Abstract
Black soldier fly (BSF) larvae are an increasingly popular source of protein in the food industry, and they are showing great potential as a sustainable alternative to traditional protein sources. However, to fully utilize the potential of insect protein as food, it is important to improve their functional characteristics. The purpose of this study was to thoroughly examine the influence of alkaline extraction and isoelectric precipitation methods assisted by salting-in (NaCl) and salting-out ((NH4)2SO4) techniques on the functional properties of BSF larvae proteins. The physicochemical and techno−functional properties of the proteins were determined. The addition of (NH4)2SO4 significantly (p < 0.05) influenced the solubility of protein, particularly at pH 2, suggesting its potential applicability in acidic food systems. Surface hydrophobicity was modulated by salt treatment, with salting-out methods reducing hydrophobicity and affecting protein functionality. The correlation analysis demonstrated a significant positive relationship (p < 0.05) between the various functional properties, emphasizing their interconnected nature. Foam capacity and foam stability showed a positive relationship with protein solubility at pH 4 (r = 0.88, p < 0.05; r = 0.74, p < 0.01, respectively). These findings imply the potential use of BSF larvae proteins in food formulations, especially considering the positive correlations observed between emulsification properties, solubility, and surface hydrophobicity. The identified correlations lay the groundwork for further exploration of BSF larvae proteins as sustainable functional ingredients in food applications, aligning with growing interest in alternative protein sources for the food industry.
1. Introduction
Given environmental concerns and a rising global population, it is crucial to develop alternative methods for a reliable protein supply [1,2]. Edible insects have emerged as a significant protein replacement with a notable protein conversion ratio among these alternatives [3]. Extensive research has shown that the consumption of edible insects is attributed to their nutritional value [4]. Enhancing education and exposure could potentially boost the acceptance of edible insects, but their impact is constrained by food neophobia [5,6]. The inclusion of edible insects in traditional food might also increase nutritional value [7,8]. The unappealing appearance and negative perception of insects hinder their promotion as a food source in Western society, which is a significant obstacle to overcome [9]. Due to prejudice, some researchers have explored ways to alter the appearance of edible insects in order to eliminate negative perceptions associated with their consumption [10]. Consequently, there is a need to improve the functionality and benefits of edible-derived proteins such as foaming capacity, foaming ability, emulsifying capacity, emulsion stability, water–oil-binding capacities, and surface characteristics [9,11,12] to promote their consumption as food ingredients.
Extensive research has explored the optimal conditions for protein extraction from diverse sources with the goal of enhancing the functional attributes of the protein extracted [13]. However, there is still a scarcity of information specifically pertaining to edible insects, with most of the available data focusing on mealworms [10,14]. Among the edible species, the black soldier fly (BSF) appears to be a highly promising insect for the commercial production of proteins, as it offers numerous advantages both for humans and the environment. Although various methods for isolating protein from insects have been documented in the existing literature [10,15], a report by [12] revealed that the value of the extracts is significantly impacted by the method of extraction.
Numerous factors can influence the extraction of proteins; for example, the addition of salts is a viable approach for controlling the ionic strength of proteins [16]. To ensure the successful utilization of insects or a specific insect as a substitute for conventional protein sources or as an ingredient in food formulation, it is crucial to effectively extract the protein and assess its functional properties. The protein extraction process can be optimized to yield a protein isolate that boasts numerous benefits when utilized in the food sector.
Alkaline extraction combined with isoelectric/acid precipitation is a highly recommended method for protein extraction due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness [12]. This technique involves solubilizing proteins in an environment with a high pH and then precipitating them by adjusting the pH to their isoelectric point [14]. Furthermore, salt may be incorporated to facilitate alkaline extraction and acid precipitation, thereby enhancing the extraction yield and purifying proteins. Salt-assisted extraction positively affects physicochemical properties, which can influence food production processes [17,18]. Lately, there has been renewed interest in using salts to assist the extraction of insect proteins. Up to now, far too little attention has been paid to the effects of salt-assisted extraction on the functional properties of BSF larvae proteins. In this study, NaCl and (NH4)2SO4 were employed to facilitate alkaline and acid extraction, respectively. In this research, sodium chloride (NaCl) and ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 were employed to facilitate the alkaline extraction and isoelectric precipitation, respectively.
Therefore, this study aimed to characterize how salt treatment affects the functional properties of BSF larvae isolates, offering a foundation for the additional investigation of BSF isolates for food and nutraceutical uses, along with an exploration of variations between the measured components of the isolates. This research provides a basis for the development of BSF larvae protein extracts that possess specific physicochemical and techno-functional properties and serves as a guide for their potential application as a nutritional supplement or functional ingredient.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
The larval stage of black soldier flies (BSF), aged ~14 days, was obtained from MaltEnto in Epping Cape Town, South Africa. The BSF larvae were bred using spent brewers’ grain as their food source. Unless stated otherwise, all chemical substances utilized in the study were of analytical grade. The following chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Johannesburg, South Africa); petroleum ether, hexane, isopropanol, bovine serum albumin (BSA), 1 M phosphate buffer, 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulphonate (ANS), Tris-Gly buffer (0.086 M Tris, 0.09 M glycine, 4 mM EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), pH 8, containing 8 M urea), Ellman’s reagent (5,5′-dithio-bis-2-nitrobenzoic acid), 2-mercaptoethanol, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Hydrochloric acid, ammonium sulfate, sodium chloride, and sodium hydroxide were acquired from Science World (Cape Town, South Africa). The storage conditions for the prepared solutions and reagents were optimized to prevent contamination or degradation. Deionized water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ.cm was used to prepare all solutions, which was acquired using the Milli-Q system (Gradient model, Millipore, Merck Life Science, Modderfontein, South Africa).
2.2. Preparation of the Insect Flour
The BSF flour was prepared according to the method of [19,20] with slight modifications. The larvae were prepared by blanching for 2 min at 100 °C. The blanched larvae were stored in a blast freezer at −80 °C (NuAire Ultra-Low Freezer NU-9483E, NuAire Limited, Plymouth, MN, USA) and stored until further processing. The objective of the process was to achieve a stable product by grinding the frozen insects using a laboratory blender and then freeze-drying them under a vacuum of 750 mTorr for three days. The subsequent step involved defatting the BSF sample, which involved stirring one gram of the ground sample with five milliliters of a 3:2 (v/v) mixture of hexane and isopropanol for two hours on a magnetic stirrer, decanting the solvent–fat mixture after the sedimentation of the solids, and repeating the procedure twice. The evaporation process was employed to eliminate the residual solvent over a period of 12 h within a fume hood. The powder was obtained by grinding the remaining defatted sample in a mortar and pestle until it became finely ground. The next step involved sifting the powder through a 500 μm-aperture-size stainless-steel sieve to separate the integument, resulting in the production of defatted BSF larvae flour.
2.3. Preparation of the Protein Isolates
Four different methods were used to prepare BSF larvae concentrate (see Figure 1). The salt extraction isolates were prepared in accordance with the method of [14] with modifications. The previously described alkaline–acid extraction (AAF) method by [21] was employed with some adjustments.
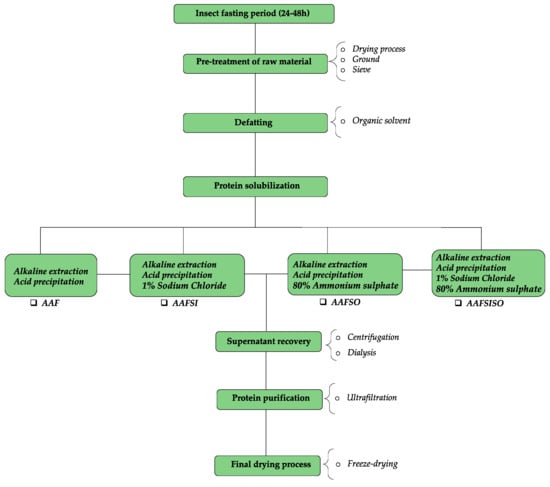
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram outlining the process of isolating protein from black soldier fly larvae.
2.3.1. Alkaline–Acid Extraction Followed by Ultrafiltration (AAF)
First, the defatted BSF larvae flour was combined with an equal amount of Milli-Q water at a ratio of 1:10 (w/v). Then, the pH was raised to 10 using a 1 M NaOH solution. The mixture was stirred for 30 min at 60 °C ± 1.0 and then allowed to cool to room temperature before undergoing centrifugation (Thermo Electron Corporation, Johannesburg, South Africa) at 25 °C and 10,000× g for 30 min. The pH of the supernatant was adjusted to 4.5 with 1 M HCl, and the suspension was left at 4 °C overnight to facilitate protein precipitation. The centrifugation process was used to separate the precipitate, which was then resuspended in 250 mL of water and its pH was adjusted to 7.0 using 1 M NaOH. The water–soluble isolate was obtained after centrifugation, and a 200 mL solution was subjected to ultrafiltration using a 3 kDa nominal molecular mass cut-off membrane in an Amicon ultrafiltration cell (8400, Amicon, Beverly, MA, USA). The retentate underwent the process of freeze-drying and was then preserved at a temperature of −18 °C for subsequent examination.
2.3.2. The Salting-In Extraction (AAFSI)
This method resembles the AAF method but differs by incorporating 1% NaCl (w/v) into the NaOH solution to improve protein solubility. This approach has been previously described in the literature by [11].
2.3.3. The Salting-Out Extraction (AAFSO)
This method employs the AAF process and further incorporates the addition of 80% (NH4)2SO4 (w/v) to the supernatant to improve protein precipitation, as described in [22].
2.3.4. The Salting-In/Out Extraction (AAFSISO)
The salting-in/out extraction process combined both salting-in and salting-out techniques. In this method, to enhance protein solubility, 1% (w/v) of NaCl was incorporated into the NaOH solution. Furthermore, 80% (w/v) of (NH4)2SO4 was added to the supernatant to facilitate protein precipitation.
2.4. Techno-Functional and Physicochemical Analyses
2.4.1. Protein Solubility
The solubility of the protein concentrates was evaluated using an adapted method based on a previously reported procedure [23]. Specifically, 400 mg of each sample was suspended in 20 mL of phosphate buffer with pH ranging from 2 to 10. The supernatant was subsequently filtered using Whatman No. 1 filter paper (Separation Scientific SA (Pty) Ltd., Cape Town, South Africa), and the protein content of the supernatant, along with the soluble protein content, was assessed using a commercial kit (DC Protein Assay, Bio-Rad Laboratories Ltd., Johannesburg, South Africa). BSA from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, served as the standard for calibration. The solubility of proteins was determined as the proportion of soluble protein in the supernatant to the total protein added to the mixture and is expressed as a percentage as follows:
2.4.2. Surface Hydrophobicity
Surface hydrophobicity was evaluated using a well-established method outlined in [24]. In summary, a range of protein solutions with concentrations between 0.1 and 0.5 mg/mL were prepared in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at a pH of 7.0. Following centrifugation at 3000× g for 20 min at 20 °C, the concentration of protein in the supernatant was assessed using the Bradford method, with BSA serving as the protein standard (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). A volume of 2 mL from each solution was combined with 10 μL of ANS (0.008 M), vortexed thoroughly, and then incubated for 15 min in darkness. The fluorescence intensity was measured at 390 nm (excitation wavelength) and 480 nm (emission wavelength) using an Infinite 200 PRO spectrofluorometer (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The degree of hydrophobicity of the protein surface was measured using linear regression between the fluorescence intensity and protein concentration.
2.4.3. Bulk Density
The method described by [25] was adopted with certain adjustments. Initially, a sample of 5 g was placed into a 50 mL cylinder that had been pre-weighed (W1). The sample was subsequently compressed by tapping until its volume stabilized. Afterward, the cylinder was re-weighed (W2), and the new volume (V1) and density (g/mL) were calculated using the given formula.
2.4.4. Water- and Oil-Binding Capacity
The water-binding capacity (WBC) of the protein concentrates was determined using a modified version of the method described by [26,27]. Briefly, in a pre-weighed centrifuge tube (Separation Scientific SA (Pty) Ltd., Cape Town, South Africa), a sample (0.5 g) was mixed with Milli-Q water (2.5 mL) at 25 °C. The tube was then thoroughly mixed using the Vor-Tex-Genie 2 device (manufactured by Scientific Industry Inc., Bohemia, NY, USA) for 2 min, followed by centrifugation for 10 min at 3000× g. Whatman No. 1 filter paper was utilized to invert the tube and place it upside down for a period of one hour before it was measured, with the water having been previously removed from the tube. The weights of the residual material and centrifuge tube were recorded, and the white blood cell count of the sample was calculated:
The mass of the centrifuge tube and protein with bound water (W2) was determined, as well as the weight of the centrifuge tube and protein without water (W1). The weight of the protein sample based on dry matter was referred to as W0. The oil-binding capacity (OBC) was determined by replacing Milli-Q water with commercial sunflower oil in the experimental procedure. The mixing step was performed for 2 min, and the process for calculating the OBC was identical to the WBC, with the exception of one step. In both methods, the OBC was determined in the same manner as WBC.
2.4.5. Foaming Capacity and Stability
The method used to evaluate the foaming properties of the protein concentrates was a modified version of one previously published from [28,29]. Protein concentrates were combined with 5% Milli-Q water and centrifuged at 10,000× g for 15 min. Then, 20 mL of the resulting supernatant was subjected to high-shear homogenization using a Polytron PT 2500E (Thermo Fisher, Cape Town, South Africa) at 16,000× g for 3 min. After homogenizing the mixture, it was transferred to a 50 mL graduated cylinder, and the total volume was measured at 0 and 30 min post-homogenization to evaluate the stability of the foam. Foaming stability and foam capacity was determined using the following formulae:
where V0 (mL) is a foam volume at 0 min, V1 (mL) is a foam volume at 30 min, and V is the initial volume of the mixture before foaming.
2.4.6. Emulsifying Properties
The sample was diluted with distilled water at a concentration of 5% w/v and spun at 9000× g for 15 min using a centrifuge (Thermo Electron Corporation, Johannesburg, South Africa). The resulting supernatant was combined with sunflower oil in a 1:1 volume ratio and homogenized at 18,000× g for 1 min using a Polytron PT 2500E homogenizer. Samples of the emulsion were centrifuged at 3000× g for 5 min, and the volume of each layer was measured using a 50 mL graduated tube (Separation Scientific SA (Pty) Ltd., Cape Town, South Africa). To determine the emulsifying capacity, the following formula was used:
The emulsion was heated in a water bath at 80 °C for 30 min in order to determine its stability values. The formula used to calculate the stability of the emulsion is as follows:
where V—total volume of tube contents, Vel—volume of the emulsified layer, and V30—volume of the emulsified layer after heating.
2.4.7. Data Analysis
All data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) to assess whether the various treatments resulted in statistically significant differences across different variables. Through the implementation of MANOVA, we effectively managed Type I error risk in contrast to conducting numerous individual univariate ANOVAs. This statistical method considers the cumulative effect of all dependent variables, thereby preserving the overall Type I error rate. To assess the significance of differences in individual means, Duncan’s multiple comparison post hoc test was conducted. The test was utilized to determine whether any observed differences were statistically significant at a p-value of less than 0.05. Duncan’s test offers a systematic approach to evaluate group means while simultaneously controlling for the family-wise error rate. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 29.0 for Windows®, with a significance level set at p < 0.05. Correlation coefficients among the physicochemical and functional parameters were computed by means of Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility of the Proteins
Protein solubility is a crucial factor that influences various functional properties, making it a critical determinant of protein functionality in the food-processing industry. The impact of pH and ionic strength on the protein isolates derived from BSF larvae was investigated, and the findings are illustrated in Figure 2. The solubility of the BSF larvae proteins followed a characteristic U-shaped curve within the examined pH range [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], indicating a substantial dependence on pH. The solubility of the AAFSO and AAFSISO proteins was significantly (p < 0.05) greater than that of the AAF and AAFSI proteins at pH 4–8 (Figure 2). The greatest levels of solubility were recorded at pH 2 (89% for AAFSISO) and pH 10 (85.21% for AAFSO), which were likely due to the attainment of the pI of protein bonds. These solubility patterns were consistent with those reported in previous studies [15,21,25]. Additionally, the results revealed that the BSF larvae isolates demonstrated remarkably enhanced solubility results at pH 2 compared to pH 8 and 10, with the exception of the AAFSO protein group. This finding aligns with prior research that reported enhanced Tenebrio molitor protein solubility at pH 2 compared to pH 10 [30].
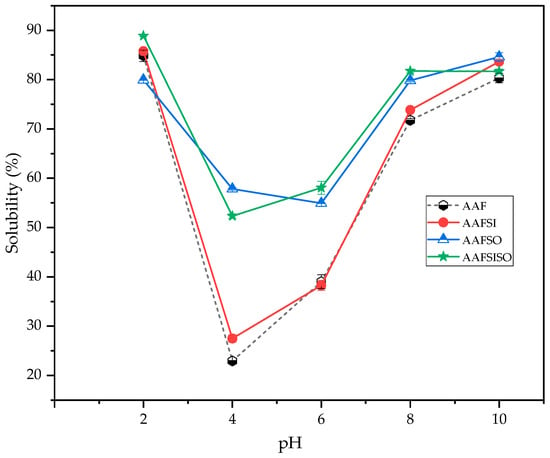
Figure 2.
Impact of extraction methods on solubility of black soldier fly larvae isolates obtained by AAF (alkaline–acid extraction—black pentagon), AAFSI (salting-in technique—red circle), AAFSO (salting-out technique—blue triangle), and AAFSISO (salting-in and out technique—green stars). Error bars show standard deviation.
According to our research findings, protein solubility at weakly acidic, alkaline, and neutral pH levels is a crucial aspect for industrial applications. Our BSF larvae meet these criteria and can be utilized in acidic food environments, including nutrition and sports drinks, as well as acidified sauces. The solubility of insect proteins may vary depending on their individual characteristics, and some proteins may aggregate and precipitate, while others may remain soluble. Our results show that both AAF and AAFSI had the lowest solubility at pH 4, while AAFSISO had the highest solubility at pH 2, which may be related to surface hydrophobicity, which is an important factor affecting solubility (Table 1).

Table 1.
Effect of extraction methods on surface hydrophobicity and bulk density of black soldier fly larvae protein isolates.
The addition of salt and the presence of ligands can influence protein solubility, serving are extrinsic factors that impact protein solubility [31]. The findings of the study suggest that the high concentration of (NH4)2SO4 can preserve the structure of proteins, leading to improved solubility [32]. No notable difference (p > 0.05) in the solubility was noted when NaCl was added to the solution at pH 2. This could be attributed to the proteins being surrounded by salt counter-ions, which neutralize surface charges and either decrease or increase electrostatic interactions between protein molecules [33]. The literature does not contain information on the protein solubility profile of BSF larvae protein extracts via salt treatment. These results indicate that both salting-in and salting-out methods can be employed to extract insect proteins. The efficacy of these methods is contingent upon the extent to which they have been optimized for the specific extraction process, as well as the degree to which the method of extraction conforms to the unique attributes of the protein under investigation, thereby ensuring the efficient and effective isolation of the protein while simultaneously preserving its integrity and functionality. These techniques are of great importance in the creation of sustainable protein sources and contribute significantly to the field of alternative protein research. The following section will explore the hydrophobic nature of protein surfaces and how the overall structure of a protein impacts the arrangement of packaging.
3.2. Surface Hydrophobicity and Bulk Density
Surface hydrophobicity is essential because it impacts the functional characteristics of a protein’s surface, including properties like foaming, as well as interactions with lipids and other proteins [24,27,34]. Table 1 shows the changes in the surface hydrophobicity of the various BSF larvae protein isolates. It is evident that salt treatment has a substantial influence (p < 0.05) on the surface hydrophobicity when compared with the untreated sample (AAF). Moreover, there were significant differences between AAF and AAFSI (1056.41 and 1021.37, respectively), which were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than those of the salting-out proteins (Table 1).
During alkaline extraction and acid precipitation, proteins may partially unfold, exposing more hydrophobic residues on the protein surface and increasing total hydrophobicity [35]. The surface hydrophobicity of AAFSO and AAFSISO was discovered to be nearer to the reported values for whey protein (468.0); both isolates had a higher value than whey protein [36]. This is attributed to partial denaturation and subsequent aggregation of hydrophobic groups, which is consistent with previous observations [37]. The higher surface hydrophobicity may result in enhanced protein functionality due to changes in interfacial or surface tension. According to [14], protein hydrophobicity increases as a result of the exposure of hydrophobic groups and regions enclosed within the molecules to the more polar surrounding environment, due to protein denaturation to a certain extent. On the other hand, a high concentration of salt can enhance surface hydrophobicity owing to the salting-out mechanism, which breaks the hydration layer on the surface and disrupts the charge balance of protein molecules. One study [38] found that surface hydrophobicity increased with increased solubility when working with soy protein isolates. This suggests that aggregating proteins are more hydrophobic and have buried hydrophobic zones inside their structure, resulting in soluble aggregates with low surface hydrophobicity. These findings may be limited by the concentration of salt ions and cannot promote competition with protein molecules in binding with water molecules, leading to aggregation of the protein and ultimately increased hydrophobicity. These findings could explain the improved solubility of salted-out proteins [12] as shown in Figure 2.
Bulk density is a crucial property employed to characterize protein products, and it holds substantial significance for both economic and functional reasons [39]. However, there were notable variations in bulk density among the BSF larval isolates, with the exception of AAF and AAFSO, as shown in Table 1. The bulk density of AAF was 1.23 g/mL, while the salt-treated isolates had values of 0.99 g/mL (AAFSI), 1.15 g/mL (AAFSO), and 1.52 g/mL (AAFSISO), respectively. Among the concentrates, AAFSI had a significantly (p < 0.05) lower bulk density than the salt-extracted concentrate. Furthermore, the bulk density of AAFSISO was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than that of AAFSO, which may be attributed to the finer particle size of the salt. What is interesting is that the addition of NaCl significantly decreased the bulk density of the BSF larvae protein, dropping from 1.23 mg/L to 0.99 mg/L, while the addition of ammonium sulfate resulted in a significant increase in bulk density (Table 1). One possible explanation could be that NaCl increased the solubility of the BSF larvae proteins, leading to a more dispersed or diluted protein solution with a lower bulk density.
The reduction in protein bulk density is attributed to the modification of protein structure [40]. Proteins with low bulk density are advantageous for transportation and distribution, as they are easier to transport and distribute [41]. These findings are consistent with that of [42], who measured the bulk density of protein concentrates prepared from Hermetia illucens, Macrotermes subhylanus, and Gonimbrasia belina, ranging from 0.51 to 0.64 g/mL. In the current study, the NaCl extraction concentrate displayed a similar value, whereas the ammonium sulfate extraction concentrate had a higher value than that reported by [42], who reported 0.57 g/mL for BSF larvae protein extract. The differences in these values may be due to factors such as processing, differences in raw materials, and extraction procedures.
3.3. Water-Binding Capacity and Oil-Binding Capacity
The capacity of a protein to bind water, known as water-binding capacity (WBC), is strongly linked to the texture, mouthfeel, and viscosity of food products [43]. Oil-binding capacity (OBC), which refers to a protein’s ability to retain absorbed oil, is also influenced by protein composition, pH, and ionic strength [30,44]. The values for the WBC and OBC of the BSF larvae proteins are illustrated in Figure 3. It is worth noting that the inclusion of NaCl salt did not produce a statistically significant change in the WBC of the protein, as shown by the results (p < 0.05). However, the AAFSISO demonstrated a higher WBC than the other proteins, although this difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). The variations in WBC across protein fractions were attributed to the amino acids outlined in the preceding work (not reported), which were impacted by the extraction method employed. To date, no research has been undertaken to investigate the WBC of BSF larvae proteins obtained through various salt-facilitated methods. The outcomes of this investigation surpassed the WBC values reported for BSF larval flour fractions in the previous literature (0.4–0.8 g/g) [15]. The highest WBC was found in the AAFSISO isolate (4.45 g/g), which significantly exceeded the WBC values of different insect species fractions documented in the literature, including Tenebrio molitor (1.87 g/g) [36] and Spodoptera gregaria (2.18 g/g) [30]. Similarly, the highest WBC was noted in the flour of Galleria sigillatus (2.34 g/g) and Spodoptera gregaria (2.18 g/g), which is likely due to the significant presence of hydrophilic amino acids (390.6 and 371.4 mg/g, respectively) [36]. These findings also suggest that BSF larvae have the potential to be a valuable ingredient in the food industry, as proteins with WBCs ranging from 1.49 to 4.72 g/g are recommended for use in viscous foods [45].
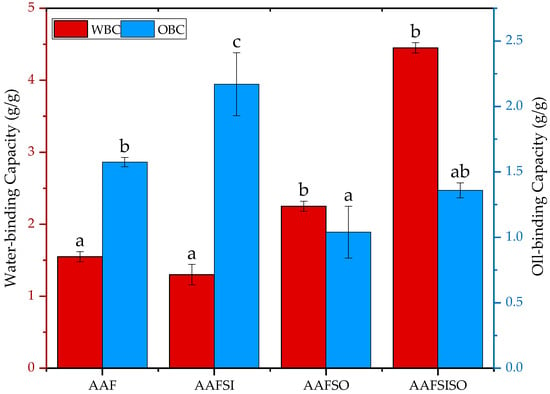
Figure 3.
Effect of extraction methods on water- and oil-binding capacity of black soldier fly larvae isolate obtained by AAF (alkaline–acid extraction), AAFSI (salting-in technique), AAFSO (salting-out technique), and AAFSISO (salting-in and out technique). Various letters suggest notable contrasts with statistical significance at p < 0.05. Error bars depict standard deviation.
The OBC of proteins is often indicative of their ability to interact with lipids, which is closely connected to factors such as emulsifying properties, flavor retention, and shelf life. This capacity can be impacted by various factors, including the type of protein, oil applied, and hydrophobicity. Furthermore, the addition of salts had a significant (p < 0.05) influence on the OBC of BSF larvae protein isolates. It is worth noting that a high degree of oil binding may be positively correlated with a protein’s high hydrophobicity. The significance of the protein-binding capacity for oils or fats extends to the creation of meat substitutes and extenders, in addition to sausages, emulsions, and cake batters [45]. AAFSI had the highest (p < 0.05) OBC in comparison to other proteins (Figure 3). These results are consistent with our earlier findings regarding the solubility of AAFSI at pH 10 and its pronounced hydrophobic nature. The values obtained for the various isolates exhibited significant variation (p < 0.05), with AAF having a content of 1.58 g/g, AAFSI at 2.17 g/g, AAFSO at 1.04 g/g, and AFFSISO at 1.36 g/g. These distinctions in the OBC could be a result of variations in the hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity of the protein surfaces, a characteristic that could be influenced by the extraction method used [19]. One can observe a significant variation between the protein isolates of AAFSI and AAFSO. This is due to the fact that precipitates obtained through salting-out may possess a distinct structure or conformation compared to those obtained via salting-in, which can influence their capacity to bind to oil. Salting-out may cause the precipitation of a wider range of proteins, including those with weaker affinity for oil binding, leading to a lower overall oil-binding capacity. The disparities observed in both WBC and OBC among BSF larval proteins offer useful insights for improving and enhancing protein concentrates in a range of insect-based food formulations.
3.4. Foaming Capacity and Stability
Foaming capacity (FC) is the ability of protein molecules to rapidly dissolve and unfurl, thereby forming a cohesive layer around a gas bubble, while foaming stability (FS) involves forming a stable foam through intermolecular polymerization that captures air [14]. Excellent foaming properties require proteins to swiftly migrate to the air–water interface, where they unfurl and reorganize [30]. Furthermore, foam properties are closely tied to protein solubility, and high solubility is a fundamental requirement for optimal FC. The FS and FC of BSF larvae isolates were measured and presented in Figure 4. In our study, all four isolates exhibited exceptional FC values, which exceeded those reported for Tenebrio Molitor and Schistocerca gregaria (34.67% and 19.33%, respectively) as per the findings of [30].
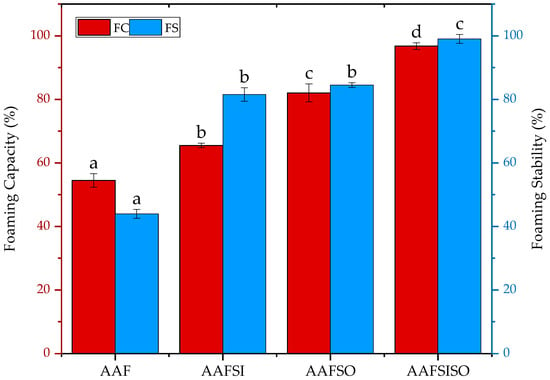
Figure 4.
Effect of extraction methods on foaming capacity and stability of black soldier fly larvae isolates obtained by AAF (alkaline–acid extraction), AAFSI (salting-in technique), AAFSO (salting-out technique), and AAFSISO (salting-in and out technique). Various letters (a, b, c, d) point to noteworthy variations at p < 0.05. Error bars show standard deviation.
The differences in the FC of AAF and AAFSI proteins were not significantly lower (p < 0.05) in comparison to the differences observed in AAFSO and AAFSISO proteins, which had values of 11.00% and 14.79%, respectively. The outcomes demonstrated that salting-out-assisted treatments significantly boosted (p < 0.05) the FC. Correspondingly, the FS results revealed that AAFSISO proteins exhibited the highest stability at 99.99%, followed by AAFSO at 84.50%. The presence of ammonium sulfate as a salt ion may enhance both FC and FS by exposing hydrophilic residues and improving protein solubility during the isolation step [14]. This result aligns with the findings of a study conducted by [17], in which the FS of cashew nutshell protein demonstrated an increase from 56.03% to 76.91% at the 60 min mark following salt addition. This increase in FS was attributed to the enhanced surface activity and solubility of the protein.
On the contrary, the low foaming capacity can be attributed to the globular proteins that are highly ordered and resist surface denaturation. For proteins to function effectively as foaming agents, they must possess the ability to (i) undergo rapid conformational changes and rearrangements at the interface and (ii) rapidly adsorb at the air–water interface during bubbling. In a study by [46], the comparison was made between the foaming properties of mealworm and cricket powders, and those of protein concentrates derived from yellow pea and faba bean. In a comparison between pulse proteins and cricket proteins, the cricket proteins produced foam that was more stable over time, while the pulse proteins generated more foam overall. These differences in FC could arise from the distinct conformational characteristics of the proteins. It has been established that the FC of proteins can be influenced by factors such as the balance of hydrophilic/hydrophobic groups and solubility, as well as the protein’s composition and structural properties [46]. Globular proteins, such as those found at the air–water interface, possess a reduced capacity to unfold, which in turn restricts their ability to capture air bubbles [47]. The scientific community is currently exploring alternatives to eggs, a widely used foaming agent in food products [23]. Presently, the food industry utilizes protein concentrates and isolates derived from wheat, soy, and dairy as ingredients. Nevertheless, both consumers and food processors are seeking alternative sources of protein to mitigate the allergenic concerns associated with the eight priority allergens, which comprise egg, soy, wheat, fish, peanut, crustaceans, dairy, and tree nuts. The findings of this study indicate that the AAFSISO protein preparation exhibits promising foaming properties and could be considered as a potential foaming agent for use in food applications.
3.5. Emulsifying Properties
Emulsification is the process by which proteins enable and maintain the interface between oil and water. Generally, soluble, amphiphilic, and versatile proteins serve as effective emulsifiers [48]. The emulsifying properties of BSF larvae were evaluated using the emulsifying activity index (EAI) and emulsion stability index (ESI), as shown in Figure 5. Our protein isolates exhibited noteworthy (p < 0.05) variations in EAI values, spanning from 32.50 to 87.78 m2/g (Figure 5). These values corresponded to, or surpassed, those reported for other edible insects, including Patanga succincta (23.23 m2/g) [49], Gryllodes sigillatus (32 m2/g) [23], and Chondracris roseapbrunner (36.96 m2/g) [49]. The salting-out proteins demonstrated the most promising results, making them suitable candidates for emulsifying agents.
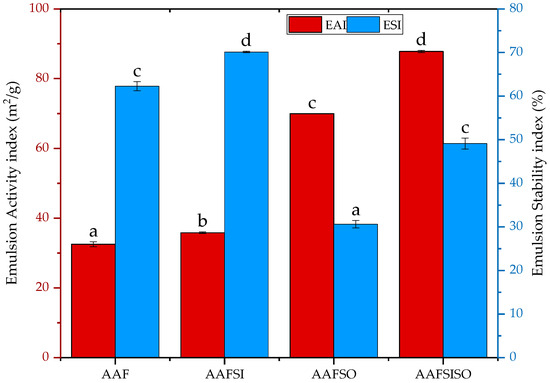
Figure 5.
Effect of extraction methods on emulsion stability index and emulsion activity index of black soldier fly larvae isolate obtained by AAF (alkaline–acid extraction), AAFSI (salting-in technique), AAFSO (salting-out technique), and AAFSISO (salting-in and out technique). Various letters suggest notable contrasts with statistical significance at p < 0.05. Error bars depict standard deviation.
Generally speaking, the phenomenon of emulsification can be attributed to the adsorption of proteins at the interface between oil droplets and the surrounding water in emulsions [24]. The observation that the salting-out group exhibited a higher EAI could be attributed to the greater availability of small, soluble proteins at the oil–water interface due to increased protein solubility [50]. The disparities in EAI are thought to be related to differences in surface hydrophobicity and protein–protein/oil interactions [51,52]. Ref. [51] suggested that proteins with a high surface hydrophobicity are prone to be adsorbed at the oil–water interface, which would enhance the emulsification effect. According to [51], a robust correlation exists between high surface hydrophobicity and a high emulsion stability index, which is consistent with our findings. Ref. [52] noted that an increase in the ionic strength of the extraction solution can enhance the shielding of surface charge, leading to an increase in protein–protein interactions while reducing protein–oil interactions. The stability of an emulsion is determined by the balance between repulsive and intramolecular forces at the water–oil interface, which can be influenced by various factors such as ionic strength, pH, amino acid polarity, and protein composition [53].
Our results, as illustrated by the ESI values, showed that the AAF and AAFSI proteins exhibited higher values (62.28% and 70.12%, respectively) compared to the T. molitor proteins (51.31%), as previously reported by [36] (Figure 5). Additionally, the fastest destabilization of the emulsions was observed in the AAFSO proteins, which was more than twice that of the AAFSI proteins (Figure 5). The results obtained from the salting-out-assisted treatments revealed a decrease in ESI, which is consistent with previous studies that found that proteins isolated by isoelectric precipitation had higher ESI levels than those isolated by ammonium sulfate precipitation [32]. The high hydrophobicity levels of BSF larvae isolates may also enhance protein adsorption at the oil/water interface, resulting in a decrease in interfacial tension and an increase in ESI levels [15]. Presently, casein and whey proteins are the most commonly utilized emulsifiers in the food industry. However, researchers are continuing to explore alternative protein sources that could potentially replace these traditional options. The BSF larvae extracts studied in this research produced similar results and could be used as alternative protein emulsifiers in both existing food products and new formulations.
3.6. Pearson’s Correlation Analysis
To investigate the possible relationship between the functional parameters of BSF larvae proteins and the variables listed earlier, the correlation coefficients were calculated between these variables. The Pearson correlation matrix is shown in Figure 6. To our knowledge, there are no comparable studies on BSF larvae protein available currently. The current session describes the results of a study in which various correlations were examined. A strong positive correlation was observed between the emulsion activity index and foam capacity (r = 0.98, p < 0.001), as well as with the solubility at pH 4 (r = 0.98, p < 0.001).
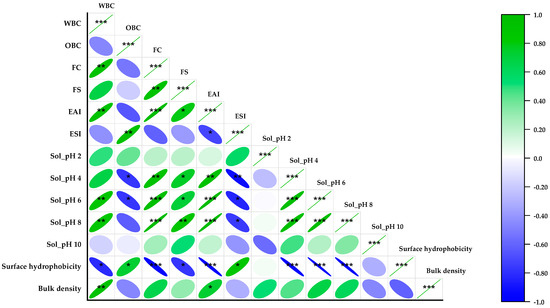
Figure 6.
Correlation matrix between the black soldier fly larvae protein isolate functional properties via Pearson’s linear correlation analysis; the color gradation and the size of the circle represent the correlation coefficient (r value). Significance levels: * p < 0.05 (moderate significance); ** p < 0.01 (higher significance); *** p < 0.001 (highest significance); blue represents negative correlation; green represents positive correlation.
Additionally, a moderate positive correlation was noted between solubility at pH 8 and foam stability (r = 0.85, p < 0.01), as well as with foam capacity (r = 0.98, p < 0.001) and water-binding capacity (r = 0.84, p < 0.01), while a negative correlation was observed with oil-binding capacity (r = −0.64, p < 0.05) and the emulsion stability index (r = −0.75, p < 0.05). Furthermore, a strong positive correlation was observed between surface hydrophobicity and oil-binding capacity (r = 0.74, p < 0.05), as well as emulsion stability index (r = 0.83, p < 0.05). The data depicted in Figure 3 and Figure 5 suggest that the enhanced oil-binding capacity and emulsion stability index observed in BSF larvae proteins after the addition of salt is attributable to the increased surface hydrophobicity, which enhances the ability to bind water and convert it into immobilized water, as well as the stronger interactions among the exposed hydrophobic group. Lastly, a weak, positive correlation was observed between bulk density and foam stability (r = 0.65, p < 0.005) and foam capacity (r = 0.31, p < 0.005).
Additionally, a statistically significant negative correlation was observed between the water-binding capacity and surface hydrophobicity (r = −0.82, p < 0.01). To the best of our understanding, this research is the first to explore the impact of salt on BSF larval proteins. The findings of this study are of significant importance in formulating alternative, sustainable food ingredients for growing populations. The results revealed significant interrelations (p < 0.05) between the functional properties of BSF larvae proteins, suggesting that BSF larvae protein could be a suitable candidate for use in food formulations.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, a thorough study of the techno-functional and physicochemical properties of BSF larvae proteins, with a specific focus on protein solubility, surface hydrophobicity, bulk density, foaming capacity and stability, emulsifying properties, and water- and oil-binding capacity has yielded valuable information regarding their potential applications in the food industry. The use of (NH4)2SO4 as a salting-out agent demonstrated a noticeable impact on protein solubility, with increased solubility at pH 2, indicating its potential for use in acidic food systems. Additionally, salt treatment had an impact on surface hydrophobicity, with salting-out methods resulting in lower hydrophobicity values, affecting the functional properties of proteins. Bulk density, a key property in characterizing protein products, varied among BSF larvae isolates, with salting-in (NaCl) decreasing bulk density, while salting-out ((NH4)2SO4) increased it, emphasizing the significance of salt treatment methods in optimizing protein extraction based on specific properties of interest. The ideal outcome would depend on the specific requirements of the protein product and its intended use. Both the decrease and increase in bulk density could be valuable depending on the desired properties and functionalities of the protein extract.
Furthermore, water- and oil-binding capacity, foaming capacity, and emulsifying properties were significantly influenced by salt treatment, with salting-out proteins exhibiting superior functional attributes. The study revealed that the AAFSISO protein obtained through salting-out demonstrated promising foaming properties and could be considered as a potential foaming agent for food applications. Correlation analyses indicated strong positive relationships between various functional properties, emphasizing the interconnected nature of these attributes in the BSF larval proteins. These findings suggest the potential use of BSF larvae proteins in food formulations, particularly when considering the positive correlations observed between emulsification properties, solubility, and surface hydrophobicity. The identified correlations provide a foundation for further exploration of BSF larvae proteins as sustainable functional ingredients in food applications, aligning with the growing interest in alternative protein sources for the food industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.Z., J.v.W., and M.W.; methodology, B.Z.; software, B.Z.; validation, B.Z., J.v.W., and M.W.; formal analysis, B.Z.; investigation, B.Z.; resources, B.Z.; data curation, B.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z.; writing—review and editing, B.Z., J.v.W., and M.W.; visualization, B.Z., J.v.W., and M.W.; supervision, J.v.W. and M.W.; project administration, M.W.; funding acquisition, B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to the Cape Peninsula University of Technology Vice Chancellor’s Prestigious Award Scholarship for covering the primary author’s living expenses and to the Agrifood Technology Station for granting access to their instruments for lab work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, T.K.; Choi, H.D.; Park, J.D.; Sung, J.M.; Jeon, K.H.; Paik, H.D.; Kim, Y.B. Optimization of Replacing Pork Meat with Yellow Worm (Tenebrio molitor L.) for Frankfurters. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.W.; Kim, S.Y.; An, K.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.; Kim, E.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.A.; Ryu, H.Y.; Yoon, H.J. Subacute Oral Toxicity Evaluation of Freeze-Dried Powder of Locusta migratoria. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.J. Cultured Meat from Stem Cells: Challenges and Prospects. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khampakool, A.; Soisungwan, S.; You, S.G.; Park, S.H. Infrared Assisted Freeze-Drying (IRAFD) to Produce Shelf-Stable Insect Food from Protaetia brevitarsis (White-Spotted Flower Chafer) Larva. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Lee, M.H.; Yu, M.-H.; Yong, H.I.; Jang, H.W.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.-S. Thermal Stability and Rheological Properties of Heat-Induced Gels Prepared Using Edible Insect Proteins in a Model System. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 134, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piha, S.; Pohjanheimo, T.; Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Křečková, Z.; Otterbring, T. The Effects of Consumer Knowledge on the Willingness to Buy Insect Food: An Exploratory Cross-Regional Study in Northern and Central Europe. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, L.W.; Pieterse, E.; Sigge, G.; Hoffman, L.C. An Exploratory Study into the Use of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae in the Production of a Vienna-Style Sausage. Meat Muscle Biol. 2019, 3, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, M.; Mishyna, M.; Martinez, J.J.I.; Benjamin, O. The Influence of Grasshopper (Schistocerca gregaria) Powder Enrichment on Bread Nutritional and Sensorial Properties. LWT 2019, 115, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Yong, H.I.; Jang, H.W.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.S. Effect of Extraction Condition on Technological Properties of Protein from Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Eisner-Schadler, V.; van Huis, A.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Extraction and Characterisation of Protein Fractions from Five Insect Species. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Lakemond, C.M.M. Extracting Tenebrio molitor Protein While Preventing Browning: Effect of PH and NaCl on Protein Yield. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Vázquez-Gutiérrez, J.L.; Johansson, D.P.; Landberg, R.; Langton, M. Yellow Mealworm Protein for Food Purposes–Extraction and Functional Properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preece, K.E.; Hooshyar, N.; Zuidam, N.J. Whole Soybean Protein Extraction Processes: A Review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 43, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Salting-in/out-Assisted Extractions on Structural, Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Larvae Protein Isolates. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bußler, S.; Rumpold, B.A.; Jander, E.; Rawel, H.M.; Schlüter, O.K. Recovery and Techno-Functionality of Flours and Proteins from Two Edible Insect Species: Meal Worm (Tenebrio molitor) and Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Heliyon 2016, 2, E00218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayas, J.F. Functionality of Proteins in Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yuliana, M.; Truong, C.T.; Huynh, L.H.; Ho, Q.P.; Ju, Y.-H. Isolation and Characterization of Protein Isolated from Defatted Cashew Nut Shell: Influence of PH and NaCl on Solubility and Functional Properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Kamaruddin, H.; Bentley, A.; Wang, S. Emulsion Stabilization by Tomato Seed Protein Isolate: Influence of PH, Ionic Strength and Thermal Treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshayisa, V.V.; Van Wyk, J.; Zozo, B. Nutritional, Techno-Functional and Structural Properties of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Flours and Protein Concentrates. Foods 2022, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zozo, B.; Wicht, M.M.; Mshayisa, V.V.; van Wyk, J. Characterisation of Black Soldier Fly Larva Protein before and after Conjugation by the Maillard Reaction. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azagoh, C.; Ducept, F.; Garcia, R.; Rakotozafy, L.; Cuvelier, M.-E.; Keller, S.; Lewandowski, R.; Mezdour, S. Extractionand Physicochemical Characterization of Tenebrio molitor Proteins. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong-Ly, K.C.; Gabelli, S.B. Salting out of Proteins Using Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 541, pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, F.G.; Jones, O.G.; O’Haire, M.E.; Liceaga, A.M. Functional Properties of Tropical Banded Cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) Protein Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mu, T.; Zhang, M.; Goffin, D.; Sun, H.; Ma, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D. Structure, Physicochemical, and Functional Properties of Protein Isolates and Major Fractions from Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) Seeds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintah, B.K.; He, R.; Agyekum, A.A.; Dabbour, M.; Golly, M.K.; Ma, H. Edible Insect Protein for Food Applications: Extraction, Composition, and Functional Properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Horn, C.; Rieder, O.; Jäger, H. Improvement of Techno-Functional Properties of Edible Insect Protein from Migratory Locust by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xie, P.; Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Chinese Quince Seed Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshayisa, V.V.; Van Wyk, J. Hermetia illucens Protein Conjugated with Glucose via Maillard Reaction: Antioxidant and Techno-Functional Properties. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 5572554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira Coelho, M.; De, M.; Salas-Mellado, M. How Extraction Method Affects the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Chia Proteins. LWT 2018, 96, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Karaś, M.; Baraniak, B. Comparison of Functional Properties of Edible Insects and Protein Preparations Thereof. LWT 2018, 91, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munialo, C.D.; Stewart, D.; Campbell, L.; Euston, S.R. Extraction, Characterisation and Functional Applications of Sustainable Alternative Protein Sources for Future Foods: A Review. Futur. Foods 2022, 6, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M. Comparative Study of Potato Protein Concentrates Extracted Using Ammonium Sulfate and Isoelectric Precipitation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2113–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranyi, I.S.; Otto, C.; Pickardt, C.; Osen, R.; Koehler, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Influence of the Isolation Method on the Technofunctional Properties of Protein Isolates from Lupinus angustifolius L. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, C2656–C2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Kasapis, S.; Adhikari, B. Molecular and Functional Characteristics of Purified Gum from Australian Chia Seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siow, H.-L.; Lim, T.S.; Gan, C.-Y. Development of a Workflow for Screening and Identification of α-Amylase Inhibitory Peptides from Food Source Using an Integrated Bioinformatics-Phage Display Approach: Case Study–Cumin Seed. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishyna, M.; Martinez, J.J.I.; Chen, J.; Benjamin, O. Extraction, Characterization and Functional Properties of Soluble Proteins from Edible Grasshopper (Schistocerca gregaria) and Honeybee (Apis mellifera). Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.A.; Saini, C.S. Rheological and Structural Properties of Protein Isolates Extracted from Dephenolized Sunflower Meal: Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Sorgentini, D.A.; Anon, M.C. Relation between Solubility and Surface Hydrophobicity as an Indicator of Modifications during Preparation Processes of Commercial and Laboratory-Prepared Soy Protein Isolates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpossan, R.A.; Digbeu, Y.D.; Koffi, M.D.; Parfait Eugène N’guessan Kouadio, J.; Ahipo Dué, E.; Kouamé, P.L. Protein Fractions and Functional Properties of Dried Imbrasia oyemensis Larvae Full-Fat and Defatted Flours. Int. J. Biochem. Res. Rev. 2015, 5, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Jiménez, N.T.; Ulloa, J.A.; Silvas, J.E.U.; Ramírez, J.C.R.; Ulloa, P.R.; Rosales, P.U.B.; Carrillo, Y.S.; Leyva, R.G. Effect of High-Intensity Ultrasound on the Compositional, Physicochemical, Biochemical, Functional and Structural Properties of Canola (Brassica napus L.) Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnana Moorthy Eswaran, U.; Karunanithi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Rout, S.; Srivastav, P. Edible Insects as Emerging Food Products–Processing and Product Development Perspective. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 60, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanqa, N.; Mshayisa, V.V.; Basitere, M. Proximate, Physicochemical, Techno-Functional and Antioxidant Properties of Three Edible Insect (Gonimbrasia belina, Hermetia illucens and Macrotermes subhylanus) Flours. Foods 2022, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojilla-Evangelista, M.P.; Evangelista, R.L. Functional Properties of Protein from Lesquerella fendleri Seed and Press Cake from Oil Processing. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishyna, M.; Keppler, J.K.; Chen, J. Techno-Functional Properties of Edible Insect Proteins and Effects of Processing. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletor, O.; Oshodi, A.A.; Ipinmoroti, K. Chemical Composition of Common Leafy Vegetables and Functional Properties of Their Leaf Protein Concentrates. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.K.; Tanaka, T.; Nickerson, M.T. Protein Quality and Physicochemical Properties of Commercial Cricket and Mealworm Powders. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundi, S.; Aluko, R.E. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Kidney Bean Albumin and Globulin Protein Fractions. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Cakebread, J.A.; Loveday, S.M. Food Proteins from Animals and Plants: Differences in the Nutritional and Functional Properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsuwan, N.; Nalinanon, S.; Puechkamut, Y.; Lamsal, B.P.; Pinsirodom, P. Characteristics, Functional Properties, and Antioxidant Activities of Water-Soluble Proteins Extracted from Grasshoppers, Patanga succincta and Chondracris roseapbrunner. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 6528312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, J.; Tan, L.; Liu, C. Effect of PH on Emulsification Performance of a New Functional Protein from Jackfruit Seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-Y.; Guo, L.-L.; Wei, F.; Li, J.-F.; Jiang, M.-L.; Li, G.-M.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Chen, H. Some Characteristics and Functional Properties of Rapeseed Protein Prepared by Ultrasonication, Ultrafiltration and Isoelectric Precipitation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S. Functionality of African Locust Bean (Parkia biglobossa) Protein Isolate: Effects of PH, Ionic Strength and Various Protein Concentrations. Food Chem. 2004, 86, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Chang, L.; Ohm, J.-B.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Structural, Functional Properties, and Volatile Profile of Hemp Protein Isolate as Affected by Extraction Method: Alkaline Extraction-Isoelectric Precipitation vs Salt Extraction. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).