Abstract
Black rice (BR) is considered one of the healthiest foods worldwide. This study assessed the bioactive compound contents and antioxidant activities of the distilled water (DW) and 80% ethanol (EtOH) extracts of BR, black rice bran (BRB), and milled black rice (MBR). In addition, their anti-obesity, anti-obesogenic, and anti-muscle atrophy effects were comparatively evaluated. The results revealed that the 80% EtOH extract of BR contained higher contents of β-glucan, total flavonoids, and total phenolics (26.97 ± 0.70 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g and 16.58 ± 0.37 mg quercetin equivalents (QE)/g, respectively) and showed higher antioxidant activity than those of the BRB and MBR extracts. On the other hand, BRB contained the highest content of γ-oryzanol, which was 15.12 ± 0.03 mg/g. Moreover, the 80% EtOH extract of BR exhibited a stronger anti-obesogenic effect by downregulating adipogenesis-related proteins (PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and FAS) and upregulating lipolysis-related proteins (PGC-1α and CPT-1), while the BRB extract effectively increased myotube diameter and fusion index. Overall, these findings indicate that the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR, particularly the BR extract, have high potential as natural antioxidants and anti-obesity agents, with BRB showing promise in preventing muscle atrophy.
1. Introduction
Black rice (BR) (Oryza sativa L.) is a distinctive rice variety primarily cultivated in Asia and is often referred to as “forbidden rice” due to its historical association with Chinese royalty [1]. BR has long been used as a medicinal food in China because of its health benefits. BR comprises an outermost layer, referred to as black rice bran (BRB), and an inner layer, referred to as milled black rice (MBR). The rice seeds are purple-black because of the rich anthocyanin pigment in the BRB layer [2,3]. Studies have shown that BR is popular not only for its unique color and flavor but also for its various health benefits [4].
BR is rich in dietary fiber, anthocyanins, phenolic compounds, flavonoids, γ-oryzanol, β-glucan, and other nutrients and bioactive substances [5]. These bioactive compounds are associated with various physiological activities that impart the BR with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity properties, thereby enhancing its reputation as a healthy food [6]. The antioxidant activity of BR has been extensively studied, with findings indicating that it possesses significantly higher antioxidant activity than other rice varieties, primarily due to the abundance of certain bioactive compounds such as anthocyanins, phenolic acids, and flavonoids [7,8]. Recent studies have suggested that BR can effectively scavenge free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress and having a positive impact on health [9].
In addition, BR has shown good application prospects and health benefits in various physiological activity studies, which are attributable to its high fiber content and multiple bioactive compounds that are closely associated with its anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-obesity, and anti-diabetic effects [3]. According to previous studies, BR is rich in antioxidant compounds and can be used to make products such as bread, cakes, and cookies, offering a healthier alternative to traditional baked goods. In addition, mead made from BR has higher antioxidant activity and provides more health benefits than mead made from ordinary grains [4]. Research has shown that BRB not only serves as a high-quality source of dietary fiber but also has multiple health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemic effects, which render it a promising raw material for developing functional foods [10,11].
Although a large number of studies have focused on the individual bioactive compounds or physiological activities of BR, comprehensive analyses and comparative studies of γ-oryzanol, β-glucan, total phenolic, and total flavonoid contents in BR and its components (i.e., BRB and MBR), as well as their antioxidant, anti-obesity, anti-obesogenic, and anti-muscle atrophy effects, are relatively limited. Therefore, this study aimed to comprehensively compare and evaluate the bioactive compound contents and physiological activities of BR, BRB, and MBR in water and 80% ethanol (EtOH) extracts to identify the most potent fractions of BR, explore their application prospects, and promote their use as healthy functional food materials. For example, they can be used in the development of dietary supplements and nutritional products to prevent diseases such as obesity, obesogenic effects, and muscle atrophy, thereby providing a deeper understanding of the application value of BR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Bovine serum (BS), phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fetal bovine serum (FBS), tryp-sin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), penicillin-streptomycin (P/S), and horse serum (HS) were obtained from Gibco (Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Quercetin, gallic acid, sodium carbonate, Folin–Ciocalteu’s reagent, isopropanol, aluminum chloride, potassium acetate, potassium persulfate, 2,4,6-tripyridyl-s-triazine (TPTZ), FeCl3·6H2O (ferric chloride), 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS), 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), insulin, dexamethasone (DEX), 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), bisphenol A(BPA), oil red O (ORO), and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (Saint Louis, MO, USA). N-methyl dibenzopyrazine methyl sulfate (PMS) reagent and 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) assay kits were obtained from WelGene (Seoul, Republic of Korea). Antibodies targeting β-actin, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBPα) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA, USA), and fatty acid synthase (FAS), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), and carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent was obtained from Bio-Rad, Inc. (Hercules, CA, USA).
2.2. Sample Preparation
The BR variety is Oryza sativa L. Joenheugmi. The BR was produced by the standard cultivation method (Paddy Crop Research Div., Rural Development Administration, Miryang, Republic of Korea) and was cultivated on Kangwon National University’s Farm. Whole BR was purchased from STR Biotech (Chuncheon, Republic of Korea). During the processing of BR, MBR was obtained by removing 80% of the bran layer, and the removed BRB was retained as a by-product. The BR, BRB, and MBR were provided by STR Biotech (Chuncheon, Republic of Korea) and used in the experiment. After BR, BRB, and MBR were pulverized and passed through a 40-mesh sieve, the obtained powders were used. The three samples were then subjected to reflux extraction with stirring at 60 °C for 3 h using 400 mL of 80% EtOH or distilled water (DW). Subsequently, the extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure (N-3000; EYELA, Tokyo, Japan). Finally, the extracts from BR, BRB, and MBR were freeze-dried with a freeze dryer (Ilshin Biobase Co., Ltd., Yangju, Republic of Korea).
2.3. Analysis of γ-Oryzanol and β-Glucan Contents
First, accurately weigh the BR, BRB, and MBR sample powders, and record the initial weights. After freeze-drying, reweigh each sample to determine the final weight. The extraction yield was calculated as follows (1):
Extraction yield (%) = [Weight of extracted powder (g)/Weight of the initial powder sample used for extraction (g)] × 100
The content of γ-oryzanol in the different extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR was analyzed via high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC; Shimadzu LC system, LC-40B XR, Shimadzu Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan), according to the method reported by Jung et al. [12]. γ-Oryzanol was separated using a Sunfire C18 column (Waters, Milford, MA, USA, 4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5.0 μm) maintained at 40 °C using an isocratic mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile, methanol, and isopropanol (50:45:5 v/v) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. γ-Oryzanol detection was achieved by measuring its absorbance at 320 nm. The chromatogram of γ-oryzanol was analyzed by recording the corresponding UV spectra at different time points using a PDA detector.
β-Glucan was quantified using a mixed-linkage beta-glucan assay kit from Megazyme, Wicklow, Ireland, following the manufacturer’s protocol, which involves the use of purified enzymes. To determine the β-glucan content, 50 mg of each sample was mixed with 0.1 mL of an aqueous ethanol solution and 2 mL of a 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5). The mixture was then heated and stirred in a water bath for 3 min. Thereafter, 0.1 mL of lichenase was added; the resulting mixture was incubated at 50 °C for 1 h and then cooled to room temperature. Next, a 200 mM sodium acetate buffer was added, and after centrifugation for 10 min, the β-glucosidase and supernatant were mixed with a 50 mM sodium acetate buffer and allowed to react at 50 °C for 10 min. Finally, 1.5 mL of the glucose oxidase/peroxidase reagent was added, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 50 °C for 20 min to quantify glucose. The absorbance of the sample was measured at 510 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Optizen POP, Mecasys Co., Ltd., Daejeon, Republic of Korea).
2.4. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents
To determine the total phenolic content, 1 mL each of the BR, BRB, or MBR extracts was mixed with 1 mL of 10% Folin–Ciocalteu’s reagent and 1 mL of 2% sodium carbonate in a test tube. The mixture was kept in the dark for 1 h, and the absorbance was measured at 750 nm (SpectraMax i3; Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The phenolic content was calculated using a gallic acid calibration curve and is expressed as mg GAE/g of the extract (GAE = gallic acid equivalent).
To determine the total flavonoid content, 0.5 mL of each of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts was mixed with 1.5 mL of 95% ethanol, 0.1 mL of 10% aluminum chloride, 0.1 mL of 1 M potassium acetate, and 2.8 mL of DW in a test tube. The resulting mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and the absorbance was measured at 415 nm. The flavonoid content was calculated by preparing a calibration curve using different concentrations of quercetin and is expressed as mg QE/g of the extract (QE = quercetin equivalent).
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
In the DPPH radical-scavenging activity assay, 0.2 mL of each of the BR, BRB, and MBR solutions was mixed with 0.8 mL of a 0.0004 M DPPH solution. The reaction mixture was then incubated in the dark for 10 min. The absorbance of DPPH was measured at 517 nm, and the radical-scavenging activity was calculated as follows (2):
DPPH radical-scavenging activity (%) = (1 − Aexperiment/Acontrol) × 100
For the ABTS radical-scavenging activity assay, 7 mM ABTS and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate solutions were mixed and incubated in the dark for 16 h to allow free radical generation. The mixture was then diluted to obtain an absorbance of 0.70 ± 0.02 at 734 nm. Afterward, 1 mL of the ABTS solution was mixed with 10 µL of each of the BR, BRB, and MBR solutions. The resulting mixture was incubated in the dark for 6 min. The absorbance of ABTS at 734 nm was measured, and the radical-scavenging activity was calculated as follows (3):
ABTS radical-scavenging activity (%) = (1 − Aexperiment/Acontrol) × 100
For the ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay, an FRAP reagent was prepared by mixing 300 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 3.6), 10 mM 2,4,6-tripyridyl-s-triazine (TPTZ), and 20 mM FeCl3·6H2O (ferric chloride) at a ratio of 10:1:1. Then, 50 µL of each of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts, 1.5 mL of the FRAP reagent, and 150 µL of DW were mixed and incubated at 37 °C for 4 min. The absorbance of the resulting mixture was measured at 593 nm.
2.6. Evaluation of the Effects of 80% EtOH Extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on Cell Viability and Lipid Accumulation in Obesity and Obesogenic Models
3T3-L1 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, CL-173; Manassas, VA, USA) and were cultured in 24-well and 96-well plates in DMEM containing 10% BS, 3.7 g/L sodium bicarbonate, and 1% P/S in a 37 °C/5% CO2 incubator until confluence. Two days later, 100% confluence was reached (day 0); the preadipocytes were cultured in 10% FBS medium with adipocyte differentiation-inducing substances (1.0 μg/mL insulin, 1.0 μM DEX, and 0.5 mM IBMX; MDI) to induce cell differentiation. After two days, the medium was changed to a 10% FBS medium containing 1.0 μg/mL of insulin to promote further cell differentiation. The medium was changed every two days, and 3T3-L1 adipocytes were obtained after 8 days of treatment. The viability of adipocytes treated with 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR was evaluated using the 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) assay kit (WelGene, Seoul, Republic of Korea). On day 8 of differentiation, a mixture of 1 mL XTT and 20 μL N-methyl dibenzopyrazine methyl sulfate (PMS) was prepared and added to each well of the 96-well plate. The plate was then incubated for 4 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. The absorbance was measured at 450 and 690 nm. Thereafter, lipid accumulation from 400 μg/mL of 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on 3T3-L1 cells was measured. The culture solution was aspirated from the 24-well plates and washed twice with PBS. Then, 500 μL of a 10% formalin solution was added to each well and incubated at room temperature for 1 h to fix the differentiated adipocytes. The cells were washed with 500 μL of a 60% isopropanol solution and dried completely at room temperature. The completely dried cells were stained with 200 μL of an ORO solution added to each well and incubated for 30 min. After washing with DW, the cells were completely dried at room temperature for 1 day. The ORO combined lipids were eluted with 100% isopropanol, and the absorbance was measured at 490 nm. Based on the above methods, the anti-obesity efficacy of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR was evaluated.
For the BPA-induced anti-obesogenic experimental group, 20 μM BPA was added 2 days after confluence was reached (day 0), and cell differentiation was induced as described above. The culture medium was replaced every two days, and 3T3-L1 adipocytes were obtained after 10 days of treatment. Cell viability was measured using the XTT assay. Similarly, 20 μM BPA was added, and the ORO assay was performed as described above after 10 days to evaluate the anti-obesogenic effects of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR.
2.7. Western Blot Analysis of the 80% EtOH Extract of BR in an Obesogenic Model
The epididymal adipose tissue and cells were lysed in protein lysis buffer and centrifuged at 12,000× g for 15 min at 4 °C. The protein concentration was quantified using a protein assay kit, and the samples were then heated at 100 °C for 5 min. The proteins were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane at 100 V for 90 min. The membrane was blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h. After blocking, the membrane was washed three times with 1× TBST and incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies (PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, FAS, PGC-1α, and CPT-1). After overnight incubation, the membrane was washed three times with 1× TBST and incubated with secondary antibodies (rabbit or mouse, diluted 1:2000) for 1 h at room temperature. The membrane was washed again, and protein bands were visualized using ECL detection reagent and imaged using Chemi Doc Image Software 5.2.1 to detect protein bands.
2.8. Evaluation of the Anti-Muscle Atrophy Effects of 80% EtOH Extracts from BR, BRB, and MBR
C2C12 myoblast cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) were cultured in 96-well and 24-well plates in DMEM containing 3.7 g/L sodium bicarbonate, 10% FBS, and 1% P/S in a 37 °C/5% CO2 incubator until confluence. After, the medium was replaced with DMEM supplemented with 2% HS to induce myoblast differentiation. The medium was then changed every 2 days. In general, the cells differentiated into C2C12 myotubes by days 5–6. Then, the cells were treated with different concentrations of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts in 80% ethanol and 200 µM DEX for 1 day.
The effects of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts on cell viability were evaluated using the XTT assay. The myoblasts were seeded into each well of a 96-well plate and cultured until they differentiated into myotubes. The cells were then treated with 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR for 24 h. Subsequently, a mixed solution of 20 μL PMS and 1 mL XTT was added to each well of the 96-well plate and incubated at 37 °C for 4 h. The absorbance was measured at 450 and 690 nm.
2.9. Jenner–Giemsa Staining
The effects of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts on DEX-induced atrophy in C2C12 myotube cells were evaluated using Jenner–Giemsa staining. First, the culture medium was aspirated into a 24-well plate, and the cells were washed twice with 1× PBS. Then, the cells were fixed with 100% methanol for 5 min, the methanol was discarded, and the cells were dried at room temperature for 10 min. After fixation, 0.3 mL of the Jenner staining solution was added to each well, allowed to react for 5 min, and the cells were washed twice with DW. Finally, the Giemsa staining solution was added to each well for 10 min and then washed twice with DW. The stained cells were observed and photographed under an inverted microscope (CKX41SF; Tokyo, Japan).
2.10. Measurement of Myotube Diameters and Fusion Index
This study followed the method of Men et al. [13] and used ImageJ software (1.53k) to measure the diameter of myotubes. After staining the myotubes, myotube cells containning at least 3 nuclei in random areas of each well in a 24-well plate were photographed using an inverted microscope at 200× magnification, and the fusion index was determined using ImageJ software. The number of nuclei in the myotubes was calculated using Formula (4):
Fusion index (%) = (Number of nuclei in myotubes/total number of nuclei) × 100
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). All data were subjected to statistical analysis via analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple range tests, with p < 0.05 regarded as statistically significance (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The significance of the correlation is expressed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
3. Results
3.1. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents and γ-Oryzanol and β-Glucan Contents in BR, BRB, and MBR
The total phenolic and flavonoid contents, along with the extraction yield in the DW and 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR, were presented in Table 1. The results revealed that the yields of the 80% ethanol and DW extracts of BRB were 10.63 ± 0.61% and 17.88 ± 0.92%, respectively, both of which were higher than the yields from BR and MBR. The contents of total phenolics and flavonoids in the 80% EtOH extract are significantly higher than those in the DW extract. Additionally, the total phenolic content in the 80% EtOH extract of BR was 26.97 ± 0.70 mg GAE/g, while the total flavonoid content was 16.58 ± 0.37 mg QE/g, both of which are significantly higher than those found in BRB and MBR. As shown in Table 1, the γ-oryzanol content in the 80% EtOH extracts was higher than that in the DW extracts. Further, its content was higher in BRB than in BR and MBR. In contrast, the β-glucan content was higher in the 80% EtOH extract of BR than in the 80% EtOH extracts of BRB and MBR.

Table 1.
Bioactive compounds and yields of 80% EtOH and DW extracts from black rice (BR), black rice bran (BRB), and milled black rice (MBR).
The standard chromatogram of γ-oryzanol (Figure 1) was obtained using the HPLC-PDA method. The chromatographic peaks of four standards were analyzed, including β-sitosterol ferulate, cycloartenyl ferulate, campesterol ferulate, and cyclobranol ferulate (Figure 1A). Figure 1B shows the contents of these components in the chromatograms of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, which are 4.11 mg/g (cycloartenyl ferulate), 5.64 mg/g (cyclobranol ferulate), 3.03 mg/g (campesterol ferulate), and 1.55 mg/g (β-sitosterol ferulate), respectively. Figure 1C shows the contents of these components in the chromatograms of the 80% EtOH extracts of BRB, which are 4.17 mg/g, 5.76 mg/g, 2.95 mg/g, and 1.94 mg/g, respectively. Figure 1D shows the contents of these components in the chromatograms of the 80% EtOH extracts of MBR, which are 0.52 mg/g, 0.76 mg/g, 0.51 mg/g, and 0.20 mg/g, respectively. Additionally, Figure 1E–G shows the contents of these components in the chromatograms of the DW extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR, respectively, all of which were below the detection limit. Therefore, they are expressed as Not Detected (N.D.).
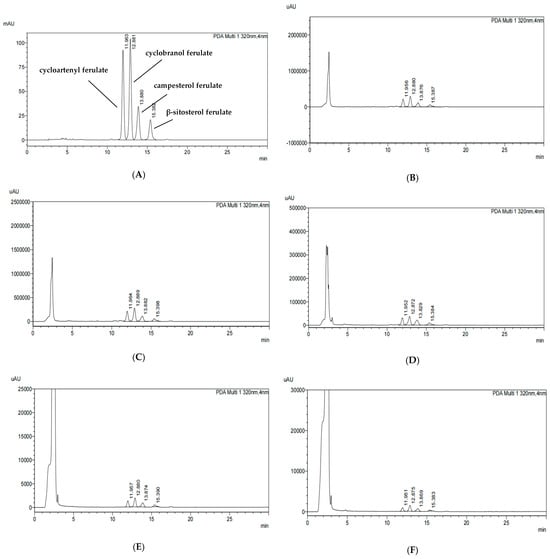
Figure 1.
HPLC chromatograms of γ-oryzanol in the 80% EtOH and DW extracts of black rice (BR), black rice bran (BRB), and milled black rice (MBR). (A) HPLC chromatograms of the γ-oryzanol standard; (B) 80% EtOH extract of BR; (C) 80% EtOH extract of BRB; (D) 80% EtOH extract of MBR; (E) DW extract of BR; (F) DW extract of BRB; and (G) DW extract of MBR.
3.2. Antioxidant Activities of BR, BRB, and MBR
This study evaluated the antioxidant activities of BR, BRB, and MBR in different extraction solvents using in vitro antioxidant activity assays, including ABTS free radical scavenging, DPPH free radical scavenging, and FRAP activity assays. The results of the DPPH free radical scavenging activity assay revealed that the scavenging activities of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR at a sample preparation concentration of 1 mg/mL were 64.02 ± 0.92, 59.3 4 ± 1.02, and 41.04 ± 1.30%, respectively. These values are superior to those of the DW extracts, with the BR extract exhibiting the highest antioxidant activity among the samples (Figure 2A). Furthermore, in the ABTS free radical scavenging activity assay, the scavenging activity of the 80% EtOH extract at a concentration of 1 mg/mL was 81.49 ± 0.26% for BR, 80.61 ± 0.41% for BRB, and 58.43 ± 0.39% for MBR, which were higher than those of the corresponding DW extracts (Figure 2B). As shown in Figure 2C, the absorbance of FRAP at 593 nm in the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR at 1 mg/mL was 0.25, 0.23, and 0.15, respectively, which were higher than those in the corresponding DW extracts, with BR showing the highest antioxidant activity.
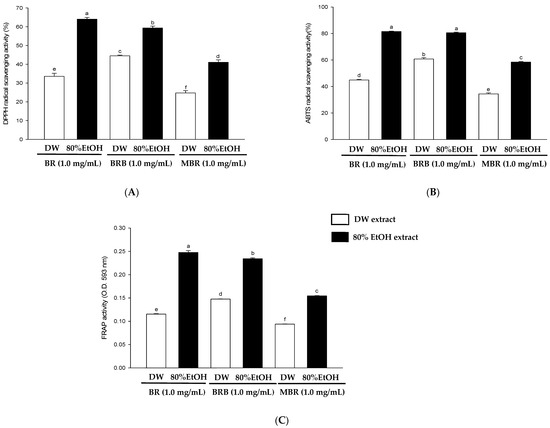
Figure 2.
Antioxidant activities of 80% EtOH and DW extracts from BR, BRB, and MBR established based on (A) DPPH radical-scavenging activity; (B) ABTS radical-scavenging activity; and (C) ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) activity. All values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Different lowercase letters on the bars indicate statistical differences at p < 0.05.
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activities of 80% EtOH and DW Extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR
To further analyze the correlation between the antioxidant activities of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR and the contents of bioactive compounds, including γ-oryzanol, and β-glucan, we used Pearson correlation analysis and present the correlation coefficients in a heat map (Figure 3). The results reveal that apart from the total phenolic and flavonoid contents, which are primarily responsible for the antioxidant properties of the extracts, the γ-oryzanol content also shows a significantly positive correlation with the antioxidant activity of the 80% EtOH BR extract. A weak negative correlation was observed between the β-glucan content and the other variables.
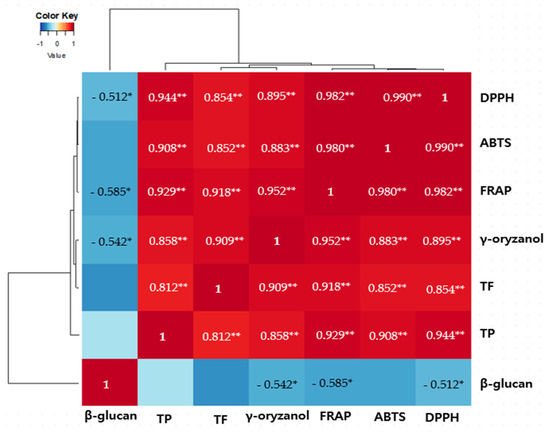
Figure 3.
Heatmap of the correlation coefficients between the total phenolic (TP) content, total flavonoid (TF) content, DPPH radical-scavenging activity, ABTS radical-scavenging activity, ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and bioactive compounds of the 80% EtOH and DW extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR. Blue and red colors indicate negative and positive correlations between individual parameters. Significant correlation differences are represented by a white asterisk, * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
3.4. Effects of the 80% EtOH Extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on Anti-Obesity and Anti-Obesogenic Activities
Based on previous experimental results, we selected the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR with the best antioxidant activities for in vitro experiments. The results of the XTT assay indicated no significant differences between the treatment groups and the control group, and the experimental groups at a concentration of 400 μg/mL had no cytotoxic effects on 3T3-L1 cells (Figure 4A). Therefore, BR, BRB, and MBR extracts in 80% EtOH at a concentration of 400 μg/mL were selected for further experiments. Lipid accumulation was determined using ORO staining. As N-acetylcysteine (NAC) inhibits lipid accumulation, it was used as a positive control group [14]. The results suggested that lipid accumulation in the 3T3-L1 cells treated with 400 μg/mL of BR, BRB, and MBR extracts was 93.16%, 96.67%, and 100.01%, respectively. The 80% EtOH extract of BR significantly reduced the accumulation of lipids (Figure 4B). Therefore, the anti-obesity effect of the 80% EtOH extract of BR was demonstrated. No cytotoxicity was observed when the 3T3-L1 cells were treated with 20 µM BPA or 400 μg/mL of BR, BRB, or MBR (Figure 4C). ORO staining was performed to confirm the effects of BR, BRB, and MBR on BPA-induced lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. The cells in the MDI (DEX-treated group) control group exhibited intense staining, which suggested a significant accumulation of lipids. In contrast, lipid accumulation was significantly reduced in the MI (without 1.0 µM DEX) control group compared with that in the MDI group. When treated with 20 µM BPA, lipid accumulation increased to 75.23%, indicating that BPA promotes adipogenesis. However, when BPA-induced cells were treated with 400 μg/mL of the 80% EtOH extract of BR, BRB, or MBR, lipid accumulation reduced to 48.82% and 56.30% in the cases of BR and BRB, respectively, both of which could inhibit lipid accumulation in adipocytes, with BR showing the most significant inhibitory effect (Figure 4D).
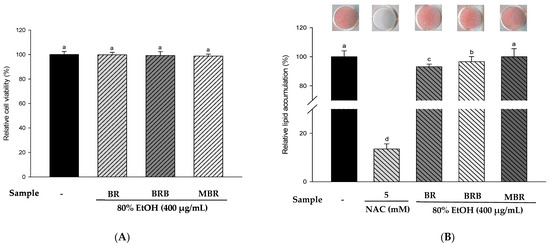
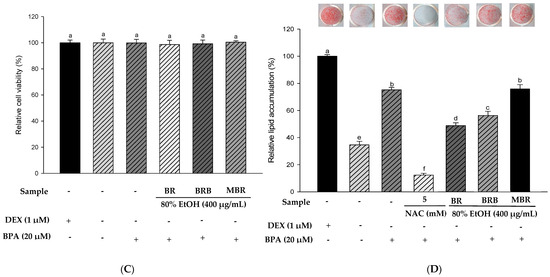
Figure 4.
Effects of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on cell viability and lipid accumulation in (A,B) the MDI group and (C,D) BPA-induced 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (A,C) Cell viability by XTT assay. (B,D) Lipid accumulation determined by ORO staining. All values are expressed as mean ± SD. Different lowercase letters on the bars indicate statistical differences at p < 0.05.
3.5. Effects of the 80% EtOH Extract of BR on Adipogenesis and Lipolysis-Related Proteins in BPA-Induced 3T3-L1 Cells
To determine the effect of the 80% EtOH extract of BR on adipogenesis-related proteins in BPA-induced 3T3-L1 cells, we measured the levels of PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and FAS proteins using Western blot analysis. Garcinia cambogia (GAR) was used as the positive control group. As shown in Figure 5A–C, the levels of PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and FAS were significantly increased in BPA-treated cells compared with those in the MI control group (without 1.0 µM DEX). However, when BPA-induced cells were treated with the 80% EtOH extract of BR, a significant decrease in the protein expression levels of FAS, C/EBP-α, and PPAR-γ was observed. Therefore, the 80% EtOH extract of BR significantly inhibited the expression levels of these markers. In addition, compared with the MI control group, the expression levels of lipolysis-related proteins (PGC-1α and CPT-1) were reduced in the BPA-treated group (Figure 5D,E). However, treatment with the 80% EtOH extract of BR, the protein expression levels of PGC-1α and CPT-1 were significantly increased. In summary, the 80% EtOH extract of BR modulates BPA-induced 3T3-L1 cells by inhibiting the expression of adipogenesis-related proteins and promoting the expression of lipolysis-related proteins.
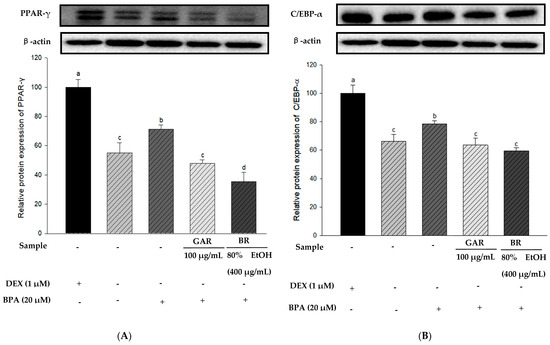
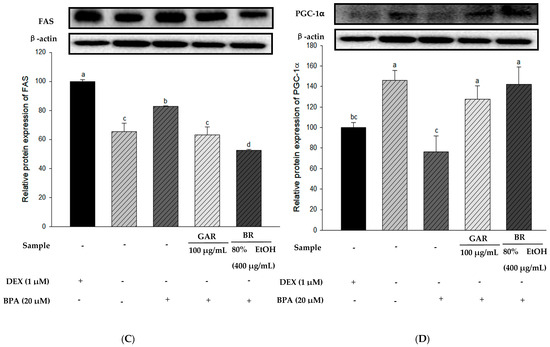
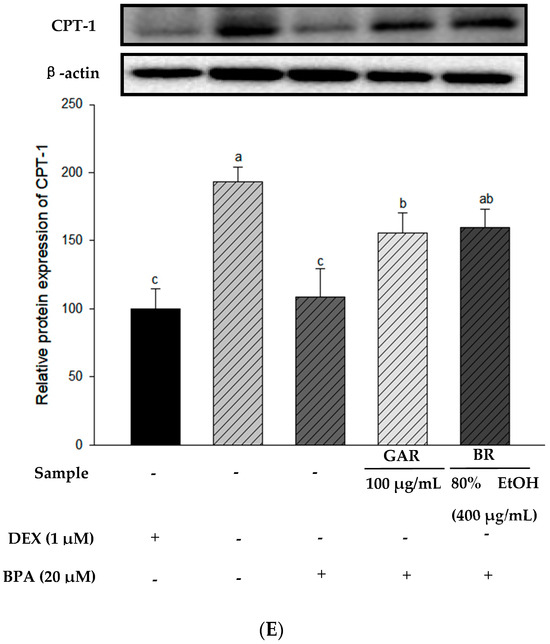
Figure 5.
Effects of the 80% EtOH extract of BR on the expression of adipogenesis and lipolysis-related proteins in BPA-induced 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (A) PPAR-γ, (B) C/EBP-α, (C) FAS, (D) PGC-1α, and (E) CPT-1. All values are expressed as mean ± SD. Different lowercase letters on the bars indicate statistical differences at p < 0.05.
3.6. Effects of the 80% EtOH Extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on Anti-Muscle Atrophy Activity
The effects of 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR at 50 and 100 µg/mL concentrations on the viability of C2C12 myotube cells were evaluated using the XTT assay, and the results revealed that these concentrations had no toxic effects on the cells (Figure 6A). To further evaluate the effects of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts on the DEX-induced viability of C2C12 myotube cells, extracts with 50 and 100 µg/mL concentrations were treated with 200 µM DEX. The results are shown in Figure 6B; cell viability significantly increased in the groups treated with BR, BRB, and MBR compared with that in the DEX group. As shown in Figure 6C, the diameter of myotubes in the DEX group decreased to 62.86% compared with that in the control group. However, when the C2C12 myotubes were co-treated with 100 µg/mL of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts and 200 µM DEX, the myotube diameter increased to 75.39%, 79.70%, and 65.23%, respectively, with the 100 µg/mL BRB extract showing the most significant effect. Therefore, high concentrations of the 80% EtOH extract of BRB can effectively inhibit DEX-induced myotube atrophy. Similarly, upon co-treating with higher concentrations of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts and DEX, the fusion index of the C2C12 myotubes increased significantly to 79.89%, 82.96%, and 71.07%, respectively (Figure 6D). In summary, these results demonstrate that relatively high concentrations of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR inhibit DEX-induced C2C12 myotube atrophy, with the 100 μg/mL BRB extract showing the most significant effect.
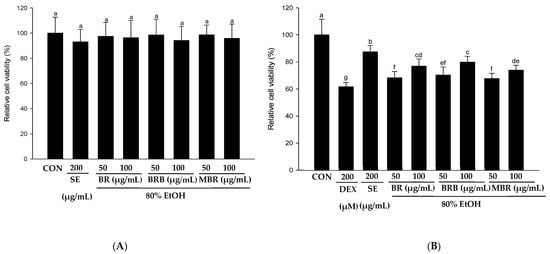
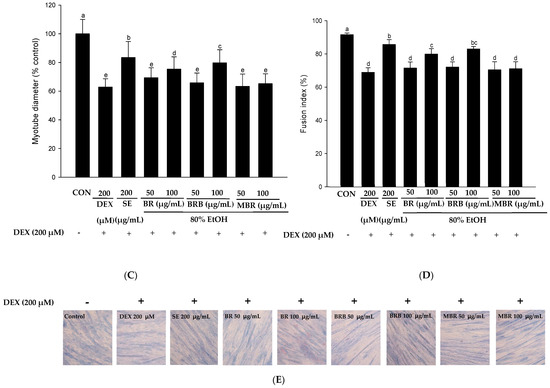
Figure 6.
Effects of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on DEX-induced C2C12 myotube cells in terms of (A) cytotoxicity, (B) cell viability, (C) myotube diameter, and (D) fusion index. (A) Cytotoxicity was evaluated at different concentrations of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts. (B) Cell viability of C2C12 myotube cells co-treated with different concentrations of the BR, BRB, and MBR extracts and 200 µM DEX. (E) Jenner–Giemsa staining of C2C12 myotube cells, and representative photographs captured under a fluorescent microscope (200× magnification). All values are expressed as mean ± SD. Bars labeled with different lowercase letters indicate statistically significant differences at p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
Currently, BR is widely regarded as a functional food due to its exceptional antioxidant properties, rich nutritional value, and significant health benefits [15]. Phenolic and flavonoid compounds present in plants have redox properties and exhibit significant antioxidant activity [16,17]. γ-Oryzanol is a natural compound primarily found in BR, particularly in BRB, and is associated with a variety of health benefits [18]. According to previous studies, the content of γ-oryzanol in BRB is relatively high and varies when extracted with different solvents [19,20]. The results indicated that the contents of γ-oryzanol, total phenolics, and total flavonoids in the 80% EtOH extract were significantly higher than those in the DW extract. Moreover, the antioxidant activity of the 80% EtOH extract was also higher than that of the DW extract, with BR exhibiting the highest antioxidant activity. The Pearson correlation analysis showed that the total phenolic and total flavonoid contents in BR extracts were significantly positively correlated with their antioxidant activity, which was consistent with previously reported results [9]. In addition, the bioactive compound γ-oryzanol in BR extract also showed a significant positive correlation with antioxidant activity.
The fundamental cause of obesity is an imbalance between energy intake and expenditure. Excessive energy intake can lead to fat accumulation owing to promoted lipogenesis [21]. Therefore, the inhibition of adipocyte formation can effectively prevent and treat obesity. This study evaluated the potential of the 80% EtOH extract of BR, BRB, and MBR to inhibit lipid accumulation and exhibit anti-obesity and anti-obesogenic effects using 3T3-L1 cells and BPA-induced 3T3-L1 cells. The results showed that BR, BRB and MBR were non-cytotoxic, and the 80% EtOH extract of BR significantly reduced lipid accumulation in adipocytes. The enhanced anti-obesity effect of the BR extract may be attributed to the abundance of bioactive compounds and antioxidants, which regulate adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis. These results indicate the potential therapeutic effect of BR against obesity [22,23]. Therefore, the anti-obesogenic effect of the 80% EtOH extract of BR was confirmed in vitro. This is in agreement with the findings of Liu et al. [24], who reported the potential of BR to significantly reduce lipid accumulation and prevent obesity in mice fed with a high-fat diet.
We also investigated the potential of the 80% EtOH extract of BR in anti-obesogenic treatment by evaluating the levels of adipogenesis and lipolysis-related proteins in BPA-induced 3T3-L1 cells. Adipogenesis is the process of differentiation of fibroblast-like preadipocytes into mature adipocytes, which involves the activation of multiple transcription factors, including PPAR-γ and C/EBP-α [25]. PPAR-γ is an important regulator of adipogenesis, and its activation leads to adipocyte differentiation and generation [26]. Our results showed that the 80% EtOH extract of BR inhibited the expression of adipogenesis-related proteins (PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and FAS). Therefore, 80% EtOH extract of BR reduces lipid accumulation by inhibiting adipogenesis-related proteins. PGC-1α is considered a key regulator that promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function [27]. CPT-1 is the rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid oxidation [28]. PGC-1α promotes fatty acid oxidation in mitochondria by regulating the expression of CPT-1 [29]. Our study found that the 80% EtOH extract of BR significantly increased the protein expression levels of PGC-1α and CPT-1. Therefore, these results indicate that the 80% EtOH extract of BR exerts anti-obesogenic effects by promoting fatty acid oxidation through the upregulating lipolysis and thermogenesis-related proteins (CPT-1 and PGC-1α).
Skeletal muscle atrophy is characterized by changes in muscle fiber contraction or loss [30]. Previous studies have shown that γ-oryzanol can promote myofiber formation and prevent muscle aging, and that supplementation with γ-oryzanol can prevent muscle disorders [31]. Therefore, the high content of γ-oryzanol and other bioactive compounds that support muscle cell growth and differentiation in the BRB extract plays a significant role in inhibiting muscle atrophy. This is consistent with previous findings that BRB supplementation can reduce muscle loss in mice by regulating factors associated with muscle atrophy, further suggesting its potential to prevent muscle atrophy [32]. Therefore, to determine the effects of the 80% EtOH extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR on DEX-induced C2C12 myotube atrophy, we measured the diameter and fusion index of the myotube cells using Jenner-Giemsa staining. Schisandra chinensis extract (SE) was used as a positive control, because SE is known to significantly inhibit myotube atrophy [33]. The results showed that both BR and BRB increased myotube diameter and fusion index compared to MBR, with BRB having a more significant effect in preventing muscle atrophy.
Our findings highlight the importance of the 80% EtOH extract in maximizing the health benefits of BR and its derivatives, particularly in terms of antioxidant, anti-obesity, and anti-muscle atrophy effects. The results suggest that they could be used in the development of dietary supplements or nutraceuticals to help prevent diseases such as obesity and muscle atrophy. In the future, they are expected to be applied in a wider range of health fields.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study evaluated and compared the bioactive compound contents and physiological activities of the extracts of BR, BRB, and MBR in different solvents (DW and 80% EtOH). The results underscore the significance of extracting BR and its derivatives with 80% EtOH in enhancing the health benefits of these food materials. Among the extracts from BR, BRB, and MBR, the 80% EtOH BR extract exhibited the highest antioxidant activity. Physiological activity assays revealed that the 80% EtOH extract of BR effectively inhibits adipocyte differentiation and reduces lipid accumulation. It significantly reduces BPA-induced adipogenesis by downregulating adipogenesis-related proteins (PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and FAS) and upregulating lipolysis and thermogenesis-related proteins (CPT-1 and PGC-1α). While the 80% EtOH BRB extract is more effective in promoting myoblast differentiation and growth. Overall, the findings of this study indicate that BR and its derivatives are potential functional foods that can help prevent and manage diseases associated with obesity and muscle atrophy.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Project administration, Visualization: X.F.; Software, Validation, Formal analysis, G.O.; Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis: J.-H.I.; Conceptualization, Investigation, Software: J.-S.L.; Resources, Validation, Investigation: M.-H.K.; Writing—review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision: O.-H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the 2023 Research Grant from SUDANG FOUNDATION, funded by the Basic Science Research Program (NRF-2021R1A6A1A03044242, 2017R1D1A3B06028469) and BK21 FOUR (Fostering Outstanding Universities for Research, Grant No. 4299990913942) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE, Republic of Korea).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ito, V.C.; Lacerda, L.G. Black rice (Oryza sativa L.): A review of its historical aspects, chemical composition, nutritional and functional properties, and applications and processing technologies. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamuangmorn, S.; Prom-u-Thai, C. The potential of high-anthocyanin purple rice as a functional ingredient in human health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Q.; Dong, L.; Jia, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, F.; Liu, G.; Sun, Z.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Phenolic profiles and bioactivities of different milling fractions of rice bran from black rice. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Dash, U.; Mahanand, S.S.; Nayak, P.K.; Kesavan, R.K. Black rice: A comprehensive review on its bioactive compounds, potential health benefits and food applications. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Umar, M.; Habib, A.; Imran, M.; Khalid, W.; Lima, C.M.G.; Shoukat, A.; Itrat, N.; Nazir, A.; Ejaz, A.; et al. Photochemistry, functional properties, food applications, and health prospective of black rice. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 2755084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, L.; Meza, S.; Peres, B.; Rodrigues, L.; Jappe, S.N.; Coradi, P.C.; Oliveira, M.D. Functional Foods from Black Rice (Oryza sativa L.): An Overview of the Influence of Drying, Storage, and Processing on Bioactive Molecules and Health-Promoting Effects. Foods 2024, 13, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Trindade, H. Rice antioxidants: Phenolic acids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, tocopherols, tocotrienols, γ-oryzanol, and phytic acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Bao, J.; Beta, T. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of breeding lines between the white and black rice. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapoung, S.; Semmarath, W.; Arjsri, P.; Thippraphan, P.; Srisawad, K.; Umsumarng, S.; Phromnoi, K.; Jamjod, S.; Prom-u-Thai, C.; Dejkriengkraikul, P. Comparative analysis of bioactive-phytochemical characteristics, antioxidants activities, and anti-inflammatory properties of selected black rice germ and bran (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, K.; Yousuf, B.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, P.; Wani, A.A. Rice bran: Nutritional values and its emerging potential for development of functional food—A review. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 6, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapwarobol, S.; Saphyakhajorn, W.; Astina, J. Biological functions and activities of rice bran as a functional ingredient: A review. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2021, 14, 11786388211058559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.D.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Woo, K.S.; Oh, S.K.; Lee, O.H. Comparative analysis of γ-oryzanol, β-glucan, total phenolic content and antioxidant activity in fermented rice bran of different varieties. Nutrients 2017, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, X.; Han, X.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, G.; Im, J.H.; Bae, K.S.; Seong, G.S.; La, I.J.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, O.H. Ginsenosides Rh1, Rg2, and Rg3 ameliorate dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in C2C12 myotubes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, D.; Martini, C.N.; Frontera, E.M.; Montaldo, L.A.; Vila, M.D.C.; Calvo, J.C.; Guerra, L.N. N-Acetylcysteine Inhibits Lipids Production in Mature Adipocytes through the Inhibition of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor. Int. J. Biochem. Res. Rev. 2020, 29, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanuja, B.; Parimalavalli, R. Role of black rice in health and diseases. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, X.P.; Silva, F.S.; Almeida, J.R.G.D.S.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; de Lima, J.T.; de Araújo Ribeiro, L.A.; Júnior, L.J.Q. Biological Oxidations and Antioxidant Activity of Natural Products; INTECH Open Access Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Seleshe, S.; Ameer, A.; Kang, S.N. Exploration of the Antioxidant Chemical Constituents and Antioxidant Performance of Various Solvent Extracts of Eighteen Plants. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Kim, D.E.; Keum, Y.S.; Saini, R.K. Metabolite profiling and antioxidant activities of white, red, and black rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; Li, K.Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, H.H. Phytochemicals and antioxidant properties of solvent extracts from Japonica rice bran. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Lee, J. Antioxidants in milling fractions of black rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, A.; Qi, W. The potential to fight obesity with adipogenesis modulating compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, S.; Spainhower, C.J.; Cottrill, C.L.; Lakhani, H.V.; Pillai, S.S.; Dilip, A.; Chaudhry, H.; Shapiro, J.I.; Sodhi, K. Therapeutic efficacy of antioxidants in ameliorating obesity phenotype and associated comorbidities. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonarski, E.; Kuasnei, M.; Cesca, K.; Oliveira, D.D.; Zielinski, A.A. Black rice and its by-products: Anthocyanin-rich extracts and their biological potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 9261–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H. Black rice (Oryza sativa L.) reduces obesity and improves lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.T.; Hochfeld, W.E.; Myburgh, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J. Impaired adipose tissue expandability and lipogenic capacities as ones of the main causes of metabolic disorders. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 970375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunkhorn, S.; Dearie, F.; Mantzoros, C.; Gami, H.; da Silva, W.S.; Espinoza, D.; Faucette, R.; Barry, K.; Bianco, A.C.; Patti, M.E. Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor γ coactivator-1 expression is reduced in obesity: Potential pathogenic role of saturated fatty acids and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15439–15450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Ma, A.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chang, H. pparβ regulates lipid catabolism by mediating acox and cpt-1 genes in Scophthalmus maximus under heat stress. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 50, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, K.; Jackson-Hayes, L.; Lavrentyev, E.N.; Cook, G.A.; Elam, M.B.; Park, E.A. Peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator (PGC-1α) stimulates carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT-Iα) through the first intron. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Struct. Expr. 2004, 1679, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, N.; Jia, W.; Wang, N.; Liang, M.; Yang, X.; Du, G. Skeletal muscle atrophy: From mechanisms to treatments. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Song, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Bioactive components in whole grains for the regulation of skeletal muscle function. Foods 2022, 11, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.X.; Yeh, C.L.; Yang, S.C.; Shirakawa, H.; Chang, C.L.; Chen, L.H.; Chiu, Y.S.; Chiu, W.C. Rice Bran Supplementation Ameliorates Gut Dysbiosis and Muscle Atrophy in Ovariectomized Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, M.; Choi, H.; Jun, H.S. Preventive effects of Schisandrin A, a bioactive component of Schisandra chinensis, on dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).