Abstract
Riceberry rice bran is the part of rice that has been scrubbed out during the coloring process. There are various health benefits to be gained from foods with a high protein content. This work aimed to study the effect of hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extracts on colon cancer cell lines compared to normal cells. The MTT assay result showed that our extract has lower cytotoxicity effects on normal cells (PCS-201-010, IC50 = 6745 µg/mL) compared to colon cancer cell lines and has a greater effect on metastatic cancer cell lines (SW-620, IC50 = 5468 µg/mL) than non-metastatic cancer cell lines (HT-29, IC50 = 6054 µg/mL). The apoptotic inductive effects of HRBE on SW-620 were observed after 72 h at a maximum rate of 76% and at maximum concentration. According to the result of the cell senescence analysis after 24 h of HRBE treatment, the percentage of HT-29 (86%) expressing SA-β-gal was much higher than that of SW-620 (32%). Consequently, the decrease in the cell population in the S and M/G2 phases indicated cell cycle arrest in HT-29 cells after being treated with HRBE. Focusing on the peptide fraction size of HRBE, the largest (>50 kDa) fraction showed the highest anticancer activity compared to other fractions. In conclusion, the hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extract induced the apoptosis process in the metastatic cancer cells and induced the senescence process in the non-metastatic cancer cells. This observed information will be useful and applicable for medical research and colon cancer treatment in the future.
1. Introduction
Colon cancer is a major health problem globally and one of the three most common cancers diagnosed in both men and women worldwide. Its incidence rapidly rises in cities with economic development. Colon cancer can be caused by accumulating mutations and epigenetic alterations [1]. Presently, various therapies have been used clinically for colon cancer, including chemotherapy. However, chemotherapy resistance remains one of the serious problems and can also cause adverse side effects. Thus, the development of anticancer natural extracts could possibly be an alternative treatment for future colon cancer patients to overcome those problems.
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is the most important crop and staple food source consumed by over half of the world population. For Thailand, rice is the most important crop that makes the country a major exporter in the world rice market. Recently, riceberry rice has become popular among health-concerned people due to its health-promoting and potential anticancer activity. Moreover, riceberry rice has been reported to have hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, antioxidant and antiinflammation properties. The active ingredients of riceberry are tocopherol, tocotrienol, β-Sitosterol, γ-oryzanol, β-Carotene and some proteins. These substances were found in most of the pericarp, also known as rice bran [2]. From previous studies, riceberry rice bran extract was shown to be a significant inhibitor of colonic carcinoma (Caco-2), breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) and acute myeloid leukemia (HL-60) by suppressing cell growth and proliferation, inducing cell cycle arrest and promoting cellular apoptosis [3]. However, the use of protein hydrolysate from riceberry rice bran on colon cancer inhibition remains limited. This is despite the rice bran being rich in proteins such as albumin, globulin, glutelin and prolamin with high nutritional value in terms of minerals, unsaturated fat and vitamins. The highest phytate content in rice bran was found in albumin and the lowest in prolamin [4,5,6], which can be a high potential source for protein hydrolysates using the Alcalase enzyme. According to a previous study, Alcalase is an alkaline endo-peptidase that can give higher protein yields, and it demonstrates its activity in hydrolyzing glutelin (MW 57 kDa), which is the main protein accounting for 60–80% of the total protein in rice [7,8].
Thus, the purpose of this study is to investigate the anticancer activity of hydrolyzed riceberry bran extract on non-metastatic and metastatic colon cancer cell lines. This investigation may give useful information that leads to future application in medical research and treatment for colon cancer patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Riceberry Rice Bran Hydrolyzation, Extraction, Anthocyanin Removal, and Fractionation
Hydrolyzation of riceberry rice bran by Alcalase was performed according to Thamnarathip et al., 2016 [9]. The hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran powder was extracted by ultrapure water at a concentration of 20 g/L. Then, the mixture was centrifuged at 2000× g for 5 min and filtered with Whatman filter paper No. 1 (size 11 µm). The filtrated hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extract (HRBE) was concentrated by freeze drying and kept at −20 °C until further use.
Isolation of anthocyanins from HRBE was performed according to Rodriguez-Saona and Wrolstad (2001) [10] to obtain the pure protein/peptide by water, methanol with 0.01% HCl and acetone. The extraction solvents (both methanol and acetone) were evaporated by rotary evaporator at 40 °C under vacuum before the freeze-drying process and kept at −20 °C until use.
The freeze-dried powder was then mixed with ultrapure water at a concentration of 50 mg/mL before being fractionated to isolate the size of peptides by Amicon Ultra-15 centrifugal filter devices into >50, 50–30, 30–10, 10–3 and <3 kDa. All HRBE fractions were freeze dried and kept at −20 °C until being sterile filtered with 0.2 µm syringe filter before the cytotoxicity test with SW- 620 cell lines. A yield percentage was calculated by
2.2. Cell Culture
Primary human dermal fibroblast cell line (PCS-201–010) and non–metastatic human colon cancer cell line (HT-29) were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium from Gibco (DMEM: Thermo Fisher Scientific, New York, NY, USA), and metastatic human colon cancer cell line (SW-620) was cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium 1640 from Gibco (RPMI 1640: Thermo Fisher Scientific, New York, NY, USA). All media were supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin from Gibco (Thermo Fisher Scientific, New York, NY, USA). Cells were maintained at 37 °C in an incubator (Binder GmbH, Tuttlingen, Germany) under 5% CO2 and 95% air atmosphere at constant humidity. Trypsin-EDTA was used for cells’ detachment at 70% confluence.
2.3. Cellular Viability by MTT Assay
The cytotoxicity of the HRBE was determined by the MTT assay. HT-29, SW-620 and PCS-201-010 cell lines were seeded at 5 × 104 cells/mL in 96-well plates for 24 h. The next day, cells were treated with different concentrations of HRBE (0–10,000 µg/mL) and mitomycin C (0–100 µg/mL) for 24, 48 and 72 h. The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control, while the mitomycin C was considered as the positive control. To harvest, MTT solution was added and incubated for 4 h at 37 °C for the formazan. Next, the excess of MTT solution was carefully removed and replaced by 100 µL DMSO to dissolve formazan crystals. Absorbance was then measured using a microplate reader at a wavelength of 570 nm (Biotek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA) [11]. The percentage of cell viability was quantified using following formula and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated.
As HRBE demonstrated the lower IC50 value in SW-620 cell line, we used only SW-620 to confirm the cell apoptosis in the next assay.
2.4. Senescence-Associated Beta-Galactosidase (SA-β-gal) Staining
SA-β-gal staining was performed using Senescence β-galactosidase staining kit (Cell signaling technology, Massachusetts, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Briefly, the cells were examined under the inverted light microscope to monitor the morphological changes. SW-620 and HT-29 cell lines were seeded at 1 ×105 cells/mL in 6-well plates before treated with different concentrations of HRBE (0, 5, 2.5, 1 and 0.5 mg/mL), 0.05 mg/mL of mitomycin c for 24 h. The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control, while the mitomycin C was considered as the positive control. The next day, the cells were washed three times with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature. The fixed cells were then incubated overnight at 37 °C with the working solution containing 0.05 mg/mL X-gal using SA-β-gal staining kit.
2.5. Acridine Orange/Propidium Iodide (AO/PI) Double Staining Test
Acridine orange (AO) and propidium iodide (PI) were used as fluorescent dyes to determine the cell culture viability and specificity for living, apoptotic and late apoptosis/necrosis states according to Foglieni et al. (2001) [12]. All cell lines were seeded at 1 × 105 cells/mL in 6-well plates before being treated with different concentrations of HRBE (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/mL). The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control. For the positive control, 0.05 mg/mL of mitomycin C and 1 µm (0.116 mg/mL) of doxorubicin were treated on all cell lines for 72 h. Trypsin-EDTA was used for cells’ detachment and the pellet was collected by centrifugation at 340 g for 100 min, then the culture medium was discarded. The cells were then washed three times with PBS and 10 µL of PBS added. Separately, 1 µL AO (10 mg/mL) was mixed with 1 µL PI (1 mg/mL) making a double-staining dye of AO/PI and kept in an ice bath in dark conditions. An aliquot of the cell suspensions (10 µL) was added to the dye mixture and transferred onto a glass slide for fluorescence viewing. Slides were observed under a UV fluorescence microscope within 30 min.
2.6. Apoptosis Assay
Apoptosis assay was performed using Muse™ Annexin V & Dead Cell Assay [13]. SW-620 cells lines were seeded at 1 × 105 cells/mL in 6-well plates and treated with different concentrations of HRBE (10, 5, 2.5 and 1.25 mg/mL) for 72 h. For the positive control, 0.05 mg/mL of mitomycin C and 1 µM (0.116 mg/mL) of doxorubicin were used. To harvest, cells were trypsinized for 5 min and collected by centrifugation at 340 g for 5 min, then washed by PBS. Cells were then moved to 1.5 mL Eppendorf and resuspended with 50 µL complete media. Then, cells were stained with 50 µL Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit (Merck KgaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and incubated at room temperature in the darkness for 50 min. The stained cells were measured using Guava Muse Cell Analyzer (Merck KgaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
HT-29 cells lines were seeded at 5 × 105 cells/mL in 6-well plates and treated with different concentrations of HRBE (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/mL) for 24 h. The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control. For the positive control, 0.05 mg/mL of mitomycin C and 1 µM (0.116 mg/mL) of doxorubicin were used. To harvest, cells were trypsinized for 5 min and collected by centrifuge at 340 g for 5 min, then washed by PBS, fixed in 200 µL of ice-cold 70% ethanol and incubated for at least 3 h at −20 °C. Then, it was centrifuged at 340 g for 5 min and washed once with PBS. Then, cells were stained with 200 µL Muse Cell Cycle reagent (Merck KgaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and incubated at room temperature in the dark for 30 min. The stained cells were measured using Guava Muse Cell Analyzer (Merck KgaA, Darmstadt, Germany).
2.8. Statical Analysis
Statistical analysis for comparisons among multiple groups (three types of cell line, extract concentrations and time point) was performed using software SPSS (version 16; SPSS Inc.; Chicago, IL, USA) for analysis of variance (ANOVA) and student’s t-test. Results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Differences with p-values of < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity of Hydrolyzed Riceberry Rice Bran Extract on Colon Cancer Cell Lines
For the aqueous extraction of hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extract (HRBE), the percentage yield was reached at 85.94%. To ensure the cytotoxicity levels on cancer and normal cells, an MTT assay was performed on a primary human dermal fibroblast neonatal cell line (PCS-201-010), a non–metastatic human colon cancer cell line (HT-29) and a metastatic human colon cancer cell line (SW-620) after they were treated with the different concentrations of HRBE (0–10,000 µg/mL) for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. For the positive control, different concentrations of mitomycin C (0–100 µg/mL) were used (Table 1).

Table 1.
IC50 values of HRBE and mitomycin C on three different cell lines.
According to the MTT assay results on cancer cell lines, a significant decrease in cell viability with a dose- and time-dependent manner was observed after they were treated with HRBE. The half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of HRBE on HT-29 of 43,677, 11,164 and 6053 µg/mL, and on SW-620 of 9880, 6870 and 5468 µg/mL were indicated at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, respectively. For the effect of HRBE on the fibroblast normal human cell line (PCS-201-010), the IC50 concentrations were 15,352, 8007 and 6745 µg/mL, respectively, (Table 1 and Figure 1), which were significantly higher than those of cancer cell lines (the responsive curve patterns can be seen in Figure S1 (Supplementary Materials)).
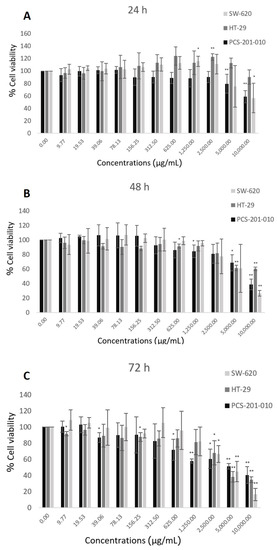
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay on normal human fibroblast cell line (PCS-201-010), non-metastatic colon cancer cell line (HT-29) and metastatic colon cancer cell line (SW-620) after being treated with HRBE concentrations (0–10,000 µg/mL) for 24 h (A), 48 h (B) and 72 h (C). The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control. The percentage of cell viability was determined as compared to an untreated condition. Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (*, p ≤ 0.05 significant; **, p ≤ 0.01 significant).
For the positive control treated with mitomycin C on HT-29, SW-620 and PCS-201-010, IC50 concentrations were indicated for HT-29 as 763, 141 and 57 µg/mL, for SW-620 as 193, 58 and 40 µg/mL and for PCS-201-010 as 210, 177 and 145 µg/mL (Figure 2) at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, respectively. The result showed that the HRBE had less effect on normal cells than the two types of cancer cells and the IC50 concentrations decreased in a dose–time-dependent manner (the responsive curve patterns can be seen in Figure S2). Since the lowest IC50 value was observed with the treated SW-620 cell line at 72 h, this metastatic human colon cancer cell line was chosen for the apoptotic inductive efficiency determination of HRBE in the next experiment.
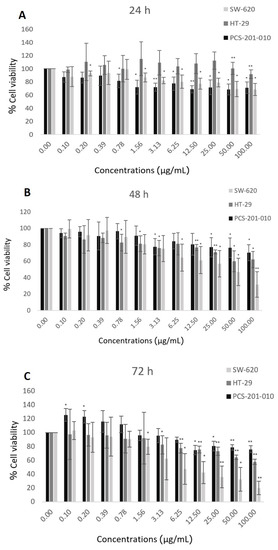
Figure 2.
Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay on normal human fibroblast cell line (PCS-201-010), non-metastatic colon cancer cell line (HT-29) and metastatic colon cancer cell line (SW-620) after being treated with mitomycin C (as the positive control) concentrations (0–100 µg/mL) for 24 h (A), 48 h (B) and 72 h (C). The percentage of cell viability was determined as compared to an untreated condition. Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (*, p ≤ 0.05 significant; **, p ≤ 0.01 significant).
3.2. Senescence Inductive Effect of Hydrolyzed Riceberry Rice Bran Extract on Colon Cancer Cell Lines
As with the effect of HRBE on cancer cell aging, morphological changes associated with cellular senescence were observed such as an enlarged and flattened cell shape and increased granularity and biochemical changes. For this particular experiment, the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining was used, which revealed the senescence inductive ability of HRBE on HT-29 and SW-620 cells at concentrations of 0, 0.5, 1, 2.5 and 5 mg/mL compared to the treatment with mitomycin C at 0.05 mg /mL (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
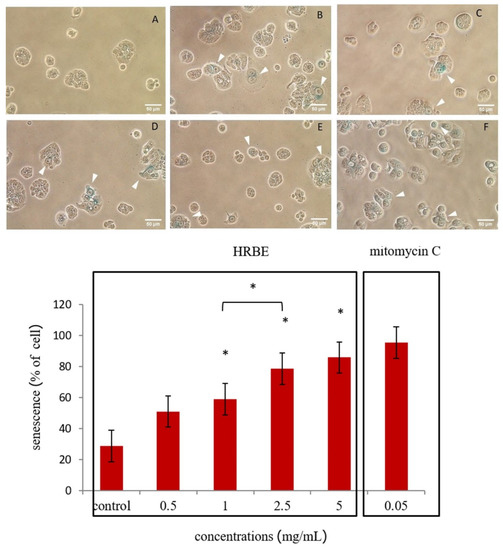
Figure 3.
Cellular senescence inducing effect of HRBE on HT-29 cells after being treated with 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 0.5 mg/mL (B), 1 mg/mL (C), 2.5 mg/mL (D) and 5 mg/mL (E) for 24 h compared to 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C treatment, considered as the positive control (F). The blue stained cells with flattened and enlarged cell morphology represent the cellular senescence status indicated by the white arrowheads. Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using student’s t-test comparing each concentration with the control group (0 mg/mL) (*, p ≤ 0.05).
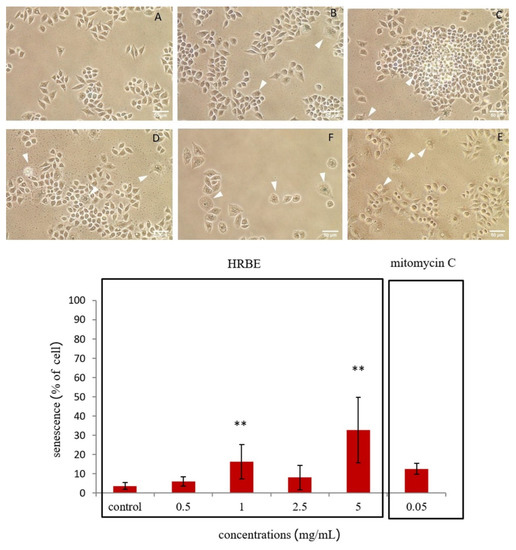
Figure 4.
Cellular senescence inducing effect of HRBE on SW-620 cells after being treated with 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 0.5 mg/mL (B), 1 mg/mL (C), 2.5 mg/mL (D) and 5 mg/mL (E) for 24 h compared to 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C treatment, considered as the positive control (F). The blue stained cells with flattened and enlarged cell morphology represent the cellular senescence status indicated by the white arrowheads. Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using student’s t-test comparing each concentration with the control group (0 mg/mL) ( **, p ≤ 0.01).
From the result in the HT-29 cell line, the approximate mean values of the SA-β-gal stained cells were indicated as being at 27, 51, 59, 79 and 86 percent, respectively, after being treated with the different concentrations of HRBE (0, 0.5, 1, 2.5 and 5 mg/mL) and 95 percent after being treated with mitomycin C at a dose of 0.05 mg/mL (Figure 3), respectively. The number of SA-β-gal-stained cells gradually increased as the concentration of the extract increased. With the cellular senescence inductive effect on the SW-620 cell line, the approximate mean values of the dyed cells were 4, 6, 16, 8 and 32, respectively, after being treated with the different concentrations of HRBE (0, 0.5, 1, 2.5 and 5 mg/mL) and 13 percent after being treated with mitomycin C at 0.05 mg/mL (Figure 4).
The positive stained cells were found to have increased after being exposed to the higher extract concentrations, and HRBE had a higher senescence inductive effect on the HT-29 cells compared to the SW-620 cells.
3.3. Apoptotic Inductive Effect of Hydrolyzed Riceberry Rice Bran Extract on Colon Cancer Cell Lines
To confirm the apoptotic inductive effect of HRBE, a quantification of the apoptotic cells was performed using a fluorescence microscope AO/PI double staining technique. The interpretation was performed based on the fact that AO is a membrane permeable nuclear dye that stains both live and dead cells (early apoptosis) in a green color, while PI is a membrane impermeable nuclear dye that stains late apoptosis dead cells red. According to the results, the morphology of SW-620 changed after being treated with HRBE for 72 h. This was characterized by apoptotic-related features such as cytoplasmic shrinkage and membrane blebbing; chromatin condensation in early apoptosis and late apoptosis was indicated by the red color from PI (Figure 5).
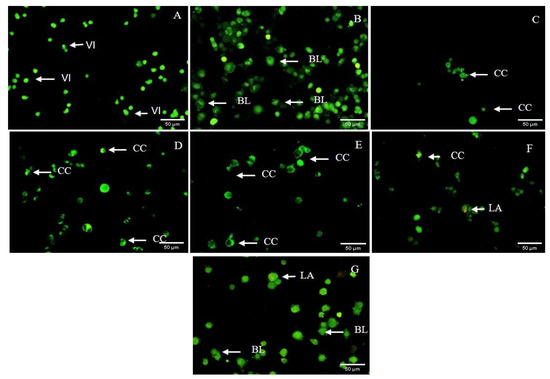
Figure 5.
Fluorescence microscope AO/PI double staining of HRBE on SW-620 cells after being treated with 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 1.25 mg/mL (B), 2.5 mg/mL (C), 5 mg/mL (D) and 10 mg/mL (E) for 72 h compared to positive control groups treated with 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C treatment (F) and doxorubicin (0.116 mg/mL) (G). VI: viable cell; blebbing of the cell membrane; CC: chromatin condensation; LA: late apoptosis.
3.4. The Analysis of Cell Apoptosis by Annexin V and Flow Cytometry
This analysis can confirm the cellular apoptotic mechanism based on the fact that the phosphatidylserine (PS) phospholipid is flipped from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane of apoptotic cells to signal for nearby phagocytic cells. Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein with a high affinity for PS [14]. This Annexin V staining is commonly co-stained with propidium iodide (PI) for the identification of the membrane potential to differentiate between early and late apoptotic cells by flow cytometry analysis in early apoptosis (Annexin V positive, PI negative), late apoptosis (Annexin V and PI positive) and necrotic (Annexin V negative, PI positive) cells [15]. According to the results on SW-620 cells after being treated with HRBE for 72 h, it can induce the cells’ apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner with significant increases after being treated with higher concentrations. The approximate cellular apoptotic percentages were determined to be 16, 51, 60 and 76% after being treated with HRBE at 1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/mL, respectively (Figure 6).
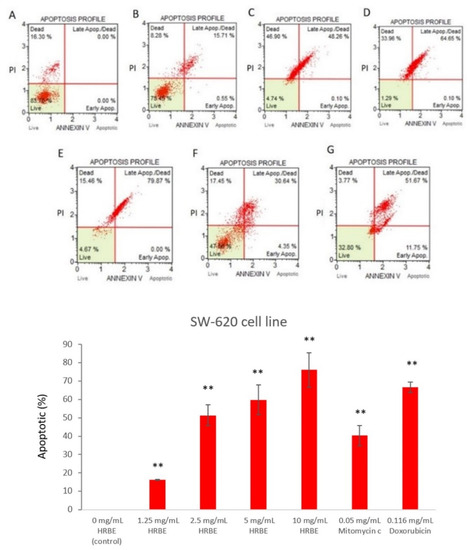
Figure 6.
The percentage of cell apoptosis on SW-620 cells at 72 h indicated by Annexin V and flow cytometry after being treated with 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 1.25 mg/mL (B), 2.5 mg/mL (C), 5 mg/mL (D) and 10 mg/mL (E) compared to positive control groups treated with 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C (F) and doxorubicin 0.116 mg/mL (G). Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using student’s t-test to compare each concentration with the control group (0 mg/mL) (**, p ≤ 0.01).
3.5. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
The cell cycle analysis using propidium iodide (PI) and RNase in a proprietary formulation was performed for the quantitative measurement of the percentages of the cell populations in the G0/G1, S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle. According to the flow cytometry result, the populations in each cell phase of the HT-29 cell line after being treated with HRBE changed significantly with the concentrations of 5 and 10 mg/mL compared to the control. The percentage number of cells increased in the G0/G1 phase (5 mg/mL = 39.63 ± 11.83%, 10 mg/mL = 61.67 ± 3.76%) but decreased in the S phase (5 mg/mL = 22.83 ± 4.57%, 10 mg/mL = 17.07 ± 2.37%) and the G2/M phase (5 mg/mL = 13.23 ± 2.81%, 10 mg/mL = 9.5 ±1.15%) (Figure 7).
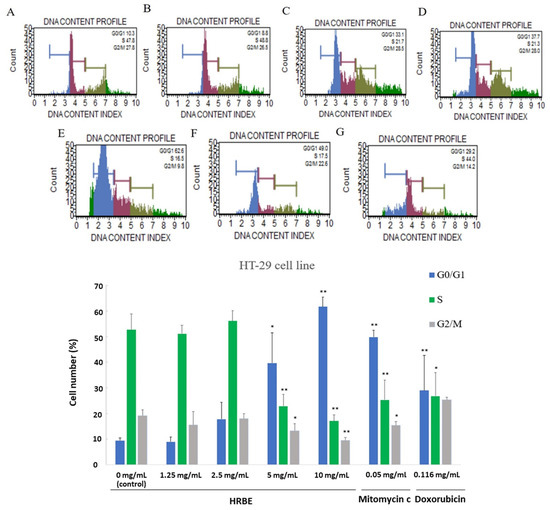
Figure 7.
The cell cycle analysis by flow cytometer of HT-29 cells at 24 h after treatment with HRBE concentration 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 1.25 mg/mL (B), 2.5 mg/mL (C), 5 mg/mL (D) and 10 mg/mL (E) compared to positive control groups treated with 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C (F) and doxorubicin 0.116 mg/mL (G). Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using student’s t-test to compare each concentration with the control group (0 mg/mL) (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01 significant).
3.6. Cytotoxicity of HRBE Fractions on Colon Cancer Cell Lines
Crude hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extract (HRBE) was prepared by alkaline endo-peptidase to obtain the bioactive peptides that can inhibit cancer cell growth. To ensure the proper size of the anticancer peptide fractions, we separated the sizes of the peptides from the crude extract using centrifugal filter devices at different molecular cutoffs in the ranges of >50, 50–30, 30–10, 10–3 and <3 kDa fractions. Each fraction was tested on the metastatic colon cancer cell line at different concentrations (0–10,000 µg/mL) for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h compared to the positive control groups treated with doxorubicin (0–116 µg/mL) and mitomycin C (0–100 µg/mL). The fractionation results show the percentage yield of each of the HRBE fractions (Table 2) and their cytotoxicity on SW-620 cells from the MTT assay (Figure 8) and the responsive curve patterns can be seen in Figure S3. The lower IC50 value indicates the better growth inhibitory activity of the >50 kDa fraction on SW-620 compared to other fractions. Moreover, the IC50 value of the >50 kDa fraction on SW-620 (4864 µg/mL) was found to be less than that of the crude extract (5468 µg/mL) 72 h after treatment (Table 3).

Table 2.
The percentage yield of HRBE fractions.
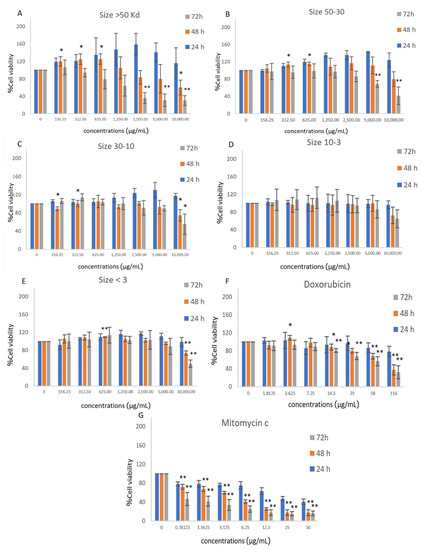
Figure 8.
Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay on SW-620 cells after being treated with fractions of HRBE concentrations 0–10,000 µg/mL including (A) >50, (B) 50–30, (C) 30–10, (D) 10–3 kDa and (E) <3 kDa fractions, (F) doxorubicin concentration 0–116 µg/mL and (G) mitomycin C concentrations 0–50 µg/mL for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. The untreated cells (0 mg/mL) were considered as negative control, while the doxorubicin and mitomycin C treatments were considered as the positive control. The percentage of cell viability was determined as compared to an untreated condition. Data are represented by the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using student’s t-test (*, p ≤ 0.05 significant; **, p ≤ 0.01 significant).

Table 3.
IC50 values of HRBE fractions, doxorubicin and mitomycin C for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h.
3.7. Apoptotic Inductive Effect of the >50 kDa HRBE Fraction on Metastatic Colon Cancer Cells
To confirm the apoptotic inductive effect of the >50 kDa HRBE fraction on SW-620 cells, quantification of the apoptotic rate using the fluorescence microscope AO/PI double staining test was performed. The cellular apoptotic morphologies of SW-620 cells such as membrane blebbing and chromatin condensation in early apoptosis and late apoptosis (indicated by the red color from PI) were characterized after being treated with different concentrations of the >50 kDa HRBE fraction for 72 h (Figure 9). This result indicates that the peptides from the >50 kDa HRBE fraction could inhibit the colon cancer cell lines via the apoptosis induction mechanism.
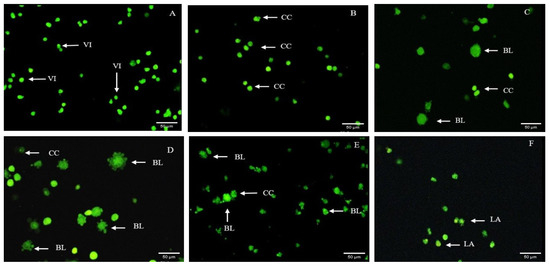
Figure 9.
Fluorescence microscope AO/PI double staining of HRBE fractions on SW-620 cells after being treated with 0 mg/mL, considered as negative control (A), 2.5 mg/mL (B), 5 mg/mL (C) and 10 mg/mL (D) for 72 h compared to positive control groups treated with 0.05 mg/mL mitomycin C treatment (E) and doxorubicin 0.116 mg/mL (F). VI: viable cell; blebbing of the cell membrane; CC: chromatin condensation; LA: late apoptosis.
4. Discussion
Colon cancer is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide [16]. There have been several studies on natural substances to replace or use in conjunction with chemotherapy drugs [17,18,19]. Moreover, it has been reported that proteins from nutrients are an efficient source for bioactive peptides with selectively anticancer properties [20,21,22,23].
In the present study, cytotoxicity tests of hydrolyzed riceberry rice bran extracts (HRBE) by MTT assay were performed on human normal fibroblast cell lines (PCS-201–010), non–metastatic colon cancer cell lines (HT-29) and metastatic colon cancer cell lines (SW-620). The percentage of cell viability after treatment decreased when increasing the concentration of the extract (dose-dependent), and considering the IC50 value was effective when cells were treated with HRBE at 48 and 72 h (time-dependent). A similar observation by Banjerdpongchai et al. (2009) [24] was comparable with our results when the cytotoxicity of purple glutinous rice extract was tested on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) and prostate cancer (LNCaP) and was found to be more effective at 48 h than 24 h. The efficacy of rice bran extract on colon cancer cells (HCT-116) and breast cancer (HTB-26) was also revealed when the cytotoxicity rate of both cancer cells increased dependent on the time [25]. Focusing on the cell-specific mechanisms, the inhibitory effects on the cell proliferation of the three cell lines were significantly different when treated with HRBE. The IC50 values of the HRBE treatment when used on HT-29 were significantly higher than those of SW-620. This phenomenon could be explained based on the morphology of non-metastatic cancer cells and the fact that they have denser adhesion between cells (cell–cell junction) than metastatic cancer so that the loss of the cell junction changes the morphology and leads to the cancer spreading to other organs [26]. This may correlate with our results that show that the HRBE had higher cytotoxic efficiency on SW-620 (metastatic colon cancer cells) than HT-29 (non-metastatic colon cancer cells) and had no effect on PCS-201-010 (normal fibroblast cells).
According to the result of the MTT assay, we selected SW-620 cells for the investigation of the apoptotic inductive effect of HRBE confirmed by the pattern of cellular apoptotic morphology using the fluorescence microscope AO/PI double staining test. The apoptosis cell morphology such as membrane blebbing and chromatin condensation in early apoptosis was observed after being treated with HRBE. Notably, the late apoptosis feature was indicated in the red color from PI that binds specifically to DNA but cannot passively traverse into cells that possess an intact plasma membrane because of the differences between the cell membranes of normal and cancer cells [27,28]. A normal cell membrane contains zwitterion phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin in an outer leaflet, and anionic phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in the PCSinner leaflet with asymmetric distribution. In contrast, a cancer cell loses asymmetric distribution, contains more negative charges and pH is altered in the cell membrane [26], the physical changes of which are caused by mutations in the proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes [29]. This is the reason why PI can indicate late apoptosis including the efficacy of the extract on cancer cells and the causes of the differences in the effect of the activity of the HRBE between HT-29 (non–metastatic) and SW-620 (metastatic) on the quantity of peptide entering the cells.
In apoptotic cells, phosphatidylserine phospholipid is flipped from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane to signal for nearby phagocytic cells. Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein with a high affinity for phosphatidylserine [14]. Therefore, the percentage of apoptosis on SW-620 after being treated with HRBE can be detected by Annexin V and flow cytometry. Our result shows that the HRBE at concentrations of 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/mL significantly increased the induction of cell apoptosis. This is consistent with previous studies on the extracts of other rice such as the aqueous extract of brewers’ rice (WBR) on HT-29, which showed characteristics of apoptosis including early and late apoptosis at 48 h [30] and induced apoptosis by the significant activation of caspase-3 and−8 activities [31]. The methanol extract of the purple rice cultivar exhibited the highest inhibitory growth effect on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and the greatest ability to induce apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway with the loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MTP) and the activation of caspase-3 and -9 [32]. Moreover, the extraction of chemical components from the riceberry rice bran induced HL-60 (promyelocytic leukemia cell line) and Caco-2 (colorectal adenocarcinoma) to apoptosis via the p53 protein that increased due to the activation of caspase-3 [3]. p53 is a this tumor-suppressing protein that regulates genes to control the cell cycle in normal cells and induces cell cycle arrest for the repair of DNA, cellular senescence and programmed cell death such as apoptosis to remove irreversibly damaged cells [33]. Therefore, the interesting study of cell cycle arrest (senescence) was also a focus in this particular study.
Cellular senescence is the stage of irreversible cell cycle arrest and can be observed by SA-β-gal staining. Our results showed that the cellular senescence inductive effects of the HRBE on HT-29 were higher than those on SW-620. This indicates that HRBE is capable not only of apoptosis induction but also cell senescence induction. Senescence cells could have initially undergone cell cycle arrest that decreased the number of cells in the S and M/G2 phases and increased the number of cells in the G1/G0 phase. For this particular quantitative measurement, flow cytometry can determine the percentage of cells in each cell phase using propidium iodide (PI) and RNase. PI has specific DNA stunning that can indicate the different stages of the cell cycle because the cells in the G1 phase have a constant DNA content (1×), while the cells in the G2/M phase have a constant DNA (2×) that is twice the intensity of the G1 phase [33]. According to the flow cytometry result in this study, the HRBE increased the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase and decreased the number of cells in the S, G2 and M phases, which also indicates the senescence inductive effect of HRBE on the HT-29 cell line. Since the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and cyclin are regular proteins controlling the cell cycle, and CDK–cyclin complexes can be regulated by a group of proteins called cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs) such as p21 that is downregulated by p53, p21 could induce G1 cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the activity of the cyclin–CDK2/4 complexes, E2F and PCNA [34]. This phenomenon correlates with the previous study on HL-60, MCF-7 and Caco-2, in which Cyclin B1 (a complex with Cdk1 controlling the S to G2 phases in the cell cycle) was significantly decreased after being treated with the dichloromethane extract of riceberry bran [3]. Similarly, the cell population at the sub-G0 phase of the HT-29 cells increased after the cells were treated with brewers’ rice extract for 48 h [30].
Focusing on the peptide fraction size of the HRBE, the lower IC50 value of the >50 kDa fraction (compared to other fractions) indicates the growth inhibitory activity of rice bran peptides. Interestingly, this >50 kDa HRBE fraction showed higher efficacy on SW-620 cells over the crude extract, which is implied by the lower IC50 value of this fraction (4908 µg/mL) than that of the crude extract (5492.31 µg/mL) at 72 h. The apoptotic morphology of SW-620 cells was also observed after being treated with the >50 kDa fraction, characterized by membrane blebbing and chromatin condensation. Rice bran is a rich source of dietary fibers and proteins such as albumin, globulin, glutelin and prolamin with high nutritional value, minerals, unsaturated fat and vitamins, where the highest phytate content was found in albumin and the lowest in prolamin [4,5,6]. Since albumin is a water-soluble protein, the aqueous extraction of albumin always results in globulin contamination because of the minerals present in the rice grain that dissolve in a water solvent. Albumins were separated into three to four subfractions using gel filtration chromatography and had a molecular weight of 100 kDa or less when analyzed by size-exclusion HPLC [35]. Rice bioactive compounds such as toco (tocopherols and tocotrienols), phytosterols and γ-oryzanols have been reported to have antioxidative properties including free radical scavenging activity and the inhibition of lipid peroxidation. These substances are valuable for health promotion being able to help reduce free radicals and cholesterol in the body. Moreover, the hydrolysis of protein with proteases produces many potential peptide sequences that provide numerous functional and antioxidative properties [11,36]. In addition, rice protein hydrolysates obtained from pepsin and trypsin hydrolysis exhibit much greater antioxidative activities than those before digestion. Previous research indicated that when peptides <5 kDa in size were separated from the hydrolysate bran protein by treating heat-stabilized defatted rice bran with the Alcalase enzyme, followed by treatment with simulated gastric and intestinal juices, resistant peptides were obtained. These hydrolyzed peptides have a high potential anticancer effect on colon cancer cells [25]. The optimal hydrolysis condition was 2 h after using an Alcalase-yielding protein content of 30.3% [9], which is comparable to the extraction yields in this study.
According to a previous study, Alcalase is an alkaline endo-peptidase that gives higher oil and protein yields. Its activity in hydrolyzing glutelin, as the main protein accounting for 60–80% of the total protein in rice, was higher than neutral protease. In addition to purified and isolated anticancer pentapeptide, Glu-Gln-Arg-Pro-Arg was obtained from rice bran, and the peptide with a molecular mass of 685.378 Da caused the growth inhibition of 84% against colon cancer cells (Caco-2 and HCT-116), 80% against breast cancer cells (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231) and 84% against liver cancer cells (HepG-2) at a dose of 600–700 µg/mL [21]. There are reported anticancer effects of the rice bran bioactive components that can induce apoptosis, inhibit cell proliferation and alter cell cycle progression in malignant cells. Rice bran bioactive components can also protect tissue damage through the scavenging of free radicals and the blocking of chronic inflammatory responses. Rice bran phytochemicals have also been shown to activate anticancer immune responses as well as affect the colonic tumor microenvironment in favor of enhanced colorectal cancer chemoprevention. Rice bran extracts and pure extracts alone can inhibit cancer cell growth without any side effects in response to the components of rice bran in normal cells. In previous studies, the cytotoxicity of purple rice extracts was tested on murine normal fibroblast NIH3T3 cells, and they showed a non-toxic effect on these normal cells [32], which is important evidence for the internal safety of rice bran use in cancer chemotherapy [37].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the results show that HRBE can effectively inhibit the colon cancer cell line depending on the time, dose and cell type including apoptosis in SW-620 and senescence in HT-29 that decreased the number of cells in the S and M/G2 phases and increased the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase. Moreover, the >50 kDa fraction of the HRBE demonstrates the ability to induce apoptosis and cytotoxicity better than the crude version. This finding can be useful and applicable for medical research and colon cancer treatment in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12146917/s1, Figure S1: Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay of HRBE, Figure S2: Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay of mitomycin c, Figure S3: Cytotoxicity test by MTT assay on SW-620 cells after being treated with faction of HRBE.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C. and M.K.; methodology, P.C., M.K. and V.W.; validation, P.C. and V.W.; investigation, P.C.; resources, S.T., P.C. and M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, V.W.; writing—review and editing, P.C.; supervision, P.C. and M.K.; project administration, P.C.; funding acquisition, P.C. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Graduate Program Scholarship from the graduate school and Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Graduate Program Scholarship from the graduate school and Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University. Cell lines were kindly provided from Mattaka Khongkaw, senior researcher from the National Nanotechnology Center (Nanotec), Thailand.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Sha, M.; Mao, G.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. DZNep inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer HCT116 cells by inducing senescence and apoptosis. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2015, 5, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juliano, C.; Cossu, M.; Alamanni, M.C.; Piu, L. Antioxidant activity of gamma-oryzanol: Mechanism of action and its effect on oxidative stability of pharmaceutical oils. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 299, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leardkamolkarn, V.; Thongthep, W.; Suttiarporn, P.; Kongkachuichai, R.; Wongpornchai, S.; Wanavijitr, A. Chemopreventive properties of the bran extracted from a newly-developed Thai rice: The Riceberry. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, A.P.; Adebiyi, A.O.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K. Isolation and characterization of protein fractions from deoiled rice bran. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hamid, A.; Luan, Y.S. Functional properties of dietary fibre prepared from defatted rice bran. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasambandam, R.; Heltiarachchy, N. Protein concentrates from unstabilized and stabilized rice bran: Preparation and properties. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanmoungjai, P.; Pyle, D.L.; Niranjan, K.; Biotechnology: International Research in Process, E.; Technology, C. Enzyme-assisted water-extraction of oil and protein from rice bran. Environ. Clean Technol. 2002, 77, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoa, T.; Kubota, M.; Suwannaporn, P.; Kadowaki, M. Characterization and bioactivities of young rice protein hydrolysates. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamnarathip, P.; Jangchud, K.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Vardhanabhuti, B. Identification of peptide molecular weight from rice bran protein hydrolysate with high antioxidant activity. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Saona, L.E.; Wrolstad, R.E. Extraction, isolation, and purification of anthocyanins. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, F1.1.1–F1.1.11. [Google Scholar]
- Meerloo, J.V.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. In Cancer Cell Culture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Foglieni, C.; Meoni, C.; Davalli, A.M. Fluorescent dyes for cell viability: An application on prefixed conditions. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 115, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognar, Z.; Cseh, A.M.; Fekete, K.; Antus, C.; Bognar, R.; Tapodi, A.; Ramadan, F.H.; Sumegi, B.; Gallyas, F., Jr. Amiodarone’s major metabolite, desethylamiodarone inhibits proliferation of B16-F10 melanoma cells and limits lung metastasis formation in an in vivo experimental model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchenko, A.P. Beyond annexin V: Fluorescence response of cellular membranes to apoptosis. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Paydar, M.; Rouhollahi, E.; Karimian, H. Annona muricata leaves induced apoptosis in A549 cells through mitochondrial-mediated pathway and involvement of NF-κB. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemeryck, L.Y.; Rombouts, C.; Hecke, T.V.; Van Meulebroek, L.; Bussche, J.V.; De Smet, S.; Vanhaecke, L. In vitro DNA adduct profiling to mechanistically link red meat consumption to colon cancer promotion. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lichota, A.; Gwozdzinski, K. Anticancer activity of natural compounds from plant and marine environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailon-Moscoso, N.; Cevallos-Solorzano, G.; Carlos Romero-Benavides, J.; Isabel Ramirez Orellana, M. Natural compounds as modulators of cell cycle arrest: Application for anticancer chemotherapies. Curr. Genom. 2017, 18, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.-F. Natural compounds as anticancer agents: Experimental evidence. World J. Exp. Med. 2012, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, H.; Kehinde, B.A.; Chhikara, N.; Sharma, D.; Panghal, A. Food-derived anticancer peptides: A review. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Yu, W.; Wu, J. Immunomodulatory and anticancer protein hydrolysates (peptides) from food proteins: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RCK Rajendran, S.; ECC Ejike, C.; Gong, M.; Hannah, W.; C Udenigwe, C. Preclinical evidence on the anticancer properties of food peptides. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Im Kang, Y.; Woo, H.J.; Lee, H.J. Anticancer activity of hydrophobic peptides from soy proteins. Biofactors 2000, 12, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.; Vousden, K.H. p53 in signaling checkpoint arrest or apoptosis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996, 6, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannan, A.; Hettiarachchy, N.; Narayan, S. Colon and breast anti-cancer effects of peptide hydrolysates derived from rice bran. Open Bioact. Compd. J. 2009, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boohaker, R.J.; Lee, M.W.; Vishnubhotla, P.; Perez, J.L.M.; Khaled, A.R. The use of therapeutic peptides to target and to kill cancer cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.L.-Y.; Smith, T.; Kumph, K.A.; Kuksin, D.; Kessel, S.; Déry, O.; Cribbes, S.; Lai, N.; Qiu, J. A high-throughput AO/PI-based cell concentration and viability detection method using the Celigo image cytometry. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kntayya, S.B.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Mohd Ain, N.; Iori, R.; Ioannides, C.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Induction of apoptosis and cytotoxicity by isothiocyanate sulforaphene in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, A.; Arnold, C. Biology and Genetics of Colorectal Cancer and Polyps and Polyposis. Textb. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Norhaizan, M.; Hazilawati, H.; Roselina, K. Brewers’ rice, a by-product from rice processing, has antiproliferative activity on human colorectal cancer (HT-29) cell line. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Huynh, K.; Heshu, S.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Hazilawati, H.; Roselina, K. Water extract of brewers’ rice induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells via activation of caspase-3 and caspase-8 and downregulates the Wnt/β-catenin downstream signaling pathway in brewers’ rice-treated rats with azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Banjerdpongchai, R.; Wudtiwai, B.; Sringarm, K. Cytotoxic and apoptotic-inducing effects of purple rice extracts and chemotherapeutic drugs on human cancer cell lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 6541–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faqua, C.F.; Akomeah, R.; Adunyah, S.E. IL-21 Signaling and Induction of Cytokine Expression in Human Leukemia Cells and Monocytes; Behzadi, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, X. Senescence regulation by the p53 protein family. Cell Senescence 2013, 37–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata, H.; Sugimoto, T.; Tanaka, K.; Kasai, Z. Biosynthesis of storage proteins in developing rice seeds. Plant Physiol. 1982, 70, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Shyu, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-K. Antioxidative properties of protein hydrolysate from defatted peanut kernels treated with esperase. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.J.; Ollila, C.A.; Kumar, A.; Borresen, E.C.; Raina, K.; Agarwal, R.; Ryan, E.P. Chemopreventive properties of dietary rice bran: Current status and future prospects. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).