Abstract
A field experiment with winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivation was conducted at the Research and Education Centre in Tomaszkowo, Poland (53°72′ N; 20°42′ E) in the years 2013–2016. Fertilisation with nitrogen at 150 and 200 kg ha−1 and foliar application of manganese at 0.5 and 1.5 kg ha−1 were the research factors. Wheat infestation by Fusarium spp. was determined by the habitat conditions during crop growth. Neither nitrogen nor manganese fertilisation affected the presence of Fusarium spp. symptoms on wheat ears, but the infestation intensity decreased with increasing nitrogen and manganese content in the grain. Only the level of deoxynivalenol (DON) was correlated with Fusarium spp. infestation. Increasing the nitrogen fertilisation rate from 150 kg ha−1 to 200 kg ha−1 resulted in higher grain contamination with toxins. Supplementation of nitrogen fertilisation with manganese reduced the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain. The grain yield was mainly affected by the varied weather conditions during the wheat-growing periods. Neither nitrogen nor manganese fertilisation differentiated the wheat grain yield. The objective of this study was to examine the impact of the weather conditions and nitrogen and manganese fertilisation on the grain yield, occurrence of Fusarium head blight and mycotoxin level in winter wheat grain.
1. Introduction
Of all the agrotechnical procedures performed in intensive wheat cultivation, fertilisation—which includes the application of both micro- and macronutrients—has the strongest impact on yield, its chemical composition and, as a consequence, its quality [1]. When not properly balanced, fertilisation can impair the soil’s physicochemical characteristics and fertility [2].
Macro and micronutrient fertilisation is of great importance in boosting wheat resistance to infestation with pathogens that cause root, culm base, leaf and ear diseases [3]. Cereal fungal diseases decrease grain yield and impair its quality [4]. The loss caused by reducing the grain mass and the number of grains per ear can reach 10 to 40% [5]. Strong plant infestation reduces the assimilation area and photosynthesis intensity [6].
Cereals are susceptible to diseases caused by Fusarium spp. fungi, and wheat is particularly susceptible to Fusarium head blight [7]. Ear infestation by Fusarium spp. can cause a loss in yield of up to 15–20%, and even 60% in extreme cases, with infested grain being of low quality [8]. The intensity of Fusarium head blight depends largely on weather conditions [9]. According to Xu et al. [10], environmental conditions influence the processes of infection and colonisation in various ways, as well as an abundance of species of the genus Fusarium spp. Humidity determines the intensity of the disease, while precipitation determines inoculum levels [11]. Significant infestation of spikes by Fusarium spp., including F. graminearum, F. culmorum, F. poae, and F. avenaceum, requires substantial moisture persisting for at least 24 h and temperatures exceeding 15 °C [12]. Factors influencing wheat infection with Fusarium spp. may include the following: agricultural technology, forecrop, fertilisation and use of fungicides [8,13]. Hazard of Fusarium spp. occurrence in wheat also depends on the genetically determined variety resistance [14]. According to Spanic [15], infected seeds with Fusarium spp. were smaller with lower 1000 kernel weight and had less endosperm, which resulted in increased protein content.
Grain infestation with fungi of Fusarium spp. results in the formation of secondary metabolites, such as mycotoxins. In Poland, these include mainly trichothecenes A and B (deoxynivalenol (DON), nivalenol and T2/HT-2 toxins), fumonisins and zearalenone (ZEA) [16]. Mycotoxins are significant cereal contaminants, generating economic losses in the fodder and food industry and having an adverse impact on human and animal health [17]. The presence and concentration of mycotoxins produced by fungi of Fusarium spp. in wheat depend on multiple factors, e.g., toxigenic potential of a specific fungus species [18], weather conditions [4,19], presence of competitive microflora [20], tolerance of the cultivar [21] and growth conditions [22]. The literature reports on the nitrogen impact on Fusarium spp. occurrence and mycotoxin production are inconclusive. According to Aufhammera et al. [23], Krnjaja et al. [24] and Cwalina-Ambroziak et al. [25], infestation by Fusarium spp. and mycotoxin production was not related to the amount of nitrogen supplied. A study conducted by Supronienė et al. [26], and Podolska et al. [27] indicates a distinct impact of N fertilisation on Fusarium spp. occurrence and mycotoxin production. Bernhoft et al. [28] and Champeil et al. [29] found nitrogen fertilisation to have the potential to damage cellular wall structures in plants and adversely impact plant chemical composition, thereby making plants more susceptible to pathogen invasions. Nitrogen excess makes plants more luxuriant and the stand denser, resulting in higher moisture content, which favours infections by Fusarium and mycotoxin production [29].
Micronutrients are involved in physiological and biochemical mechanisms of defence against pathogens. Manganese participates in the synthesis of lignin, which constitutes a physical barrier against pathogen infiltration [30,31].
There have been multiple studies on the impact of nitrogen fertilisation on Fusarium blight and mycotoxin occurrence in cereals, but there have been none dealing with a combined impact of nitrogen and manganese fertilisation and habitat conditions on their presence in wheat.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions
The field experiment with winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivation was conducted at the Research and Education Centre in Tomaszkowo, Poland (53°72′ N; 20°42′ E) in the years 2013–2016. The experiment was set up in the randomised block design in triplicate. A description of the agrotechnical procedures, the soil characteristics before the experiment was set up and the winter wheat main growth stages are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of the agrotechnical procedures, soil characteristics and main growth stages of winter wheat.
2.2. Design of Experiment
Fertilisation with nitrogen at 150 and 200 kg ha−1 and foliar application of manganese at 0.5 and 1.5 kg ha−1 were the research factors. The nitrogen and manganese rates and the dates of application are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Design of the field experiment. Dose and date of application fertilisers used in the field experiment.
2.3. Weather Conditions
The weather conditions in the years of study varied (Table 3). The average temperatures between September and August were higher by 0.6 °C than the multi-year average during all three years of study. September 2013 was the coldest month during the period of initial plant growth (lower temperature by 2.3 °C than in 2014 and 2015). A lower temperature in September 2013 caused better tillering, and a higher temperature in November extended their growing period. The rapid temperature decrease in early January 2016 caused considerable plant freezing, which subsequently affected the yield. The temperatures in winter helped plants to last through the cold period during the other years of the study. Higher temperatures in spring (March–April) 2014 induced the rapid emergence of wheat.

Table 3.
Monthly air temperature and monthly rainfall in the 2013–2016 season. Meteorological data against the years 1981–2010 (data obtained from the Meteorological Station at Tomaszkowo, (53°71′ N, 20°43′ E), Poland.
The highest total rainfall was determined in the growing season of 2015/2016. However, over 20% of the precipitation occurred during the pre-harvest period, hindering the harvest and, in effect, increasing the loss in yield due to freezing. September 2013 was the most humid month during the initial plant-growing period, which had an impact on water accumulation and its effective use during the plant tillering. It is of key importance for achieving better yield to supply sufficient amounts of water during the period of plant emergence (March). That was the case in 2014 and in 2015.
2.4. Determination of N and Mn Content of Grain
Ground grain samples were mineralised in concentrated H2SO4 with K2SO4 and CuSO4 (as an oxidiser). Protein content in wheat grain was determined by the Kjeldahl method (N × 5.7) in the KjelFlex K-360 apparatus (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland). For Mn determination, ground grain was mineralised in a mixture of HNO3 and HClO4 (at 4:1). Manganese content was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) in a Hitachi Z-8200 apparatus (Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. The Severity of Fusarium Head Blight (Fusarium spp.) in Winter Wheat
During the wheat-growing period, the intensity of Fusarium head blight symptoms was assessed visually in principal growth stage 7: development of fruit—late milk (BBCH 77). An analysis was performed for 25 randomly selected plants on a plot using a 5-degree scale. Following the conversion, the results were given in % as the infestation index. The results for the disease intensity were calculated from McKinney’s formula [32] and presented as infestation index in percent:
where ∑ (a × b) is the sum of products from multiplying the number of plants (a) on a given degree of scale (b), N is number of plants under analysis and I is the highest degree of the scale.
2.6. Mycotoxin Analysis
All mycotoxins (MON, ZEA, DON, NIV) from plant material were extracted and purified according to the detailed procedure described elsewhere [33,34]. A total of 10 g of ground samples of winter wheat (each sample in three repetitions) were homogenised for 3 min in 30 mL of acetonitrile:water (80:20, v/v) and filtered through Whatman no. 4 filter paper (Whatman International Ltd., Maidstone, UK). The elute was evaporated to dryness at 40 °C under a stream of nitrogen. The dry residue was stored at −20 °C until HPLC analyses. The chromatographic system consisted of a Waters 2695 high-performance liquid chromatograph (Waters, Milford, CT, USA) with the following detectors: a Waters 2996 Photodiode Array Detector with a Nova Pak C-18 column (300 × 3.9 mm) for DON, NIV (λmax = 224 nm) and MON (λmax = 229 nm) analysis; a Waters 2475 Multi λ Fluorescence Detector (λex = 274 nm, λem = 440 nm) and a Waters 2996 Photodiode Array Detector with a Nova Pak C-18 column (150 × 3.9 mm) for ZEA analysis. The mycotoxins were quantified by measuring peak areas and retention times using the calibration curve. The limits of detection were as follows: 1 ng g−1 for ZEA; 10 ng g−1 for DON, NIV and MON.
2.7. Grain Yield
A plot combine harvester (Wintersteiger Classic 1540, STEURER Trocknungs- und Aufbewahrungssysteme GmbH, Altach, Austria) was used for wheat grain harvest during the technical ripeness stage (BBCH 91). The grain harvested from the plots was used to determine the yield per 1 ha and for further analysis. A hygrometer (GMS v2, Dramiński, Gietrzwałd, Poland) was used to determine the grain moisture content, and the wheat grain yield was determined per 1 ha after converting to the same moisture content of 15% with the scales (WTC 2000, Radwag, Radom, Poland).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistica v.13.1 software was used for the statistical analysis of the study results. Statistical inference consisted of the demonstration of significant differences in fertilisation variants by one-way analysis of variance. Homogeneous groups were determined by Tukey’s test. The calculations were made at the level of significance of α = 0.05. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was calculated, followed by the linear regression equation. The relationships between the two characteristics are shown in the dispersion diagrams.
3. Results
3.1. N and Mn Content of Wheat Grain
The impact of weather conditions on the nitrogen content in the years of the study was different than that on the grain yield (it was the highest in 2016 and the lowest in 2014) (Table 4). The nitrogen fertilisation at 150 and 200 kg (without Mn) increased the N content in grain of statistically significant value compared to the level on the plots without fertilisation (by 20.2 and 30.1%, respectively).

Table 4.
Content of N in grain after application of N and Mn fertilisers, g kg−1.
The highest Mn content was determined in grain obtained in 2016, and it was higher by 37% on average compared with the Mn content in 2014 and 2015 (Table 5). The lowest average Mn content was found in the grain harvested on non-fertilised plots. However, no statistically significant differences in the element content were demonstrated compared with the grain obtained from plots fertilised with 150 kg N and 150 kg N + 0.5 kg Mn. As a result of the combined effect of the fertilisation and the study years, the application of 150 kg N ha−1 + 1.5 kg Mn ha−1 increased the Mn content in grain compared with the plots fertilised by nitrogen at the same rate without Mn. The application of 200 kg N ha−1 with 1.5 kg Mn ha−1 in 2016 increased the Mn content statistically significantly compared with the variant of 200 kg N ha−1 without manganese.

Table 5.
Content of Mn in grain, after application of N and Mn fertilisers, mg kg−1.
3.2. Infestation with Fusarium spp.
Fungi of Fusarium spp. occurred in wheat heads with the greatest intensity in 2014. However, those were not the amounts of fungi that might pose a considerable threat to the wheat head condition (Table 6). The higher intensity of Fusarium head blight was caused by favourable conditions for plant growth, manifesting themselves in higher stand density, which caused the deterioration in the phytosanitary conditions at the end of the growing period. The infestation was under the harmfulness threshold in the other two years of the study. No impact of the nitrogen or manganese fertilisation on the Fusarium head blight symptom occurrence on wheat heads was demonstrated during the study years.

Table 6.
Infestation with Fusarium spp. after application of N and Mn fertilisers, infection index %.
The coefficient of determination (R2) reveals that over 50% of the infestation severity caused by Fusarium spp. was influenced by the nitrogen content of grain in plots treated with nitrogen fertilisation at rates of 150 and 200 kg N. (R2 = 0.69 and r2 = 0.67), as well as Mn at 1.5 kg (R2 = 0.63 and R2 = 0.56) (Figure 1). Fusarium head blight was not affected by the Mn content of the grain.
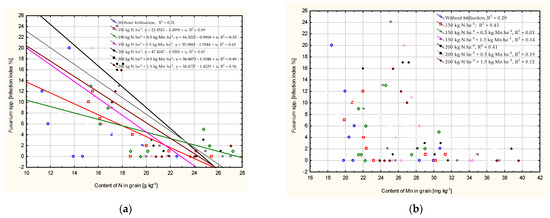
Figure 1.
Dependence of intensity of Fusarium head blight on content of N (a) and Mn (b) in grain (calculated at significance α = 0.05).
3.3. Mycotoxin Content
Four mycotoxins were found in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON), nivalenol (NIV), zearalenone (ZEA) and moniliformina (MON) (Table 7, Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10). The weather conditions during the study years were found to have a varied impact on cereal grain contamination with mycotoxins produced by Fusarium. The largest amounts of DON and NIV were found during the first growing season (2014), whereas the largest amounts of MON were found in 2015, and of ZEA, they were found in 2016.

Table 7.
Concentrations of deoxynivalenol (DON) in winter wheat grain after application of N and Mn fertilisers, µg g−1.

Table 8.
Concentrations of Nivalenol (NIV) in winter wheat grain after application of N and Mn fertilisers, µg g−1.

Table 9.
Concentrations of Zearalenone (ZEA) in winter wheat grain after application of N and Mn fertilisers, µg g−1.

Table 10.
Concentrations of moniliformina (MON) in winter wheat grain after application of N and Mn fertilisers, µg g−1.
The application of nitrogen at 150 kg (without Mn) resulted in the presence of the highest grain mycotoxin content. However, the differences were not statistically significant compared with the plot with no fertilisation in the case of MON content. Supplementation of nitrogen fertilisation with manganese reduced the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain, which was confirmed by statistical analysis.
The DON content in the fertilised plot in which 150 kg N and 0.5 kg Mn were applied was determined at 93% by the N content of the grain (Figure 2). The calculated coefficient of determination (R2) shows that the NIV level in all the variants was determined by the nitrogen content of the grain (from 88% to 96%). The coefficient of determination (r2) for the level of MON was higher than 50% at the no-fertilisation plot and at the plot fertilised with 200 kg N and 1.5 kg Mn. The ZEA level was determined (from 64% to 72%) by the N content of grain at the no-fertilisation plot and in the following variants: 150 kg N, 200 kg N and 200 kg N + 0.5 kg Mn.
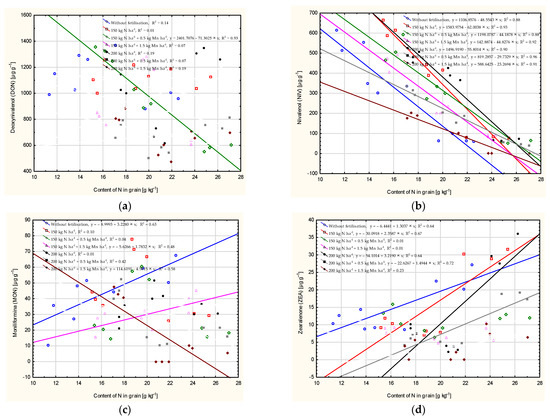
Figure 2.
Dependence of content of N on the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON) (a), nivalenol (NIV) (b), moniliformin (MON) (c), zearalenone (ZEA) (d), calculated at significance α = 0.05).
The inclusion of 150 kg of nitrogen along with manganese (0.5 and 1.5 kg) resulted in the Mn content of grain accounting for 56–68% of the variation in the DON level (Figure 3). The NIV level was the most weakly determined when 150 kg N and 1.5 kg Mn were applied (R2 = 0.37) and the most strongly determined when 150 kg N was applied (R2 = 0.91). The MON level was determined by the Mn content in the no-fertilisation plot (50%) and in the plot where 150 kg N and 1.5 kg Mn were applied (56%). The ZEA level was determined by the Mn content in the no-fertilisation plot (82%) and in the plot where 150 kg N (90%), 200 kg N + 0.5 kg Mn (94%) and 200 kg N + 1.5 kg Mn (66%) were applied.
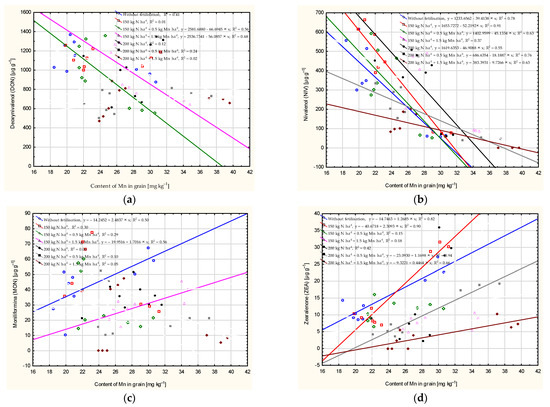
Figure 3.
Dependence of content of Mn on the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON) (a), nivalenol (NIV) (b), moniliformin (MON) (c), zearalenone (ZEA) (d), calculated at significance α = 0.05).
The DON level was determined at 71% by the occurrence of Fusarium spp. following the application of 200 kg N ha−1 and 1.5 kg Mn ha−1 (Figure 4). The coefficient of determination for the NIV level exceeded 50%, except in plots where 150 kg N ha−1, 0.5 kg Mn ha−1 (R2 = 0.35) and 200 kg N ha−1 were applied (R2 = 0.47). The MON level was determined by grain contamination with Fusarium spp. in the no-fertilisation plot (R2 = 0.61) following the application of 200 kg N ha−1 with Mn (R2 = 0.72–0.86). The ZEA level was not determined by Fusarium spp. infestation.
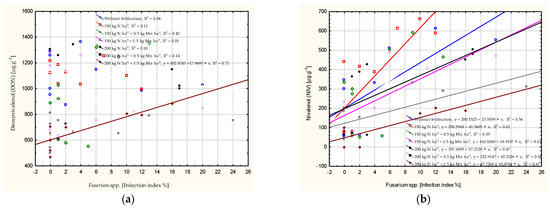
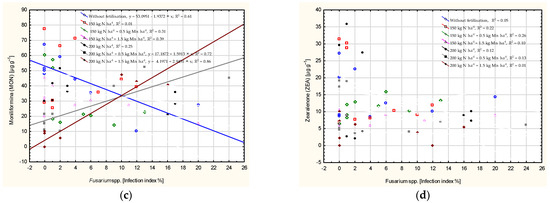
Figure 4.
Dependence of intensity of Fusarium head blight on the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON) (a), nivalenol (NIV) (b), moniliformin (MON) (c), zearalenone (ZEA) (d), calculated at significance α = 0.05).
3.4. Winter Wheat Grain Yield
The highest grain yield was obtained in 2014 (10.60 t ha−1), and the smallest was obtained in 2016 (2.69 t ha−1) (Table 11). The grain yield was mainly affected by the varied weather conditions during the wheat-growing periods. Thus, the low wheat grain yield in the last study year (2016) was a consequence of adverse thermal conditions in winter. Due to the high temperatures in November and December, the plants’ vegetation did not stop, and the sudden temperature drop in early January, combined with no snow cover, froze part of the plants. Excessive rainfall during the initial period of the growing season (November 2015) hindered plant growth and left them ill-prepared for the winter season. Moreover, large amounts of rainfall at the end of the growing season (July and August) did not favour the plant ripening and hindered the harvest. Irrespective of the rate, nitrogen or manganese fertilisation did not differentiate statistically significantly the wheat grain yield.

Table 11.
The grain yield after application of N and Mn fertilisers, t ha−1.
The coefficient of determination (R2) shows that the grain yield was determined in most experimental plots by the Fusarium spp. infestation (except in the plot where 150 kg N ha−1 and 0.5 kg Mn ha−1 were applied) (Figure 5).
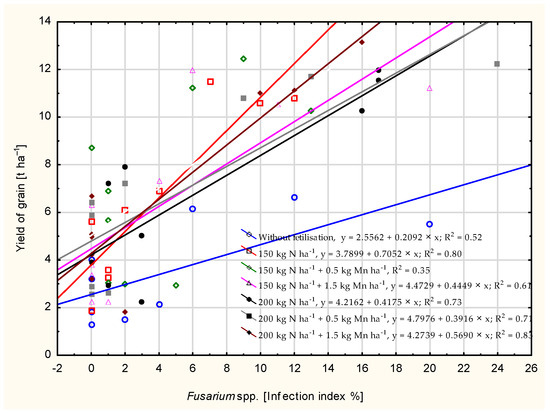
Figure 5.
Dependence of intensity of Fusarium head blight on the grain yield, calculated at significance α = 0.05).
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The analysis of the impact of weather conditions (rainfall and temperature) and the use of nitrogen and manganese fertilisation in winter wheat cultivation on the content of N, Mn, grain yield, ear infection by Fusarium spp. and the content of mycotoxins in grain was complemented by the determination of the correlation between the above-mentioned factors. To this end, the principal component analysis (PCA) method was used to determine the links (the strength and direction of the correlation) between the measurement variables. PCA showed that the air temperature in the growing seasons (September–August) had an effect on grain yield (Figure 6). The fertilisation variant had an impact on the formation of nitrogen content in the grain. The year of cultivation and the amount of rainfall affected the content of manganese in grain. The performed PCA showed that the temperature (IV–VIII) had an effect on the infection of spikes by Fusarium spp. (Figure 7). During the growing season in spring and summer, temperature and rainfall had no effect on the development of MON and DON mycotoxins.
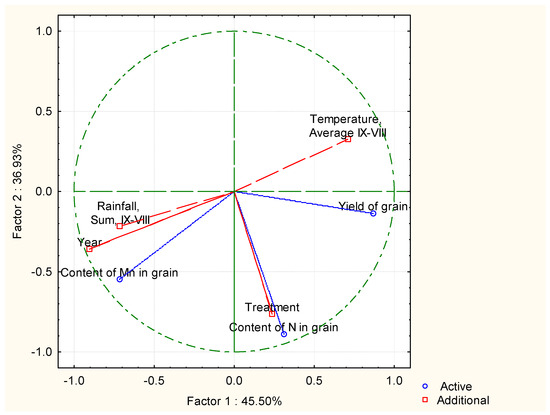
Figure 6.
The correlation of the influence of weather conditions (rainfall and temperature IX–VIII) on the content of Mn, N and the yield of wheat grain.
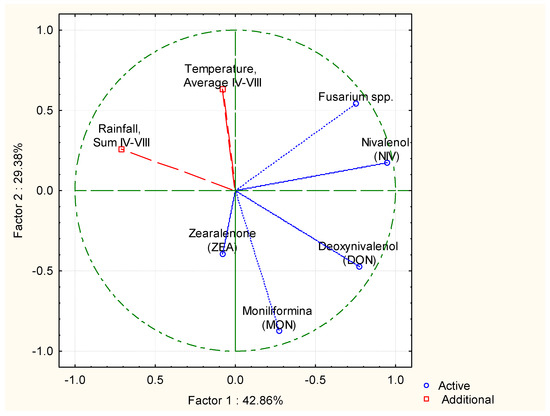
Figure 7.
The correlation of the influence of weather conditions (rainfall and temperature, IV–VIII) on the intensity of Fusarium head blight and number of mycotoxins in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON); nivalenol (NIV); moniliformin (MON); zearalenone (ZEA).
4. Discussion
4.1. N and Mn Content of Wheat Grain
The diversity of nitrogen and manganese content during the study years was an effect of varied yield (a higher yield in 2014 corresponded to a low N and Mn content, and a low grain yield in 2016 corresponded to a high N and Mn content of grain). The low nutrient content of grain in high-output cultivation is associated with intensive yield mass growth relative to mineral component absorption [35]. The effects of dilution of mineral components in the yield are presented in papers by Murphy et al. [36], Hussain et al. [37], Guttieri et al. [38] and Smith et al. [39] and not confirmed in studies by Shi et al. [40], Hamnér et al. [41] and Marles [42].
The nitrogen and manganese fertilisation as applied in the experiment conducted by these authors caused an increase in the nitrogen content of grain compared with the grain obtained in non-fertilisation plots. Nitrogen and manganese fertilisation did not have an equal impact on the manganese content of the grain. Mn is essential in N metabolism, and it takes part in nitrate reduction [43]. Shi et al. [40], Wojtkowiak et al. [1,44] and Jańczak-Pieniążek et al. [45] found that nitrogen fertilisers did not have an impact on the Mn content of winter wheat grain, and studies by Svecnjak et al. [46], Klikocka and Marks [47] and Dolijanović et al. [48] showed the opposite tendencies, i.e., that the manganese concentration increased with increasing the N rate.
4.2. Fusarium spp. Infestation and Mycotoxin Level
Fusarium head blight was determined by the habitat conditions during the crop-growing period. The weather conditions at the beginning of autumn in 2013 favoured a higher plant density and stronger tillering. These conditions during the final growing period, combined with increased humidity and temperature, resulted in a deterioration in the phytosanitary conditions, manifesting themselves in more intensive infestation with Fusarium spp. A lower plant density favours the creation of a beneficial microclimate, which is important when higher rainfall is combined with higher temperatures [29]. This kind of microclimate boosts the growth of kernels, accelerates wheat head drying and shortens the time of exposure to infestation with Fusarium spp. According to Bryła et al. [16] and El Chami et al. [4], the development, growth and propagation of Fusarium in wheat depends on the amount of rainfall. Czaban et al. [13] and El Chami et al. [4] found infestation with Fusarium to be impacted by high rainfall during cereal blossoming. Fusarium head blight is favoured by long periods of high humidity, higher temperatures (between 15 and 30 °C) and the occurrence of air currents, disseminating fungi spores during and after the wheat-blossoming period [49].
Nitrogen or manganese fertilisation, as examined in a study conducted by the current authors, did not have an impact on the appearance of Fusarium spp. symptoms on wheat heads. However, the infestation intensity decreased with increasing nitrogen and manganese content. Infestation with Fusarium spp. depends on agronomic procedures, the effectiveness of the fungicides applied and the host’s resistance [8]. Despite the association with Fusarium spp. infestation, the presence of mycotoxins is largely dependent on the land tilling systems, crop rotation, fertilisation and grain storage [50]. Balanced fertilisation, applied in proper form, can provide suitable nutrients and, therefore, make plants more resistant to pathogen infiltration [51]. Most studies dealing with Fusarium spp. infestation and grain contamination with mycotoxins focus on the impact of nitrogen fertilisation [52,53,54] Applying excessive amounts of nitrogen results in extended plant vegetative growth, making leaves more exposed to pathogens and the cellular wall thinner and more susceptible to penetration by fungi [55]. According to Lemmens et al. [22] and Piekarczyk i Lemańczyk [56], increasing nitrogen fertiliser rates had a significant impact on higher wheat infestation by Fusarium. The results of the experiments conducted by Aufhammer et al. [23], Krnjaja et al. [24] and El Chami et al. [4] did not show a significant impact of nitrogen fertilisation on infestation by Fusarium spp. and mycotoxin production in wheat grains.
Four mycotoxins were found in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON), nivalenol (NIV), zearalenone (ZEA) and moniliformin (MON). The weather conditions were found to have a varied impact on the cereal grain contamination with mycotoxins produced by Fusarium. A study conducted by El Chami et al. [4] demonstrated a significant impact of the growing season on mycotoxin production due to higher rainfall during the blossoming period when the wheat head is the most susceptible to Fusarium infestation. Only the deoxynivalenol level, as determined in the current study, was correlated with Fusarium spp. infestation. The study conducted by Góral et al. [57] did not show any correlation between the Fusarium head blight index and the DON level, but a correlation was found to exist with contamination by NIV. Wickiel and Filoda [58] analysed the intensity of Fusarium head blight and DON level in spelt grain and found no correlation between the symptom intensity and the toxin level. Nitrogen application at 150 kg ha−1 (without Mn) in the current study caused higher grain contamination with toxins than at 200 kg ha−1 N. The results of an experiment conducted by Aufhammer et al. [23], Czaban et al. [16] and El Chami et al. [4] did not show a significant impact of nitrogen fertilisation on infestation by Fusarium spp. or mycotoxin production in wheat grains. As mentioned above, Lemmens et al. [22] linked mycotoxin occurrence with increased nitrogen fertiliser rates.
Supplementation of nitrogen fertilisation with manganese in this study reduced the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain. Micronutrients contribute to the development of plant resistance to pathogens [59]. Manganese is an important micronutrient for plant growth and development [60,61]. It plays some metabolic roles in various processes of the plant life cycle, such as photosynthesis, respiration and the uptake of reactive oxygen species [62,63]. The presence of Mn is important for building structures of plant tissues, which is a physical barrier for pathogens [30,31].
4.3. Grain Yield
Net nitrogen productivity varied widely during the study years, and weather conditions largely decided the effectiveness of nitrogen fertilisation [64]. The grain yield determined in the current study was mainly affected by the varied weather conditions during the wheat-growing periods. Neither nitrogen nor manganese fertilisation differentiated the wheat grain yield. It has been shown in many studies [65,66] that foliar application of small amounts of micronutrients (alone or in combination with other essential nutrients) can increase the yield and its components, thereby improving wheat growth and quality. The grain yield was correlated with Fusarium spp. infestation since Fusarium head blight has an adverse impact on wheat grain yield [67]. This disease, as examined by Spanic [68], reduced the grain yield in some wheat cultivars by up to 64%.
5. Conclusions
Wheat infestation by Fusarium spp. was determined by the habitat conditions during crop growth. The performed PCA showed that the temperature (IV-VIII) had an effect on the infection of spikes by Fusarium spp. During the growing season in spring and summer, temperature and rainfall had no effect on the development of MON and DON mycotoxins. Neither nitrogen nor manganese fertilisation affected the presence of Fusarium spp. symptoms on wheat ears, but the infestation intensity decreased with increasing nitrogen and manganese content in the grain. Four mycotoxins were found in wheat grain: deoxynivalenol (DON), nivalenol (NIV), zearalenone (ZEA) and moniliformin (MON). Only the deoxynivalenol level was correlated with Fusarium spp. infestation. Nitrogen application at 150 kg ha−1 (without Mn) caused more intensive grain contamination with toxins than at 200 kg ha−1 N. Supplementation of nitrogen fertilisation with manganese reduced the number of mycotoxins in wheat grain (with the exception of ZEA content, which was unproved by statistical means). The grain yield was mainly affected by the varied weather conditions during the wheat-growing periods. Neither nitrogen nor manganese fertilisation differentiated the wheat grain yield.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.S., K.W., B.C.-A. and A.W.; methodology, A.S., K.W., B.C.-A. and A.W.; validation, A.S. and K.W.; formal analysis, A.S. and K.W.; investigation, A.S. and B.C.-A.; resources, A.S., K.W., B.C.-A. and A.W.; data curation, A.S., K.W., B.C.-A. and A.W.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S. and K.W., writing—review and editing, A.S. and K.W.; visualisation, A.S.; supervision, A.S. and K.W., project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, A.S., K.W. and B.C.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The results presented in this paper were obtained as part of a comprehensive study financed by the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry, Department of Agroecosystems and Horticulture (grant N 30.610.015–110).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wojtkowiak, K.; Warechowska, M.; Stępień, A.; Raczkowski, M. Crop yield and micronutrient contents (Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) in spring wheat grain depending on the fertilization method. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2017, 18, 135–149. Available online: https://hrcak.srce.hr/178340 (accessed on 31 July 2023). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquee, F.S.; Diakite, S.; Kavhiza, N.J.; Pakina, E.; Zargar, M. The Efficacy of Micronutrient Fertilizers on the Yield Formulation and Quality of Wheat Grains. Agronomy 2023, 13, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Chami, J.; El Chami, E.; Tarnawa, Á.; Kassai, K.M.; Kende, Z.; Jolánkai, M. Effect of Fusarium infection on wheat quality parameters. Cereal. Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hýsek, J.; Vavera, R.; Růžek, P. Influence of temperature, precipitation, and cultivar characteristics on changes in the spectrum of pathogenic fungi in winter wheat. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Luo, P. Changes in photosynthesis could provide important insight into the interaction between wheat and fungal pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegulo, S.N.; Baenziger, P.S.; Nopsa, J.H.; Bockus, W.W.; Hallen-Adams, H. Management of Fusarium head blight of wheat and barley. Crop Prot. 2015, 73, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różewicz, M.; Wyzińska, M.; Grabiński, J. The most important fungal diseases of cereals-Problems and possible solutions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaban, J.; Wróblewska, B.; Sułek, A.; Podolska, G. The influence of different production technologies of winter wheat on colonization of its grain by fungi of the genus fusarium. Pol. J. Agron. 2011, 5, 11–20. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.M.; Nicholson, P.; Thomsett, M.A.; Simpson, D.; Cooke, B.M.; Doohan, F.M.; Brennan, J.; Monaghan, S.; Moretti, A.; Mule, G.; et al. Relationship between the fungal complex causing Fusarium head blight of wheat and environmental conditions. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francl, L. Development of Fusarium head blight in relation to environment and inoculum. In Proceedings National Fusarium Head Blight Forum; Michigan State University, University Printing: East Lansing, MI, USA, 1998; pp. 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Doohan, F.M.; Brennan, J.; Cooke, B.M. Influence of climatic factors on Fusarium species pathogenic to cereals. In Epidemiology of Mycotoxin Producing Fungi: Under the Aegis of COST Action 835 ‘Agriculturally Important Toxigenic Fungi 1998–2003′, EU Project (QLK 1-CT-1998–01380); Kluwer Academic Publishers: Norwell, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 755–768. [Google Scholar]
- Czaban, J.; Wróblewska, B.; Sułek, A.; Mikos, M.; Boguszewska, E.; Podolska, G.; Nieróbca, A. Colonisation of winter wheat grain by Fusarium spp. and mycotoxin content as dependent on a wheat variety, crop rotation, a crop management system and weather conditions. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 874–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Raza, W.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q. Control of Fusarium wilt disease of cucumber plants with the application of a bioorganic fertilizer. Biol. Fert. Soils 2008, 44, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanic, V.; Cosic, J.; Zdunic, Z.; Drezner, G. Characterization of agronomical and quality traits of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) for fusarium head blight pressure in different environments. Agronomy 2021, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryła, M.; Ksieniewicz-Woźniak, E.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Szymczyk, K.; Jędrzejczak, R. Natural occurrence of nivalenol, deoxynivalenol, and deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in Polish winter wheat. Toxins 2018, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya, R.S.; O’Brien, J.; Cummins, E. Feed to fork risk assessment of mycotoxins under climate change influences-recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 126, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.E.H.; Steier, I.; Köppen, R.; Siegel, D.; Proske, M.; Korn, U.; Koch, M. Cocultivation of phytopathogenic Fusarium and Alternaria strains affects fungal growth and mycotoxin production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryła, M.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Podolska, G.; Szymczyk, K.; Jędrzejczak, R.; Damaziak, K.; Sułek, A. Occurrence of 26 mycotoxins in the grain of cereals cultivated in Poland. Toxins 2016, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochiieru, Y.; Mankevičienė, A.; Cesevičienė, J.; Semaškienė, R.; Ramanauskienė, J.; Gorash, A.; Janavičienė, S.; Venslovas, E. The impact of harvesting time on Fusarium mycotoxins in spring wheat grain and their interaction with grain quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, M.; Petry, L.; Barkusky, D.; Büttner, C.; Müller, M.E. Infected grasses as inoculum for Fusarium infestation and mycotoxin accumulation in wheat with and without irrigation. Mycotoxin Res. 2023, 39, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, M.; Haim, K.; Lew, H.; Ruckenbauer, P. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on Fusarium head blight development and deoxynivalenol contamination in wheat. J. Phytopathol. 2004, 152, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufhammer, W.; Kübler, E.; Kaul, H.P.; Hermann, W.; Höhn, D.; Yi, C. Infection with head blight (F. graminearum, F. culmorum) and deoxynivalenol concentration in winter wheat as influenced by N fertilization. Pflanzenbauwissenschaften 2000, 4, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Krnjaja, V.; Mandić, V.; Lević, J.; Stanković, S.; Petrović, T.; Vasić, T.; Obradović, A. Influence of N-fertilization on Fusarium head blight and mycotoxin levels in winter wheat. Crop Prot. 2015, 67, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwalina-Ambroziak, B.; Stępień, A.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Grzywińska-Rąpca, M. The Effect of Foliar Fertilization with Micronutrients on Disease Severity and Mycotoxin Concentrations in the Grain of Winter Spelt (Triticum aestivum spp. Spelta L.): A Case Study. Agronomy 2021, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supronienė, S.; Mankevičienė, A.; Kadžienė, G.; Kačergius, A.; Feiza, V.; Feizienė, D.; Semaškienė, R.; Dabkevičius, Z.; Tamošiūnas, K. The impact of tillage and fertilzation on Fusarium infection and mycotoxin production in wheat grains. Zemdirb. Agric. 2012, 99, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Podolska, G.; Bryła, M.; Sułek, A.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Szymczyk, K.; Jędrzejczak, R. Influence of the cultivar and nitrogen fertilisation level on the mycotoxin contamination in winter wheat. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crop. Foods 2017, 9, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, A.; Torp, M.; Clasen, P.E.; Løes, A.K.; Kristoffersen, A.B. Influence of agronomic and climatic factors on Fusarium infestation and mycotoxin contamination of cereals in Norway. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeil, A.; Doré, T.; Fourbet, J.F. Fusarium head blight: Epidemiological origin of the effects of cultural practices on head blight attacks and the production of mycotoxins by Fusarium in wheat grains. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1389–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas, C. Role of nutrients in controlling plant diseases in sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, A.L.; Guerinot, M.L. Mn-euvering manganese: The role of transporter gene family members in manganese uptake and mobilization in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łacicowa, B. Investigations on Helminthosporium sorokinianum (H. sati um) strains and on the resistance of spring barley varieties to this pathogenic factor. Acta Mycol. 1970, 6, 184–248. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Goliński, P.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Wiśniewska, H.; Kiecana, I.; Mielniczuk, E.; Gromadzka, K.; Kostecki, M.; Bocianowski, J.; Rymaniak, E. Reaction of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars to infection with Fusarium spp.: Mycotoxin contamination in grain and chaff. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waśkiewicz, A.; Irzykowska, L.; Drzewiecka, K.; Bocianowski, J.; Dobosz, B.; Weber, Z.; Karolewski, Z.; Krzyminiewski, R.; Goliński, P. Plant-pathogen interactions during infection process of asparagus with Fusarium spp. Open Life Sci. 2013, 8, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrell, W.M.; Beverly, R.B. The dilution effect in plant nutrition studies. Adv. Agron. 1981, 34, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Reeves, P.G.; Jones, S.S. Relationship between yield and mineral nutrient concentrations in historical and modern spring wheat cultivars. Euphytica 2008, 163, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Larsson, H.; Kuktaite, R.; Johansson, E. Mineral composition of organically grown wheat genotypes: Contribution to daily minerals intake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3442–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttieri, M.J.; Baenziger, P.S.; Frels, K.; Carver, B.; Arnall, B.; Waters, B.M. Variation for grain mineral concentration in a diversity panel of current and historical Great Plains hard winter wheat germplasm. Crop. Sci. 2015, 55, 1035–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.G.; Janzen, H.H.; Ellert, B.H. Effect of fertilizer and cropping system on grain nutrient concentrations in spring wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 98, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, F.; Römheld, V.; Zou, C. Influence of long-term nitrogen fertilization on micronutrient density in grain of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamnér, K.; Weih, M.; Eriksson, J.; Kirchmann, H. Influence of nitrogen supply on macro-and micronutrient accumulation during growth of winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2017, 213, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marles, R.J. Mineral nutrient composition of vegetables, fruits and grains: The context of reports of apparent historical declines. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 56, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, B.B.; Gruissem, W.; Vickers, K.; Jones, R.L. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants; Wiley-Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtkowiak, K.; Stepien, A.; Pietrzak-Fiecko, R.; Werechowska, M. Effects of nitrogen fertilisation on the yield, micronutrient content and fatty acid profiles of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Buczek, J.; Jarecki, W.; Bobrecka-Jamro, D. Effect of high nitrogen doses on yield, quality and chemical composition grain of winter wheat cultivars. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svecnjak, Z.; Jenel, M.; Bujan, M.; Vitali, D.; Dragojević, I.V. Trace element concentrations in the grain of wheat cultivars as affected by nitrogen fertilization. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klikocka, H.; Marks, M. Sulphur and nitrogen fertilization as a potential means of agronomic biofortification to improve the content and uptake of microelements in spring wheat grain DM. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 9326820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolijanović, Ž.; Nikolić, R.S.; Kovacević, D.; Djurdjić, S.; Miodragović, R.; Todorović-Jovanovic, M.; Djordjević, P.J. Mineral profile of the winter wheat grain: Effects of soil tillage systems and nitrogen fertilization. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 11757–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, J.; Bateman, G.L.; Mirocha, C.J. Effects of infection time and moisture on development of ear blight and deoxynivalenol production by Fusarium spp. in wheat. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1999, 134, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyneri, A. The role of climatic condition on micotoxin production in cereal. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, H.; Nabizadeh, E.; Hossienpour, M. The effect of Fertilizers and biologiical nitrogen and planting density on yield quality and quantity. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 2, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Hassegawa, R.H.; Fonseca, H.; Fancelli, A.L.; da Silva, V.N.; Schammass, E.A.; Reis, T.A.; Corrêa, B. Influence of macro-and micronutrient fertilization on fungal contamination and fumonisin production in corn grains. Food Control 2008, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, M.; Vuković, R.; Vrandečić, K.; Štolfa Čamagajevac, I.; Ćosić, J.; Vuković, A.; Sabljić, K.; Sabo, N.; Dvojković, K.; Novoselović, D. Oxidative status and antioxidative response to Fusarium attack and different nitrogen levels in winter wheat varieties. Plants 2021, 10, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maywald, N.J.; Francioli, D.; Mang, M.; Ludewig, U. Role of Mineral Nitrogen Nutrition in Fungal Plant Diseases of Cereal Crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2023, 42, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, L.M.; Zhu, X.; Ma, B.L. Crop rotation and nitrogen effects on maize susceptibility to gibberella (Fusarium graminearum) ear rot. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarczyk, M.; Lemańczyk, G. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on health status of some winter wheat cultivars grown on light soil. Prog. Plant Prot. 2013, 53, 494–497. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Góral, T.; Wiśniewska, H.; Ochodzki, P.; Nielsen, L.K.; Walentyn-Góral, D.; Stępień, Ł. Relationship between Fusarium head blight, kernel damage, concentration of Fusarium biomass, and Fusarium toxins in grain of winter wheat inoculated with Fusarium culmorum. Toxins 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickiel, G.; Filoda, G. Fungicide protection and presence of fusarium ear symptoms and deoxynivalenol content in the grain of winter spelt. Ochrona fungicydowa a obecność objawów fuzariozy kłosów i deoksyniwalenolu w ziarnie pszenicy ozimej orkisz. Prog. Plant Prot. 2012, 52, 676–679. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Arif, N.; Yadav, V.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Ahmad, P.; Mishra, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, D.K.; Dubey, N.K.; Chauhan, D.K. Influence of high and low levels of plant-beneficial heavy metal ions on plant growth and development. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.; Mishra, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Dubey, N.K. Micronutrients and their diverse role in agricultural crops: Advances and future prospective. Acta Physiol. Plant 2015, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Singh, P.K.; Mankotia, S.; Swain, J.; Satbhai, S.B. Iron homeostasis in plants and its crosstalk with copper, zinc, and manganese. Plant Stress 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millaleo, R.; Reyes-Díaz, M.; Ivanov, A.G.; Mora, M.L.; Alberdi, M. Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: Transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.B.; Eisenhut, M.; Schneider, A. Chloroplast transition metal regulation for efficient photosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierna, A.; Lombardo, G.M.; Mauromicale, G. Yield, nitrogen use efficiency and grain quality in durum wheat as affected by nitrogen fertilization under a Mediterranean environment. Exp. Agric. 2016, 52, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K. Effect of foliar application of Cu, Zn, and Mn on yield and quality indicators of winter wheat grain. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 76, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.Z.; Yaseen, M.; Abbas, T.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Hamid, Y.; Saeed, Q.; Xu, M.G. Foliar application of micronutrients enhances crop stand, yield and the biofortification essential for human health of different wheat cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweba, C.C.; Figlan, S.; Shimelis, H.A.; Motaung, T.E.; Sydenham, S.; Mwadzingeni, L.; Tsilo, T.J. Fusarium head blight of wheat: Pathogenesis and control strategies. Crop Prot. 2017, 91, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanic, V.; Lemmens, M.; Drezner, G. Variability of components of Fusarium head blight resistance among wheat genotypes. Cereal Res. Commun. 2013, 41, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).