Abstract
The integration of variable stiffness materials and structures into soft robots is a popular trend, allowing soft robots to switch between soft and rigid states in different situations. This concept combines the advantages of rigid mechanisms and soft robots, resulting in not only excellent flexibility but also tunable stiffness for high load capacity and fast and precise operation. Here, a stiffness-tunable soft actuator based on wire/fiber jamming structure is proposed, where the fiber-reinforced soft actuator is responsible for the bending motion, and the jamming structure acts as a stiffness-tunable layer controlled by vacuum pressure. The primary design objective of this study is to fabricate a jamming structure with wide-range stiffness, universal adaptability and high dexterity. Thus, the behaviors of wire/fiber jamming structures with different layouts, materials and wire arrangements are analyzed, and a theoretical model is developed to predict the effect of geometric parameters. Experimental characterizations show that the stiffness can be significantly enhanced in the bending direction, while the stiffness is smaller in the torsion direction. Additionally, by integrating Velcro strips into the design, a quick and detachable scheme for the stiffness-tunable soft actuator is achieved. Application examples exhibit high load capacity and good shape adaptability.
1. Introduction
Soft machines fabricated with soft materials have been rapidly developed in recent years. They have proven to have great potential for applications in industrial robot manipulators, medical devices, biomimetic robots, wearable exoskeletons and aerospace structures [1,2,3,4,5]. The Young’s modulus of soft materials is defined in the order of 104–109 Pa [1]. Compared with conventional rigid mechanisms, soft machines and actuators can handle fragile or irregular objects without massive computations or sensing systems, and interact with human bodies safely [6], but still carry with drawbacks due to their low stiffness and hyper-elastic properties. Soft actuators are unsuitable for working in areas with large load capacity, high-speed motion and precise control. Many soft robots can be stiffened by simply increasing air pressure, reducing size, adding rigid components or using higher hardness materials [7,8,9]. However, these solutions have limited effect and may lead to reduced flexibility.
In order to address these drawbacks, researchers have focused on developing stiffness tunable materials and structures such as shape memory alloys (SMAs), shape memory polymers (SMPs), low melting point alloys and jamming structures [10,11,12,13,14]. Among these stiffness-tunable schemes, jamming structures are favored by scholars owing to their advantages of structure simplicity, ease of fabrication and wide range of stiffness variation. Two main types of jamming structures, granular and laminar jamming structures, have been extensively studied [15]. Granular jamming consists of particle elements such as grains, coffee grounds, hollow spheres or interlocked granular particles in an airtight envelope [13,16,17,18]. The jamming principle is to change the particles from a flowing state to a solid-like state by applying vacuum pressure or external force [19,20]. These granular jamming mechanisms have been integrated into soft actuators and soft robotic grippers, which fit well on irregular surfaces and provide significant stiffness tunability [21,22,23]. However, passive jamming of particles due to bending behavior can reduce the bending range of the integrated soft actuator [22]. Depending on the applications, there are challenges in selecting the optimal particle size, shape and material. For example, smaller irregular particles lead to poor fluidity and thus affect the flexibility of the jamming structure, while larger particles reduce the compliance to object shape. In addition, it is difficult to resist significant tensile stresses with vacuum-driven granular jamming structures [24]. Laminar jamming structures, also known as layer jamming, are developed using papers or other flexible layers [25,26,27]. When vacuum pressure is applied, the raised friction between the layers will prevent them from sliding against each other. The tunable-impedance mechanisms based on laminar jamming were well studied by Narang et al. [28,29,30]. The layer jamming structure exhibits beam-like deflection characteristics when the vacuum pressure is open, showing a higher performance-to-mass ratio compared to other variable stiffness structures. In addition, layer jamming has a compact structure often applied to slender soft robots. However, these stacked planar layers are only suitable for movement in a single plane. The deformability of layer jamming is lower than that of granular jamming. Therefore, a reconfigurable jamming skin has been designed [31]. This structure consists mainly of small overlapping sheets that allow for stretching and 3D deformation. However, this structure is more complex, and some mechanical problems still need to be optimized.
Recent investigations have shown that fiber jamming is an alternate scheme for tunable stiffness mechanisms in which fibers or wires are used as the jamming medium [32,33]. Fiber jamming, which can also be called wire jamming [34], exhibits features similar to granular jamming and layer jamming in cross-sectional and axial planes, respectively. Based on the characteristics of fiber jamming, researchers presented three arrangement options and applied fiber jamming transition to a manipulator [35,36]. In addition, hybrid jamming structures have been reported, consisting of two or more different jamming media. Therefore, these hybrid structures combine the advantages of different jamming schemes [37,38,39]. At present, the research areas of fiber jamming and hybrid jamming are still in their infancy and many factors have not been studied.
During the design of soft actuators and stiffness-tunable structures, 3D printing technology provides an excellent, systematic tool to directly fabricate structures with elastomeric materials [11,26,40]. Bastola et al. [41] developed soft robots that mimicked cactus stem geometries and used 3D printing technology to fabricate thin elastomeric layers. In order to solve the problem of fabricating soft actuators with complex inner geometry, a method of 3D printing with fused deposition modelling (FDM) is proposed [42]. Ma et al. [43] presented a magnetic multi-material printing technique and fabricated soft programmable composites with tunable Poisson’s ratio and shiftable mechanical behaviors. However, current 3D printing technology still has some limitations, such as speed, material compatibility and resolution [40]. Therefore, further research is needed for 3D printing materials and printing devices applied to soft robots. To further study the properties of the stiffness tunability of wire/fiber jamming structures and explore their applications (Figure 1a,b), we propose a paradigm to design and fabricate a type of tunable-stiffness soft actuator based on wire/fiber jamming. The stiffness-tunable soft actuator mainly consists of a soft pneumatic actuator and a wire/fiber jamming mechanism. Through rigorous analysis of various operating conditions, a new wire jamming structure with flexible 3D bending capability and a wide range of stiffness variation is developed to meet the needs of different applications. Bending and torsion experiments are carried out to investigate the performance of our wire jamming mechanisms, and the results show a remarkable rise in bending stiffness under vacuum pressure.
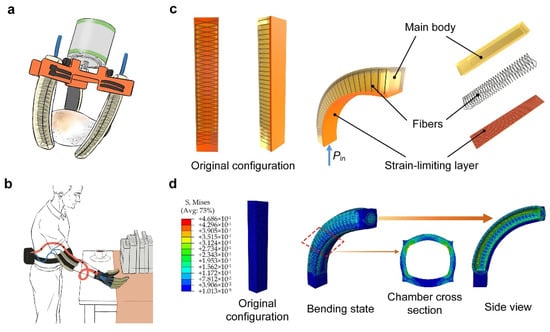
Figure 1.
Application scenarios and characteristics analysis of the soft pneumatic actuators. (a,b) Soft actuators are applied to a robotic gripper and a wearable exoskeleton. (c) Bending display of a fiber-reinforced soft actuator with rectangular cross-section, where Pin is the air pressure. (d) FE simulation of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator (Pin = 64 kPa), where the air channel modeling is ignored, and the fibers are hidden from the results.
In this study, a fiber-reinforced pneumatic actuator is used as a driving unit because it not only has a flat surface but also has a smaller expansion coefficient under air pressure (Figure 1c) [44,45,46]. To understand the bending performance of the fiber-reinforced actuator, we develop a theoretical model and determined the geometric parameters of the soft actuator (Section S1 and Figures S1 and S2 Supplementary Materials) [45]. In addition, uniaxial tensile tests are conducted to analyze the tensile properties of silicone rubber (see Section S2 and Figure S3 in the Supplementary Materials for details). The bending state of the actuator can be obtained from FE simulation results (Figure 1d). Since both the inner chamber structure and the outer structure are quite simple, the fiber-reinforced soft actuators are fabricated by 3D-printed molds.
In order to improve the flexibility and universal adaptability, we use a modular approach by integrating Velcro into the design of variable stiffness actuators, where the Velcro acts as an inextensible layer as well as a standardized connector for the actuator and wire jamming mechanism. Because of the advantages of rapidity, convenience and reliability, this paper applies Velcro to wearable devices, such as detachable soft gloves. At present, scholars have developed a variety of functional gloves. For example, Kadumudi et al. [47,48] developed multifunctional materials with self-healing, conductive and stretchable properties, and applied them to wearable sensors and bionic gloves. Cheraghi Bidsorkhi et al. [49] designed a waterproof and flexible nanocomposite membrane and attached it to a commercial glove to detect joint movements. Compared with these gloves, the soft gloves designed in this paper not only have the function of tuning their stiffness but also can add or replace sensing and driving devices according to different needs. However, Velcro is not stretchable, so its use limits the application of some materials in soft gloves.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Wire Jamming Structures
In order to achieve wire jamming structures with high load capacity, good reversibility and universal adaptability, many critical factors such as installation layouts, materials and dimensions, and wire arrangements need to be explored. As shown in Figure 2a, there are three candidate layouts for the wire jamming structures, where the main body and the limiting layer represent the fiber-reinforced actuator. Comparing these three layouts, we can find that layout 2 does not cause severe compression or stretching after bending (Figure 2b,c), and therefore the internal structure design is the simplest (see Section S3 and Figure S4 in the Supplementary Materials for details). To realize the function of jamming or shape-locking, we should choose inextensible materials. Here, we propose three different materials (kraft rope, hemp rope and nylon wire) as optional jamming media, which have different bending stiffness, surface friction characteristics and twisting methods (Figure 2d, and see details in Figure S5 in the Supplementary Materials). It should be mentioned that the diameter of wires affects many properties. Smaller wire diameters may result in severe localized geometric jamming and rearrangement, while larger diameters result in poor flexibility and a small range of stiffness. Therefore, considering the jamming properties of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, we empirically choose 1 mm diameter wires as the jamming material. Figure 2e,f shows two popular wire arrangement schemes. Compared to the rectangular arrangement, the circular arrangement is more prone to wire circumferential sliding after the bending, which we have observed by making samples. This circumferential sliding of wires may lead to misalignment and pre-jamming (Figure S6, Supplementary Materials). Therefore, we choose the rectangular arrangement as the final solution.
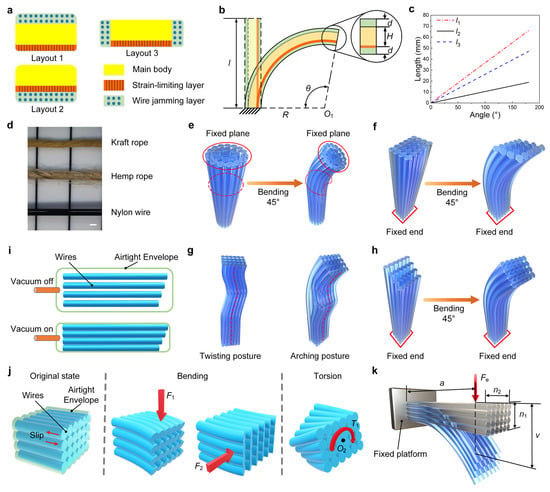
Figure 2.
Design and analysis of Wire jamming structures. (a) Installation methods for wire jamming structures. (b,c) Illustration of wire jamming structures under bending state, where d, H, l, θ, R are jamming structure thickness, actuator thickness, actuator length, bending angle and bending radius, respectively. l1, l2, l3 are the maximum stretch or compression length after bending for layout 1, layout 2, layout 3, respectively. (d) Demonstration of kraft rope (one-strand twisted kraft paper), hemp rope (two-strand twisted rope) and nylon wire (PA6, Alead Rubber & Plastic Products Co. Ltd., Hangzhou, China). Scale bar is 1 mm. (e,f) Presentation of jamming arrangements of circular cross-section and rectangular cross-section. (g) Two localized postures (twisting and arching) should be avoided. (h) The trimmed free end weakens the gradient effect after bending. (i) Schematic operation principle of the wire jamming structure. (j) Three main types of external forces. (k) Illustration of the bending state of the wire jamming structure under applied force Fe.
During the bending motion, another problem is also presented, seen in Figure 2f. Due to the difference in bending radius, a gradient effect appears at the free end of the wires. As expected, the membrane wrapped around the outside of the wires also shrinks with the bending, in which the wires show an elongation-like phenomenon. When the wires reach the top of the membrane, localized twisting or arching is inevitable (Figure 2g), leading to irreversible deformation. Therefore, the internal length of the envelope should be slightly larger than the length of the wires. A more effective method is to trim the wires at the free end in reverse gradient, which does not require a large space inside the envelope. As shown in Figure 2h, the trimmed wires weaken the gradient effect after bending. Based on the above analysis, we choose the rectangular cross-section as the final wire arrangement and use layout 2 as the installation scheme. Vacuum pressure is used as the actuation method for wire jamming structures.
2.2. Modeling
In this section, the stiffness characteristics of the wire jamming structure are further analyzed using theoretical models. The wire jamming structure consists of an airtight envelope, a vacuum line and wires. The principle of operation is to transform wires from an unjammed state to a jammed state by changing the vacuum pressure inside the envelope. The friction between wires is varied by the vacuum pressure, thus achieving a tunable stiffness (Figure 2i). We present the three most common states, where F1 is the applied force in normal working state, while F2 and T1 are often found in the applications of robotic grippers and wearable exoskeletons, such as grasping irregular objects or joint rotation (Figure 2j) [17,22,23]. The sliding between wires is relatively stable under F1 and F2, but the rotation under torque T1 complicates the contact surface between wires. Additionally, these three states reflect the three rotational degrees of freedom (DOF) at the free end of the wire jamming structure, the combination of which allows for a tunable stiffness in three dimensions.
In practice, the main bending state of the wire jamming mechanism can be referred to as a cantilever beam, where one end is fixed to the platform and the other end is under the force Fe. As shown in Figure 2k, n1 and n2 are the numbers of wires in thickness and width, respectively. a is the distance from applied force Fe to the fixed platform, and v is the deflection under the applied force Fe. Since the gap between wires cannot be neglected, we assume that each wire acts as an independent beam when the vacuum is off. The wires enter the jammed state after the vacuum is on. Thus, these wires are analyzed as a single beam. According to the Euler-Bernoulli equation for the cantilever beam, we can obtain a theoretical model (see Section S4 and Figure S7 in the Supplementary Materials for details). The stiffness of the wire jamming structure is related to the number of wires, the diameter of a single wire and the material properties. Moreover, it can be found that stiffness increases remarkably with the increase of n1. In order to quantify the effect of geometric parameters on stiffness performance, as well as to address the assembly issues with the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, we determined the dimensional parameters of the wire jamming structure and the number of wires inside the airtight envelope (see Section S5 and Figure S8 in the Supplementary Materials for details).
2.3. Fabrication
The fabrication process of the wire jamming structure is divided into three main steps. As shown in Figure 3a, the first major step is to cut wires into a specified length (i.e., 150 mm) using a commercial laser cutting machine (T1, Diaotu Industrial Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China). Due to the different packing and delivery methods (e.g., reel and carboard), wires or ropes require pre-cutting before being fixed on the working platform. The second major step is to fabricate the airtight envelopes with rectangular cross-sections. Considering the layout and bending state of wire jamming structures, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is adopted as the envelope material (see Section S3 in the Supplementary Materials for details). The HDPE film has high ductility and toughness, puncture resistance and excellent chemical resistance, as well as low friction, and is often applied to agricultural greenhouses. In Figure 3b, the HDPE film is cut into four strips and then the strips are combined into a rectangular cross-section structure using a heat-sealing machine (FKR200, Yinuo Packaging Material Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China). The third major step focuses on sealing the wires into the airtight envelope (Figure 3c). The specific method is to insert the wires from one side of the rectangular cross-section structure and seal one end. Following the gradient effect solution discussed in Section 2.1, we trim wires and seal the other end. Finally, a plastic hose coupler is installed on the wire jamming structure for air tube connection.
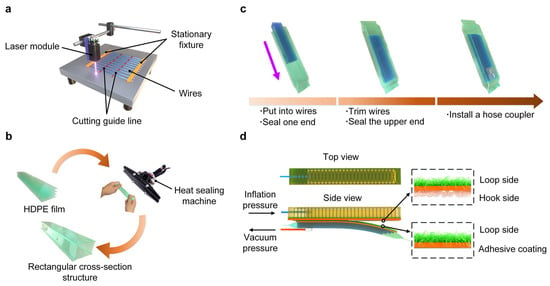
Figure 3.
Fabrication processes of the wire jamming structure. (a) Illustration of cutting process of wires. (b) Heat sealing process of rectangular cross-section structure using HDPE films (film thickness 0.08 mm). (c) Assembly process of trimmed wires and airtight envelope. (d) Illustration of the soft pneumatic actuator based on wire jamming structure, including local details of double-sided Velcro strip and knit loop fastener with pressure-sensitive adhesive.
An important issue that we also need to consider is how to combine the actuator unit with the tunable stiffness structure. The traditional approaches are integrated designs or permanent adhesion [22,23,26]. These approaches reduce the reliability and versatility of the whole structure. For example, the whole structure needs to be replaced after leakage and fouling, as well as in the case of applications where multiple jamming structures are required. Therefore, the modular concept is introduced into the design of the soft actuator with tunable stiffness, where the key factor is the use of Velcro strips (a.k.a., “hook-and-loop fastener”). Because the loop side fastener is covered with dense fibers, it can be robustly bonded to the silicone rubber, which offers numerous possibilities for combining rigid and soft materials. In order to confirm the advantages of Velcro, a set of tensile tests are performed to compare the different attaching methods (Figures S9 and S10, Supplementary Materials). Here, we use double-sided hook and loop fasteners (ONE-WRAP 29, Velcro USA Inc., Manchester, NH, USA) as a strain-limiting layer of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, in which the main silicone body is cured on the loop side (Figure 3d). The details of fabrication processes are available in Section S6 and Figure S11 in the Supplementary Materials. In addition, knitted loop fasteners (velour 3165, Velcro USA Inc., Manchester, NH, USA) with an adhesive coating on the opposite side are used for the wire jamming structure. Finally, with the detachable support of Velcro strips, soft actuators based on jamming structures are capable of handling a variety of applications.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Bending and Torsional Stiffness
In order to investigate stiffness characteristics of wire jamming structures in terms of response to deflection, vacuum pressure, thickness and rotation angle, three-point bending experiments and torsion experiments are performed. Figure 4a presents the experimental setup for three-point bending experiments, where a wire jamming structure is placed on the support platform and an air tube (orange color) is connected to a vacuum system. The vacuum is provided by a peristaltic vacuum pump (KVP8 PLUS-KB-S, Kamoer Fluid Tech Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) and the vacuum pressure is controlled through a pressure regulator (ITV2090-312BL5, SMC Corp., Tokyo, Japan). In this study, the force sensor moves at a slow speed during measurement processes so that the applied force can be considered equal to the elastic force generated by the wire jamming mechanism. Therefore, the stiffness property can be reflected by comparing values of the force sensor under the same deflection. Moreover, it should be mentioned that each test in this section is repeated five times. As shown in Figure 4b, three different jamming materials (i.e., kraft rope, hemp rope and nylon wire) presented in Figure 2d are tested, and all applied force-deflection curves show an increasing trend in that the applied force increases as the deflection increases. The detailed demonstration of hemp rope and nylon wire is presented in Figure S12 in the Supplementary Materials. For each jamming material, two sets of experiments under different vacuum pressures (0 kPa and −60 kPa) are performed. It can be seen that the stiffness of all three materials has obviously increased after the vacuum is switched to −60 kPa, proving that all these materials can be applied to wire jamming. Comparing the results of these materials, kraft rope and hemp rope have similar stiffness characteristics, while the stiffness of nylon wire is significantly higher than the other two materials. The relatively low stiffness of hemp rope is probably due to increased frictional sliding and spacing between ropes caused by thin fiber branches around the surface of ropes. Additionally, nylon wire also has some issues, such as high initial stiffness (i.e., unjammed stiffness) and localized rearrangement. Therefore, kraft rope is selected as the jamming material for subsequent studies. To compare the performance of different jamming structures, we also conduct the three-point bending test on layer jamming structures with the same dimensions (Figures S13 and S14, Supplementary Materials).
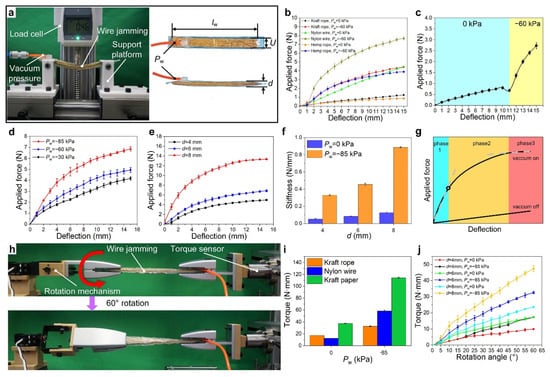
Figure 4.
Characterization of bending and torsional stiffness of wire jamming structures. (a) Experimental setup for three-point bending stiffness tests and detail display of wire jamming structure using kraft rope, where lw is the length of wires (range from 140 to150 mm), U is the width, Pw is the vacuum pressure, and d is the thickness of jamming structures. (b) Applied force versus deflection curves of wire jamming structures (d = 6 mm) using three different jamming media (i.e., kraft rope, nylon wire and hemp rope) at 0 kPa and −60 kPa vacuum pressure. (c) Applied force versus deflection curve with a vacuum pressure change at a deflection of 11 mm. (d) Influence of different confined vacuum pressures on the bending stiffness. The thickness d is 6 mm. (e) Influence of different confined thicknesses on the bending stiffness. The vacuum pressure is −85 kPa. (f) Comparison of bending stiffness with different thicknesses at a deflection of 15 mm. (g) A typical mechanical behavior curve of wire jamming structures. (h) Experimental setup for torsional stiffness. (i) Comparison of the torsional stiffness at a rotation angle of 60°. The thickness of all jamming structures is 6 mm. (j) Torque versus rotation angle curves under different thicknesses, where kraft rope is used as jamming material.
Moreover, Figure 4b shows that the curves exhibit good linearity at a vacuum pressure of 0 kPa, while they show pronounced nonlinear characteristics after the vacuum pressure decreases from 0 to −60 kPa. This phenomenon indicates that the jamming structures are mainly governed by elastic behaviors before the vacuum is off, and friction takes an important role in changing the stiffness characteristics after the vacuum is on. To further demonstrate the above phenomenon and the change in stiffness, the experiment is conducted by varying the vacuum pressure after the deflection reaches 11 mm. In Figure 4c, it can be clearly observed that the jamming structure shows low stiffness and the curve is very linear at a vacuum pressure of 0 kPa, while the stiffness is higher and shows pronounced nonlinearity at a vacuum pressure of −60 kPa. Since there is a gap between wires when the vacuum is off, the applied force has a period of decline after the vacuum is on.
In Figure 4d, the applied forces of the wire jamming structure are measured under three different vacuum pressures, where the tests use the same jamming structure with a width d of 6 mm. As the vacuum pressure increases from −30 kPa to −85 kPa, the friction between the wires increases, thus changing the threshold point at which the relative sliding of the wires occurs. With the vacuum pressure from −30 kPa to −85 kPa, the sliding point occurs at deflections of 0.5 mm, 1 mm and 3 mm, respectively. This phenomenon is similar to the experiments with wires of square cross-section [33]. In addition, we compare the force versus deflection curves for three different thicknesses, and the results demonstrate that the applied force increases dramatically with the increasing thickness of the wire jamming structure (Figure 4e). To quantify the bending stiffness in the three-point bending test, we defined bending stiffness as the ratio of applied force to deflection. Figure 4f compares the bending stiffness of the jamming structures with different thicknesses, where the best stiffness performance (i.e., bending stiffness is 0.89 N mm−1) is obtained for a thickness of 8 mm. The maximum increase in stiffness is nearly seven times after the vacuum pressure is switched from 0 to −85 kPa. It should be noted that the thickness of the jamming structure should not be too large, which would lead to an increase in the initial bending stiffness (Figure S15, Supplementary Materials) and volume, as well as a more severe gradient effect.
To further understand the bending stiffness characteristics of jamming structures, we present a conceptualized curve of applied force versus deflection (Figure 4g). When the vacuum is off, the wire jamming structure is in an unjammed state, resulting in low stiffness. When the vacuum is on, the jamming structure enters a jammed state and shows similar mechanical behavior to the layer jamming structure [29]. The jammed state can be divided into three phases: (1) during phase 1 (pre-slip regime), the applied force shows a rapid linear increase as the deflection increases, during which the wires are cohesive without slipping; (2) during phase 2 (transition regime), the growth of the applied force slows down and the wires start to slip. In this phase, the curve shows a remarkably nonlinear characteristics; (3) during phase 3 (post-slip regime), the applied force shows a slow linear increase, similar to the characteristics seen when the vacuum pressure is off and the wires enter into a full slip.
Figure 4h shows the experimental setup for the torsional stiffness of wire jamming structures. In order to approximate the real torsional condition, the side with an air hose coupler is fully locked to the right fixture, while the left fixture provides torque as the servo rotates, leaving the front side of the jamming structure free to slide. Similar to the bending stiffness, the rotational stiffness can be reflected by comparing values of the torque sensor under the same rotation angle. As shown in Figure 4i, two jamming structures made of nylon wire and kraft paper (i.e., layer jamming material) are introduced as a comparison. The experimental results reveal that the torsional stiffness of the layer jamming structure is the highest before and after the vacuum is turned on. In fact, we prefer to have lower torsional impedance for good shape adaptivity in the unjammed state and higher impedance for a robust grasp in the jammed state. Therefore, according to the experimental results, the wire jamming structure made of nylon wires has the best performance. In order to improve the torsional stiffness performance of kraft rope, we perform torsional experiments of different thicknesses (Figure 4j). Compared to the wire jamming structure using kraft rope material in Figure 4i, the maximum torsional stiffness of the wire jamming structure using 8 mm thickness improved from 32.63 to 47.5 N·mm, and the torsional stiffness range improved from 1.88 to 2.02. The results also show that the torque increases linearly with the angle from 0° to 60°, and the torsional stiffness increases as the thickness d increases. A comprehensive analysis in terms of the performance of initial stiffness, stiffness range, localized rearrangement and mass is presented in Figure S16 in Supplementary Materials. For the same dimensions, the layer jamming structure is better than the wire jamming structure in both the initial bending stiffness and the range of bending stiffness. However, the torsional stiffness performance of the wire jamming structure is better than that of the layer jamming structure. Therefore, the layer jamming structure is suitable for bending motions in a single plane. The wire jamming structure can be flexibly bent and twisted in multiple directions, which is well suited for surgical manipulators and wearable devices that multiple degrees of freedom of motion are required. In the end, a wire jamming structure made of kraft rope with a thickness of 8 mm is selected as the subsequent application study. A video of experimental platforms and stiffness performance experiments is available in Movie S1 in Supplementary Materials.
3.2. Applications
In the previous section, we used three-point bending experiments and torsional stiffness experiments to study the stiffness performance of wire jamming structures. In this section, we first investigate the influence of the wire jamming structure on the bending and stiffness performance of a single assembled stiffness-tunable soft actuator, and then use the soft robotic gripper and wearable exoskeleton as application examples to demonstrate its load capacity and universal adaptability. Figure 5a,b illustrates the unloaded bending experiments of a fiber-reinforced soft actuator and an assembled stiffness-tunable soft actuator, respectively. The results show a significant decrease in bending performance after the soft actuator is assembled with a wire jamming structure (Figure 5c). For a bending angle of 90°, the assembled soft actuator requires a positive air pressure of 145 kPa, while only about 87 kPa is required for the soft actuator alone. In order to explore the stiffness characteristics of the assembled soft actuator, we apply an external force to the tip of the actuator and record the force versus deflection curves at the contact point (Figure 5d,e). The experimental process is first to adjust the positive air pressure of the soft actuator to allow it to bend freely, then adjust the vacuum pressure of the wire jamming structure and finally adjust the initial position of the load cell so that it moves in a direction perpendicular to the contact surface. The experimental results show a phenomenon similar to the three-point bending experiment (Figure 5f). After the vacuum air pressure inside the jamming structure is switched from 0 to −85 kPa, the bending stiffness of the assembled soft actuator is remarkably enhanced. In addition, bending stiffness experiments are performed on a single wire jamming structure. The details of the experiments are shown in Figures S17 and S18 in the Supplementary Materials.
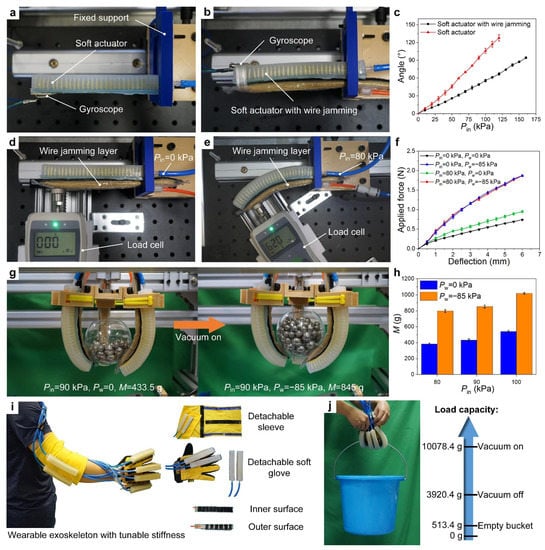
Figure 5.
Applications of an assembled soft actuator with tunable stiffness. (a,b) Experimental setup for a single soft actuator and an assembled soft actuator installed with a wire jamming structure, respectively. A nine-axis gyroscope (JY901S, WitMotion Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China) is used to measure the bending angle with different inflation pressure. The gyroscope is attached to the tip of the soft actuator. (c) Angle versus positive air pressure Pin curves of the soft actuator before and after assembly. (d,e) Bending stiffness experiments of the assembled soft actuator under two different positive air pressures. (f) Applied force versus deflection curves of the bending stiffness experiments. (g) Demonstration of the grasping process of the soft robotic gripper. (h) Comparison of maximum grasping mass at different positive air pressures. (i) An application example of a wearable exoskeleton, which only shows the wearing effect on the right arm. (j) The experiment of load capacity of a detachable soft glove, where the positive air pressure is 165 kPa, and the vacuum pressure is −85 kPa.
To further demonstrate the versatility of the soft assembly actuator with tunable stiffness, we developed a soft robotic gripper, which consists of three assembled soft actuators. The experimental scheme is to grasp a hollow plastic carrier at a confined positive air pressure, then set a specified vacuum pressure and finally increase the overall mass continuously by adding steel balls until the grasping fails (Figure 5g). A video of the grasping demonstration is available in Movie S1 in Supplementary Materials. The maximum mass successfully grasped is recorded and shown in Figure 5h. The maximum grasping mass of the soft gripper is increased by two times when the vacuum pressure is changed from 0 to −85 kPa. Figure 5i shows an application example of a wearable exoskeleton, where the yellow detachable areas use loops fasteners. The detachable sleeves can be attached by simply turning the side with the dark Velcro (hook side) outward, wrapping the yellow Velcro around the elbow and finally fastening the end of the yellow Velcro to the dark Velcro. The inner and outer surfaces of the variable stiffness structures are attached with loop and hook side Velcro blocks, respectively. Thus, the outer surface with the hook side can be fastened to the yellow area. Depending on the working conditions, the detachable elbow sleeves and detachable gloves allow for flexible installation of different numbers and performance of assembled soft actuators or only variable stiffness structures. Figure 5j shows a typical application of the detachable glove that assists the human hand in grasping heavy objects. In order to objectively test the grasping load capacity of the glove, we use only an empty glove without human hands to participate in this experiment. A video demonstration of the soft glove is available in Movie S1 in Supplementary Materials. The experimental process is to first turn on the positive pressure and then grasp the empty plastic bucket, then gradually fill the bucket with water until the grasp fails and finally record the final weight of the bucket with water. The results show that the glove can lift a load of more than 10,000 g when the vacuum is turned on, satisfying the needs of different working environments and daily life.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, an assembled stiffness-tunable soft actuator is proposed, which consists of a fiber-reinforced soft bending actuator and a wire jamming structure. For the issues of localized rearrangement and tip gradient effect in the bending state, we develop a structural jamming scheme and design a fabrication process. With the help of Velcro strips, a quick and detachable assembly of the soft actuator and the jamming structure is achieved. We reveal the influence of vacuum pressure and wire thickness on the stiffness performance of the wire jamming structure through three-point bending experiments and conclude the trend of bending stiffness with increasing deflection. In addition, layer jamming structures are fabricated to compare the performance of wire jamming structures in bending and torsional stiffness. The results show that the layer jamming and wire jamming structures are superior in bending and torsional stiffness, respectively. In order to understand the performance of the assembled stiffness-tunable soft actuators, a soft robotic gripper and a suit of a wearable exoskeleton are fabricated. Experiments on the soft gripper show low bending and torsional impedance for good shape adaptivity in the unjammed state and high stiffness for a robust grasp in the jammed state. The detachable soft gloves have also proven to be effective in enhancing stiffness, with one glove capable of lifting weights over 10,000 g. Moreover, the stiffness-tunable soft actuators show excellent application prospects in medical devices, biomimetic robots and immersive haptic support for VR/AR.
Supplementary Materials
The following Supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12073582/s1, Section S1: Theoretical model of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, Section S2: Uniaxial tensile test, Section S3: Installation layouts of tunable stiffness layer, Section S4: Analytical model, Section S5: Geometric design parameters of wire jamming structure, Section S6: Fabrication of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, Figure S1: Illustration of a fiber-reinforced soft actuator in bending state, Figure S2: The influence of air chamber height h on bending angle, Figure S3: Uniaxial tensile test of the silicone rubber, Figure S4: Demonstration of installation methods for wire jamming structure, Figure S5: Demonstration of twisting methods for hemp rope and kraft rope, Figure S6: Local rearrangement of wires in cross-section view, Figure S7: Schematic of a wire jamming structure under external forces, Figure S8: Illustration of wires on the cross-section of the jamming structure, Figure S9: Comparative experiments of detachable solutions, Figure S10: Experimental setup for detachable solutions, Figure S11: Fabrication process of the fiber-reinforced soft actuator, Figure S12: Demonstration of wire jamming structures made of hemp rope and nylon wire, Figure S13: Demonstration of a layer jamming structure with three different states, Figure S14: Comparison of the wire jamming structure with the layer jamming structure, Figure S15: Applied force versus deflection curves of kraft rope at 0 kPa, Figure S16: Spider plot with three different jamming structures, Figure S17: Bending stiffness experiments of single wire jamming structure, Figure S18: Applied force versus deflection curves for a wire jamming structure, Movie S1: Demonstration of experiment platforms, stiffness experiments, grasping process and soft glove.
Author Contributions
L.B. and H.Y. designed and fabricated the prototype; J.L., P.H. and L.B. performed the bending and application experiments; data curation and visualization, J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B. and J.L.; H.Y. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Key Laboratory of Vehicle Advanced Manufacturing, Measuring and Control Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Ministry of Education, China.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majidi, C. Soft Robotics: A Perspective—Current Trends and Prospects for the Future. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.K.; Won, P.; Hong, S.; Ko, S.H. Biomimetic chameleon soft robot with artificial crypsis and disruptive coloration skin. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, B.; Yin, S.; et al. Self-powered soft robot in the Mariana Trench. Nature 2021, 591, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Mousa, M.A.; Saleh, M.A.; Elsamanty, M.; Radwan, A.G. Modelling and implementation of soft bio-mimetic turtle using echo state network and soft pneumatic actuators. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z. A variable structure pneumatic soft robot. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, J.; Wakimoto, S.; Satoh, T.; Saga, N.; Suzumori, K. Design of a variable-stiffness robotic hand using pneumatic soft rubber actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Shan, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Yu, H. Modeling and Experimental Study of a Novel Multi-DOF Parallel Soft Robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62932–62942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, M.; Cacucciolo, V.; Cianchetti, M. Stiffening in Soft Robotics: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M.; Calisti, M.; Margheri, L.; Kuba, M.; Laschi, C. Bioinspired locomotion and grasping in water: The soft eight-arm OCTOPUS robot. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, N.; Hingorani, H.; Ding, N.; Wang, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, B.; Gu, G.; Ge, Q. Fast-Response, Stiffness-Tunable Soft Actuator by Hybrid Multimaterial 3D Printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatari, M.; Kamrava, S.; Ghosh, R.; Nayeb-Hashemi, H.; Vaziri, A. Bending behavior of biomimetic scale covered beam with tunable stiffness scales. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, I.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. A soft multi-module manipulator with variable stiffness for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 056008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Zhu, J.; Fish, F.E.; Kerr, S.J.; Downs, A.M.; Bart-Smith, H.; Quinn, D.B. Tunable stiffness enables fast and efficient swimming in fish-like robots. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabe4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, B.; Narang, Y.S.; Vasios, N.; Bertoldi, K.; Howe, R.D. A Modeling Framework for Jamming Structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Lekstutyte, L.; Althoefer, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Nanayakkara, T. Robotic Granular Jamming: Does the Membrane Matter? Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Passive Particle Jamming and Its Stiffening of Soft Robotic Grippers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Hofmann, D.; Andrade, J.E.; Daraio, C. Structured fabrics with tunable mechanical properties. Nature 2021, 596, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Rodenberg, N.; Amend, J.; Mozeika, A.; Steltz, E.; Zakin, M.R.; Lipson, H.; Jaeger, H.M. Universal robotic gripper based on the jamming of granular material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18809–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amend, J.; Cheng, N.; Fakhouri, S.; Culley, B. Soft Robotics Commercialization: Jamming Grippers from Research to Product. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. A soft robotic spine with tunable stiffness based on integrated ball joint and particle jamming. Mechatronics 2016, 33, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, T.; Chen, Q.; Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. A Novel, Variable Stiffness Robotic Gripper Based on Integrated Soft Actuating and Particle Jamming. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M.Z.Q.; Chen, Y. A variable stiffness gripper based on differential drive particle jamming. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 036009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.; Majit, M.R.A.; Shih, B.; Schulze, J.P.; Tolley, M.T. Variable Stiffness Devices Using Fiber Jamming for Application in Soft Robotics and Wearable Haptics. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Cheng, S.; Kim, S.; Iagnemma, K. A Novel Layer Jamming Mechanism With Tunable Stiffness Capability for Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 29, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Mori, Y.; Wakayama, T.; Wada, A.; Kawamura, S. A Fully Multi-Material Three-Dimensional Printed Soft Gripper with Variable Stiffness for Robust Grasping. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Hong, J.; Wang, M.Y. Electrostatic Layer Jamming Variable Stiffness for Soft Robotics. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, Y.S.; Degirmenci, A.; Vlassak, J.J.; Howe, R.D. Transforming the Dynamic Response of Robotic Structures and Systems Through Laminar Jamming. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, Y.S.; Vlassak, J.J.; Howe, R.D. Mechanically Versatile Soft Machines through Laminar Jamming. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narang, Y.S.; Aktaş, B.; Ornellas, S.; Vlassak, J.J.; Howe, R.D. Lightweight Highly Tunable Jamming-Based Composites. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.S.; Yang, E.J.; Yuen, M.C.; Huang, E.C.; Kramer Bottiglio, R. Jamming Skins that Control System Rigidity from the Surface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, P. A bio-inspired soft-rigid hybrid actuator made of electroactive dielectric elastomers. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, B.; Howe, R.D. Tunable Anisotropic Stiffness with Square Fiber Jamming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 15 May–15 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishida, D.; Ogata, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Tabata, O.; Sugiyama, S. Development of passive elements with variable mechanical impedance for wearable robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Brancadoro, M.; Manti, M.; Tognarelli, S.; Cianchetti, M. Fiber Jamming Transition as a Stiffening Mechanism for Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancadoro, M.; Manti, M.; Grani, F.; Tognarelli, S.; Menciassi, A.; Cianchetti, M. Toward a Variable Stiffness Surgical Manipulator Based on Fiber Jamming Transition. Front. Robot. AI 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, Z.; Zeng, J.; Wang, M.Y. Hybrid Jamming for Bioinspired Soft Robotic Fingers. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.G.; Delaney, G.W.; Howard, D. A Review of Jamming Actuation in Soft Robotics. Actuators 2020, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, A.K.; Garcia, L.R.; Liu, Z.K.; Doan, J.; Meyers, M.A.; Mckittrick, J. Applying Bio-Inspired hierarchical design to jamming technology: Improving density-efficient mechanical properties and opening application spaces. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15555–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, A.K.; Rodriguez, N.; Behl, M.; Soffiatti, P.; Rowe, N.P.; Lendlein, A. Cactus-inspired design principles for soft robotics based on 3D printed hydrogel-elastomer systems. Mater. Des. 2021, 202, 109515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, C. High-Force Soft Printable Pneumatics for Soft Robotic Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, S.; Ze, Q.; Kuang, X.; Zhang, R.; Qi, H.J.; Zhao, R. Magnetic Multimaterial Printing for Multimodal Shape Transformation with Tunable Properties and Shiftable Mechanical Behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12639–12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J. Pneumatically Actuated Self-Healing Bionic Crawling Soft Robot. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 100, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of Soft Fiber-Reinforced Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connolly, F.; Polygerinos, P.; Walsh, C.J.; Bertoldi, K. Mechanical Programming of Soft Actuators by Varying Fiber Angle. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadumudi, F.B.; Hasany, M.; Pierchala, M.K.; Jahanshahi, M.; Taebnia, N.; Mehrali, M.; Mitu, C.F.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Zsurzsan, T.G.; Knott, A.; et al. The Manufacture of Unbreakable Bionics via Multifunctional and Self-Healing Silk–Graphene Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolina Pierchala, M.; Kadumudi, F.B.; Mehrali, M.; Zsurzsan, T.G.; Kempen, P.J.; Serdeczny, M.P.; Spangenberg, J.; Andresen, T.L.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A. Soft Electronic Materials with Combinatorial Properties Generatedvia Mussel-Inspired Chemistry and Halloysite Nanotube Reinforcement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9531–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi Bidsorkhi, H.; D’Aloia, A.G.; Tamburrano, A.; De Bellis, G.; Sarto, M.S. Waterproof Graphene-PVDF Wearable Strain Sensors for Movement Detection in Smart Gloves. Sensors 2021, 21, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).