Abstract
Background: to analyze the dento-alveolar effects induced by two treatment appliances (i.e., RME and Clear Aligners) in growing subjects presenting with early mixed dentition and mild maxillary deficiency. Methods: digital casts of 32 children treated with RME (RG: 17 subjects) or with Clear aligners (CAG: 15 subjects) were collected. Linear and angular values were measured in both groups on the upper arch for both pre- (T1) and post-treatment (T2) models. An unpaired t-test was used to test significant differences between groups (p < 0.05). Results: the comparison of T2-T1 changes for linear measurements between groups showed a greater increase in the inter-canine width (+1.5 mm ± 0.5 mm) and in the first inter-deciduous molar width (+1.4 ± 0.4 mm), also at the trans-palatal level in the CAG group. Conversely, in the posterior region of the upper arch, a greater increase in the first inter-molar distal width was found in the RG group (+1.2 ± 0.4 mm) when compared with the CAG group. A significant increase in the crown angulation in the CAG group was found for all the teeth except for the first molars. Conclusions: the rapid palatal expander widened the palate, tipping the first upper molars buccally to a greater extent, whereas the Clear aligners caused a greater increase in the canine width.
1. Introduction
The rationale of interceptive treatment in mixed dentition is to create appropriate space for the alignment of the permanent teeth prior to complete eruption and to solve transverse discrepancies [1]. When crowding is limited to a few millimeters, normal growth could provide adequate space, but when the crowding exceeds this amount, orthodontic expansion could represent an effective procedure [1]. The expansion of the maxillary arch is differentiated into orthopedic or dentoalveolar types [2].
One of the most common orthopedic procedures is the opening of the mid-palatal suture through Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) [3,4,5]. The orthopedic management of maxillary transverse deficiency was first reported in 1860 [1] by exerting expansion forces at the mid-palatal and intermaxillary sutures [2,3]. Since then, the RME has been widely used and proven to be effective for the correction of maxillary posterior crossbites [4], transverse dental arch discrepancies [5], and deficient arch perimeter [1,3,4,5,6,7].
On the other hand, dentoalveolar expansion can be performed using several conventional fixed, removable appliances or aligners. When aligners are used, the force is applied directly to the teeth, producing a lateral displacement of the upper dento-alveolar structures. Clear aligners can be adjusted to expand the molars and anterior teeth differentially, and they have the ability to rotate molars [2]. Few authors have investigated the changes in the upper maxillary arch under the influence of Clear aligners in adults, and to our best knowledge, very few studies have analyzed the effects induced by Clear aligners in mixed dentition [8,9].
In 2021, Levrini et al. [8] evaluated the dentoalveolar changes in 20 patients treated with Clear aligners in mixed dentition. In this study, the superimpositions of pre- and post-treatment dental models revealed that Clear aligners could be a great alternative to Slow Maxillary Expansion in the case of mild crowding or limited transverse deficiency.
A further study was published by Lione et al. [9], in 2021. In this prospective investigation, transverse widths were measured in the upper arch on digital models obtained at the beginning and at the end of treatment performed by Clear aligners. The authors concluded that the Clear aligner can be considered in growing patients who require maxillary arch form changes, especially in the anterior and lateral regions.
Therefore, the objective of this retrospective study was to analyze the dento-alveolar effects induced by two treatment appliances (i.e., RME and Clear aligners) in growing subjects presenting with early mixed dentition and mild maxillary deficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
This study followed the principles laid down by the World Medical Assembly in the Declaration of Helsinki 2008 on medical protocols and ethics, it was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of University of Rome “Tor Vergata” (protocol number: 257/21), and informed consent was obtained from the patients’ parents.
Digital dental casts of 32 children consecutively treated either with RME (RG group: n = 17, 8 males, 9 females; mean age 8.1 ± 0.8 years) or the Clear aligners (CAG group: n = 15, 7 males, 8 females; mean age 8.4 ± 1.1 years) were collected. Study subjects were retrieved from the records of patients treated at the Department of Orthodontics at the University of Rome “Tor Vergata”.
The inclusion criteria consisted of European ancestry, posterior transverse discrepancy between maxillary and mandibular arches of up to 6 mm [10], mixed dentition, mesial step or flush terminal plane molar relationship, fully erupted first molars, and a high level of compliance. The posterior transverse inter-arch discrepancy was obtained by calculating the difference between the maxillary intermolar width (distance between the central fossae of right and left first maxillary molars) and the mandibular intermolar width (distance between the mesio-vestibular cusps of right and left first mandibular molars) [10].
The exclusion criteria included multiple and/or advanced caries, tooth agenesis, supernumerary teeth, cleft lip and/or palate, Class III malocclusion, and oral breathing.
2.1. Treatment Protocol
RG subjects were treated with a butterfly palatal expander (Figure 1) [11]. This appliance has a butterfly-shaped stainless-steel framework banded on the first maxillary molars, which extends forward to the palatal surfaces of maxillary deciduous molars. The screw was activated by the parents at 1/4 turns per day (one activation, 0.25 mm per turn) and the activation of the screw commenced immediately after the appliance was cemented in place.
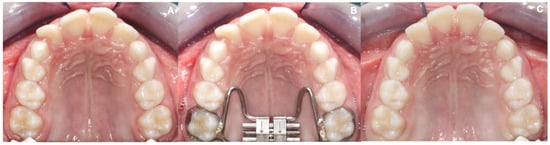
Figure 1.
(A) Pre-treatment maxillary arch; (B) RME appliance; (C) post-treatment maxillary arch.
The expansion screw was activated until the palatal first maxillary molar cusps touched the vestibular first mandibular molar cusps, and the expanders were kept on the teeth as a passive retainer and removed 8 months after their application. During active treatment, patients were checked every 2 weeks to monitor the activation of the screw [12]. The average treatment time was 8 months and intra-oral scans were taken 3 months after the end of active therapy to create digital dental casts.
CAG subjects underwent a non-extraction treatment protocol with Invisalign® Clear aligners with no other auxiliaries than attachments and no enamel Interproximal Reduction (IPR) (Figure 2).
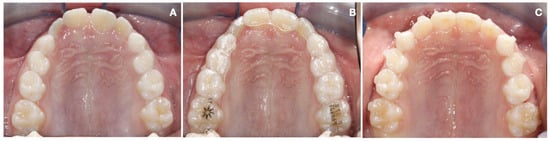
Figure 2.
(A) Pre-treatment maxillary arch; (B) Clear aligners application; (C) post-treatment maxillary arch.
The ClinCheck® for each patient was planned with the same standardized expansion protocol: sequential staging pattern for upper arch expansion and “molars move first”, followed by the simultaneous expansion of the posterior deciduous teeth and canines. The level of arch expansion was 0.25 mm per stage [9].
For upper first molars, a simultaneous distorotation according to Rickett’s line [13] and 2 degrees of extra buccal root torque were required for each phase of expansion. Overcorrection of the transverse upper dimension was never prescribed, but a cusp–fossa relationship was digitally planned [9].
All patients were instructed to wear their aligners full time. The patients changed the aligners every 7 days and every 4 stages the clinician checked the good aligner fit. Optimized attachments were placed on the basis of the tooth surface by the software. The treatment lasted 8 months and the digital scans were taken 3 months after the end of the therapy to create digital dental casts.
In both groups, no retention appliance was applied at the end of active therapy.
2.2. Measurement Protocol
For both RG and CAG groups, pre- (T1) and post-treatment (T2) digital casts were created from an iTero scan. All models were exported in a Standard Tessellation Language format (.stl digital file).
Then, the files were uploaded in the Viewbox 4 software (dHAL software, Kifissia, Greece) in order to digitize the casts and to perform the arch change evaluation.
The following transversal linear values were measured (Figure 3) [9]:
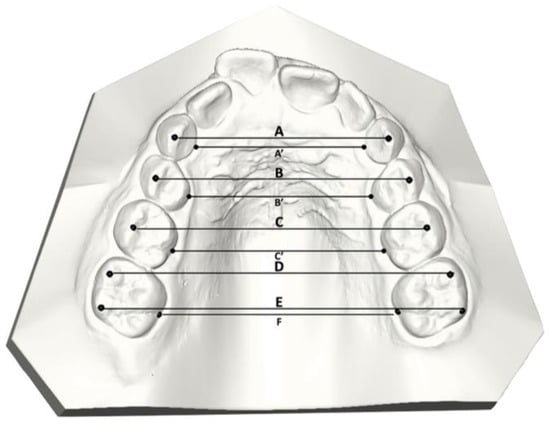
Figure 3.
Upper maxillary arch linear measurements.
- Inter-canine width: linear distance between cusp tips of the deciduous canines (A);
- First inter-deciduous molar width: linear distance between the vestibular cusp tips of the first deciduous molars (B);
- Second inter-deciduous molar width: linear distance between the sulcus of the second deciduous molars (C);
- First inter-molar mesial width: linear distance between the mesiobuccal cusp tips of the first molars (D);
- First inter-molar distal width: linear distance between the distobuccal cusp tips of the first molars (E);
- First inter-molar transpalatal width: linear distance between the groove of the first molars at the mucosa (F);
- Inter-canine transpalatal width: linear distance between the groove of the deciduous canines at the mucosa (A’);
- First inter-deciduous molar transpalatal width: linear distance between the groove of the first deciduous molars at the mucosa (B’);
- Second inter-deciduous molar transpalatal width: linear distance between the groove of the second deciduous molars at the mucosa (C’).
To evaluate the tooth inclination, a best-fit occlusal plane was set passing through the buccal cusp tips of the first molars, first and second deciduous molars, deciduous canines, and the incisal edges of lateral and central incisors. This plane was used as a reference for generating one additional reference plane, i.e., the para-coronal plane. The upper arch was divided into four sectors: from the first left molar to the deciduous first left molar, from the first left deciduous molar to the lateral left incisor, from the lateral right incisor to the first right deciduous molar, and from the first right deciduous molar to the first right molar. For each sector, the para-coronal plane was obtained perpendicular to the occlusal plane. For every analyzed tooth, a curve passing through the long axis was drawn, and the best fit line was set using the most occlusal and the most gingival points of the curve as references. Tooth inclination was obtained by the angle formed between the best-fit line of each tooth and the para-coronal plane (Figure 4) [14].
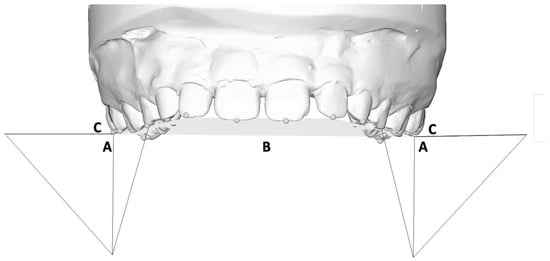
Figure 4.
Crown angular measurements: For both left and right sectors, a para-coronal plane (A) was obtained perpendicularly to the occlusal plane (B). A curve passing through the first molar long axis was drawn and a best-fit line was set using the most occlusal and the most gingival points of the curve as reference (C). Tooth inclination was obtained from the angle formed between the best fit line of each tooth and the para-coronal plane [14].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
In a pilot study, 10 patients were used to calculate the reproducibility and the sample size, which indicated the need for approximately 20 patients (10 for each group) to estimate the inter-canine width with a 95% confidence interval (CI), a minimum difference of 2.5 mm and a standard deviation (SD) of 2.0 mm, with a power of 80%.
To determine the reliability of the method, all the measurements on dental casts were performed by one trained examiner (ECL) and repeated by the same examiner after an interval of approximately 2 weeks. A paired t-test was used to compare the two measurements (systematic error, p value < 0.05). The magnitude of the random error was calculated by using the method of moments estimator [15].
An unpaired t-test was used to perform the analysis of the staring forms and the statistical comparison of T2-T1 changes for all the performed measurements between CAG and RME groups.
3. Results
No systematic error was found. The random error for the linear measurements ranged from 0.08 mm (F) to 0.26 mm (E) and for the angular measurements ranged from 0.29° (element 64) to 0.43° (element 53).
As reported in Table 1, the analysis of the starting forms showed no statistically significant differences at T1 between the groups for all measurements.

Table 1.
Starting forms for linear and angular measurements between Clear aligners and RME groups.
Transverse discrepancy at the start of the treatment resulted mild of 5.1 ± 0.6 mm in RG group and of 4.6 ± 0.3 mm in CAG group. The pre-treatment value of the transpalatal arch width was of 34.7 mm for the CAG and of 33.3 mm for the RG and therefore within normal limits for both groups with a dento-alveolar origin of the transversal constriction.

Table 2.
Descriptive and statistical comparison of T2-T1 changes for linear measurements between Clear aligners and RME groups.

Table 3.
Descriptive and statistical comparison of T2-T1 changes for angular measurements between Clear aligners and RME groups.
The comparison of T2-T1 changes for transversal linear measurements between RG and CAG groups showed statistically significant differences in the inter-canine width (+1.5 mm ± 0.5 mm in CAG), in the first inter-deciduous molar width (+1.4 mm ± 0.4 mm in CAG), in the first inter-molar distal width (+1.2 mm ± 0.4 mm in RG), in the inter-canine transpalatal width (+1.5 mm ± 0.5 mm in CAG), and in the first inter-deciduous molar transpalatal width (+1.4 mm ± 0.4 mm in CAG). Moreover, the comparison of T2-T1 changes for angular measurements showed a statistically significant increase in the crown angulation for all the examined teeth in patients treated with aligners, except for the first molars.
4. Discussion
Over the years, several appliances have been proposed for the treatment of transverse discrepancy, and among these one of the most commonly used for orthopedic expansion is the Rapid Maxillary Expander (RME) [1,3,4,5,6,7]. However, in recent years, Align Technology introduced Invisalign® First System as an orthodontic approach that can be used to resolve crowding, improving the dental arch form by inducing dento-alveolar changes in growing subjects presenting with early mixed dentition [8,9].
The purpose of this study was to analyze the dento-alveolar changes obtained on the maxillary arch at the end of treatment with RME and Clear aligners. These two appliances are different from each other; the RME is an orthopedic device which aims to have skeletal effects rather than dental by opening the mid-palatal suture in growing individuals [15,16], whereas Clear aligners operate by pushing on the clinical dental crown, inducing dento-alveolar modifications [9].
The choice to select patients with the RME anchored on the first maxillary molars was taken to make the two study samples as homogenous as possible even if the second deciduous molars were suitable for anchorage.
The results of the present study showed a greater increase in the inter-canine width (+1.5 mm ± 0.5 mm) and in the first inter-deciduous molar width (+1.4 mm ± 0.4 mm), and also at the transpalatal level, in the CAG group when compared with the RG group (Table 2).
Conversely, in the posterior region of the upper arch, a greater increase in the first inter-molar distal width was found in the RG group (+1.2 mm ± 0.4 mm) when compared with the CAG group. This could be explained by the reverse “V” pattern RME expansion related to the anteroposterior increase in skeletal resistance. In fact, in the anterior region, where skeletal resistance is minimal, no dental compensation was observed, while across the molar region, where maximal skeletal resistance occurs, minor sutural and major dental response was realized [16], as overall maxillary expansion is a result of both skeletal and dentoalveolar displacement.
On the other hand, Clear aligners push against the palatal tooth surface, inducing lateral dental displacement and an increase in the distance among dental cusps. For this reason, at the level of second deciduous molars no significant differences were found between groups in both linear and angular values.
Due to skeletal and dental contribution to expansion, a significantly greater increase in the inter-molar distance could be observed in the RME group at the level of disto-vestibular cusps for both linear and angular measurements. However, the inter-group difference in intermolar distance at the level of mesio-vestibular cusps was not statistically significant, probably as an effect of the rotational component, which occurs during expansion in Clear aligners treatment [9]. Those results suggested that Clear aligners are able to determine dento-alveolar ex-pansion in the inter-canine width changing the arch-form especially in the anterior and lateral regions. Clear aligners appliance can increase dental width differentially anteroposteriorly, whereas the rapid expander cannot. For this reason, when skeletal expansion is required, a palatal expander designed with anterior extension until de-ciduous canines is recommended to obtain a simultaneous increase of the intercanine width and a modification of the maxillary arch form.
Similar observations were reported by Lione et al. [9], showing that Clear aligners allow the expansion of a narrow maxilla, changing the arch form. In this cited study, the greatest increase was detected at the level of the first deciduous molars (+3.7 ± 1.4 mm), followed by the second deciduous molars (3.4 ± 1.6 mm) and the deciduous canine (2.6 ± 2.0 mm). Moreover, when analyzing the movements of the first molars, the authors found a greater expansion of the intermolar mesial width (+3.2 ± 1.2 mm) than of the intermolar distal (+1.7 ± 1.2 mm) and trans-palatal widths (+1.2 ± 1.2 mm) due to the movement of the first molars, which tipped buccally and simultaneously rotated around the palatal root [9].
Also, Levrini et al. [8] reported a significant increase for all the measurements regarding the arch width, with an increase in the inter-canine width of 2.8 mm at cusp level and 2.01 mm at gingival level, an increase in the first deciduous molars width of 3.28 mm at cusp tip level and of 2.24 mm at gingival level, and an increase in the second deciduous molar width of 3.72 mm at cusp tip level and of 2.59 mm at gingival level.
In the present study, the CAG group showed good control of the crown angulation of the upper first molars due to the overcorrection of 2 degrees extra buccal root torque to overcome the side effects of dental tipping. The evaluation of the first molars angulation was performed 3 months after the end of the active phase of treatment to allow the recovery from transient dental tipping [17]. From our results, a significantly greater crown angulation was still present in RME patients when compared with FG subjects.
In accordance with our study, Levrini et al. [8] analyzed the molar inclination in patients treated with Clear aligners in mixed dentition, finding a significant decrease of 4.64 degrees.
A previous study published by McNamara et al. [18] confirmed our results about the changes in the molar crown angulation with RME treatment. McNamara et al. [18], evaluating short- and long-term changes in dental arch dimensions in patients treated with RME, found an increase in the crown angle of the first permanent molars of 4.8° at the end of the active treatment.
Limitations of the Study
A limitation of the present retrospective study is the bidimensional nature of the measurements performed on the available digital casts. For this reason, it was not possible to measure the contributions of bone, teeth, and tipping to evaluate the reliability of the results. Moreover, a further limitation of the present investigation was its short-term nature and the small sample size of the treated groups. Therefore, further evaluations are necessary to increase the sample size and to analyze the stability of the results obtained in the long-term.
5. Conclusions
In the current study, performed on digital casts of growing subjects, the rapid palatal expander widened the palate to a greater extent with an associated buccal tipping of the first upper molars, whereas the Clear aligners caused a greater increase in the inter-canine width.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L. and P.C.; methodology, C.P.; software, C.P.; validation, R.L., P.C. and E.C.L.; formal analysis, S.F.; investigation, S.F.; resources, E.C.L.; data curation, R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F.; writing—review and editing, E.C.L.; visualization, R.L.; supervision, R.L.; project administration, P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Rome “Tor Vergata” (protocol code 257/21; date of approval 22 December 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the parents of all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request due to restrictions, e.g., privacy or ethical.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report a funding relationship between themselves and Align Technology. However, Align Technology had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rosa, M.; Lucchi, P.; Manti, G.; Caprioglio, A. Rapid Palatal Expansion in the absence of posterior cross-bite to intercept maxillary incisor crowding in the mixed dentition: A CBCT evaluation of spontaneous changes of untouched permanent molars. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2016, 17, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Bernárdez, M.L.; Vilches-Arenas, Á.; Sonnemberg, B.; Solano-Reina, E.; Solano-Mendoza, B. Efficacy and predictability of maxillary and mandibular expansion with the Invisalign® system. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e669–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, M.D.; Nanda, R.S.; Currier, G.F. Arch perimeter changes on rapid palatal expansion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1990, 97, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lione, R.; Ballanti, F.; Franchi, L.; Baccetti, T.; Cozza, P. Treatment and posttreatment skeletal effects of rapid maxillary expansion studied with low-dose computed tomography in growing subjects. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 134, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lione, R.; Franchi, L.; Fanucci, E.; Laganà, G.; Cozza, P. Three-dimensional densitometric analysis of maxillary sutural changes induced by rapid maxillary expansion. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2013, 42, 71798010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerruto, C.; Ugolini, A.; Di Vece, L.; Doldo, T.; Caprioglio, A.; Silvestrini-Biavati, A. Cephalometric and dental arch changes to Haas-type rapid maxillary expander anchored to deciduous vs permanent molars: A multicenter, randomized controlled trial. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2017, 78, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.N.; Araujo, E.A.; Oliver, D.R.; Kim, K.B. Long-term stability of rapid palatal expansion in the mixed dentition vs the permanent dentition. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrini, L.; Carganico, A.; Abbate, L. Maxillary expansion with clear aligners in the mixed dentition: A preliminary study with Invisalign® First system. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2021, 22, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lione, R.; Cretella Lombardo, E.; Paoloni, V.; Meuli, S.; Pavoni, C.; Cozza, P. Upper arch dimensional changes with clear aligners in the early mixed dentition: A prospective study. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2021, 84, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollaro, I.; Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Tanasescu, C.D. Role of posterior transverse interarch discrepancy in Class II, Division 1 malocclusion during the mixed dentition phase. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1996, 110, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, P.; Giancotti, A.; Petrosino, A. Butterfly expander for use in the mixed dentition. J. Clin. Orthod. 1999, 33, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paoloni, V.; Giuntini, V.; Lione, R.; Nieri, M.; Barone, V.; Merlo, M.M.; Mazza, F.; Passaleva, S.; Cozza, P.; Franchi, L. Comparison of the dento-skeletal effects produced by Leaf expander versus rapid maxillary expander in prepubertal patients: A two-center randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 44, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, R.M. Occlusion—The medium of dentistry. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1969, 21, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lione, R.; Paoloni, V.; Bartolommei, L.; Gazzani, F.; Meuli, S.; Pavoni, C.; Cozza, P. Maxillary arch development with Invisalign system. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springate, S.D. The effect of sample size and bias on the reliability of estimates of error: A comparative study of Dahlberg’s formula. Eur. J. Orthod. 2012, 34, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.J. Palatal expansion: Just the biginning of facial orthopedics. Am. J. Orthod. 1970, 57, 219–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovitch, M.; Efstathiou, S.; Sarne, O.; Vardimon, A.D. Skeletal and dental response to rapid maxillary expansion with 2- versus 4-band appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Herberger, T.A. Rapid maxillary expansion followed by fixed appliances: A long-term evaluation of changes in arch dimensions. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).