Abstract
The aim of the present study was to induce malolactic fermentation (MLF) after alcoholic fermentation (AF) of must of the Moschofilero cultivar, the only ‘gris’ native grape variety that is cultivated in Greece. For this purpose, Oenococcus oeni strains Viniflora® CH16, Viniflora® Oenos and Viniflora® CiNe were inoculated after the completion of AF driven by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UCLM S325. Growth of the aforementioned starter cultures was assessed during fermentation by classical microbiological techniques, and verification of their dominance was performed by (GTG)5 fingerprinting. Assessment of standard enological parameters and colorimetric analysis were performed by established approaches. Identification and quantification of organic acids, ethanol and glycerol was performed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), while the solid-phase microextraction method (SPME), coupled with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS), was employed for the identification and quantification of volatile compounds. Finally, sensory analysis took place according to ISO 13299:2016. The suitability of the starter cultures employed to drive AF and MLF was exhibited; AF and MLF of the white and rosé wines were completed after 15 days. Upon completion of AF, substantial differences were observed in the chemical characteristics of the white and rosé wines, which were also reflected in the balance descriptor. MLF also resulted in significant changes. In all cases total acidity decreased and volatile acidity and pH value increased, while the vanilla and butter descriptors increased. Interestingly, the color intensity of the rosé wines also increased. A series of strain-dependent changes in the chemical composition and sensory analysis of both white and rosé wines was also observed.
1. Introduction
Malolactic fermentation (MLF) is driven by lactic acid bacteria and involves the conversion of L-malic acid to L-lactic acid, with the simultaneous release of CO2. It is considered an essential step for the majority of red wines and has also been proposed for a few white ones, including Chardonnay [1]. Substitution of the dicarboxylic malic acid with the monocarboxylic lactic acid results in deacidification of the wine and modification of the taste profile, since the harsh taste that characterizes L-malic acid is replaced by a milder one. In addition, malic acid could serve as a carbon source for a number of microorganisms, mainly yeasts, that have been associated with wine spoilage [2]; therefore, its removal enhances the microbial stability of the product. Finally, a series of additional modifications are likely to occur, depending on the capacity of the strain, or strains, that drives MLF, the grape cultivar as well as its technological parameters [3,4].
Moschofilero is the only ‘gris’ native grape variety that is cultivated in Greece. Due to the pink/purple color of the grape’s skin and the relatively intense terpenoid character, it is known for its use in the production of both white and rosé wines, in dry and sparkling form. The variety usually features in high acidity and low alcohol wines, with a delicate but intense aroma of rose petals, citrus fruits and pear, while it usually lacks body. The alcoholic fermentation may take place either spontaneously or by the addition of selected strains that highlight the varietal wine character, while malolactic fermentation in the majority of the cases is not sought. Given the revived worldwide interest on MLF, which arose from the benefits that it might exert on the final product [5,6,7], assessment of the impacts that MLF might have on the qualitative characteristics of white and rosé wines from the Greek Moschofilero grape variety, constitutes a very interesting topic. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to induce MLF in rosé and white wines made from the Greek Moschofilero grape variety and evaluate, for the first time, its technological interest and its effect on sensorial quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UCLM S325 (Fermentis, Marcq-En-Baroeul, France) and Oenococcus oeni strains Viniflora® CH16, Viniflora® Oenos and Viniflora® CiNe (Hansen, Hoersholm, Denmark) were used throughout the study. Inoculation of the microorganisms was performed according to the recommendations of the manufacturer.
2.2. Experimental Design and Winemaking Conditions
Grapes of the Greek Moschofilero variety were harvested from the same vineyard during the 2015 vintage, in the PDO wine zone of Mantineia in Peloponnese, at an altitude of 650 m. Destemming and crushing were performed manually after storage of the grapes for 24 h at 4 °C. In the case of rosé wine production, skin contact with the must was allowed for 15 h at 10 °C. In both cases 3 g/hL of sodium metabisulfite (Scharlab S.A, Barcelona, Spain) and 3 g/hL of pectolytic enzymes (Safizym® Clean, Fermentis, Lambersart, France) were added to the must. After 24 h at 10 °C, the clarified must was inoculated with a commercial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, UCLM S325, at approximately 6.5 log CFU/mL. Alcoholic fermentation (AF) took place in stainless-steel tanks of 50 L at 20 °C until residual sugar concentration was below 2 g/L. Alcoholic fermentation was performed in duplicate. Twenty-four hours after yeast inoculation, 200 mg/L of SpringFerm™ (Fermentis, France) were added. After the completion of alcoholic fermentation, the wine was transferred into stainless-steel tanks of 5 L each and the following five cases were assessed: 1. wine without malolactic fermentation (MLF), in this case 8 g/hL sodium metabilsufite was added to the wine in order to stop MLF (control condition-C); 2. wine with spontaneously driven MLF (S); 3. MLF driven by the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CH16 (CH16); 4. MLF driven by the O. oeni strain Viniflora® Oenos (Oenos); 5. MLF driven by the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe (Cine). Each O. oeni strain was inoculated at approximately 4.5 log CFU/mL. Each case was studied in duplicate from each AF tank, therefore MLF was assessed in quadruplicate. After the end of MLF (malic acid below 0.1 g/L), 8 g/hL sodium metabilsufite was added and the wines were then kept at 10 °C for one week and decanted into glass bottles for further chemical and sensory analyses.
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
Yeast and lactic acid bacteria populations were monitored during alcoholic and malolactic fermentation, respectively, on a daily basis. Samples (10 mL) were thoroughly mixed with 90 mL sterile saline and serially decimally diluted in the same diluent. Total yeast count was obtained after plating serial dilutions on Rose Bengal Chloramphenicol agar (RBC) (LAB M, Lancashire, UK) and incubated at 25 °C for 5 days. The population of lactic acid bacteria was enumerated after pour-plating serial dilutions in MRS agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK), supplemented with 0.1 g/L cycloheximide and incubated for up to 20 days at 28 °C, under anaerobic conditions.
Verification of the yeast and LAB identity was performed by (GTG)5 fingerprinting. More specifically, all colonies enumerated in the final dilutions of RBC and MRS agar during days 3 and 15, of both AF and MLF, were purified by successive subculturing on the same media. Pure isolates were inoculated in BH broth (LAB M) and MRS broth (Oxoid) and incubated at 25 °C for 5 days and 28 °C for up to 20 days, for yeasts and LAB, respectively. For the extraction of DNA, (GTG)5 fingerprinting, gel scanning and analysis took place according to Hadjilouka et al. [8]. The commercial strains used for inoculation were also subjected to the same analysis. Two isolates were considered as identical when the respective genotypic profiles were identical.
2.4. Chemical Analyses
2.4.1. Monitoring of AF and MLF
AF and MLF were monitored on a daily basis, the former through quantification of the reducing sugars using the 3,5-dinitrosalicyclic acid (DNS) method [9] and the latter through detection of malic acid by thin layer chromatography, according to Iland et al. [10], while the mid-fermentation was monitored by using enzymatic kits adapted for a Y15 Biosystems auto-analyzer (Barcelona, Spain).
2.4.2. Standard Enological Parameters
At the end of AF and MLF, the pH value, total and volatile acidity and chromatic characteristics were assessed according to the official method of the International Organization of Vine and Wine (OIV) [11].
2.4.3. Colorimetric Analysis
Color intensity was determined directly on wine samples placed in a cuvette with a path length of 1 mm using a UV/VIS spectrophotometer (Jasco Corp., Tokyo, Japan) according to OIV [11]. The color intensity for both the rosé and white wines was expressed as the absorbance at 420 nm.
2.4.4. Identification and Quantification of Volatile Compounds
The solid-phase microextraction method (SPME) coupled with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used for identification and quantification of volatile compounds [12]. In brief, headspace SPME sampling was performed at 40 °C for 30 min using 1-octanol as the internal standard and a DVB/CAR/PDMS, 2 cm SPME fiber (Sigma Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany). Volatile compound separation was performed in a DB-WAX capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 µm film thickness, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) using helium as the carrier gas (constant linear velocity 36 cm/s). The oven temperature was initially set at 40 °C for 5 min. It was then increased by 5 °C/min to 180 °C and then further by 30 °C/min up to 240 °C, at which it remained for 5 min. Source and interface temperatures were set at 200 °C and 240 °C, respectively. Analysis was performed using an Agilent 7890A GC, equipped with an Agilent 5873C MS detector.
2.4.5. Identification and Quantification of Organic Acids, Ethanol and Glycerol
High performance liquid chromatography was used for the detection and quantification of organic acids, glycerol and ethanol [13]. In brief, separation of the compounds was performed using the Aminex HPX-87H column (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) on the Waters Association 600E apparatus equipped with an RI detector (Waters 410, Midland, ON, Canada). Analysis was performed isocratically at 65 °C with H2SO4 as the mobile phase and a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min.
2.5. Sensory Analysis
The sensory analysis of all the wine samples (50 mL/glass) was performed at a controlled room temperature, in individual booths, according to the International Organization for Standardization, standard ISO 13299:2016. The panel consisted of 14 panelists that were trained according to Nanou et al. [14]. Each sample was presented twice during each session and the panel was asked to rate the intensity of four odor descriptors (vanilla, butter, citrus, rosé) and of three mouth descriptors (acidity, balance, body) on a 10 cm scale printed on paper. Sample presentation was randomized among the panelists.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using Statistica V.7 (Statsoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). The differences between the chemical parameters and sensorial descriptors were assessed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) procedure (p < 0.05).
3. Results
Alcoholic fermentation, of both the white and rosé wines, was completed within 15 days. Then, malolactic fermentation was effectively driven by the starter culture that was added in each experimental case. Degradation of malic acid started 48 h after inoculation with the O. oeni strains and could be considered as completed (malic acid < 0.1 g/L) after 15 days. On the contrary, during spontaneously driven MLF, malic acid degradation started after 5 days and complete degradation was not achieved, even upon prolongation of the MLF duration to 19 days.
3.1. Microbiological Characteristics
During AF, the population of the yeast strain increased, from the initial 6.33 and 6.45 log CFU/mL to 7.62 and 7.68 log CFU/mL, during the first 2 days of white and rosé wine fermentations, respectively. Then, it remained without a statistically significant change until the 10th day of AF. Then, in both cases, a slight decrease in the population was evident. Final populations of 6.87 and 6.79 log CFU/mL were reached at the end of AF, for the white and rosé wine fermentation, respectively (Figure S1).
During MLF, all three strains employed presented with nearly identical growth kinetics in both white and rosé wine fermentations. More specifically, the population of all strains increased, from an initial value in the range 4.27–4.58 log CFU/mL to a value in the range 7.43–7.62 log CFU/mL during the first 2 days of MLF and remained without a statistically significant change until the end of MLF (Figure S2).
During AF and MLF the uniformity of the enumerated colonies was evident. The identity of the yeast and LAB isolates was verified by (GTG)5 fingerprinting. A total of 55 yeast and 180 LAB isolates were subjected to the analysis, producing identical genotypic profiles.
3.2. Chemical Characteristics
The standard enological parameters of the white and rosé wines produced are presented in Table 1. Upon completion of alcoholic fermentation, substantial differences were observed between the produced white and rosé wines. More specifically, apart from the chromatic characteristics, the white wine was characterized by a lower pH value with less ethanol, residual sugars and volatile acidity but a higher total acidity. Malolactic fermentation also resulted in significant changes. More specifically, the decrease in total acidity and the increase in volatile acidity and pH value were evident in all cases. Increase of the pH value and reduction of total acidity were less pronounced in spontaneously driven MLF. Increase of volatile acidity seemed to be strain dependent; the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe produced the lower amount of volatile acidity, which was normal as this strain does not metabolize citric acid. As far as color intensity was concerned, MLF resulted in a statistically significant increase in the rosé wine, which was most evident in the spontaneously driven MLF and with the use of starter culture; the highest increase in color intensity was observed when the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe was used as a starter culture. On the contrary, in the white wines, an increase in color intensity was observed only when MLF was driven by O. oeni strain Viniflora® CH16.

Table 1.
Standard enological parameters at the end of alcoholic and malolactic fermentations.
In Table 2, the volatile and non-volatile compounds quantified in the rosé and white wines after AF and MLF, are presented. Upon completion of AF, the concentration of malic acid, citric acid, ethyl butyrate, ethyl caproate, ethyl laurate, isoamyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol was higher in the rosé wine, whereas the concentration of glycerol and lactic acid was higher in the white wine. MLF was characterized by a reduction in malic acid and an increase in lactic acid concentration in both wines; after MLF a higher lactic acid concentration was observed in the rosé wine compared to the white wine.

Table 2.
Volatile and non-volatile compounds present in the white and rosé wines at the end of AF and MLF.
In the case of the rosé wine, MLF also resulted in a decrease in citric acid, ethyl butyrate, ethyl caproate, isoamyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol concentration, either MLF was conducted spontaneously or with the addition of a starter culture. On the contrary, the fate of glycerol, ethyl butyrate, ethyl-2-methyl butyrate, ethyl laurate and phenethyl alcohol seemed to be affected not only by the addition of a starter culture but by the specific strain as well. More specifically, an increase in the concentration of ethyl butyrate and phenethyl alcohol was observed when MLF took place spontaneously or with the addition of the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe. Use of the latter strain also resulted in an increase in ethyl-2-methyl butyrate concentration. Use of the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CH16 resulted in an increase in ethyl-2-methyl butyrate and a decrease in ethyl laurate concentration.
When MLF was conducted by the O. oeni strain Viniflora® Oenos, an increase in glycerol and a decrease in ethyl laurate concentration was observed.
In the case of the white wine, MLF resulted in a reduction in ethyl caproate concentration and had no effect on the concentration of ethyl butyrate, ethyl-2-methyl butyrate, ethyl decanoate and isoamyl acetate. The fate of the rest of the volatile and non-volatile compounds seemed to depend on the strain conducting the MLF. More specifically, an increase in the concentration of ethyl isobutyrate, isoamyl alcohol, phenethyl alcohol and linalool was noticed when MLF was conducted by the O. oeni strains Viniflora® CiNe and Viniflora® CH16. Use of the latter strain also resulted in an increase in ethyl laurate and a decrease in the citric acid and glycerol concentrations. Use of the O. oeni strain Viniflora® Oenos also resulted in a decrease in glycerol and citric acid concentrations and an increase in the ethyl isobutyrate concentration. A reduction in citric acid concentration was also noted when MLF took place spontaneously.
The 14 volatile and non-volatile compounds with enological interest, which were quantified in all fermentation cases assessed, were further analyzed by PCA to enhance the visualization of the diversity of the produced wines through different inoculation schemes (Figure 1). The PCA plot of the first two components explained 66.2% of the wine variation; variations with a component 1 rating accounted for 42.8% of the total and variations with a component 2 rating accounted for 23.4% of the total. PCA analysis clearly distinguished the wine in which no MLF took place (C) on the positive right side of the map, connecting to the malic, citric acid, isoamyl acetate and isoamyl alcohol as well as some medium chain fatty acids. The strains Viniflora® CH16, Viniflora® Oenos and Viniflora® CiNe were associated with lactic acid, ethyl-2-methyl butyrate, phenethyl alcohol and ethyl isobutyrate. The rosé wines were loaded on the upper part of component 2, while the white ones were on the lower part.
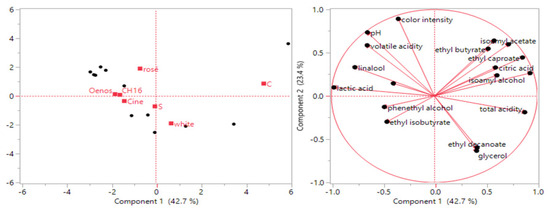
Figure 1.
Principal component analysis of 14 metabolites of Moschofilero rosé and white wines fermented under different malolactic fermentation schemes. The O. oeni strains used to drive the malolactic fermentation were Viniflora® CH16 (CH16), Viniflora® Oenos (Oenos) and Viniflora® CiNe (Cine). Spontaneous fermentation is denoted by (S) and wines in which no MLF took place are denoted by (C).
3.3. Sensory Analysis
In Table 3, the sensory analysis after AF and MLF of the produced rosé and white wines, is exhibited. In general, MLF improved the rating of vanilla and butter descriptors and reduced acidity perception. In addition, balance was also improved in the white wine. The rose petal descriptor received a higher rating when the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CH16 was used and the citrus descriptor received a lower rating when the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe was employed. In addition, the sensation of body was improved when using malolactic starters and especially when using Viniflora® CH16. In the rosé wine, balance and body received higher ratings when MLF was driven by the O. oeni strain Viniflora® CiNe in the first case and O. oeni strains Viniflora® CiNe and Viniflora® CH16 in the second case.

Table 3.
Sensory analysis of the white and rosé wines.
The effect of both wine style and bacterial strain on the sensory profile of Moschofilero wines is illustrated in Figure 2. Malolactic fermentation had a significant effect on both acidity and butter flavor. More precisely, the acidity of the control condition (i.e., wine without MLF) was significantly higher (p < 0.001) than the acidity after MLF took place, independent of the bacterial strain used. The opposite effect was observed for the buttery notes, which were much higher after malolactic fermentation. The interaction effect of both wine style and malolactic fermentation mode (p < 0.05) took place for the balance and body sensory descriptors.

Figure 2.
Interaction plot of the means of the sensory descriptors (acidity, balance, body, butter, citrus, rose) taken versus the malolactic fermentation scheme for Moschofilero rosé and white wines. The O. oeni strains used to realize the malolactic fermentation were Viniflora® CH16 (CH16), Viniflora® Oenos (Oenos) and Viniflora® CiNe (Cine). Spontaneous fermentation is denoted by (S) and wines in which no MLF took place are denoted by (C). Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean values.
4. Discussion
MLF is more commonly performed in red wines than in white ones, due to the reduction in the tart taste of malic acid resulting in a more palatable wine with greater ageing potential [15]. From a technological point of view, MLF is much more than the decarboxylation reaction, as many enzymatic activities of LAB have been reported in the wine environment with both beneficial and detrimental effects [4,5,6,16,17,18]. Thus, the proper use of LAB, which could lead to a desirable result, is really challenging for the winemaker. In our present work, the effect of MLF with different O. oeni strains, for the production of two different wine styles, white and rosé, from the same Greek grape variety, Moschofilero, was studied for the first time.
A series of starter cultures was developed for the induction of MLF, some of which, including the ones employed in the present study, were presented by Lerm et al. [3]. More specifically, the suitability of the O. oeni strains Viniflora® CiNe, Oenos and CH16 for MLF in rosé wines and the two formers also in white wines, was presented. In the present study, the effectiveness of these strains to carry out MLF in both rosé and white wines made using the Moschofilero cultivar, was exhibited. On the other hand, the autochthonous bacteria could sometimes lead to slow or incomplete fermentation, as observed in our case [4,5]. As expected, the wines that underwent MLF had higher pH values and lower acidity compared to the control condition.
The temporal relationship between AF and MLF is a very important practical issue, and, therefore, has been extensively assessed. More specifically, the effect that the yeast-LAB metabolic co-existence or succession may have on the sensorial properties of the final product has been in the epicenter of intensive research, leading to the conclusion that the outcome depends upon factors such as the capacity and compatibility of the microbial strains utilized, the winery, the vintage, the cultivar and the fermentation temperature [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. In the present study, a sequential approach was employed with AF preceding MLF, which is closer to the traditional practice, and no issues regarding the compatibility between the yeast and the LAB strains employed was observed.
Regarding the chromatic characteristics of the wines that underwent MLF, the loss of color seemed to be frequently reported and attributed to LAB metabolic activities and, more specifically, to acetaldehyde metabolism [29] as well as absorption and enzymatic degradation of anthocyanin glucosides [30]. However, there are studies that report a strain-dependent increase in color intensity, such as the ones by Delaquis et al. [31] and Olguin et al. [32] and the present one. The latter studies concur with the conclusion reached by Olguin et al. [33] that the effect that MLF may have on wine color depends upon the strain that drives the MLF and the grape variety, as well as the winemaking practices. Interestingly, a study conducted by El Khoury et al. [34], which was based on O. oeni isolates from various wines, mainly from France, showed that two genetic groups were created based on the wine color, red or white, which possibly suggested an adapting evolution due to the type of wine.
The malolactic fermentation of rosé and white Moschofilero wines resulted in the enhancement of vanilla and buttery notes in all cases and the improvement of balance in the white wine. Improvement of buttery and vanilla notes, among others, were reported by Bartowsky et al. [35] as the descriptors that distinguished wines that had undergone MLF from the ones that had not. In the case of Chardonnay wines, this was also reported to occur after the MLF of Chardonnay wine [36]. Citric acid metabolism has been implicated in buttery notes enhancement through the production of diacetyl via the activation of the citrate pathway [37]. The level of production plays a crucial role as the detection threshold is low and highly dependent upon the bacterial strain and the composition of the fermentation niche. According to our results, citric acid consumption led to wines with significantly increased buttery notes compared to the control condition. Even though the citric acid degradation capacity was significantly different among the tested conditions, the relative effect on buttery wine notes was only slightly different between the bacterial strains used. It should be taken into consideration that some bacterial strains are also able to reduce diacetyl to the corresponding alcohol, 2,3-butandiol, which is a compound with no aromatic impact [38].
The ester groups have a great impact on the fruity sensory profile of wine, and they are formed during alcoholic and malolactic fermentation [39]. MLF fermentation can lead to either an increased or a decreased content of esters, influencing the aromatic composition of the wine [18,40]. LAB have been reported to both synthesize and hydrolyze esters through their esterase activities [41]. In our present study, we showed that the impact of MLF fermentation on ethyl esters was highly strain-dependent and less influenced by the wine type, which was in accordance with the literature [41,42]. However, [43] reported that only the branched hydroxylated esters, especially the R form, were strongly influenced by the bacterial strain.
5. Conclusions
The suitability of the starter cultures employed to drive alcoholic and malolactic fermentation in the must of the Moschofilero cultivar was exhibited. Although the effect of MLF on the chemical composition and sensorial analysis of the wines was strain-dependent, in all cases an enhancement of the buttery and vanilla notes was observed. Further research, including the evaluation of additional strains being taking into consideration in the inoculation strategy, is necessary in order to optimize the sensory outcome.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12115722/s1, Figure S1: Yeast population (in log CFU/mL) during alcoholic fermentation of Moschofilero must for white (yellow) and rosé (red) winemaking; Figure S2: LAB population (in log CFU/mL) during spontaneous MLF (yellow), or after inoculation with Oenococcus oeni strains Viniflora® CH16 (blue), Viniflora® Oenos (green) and Viniflora® CiNe (red) during white (A) and rosé (B) winemaking; Figure S3: Reducing sugars consumption during alcoholic fermentation of Moschofilero must for white (yellow) and rosé (red) winemaking by Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain UCLM S325.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K. and M.D.; methodology, Y.K., M.D. and V.T.; formal analysis, Y.K., M.D., N.P. and V.T.; data curation, Y.K., M.D., N.P. and V.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D., S.P. and Y.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.K., M.D., S.P., N.P. and V.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Marilena Panagopoulou, Eustathios Sideris and Fotios Fragos for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Semon, M.J.; Edwards, C.G.; Forsyth, D.; Dinn, C. Inducing malolactic fermentation in Chardonnay musts and wines using different strains of Oenococcus oeni. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2001, 7, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Mendes-Faia, A. The role of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria on the metabolism of organic acids during winemaking. Foods 2020, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerm, E.; Engelbrecht, L.; du Toit, M. Malolactic fermentation: The ABC’s of MLF. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2010, 31, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virdis, C.; Sumby, K.; Bartowsky, E.; Jiranek, V. Lactic acid bacteria in wine: Technological advances and evaluation of their functional role. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 612118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonvaud-Funel, A. Lactic acid bacteria in the quality improvement and depreciation of wine. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999, 76, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulou, M.; Raffenne, J.; Claisse, O.; Miot-Sertier, C.; Iturmendi, N.; Moine, V.; Coulon, J.; Dols-Lafargue, M. Oenococcus oeni exopolysaccharide biosynthesis, a tool to improve malolactic starter performance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumby, K.M.; Bartle, L.; Grbin, P.R.; Jiranek, V. Measures to improve wine malolactic fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2033–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjilouka, A.; Andritsos, N.D.; Paramithiotis, S.; Mataragas, M.; Drosinos, E.H. Listeria monocytogenes serotype prevalence and biodiversity in diverse food products. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.-L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iland, P.; Ewart, A.; Sitters, J.; Markides, A.; Bruer, N. Techniques for Chemical Analysis and Quality Monitoring During Winemaking; Patrick Iland Wine Promotions: Campbelltown, NSW, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- OIV (International Organisation of Vine and Wine). Compendium of International Methods of Wine and Must Analysis; OIV: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dimopoulou, M.; Troianou, V.; Toumpeki, C.; Gosselin, Y.; Dirignac, E.; Kotseridis, Y. Effect of strains from different Saccharomyces species used in different inoculation schemes on chemical composition and sensory characteristics of Sauvignon blanc wine. OENO One 2020, 54, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Gerbi, V.; Redoglia, M. A rapid HPLC method for separation and determination of major organic acids in grape musts and wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1987, 38, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nanou, E.; Mavridou, E.; Milieros, F.S.; Ppadopoulos, G.; Tempere, S.; Kotseridis, Y. Odor characterization of white wines produced from indigenous Greek grape varieties using the frequency of attribute citation method with trained assessors. Foods 2020, 9, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Martín-Alvarez, P.J. Evolution of red wine anthocyanins during malolactic fermentation, postfermentative treatments and ageing with lees. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versari, A.; Parpinello, G.P.; Cattaneo, M. Leuconostoc oenos and malolactic fermentation in wine: A review. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 23, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q. A review: Malolactic fermentation in wine beyond deacidification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, M.S.; Zapparoli, G.; Logrieco, A.; Bartowsky, E.J. Linking wine lactic acid bacteria diversity with wine aroma and flavour. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 243, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussier, D.; Morneau, A.D.; de Orduna, R.M. Effect of simultaneous inoculation with yeast and bacteria on fermentation kinetics and key wine parameters of cool-climate Chardonnay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massera, A.; Soria, A.; Catania, C.; Krieger, S.; Combina, M. Simultaneous inoculation of Malbec (Vitis vinifera) musts with yeast and bacteria: Effects on fermentation performance, sensory and sanitary attributes of wines. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 47, 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Antalick, G.; Perello, M.C.; de Revel, G. Co-inoculation with yeast and LAB under winery conditions: Modification of the aromatic profile of Merlot wines. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 34, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izquierdo-Cañas, P.M.; García Romero, E.; Perez-Martín, F.; Prieto, S.; Palop Herreros, M.L. Sequential inoculation versus co-inoculation in Cabernet Franc wine fermentation. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2014, 21, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Cañas, P.M.; Ríos-Carrasco, M.; García-Romero, E.; Mena-Morales, A.; Heras-Manso, J.M.; Cordero-Bueso, G. Co-existence of inoculated yeast and lactic acid bacteria and their impact on the aroma profile and sensory traits of Tempranillo red wine. Fermentation 2020, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Versari, A.; Patrizi, C.; Parpinello, G.P.; Mattioli, A.U.; Pasini, L.; Meglioli, M.; Longhini, G. Effect of co-inoculation with yeast and bacteria on chemical and sensory characteristics of commercial Cabernet Franc red wine from Switzerland. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristezza, M.; di Feo, L.; Tufariello, M.; Grieco, F.; Capozzi, V.; Spano, G.; Mita, G.; Grieco, F. Simultaneous inoculation of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria: Effects on fermentation dynamics and chemical composition of Negroamaro wine. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereni, A.; Phan, Q.; Osborne, J.; Tomasino, E. Impact of the timing and temperature of malolactic fermentation on the aroma composition and mouthfeel properties of Chardonnay wine. Foods 2020, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavsa, T.; Jagatic Korenika, A.-M.; Lukic, I.; Bubola, M.; Jeromel, A. Influence of different malolactic fermentation techniques on changes in chemical properties and volatile compounds of cv. Teran red wine (Vitis vinifera L.). J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2021, 22, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhao, H.; Kang, X.; Ge, X.; Zheng, M.; Hu, Z.; Tao, Y. Fruity aroma modifications in Merlot wines during simultaneous alcoholic and malolactic fermentations through mixed culture of S. cerevisiae, P. fermentans, and L. brevis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, T.R.; Osborne, J.P. Loss of Pinot noir wine color and polymeric pigment after malolactic fermentation and potential causes. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2015, 66, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.; Aiyappaa, A.A.K.; Waterhouse, A.L. Adsorption and biotransformation of anthocyanin glucosides and quercetin glycosides by Oenococcus oeni and Lactobacillus plantarum in model wine solution. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2019, 100, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaquis, P.; Cliff, M.; King, M.; Girard, B.; Hall, J.; Reynolds, A. Effect of two commercial malolactic cultures on the chemical and sensory properties of Chancellor wines vinified with different yeasts and fermentation temperatures. Am. J. Enol Vitic. 2000, 51, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Olguin, N.T.; Delfederico, L.; Semorile, L. Colour evaluation of Pinot noir and Merlot wines after malolactic fermentation carried out by Oenococcus oeni and Lactobacillus plantarum Patagonian native strains. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2020, 41, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin, N.T.; Delfederico, L.; Semorile, L. Relationship between lactic acid bacteria, malolactic fermentation and wine colour. IVES Tech. Rev. Vine Wine 2021, 20, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, M.; Campbell-Sills, H.; Salin, F.; Guichoux, E.; Claisse, O.; Lucas, P.M. Biogeography of Oenococcus oeni reveals distinctive but nonspecific populations in wine-producing regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02322-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartowsky, E.J.; Costello, P.; Henschke, P.A. Management of malolactic fermentation—Wine flavour manipulation. Aust. N. Z. Grapegrow. Winemak. 2002, 461, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvageot, F.; Vivier, P. Effects of malolactic fermentation on sensory properties of four burgundy wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1997, 48, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Olguin, N.; Bordons, A.; Reguant, C. Influence of ethanol and pH on the gene expression of the citrate pathway in Oenococcus oeni. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, B.; Henick-Kling, T. Formation and degradation of diacetyl in wine during alcoholic fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain EC 1118 and malolactic fermentation with Leuconostoc oenos strain MCW. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1995, 46, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse, A.L.; Sacks, G.L.; Jeffery, D.W. Understanding Wine Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ugliano, M.; Moio, L. Changes in the concentration of yeast-derived volatile compounds of red wine during malolactic fermentation with four commercial starter cultures of Oenococcus oeni. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 10134–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumby, K.M.; Jiranek, V.; Grbin, P.R. Ester synthesis and hydrolysis in an aqueous environment, and strain specific changes during malolactic fermentation in wine with Oenococcus oeni. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammacurta, M.; Lytra, G.; Marchal, A.; Marchand, S.; Christophe Barbe, J.; Moine, V.; de Revel, G. Influence of lactic acid bacteria strains on ester concentrations in red wines: Specific impact on branched hydroxylated compounds. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytra, G.; Tempere, S.; de Revel, G.; Barbe, J.C. Distribution and organoleptic impact of ethyl 2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate enantiomers in wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).