Abstract
Decellularized skeletal muscle (dSkM) constructs have received much attention in recent years due to the versatility of their applications in vitro. In search of adequate in vitro models of the skeletal muscle tissue, the dSkM offers great advantages in terms of the preservation of native-tissue complexity, including three-dimensional organization, the presence of residual signaling molecules within the construct, and their myogenic and neurotrophic abilities. Here, we attempted to develop a 3D model of neuromuscular tissue. To do so, we repopulated rat dSkM with human primary myogenic cells along with murine fibroblasts and we coupled them with organotypic rat spinal cord samples. Such culture conditions not only maintained multiple cell type viability in a long-term experimental setup, but also resulted in functionally active construct capable of contraction. In addition, we have developed a customized culture system which enabled easy access, imaging, and analysis of in vitro engineered co-cultures. This work demonstrates the ability of dSkM to support the development of a contractile 3D in vitro model of neuromuscular tissue fit for long-term experimental evaluations.
1. Introduction
In recent years, it has become evident that decellularized tissues represent a valuable tool in the field of tissue engineering. Along with their application in regenerative medicine strategies, decellularized scaffolds provide a 3D native-like environment for three-dimensional (3D) in vitro modeling of tissues or organs [1,2,3].
The decellularized tissues are obtained via chemical, enzymatic, or physical methods to yield an acellular scaffold which preserves the complex 3D architectural organization, biochemical features, and biomechanical properties of the native tissue, including the extracellular matrix (ECM) [4]. The applicability of decellularized tissues and organs in translational studies is enhanced by the low immunogenicity of such scaffolds, enabling the use of xenograft materials, and by their structural and molecular properties that allow myogenesis and promote reinnervation and vascularization within the host [4,5,6]. An important aspect, specifically for skeletal muscle tissue engineering, is the ability to produce a sizable graft. This, in addition to recapitulation of structural and topographical complexity of the skeletal muscle tissue, had been a challenge, especially considering the necessity of such grafts for conditions associated with volumetric muscle loss [1]. Due to their porosity and functionalization capacity, decellularized tissues can also be used as vehicles for drug and small molecule delivery for therapeutic purposes [7,8,9]. Recent advances in three-dimensional bioprinting technology enabled better control of the precise organization of larger in vitro hydrogel-based constructs, including hydrogels derived from decellularized tissues [10]. However, compared to dSkM, hydrogels alone offer suboptimal bioactivity and limited control of the overall 3D architecture that cannot reach the native-tissue complexity [1]. Besides their use in regenerative medicine, dSkM have also been utilized to reinstate the native tissue environment in vitro through tissue modeling. It is known that decellularized tissues act as a reservoir of signaling and attachment molecules that guide cell behavior native to the tissue of the decellularized construct [11]. Moreover, dSkM tissue has unique trophic and topographic properties which enhance repopulation, alignment and differentiation of myogenic cells [1]. These advantages pave the way to various applications of dSkM in vitro, e.g., investigation of cell viability and infiltration upon long-term culture [12,13], evaluation of tissue ECM and drug interaction mimicking intramuscular injections [14], or the use of dSkM-based hydrogel for in vitro and in vivo studies [15,16]. Our recent work has demonstrated that the dSkM retains a multitude of structural and other proteins that can enhance the repopulation of seeded myogenic cells [17]. In addition, we have demonstrated that dSkM has neurotrophic properties guiding the directionality of axonal projections when cocultured with organotypic spinal cord culture (oSpC) [17]. It is well known that, during development, regeneration, and homeostasis, skeletal muscle is highly dependent on the presence of neuronal input [18,19]. Moreover, innervated 3D skeletal muscle constructs are crucial for disease modeling, drug screening, and molecular biology studies of neuromuscular healthy tissue and disorders [20,21]. Based on our previous observations indicating the intrinsic ability of dSkM to attract neural axons [17], in the present study we wanted to investigate the possibility to develop an in vitro model of neuromuscular tissue using dSkM. Until now, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no previous report of neural and muscular co-culture within 3D dSkM scaffolds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Sprague Dawley rats (250–350 g) were used for the preparation of dSkM with all the procedures carried out in accordance with Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. To acquire spinal cord cultures, E14 fetuses were obtained from pregnant Sprague Dawley rats (Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA, USA). The procedures performed on animals were in accordance with Italian National laws and policies (D.L. n. 26, 14 March 2014), following the guidelines established by the European Community Council Directive (2010/63/EU), and with the approval of the Italian Ministry of Health (authorization number: D2784.N.I6Q).
2.2. Tissue Decellularization
To perform decellularization, rat leg skeletal muscle was obtained by dissecting the limb at the pelvic region and following the decellularization procedure as previously described [22]. Briefly, the decellularization was initiated by introducing a 24 gauge cannula into the abdominal iliac artery for limb perfusion with 0.25% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, Sigma) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min for 72 h followed by a deionized water wash step for 48 h. Subsequently, the decellularized muscles of interest were dissected, irradiated (137Cesium irradiator; IBL 437C), and maintained in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, Gibco) with 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin (P/S, Gibco) at 4 °C.
2.3. Cell Culture
Human Skeletal Myoblasts (GIBCO, A12555) were cultured in a cell incubator at 37 °C using a proliferating medium composed of DMEM/F12 (Thermofisher, 11320-033) supplemented with 20% Fetal bovine serum (FBS—Thermofisher, 10270-106), 1% P/S, 10 ng/µL human fibroblast growth factor basic (bFGF—Invitrogen, PHG0264) and 10 µg/µL human Insulin (SIGMA I9278). Cells were split with 0.025% Trypsin–EDTA (Thermofisher, 25200-056) when they reached 70% confluency at 1:5 ratio until use (maximum at passage number 6 to preserve myogenicity). Primary murine muscular fibroblasts (mFBs) were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6J mice as previously described [23] and maintained in culture in DMEM (Thermofisher 41965-039) supplemented with 20% FBS and 1% P/S. Cells were split with 0.025% Trypsin–EDTA at confluency
2.4. Repopulation of the Scaffold and Co-Culture with oSpC
For repopulation experiments, the scaffolds were segmented into sections of ~1 × 2 × 4 mm format. A mixture of 7 × 105 human skeletal myoblasts and 3 × 105 mFBs was injected into the scaffold section, put on a glass coverslip using insulin syringes, and kept in culture for 3 weeks in proliferating medium. Organotypic spinal cord 3D culture was prepared as previously described [17]. For co-culture experiments, isolated oSpCs were dissected into three segments of ~1 × 1 × 2 mm format of apical, central, or caudal identity. Next, each oSpC segment was added on top of individual scaffold section and covered by a 10 μL droplet of Matrigel (Corning 354230). Co-culture was maintained in Neurobasal medium (Gibco 21 103 049) supplemented with B-27 supplement (Gibco 17 504 044) 1X, 0.5 mM GlutaMAX Supplement (Gibco 35 050 038), 2% Horse serum (Gibco 16 050 122), 25 μM L-Glutamic acid (Sigma G8415), 25 μM 2-Mercaptoethanol (Gibco 31 350 010), Gentamicin/Amphotericin (Gibco R01510), 10 ng/mL glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor (Peprotech 450-10), and 10 ng/mL glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF, Peprotech 450-10). Samples were maintained in culture for 21 days and half the proliferation medium was changed every 3 days.
2.5. Custom-Made Culture Chamber
To avoid mechanical influence of the glass coverslip on the co-culture, we designed a custom-made bioreactor in order to maintain our culture in suspension. We prepared a rectangular culture chamber (3 × 2 × 1 cm, 0.5 cm thick) using Sylgard 184 polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) in a 10:1 base:curing agent ratio and attached them to a dry, clean glass slide using an oxygen plasma cleaner. Inside the chamber, we also attached two PDMS pillars to sustain the culture. Scaffold was fixed to the pillars using suture thread and culture chamber filled with co-culture medium. Samples were maintained in culture for 3 weeks. Half medium was changed every 3 days.
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
The viability of cell culture was evaluated using calcein, AM (LifeTechnologies, Waltham, MA, USA, C3099). Briefly, samples were first subjected to a PBS wash twice and then incubated with 3 μM calcein, AM (LifeTechnologies, Waltham, MA, USA C3099) for 30 min in serum-free medium. Following calcein staining, samples were again washed twice in PBS. The analysis of samples was performed with either a fluorescence stereomicroscope Leica MZ16F and/or two-photon microscope (Thorlabs, Newton, NJ, USA or Scientifica, TN22 1QQ, UK).
2.7. Immunofluorescence Characterization
To prepare samples for immunofluorescence characterization, they were first fixed in 3% PFA for 45 min and washed twice in PBS. Further steps were performed on either whole-mount samples or on longitudinal and cross-sections of 20 μm thickness. Samples were blocked for 2 h at room temperature in solution composed of 0.5% Triton (Sigma, St. Louis, MI, USA) and 1% BSA (Gibco) in PBS. For incubation with primary antibody, samples were kept at 4 °C for 24 h (whole-mount) or overnight (sections). Following the PBS wash, samples were incubated with secondary antibodies solution for 2 h at room temperature. For sample analysis, the following primary and secondary antibodies were used: rat anti-α-Laminin for the extracellular matrix protein laminin (Sigma, L0663; 1:100); rabbit anti-βIII-Tubulin for the neural microtubule protein βIII-Tubulin (Tuj1—SYSY, 302302; 1:500); rabbit anti-MyoG for the skeletal muscle-specific transcription factor myogenin (Santa Cruz, sc-576; 1:25); mouse anti-Desmin for the muscle-specific intermediate filament protein desmin (Dako, M0760; 1:250); donkey anti-rabbit 488 (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA, A21206; 1:200); donkey anti-mouse 594 (ThermoFisher, A21203; 1:200); goat anti-rat Cy2 (Jackson, 112-225-167; 1:100); Phalloidin 647 (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA, A22287; 1:200). To counterstain the nuclei, 10 μg/mL Hoechst 33342 (ThermoFisher, H1399) was used.
2.8. Calcium Imaging
Samples were washed with PBS twice and incubated for 30 min with 5 µM Fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen F14201), 5 µL/mL Pluronic, and 12.5 µL/mL sulfin pyrazone in cell medium. Sulfin pyrazone is an organic anion-transport inhibitor that reduces leakage of the de-esterified indicator, while non-ionic detergent Pluronic assists in dispersion of the nonpolar AM ester in aqueous media. After incubation, samples were washed with PBS two times and analyzed with either a fluorescence microscope Olympus IX81 and/or two-photon microscope (Thorlabs, Newton, NJ, USA or Scientifica, TN22 1QQ UK). For glutamate stimulation studies, we added 50 µM Glutamate (Sigma G5889) during live imaging.
2.9. Image Acquisition and Analysis
The following microscopes were used to acquire imaging: epifluorescence Olympus BX60; fluorescence stereomicroscope Leica MZ16F with Canon EOS1000D camera; fluorescence microscope Olympus IX81; modular multiphoton microscope (Bergano-II, Thorlabs, Newton, NJ, USA); confocal Leica TCS SP5 microscope; confocal ZEISS LSM 800 microscope; wide-field motorized stage Leica DM6B. We used ImageJ software to adjust contrast and intensity, for 3D reconstruction and mean fluorescence intensity. For the calcium fluorescent ratio, Fluo-4 signals were measured in 3 independent experiments as relative changes of fluorescence emission intensity F/F0, where F0 is the pre-stimulus basal fluorescence intensity at time 0 and F is the fluorescence intensity at time t.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The analysis was performed by using GraphPad Prism 9 software. Plotted data were expressed as mean ± SEM. We determined statistical significance by unequal variance Student’s t test. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Decellularized Muscles Allow 3D Co-Culture of Human Myogenic Cells and oSpC Sections
With the aim to repopulate dSkM with human myogenic cells, we first proceeded with their characterization (Figure 1). Cell myogenic identity was confirmed in standard culture conditions by the presence of MyoD-positive cells and by the presence of multinucleated myotubes in both proliferating and differentiating culture conditions (Figure 1A). According to the evidence that fibroblasts are necessary to drive dSkM repopulation by myogenic cell in vitro [16], human myogenic cells were combined with murine fibroblasts in a defined ratio [16], seeded within the dSkM, and co-cultured for 21 days (Figure 1B). Fluorescence stereomicroscope imaging of calcein incorporation demonstrated the viability of the cells (Figure 1B, left panels). Further investigation performed by 2-photon calcein live imaging analysis confirmed the presence of living cells within the dSkM with elongated morphology (Figure 1B, right panel).
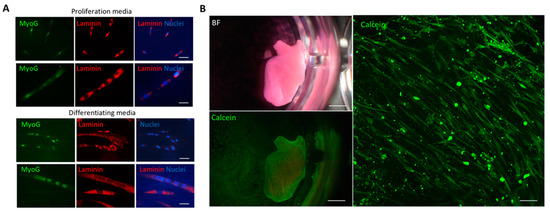
Figure 1.
Characterization of human myogenic cells and seeding into dSkM. (A) Representative images of immunofluorescence analysis performed for MyoG (green), Laminin (red), Nuclei (blue) in proliferating media (upper panel) or differentiating media (lower panel). Scale bars, 50 μm upper panels, 20 μm lower panels. (B) Representative bright field and calcein stereomicroscope (left panels), and 2-photon microscope (right panel) images of dSkM seeded with human myogenic cells and murine fibroblasts 21 days after seeding. Scale bars, 1 mm left panels, 200 μm right panel.
Based on our previous results and on the neurotrophic properties of dSkM [16,17], we generated the neuromuscular construct by co-seeding human myogenic cells and murine fibroblasts into the dSkM together with oSpC onto the scaffold (Figure 2A). Calcein live-imaging performed at the fluorescence stereomicroscope, confirmed the presence of viable cells after 21 days of co-culture (Figure 2B). We did not observe significant differences in biological and technical replicates of the developed co-cultured models in terms of cell viability, morphology, and scaffold repopulation at the end of the experiments. Interestingly, 2-photon imaging analysis revealed the presence of elongated cells resembling myotubes in strict proximity to cellular projections similar to neural axons (Figure 2C). Confirmation of the preservation of both neural and myogenic cells was provided by immunofluorescence analysis for the marker class III-beta tubulin (Tuj1) and desmin, respectively (Figure 2D). Moreover, these data also confirmed that neural extensions and myogenic cells were in close proximity to each other within the dSkM (Figure 2D). Based on these findings, we wanted to investigate whether such co-culture could have a basal physiological activity. To do so, 3D neuromuscular constructs were cultured for 21 days, treated with the Fluo-4 calcium dye, and subjected to live imaging analysis to eventually reveal calcium fluxes into the myogenic compartment. Despite the fact that monitoring Fluo-4 within the 3D neuromuscular construct was not possible due to thickness and autofluorescence of the construct, myotubes located to the margins between the spinal cord and the dSkM clearly showed physiological activity (Figure 2E and Supplementary Video S1) with quantifiable calcium spikes (Figure 2E, left panel).
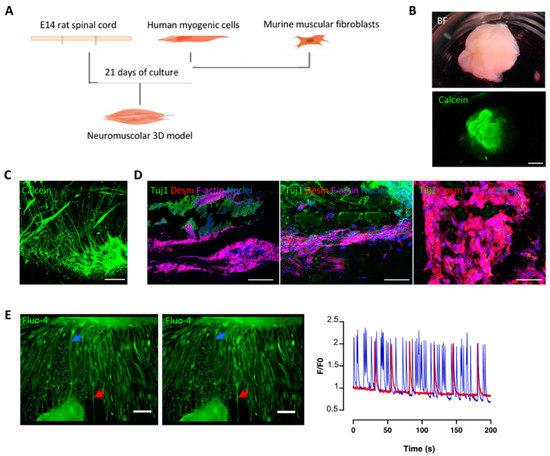
Figure 2.
Decellularized scaffolds support 3D muscular and neural co-culture. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental set-up. (B) Bright field (above) and calcein (below) stereomicroscope images of the dSkM repopulated with muscular and neuronal cells. Scale bar, 1 mm. (C) 2-photon microscope live imaging of calcein incorporation of the 3D neuromuscular construct. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Representative images of immunofluorescence analysis performed for βIII-Tubulin (Tuj1, green), Desmin (red) and F-actin (magenta). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 250 μm left panel, 50 μm middle panel and 20 μm right panel. (E) Left panel, representative Fluo-4 live imaging at two different time points. The arrows point at two myotubes (blue and red) that showed calcium waves, as quantified by the calcium fluorescent ratio (F/F0; blue and red, respectively). Scale bar, 300 μm.
3.2. Optimization and Characterization of 3D Neuromuscular Cultures
It is reported that mechanical stretching promotes cellular myogenic differentiation and myotube alignment, maturation and function of newly formed myofibers [18,19]. Based on that, and on our previous results [17], we developed a custom-made culture chamber in order to apply a linear constant stretching to the neuromuscular 3D construct (Figure 3A). Moreover, the chamber was designed to provide free access for imaging analysis. Therefore, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) was used to create the walls of the chamber located on the top of a glass coverslip (Figure 3B). Two PDMS pillars were also included within the chamber and used to tie the repopulated scaffolds via surgical stiches and to permit the constant stretching of the 3D culture system (Figure 3B). Since elongated stripes of dSkM were used as the scaffold in this experimental setup, we first monitored the ability of the oSpC to be firmly integrated into this new culture set-up. Then, human myogenic cells and muscular fibroblasts were seeded within the dSkM. The construct was stretched within the culture chamber and the oSpC was positioned onto the repopulated dSkM. Imaging analysis performed during the culture showed the progressive adhesion of the oSpC to the repopulated dSkM (Figure 3C). We then confirmed that our experimental setup allowed live 2-photon and second harmonic generation imaging analysis of living cells located deep within the dSkM (Figure 3D). Immunofluorescence analysis also indicated that myogenic (Desmin-positive) and neural (Tuj1-positive) cells were preserved in the developed culture set-up (Figure 3E). Importantly, contraction of the neuromuscular 3D model was observed in some areas of the construct and monitored by using 2-photon imaging analysis of calcein incorporating cells (Supplementary Video S2). To confirm the presence of MNs within our neuromuscular model, the 3D constructs were treated with Fluo-4 calcium dye, subjected to live imaging analysis, and stimulated with glutamate, the neurotransmitter of MN required for their depolarization, release of acetylcholine and induction of myofiber contraction [24]. Live imaging analysis performed with a 2-photon microscope of the 3D neuromuscular models located within the chamber revealed increased calcium flux after glutamate stimulation of cells located within the dSkM (Figure 3F).
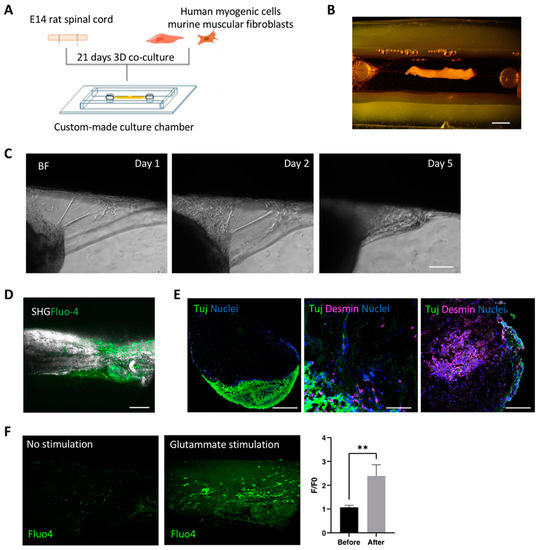
Figure 3.
Characterization of 3D neuromuscular construct cultured in custom-made PDMS chamber. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental set-up within the custom culture chamber. (B) Representative image of muscle scaffold allocated into the PDMS chamber. Scale bar, 1 mm. (C) Bright field high magnification images of organotypic spinal cord section 1, 2 and 5 days after seeding. Scale bar, 500 μm. (D) Representative 2-photon and second harmonic generation imaging of Fluo-4-positive (green) cells within dSkM ECM (white). Scale bar, 500 μm. (E) Representative images of immunofluorescence analysis for βIII-Tubulin (Tuj1, green) and nuclei (blue) of the 3D neuromuscular constructs. Scale bars, 500 μm, left and right panels; 200 μm, middle panel. (F) Left panel, Fluo4 two photon-mediated calcium imaging of 3D constructs before (left) and after (right) glutamate stimulation. Right panel, Scale bar, 500 μm. Right panel, quantification of calcium fluorescent ratio (F/F0) of images acquired before and after glutamate stimulation. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. of three independent replicates; **, p < 0.05.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
The development of neuromuscular in vitro models implies a recapitulation of the native-like structural and functional complexity of the interactions existing between the two tissues. The structural architecture relies on 3D organization of the construct and its functionality depends on the degree of maturation of the cellular components within the construct. The advantages related to the use of dSkM in reconstructing skeletal muscle tissue [4,5] and our own previous results from studying dSkM neurotrophic properties [17] drove our interest in the development of a 3D in vitro neuromuscular model based on a repopulated dSkM scaffold.
Our initial evaluation of repopulated dSkM confirmed the ability of the scaffold to support the migration and differentiation of myogenic cells. In addition, the scaffold enabled cell culture for up to 21 days and supported the co-culture of both the myogenic and neural compartments. Based on the evaluation of the physiological activity of our in vitro model and its imaging analysis, dSkM not only allowed the assisted juxtaposition of different cell types, but also nurtured the maturation of myogenic cells, resulting in the generation of calcium spikes.
Our optimized, custom-made chamber introduced yet another advantage to the development of our model. Specifically, the suspension of the construct on PDMS pillars allows for easer live imaging analysis of the 3D neuromuscular construct. Stretch has important implications for alignment, differentiation, and maturation of the myogenic cell populations in vivo and in vitro [18,19]. Indeed, during co-culture in chambers, we observed spontaneous contractions within the scaffold, indicating enhanced maturation of myogenic cells and possible communication with the neural counterpart. In the future, further analysis will be required to evaluate the presence of structurally and functionally competent neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and their state of maturation. Further design iterations will be focusing on integrating an adjustable tensioner, allowing to adjust the level of stretching applied to the constructs.
Overall, our findings provide evidence of the possibility to develop functional neuromuscular in vitro constructs using dSkM as a 3D scaffold.
We also acknowledge that our study has certain limitations. The major limitation would be the investigation of interactions of cell types derived from different species. While the most optimal representation of neuromuscular tissue would be a combination of human-only cell sources, we have previously proven in other engineered models that a xenogeneic in vitro system can replicate biological models with fidelity [25]. Current developments in differentiation methods have enabled the generation of human-based motor neuron cell cultures which could be utilized to build humanized in vitro models in the future. At the same time, the presence of supportive glial cells within the oSpC could play a role in neural axonal path guidance and sprouting, as well as in the establishment and stabilization of the NMJ, possibly enhancing the functional outcome of our in vitro model.
Supplementary Materials
Video S1: Calcium flux live imaging analysis of neuromuscular constructs, available online at: https://wetransfer.com/downloads/1258d6748efabf31820781551b97bfa920211013061459/25a4cb32e4c797f04dc155a04b18e9a420211013061520/d1cc3e; Video S2: Calcium live imaging analysis revealed spontaneous contraction of the neuromuscular constructs, available online at: https://wetransfer.com/downloads/2e4a56dc24b0fcb30a44f38d0573ab7120211013061904/9632a7dc148b02f2777e22470ca286ed20211013062003/7b9d89.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.U.; methodology, P.R., V.S., P.C., A.U., M.F.M.G. and S.P.; investigation, P.R. and V.S.; data curation, P.R., V.S., M.E., B.A. and F.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R., M.E., B.A., F.C. and A.U.; writing—review and editing, M.F.M.G., S.P., P.C., N.E. and P.D.C.; visualization, A.U.; supervision, A.U.; project administration, A.U.; funding acquisition, A.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by STARS Starting Grant 2017 of University of Padova (grant code LS3-19613) and IRP Consolidator Grant (grant code: 21/05 Irp) to AU, and AFM-Telethon Research Grant 2020 (grant code 23284) to N.E. P.D.C. is supported by National Institute for Health Research (NIHR-RP-2014-04-046).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All research at Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health is made possible by the NIHR Great Ormond Street Hospital Biomedical Research Centre. The views expressed are those of the author (s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. The procedures performed on animals were in accordance with Italian National laws and policies (D.L. n. 26, 14 March 2014), following the guidelines established by the European Community Council Directive (2010/63/EU), and with the approval of the Italian Ministry of Health (authorization number: D2784.N.I6Q).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting results are presented within the article and the supplementary materials. The raw data are available on request from the corresponding author, A.U.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lifelab Program, Consorzio per la Ricerca Sanitaria-CORIS, Veneto Region, Via Giustiniani 2, 35128 Padua, Italy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Urciuolo, A.; De Coppi, P. Decellularized Tissue for Muscle Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Costa, J.M.; Fernández-Garibay, X.; Velasco-Mallorquí, F.; Ramón-Azcón, J. Bioengineered in vitro skeletal muscles as new tools for muscular dystrophies preclinical studies. J. Tissue Eng. 2021, 12, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, A.; Ngan, C.; Firipis, K.; O’Connell, C.D.; Pirogova, E.; Moulton, S.E.; Williams, R.J.; Kapsa, R.M. Towards bioengineered skeletal muscle: Recent developments in vitro and in vivo. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendibil, U.; Ruiz-Hernandez, R.; Retegi-Carrion, S.; Garcia-Urquia, N.; Olalde-Graells, B.; Abarrategi, A. Tissue-Specific Decellularization Methods: Rationale and Strategies to Achieve Regenerative Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Gordián-Vélez, W.J.; Ledebur, H.C.; Mourkioti, F.; Rompolas, P.; Chen, H.I.; Serruya, M.D.; Cullen, D.K. Innervation: The missing link for biofabricated tissues and organs. NPJ Regen. Med. 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.M.; Lowdell, M.W.; Urbani, L.; Ansari, T.; Burns, A.J.; Turmaine, M.; North, J.; Sibbons, P.; Seifalian, A.M.; Wood, K.J.; et al. Immunomodulatory effect of a decellularized skeletal muscle scaffold in a discordant xenotransplantation model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14360–14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, M.; Wei, S.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, Y.; Bai, H.; et al. Programmed death-1 mediates venous neointimal hyperplasia in humans and rats. Aging 2021, 13, 16656–16666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Sun, P.; Wei, S.; Xie, B.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; et al. A novel intramural TGF β 1 hydrogel delivery method to decrease murine abdominal aortic aneurysm and rat aortic pseudoaneurysm formation and progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Lan, Q.-H.; Kou, L.; Xu, H.-L.; Zhao, Y.-Z. Recent development and biomedical applications of decellularized extracellular matrix biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Seol, Y.-J.; Ko, I.K.; Kang, H.-W.; Lee, Y.K.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. 3D Bioprinted Human Skeletal Muscle Constructs for Muscle Function Restoration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gresham, R.C.; Bahney, C.S.; Leach, J.K. Growth factor delivery using extracellular matrix-mimicking substrates for musculoskeletal tissue engineering and repair. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ju, Y.M.; Kim, I.; Elsangeedy, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. A novel decellularized skeletal muscle-derived ECM scaffolding system for in situ muscle regeneration. Methods 2020, 171, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.; Elsangeedy, E.; Lee, H.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J.; Lee, S.J.J.; Ju, Y.M. In vitro evaluation of functionalized decellularized muscle scaffold for in situ skeletal muscle regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, J.W.; Boss, G.R.; Christman, K.L. Decellularized skeletal muscle as an invitro model for studying drug-extracellular matrix interactions. Biomaterials 2015, 64, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, C.A.; Flaibani, M.; Blaauw, B.; Pozzobon, M.; Figallo, E.; Reggiani, C.; Vitiello, L.; Elvassore, N.; De Coppi, P. In vivo tissue engineering of functional skeletal muscle by freshly isolated satellite cells embedded in a photopolymerizable hydrogel. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boso, D.; Carraro, E.; Maghin, E.; Todros, S.; Dedja, A.; Giomo, M.; Elvassore, N.; De Coppi, P.; Pavan, P.; Piccoli, M. Porcine Decellularized Diaphragm Hydrogel: A New Option for Skeletal Muscle Malformations. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, P.; Scattolini, V.; Gerli, M.F.M.; Perin, S.; Cui, M.; De Coppi, P.; Elvassore, N.; Caccin, P.; Luni, C.; Urciuolo, A. Decellularized skeletal muscles display neurotrophic effects in three-dimensional organotypic cultures. STEM CELLS Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, B.M. The biology of long-term denervated skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2014, 24, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert-Honick, J.; Grayson, W. Vascularized and Innervated Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 9, e1900626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakooshli, M.A.; Lippmann, E.S.; Mulcahy, B.; Iyer, N.; Nguyen, C.T.; Tung, K.A.; Stewart, B.; Dorpel, H.V.D.; Fuehrmann, T.; Shoichet, M.; et al. A 3D culture model of innervated human skeletal muscle enables studies of the adult neuromuscular junction. eLife 2019, 8, e44530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert-Honick, J.; Iyer, S.R.; Somers, S.M.; Takasuka, H.; Lovering, R.M.; Wagner, K.R.; Mao, H.-Q.; Grayson, W.L. Engineering 3D skeletal muscle primed for neuromuscular regeneration following volumetric muscle loss. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urciuolo, A.; Urbani, L.; Perin, S.; Maghsoudlou, P.; Scottoni, F.; Gjinovci, A.; Collins-Hooper, H.; Loukogeorgakis, S.; Tyraskis, A.; Torelli, S.; et al. Decellularised skeletal muscles allow functional muscle regeneration by promoting host cell migration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urciuolo, A.; Quarta, M.; Morbidoni, V.; Gattazzo, F.; Molon, S.; Grumati, P.; Montemurro, F.; Tedesco, F.S.; Blaauw, B.; Cossu, G.; et al. Collagen VI regulates satellite cell self-renewal and muscle regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotundo, R.L. The NMJ as a model synapse: New perspectives on formation, synaptic transmission and maintenance: Acetylcholinesterase at the neuromuscular junction. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 735, 135157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, L.; Camilli, C.; Phylactopoulos, D.-E.; Crowley, C.; Natarajan, D.; Scottoni, F.; Maghsoudlou, P.; McCann, C.J.; Pellegata, A.F.; Urciuolo, A.; et al. Multi-stage bioengineering of a layered oesophagus with in vitro expanded muscle and epithelial adult progenitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).