0.
3. Results
3.1. Detoxification of AFB1 and ZEN by Different Fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
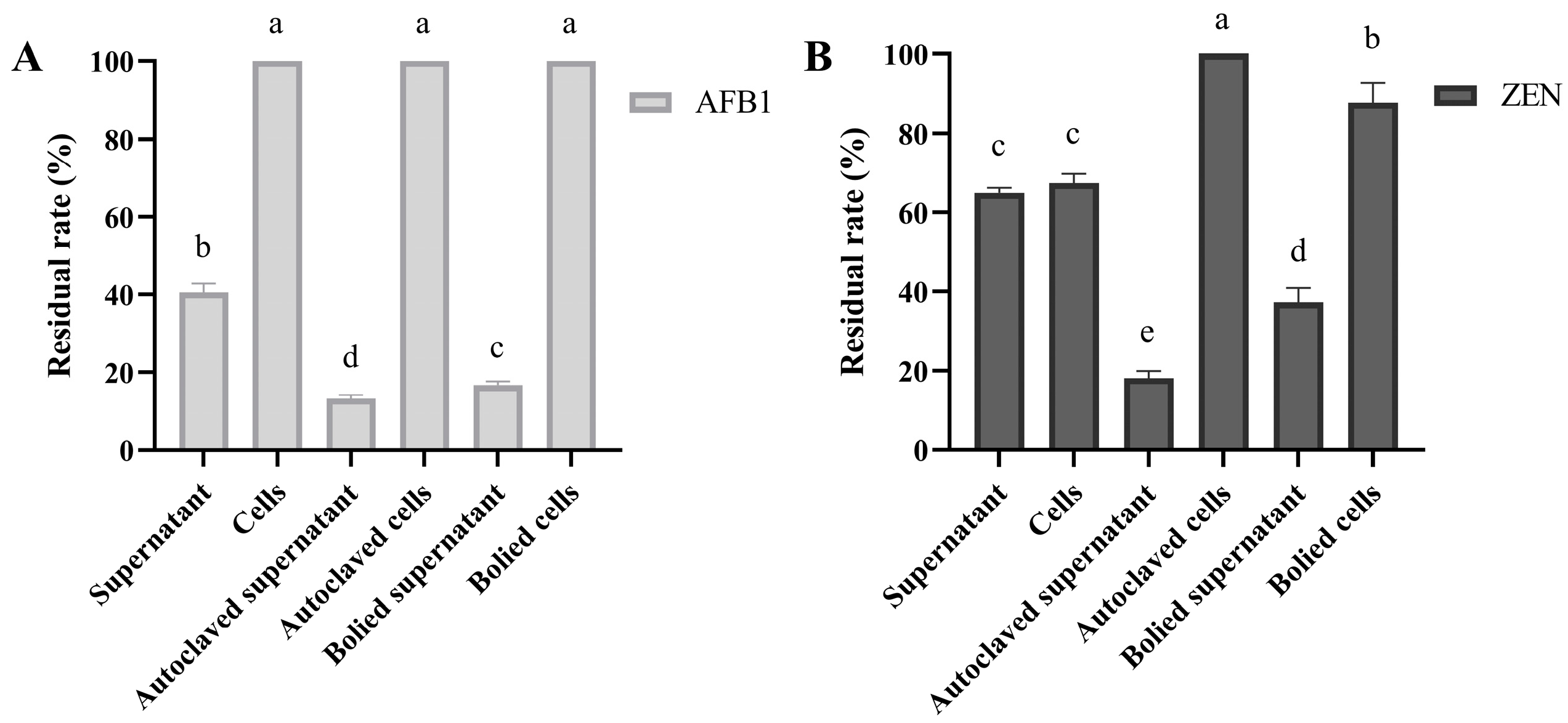
Mycotoxins (10 mg/L) were added to various fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, including cell-free supernatants and bacterial cells, and incubated for 48 h. The results showed that the residual rates of AFB1 and ZEN in the cell-free supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 were 40.55% and 48.75%, respectively. Autoclaved and boiled supernatants from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 significantly increased the degradation of AFB1 (with residual rates of 13.29% and 16.75%) and ZEN (18.12% and 37.24%) (Figure 1). After incubation with cells or autoclaved/boiled bacterial cells, the residual rate of AFB1 remained at 100% (Figure 1A). However, autoclaved and boiled bacterial cells increased the residual rate of ZEN from 67.40% to 100% and 87.67%, respectively (Figure 1B).
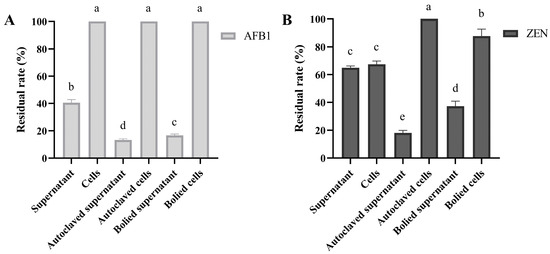
Figure 1.
Effects of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 on 10 mg/L ZEN and AFB1 detoxification. (A) Effects of different fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 on AFB1 degradation. (B) Effects of different fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 on ZEN degradation. Different letters indicate significant differences between the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05). The different fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 included cell-free supernatants, autoclaved supernatants, boiled supernatants, bacterial cells, autoclaved bacterial cells, and boiled bacterial cells.
3.2. Factors Influencing the Degradation of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
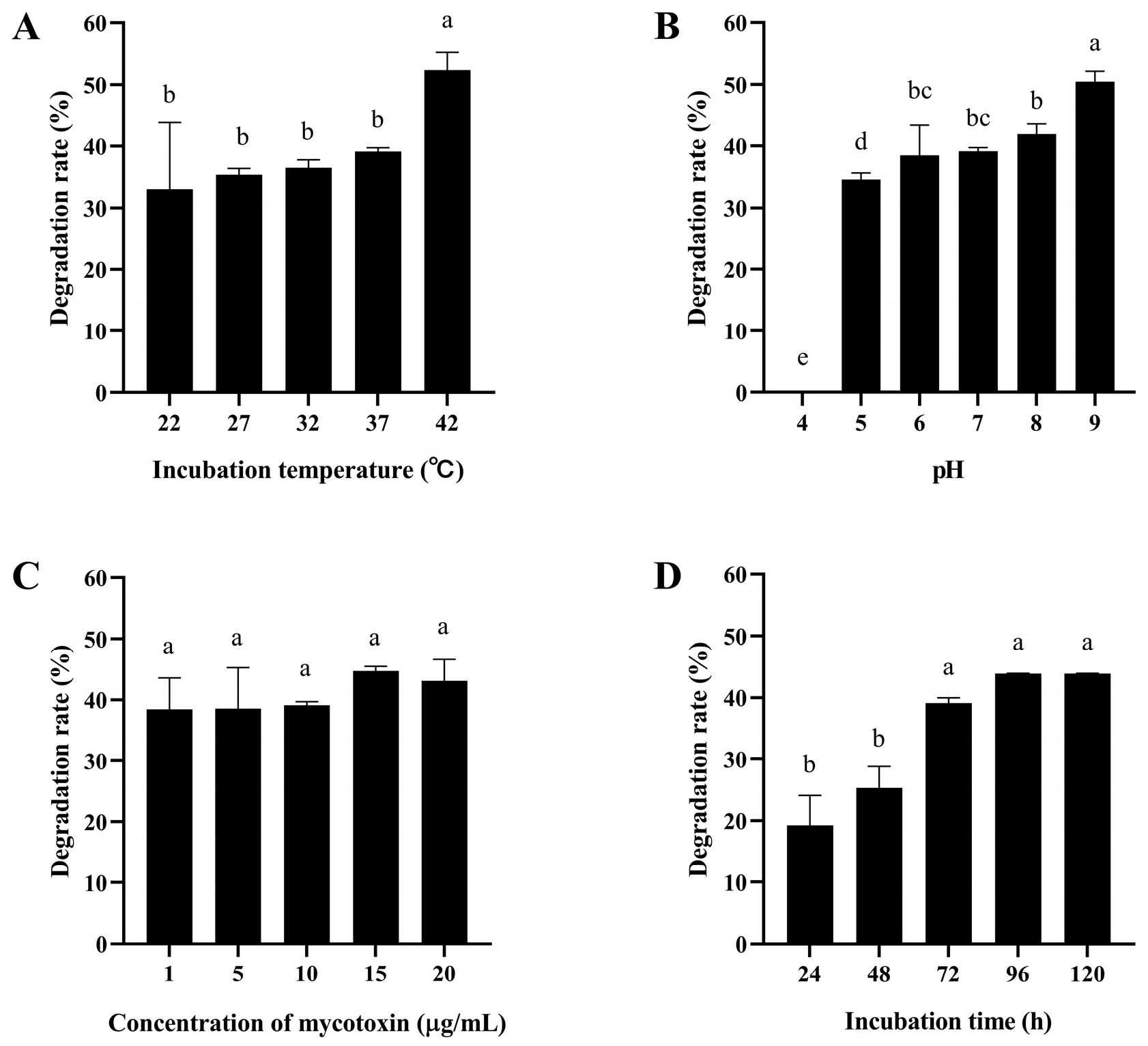
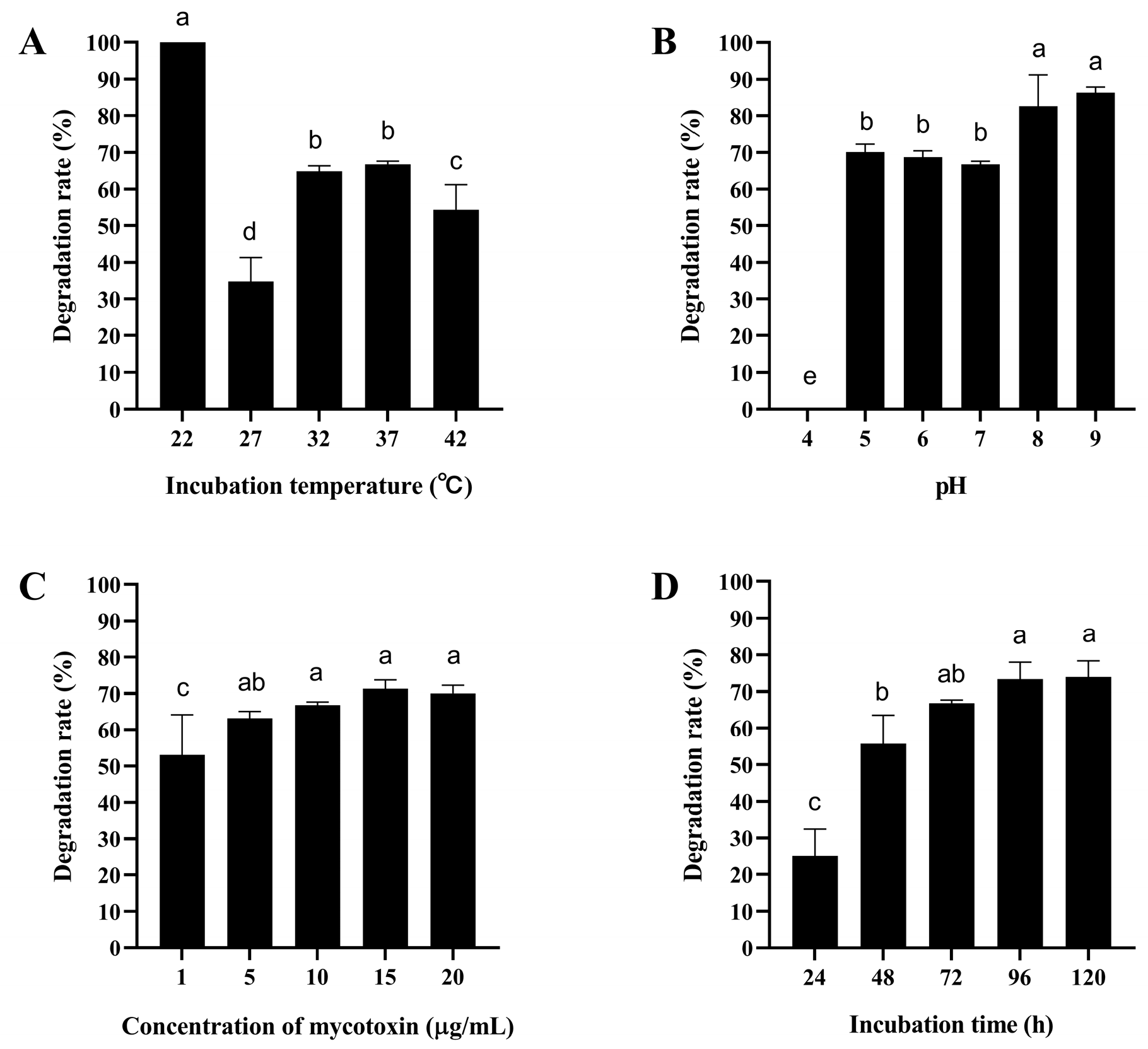
As shown in Figure 2A and Figure 3A, the degradation rate of mycotoxins by the ZJ-2019-1 strain increased with rising temperature. At 42 °C, the maximum degradation rate for AFB1 (10 mg/L) was 52.37%, while at 22 °C it reached 100% for ZEN. However, the activity of the ZJ-2019-1 strain was completely lost at pH 4.0. The degradation of both mycotoxins showed an increasing trend as pH values rose from 5.0 to 9.0, with this strain degrading 50.44% of AFB1 and 86.32% of ZEN at pH 9.0 (Figure 2B and Figure 3B). Moreover, there were no significant differences in the degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 at the concentrations ranging from 1–20 μg/mL (Figure 2C and Figure 3C). However, both mycotoxins exhibited a notable increase in degradation rates with the increase in incubation time; the maximum degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN reached 43.82% at 96 h, while that of ZEN reached 73.31%. There was no further significant increase in degradation observed even after an extended incubation time of 120 h (Figure 2D and Figure 3D).
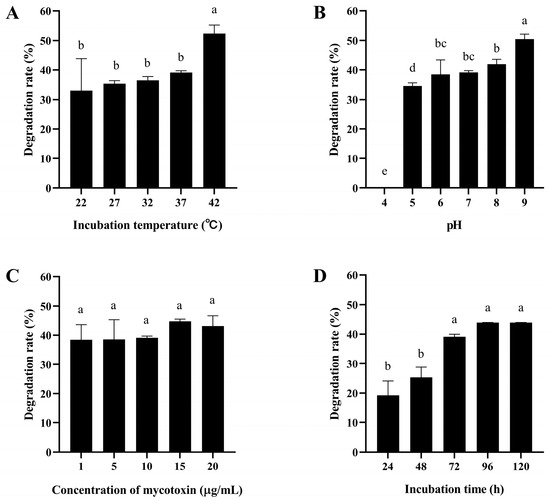
Figure 2.
Degradation of AFB1 by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 under different conditions. (A) Effect of temperature on AFB1 degradation. (B) Effect of pH on AFB1 degradation. (C) Effect of toxin concentration on AFB1 degradation. (D) Effect of incubation time on AFB1 degradation. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
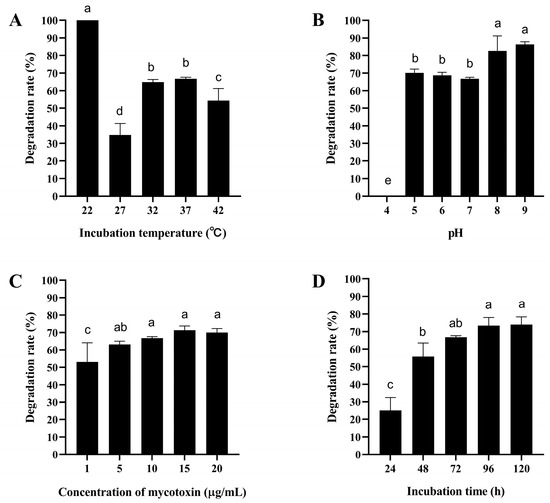
Figure 3.
Degradation of ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 under different conditions. (A) Effect of temperature on ZEN degradation. (B) Effect of pH on ZEN degradation. (C) Effect of toxin concentration on ZEN degradation. (D) Effect of incubation time on ZEN degradation. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Identification of Active Components of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
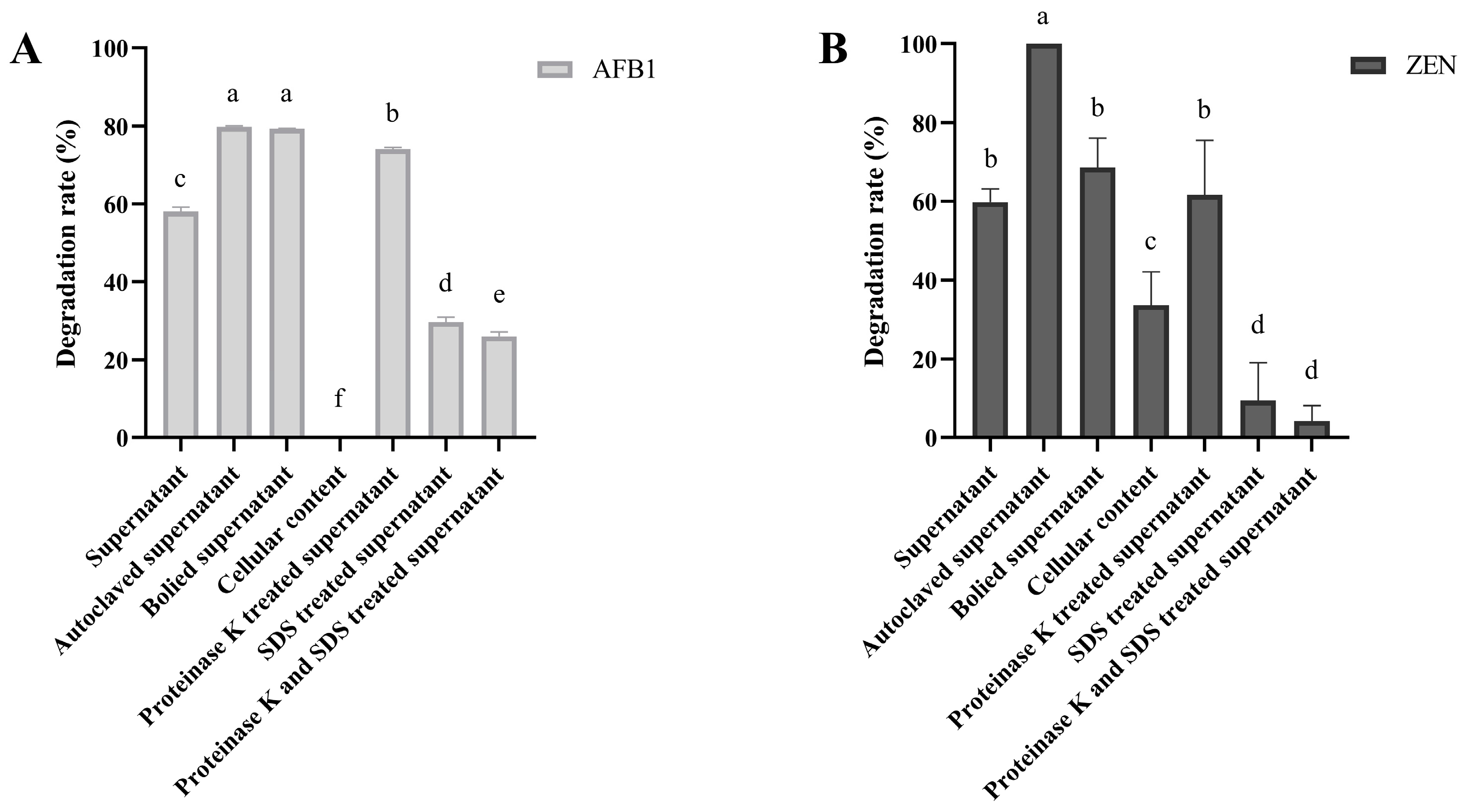
To determine the fraction responsible for degrading mycotoxins, we collected the supernatants and cellular contents of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, which were then subjected to treatments involving heating, SDS or protease K. Subsequently, these treated samples were incubated with 1 mg/L AFB1 or ZEN. As shown in Figure 4A, the degradation rate of AFB1 by the autoclaved and boiled supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 reached 79.85% and 79.34%, respectively, higher than that of the untreated supernatants (58.03%). However, no degradation of AFB1 was observed with the cellular contents of B. subtilis. Similarly, the degradation rate of ZEN by the autoclaved supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 reached 100%, which was superior to that of the boiled supernatants (68.53%), untreated supernatants (59.77%), and cellular contents (33.66%) (Figure 4B).
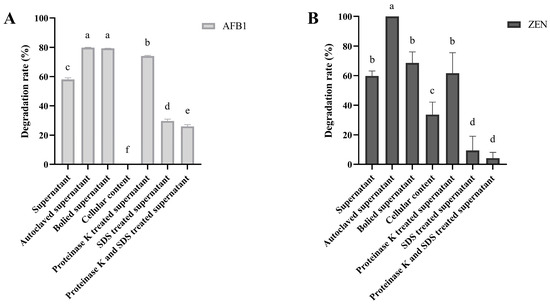
Figure 4.
Effects of different treatments of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 fractions on mycotoxin (1 mg/L) degradation. (A) Effects of B. subtilis fractions on AFB1 degradation. (B) Effects of B. subtilis fractions on ZEN degradation. The supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 were autoclaved or boiled. Additionally, the supernatants were treated with proteinase K, SDS, or both at 58 °C for 3 h. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
After treatment with protease K, the cell-free supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 exhibited enhanced degradation efficiency towards AFB1 (74.02%) and ZEN (61.64%) (Figure 4). However, after treatment with 1% SDS, the degradation capacity of the supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 decreased to 29.65% for AFB1 and 9.36% for ZEN. Similarly, co-treatment with proteinase K and 1% SDS resulted in a further reduction in degradation activity to 26.00% for AFB1 and 4.23% for ZEN.
3.4. Effects of Different Factors on AFB1 and ZEN Degradation by the Crude Enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1
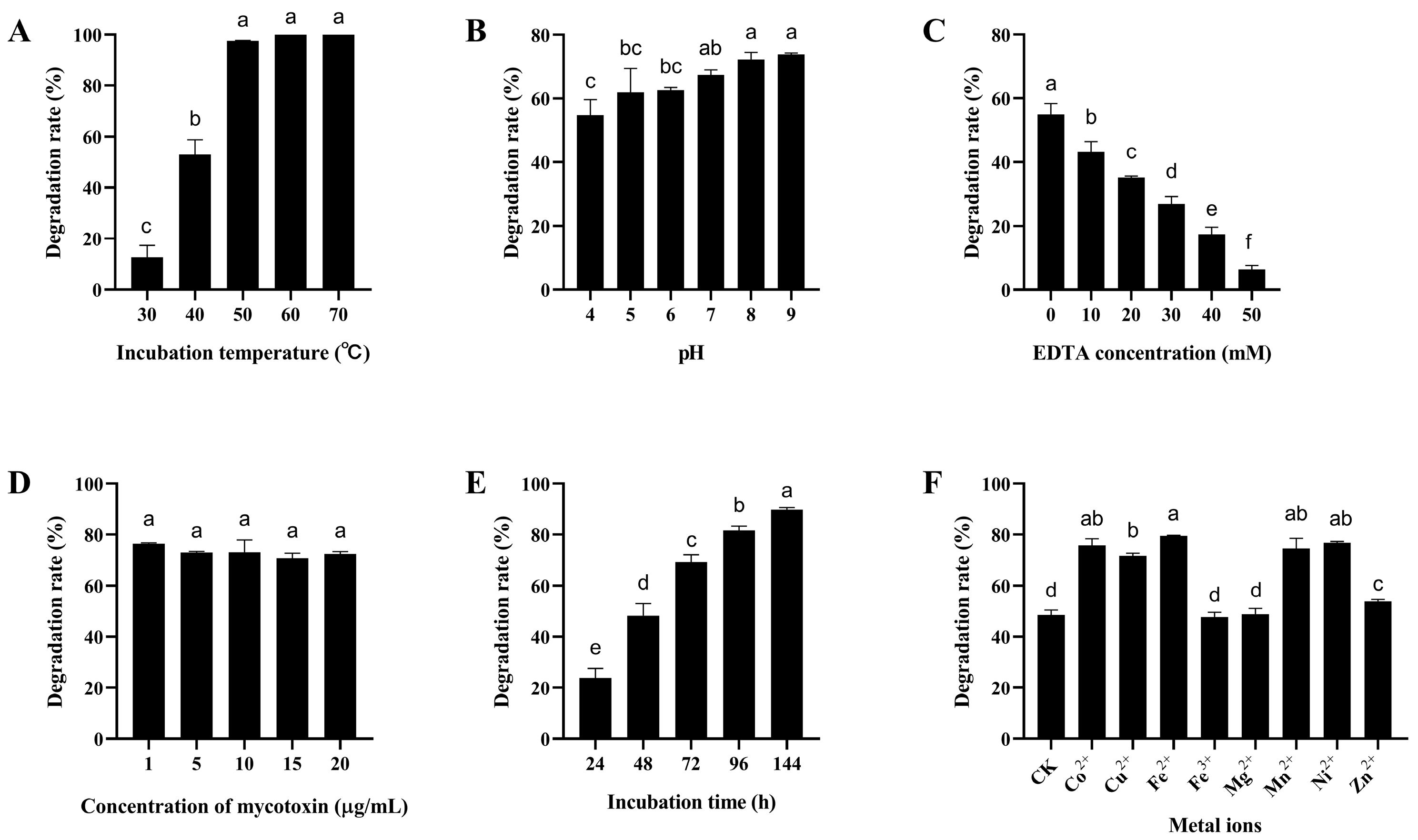
As shown in Figure 5A and Figure 6A, the degradation rate of mycotoxins by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 increased with temperature rising from 30 °C to 70 °C. The maximum degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN was 100% and 94.29%, respectively, at a temperature of 70 °C. The degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN by the crude enzymes increased as the pH values ranged from 4.0 to 9.0, with the highest degradation rates of 73.91% and 46.11%, respectively.
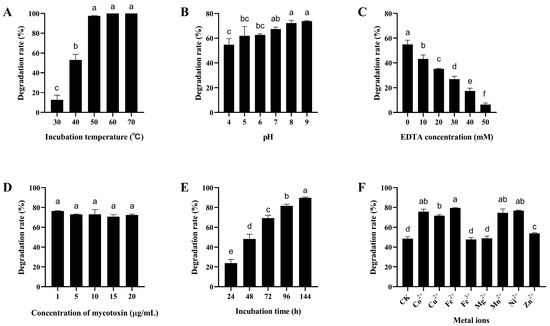
Figure 5.
Degradation of AFB1 by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 under different conditions. (A) Effect of different temperatures on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (B) Effect of pH on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (C) Effect of EDTA concentration on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (D) Effect of toxin concentration on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (E) Effect of incubation time on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (F) Effect of metal ions on AFB1 degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
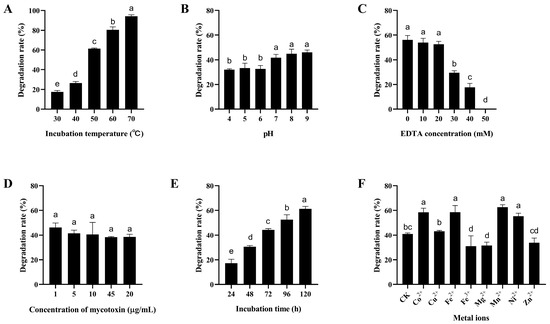
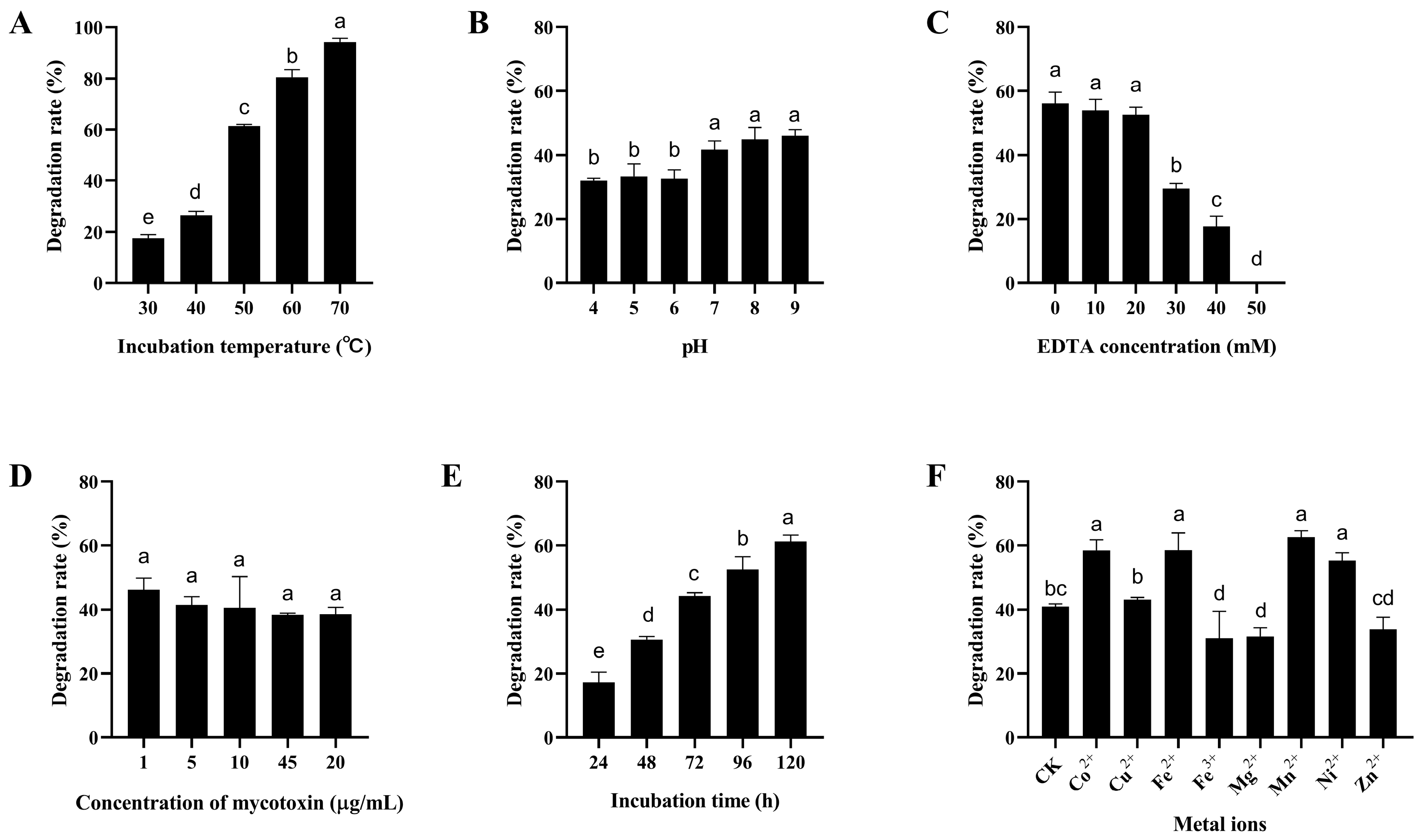
Figure 6.
Degradation of ZEN by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 under different conditions. (A) Effect of different temperatures on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (B) Effect of pH on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (C) Effect of EDTA concentration on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (D) Effect of mycotoxin concentration on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (E) Effect of incubation time on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. (F) Effect of metal ions on ZEN degradation by the crude enzymes of ZJ-2019-1. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
Some proteases may require EDTA as a co-factor for the degradation of mycotoxins [41]. The degradation rate of AFB1 by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 markedly decreased from 54.94% to 6.35% with an increase in EDTA concentration from 0 to 50 mM (Figure 5C). Similarly, the degradation rate of ZEN by the crude enzymes decreased from 56.12% to 0.00% as the EDTA concentration increased from 0 to 50 mM (Figure 6C).
To evaluate the impact of mycotoxin concentrations on degradation, different concentrations of AFB1 and ZEN (1, 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL) were added to the crude enzymes from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and incubated at 37 °C for 72 h. The results showed that different mycotoxin concentrations did not exert significant effects on the degradation of AFB1 and ZEN by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1; the maximum degradation rates of AFB1 or ZEN were 76.46% and 46.23% at a concentration of 1 µg/mL (Figure 5D and Figure 6D). The impact of different incubation time on mycotoxin degradation by crude enzymes from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 was also investigated. It was found that degradation rates of AFB1 and ZEN increased significantly with longer incubation time, reaching maximum degradation rates of 89.74% for AFB1 and 61.25% for ZEN at 144 h (Figure 5E and Figure 6E).
The effect of divalent metal ions on mycotoxin degradation by the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 was also assessed. As shown in Figure 5F, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, and Ni2+ exhibited significant enhancement in the activity of crude enzymes from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 for AFB1 degradation, resulting in a maximum degradation increase of 31.07%. Similarly, Co2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, and Ni2+ augmented the capability of the crude enzymes to degrade ZEN, whereas Fe3+ and Mg2+ inhibited ZEN degradation, with reduced degradation rates of 9.40% and 7.29%, respectively (Figure 6F).
3.5. Application of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 in Corn Gluten Meals
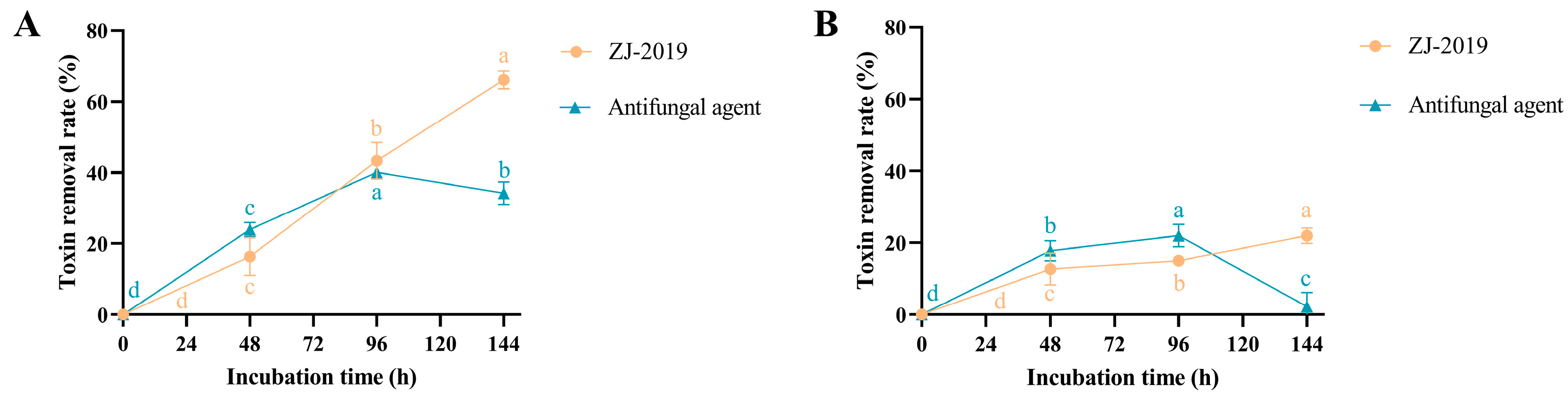
The ability of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 to degrade mycotoxins was further evaluated in moldy feed materials. As shown in Figure 7, the degradation efficiency of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 increased with prolonged incubation time when applied to moldy corn gluten meal. Within 144 h, B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 achieved the highest removal rates for AFB1 (66.08%) and ZEN (22.01%), higher than those of conventional antifungal agents (34.17% and 2.28%, respectively). The antifungal agent exhibited maximum removal rates for AFB1 (40.04%) and ZEN (21.98%) within 96 h.
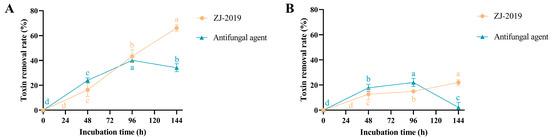
Figure 7.
Degradation of AFB1 (0.8 mg/kg) and ZEN (3 mg/kg) in corn gluten meal by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 and a mold remover (the antifungal agent). (A) Degradation of AFB1 in corn gluten meal. (B) Degradation of ZEN in corn gluten meal. Different letters indicate significant differences among the means according to Duncan’s test (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Both AFB1 and ZEN are the two most prevalent mycotoxins that contaminate food and animal feed, posing a serious threat to human and animal health. There are various biodegradation methods for mycotoxins. Microbial degradation is considered an attractive method for removing mycotoxins [42]. Xu [43] isolated the P. aeruginosa M-4 strain, which achieved a degradation rate of 90.57% for AFB1 in maize. Active substances from Pseudomonas strains found in seawater were capable of degrading AFB1 [44]. Both P. episeptica and P. fluorescens demonstrated the ability to degrade AFB1 [45]. Furthermore, a combination of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. bulgaricus, and L. acidophilus effectively inhibited the growth of A. flavus in silage while also degrading its toxic metabolites. Moreover, Rhodococcus species exhibited effective degradation of ZEN [46,47,48,49], with intracellular enzymes being the main active substances involved in degradation, resulting in a degradation rate of 90%. Acinetobacter calcinetoacetate isolated from the moldy-stained root mass of radix Daustellariae has also exhibited efficient ZEN degradation [50].
Currently, probiotic Bacillus species are extensively utilized as dietary supplements in food and animal feed to modulate the gut microbiota and improve health and immunity [51]. Furthermore, various Bacillus species, including B. subtilis, B. velez, B. schafferii, and B. amylolyticus have demonstrated the ability to degrade AFB1 and ZEN [52,53,54]. The primary bioactive substances are commonly found in bacterial fermentation supernatants. ZEN-phosphotransferase of B. subtilis Y816 [55] and CotA laccase of B. subtilis [56] exhibit potential in reducing ZEN toxicity. Additionally, BsDyP peroxidase from B. subtilis SCK6 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21/pG-Tf2 cells efficiently degrades ZEN and other mycotoxins [57]. Active substances of B. amylolytic FS-3 and B. amylolytic H6 were found to degrade ZEN, while the thioesterase from the H6 strain was able to detoxify ZEN and reduce its estrogen toxicity [58,59]. Additionally, extracellular enzymes produced by B. amylolyticus 7D3-2 effectively degraded ZEN [60], whereas Bacillus T-246 and B. pumilus T-420 removed ZEN through a combination of adsorption and degradation by extracellular enzymes [61]. In our study, B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 demonstrated the ability to simultaneously degrade AFB1 and ZEN while exhibiting greater thermal and alkaline stability (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 achieved a residual rate of 40.55% for 10 mg/L AFB1 and 48.75% for ZEN, which was lower than that observed in cells (Figure 1). The cell-free supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 showed superior efficacy in detoxifying both AFB1 and ZEN compared to the bacterial cells, suggesting that the fractions of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 responsible for degrading these mycotoxins may be secreted into the culture media. B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 appears to eliminate AFB1 by degradation and detoxify ZEN by degradation and adsorption. Similar findings were observed for AFB1 degradation by the culture supernatants (over 90%) of B. licheniformis CFR1, which exhibited higher efficiency than the cell lysates (12.26%) [29]. Notably, following thermal treatment in an autoclave at 121 °C for 15 min or boiling water at 100 °C for 3 h, the supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 promoted the degradation of AFB1 and ZEN (Figure 1 and Figure 4). This indicates that the fractions responsible for degrading AFB1 and ZEN from B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 may be actively secreted into the culture media, while demonstrating a remarkable temperature resistance ranging from 100 to 120 °C. In the previous study, it was found that the supernatants of Microbacterium proteolyticum B204 exhibited a remarkable AFB1 degradation capacity of 70% after being subjected to boiling water treatment at 100 °C for 20 min [35]. These findings suggest that the bacterial supernatants have exceptional thermal and pressure stability. Subsequent proteinase K treatment slightly decreased the degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN in the supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1. However, when treated with either SDS alone or a combination of proteinase K and SDS, there was a significant reduction in the ability of the supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 to degrade AFB1 and ZEN (Figure 2 and Figure 3), which is consistent with previous studies [57,62].
The crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 exhibited enhanced AFB1 and ZEN degradation activity at elevated temperatures, achieving degradation rates of 100% and 94.29%, respectively (Figure 5 and Figure 6). This suggests the potential application of these bacteria in food or feed processing [57]. Furthermore, the crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 demonstrated improved mycotoxin degradation within a pH range of 7.0–9.0 (Figure 5 and Figure 6), indicating that acidic conditions reduce the activity of crude enzymes in degrading AFB1 and ZEN. Previous studies have shown that certain metal ions, including CO2+, Fe2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+, can significantly enhance the mycotoxin degradation activity of bacteria and secreted enzymes; moreover, these ions may competitively or non-competitively promote or inhibit the activity of active enzymes in bacterial supernatants [61]. In this study, CO2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, and Ni2+ significantly enhanced the degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, suggesting their potential role as electron carriers in enzymatic reactions involved in degradation. Conversely, Fe3+ and Mg2+ exhibited inhibitory effects on mycotoxin degradation by crude enzymes of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 (Figure 6), consistent with previous findings [39,57]. Both Fe3+ and Mg2+ may act as inhibitors for the enzymatic system responsible for AFB1 and ZEN degradation. Furthermore, EDTA markedly attenuated the degradation rate of AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 within 72 h (Figure 5 and Figure 6). It has been demonstrated that the presence of EDTA can significantly inhibit the AFB1-degradation activity of recombinant laccase, potentially due to conformational changes in mycotoxin-degrading enzymes, leading to their deactivation or reduced affinity for mycotoxins [57,63]. In further studies, it is necessary to identify and evaluate the cytotoxicity of degradation products derived from AFB1 and ZEN by B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 towards animals.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 effectively degraded both AFB1 and ZEN simultaneously. The active components were primarily found in the supernatants of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1, which significantly enhanced mycotoxin degradation at high temperature (70 °C), alkaline conditions (pH 9.0), and in the presence of various metal ions (including Co2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, or Ni2+). The degradation efficiency of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 towards AFB1 and ZEN in raw feed materials surpassed that of commercially available mold removers on the market. The study highlights the potential of B. subtilis ZJ-2019-1 as a promising candidate for mycotoxin removal in food and animal feed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. (Jianwen Wu), X.W. and H.L.; methodology, Z.W.; software, J.W. (Jianwen Wu); validation, J.W. (Jianwen Wu), B.G. and W.A.; formal analysis, H.T.; investigation, B.H.; resources, J.W. (Jinquan Wang); data curation, C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W. (Jianwen Wu); writing—review and editing, J.W. (Jianwen Wu) and X.W.; visualization, J.W. (Jianwen Wu) and B.G.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, J.W. (Jinquan Wang); funding acquisition, X.W. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP) from the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), China (no. CAAS-IFR-ZDRW202302).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Čolović, R.; Puvača, N.; Cheli, F.; Avantaggiato, G.; Greco, D.; Đuragić, O.; Kos, J.; Pinotti, L. Decontamination of mycotoxin-contaminated feedstuffs and compound feed. Toxins 2019, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D. Understanding mycotoxin-induced illness: Part 1. Altern. Ther. Health. Med. 2022, 28, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, A.P. Mycotoxin illness: Recognition and management from functional medicine perspective. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 33, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Hajeb, P.; Ehsani, R.J. Application of ozone for degradation of mycotoxins in food: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1777–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Romvári, R.; Kovács, M. Individual and combined haematotoxic effects of fumonisin B(1) and T-2 mycotoxins in rabbits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, P.D.; Iaria, C.; Capparucci, F.; Arangia, A.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spanò, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Impact of mycotoxin contaminations on aquatic organisms: Toxic effect of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 mixture. Toxins 2022, 14, 518. [Google Scholar]
- Csenki, Z.; Garai, E.; Faisal, Z.; Csepregi, R.; Garai, K.; Sipos, D.K.; Szabó, I.; Kőszegi, T.; Czéh, Á.; Czömpöly, T.; et al. The individual and combined effects of ochratoxin A with citrinin and their metabolites (ochratoxin B, ochratoxin C, and dihydrocitrinone) on 2D/3D cell cultures, and zebrafish embryo models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Jiang, H.M.; Fang, J.; Tian, Y. Prevention and control technology on Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin. Food Ind. 2018, 39, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Hong, S.B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.J.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.O.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; et al. Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and other mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z. Effects of aflatoxin b1 on T-cell subsets and mRNA expression of cytokines in the intestine of broilers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6945–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devreese, M.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Overview of the most important mycotoxins for the pig and poultry husbandry. Vlaams Diergen. Tijds. 2013, 82, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pierron, A.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Oswald, I.P. Impact of mycotoxin on immune response and consequences for pig health. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Bai, H.; Chang, X.; Wu, Z.; Dong, W.; Ma, Q.; Yang, J. Aflatoxin B1-induced early developmental hepatotoxicity in larvae zebrafish. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Aflatoxin B1 induces liver injury by disturbing gut microbiota-bile acid-FXR axis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, H.; Yu, Y. Oxidative DNA damage and multi-organ pathologies in male mice subchronically treated with aflatoxin B1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, H.; Shim, J.Y.; Sayama, K.; Tsubura, A.; Zhu, B.T.; Shimoi, K. Characterization of the estrogenic activities of zearalenone and zeranol in vivo and in vitro. J. Steroid. Biochem. 2007, 103, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Fu, W.; Zhao, X.; Chang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; et al. Zearalenone disturbs the reproductive-immune axis in pigs: The role of gut microbial metabolites. Microbiome 2022, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.K.; King, E.H.; Bowers, S.D.; Ryan, P.; Walters, K.; Shappell, N.W. Reproductive performance of mares fed dietary zearalenone. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, F.; Dell’Aquila, M.E. Zearalenone and reproductive function in farm animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2570–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Ren, X.; Li, B.; Wang, S. Male reproductive toxicity of zearalenone-meta-analysis with mechanism review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Feng, N.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Bian, J. Zearalenone damages the male reproductive system of rats by destroying testicular focal adhesion. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgaru, C.V.; Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Taranu, I. Zearalenone and the immune response. Toxins 2021, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bódi, V.; Csikós, V.; Májer, T.; Tóth, A.; Dobolyi, Á.; Világi, I.; Varró, P. Zearalenone alters the excitability of rat neuronal networks after acute in vitro exposure. Neurotoxicology 2021, 86, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoutte, I.; Audenaert, K.; De, G.L. Biodegradation of mycotoxins: Tales from known and unexplored worlds. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Drouin, P.; Lepp, D.; Li, X.Z.; Zhu, H.; Castex, M.; Zhou, T. A novel microbial zearalenone transformation through phosphorylation. Toxins 2021, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.C.; Ao, X.; Lei, Y.P.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q.J. Bacillus subtilis ANSB01G culture alleviates oxidative stress and cell apoptosis induced by dietary zearalenone in first-parity gestation sows. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.N.; Peng, D.D.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.D.; Huang, J.H.; Liu, N. Optimization of fermentation conditions for degradation of AFB1 by Bacillus subtilis Q125 and preliminary exploration of active substance. J. Henan Univ. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 42, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Hahn, J.; Toth, S.; Nagy, I.; Kukolya, J. Mycotoxin-degradation profile of Rhodococcus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, A.; Bulat, T.; Wishah, R.; BoyacI, I.H. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and patulin by Enterococcus faecium strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P. Investigation of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain 3JW1 on preventing and reducing aflatoxin contaminations in peanuts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N. Screening of Zearalenone Detoxifying Bacteria, Study and Application of Detoxifying Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, M.X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Ding, Q.; Cai, J. In vitro degradation of zearalenone by culture supernatant of Bacillus subtilis. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Gu, M.Y.; Chu, M.; Zhu, J.; Ghenijan, O.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.D. Identification and degradation characteristics of a zearalenone degrading bacterium. Microbiol. China 2021, 48, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Isolation and aflatoxin B1-degradation characteristics of a Microbacterium proteolyticum B204 strain from bovine faeces. Toxins 2022, 14, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, C.; Yu, Y.; Han, J.; Hu, J.; He, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Mohamed, S.R.; Dawood, D.H.; Wang, G.; et al. Isolation, characterization, and application of Clostridium sporogenes F39 to degrade zearalenone under anaerobic conditions. Foods 2022, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhong, L.; Lu, Z.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F. Characterization of deoxynivalenol detoxification by Lactobacillus paracasei LHZ-1 isolated from yogurt. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Kim, W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, C.R.; Chung, S.; Lee, C. The occurrence of zearalenone in South Korean feedstuffs between 2009 and 2016. Toxins 2017, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Sun, X.L. Isolation and mechanistic characterization of a novel zearalenone-degrading enzyme. Foods 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Lan, L.; Qi, G.; Hong, W.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xiu, W.; Zhi, S. Determination of Zearalenone in Feed-High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method with Immunoaffinity Column Clean-Up; SPC: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, W.T.; Liu, Z.H.; Xue, X.L.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Isolation and identification of a Cytobacillus oceanisediminis strain with ochratoxin A detoxification ability. Food Control 2023, 151, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.J.; Fang, Q.A.; Liao, Z.L.; Xu, C.W.; Liang, Z.B.; Liu, T.; Zhong, Q.P.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.; Wang, J. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by a potential probiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens WF2020. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 91091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Dong, H.Y.; Liu, C.X.; Lou, H.W.; Zhao, R.Y. Efficient aflatoxin B1 degradation by a novel isolate, Pseudomonas aeruginosa M-4. Food Control 2023, 149, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.N.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, C.S.; Bi, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, B. Screening and identification of aflatoxin B1-degrading strains. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2018, 39, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Sidu, S.; Tlou, M.G.; Mavumengwana, V. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by liquid cultures and lysates of three bacterial strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourama, H.; Bullerman, L.B. Inhibition of growth and aflatoxin production of Aspergillus flavus by Lactobacillus species. J. Food Prot. 1995, 58, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krifaton, C.; Kriszt, B.; Risa, A.; Szoboszlay, S.; Cserhati, M.; Harkai, P.; Eldridge, M.; Wang, J.; Kukolya, J. Application of a yeast estrogen reporter system for screening zearalenone degrading microbes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, E.; Risa, A.; Varga, E.; Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Urbanyi, B.; Csenki, Z. Evaluation of the multimycotoxin-degrading efficiency of Rhodococcus erythropolis NI1 strain with the three-step zebrafish microinjection method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriszt, R.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Kukolya, J.; Czeh, Á.; Feher-toth, S.; Torok, L.; Szoke, Z.; et al. A new zearalenone biodegradation strategy using non-pathogenic Rhodococcus pyridinivorans K408 strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Yuan, Q.S.; Zhou, T.; Guo, L.P.; Jiang, W.K.; Zhou, S.H.; Yang, C.G.; Kang, C.Z. Screening of zearalenone-degrading bacteria and analysis of degradation conditions. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021, 46, 5240–5246. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics regulate gut microbiota: An effective method to improve immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Cai, G.L.; Zhu, D.W.; Wang, L.L.; Lu, J. Isolaion and identification of strain degrading aflatoxin B1 and its application in peanut meal. China Oils Fats 2015, 40, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.R.; Vipin, A.V.; Hariprasad, P.; Anu, A.K.A.; Venkateswaran, G. Biological detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by Bacillus licheniformis CFR1. Food Control 2017, 71, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Mao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Deng, Y.; Yang, H.Q.; Zhang, Z.M. Isolation and identification of aflatoxin B1 degrading bacteria and optimization of culture conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 44, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.B.; Zheng, H.C.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Shu, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Song, H.; Ma, Y.H. New Biotransformation mode of zearalenone identified in Bacillus subtilis Y816 revealing a novel ZEN conjugate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7409–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Bai, Y.G.; Huang, H.Q.; Tu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Luo, H.Y.; Yao, B.; Su, X.Y. Degradation of aflatoxin B1 and Zearalenone by bacterial and fungal laccases in presence of structurally defined chemicals and complex natural mediators. Toxins 2019, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Su, X.Y.; Tu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.G.; Yao, B.; Luo, H.Y.; et al. Enzymatic degradation of multiple major mycotoxins by dye-decolorizing peroxidase from Bacillus subtilis. Toxins 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Liu, H.J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Sun, C.P. Isolation, identification and preliminary application of zearalenone-degrading bacterium under acidic condition. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2018, 26, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Adegoke, T.V.; Yang, B.; Tian, X.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Si, P.; Li, R.; Xing, F. Simultaneous degradation of aflatoxin B and zearalenone by porin and peroxiredoxin enzymes cloned from Acinetobacter nosocomialis Y1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.T.; Xu, S.J.; Hu, X.D.; Xu, L.M.; Shi, J.R.; Gu, Z.X.; Xu, J.H. Isolation, identification and its degradation characteristics of zearalenone-degrading bacteria. J. Chinese Cereals Oils Assoc. 2018, 33, 113–119 and 126. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, C.C.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X.L. Screening of Bacillus being able to degrade zearalenone. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2015, 23, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z. Effect of ions and other compatible solutes on enzyme activity, and its implication for biocatalysis using ionic liquids. J. Mol. Catal. 2005, 37, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, D.; Wen, J.; Lu, G.; Li, T.; Long, M. Isolation, purification, and characterization of a laccase-degrading aflatoxin B1 from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B10. Toxins 2022, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).