Abstract
The wood ash from seven plant species (sessile oak, European beech, European hornbeam, silver fir, European spruce, common alder, and Spanish chestnut) was tested against Spanish slug (Arion vulgaris) as an environmentally acceptable alternative to chemical bait pellets. We carried out laboratory and semi-field experiments to assess the contact and barrier efficacy of selected wood ash. To demonstrate the contact efficacy, slugs were rolled in the wood ash. Geochemical analysis of wood ash was carried out as well. The highest concentrations of chemical compounds SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO and MnO and elements Ba, Co, Cs, Ga, Cu, Pb and Zn were identified in the most effective ashes (beech, oak, fir, and spruce) compared to the ineffective ashes (hornbeam, chestnut, black ader). The concentration of cobalt was comparably higher, while the concentration of molybdenum was comparably lower in the four most effective wood ashes. The results of our studies revealed that the wood ash of oak and spruce have great contact efficacy. The oak and beech wood ash showed the strongest barrier efficacy against slugs. In the semi-field trials, only 10% of the plants treated with oak wood ash were damaged by slugs. The oak wood ash is an efficient alternative for slug control, however, further studies and biotechnical enhancement are needed.
1. Introduction
The increased importance of slugs (Mollusca, Gastropoda) as pests became apparent worldwide [1,2]. Slug numbers can vary considerably from year to year, and population modelling has shown this variation to be mainly driven by weather [3]. In areas with moist climates, terrestrial gastropods are of major importance in agricultural production [1,4]. In arable fields across Europe, several slug species can cause severe damage to cultivated plants, including Deroceras reticulatum (Müller), Tandonia budapestensis Hazay, Arion distinctus Mabille, Arion hortensis (Férussac), Arion intermedius Normand, Arion rufus (L.), and Arion vulgaris Moquin-Tandon [1,5].
The Spanish slug, A. vulgaris, is damaging plant shoots, roots, and fruit near the soil surface [1,5]. This pest can reach densities greater than 50 slugs per square meter in some vegetable and fruit crops [6]. There are also reports that local populations of other Arion species often decline or vanish following the establishment of the Spanish slug [1].
In intensive agriculture, chemical plant protection products are mainly applied against slugs [7,8]. Three types of chemical bait pellets are now widely available—those based upon carbamates, metaldehyde, or iron (ferric) phosphate [8,9]. Carbamates (e.g., methiocarb) are effective but also kill natural enemies of slugs (e.g., carabid beetles) [10]. Due to its toxicological aspects, the most efficient chemical molluscicide has been withdrawn from the market following a ban by the European Commission [8]. Metaldehyde is equally effective but has also recently come under scrutiny by the UK government, with the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) announcing a ban on metaldehyde in December 2018 based on the impact this chemical has on birds and mammals [8,11]. However, this ruling was overturned in July 2019 after the decision-making process by the former Defra secretary was considered unlawful [8]. However, metaldehyde has remained in the spotlight in the UK due to its impact on water systems, with concentrations greater than the EU statutory drinking water limit of 0.1 µg L−1 frequently recorded [8,12]. Iron phosphate pellets are certified for use in organic growth because they are based on a naturally occurring chemical that interferes with calcium metabolism in the gut of the target host, causing mortality within three to six days [13]. This molluscicide is relatively less toxic to animals than other molluscicides, although Langan and Shaw [14] noted that it causes increased mortality, decreased mass, and reduced surface foraging in earthworms.
As many chemical control products come under scrutiny, there is a drive from farmers and growers to develop sustainable control systems. In addition to chemical control, other control strategies include biorational products, physical barriers, agronomic practices, cultural practices, monitoring, and biological control [8]. Three decades ago, the parasitic nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita was proposed as a biological molluscicide [15], and four years later it was placed as a biological plant protection product on the market. An administrative burden for distributors and farmers in many countries is imposed by strict regulations which allow only indigenous nematode species to be used against slugs [16]. The main disadvantage of this biological tool is resistance in larger slugs. Furthermore, the slugs could live and create damage up to 21 days after nematode infection. The assessment of new naturally based compounds could lead to the development of possibly safer slug control agents and help satisfy increasing market demands for environmentally acceptable products. The alternative to chemicals should be suitable within integrated slug management (IPM) programs [17].
The focus of new studies has been on new methods and plant protection products with no or minimal impact on non-target organisms [2]. Terrestrial slugs migrate towards moist environments and avoid dry areas that would cause their abrasion and desiccation. When exposed to dry conditions, slugs are protected by a layer of slime that they deposit while they move. Wood ash can affect the slug’s physiology by disruption of the water balance, resulting in their desiccation. Wood ash is considered as antifeedant and a physical barrier for slugs [2]. To assess the potential of safer slug control products, we tested wood ash from seven woody plant species: sessile oak (Quercus petraea [Matt.] Liebl.), European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.), European hornbeam (Carpinus betulus L.), silver fir (Abies alba Mill.), European spruce (Picea abies [L.] H. Karst.), common alder (Alnus glutinous [L.] Gaertn.), and Spanish chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) These woody plant species were selected because they are widespread across their habitat in central and northern Europe. The main idea was to test the variability of wood ash in slug control and determine whether wood ash could serve as a good alternative in plant protection programmes. We aimed to assess (1) the contact control efficacy of the selected wood ash, (2) the barrier effect of the selected wood ash, and (3) the impact on slug food consumption under laboratory and semi-field trials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Slugs
The studies were carried out at the Laboratory of Entomology and the experimental field of the Biotechnical faculty (Department of Agronomy, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia). The Spanish slugs were collected from the experimental field of the Biotechnical faculty in Ljubljana (46°04′ N, 14°31′ E, 299 m a.s.l.) in May and August 2018. To determine the species, slugs were identified according to the morphological characteristics [1]. The collection of slugs comprised individuals of different lengths and ages since we wanted to analyses a mixed population of slugs that are as close to their realistic occurrence in nature [17]. Prior to the experiments, the slugs were weighed and starved for 48 h [18]. In our study, the average weight of the slugs in each treatment was 6.1 ± 0.7 g. Slug mortality, feeding behavior and ability to cross the barrier were assessed. The intensity of slug attack and damage potential was measured in semi-field trials. The methodology was done according to Laznik et al. [17].
2.2. Experimental Design
The wood ash from seven wood plant species: sessile oak, European beech, European hornbeam, silver fir, European spruce, common alder, and Spanish chestnut was used in the study. Wood material from the selected plant species was obtained from the Slovenian Forestry Institute. Wood ash was collected from a fireplace (KWB CF1 20) after burning the wood and crushed in a mortar. The laboratory experiments were carried out in a growth chamber (RK-900 CH, Kambič laboratorijska oprema d.o.o., Semič) at 22 °C and 75% relative air humidity.
2.2.1. Study of the Contact Efficacy of the Wood Ash (Experiment A)
Eighty slugs were rolled in 20 g of selected wood ash or sprinkled with water and placed in Petri dishes (150 × 20 mm) to test the contact efficacy of the wood ash. A disc of fresh lettuce leaf (approx. 50 mm in diameter) and moistened cotton (35 × 11 mm) were placed in each Petri dish containing 1 slug. Lettuce discs were replaced daily, the cotton was additionally moistened, and the control slugs were sprinkled with water. The test was conducted for 48 h with two observations of the slugs’ mortality and feeding ability. The slugs underwent 8 different treatments that were repeated 10 times.
2.2.2. Study of Wood Ash as a Barrier for Slugs (Experiment B)
Similarly, as in the study for the contact efficacy, to test the wood ash as a physical barrier against slugs, the experiment was conducted for 48 h and 80 slugs were used in 8 different treatments that were repeated 10 times. The experiment was carried out in a glass insectarium (Ø = 300 mm, h = 100 mm) with an added disc of fresh lettuce leaf (approx. 50 mm diameter) and moistened cotton (35 × 11 mm). A barrier (40 g of a selected wood ash; 3 cm wide and 2 cm thick) was placed around the leaf discs in the insectarium. In the control treatment, no barrier was used. The slugs were monitored twice (after 24 and 48 h), to observe their ability to cross the barrier and damage the leaf disc. The leaf discs were replaced, the cotton was moistened and the barriers were repaired if damaged during each observation.
2.2.3. Study of Wood Ash in the Semi-Field Trials (Experiment C)
The main experiments were conducted in 2018, however, the fields were prepared earlier, in 2017 [17]. In semi-field trials, only oak wood ash was tested for 72 h, since it proved to have potential as a control product under laboratory conditions. Twenty-five custom made wooden frames (1 m × 1 m × 0.5 m) were used to form a box with net covers. The boxes were randomly distributed in a field and installed into the soil to the depth of approx. 40 cm, while the height of the frames was at least 10 cm above the soil surface to prevent the slugs from escaping from the boxes. Untreated lettuce seedlings in density of 5 plants per square meter were transplanted in the boxes. Five slugs (A. vulgaris) were placed in each box (except in the positive control treatments), with a total of 100 slugs for the whole experiment. A tile was placed in the corner of each box as a hiding area for the slugs. The experiment consisted of five treatments that were repeated five times: (a) dusting (slugs were dusted with selected wood ash; 20 g of selected wood ash was used per experimental box), (b) barrier (a barrier around the lettuce seedlings was constructed; 40 g of selected wood ash was used per experimental box), (c) combined (the slugs were dusted with oak wood ash and a barrier was placed around the lettuce seedlings), (d) positive control (lettuce seedlings without slugs), and (e) negative control (lettuce seedlings with slugs). After 72 h, each lettuce plant was cut at the soil surface. The total weight and the weight of damaged and undamaged leaves were measured.
2.3. Geochemical Analysis of Wood Ash
Chemical compounds in the wood ash were identified via inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy (ICP-ES) and mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) at Bureau Veritas Mineral Laboratories Vancouver, Canada (Bureau Veritas, Mineral Laboratories, 2018). The analytical quality was determined by international standards. The samples were mixed with LiBO2/Li2B4O7 and fused in a furnace. The cooled bead was analyzed according to Bohinc et al. [19]. The LF100 trace elements via fusion ICP-MS were analyzed by an ELAN 9000. A Spectro Ciros Vision spectrometer was used to identify the AQ200 trace elements via aqua regia ICP-MS, and the LF300 (major elements detected via fusion ICP) and CS230 for the C and S by Leco. The results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical compounds detected in tested wood ash.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To assess the effect of different treatments on the Arion slugs in all experiments, analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed. Bartlett’s test was used to test the homogeneity of variances. Statistical significance for the differences between individual treatment means (experiments A and B) was determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (α = 0.05) with data containing homogeneous variances. For the data obtained in experiment C, Student’s multiple range test (p < 0.05) was used to identify the mean differences between the treatments for the observed variables. The data in all figures are presented as the untransformed means ± SE. Statistical analyses were done using STATGRAPHICS Plus for Windows 4.0 (Manugistics, Rockville, MD, USA).
3. Results
The data analyzed using ANOVA showed significant effects of treatments and exposure time to wood ash on slug’s mortality, slugs feeding, ability to cross the barrier and attack plants, as well as damage potential (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Results of ANOVA showing data for experiments A (df for the error term: 239), B (df for the error term: 239), and C (df for the error term: 74).
3.1. Analysis of Group of Experiments: Experiment A
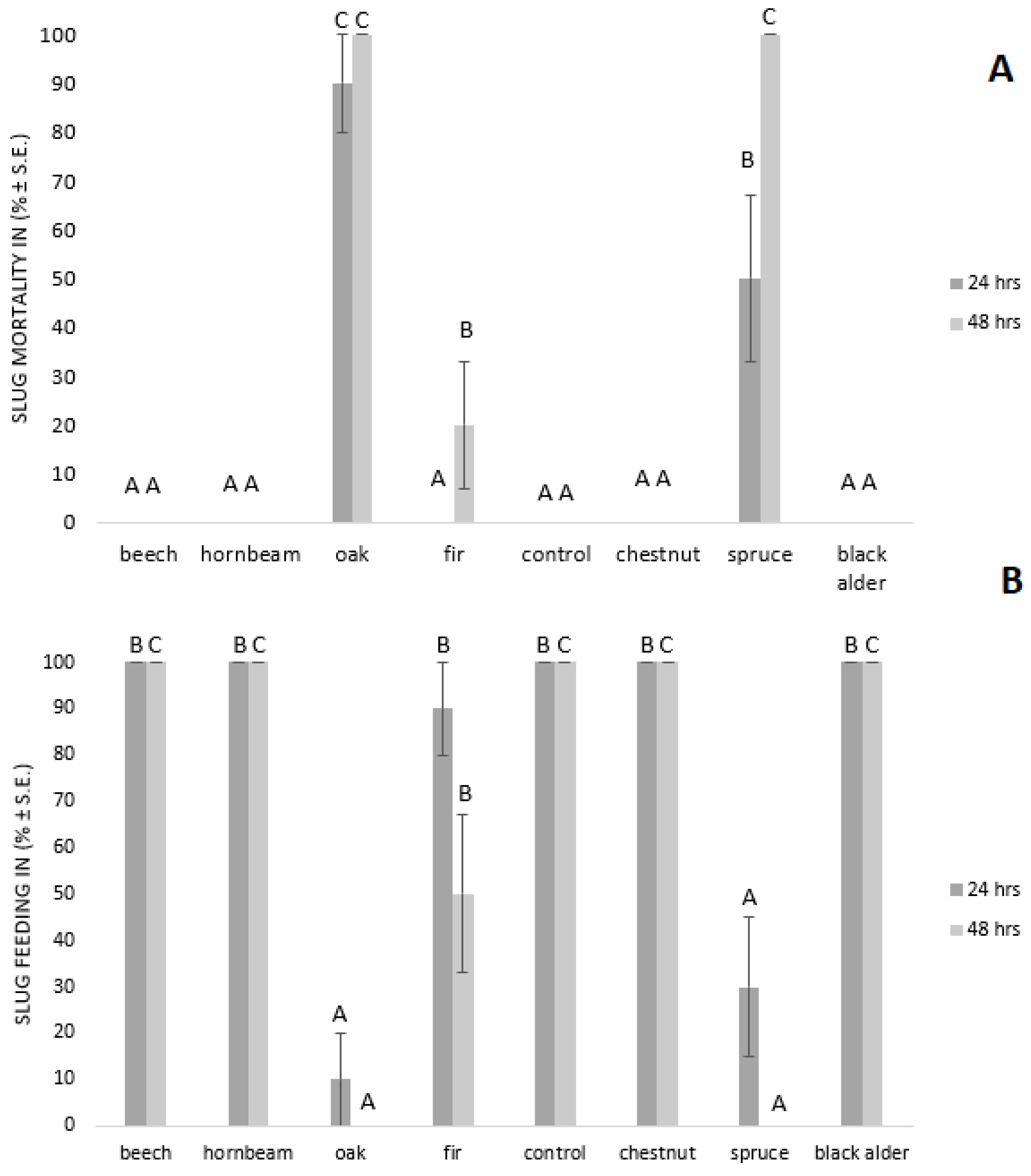
The contact efficiency of wood ash after 24 h under laboratory conditions resulted in 90 ± 10% (N = 10) mortality of the slugs treated with oak wood ash (see Figure 1A). High slug mortality was also achieved after 24 h of treatment with spruce wood ash (50 ± 17%, N = 10) (see Figure 1A). Except for oak and spruce, wood ash from other plant species did not cause slug mortality after 24 h. Our results showed that 100 ± 0% (N = 10) of the slugs treated with oak and spruce wood ash died after 48 h. Besides oak and spruce, 48 h after the slugs’ exposure to fir wood ash also caused the slugs mortality (20 ± 10%, N = 10). However, wood ash from other tested plant species did not impact slug mortality (see Figure 1A).
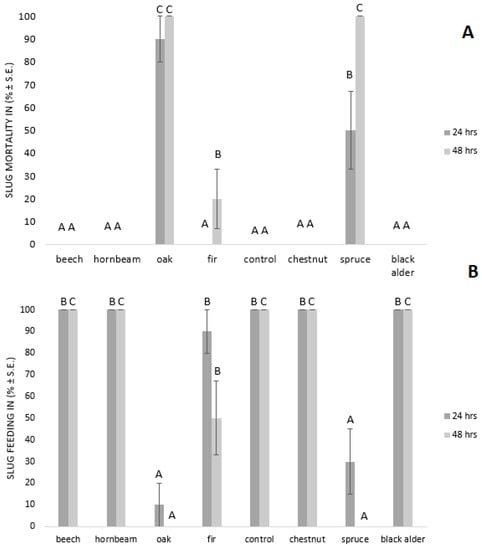
Figure 1.
Effect of the wood ash on slug mortality (A) and slug feeding (B). The means marked with different letters are significantly different at p = 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test) between the treatments in periods of 24 and 48 h.
The effect of wood ash on slug feeding after 24 and 48 h is presented in Figure 1B. The results obtained reveal that only 10 ± 10% (N = 10) of slugs treated with oak wood ash fed on plant seedlings after 24 h. The inhibition of feeding was observed also in the treatment with spruce wood ash. Similar to results obtained for contact efficacy after 24 h, wood ash from plant species other than oak and spruce did not impact slugs feeding (see Figure 1B). Slugs did not damage the lettuce seedlings 48 h after treatments with oak and spruce, and total feeding inhibition (100 ± 0%; N = 10) was achieved. Fir wood ash reduced slugs’ food consumption by 50% (N = 10). Wood ash from plant species other than oak, spruce, and fir did not impact slugs feeding behavior after 48 h (see Figure 1B).
3.2. Analysis of Group of Experiments: Experiment B
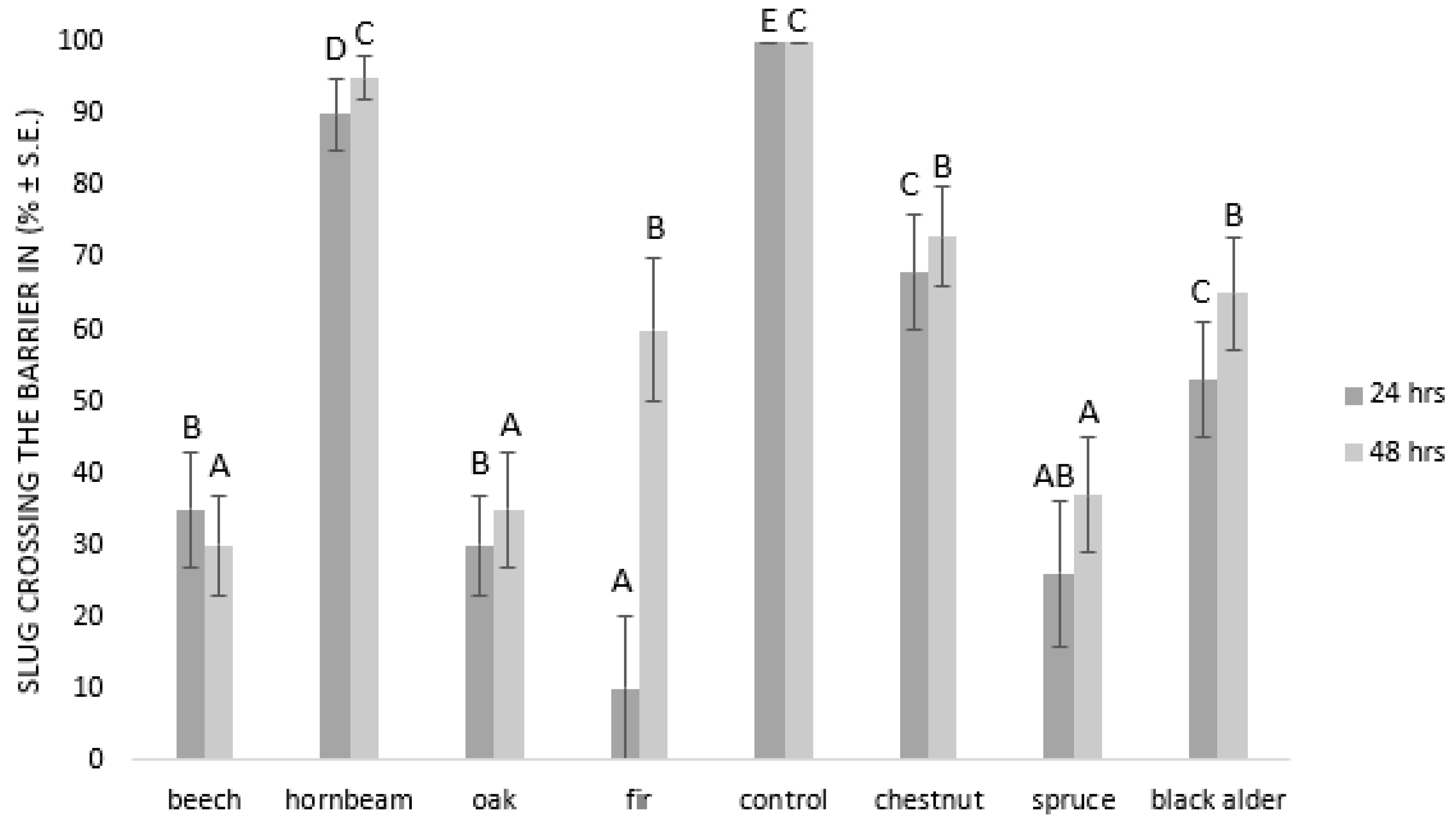
The effect of wood ash as a physical barrier for slugs to cross in periods 24 and 48 h after treatment are presented in Figure 2. The efficacy of fir wood ash as a slug barrier was 90% (N = 10) after 24 h since only 10 ± 10% (N = 10) of tested slugs crossed the barrier. After 24 h, less than 40% (N = 10) of slugs crossed the barriers made from spruce, oak, and beech wood ash. Hornbeam wood ash proved to be the least effective since more than 90% (N = 10) of slugs crossed the barrier after 24 h (see Figure 2). The efficacy of beech wood ash as a slug barrier was 70% (N = 10) after 48 h since only 30 ± 7% (N = 10) of tested slugs crossed the barrier. After 48 h, less than 40% (N = 10) of the slugs crossed the barriers made from oak and spruce wood ash. Hornbeam wood ash again proved to be the least effective, since more than 95% (N = 10) of the slugs crossed the barrier after 48 h (see Figure 2).
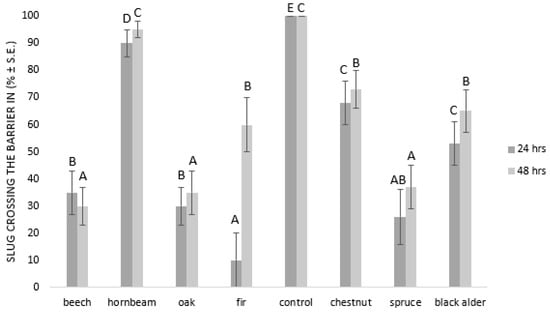
Figure 2.
Efficacy of wood ash as a physical barrier. The means marked with different letters significantly differ at p = 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test) between the treatments in periods of 24 and 48 h.
3.3. Analysis of Group of Experiments: Experiment C
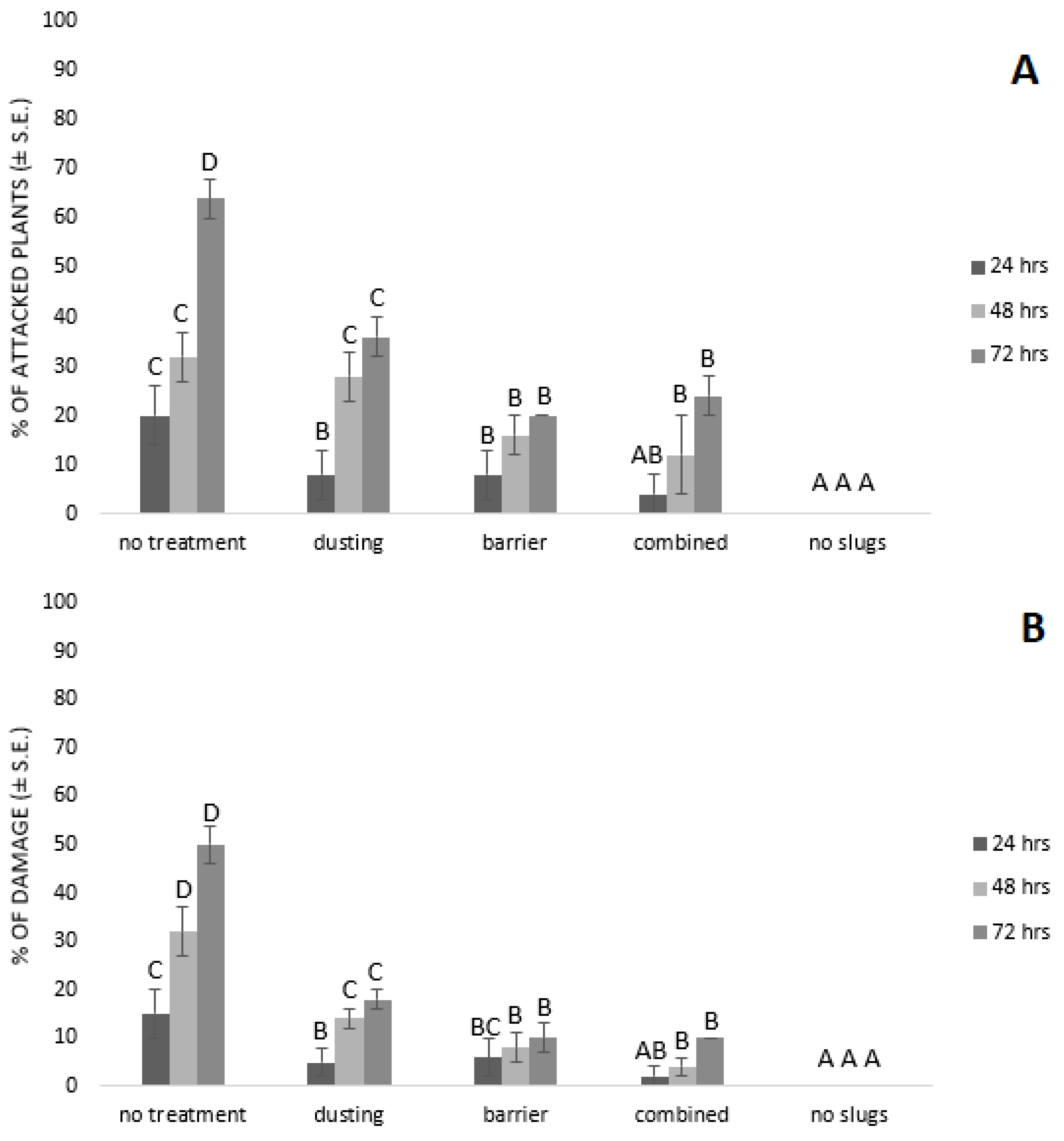
Significant differences (F = 2.69; p = 0.0406) were found between the treatments in semi-field trials for the percentage of attacked plants after 24 h Attacked plants were found in all treatments except in the positive control (see Figure 3A). The lowest intensity of slugs’ attack (only 4 ± 4%; N = 25) was found after 24 h in the treatment where the combination of techniques was used. In the same period, 20 ± 6% (N = 25) of the plants were attacked in the negative control. Significant differences for the intensity of slugs attack (F = 6.44; p = 0.0017) were found between the treatments after 48 h as well, and slugs attacked plants to a certain extent in all except positive control treatment (see Figure 3A). When the combined method was used, the intensity of the slug attack was the lowest (12 ± 8%, N = 25). This treatment differed significantly when compared to the negative control (32 ± 5%, N = 25) and dusting (28 ± 5%, N = 25). Significant differences for the intensity of attack (F = 57.83; p < 0.0001) were found also between the treatments after the third observation (72 h), and slugs attacked plants in all treatments besides the positive control (see Figure 3A). When a barrier was used in semi-field trials, only 20 ± 0% (N = 25) of attacked plants were recorded, while in the same period 64 ± 4% (N = 25) of attacked plants were observed in the negative control (see Figure 3A).
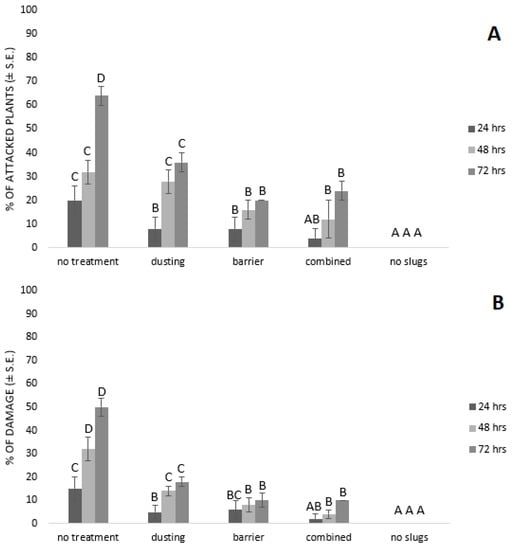
Figure 3.
Effect of oak wood ash on the intensity of slugs attack (A) and plant damage (B) in semi-field trials. The means marked with different letters significantly differ at p = 0.05 (Student’s multiple range test) between the treatments in periods of 24, 48, and 72 h.
Analysis of the percent of damaged plants revealed significant differences (F = 2.77; p = 0.0453) between the treatments after 24 h The lowest damage occurred after 24 h in treatment with combined techniques, where only 2 ± 2% (N = 25) of the plants were damaged by slugs, while 15 ± 5% (N = 25) of the plants were damaged in negative control in the same period (see Figure 3B). Significant differences (F = 17.42; p < 0.0001) were found after 48 h between the treatments for damaged plants. Combined treatment was the least affected, with only 4 ± 2% (N = 25) of the plants damaged by slugs, while in the same period 32 ± 5% (N = 25) of the damaged plants were found in the negative (see Figure 3B). Significant differences for plant damage (F = 58.54; p < 0.0001) were found between the treatments in the last observation (after 72 h) as well. Wood ash as a barrier alone or in combination with dusting proved to be the most effective method, since in both cases, it resulted in only 10% (N = 25) damaged plants, while in the same period slugs damaged 50 ± 4% (N = 25) of the plants in the negative control (see Figure 3B).
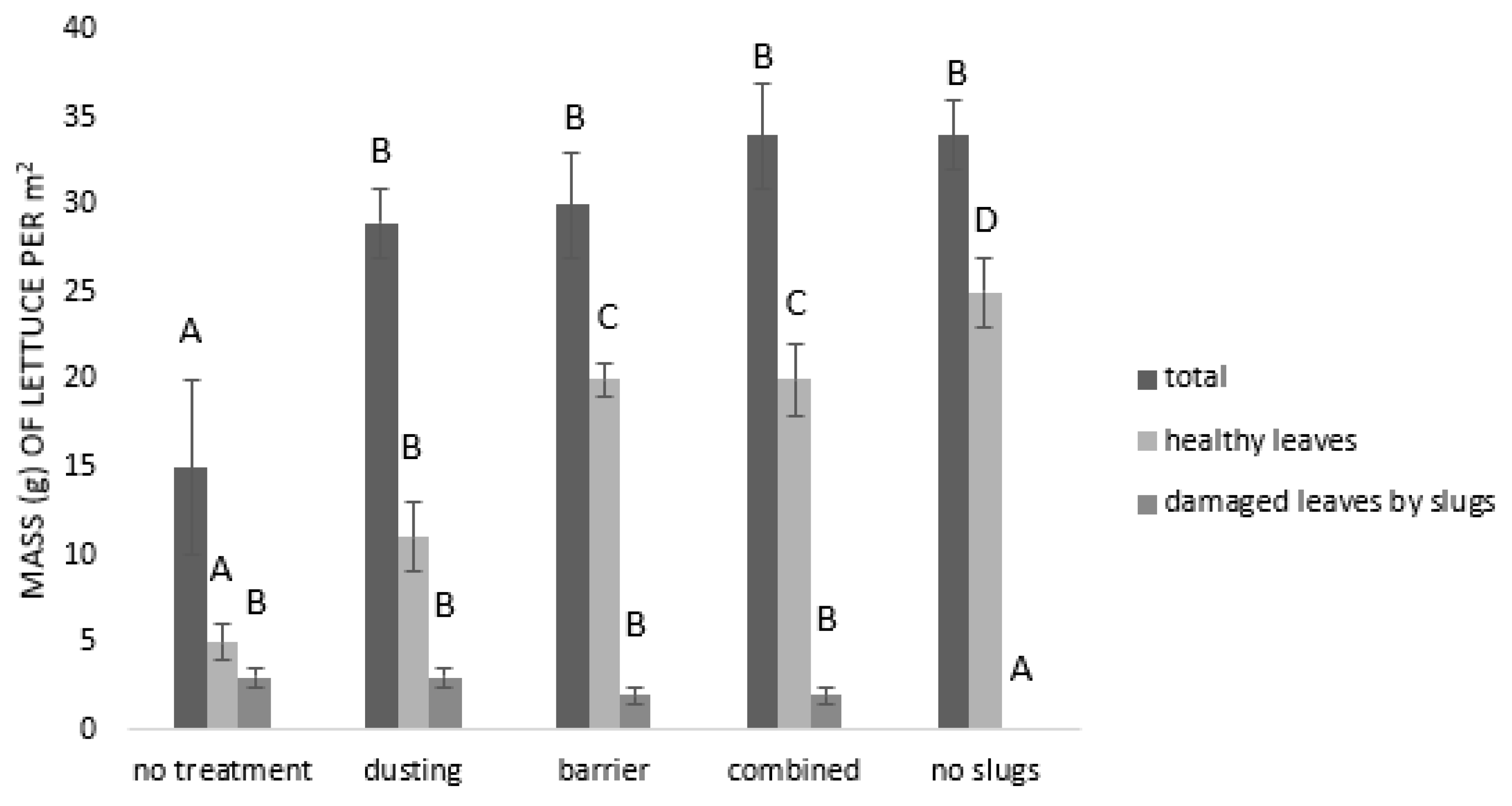
Slugs significantly affected the total yield (F = 6.24; p = 0.0020) of lettuce seedlings (see Figure 4). Combined techniques were the best protective method against the slugs since the highest yields were measured in this treatment (34 ± 4 g plant), while the lowest yield was measured in the negative control (15 ± 5 g plant). The yield of the healthy leaves differed also significantly among the treatments (F = 20.34; p < 0.0001). The highest yields were measured in the positive control (25 ± 2 g plant), and the lowest were obtained in the negative control (5 ± 2 g plant). There were no significant differences between the barrier alone (20 ± 1 g plant) or the combined method (20 ± 2 g plant); however, both methods proved to yield more healthy leaves than only the dusting of slugs (11 ± 2 g plant) (see Figure 4). Significant differences (F = 15.05; p < 0.0001) for a yield of the damaged leaves were found between the treatments. Similarly to the results of total yield and yield of healthy leaves, the mass of damaged leaves was highest in the negative control (3 ± 1 g plant), and the lowest in the positive control (0 ± 0 g plant).
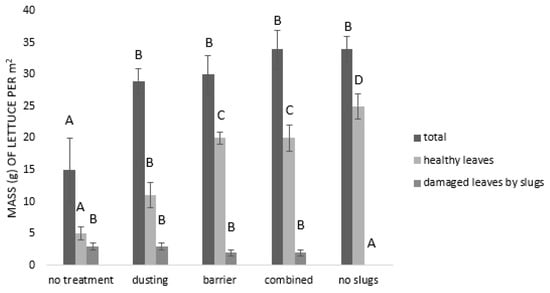
Figure 4.
Effect of wood ash on the damage potential of slugs in semi-field trials. The means (mass of lettuce (g) ± S.E.) with different letters significantly differ at p = 0.05 (Student’s multiple range test) between the treatments in periods of 24, 48, and 72 h.
4. Discussion
Traditionally, slugs are controlled by chemical bait pellets based upon carbamates, metaldehyde, or iron (ferrous) phosphate [9]. However, molluscicides are toxic and give inconsistent results. They are poisonous to vertebrates, entomophagous invertebrates, and earthworms [9,10]. In environments with wet conditions, the efficiency of chemical bait pellets is very low [20]. Decreased efficiency of bait pellets also occurs when slugs cover the pellets with slime thus protecting slugs from coming in contact with skin and diluting the toxin [21,22]. Potential human health implications of exposure to agricultural pesticides in chemical bait pellets forced farmers and industry to search for new alternatives [23].
Recently, new molluscicidal substances that are environmentally acceptable have been proposed [22,24,25]. New natural compounds are characterized as selective and highly toxic to target pests, safe for non-target organisms, low cost, and biodegradable [1,25]. The use of wood ash has been noted among these compounds [2,25]. Therefore, we conducted laboratory and semi-field experiments to assess the contact efficacy, antifeedant, and barrier efficacy of wood ash derived from seven plant species (sessile oak, European beech, European hornbeam, silver fir, European spruce, common alder, and Spanish chestnut). The novelty of the present study lies in the results of interspecific variability of wood ash in controlling arionid slugs.
The highest mortality of slugs rolled in the wood ash was recorded under the oak and spruce wood ash treatments (Figure 1). Geochemical analysis of wood ash showed that oak and spruce wood ash comprised relatively high levels of copper (Table 1). Copper has been previously reported as an efficient mechanical and physiochemical barrier for slugs [18,24]. Mollusks take up copper, in the form of copper compounds [26], through ingestion [27] and directly through their foot, causing internal damage and irritation [18]. Furthermore, several wood ashes (beech, oak, fir, and spruce) showed satisfactory results as a physical barrier against slugs. The most effective ashes (beech, oak, fir, and spruce) compared to the ineffective ashes (hornbeam, chestnut, black ader) contain the highest concentrations of the most of identified chemical compounds (Si02, Al2O3, Fe2O3, MgO, and MnO) and elements (Ba, Co, Cs, Ga, Cu, Pb, and Zn). Silicon dioxide consists of many tiny abrasive crystals, that can cause small abrasions on the body of any pest that comes in contact with the powder. The pest gradually loses its body fluids, dehydrated and dies [18,25,28]. Arionid slugs are reported fairly tolerant to heavy metals which they tend to accumulate in high concentrations in their midgut gland. However, excessive concentrations of zinc, lead, and copper are toxic and can negatively impact the slug’s metabolism of other essential metal ions [29]. It has been reported that heavy metals could be used in slug control programs as an antifeedant and so-called bioactive repellents [30], but there is still inconsistency in efficiency since the toxicity of Zn, Pb or other heavy metals is dosage-dependent [31]. In our study, we found calcium oxide of minor importance for arionid slug since ineffective hornbeam ash had similar concentrations (more than 50%) compared to fir ash, which was among the most effective ashes. This is surprising, since calcium-rich eggshell powder is often recommended as a slug control tool for small gardeners. Furthermore, we detected the lowest concentrations (below 0.0003%) of molybdenum in the four most effective wood ashes, when compared to other three ineffective wood ashes. Molybdenum is often used in form of inorganic salts in paints and hydraulic fluids to prevent corrosion, however, it can cause hypocuprosis in animals fed on plants high in molybdenum [32]. In snails, molybdenum can adversely impact metabolism of calcium and other functions leading to inhibition of growth and feeding, however it cannot affect snail’s mortality [32]. We found comparable higher concentrations of cobalt in the four most effective wood ashes. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the effect of cobalt on arionid slug’s behavior or mortality. Cobalt is a relatively rare element in nature. Agricultural chemicals such as fertilizers can be enriched with cobalt to amend soils that are cobalt-deficient. Cobalt ions affect natural proteins in different ways, however, their function has rarely been studied. It is known that higher concentrations are toxic in humans, terrestrial and aquatic animals and plants [33]. Further studies are needed to test physical properties of the most effective wood ashes, and mechanisms of action of the most promising wood ashes.
In the second experiment (B), wood ash was used as a barrier for the slugs. The slugs produced an excessive amount of slime in all treatments. The efficacy of beech wood ash was 70% after 48 h (Figure 2). The efficiency of the wood ash was found to be similar to plant powder [17] and hydrated lime [25]. As expected, these compounds cause slugs dehydration and blockage of the breathing structures. Slugs tend to dehydrate in conditions of stronger evaporation across their body, but also through mucus secretion [28]. Slugs’ inability to deposit mucus limits their performance and increased secretion could impact their feeding behavior. Further research is needed to confirm this statement.
In semi-field trials (experiment C), we were aiming to investigate the impact of different techniques of wood ash (as a barrier or slug dusting) on the intensity of slug attack and slug damage potential (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Oak wood ash was used in this experiment as the most promising material. We achieved the best results in treatments with a combination of both techniques (only 10% of damaged plants by slugs were observed). In the control treatment, more than 50% of plants were damaged by slugs. Previous studies have shown that slugs avoid a dry surface such as continuous lines of sawdust or hydrated lime that are used in a physical barrier [25]. A disadvantage of the physical barriers is low efficiency when they become which is almost immediately when applied to wet soil [2]. Capinera [2] suggested a solution for this problem, namely, to place a waterproof collar around the plants and to put the barriers on top of it. The disadvantage of this method is impracticability, increased costs for the waterproof material, and frequent replacement of the material. In crop farming, the practice of incorporating wood ash in the soil has been used, in which context it serves for liming and as an N-free fertiliser rich in major elements, notably p, Ca, Mg, and K. Wood ash changes the soil texture, impacting on the soil aeration, water retention, and salinity [34]. Due to its liming effect and increase in soil organic matter mineralization, wood ash stimulates the soil microflora and microfauna activity and modifies their species composition [35]. Wood ash causes significant changes to the mineral compositions and an increase in pH units of soil in the first five years after application only if incorporated in the soil in high doses [36]. Application of wood ash in slug control programs that is presented in our study would have minor effect on the soil properties. We are proposing wood ash as a physical barrier with lethal properties for slugs. If wood ash would be deposited on a waterproof material as proposed, and frequently replaced, it might come into contact with surrounding soil only superficially. This led us to a hypothesis of its insignificant effects on soil properties.
Integrated slug control is a desirable strategy that employs methods using cultural practices and chemical molluscicides as a last resort. The slug control program should be regarded as satisfactory if it limits slugs’ damage potential, rather than their eradication. The development of an efficient and consistent non-chemical slug control method is a necessity for organic growers. Different methods are proposed for organic growers; however, their efficiency is not fully tested or satisfactory. In this study, we demonstrated that oak and spruce wood ash are promising materials for the control of slugs since it caused high mortality and inhibited slugs’ feeding in 24 h after treatment. This research delivers a low-cost and environmentally acceptable solution for small-farm growers. It is necessary to mention that during our semi-field trials, the weather conditions were dry. We recognize the challenge for growers on large-scale farms to protect plants against slugs since wood ash will absorb moisture from the soil, becoming wet and ineffective. In this case, the wood ash as a barrier would require protection by waterproof material placed near plants, underneath the barriers to prevent water uptake and/or frequent re-application. Our results can serve as a basal point in further studies aiming to provide biotechnological enhancement of the wood ash as a slug contact suppressant, a physical barrier against slugs or being used in a trap as desiccant.
5. Conclusions
The wood ash of oak and spruce showed great contact efficacy, while that of oak and beech wood ash showed the strongest barrier effects against slugs. The oak wood ash showed great potential as a protective measure against slugs in the semi-field trials as well, since the damage potential of slugs was measured as low as 10% for plants treated with oak wood ash. Our results can be implemented at a low cost in integrated slug management programs at small-scale farms.
Author Contributions
Ž.L and S.T. conceived and designed the experiments. I.M. performed statistical analyses. A.H. performed geochemical analyses. Ž.L. and I.M. prepared the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by Slovenian Research Agency under programme Horticulture No. P4-0013-0481.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their thanks to Kristina Košelnik, Klavdija Luzar, Katja Mavec and Jaka Rupnik from the Biotechnical faculty for their technical assistance. Sincere thanks to Susie Woo from Bureau Veritas Commodities Canada, Ltd. for ensuring the description of the methods and equipment used for the geochemical analysis of the wood ash.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rowson, B.; Anderson, R.; Turner, J.A.; Symondson, W.O.C. The slugs of Britain and Ireland: Undetected and undescribed species increase a well-studied, economically important fauna by more than 20%. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinera, J.L. Assessment of barrier materials to protect plants from Florida leatherleaf slug (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Veronicellidae). Florida Entomol. 2018, 101, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Bohana, D.A.; Potting, R.P.J.; Semenov, M.A.; Glen, D.M. Individual based model of slug population and spatial dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, M.R.; Tooker, J.F. Slug (Mollusca: Agriolimacidae, Arionidae) Ecology and Management in No-Till Field Crops, With an Emphasis on the mid-Atlantic Region. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2012, 3, C1–C9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotsbo, S.; Damgaard, C.; Hansen, L.M.; Holmstrup, M. The influence of temperature on life history traits in the Iberian slug, Arion lusitanicus. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 162, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, J. The distribution, biology, population dynamics and harmfulness of Arion lusitanicus Mabille, 1868 (Gastropoda: Pulmonata: Arionidae) in Poland. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2007, 47, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.J.G.; Ferreira, N.G.C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Toxic effects of molluscicidal baits to the terrestrial isopod Porcellionides pruinosus (Brandt, 1833). J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.L. Riding the Slime Wave: Gathering Global Data on Slug Control; The Nuffield Farming Scholarships Trust Report; The Nuffield Farming Scholarships Trust: Taunton, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.E.R. Molluscicidal baits for control of terrestrial gastropods. In Molluscs as Crop Pests; Barker, G.M., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Purvis, G.; Bannon, J.W. Non-target effects of repeated methiocarb slug pellets application on carabid beetle (Coleoptera, Carabidae) activity in winter-sown cereals. Annal. Appl. Biol. 1992, 121, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOV. Restrictions on the Use of Metaldehyde to Protect Wildlife; Crown Copyright: London, UK, 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/restrictions-on-the-use-ofmetaldehyde-to-protect-wildlife (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Castle, G.D.; Mills, G.A.; Gravell, A.; Jones, L.; Townsend, I.; Cameron, D.G.; Fones, G.R. Review of the molluscicide metaldehyde in the environment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, K.; Bond, C.; Stone, D. Iron Phosphate General Fact Sheet; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2013; Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/ironphosphategen.html (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- Langan, A.M.; Shaw, E.M. Responses of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (L.) to iron phosphate and metaldehyde slug pellet formulations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2006, 34, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Glen, D.M.; George, S.K.; Butler, R.C. The rhabditid nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita, as a potential biocontrol agent for slugs. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1993, 3, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laznik, Ž.; Majić, I.; Trdan, S.; Malan, A.P.; Pieterse, A.; Ross, J.L. Is Phasmarhabditis papillosa (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) a possible biological control agent against the Spanish slug, Arion vulgaris (Gastropoda: Arionidae)? Nematology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laznik, Ž.; Bohinc, T.; Franin, K.; Majić, I.; Trdan, S. Efficacy of invasive alien plants in controlling Arionidae slugs. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüder, I.; Port, G.; Bennison, J. Barriers, repellents and antifeedants for slug and snail control. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohinc, T.; Horvat, A.; Andrić, G.; Pražić Golić, M.; Kljajić, P.; Trdan, S. Comparison of three different wood ashes and diatomaceous earth in controlling the maize weevil under laboratory conditions. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2018, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.Y.; Hara, A.H.; Hu, B.K.S. Molluscicides and mechanical barriers against slugs Vaginula plebeia Fischer and Veronicella cubensis (Pfeiffer) (Stylommatophora:Veronicellidae). Crop Prot. 1997, 16, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, B.; Kistler, C. Field tests with a molluscicide containing iron phosphate. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cruz, D.; San Martín, R. Molluscicidal effects of saponin-rich plant extracts on the grey field slug. Cien. Inv. Agric. 2013, 40, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical pesticides and human health: The urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laznik, Ž.; Križaj, D.; Trdan, S. The effectiveness of electrified fencing using copper electrodes for slug (Arion spp.) control with direct electric current and voltage. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 9, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laznik, Ž.; Trdan, S. Is a combination of different natural substances suitable for slug (Arion spp.) control? Span. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 14, e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, T.A.; Bowen, I.D. The slug foot as a site of uptake of copper molluscicide. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1977, 30, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, B.; Dallinger, R. Accumulation of cadmium and copper by the terrestrial snail Arianta arbustorum L.: Kinetics and budgets. Oecologia 1989, 79, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, D.J. Water regulatory behaviour in terrestrial gastropods. Biol. Rev. 1985, 60, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, M.; Schnegg, R.; Salvenmoser, W.; Palacios, Ò.; Lindner, H.; Zerbe, O.; Hansel, A.; Leiminger, M.; Steiner, G.; Dallinger, R.; et al. Distinct pathways for zinc metabolism in the terrestrial slug Arion vulgaris. Sci. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capinera, J.L. Evaluation of copper hydroxide as a repellent and feeding deterrent for Cuban brown snail (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Pleurodontidae). Fla. Entomol. 2018, 101, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkiss, K.; Watkins, B. The influence of gut microorganisms on zinc uptake in Helix aspersa. Environ. Pollut. 1990, 66, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, M.P. Interaction and effects of molybdenum compounds on growth and mineral content of Achatina fulica and Arion ater (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1994, 107, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechev, J.; Stefanov, K.; Popov, S. Effect of cobalt ions on lipid and sterol metabolism in the marine invertebrates Mytilus galloprovincialis and Actinia equina. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2006, 144, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeyer, A.; Nkana, J.V.; Verloo, M.G. Characteristics of wood ash and influence on soil properties and nutrient uptake: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkiömäki, J.; Fritze, H. Short and long-term effects of wood ash on the boreal forest humus microbial community. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.; Watmough, S.A. Evaluating the effects of liming and wood-ash treatment on forest ecosystems through systematic meta-analysis. Can. J. For. Res. 2014, 44, 867–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).