Abstract
Although graph convolutional networks (GCNs) have shown their demonstrated ability in skeleton-based action recognition, both the spatial and the temporal connections rely too much on the predefined skeleton graph, which imposes a fixed prior knowledge for the aggregation of high-level semantic information via the graph-based convolution. Some previous GCN-based works introduced dynamic topology (vertex connection relationships) to capture flexible spatial correlations from different actions. Then, the local relationships from both the spatial and temporal domains can be captured by diverse GCNs. This paper introduces a more straightforward and more effective backbone to obtain the spatial-temporal correlation between skeleton joints with a local-global alternation pyramid architecture for skeleton-based action recognition, namely the pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer (PGT). The PGT consists of four stages with similar architecture but different scales: graph embedding and transformer blocks. We introduce two kinds of transformer blocks in our work: the spatial-temporal transformer block and joint transformer block. In the former, spatial-temporal separated attention (STSA) is proposed to calculate the connection of the global nodes of the graph. Due to the spatial-temporal transformer block, self-attention can be performed on skeleton graphs with long-range temporal and large-scale spatial aggregation. The joint transformer block flattens the tokens in both the spatial and temporal domains to jointly capture the overall spatial-temporal correlations. The PGT is evaluated on three public skeleton datasets: the NTU RGBD 60, NTU RGBD 120 and NW-UCLA datasets. Better or comparable performance with the state of the art (SOTA) shows the effectiveness of our work.
1. Introduction
Skeleton-based action recognition has been a hot topic with vast application areas: surveillance systems, human–computer interaction, medical care assistance, etc. Due to the development of depth cameras and pose estimate algorithms, human skeletons are much easier to obtain as efficient data. Therefore, many skeleton-based action recognition algorithms have been proposed in recent years. Compared with the RGB images and videos, the skeleton data consisting of 3D joint coordinates show advantages in the following aspects: being robust to illumination, stable to the background and lightweight.
The semantic information of skeleton data was extracted with handcrafted features in the early years [1]. Vemulapalli et al. [1] adopted lie group theory in this task for the features of the joints and angles. However, with the development of deep learning, many works introduced convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) into their models to learn powerful features with high-level semantics. The CNN-based methods construct the skeleton joints into a 2D pseudo-image, and the popular CNN architectures are applied to classify the images into a special spectral form [2,3,4,5]. RNN-based methods treat the skeletons as a series of feature vectors and construct a deep network in the spatial domain with long short-term memory (LSTM) units [6,7,8,9]. Therefore, the dynamic changes over a long period of time are captured.
Then, a series of graph convolution networks (GCNs) was proposed and showed steps of improvement compared with previous works [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Yan et al. [10] were the first to propose the graph convolution operation and treat the skeletons as non-Euclidean graphs. The key to graph convolution lies in constructing the learnable graph convolution kernels. Based on this work, Shi et al. [11] proposed a two-stream graph convolution network with an adaptive mechanism to learn the adjacency matrix. Cheng et al. [12] further presented a shift graph convolution operation with a similar backbone. Inspired by previous works, Plizzari et al. [14] introduced the attention mechanism into their two-stream architecture to improve the performance with more learnable parameters.
Previous GCN-based methods mainly explored a dynamic network based on a graph convolution backbone proposed by [10]. The graph convolution kernel is fixed, and the network is suitable for the static topology of graphs. However, the spatial-temporal correlations between all nodes are essential. At the same time, GCN-based methods adopt a cascading spatial graph convolution and temporal convolution layers to learn this information, as shown in Figure 1. As graph convolution operation is inferred from CNNs, it means GCNs will also come across the problem of the local receptive field. As far as we are concerned, these multi-layer GCN-based methods perform poorly in the dynamic fusions of the global joints. For example, the correlation between the joint of the hand in the first frame and the joint of the foot in the last frame cannot be measured in most cases, which may be crucial spatial-temporal information for the perception of actions.
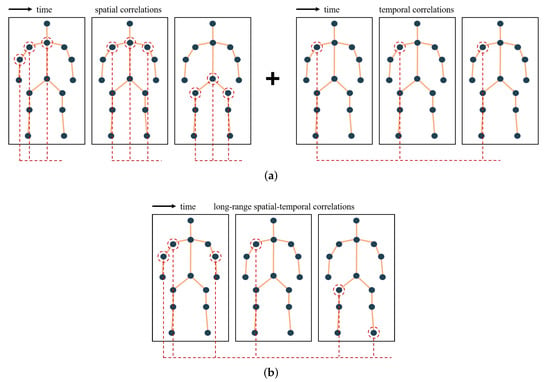
Figure 1.
The method for capturing spatial-temporal correlations for skeleton graphs. Previous GCNs adopted a spatial-temporal cascaded backbone to learn their representations. However, the transformer architecture is able to capture the long-range correlations for skeleton graphs. (a) Cascaded spatial-temporal correlations via GCNs. (b) Long-range spatial-temporal correlations via transformer.
Therefore, we propose a new backbone based on transformers to learn the long-range dependencies in the spatial and temporal domains. The transformer architecture was proposed in recent years and has shown itself to be a strong backbone for natural language processing (NLP) tasks. For computer vision (CV) tasks, the vision transformer (ViT) has also demonstrated more robust effects compared with CNNs or RNNs. Inspired by this architecture, we propose a pyramid transformer backbone named PGT, which can provide multi-scale features with a four-stage architecture for skeleton graph data. The long-range, multi-scale spatial-temporal correlations are learned through an alternate connection structure of the GCN module and the transformer module. Concretely, the GCN module is called graph embedding, having an efficient separate convolution operation, and we introduce two kinds of transformer blocks: spatial-temporal transformer blocks and joint transformer blocks. The spatial-temporal transformer block calculates the spatial self-attention and temporal self-attention separately, while the joint transformer block discovers the global self-attention of all nodes in the graphs.
The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
- A pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer backbone (PGT) is proposed in this work which shows a powerful ability to learn robust features for skeleton graphs with dynamic attention.
- Two kinds of transformer blocks are introduced and applied to discover the long-range spatial-temporal correlations in human actions, and the separate convolution operation in graph embedding makes the model go deeper with high-level semantics.
- Extensive experiments are performed in this work, and the ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness of our backbone. Finally, the experiments show better comparable performance with the state-of-the-art methods and show the potential of this backbone.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the related work in the field of skeleton-based action recognition and some work on the vision transformer method. Section 3 presents the architecture design of our PGT. Section 4 provides the experiment results, ablation study and comparisons with the state-of-the-art methods. The conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Related Work
2.1. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
Instead of searching for high-level semantic information based on RGB videos, skeleton-based action recognition is committed to extracting the spatial-temporal features of the highly condensed joints. Earlier works rely on extracting handcrafted features from the 3D skeleton sequences. Hussein et al. [16] proposed a covariance descriptor extracted from the covariance matrix for skeleton joint locations over time. In a previous work [1], handcrafted features based on the lie group were applied to represent the dynamic skeleton information.
As deep learning algorithms have gained absolute dominance in various computer vision tasks, convolutional neural network (CNN)- and recurrent neural network (RNN)-based models are widely used to learn spatial-temporal correlations and variations. CNN-based methods arrange the 3D skeleton joints to form a pseudo-image, in which the width of the image represents the joints and the length denotes the frames. These methods take great advantage of the powerful representation ability of CNNs through various ingenious convolution structures. Kim et al. [17] introduced a temporal convolutional network instead of the LSTM-based RNNs to learn the spatiotemporal representations explicitly. Liu et al. [2] transformed the skeleton sequences through a visual-enhanced method and predicted the action with a multi-stream CNN model. The fused features show the robustness of the changes in the viewing angles. Li et al. [4] proposed a CNN-based model which contained a practical skeleton-rearranged module and a two-stream network with seven layers. Banerjee et al. [18] proposed using four feature representations to capture various aspects of skeleton sequences with a fuzzy combination of CNNs. Wang et al. [19] focused on the edge motion, which contains the angle changes and movements, and showed the effectiveness of this operation.
Unlike the CNN-based methods, which transform the skeletons into a pseudo-image, RNN-based models take the skeleton coordinates as a series of signals in the time domain to learn deep temporal networks. The output of the previous moment of the RNN network is taken as the input of the next moment, which enables the model to represent the temporal dynamics. Liu et al. [6] introduced a long-short-term memory (LSTM)-based network to learn the hidden action-related information in both the spatial and temporal domains simultaneously. Song et al. [7] incorporated the LSTM unit with an additional attention subnetwork, which was able to assign different weights to different frames. Diao et al. [20] presented a multi-term strategy by combing both an MTA-RNN and ST-CNN. In [21], Jiang et al. rethought the spatial information with previous handcrafted features and proposed a spatial-temporal skeleton transformation descriptor (ST-STD). A three-layer LSTM to learn the temporal dynamics reduces the action misalignment. Gao et al. [22] proposed an LSTM-based deep attention network with a new triplet loss function.
However, graph convolutional network (GCN)-based models soon replaced the CNN and RNN models because of their powerful ability to represent the spatial-temporal skeleton features. The graph convolution operation, extended from CNNs, is applied to the non-Euclidean graph data. Earlier, Yan et al. [10] first proposed a spatial-temporal graph convolutional network (ST-GCN) and provided a robust GCN backbone for skeleton-based action recognition. The backbone consists of cascading spatial graph convolution (SGC) and temporal convolution (TC) modules.
Inspired by this work, many researchers have decided to construct skeleton graphs for human skeletons, which are more intuitive and able to achieve better performance. Liu et al. [23] proposed capturing spatial-temporal correlations with a unified graph convolution operation named G3D, which can be seen as a dynamic method. Huang et al. [24] also introduced a multi-scale dynamic approach with an extra inference module to be adaptive for various actions. Li et al. [25] proposed the concept of an actional link and structural link to learn the correlated joints, such as the hand joint and the foot joint in the action of “walking”. Chen [26] aimed to discover the spectral-domain information and propose a dual-domain GCN network based on both vertex graph convolution and spectral graph convolution operations. Zheng et al. [27] proposed a multi-scale adaptive aggregate GCN to model the remote dependency between joints, which is able to fuse particular global information.
Some works focus on the pattern-level perception and propose a multi-stream architecture. Shi et al. [11] proposed an attention augmentation model with a two-stream network, which combines the joint feature and bone feature for a more robust representation. Then, they provided a stronger model with a four-stream architecture by introducing the preprocessed joint motion and bone motion data [28]. Cheng et al. [12] further proposed a four-stream network while introducing a graph shift operation from CNNs. The extra joint and bone motion streams are added as handcrafted prior knowledge. Chen et al. [29] and Cheng et al. [30] focused on the topology-non-shared models, which means the topologies in different channels are learned dynamically during inference. In [30], the skeleton features were aggregated with a channel-wise topology module for high-level representation.
2.2. Vision Transformer
The transformer [31] was first proposed for natural language processing (NLP) tasks with a self-attention mechanism, which enables the model to capture long-range correlations dynamically. Then, Dosovitskiy et al. [32] introduced a vision transformer backbone (ViT) by embedding image patches of pixels. The backbone consists of an image tokenizer module, positional embedding layers and transformer encoder layers. The local information is reweighted by a global attention mechanism named multi-head self-attention (MSA).
Thereafter, Srinivas et al. [33] introduced bottleneck layers into ViT and constructed a bottleneck transformer for vision segmentation and detection. Carion et al. [34] presented a transformer-based encoder-decoder backbone called a detection transformer (DETR), which combines CNN architectures together. Touvron et al. [35] further proposed an efficient model with no convolution layers. Yuan et al. [36] proposed a more efficient attention backbone which incorporates a token-to-token transformation module and a deep-narrow architecture. Wang et al. [37] raised a pyramid vision transformer (PVT) to replace CNN backbones. Similar to the classic ResNet [38], a PVT is composed of four stages with different feature scales while sharing a similar architecture.
ViT models show superiority for various vision tasks based on RGB images and videos. Owing to the attention mechanism, the weights of the essential pixels are amplified. Therefore, the models can be trained dynamically based on the input data. As for skeleton-based action recognition, Plizzari et al. [14] raised the effectiveness of applying the self-attention module to the skeleton recognition task, and the two-stream model makes a further improvement based on the ST-GCN to capture the spatial-temporal correlations. Zhang et al. [39] proposed a spatial-temporal transformer model consisting of a spatial transformer block and a directional temporal transformer block in the spatial and temporal dimensions, respectively.
3. Method
In this section, the details of the architecture of our pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer are illustrated. The preliminaries subsection presents the fundamentals of the relevant mathematical theory. Then, the three main designs are described in sequence: the graph embedding module, spatial-temporal transformer attention and the pyramid architecture. As shown in Figure 2, the PGT is designed as a pyramid architecture with four stages consisting of similar modules for different scales. The long-range multi-scale spatial-temporal correlations are learned and shown to be effective with this efficient model. The detailed parameters are shown in Table 1.
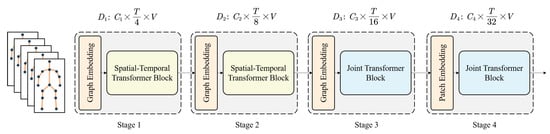
Figure 2.
Implementation of the pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer (PGT). A pyramid architecture is designed for multi-scale feature learning. The model consists of four stages with similar modules to capture the long-range correlations in the spatial and temporal dimensions. Each stage has a graph embedding module and a spatial-temporal transformer block. The temporal dimension decreases exponentially with each stage, while the spatial dimension stays the same. In this way, the spatial granularity is retained, and temporal redundancy is removed.

Table 1.
The architecture parameters of the pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer on the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset.
3.1. Graph Embedding
The skeleton data used for action recognition consisted of several joints of humans, which were the 3D coordinates specifically. Unlike image data, skeleton graphs are more lightweight and more structurally relevant. For one action, they have three-dimensional parameters, such as the frame, joint number and coordinate. To transform the skeleton graph into a uniform pattern, we propose a graph embedding module for the pyramid architecture. For traditional vision transformer models, a graph embedding module is utilized to obtain a series of feature tokens sent to the multi-head self-attention (MHSA) in the transformer block to reweight the local features based on long-range attention. However, for skeleton graphs, we introduce a GCN-based embedding module to enhance the spatial-temporal correlations as shown in Figure 3. Meanwhile, the graph embedding module plays a vital role in the information aggregation in the temporal dimension of the skeleton graphs. As shown in Figure 2, the temporal dimension shrinks with the stage progression, which forms a deep pyramidal structure for high-level semantic learning.
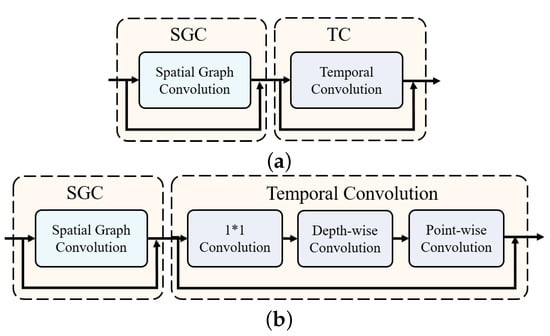
Figure 3.
Illustration of the basic ST-GCN unit and the graph embedding. The SGC represents the spatial graph convolution module, and the temporal convolution adopts a separate convolution structure in our graph embedding. (a) Basic ST-GCN unit. (b) Graph embedding.
Unlike the image-based vision tasks, we denote the 3D skeleton coordinate sequences as , where T, V and C represent the frame, joint number and coordinates, respectively. At the start of each stage i, a spatial graph convolution is first applied to aggregate local information from neighbors according to the natural connection of joints. According to the network in [10], the vertex-domain graph convolution operation is as follows:
where denotes the skeleton joint at time t and calculates the distance partitioning to determine the neighborhood of the graph convolution kernel. Cardinality Z shows the contribution of the neighbor joints. Concretely, the spatial graph convolution takes the adjacency matrix as the distance instruction, and the formula is transformed as follows:
where the input feature map is weighted with the normalized adjacency matrix with . The kernel learns the weights, denoted as . denotes a learnable attention map to adjust the importance of each vertex.
Then, a temporal convolution module is followed to fuse the local information in the temporal domain. We adopted a separate convolution method to make the calculation more efficient. MobileNet first introduced this design for less computation, and it was also applied in [15]. As shown in Figure 3, the 1 × 1 convolution layer is used to adjust the channel dimension. Next, the depth-wise convolution layer is applied to one corresponding channel, while the point-wise convolution takes charge of the transformation for the output dimension. During this step, temporal pooling is applied to concentrate the joint information in the time domain.
3.2. Transformer Block
Two kinds of transformer blocks are adopted in our pyramid architecture: spatial-temporal transformer and joint transformer blocks, as shown in Figure 4. The vision transformer uses qkv self-attention [31] for a sequence of tokens , which is computed as follows:
where Q, K and V are the query, key and value of the token vector, respectively, and is a learnable weight matrix. The difference between these two transformer blocks lies in the self-attention operation, as shown in Figure 4. As the number of tokens can be very large due to redundancy in the time domain, the computation cost is extremely high for the regular multi-head self-attention (MSA), which can be written as follows:
where denotes the output of the self-attention and is a learnable matrix. Note that the number of head h is set to 1, 2, 4 or 8 for four stages. The formula of each head is as follows:
where , and are learnable matrix projections for the query, key and value of the tokens. Furthermore, as denoted in [31], the single-head attention is as follows:
where denotes the scaling factor. The attention mechanism reweights the representation vectors by a global connection of all tokens.
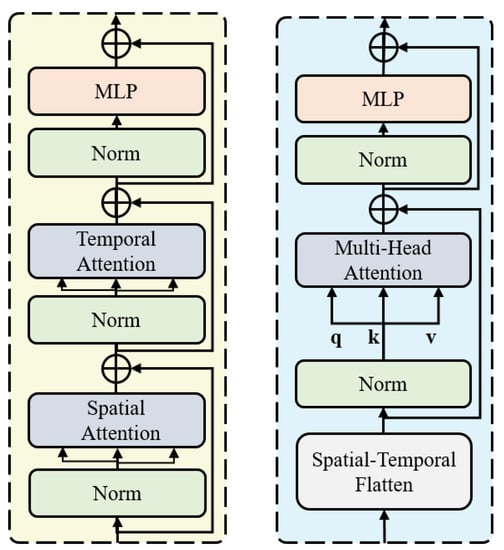
Figure 4.
The spatial-temporal transformer block (left) vs. the joint transformer block (right).
For the first two stages with a large time dimension, we propose a separate spatial-temporal attention architecture, shown in Figure 4. For the last two stages, we prefer to flatten the skeleton tensor in both the spatial and temporal dimensions and calculate the joint spatial-temporal correlations. The computations of the blocks are calculated as follows:
where MLP represents the multi-layer perceptron layer. Different from the multi-head self-attention (MSA) in the last two stages, the first two stages are optimized using spatial self-attention (SSA) and temporal self-attention (TSA) separately.
3.3. Pyramid Architecture
In our work, a pyramid architecture is introduced inspired by PVT [37]. In the previous the PVT for image-based vision tasks, and multi-scale feature maps are generated for more robust representations. Therefore, our PGT adopts a similar architecture consisting of four stages, and all of them share a similar structure. In the first stage, the input skeleton tensor of a size is calculated with a spatial-temporal graph convolution module named graph embedding. Then, the tensor is divided into V tokens in the spatial domain and in the temporal domain for the cascaded spatial attention (SSA) and temporal self-attention (TSA). After that, the local feature of each node of the graph is reweighted with the global nodes according to the transformer block. By this operation, the following feature maps are obtained: and . The pooling operation reduces the redundancy in the temporal domain.
4. Experiments
In this section, our PGT model is evaluated on three public datasets: NTU-RGBD 60 [40], NTU-RGBD 120 [41] and Northwestern-UCLA [42]. First, we introduce the datasets and implementation details of the experiment. Then, the ablation study shows the effectiveness of our model design. Lastly, comparisons with the state of the art are conducted.
4.1. Datasets
NTU-RGBD 60. The NTU-RGBD 60 dataset [40] is a widely used skeleton-based action recognition dataset consisting of 56,880 samples divided into 60 categories. These samples were performed by 40 different persons and captured by 3 cameras to ensure the diversity of the actions. Each sample comprised 25 joints of humans, which were the 3D coordinates specifically. The evaluation of this dataset included both the cross-view (CV) benchmark and the cross-subject (CS) benchmark. They verified the diversity of the actions by the model under different viewpoints and by different characters. For the CV benchmark, the training data came from camera 2 and 3, and the testing data came from camera 1. For the CS benchmark, the training data were from 20 subjects, and the testing data were from the other 20 subjects.
NTU-RGBD 120. The NTU-RGBD 120 dataset [41] is a large 3D skeleton dataset for human action recognition which is an extension of the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. This version has 113,945 skeleton clips categorized into 120 classes. These actions are performed by 106 persons captured by 3 cameras as well. The validation benchmarks also have two methods: cross-subject (X-sub) and cross-set-up (X-set). The training data came from 53 subjects, and the testing data came from the other 53 subjects for the X-sub benchmark. For the X-set benchmark, the training data were from samples with even collector set-up IDs, and the testing data were from samples with odd IDs.
Northwestern-UCLA. The Northwestern-UCLA dataset [42] is a popular skeleton dataset captured by Kinect cameras. The actions are divided into 10 classes for 1494 skeleton sequences. Concretely, the actions were performed by 10 different subjects. The evaluation set-ups were similar to the cross-view benchmark of the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. The training data were captured by cameras 1 and 2, and the testing data were from camera 3.
4.2. Implementation Details
All our experiments were conducted on two GeForce RTX 3090 GPUs with a Pytorch deep learning framework, which is developed by Meta Platforms. The Pytorch version is 1.10.1 and the python version is 3.7. Concretely, the training epoch was set to 300 with an initial learning rate of 0.1. The learning rate decayed at a factor of 0.1 at epochs 150 and 250. However, at the start of the training process, the warm up strategy proposed in [38] was adopted. The PGT chose the SGD optimizer with a momentum of 0.9 and a weight decay of 0.0004. The batch sizes for the NTU-RGBD 60 and 120 datasets were set to 64. The skeleton data were preprocessed in the same way as in [43], in which the frame of the skeleton sequences was set to 64, while for the Northwestern-UCLA dataset, the batch size was set to 16. The preprocessing method was inspired by [12].
4.3. Ablation Study
The proposed pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer was analyzed through various ablation studies in this section. The experiments were conducted on the CS benchmark of the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. Both the accuracy and the model complexity are denoted in the following results. The model complexity contained the floating-point operations per second (FLOPs, which means the computation speed) and the number of parameters in the model.
4.3.1. The Effect of the ST-Joint Transformer Block
As shown in Table 2, the effect of our attention design in the transformer was explored based on the CS benchmark of the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. The separate spatial-temporal (ST) transformer block increased the complexity of the model compared with the joint transformer block, which flattened the skeletons in both the spatial and temporal domains to obtain long-range global correlations. According to our experiments, the accuracy was best when there were two ST transformer blocks and two joint transformer blocks. Compared with the model that adopted four ST transformer blocks, the PGT performed more robustly with high-level semantics. The predefined spatial self-attention and temporal self-attention enabled the model to focus better on its single domain information in the previous layers. As far as we are concerned, the increases in the parameters and FLOPs show its effectiveness, but the global attention of the nodes in the graph is also crucial in the subsequent layers, which brings a spatial-temporal information fusion.

Table 2.
The ablation study on the NTU-RGBD 60 CS benchmark, denoting the effect of ST and joint transformer blocks.
4.3.2. The Effect of Four-Stream Fusion
As with many state-of-the-art methods [12,13,15,28], we also adopted a multi-stream fusion strategy in our work for fair comparison. Four streams were applied as input skeleton data. The joint stream was the original 3D skeleton coordinates, and the second stream was the bone stream, which was the differential of the spatial coordinates. Both the joint and bone streams were calculated through the differential in the temporal dimension, called the joint motion stream and the bone motion stream. As shown in Table 3, the results of the four-stream fusion strategy brought a great gain for the final accuracy. The four kinds of skeleton data provided additional prior knowledge for skeleton-based action recognition. At the same time, our PGT was able to learn robust representation for these data.

Table 3.
The ablation study on the NTU-RGBD 60 CS benchmark denoting the effect of the four-stream fusion strategy.
4.3.3. The Effect of Separate Convolution in Graph Embedding
As shown in Table 4, the effect of the separate convolution operation in graph embedding was evaluated. The difference between the basic module and graph embedding can be seen in Figure 3. The model showed itself to be more efficient and powerful with the structure of separate convolution inspired by [15]. Owing to the depth-wise and point-wise convolution layers, the network became deeper and able to learn the high-level semantics in the features. Meanwhile, the graph convolution was shown to be more efficient with fewer FLOPs and parameters. The accuracy was even 1.7% higher on the NTU-RGBD 60 CS benchmark. As far as we are concerned, with a more powerful GCN-unit design, the accuracy of our PGT backbone can be further improved.

Table 4.
The ablation study on the NTU-RGBD 60 CS benchmark, denoting the effect of separate convolution in graph embedding.
4.4. Comparisons with Other Approaches
We compared the performance with the SOTA methods on three public skeleton action datasets: the NTU-RGB 60 [40], NTU-RGB 120 [41] and Northwestern-UCLA [42] datasets. As in many SOTA methods, we adopted a multi-stream fusion network by utilizing joints, bones and their motion information as inputs. The effectiveness of our model is shown below, with various comparisons with other approaches.
4.4.1. Experiments on the NTU-RGBD 60 Dataset
The performance of our PGT was evaluated on both the CS and CV benchmarks as in [40]. As shown in Table 5, we compared our PGT with four kinds of methods: handcrafted features, RNN-based methods, CNN-based methods and GCN-based methods. GCN methods are generally the newest and most effective, and our work combined the architecture of graph convolution in GCNs with the self-attention in transformers to fuse local and global information.

Table 5.
Comparison of the experiment results on the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset.
When compared with the RNN-based and CNN-based methods, our PGT demonstrated superiority in graph convolution operations, which is more consistent with the data structures of skeletons. The accuracy increased by 6.7% or 6.2% when compared with the fuzzy-CNN [18], which extracted four complementary feature vectors by a fuzzy integral to capture different spatiotemporal dynamics. When compared with the RNN-based DS-LSTM [21], our model greatly improved the accuracy with a more rational structure instead of focusing on learning the temporal information with LSTM.
As for most GCN-based methods, our PGT showed better performance with the proposed pyramid network consisting of graph embedding and self-attention modules. Additionally, based on the four-stream converged network architecture, the accuracy of our method was 0.9% and 1.7% higher than the MS-AAGCN [28] on both CS and CV, respectively. Compared with the outstanding shift-GCN [12], our method still performed better on the CS benchmark, which meant a more robust representation of various actions performed by different persons. Compared with the DC-GCN [30], our method showed a comparable performance. The DC-GCN adopted the decoupling aggregation mechanism in CNNs and a more effective dropout design (ADG) for graphs. It was noticed that the efficient-GCN [15] performed better than ours on the CS benchmark. However, our PGT still showed a comparable ability by combining graph convolution with the transformer attention mechanism.
Most GCN-based methods follow the backbone of the ST-GCN [10] and make efforts for a more robust representation, a more efficient architecture, a more dynamic topology, etc. However, our PGT introduced a novel backbone which showed excellent potential by taking advantage of both GCNs and transformers.
4.4.2. Experiments on the NTU-RGBD 120 Dataset
The performance of the NTU-RGBD 120 dataset was also evaluated on both the X-sub and X-set benchmarks. As shown in Table 6, the PGT performed better than most recent works. Compared with the four-stream shift-GCN, the accuracy of our PGT was 0.6% and 1.2% higher on the X-sub and X-set benchmarks, respectively, while compared with the three-stream RA-GCN [13], our PGT achieved 5.4% higher accuracy on the X-sub benchmark and 6.1% higher accuracy on the X-set benchmark.

Table 6.
Comparisons of the experiment results on the NTU-RGBD 120 dataset.
The ST-TR-AGCN [14] also applies a self-attention mechanism in its architecture. However, multi-head self-attention is added separately for spatial graph convolution and temporal graph convolution with a two-stream network similar to the work in [10]. The core ST-GCN unit was also adopted in our graph embedding to obtain the local information in the vertex domain. Furthermore, our work took a pyramid transformer as the main structure to give full play to the long-range attention ability of the temporal-spatial joints. Concretely, our PGT applied both spatial-temporal transformer and joint transformer design for long-range correlations in both the spatial and temporal domains. The accuracy of the PGT was 3.8% and 3.8% higher than the work in [14].
The performance of the GCN-based method, efficient-GCN [15], was better than our method on this dataset. As far as we are concerned, we paid more attention to the lightness of the network, particularly in the adjustment of the hyperparameters of the model. The FLOPs of the four-stream PGT were 4 GFLOPs, nearly one-fourth the amount of the efficient-GCN. Therefore, on a small dataset such as NTU-RGBD 60, our performance was even better on the CV benchmark. If the computational complexity of our pyramid network is improved, then the experimental results will be further increased as well.
4.4.3. Experiments on the Northwestern-UCLA Dataset
Northwestern-UCLA is a small dataset, and pretraining is needed for the pyramid backbone with the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. This was also conducted in previous work, such as [48,49]. As shown in Table 7, the performance of our PGT showed strong ability on this dataset and outperformed the SOTA method by 0.8%. Compared with the mature GCN-based model DC-GCN [30] with a drop graph operation (ADG), the PGT was slightly better.

Table 7.
Comparisons of the experiment results on the Northwestern-UCLA dataset.
4.4.4. Model Complexity
In this section, we present comparisons with other GCN-based methods from the aspect of model complexity (FLOPs and parameters). As shown in Table 8, our backbone was more efficient compared with most previous GCN-based methods evolved from the ST-GCN [10]. The FLOP count was one-fourth of that of the earliest ST-GCN backbone. However, the number of parameters was larger than most GCN works because of the transformer architecture, which contained more trainable weights. Note that our PGT backbone with only one stream had one-fourth of the FLOPs and parameters shown in Table 8, which were only 1.00 GFLOPs and 4.09 M parameters on the NTU-RGBD 60 dataset. The joint stream achieved an accuracy of 87.3%, being better than the AS-GCN [25] in terms of both accuracy and model complexity.

Table 8.
The model complexity on the NTU-RGBD 60 CS benchmark denoting the efficiency of the PGT.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposed a pyramid spatial-temporal graph transformer backbone (PGT) for skeleton-based action recognition. We introduced the self-attention mechanism into graph convolution blocks to extract spatial-temporal correlations. According to the pyramid-alternated architecture, the local information extracted by the graph embedding module was fused by the spatial-temporal and joint transformer blocks layer by layer. Both the local information and global information were iterated alternately through the model. Meanwhile, the graph embedding module adopted a separate convolution design to make the model more efficient and deeper. The spatial-temporal separate self-attention proposed for the former layers in the PGT was able to handle a wealth of tokens of skeleton joints. At the same time, the joint transformer self-attention focused on the long-range correlation fusion in both the spatial and temporal domains. Extensive experiments were conducted on the NTU-RGBD 60, NTU-RGBD 120 and Northwestern-UCLA datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of our work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., K.X., X.J. and T.S.; methodology, S.C. and K.X.; software, S.C.; validation, K.X., X.J. and T.S.; formal analysis, S.C., K.X., X.J. and T.S.; investigation, S.C. and X.J.; resources, X.J. and T.S.; writing, S.C., K.X., X.J. and T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Nature Natural Science Foundation of China (62002220).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vemulapalli, R.; Arrate, F.; Chellappa, R. Human Action Recognition by Representing 3D Skeletons as Points in a Lie Group. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2014, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, C. Enhanced skeleton visualization for view invariant human action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 68, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; He, M. Skeleton based action recognition using translation-scale invariant image mapping and multi-scale deep CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops, ICME Workshops, Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. Skeleton-based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops, ICME Workshops, Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 597–600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. View Adaptive Neural Networks for High Performance Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 1963–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Xu, D.; Wang, G. Spatio-Temporal LSTM with Trust Gates for 3D Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016—14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Part III Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Volume 9907, pp. 816–833. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Liu, J. An End-to-End Spatio-Temporal Attention Model for Human Action Recognition from Skeleton Data. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 4263–4270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. View Adaptive Recurrent Neural Networks for High Performance Human Action Recognition from Skeleton Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2136–2145. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Relational Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, ICME 2019, Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 826–831. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 7444–7452. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Two-Stream Adaptive Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 12026–12035. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition With Shift Graph Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Richly Activated Graph Convolutional Network for Robust Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plizzari, C.; Cannici, M.; Matteucci, M. Skeleton-based action recognition via spatial and temporal transformer networks. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2021, 208, 103219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Constructing stronger and faster baselines for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.E.; Torki, M.; Gowayyed, M.A.; El-Saban, M. Human Action Recognition Using a Temporal Hierarchy of Covariance Descriptors on 3D Joint Locations. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2013, Beijing, China, 3–9 August 2013; pp. 2466–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.S.; Reiter, A. Interpretable 3D Human Action Analysis with Temporal Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, CVPR Workshops 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1623–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Singh, P.K.; Sarkar, R. Fuzzy Integral-Based CNN Classifier Fusion for 3D Skeleton Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, B.; Xia, K.; Li, J.; Zuo, X. Skeleton edge motion networks for human action recognition. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Li, X.; Huang, C. Multi-term attention networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, K.; Sun, T. Action Recognition Scheme Based on Skeleton Representation With DS-LSTM Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Cai, X.; Ye, M.; Yuan, H. A Deep Attention Model for Action Recognition from Skeleton Data. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, W. Disentangling and Unifying Graph Convolutions for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Shen, X.; Tian, X.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Hua, X. Spatio-Temporal Inception Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the MM ’20: The 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event/Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. Actional-Structural Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3595–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, K.; Mi, Z.; Jiang, X.; Sun, T. Dual-domain graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Mach. Learn. 2022, 111, 2381–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Multi-Scale Adaptive Aggregate Graph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition With Multi-Stream Adaptive Graph Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9532–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Channel-wise topology refinement graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13359–13368. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Decoupling GCN with DropGraph Module for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020—16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part XXIV. Volume 12369, pp. 536–553. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, A.; Lin, T.; Parmar, N.; Shlens, J.; Abbeel, P.; Vaswani, A. Bottleneck Transformers for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2021, Virtual Event, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 16519–16529. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020—16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science Part I. Volume 12346, pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. Volume 139, pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tay, F.E.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token vit: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid Vision Transformer: A Versatile Backbone for Dense Prediction without Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2021, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, W.; Duan, L.; Gan, C. STST: Spatial-Temporal Specialized Transformer for Skeleton-based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3229–3237. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. NTU RGB+D: A Large Scale Dataset for 3D Human Activity Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Perez, M.; Wang, G.; Duan, L.; Kot, A.C. NTU RGB+D 120: A Large-Scale Benchmark for 3D Human Activity Understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2684–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Nie, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, S. Cross-View Action Modeling, Learning, and Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2014, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Xing, J.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. Semantics-Guided Neural Networks for Efficient Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Maqbool, M.H.; Liu, F.; Foroosh, H. Self-Attention Network for Skeleton-based Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2020, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 624–633. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xia, R. Adaptive multi-view graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Neurocomputing 2021, 444, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, C.; de Souza, J.S.; Brémond, F.; dos Santos, J.A.; Schwartz, W.R. SkeleMotion: A New Representation of Skeleton Joint Sequences based on Motion Information for 3D Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, AVSS 2019, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–21 September 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Caetano, C.; Brémond, F.; Schwartz, W.R. Skeleton image representation for 3d action recognition based on tree structure and reference joints. In Proceedings of the 2019 32nd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–30 October 2019; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Dai, R.; Koperski, M.; Minciullo, L.; Garattoni, L.; Bremond, F.; Francesca, G. Toyota smarthome: Real-world activities of daily living. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Sharma, S.; Dai, R.; Bremond, F.; Thonnat, M. VPN: Learning video-pose embedding for activities of daily living. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 72–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.; Kim, D.; Kang, S.; Lee, S. Ensemble deep learning for skeleton-based action recognition using temporal sliding lstm networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1012–1020. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).