Abstract
Soil erosion is a considerable concern in the upland areas of Central Vietnam. This situation is most serious in regions, where the terrain is sloped and subjected to heavy rainfall. Our research was conducted in a mountainous area, belonging to Central Vietnam, the area of Song Kon commune in the Dong Giang district. The objective of this study is first to estimate the impact of soil erosion risk in these areas, and second to assess the capacity of farming systems which are based on indigenous knowledge (IK) to respond to soil erosion. Our data were collected by Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) and processed using Geographical Information System (GIS) methods. We then interpreted this research using the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) in order to calculate the soil erosion rate. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) were also used as measurements to compare the difference of land surface covers between different farming systems. The results showed that the lowest soil erosion rate was found in the narrow valley regions, which are populated by both agricultural and residential areas. On the other hand, soil erosion was extremely high in the more northerly quadrant of our research area. Our findings also indicate that local farmers are highly aware of soil erosion, which has positively influenced the adoption of adaptation measures (AMs) in their agricultural activities. The most common AMs are as follows: changes in cropping patterns, the adjustments of their planting calendars, the use of native varieties, and intercropping methods. These AMs are mediated by the cultural observances of the local ethnic minority peoples in relation to their IK. We have concluded that when farmers apply IK in their farming systems, the soil erosion rate tends to decrease as compared with non-indigenous knowledge (NIK) practices. We hope to bring a better understanding of the processes that shape farmers’ AMs and thereby to develop well-targeted adaptation policies that can then be applied at the local level. Our findings may be instrumental in future adaptation planning and policies in regard to climate change, and that they will help to increase awareness not only in matters of the soil erosion but also in other interconnected aspects of climate change in these areas.
1. Introduction
As was noted in the Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) by the International Panel on Climate Change, the negative influences of climate change on human beings is clearly evident and it is growing in impact. This has been observed and documented across all continents and ocean bodies over the world [1]. These changes are increasingly threatening to countries with concentrated populations and who have significant economic activity in vulnerable regions [2]. As a developing country with an agricultural and resource-based economy, Vietnam is identified as one of the most vulnerable nations in this regard. It has been cited as the nation most severely impacted by climate change in Asia [3]. Indeed, during the past three decades in Vietnam, the frequency and severity of floods and typhoons have markedly increased, and have caught many communities unawares [4]. A report of the World Bank (2010) described a steady increase in annual mean temperatures by 0.5 °C to 0.7 °C from 1958 to 2007 and this projected to increase to 2.5 °C by the year 2070 [5]. Because of the increasing temperature, the evapotranspiration rate will also increase and reduce the growing season by depleting soil moisture more rapidly. Another result is reduced stream flow and a degraded water quality [6]. Moreover, it can be predicted that because of more concentrated rainfall in the rainy season, rainfall in the dry season will decrease by the year 2070 in Central Vietnam, and droughts will occur more frequently [5]. Over 10 years ago, 70% of the 73 million people of Vietnam lived in disaster-prone areas, with the majority of these people residing in the Central region [4]. The Central region of Vietnam is the most underdeveloped area of the country, as compared to Northern and Southern regions [7]. Within the central part of Vietnam, significant changes in rainfall patterns and tropical storms trends are notably on the increase [8]. The resulting factors of this are unprecedented flooding, and consequential soil erosion. This of course drastically affects agricultural production, which is the major source of livelihoods within these predominantly rural communities [4]. In comparison to other regions of the country, Central Vietnam is facing the risk of soil erosion quite severely because of the terrain conditions [9]. Preventing soil erosion is the most important adaption measure that needs to be implemented in order to reduce the negative impact of climate change on agriculture in this area [10].
In recent years, GIS and remote sensing have increasingly played an important role in the study of soil erosion [11,12]. These studies require a significant amount of spatial data, which GIS and remote sensing can solve through raster data analysis tools [9]. Several studies have integrated GIS and soil erosion assessment models into web applications [13]. As a result, the users can assess soil erosion quickly and accurately. Worldwide, researchers have developed tools for soil erosion estimation such as the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP), the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) [14]. The USLE is the most popular method for soil erosion estimation because of its simple means of application [14,15,16] and that it is free to access the database input [9,17]. The USLE method predicts the long-term average annual rate of erosion based on rainfall, characteristics of soil type, terrain, land surface cover, and management practices.
In recent studies conducted in Vietnam, it is stated that climate change has a severely negative impact upon the indigenous peoples of the mountainous areas, and along the coastal regions. This affects every area of their lives: ecological, sociocultural, economic, and is pervasive in regard to general health and safety [18,19,20]. Accordingly, it is the ethnic minorities of Vietnam, who are mainly living in or around mountainous areas, which are often treated in a peripheral manner with regard to national policy. These populations are particularly sensitive and vulnerable to the environment’s changes [21]. In the geographical context of Vietnam, local or indigenous knowledge (IK) refers to the activities of the country’s many ethnic minority communities. This knowledge is used as a very effective tool in adapting and coping with environmental changes [21]. According to Kapoor and Shizha [22], IK emerges from careful long-term observation of natural phenomena. These approaches are basically an understanding of the relationship between specific biological entities (plants, mammals, birds, insects) and among biological landforms (mountains, isolated hills), and meteorological phenomena [23]. Kapoor and Shizha [22] have argued that IK is socially dynamic and culturally appropriate as it is inherent to the specific local environment in which it is derived, and is in harmony with local cultural norms. IK has evolved from years of collective learning and it is the result of experience that is gained through an extended process of practical experimentation which is organically conceived within a given area. The aspects of this IK are formed, accumulated, evolved, and disseminated orally from generation to generation. That is to say, this IK is transmitted throughout the entire community by “word of mouth” and also by physical demonstration. It provides the basis for local-level decision-making in many rural communities [21]. It is most notably, indigenous weather forecasting knowledge, which is based on physical observation and accumulated historical experience, and can be applied in an improvised fashion as it does not rely solely on electronic devices. Thus, IK can be used effectively for disaster risk reduction in remote and inaccessible areas, or in regions where there are changeable micro-climates [24]. In a long-term way, the community is able to use their IK to adapt their agricultural systems to partially offset the effects of climate change and the risks of natural disasters [25]. It is ironic that even though the Vietnamese government has attempted to promote economic development and sustainable livelihoods in the uplands and mountainous areas through new policies, and agricultural programs that correspond with national strategies [26], the local people have become more destitute [27]. As a result, observers from outside the immediate vicinity usually misunderstand local farming systems, particularly members of their own governments who are charged with helping them to overcome their livelihood challenges with dignity [28]. This is a dilemma which clearly needs to be given more attention. It shows that existing national and regional policies need to be re-examined and fine-tuned in these areas to better coincide with the changing natural conditions.
It is important to note the ways in which farmers of the upland areas have adapted their farming practices in response to contemporary climate changes, and to look at the agricultural management systems that have enabled them to continue farming in a sustainable manner. There have been numerous studies done worldwide that look at the role of how specific ethnic groups have used their indigenous knowledge in order to combat soil erosion in their given regions [29]. For example, Teklu and Gezahegn [30] indicated that in Ethiopia, crop selection and agricultural management based on IK were well integrated into the local farming systems, and most specifically in order to prevent soil erosion. The IK of Konso people in Ethiopia is considered to be one of the most successful farming endeavors in the world for soil conservation. They have used as many as nine adaptation measures such as contour ploughing, crop rotation, mixed cropping, etc., to achieve their success in soil management [31]. In another African agricultural study, local people in Kaware State, Nigeria, often implement six control measures to avoid and reduce the negative influences of soil erosion on agricultural production [32]. Prudat (2018) assessed the local soil quality of north-central Namibia by using integrating the farmers’ inherent knowledge with scientific knowledge [33]. Suffice to say that in the overwhelming majority of the studies in regard to this concern, the use of IK-based approaches has been a key factor in re-calibrating farming systems in order to prevent soil erosion.
In Vietnam, most of the researches in this regard has been concentrated in the most Northerly regions of the country, and the opposing Southerly regions of the Mekong Delta respectively. There is a need for further studies to be done in the Central regions that relate to the changes in agricultural farming systems and indigenous experience in adaptations to modern climate risks [20,21,34]. Also, the research that has been conducted in the Central region has been mostly conducted in coastal areas [19,35]. Studies focusing on the ethnic communities of the mountainous regions are extremely rare, and are thus in need of further attention. Consequently, this paper aims to understand the indigenous farming systems that are used to respond to climate change within the mountainous regions of Central Vietnam. We have conducted our study through the gathering of empirical evidence, personal observation, and scientific data analysis. As noted, there has been very little, if indeed any, detailed scientific research geared toward investigating the links between local indigenous farming systems and the increasing problem of soil erosion that is due to contemporary changes in climatic patterns of their specific regions. Given this, we have focused this study on the mountainous areas that belong to Central Vietnam. Our objectives are: (i) to determine the risks of soil erosion in this region and (ii) to assess the capacity and effectiveness of IK farming systems to respond to the soil erosion rate in comparison to NIK farming systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This research was conducted in Song Kon commune, located in the North Central region of Dong Giang district with a total area of 7870 hectares (Figure 1). As a mountainous and remote region, it is home to nearly 2500 people, over 90% of whom are ethnic minority groups. Of these upland dwellers, with a population of 2090 people, the “Co Tu” people are the largest ethnic minority group living in and around the remote hills and uplands of the district [36]. These populations are predominantly small-scale farmers who grow rice, and maize as their staple crop, and cultivate acacia in the mid-land hills as their main source of income. Official poverty rates are high, standing at an average of 57.15% (379 out of 663 total households) in this upland region, compared with 9.8% countrywide [37]. Some previous reports [38,39] pointed out several reasons that contribute to the disadvantage that these people are faced with. Those mainly being the varied and challenging topography, the difference in cultural norms, inherent generational lack of economic opportunities, and the remoteness of their locations. These factors have thus caused these ethnic minority groups to be particularly vulnerable to natural hazards and extreme weather variability [20].
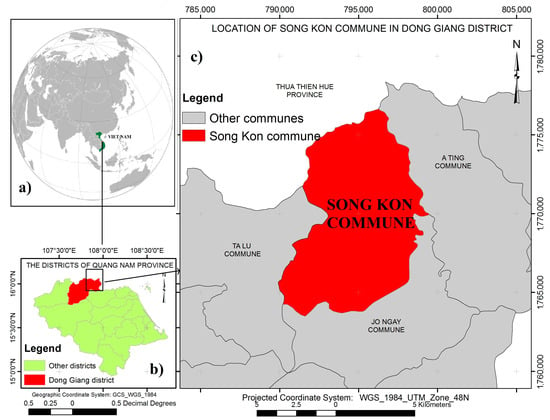
Figure 1.
Map of study area; Central Vietnam (a); Dong Giang district in Quang Nam province (b) and Song Kon commune in Dong Giang district (c).
This region subject to a humid tropical monsoon climate, which has created a complex terrain that is characterized by steep slopes. 30% of the total area is at an incline of more than 30 degrees. It has a range in elevation from 293 m to 1070 m above sea level, which increases from the Southern to the Northern parts [40]. The area is characterized by two distinct seasons the rainy season (from September to January) and the dry season (from February to August). The yearly precipitation is around 2350 mm. There are two-to-three tropical storms that hit this area from September to November [36]. Because of such complex terrain and climate, agricultural activities are often affected by natural disasters. The variability and extremity of local weather events include flooding in the mid-low land areas, while soil erosion is most predominant in the upland areas. But despite these conditions, the “Co Tu” people, who are indigenous to this complex region, have survived throughout generation by developing agricultural systems and native customs that blend with their environment and result in a symbiotic relationship with their use of the land. The traditional knowledge of the “Co Tu” people in relation to their local ecological systems remains a core strength in coping with, and adapting to the modern effects of CC. Also, the IK that the “Co Tu” people have developed over a significant period of time and has helped them to negotiate through the socio-cultural incongruities which exist between themselves and the surrounding regions [21]. They can rely on natural phenomena such as the appearance of animals or changes in the growth of bamboo trees to forecast weather over a long period of time in the future [39].
2.2. Methods
This study was conducted with both qualitative and quantitative methods for collecting data during the period between January–August 2019. A mixture of several methodological approaches was applied to collect the data. The data were collected related to various aspects of “Co Tu” life. These included the farmers’ perceptions as well as their experiences. We gathered this information in a number of ways, including open in-depth interviews with key members of the community (n = 9), three focus group discussions (FGDs), structured interviews with the broader community (n = 84), and participant observation. This was further augmented by the insights, inference, and experience of participating scientists, local decision-makers, resource managers, published and unpublished literature, and other available sources of information. In addition, the USLE was applied to predict the soil erosion rate, the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) was used to calculate the cropping management factor and the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) was also applied to measure the land surface cover of different farming systems.
2.2.1. The Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) Method
The majority of the previous studies that relate to the local community have used the PRA method for determining information [41,42]. This method is particularly effective among small groups. It is effective in enabling the local people to comfortably share their experiences in a way that enhances their own knowledge and analysis of their lives and the condition in which they live. With the help of this modality, they can also plan a course of action that they can be apply in improving their given circumstance [43]. The basic techniques used here include a system of interviewing, surveying, and sampling that lead to deeper understanding of group dynamics and enable the creation of community consensus [44,45]. Accordingly, nine in-depth interviews were conducted with local representatives of varying social and economic groups. The purpose of these interviews was to explore various topics related to agricultural production, to weather extremes, to the impacts of soil erosion and to the changes in the indigenous farming systems used to adapt to soil erosion. After classifying the data that were collected through the in-depth interviews, a semi-structured questionnaire was designed which was used when interviewing individual households.
In total, 84 households were selected. This is 10% of the agricultural households, who each had at least 10 years of agricultural experience. The interviews were carried out during August 2019. The questionnaire was divided into three parts to collect data related to socio-demographic characteristics, agricultural farming systems, and soil erosion issues. Three FGDs were organized to study village group dynamics in the acquisition of information, and to cross-check data that had been collected by other means. The FGDs were conducted with 5–8 key participants, both men and women, ranging in age from 35 to 60 years old. The participants were observed particularly in order to gain insights into the impact of climate hazards on agriculture, especially of soil erosion on specific plots of land, and also to determine what the effects of this were on their livelihoods. This aspect was instrumental in gaining an understanding of the practices of IK in their agricultural systems.
2.2.2. The USLE Calculation
The USLE was developed by Wischmeier and Smith in the year of 1978 [46]. The initial purpose of this equation was to measure the average soil loss per year for gentle terrain [47,48]. Recently, the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) has been developed and applied with similar structure of the USLE, but contains some improvements of input factors based on an updated database in the United States (US) [49]. For example, the data from more than 1000 locations were analyzed to calculate the rainfall erosivity. These modifications are useful to help the accuracy of the model in the US, but not for other regions in the world like Vietnam [9]. The USLE is expressed by Equation (1):
where A is the average soil loss (t/ha/year); R is rainfall erosivity (MJ·mm/ha·h·year); K is the soil erodibility factor (t·h/MJ·mm); LS is the topographic factor (unitless); C is the cropping management factor (unitless); P is the practice support factor (unitless).
Rainfall Erosivity (R)
There are many models that use rainfall data to calculate the rainfall erosivity factor [50], most of them are in relation to annual rainfall as the input data for R calculation [51,52]. Because of the lack of available rainfall intensity data as well as the unique characteristic of each eco-region, the formula could be used in different ways [53]. In this research, the R was calculated based on the suggestion (Equation (2)) of Nguyen [54], who conducted research by the observed data of 253 hydrometeorology stations in the entire country over 54 consecutive years. This was used to calculate the rainfall erosivity in relation to the sloped land specifically in the conditions present in Vietnam.
where P is precipitation (mm). The annual rainfall in this study was calculated on the observed measurement of six hydrometeorology stations around the research site with the shortest and longest distances to the center of Song Kon commune being 13 km and 27 km respectively. The data of rainfall were collected in the period from 2008 to 2018. The map of R factor was obtained by inverse distancing weight (IDW) interpolation method using ArcGIS 10.2.
Erodibility Factor (K)
Soil texture and soil organic matter content are often used for the measurement of the K factor [55,56]. The information needed to acquire these soil indicators is dependent on K identification. As a result, K is one of the most challenging factors to determine. In Vietnam, most of the soil erosion researches that have been conducted in the Central region have used the K factor suggested by Nguyen [57]. This research was conducted in Central Vietnam based on soil analysis of a vast area which stretches over 50.000 square kilometers. For the Song Kon commune, there are three soil types: Arenic Acrisols (86% of total area), Ferralic Arcrisols (12%), and Dystric Fluvisols (2%). The soil type was extracted from the soil map (1:100,000) of Quang Nam province which was mapped by Vietnam National Institute of Agricultural Planning and Projection (NIAPP) in 2005 [58], and its K value is presented by Table 1.

Table 1.
K factor and soil type in research site.
Topographic Factor (LS)
In Central Vietnam, the topography is the most significant feature to have impact on the soil erosion rate [9]. The topographic factor is combined with the impact of slope length (L) and slope steepness (S) to determine the rate of soil erosion. Most of the research [9,12] measured the LS factor by using the formula proposed by Moore and Wilson [59] or Mitasova and Mista [60]. In addition, the use the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in Geographical Information Systems (GIS) is a popular approach to enable researchers to calculate the LS factor [61]. Moreover, the resolution of DEM data has influenced the accuracy of LS value, especially in the complex terrain regions [62,63]. The flow direction algorithm is also an effective tool in determining the LS value [64,65]. Given the necessity of these determining factors, we can conclude that the LS is a sensitive aspect of soil loss prediction by the USLE model [66]. The LS factor is usually limited to a maximum slope angle by 26.6 degrees [67]. Many researchers have proposed a variety of algorithms to overcome this limitation [68,69]. For example, a recent research [61] has suggested that the formula to calculate L (Equation (3)) which was proposed by Desmet and Govers [70] is appropriate for landscape-scale soil erosion modeling and can capture complex topography.
where is the contributing area at the inlet of the grid cell (i,j) measured in m2; is the grid cell size in meters; is equal to whereas is the aspect direction of the grid cell (i,j); is related to the ratio β of the rill to interill erosion. It is calculated by Equations (4) and (5).
In accounting for S factor, the research method of Nearing [68] suggests a continuous logistic function (Equation (6)) to estimate the S in the upland area.
where is slope angle in degrees.
Cropping Management Factor (C)
This factor depends on the type of crop and the duration of growth, however growing conditions tend to change locally, and the harvesting time is unpredictable [71,72], therefore it is a difficult factor to measure. Considering this, to determine the C factor it is helpful to reference studies that have reported values for similar land cover [49]. Also, remote sensing data are able to provide information on environmental covariates to predict the C. This helps to avoid the time and cost for investigation in the field [73]. In addition, NDVI which is gathered from satellite imagery, is a common indicator of the C factor calculation [74,75]. For the tropical regions, Durigon et al. [76] developed an equation for obtaining the C-factor by using NDVI. It was applied in this research as Equations (7) and (8).
where
In the case, NIR is the surface spectral reflectance in the near-infrared band and RED is the surface spectral reflectance in the red band. NIR and RED were extracted from Landsat 8-Operational Land Imager (OLI) images which were downloaded from the website of the US Geological Survey (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov). The information of images data are described in Table 2.

Table 2.
The Landsat 8-OLI images information.
Practice Support Factor (P)
In the USLE equation, the P factor is used to assess the effectiveness of farming methods, which reflects the effect of practices to protect and limit soil erosion. The values for the P factor are the least reliable in comparison to other factors of the USLE equation [59,77]. As a result, some researchers often skip this factor and assigned it a value of 1 [11,78]. However, a number of studies have reported that P factors can be determined based on remote sensing data or previous studies [49,61]. Some studies used slope classification as a source to calculate p-value [79], while others used the land use type [80] as an identified indicator for p-value. In this research, in order to get the most accurate calculation for the P factor, we used a combination of land-use type extracted from a land-use map, and slope degree based on DEM data [81]. This approach has also been used in previous research [9] done in Central Vietnam (Table 3).

Table 3.
p-Value based on slope and land use type.
2.2.3. Data Analysis
The data from the interviews was collected, synthesized, and analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS), version 22 which was widely used in the social and behavioral sciences [82]. Among the factors of the USLE model, only C and P are related to the farming systems. The P factor was calculated based on the land use type and slope of the given land area (Table 3). When we focus on a specific type of land use in the same terrain and soil type, the influence of P factor to soil erosion rate between these locations can be omitted. In this case, we consider that only the C factor has an impact on the soil erosion rate when the land is used in the same way on similar slope degrees. Since acacia is the most popular tree on the research site, we chose acacia land use in order to compare the impact of different farming system on the soil erosion rate (Figure 2).
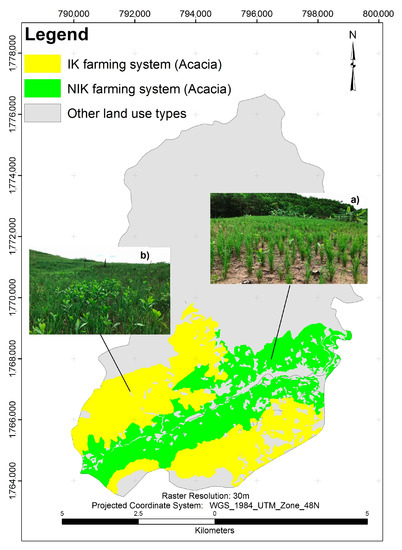
Figure 2.
The indigenous knowledge (IK) farming system (a); and non-indigenous knowledge (NIK) farming system (b).
In terms of NIK methods, farmers cultivate acacia according to technical instructions including density, quantity, distancing, etc. These farmers often buy acacia seedlings from nurseries and use indirect transplanting with a density of 2500 to 3000 trees per hectare (Figure 2a). In contrast, the IK is used in acacia fields by applying two methods of acacia cultivation without following technical instructions. One is that they sow acacia seeds that are collected and stored from the previous crop, directly on the field. They also use the natural deciduous tree seed of old acacia trees, so that it is accustomed to growing naturally in the same fields of cultivation. In this farming system, local people often use about 700 g of acacia seeds per hectare. The number of acacia seeds varies from 6600 to 11,600 per kilogram [83]. As a result, the number of acacia seeds that are used fluctuates from 4500 to 8000 per hectare (Figure 2b). Farmers reported that not all households used the IK method. This depends on three main factors. The first is the location of the acacia field, that being its accessibility from the main road (over 500 m). The second is the complexity of the sloping of the terrain. The third factor is dependent upon the individual experience of each farming household. Older and more agriculturally experienced farmers traditionally apply the IK as opposed to their younger counterparts.
We used the participatory GIS method in the FGDs. By this method, indigenous people’s capacity for accurate spatial perception is factored into the digital map systems in order to identify the different farming systems within a given area. We invited 6–8 participants, who were the most knowledgeable on the subject within their communities to participate in this aspect. Through this, we were able to determine the exact areas where acacia planting was done by indigenous farming systems as opposed to more modern farming systems. This was based on maps drawn by the participants themselves. Then the C factor values of these areas were extracted from the C map (Figure 3e) and compared at a confidence level of 95% (p < 0.05). In total, a mean of 13,719 values of C factors relating to NIK farming system and 16,563 values in IK farming system areas were compared by t-test [84]. Moreover, the EVI was used to describe the difference of surface cover between IK and NIK farming systems. The EVI was calculated based on the Landsat 8 images by Equation (9) suggested by USGS [85].
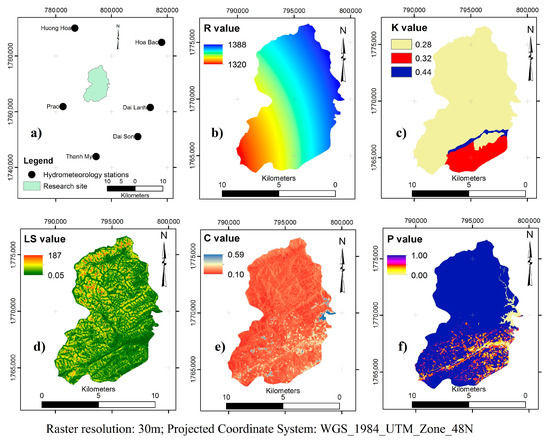
Figure 3.
The component factors of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) in Song Kon commune: (a) Location of hydrometeology stations, (b) R factor, (c) K factor, (d) LS factor, (e) C factor, and (f) P factor.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Erosion within the Research Site
The R factor map was obtained from six hydrometeorology stations around of research site (Figure 3a). The difference of R factor between the locations in the research site is very small, only 3% when comparing the highest and lowest value of this factor within the research site. The lowest value (1320 MJ·mm/ha·h·year) belongs to the Southwest part, while the highest value (1387 MJ·mm/ha·h·year) located in the Northeast corner of the commune. The R factor is shown in Figure 3b.
The K value of soil within the region of the commune fluctuated from 0.28 to 0.44 and is shown in Figure 3c. The Arenic Arcrisols have the lowest K value meanwhile the Dystric Fluvisols have the highest value. The K value of Ferralic Acrisols is 0.32.
The slope of the research site ranged from zero to over 54 degrees with a mean of 21 degrees. As a result, the topographic factor of the research site is a very complicated aspect, and has high LS value. The highest LS value is concentrated in the Northern part of commune where land use is the natural forest of Bach Ma National Park (BMNP). This factor leads to a very heavy rain flow rate and makes the soil erosion more serious. The LS factor is described in Figure 3d.
The results show that the C factor of the research site ranged from 0.01 to 0.59 (Figure 3e). The forest areas have the lowest C value, which means that these areas were deficient in preventing soil erosion. A serial Landsat 8 images in the year of 2019 was downloaded and then adjusted atmospherically and radiometrically to calculate the mean of NDVI, which was then used to measure the C factor. The results indicated that the C factor values of IK farming systems are lower than NIK (in acacia planting areas) significantly at the confidence level of 95% (p-value < 0.05). The comparison is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
The difference of C value between IK and NIK farming systems in acacia planting areas.
The P factor was created based on the slope map and land use map of Song Kon commune, which was mapped in 2017 and updated in 2019 by Natural Resource and Environment Department of Dong Giang district [40]. In the area where the p-value is up to 1 it is indicated that the soil erosion process in these areas occurs naturally without any protection measures. The P factor is shown in Figure 3f.
The soil erosion rate map is described in Figure 4. This map showed that the lowest soil erosion rate of the Song Kon commune is located in the narrow valley that stretches across the region from the East to the West. The main land use types within the valley are both agricultural and residential areas. In general, the degrees of sloping are not too extreme compared with other areas of the commune. The rate of soil erosion among many specific locations within the commune tends to have a large variation given the terrain conditions. But it is significant that there is an extremely high rate of soil erosion in the most northerly part.
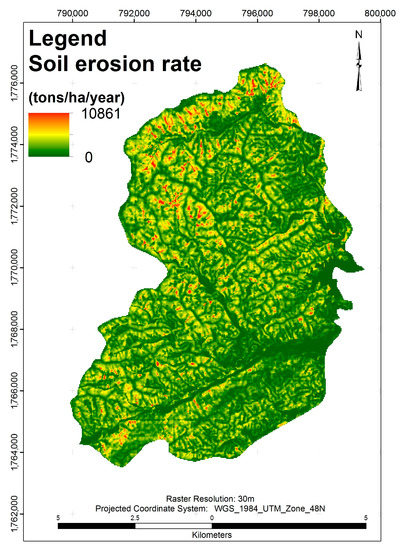
Figure 4.
Soil erosion rate using USLE model in Song Kon commune.
We conducted a comparison of the soil erosion rate within the locations where IK and NIK farming systems were applied. We selected points at the same slope degree (4 levels) and with the same soil type (only Ferralic Arcrisols) for both systems. This was done to synthesize the factors that contribute to the rate of soil erosion. The results showed that the soil erosion rate of IK farming systems is significantly lower than those of NIK farming systems, p < 0.05 (Table 5).

Table 5.
A comparison of soil erosion rate between IK and NIK farming systems.
When the EVI (Figure 5) of the IK and NIK farming systems were compared, it showed that the vegetation cover of IK areas was significantly higher than that of the NIK farming areas. This difference is showed by the histogram which was created based on the EVI value of IK and NIK via Rstudio software (Figure 6).
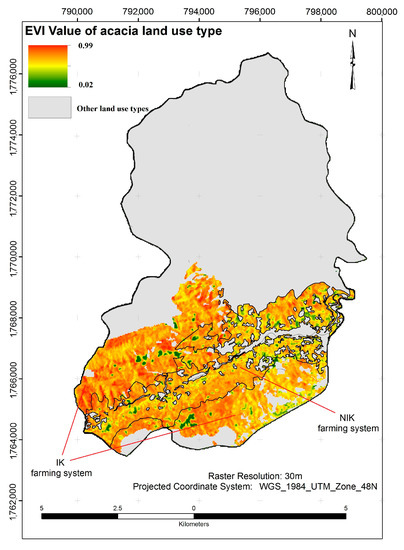
Figure 5.
The Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) map of IK and NIK farming system areas.
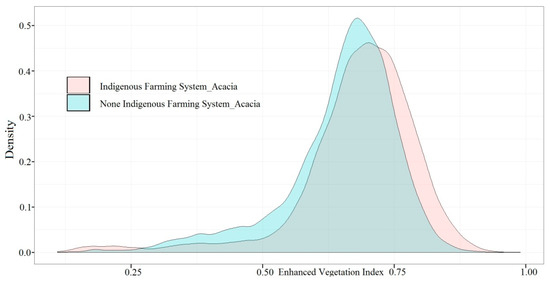
Figure 6.
The comparison of EVI between IK and NIK farming systems.
3.2. Understanding Local Farming Systems in the Case Study
3.2.1. Social-Economic Background of Respondents
A survey was designed to gather basic socio-economic data concerning the inhabitants of the Song Kon commune. The results of which are presented in Table 6. Based on a review of their experiences, three main findings include: first, all households are ethnic minorities (100%) and their main incomes are reliant upon agricultural and forestry practices (81.26%). There are two local varieties of dry rice cultivated. In addition, wet rice, cassava, and a variety of vegetables are popular as crops in this study area. According to our “in-depth-interviews,” around 30% of the agricultural land could not be cultivated in the Winter-Spring season in 2019 because of an increase drought. They are also highly vulnerable to the risk of soil erosion, which frequently occurs in the hilly regions. As a result, yield loss of wet rice happens quite predominantly. The seasonal calendar is shown in detail in Figure 7. Second, the level of education is low with 42.86% of household heads lacking even primary school education, 15.48% of them have no academic education whatsoever. A contributing factor to this aspect is that the poorer households occupy approximately 26.19% of our total samples. Third, a high proportion of males (69.04%) within the household provided the answers for our interview. This is due to the gender divisions within their culture, where the men are the ones who stay at home to care for their children, and who most often drink alcohol during this time, while women were hired laborers. These communities have low levels of education while also lacking proper clothing, and healthcare services, which is mainly due to the remoteness of their locations and the lack of financial assistance to establish the necessary infrastructures. In this, however, there are also some discrepancies in the cultural lifestyles of the people that create some obstacles in improving their situation.

Table 6.
Social-economic background of respondents.
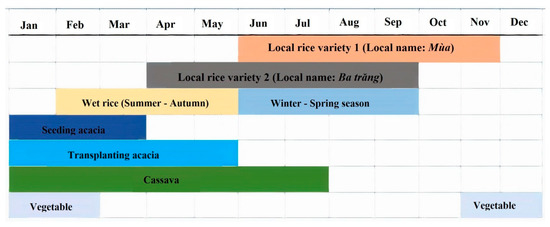
Figure 7.
Adjusting the seasonal calendar.
In Vietnam, the local government is the one who ostensibly holds the responsibility for agricultural development and crop management for whole communes. However, in the minor ethnic communities, they often do not follow the plans recommended by the local authorities. In fact, the development of agriculture is highly dependent on the decisions of each household. These farmers make their decisions based on a combination of their social experience and their economic conditions. The annual seasonal agricultural production calendar can vary markedly from area to area. Generally, within our study group, they have a practice of cultivating wet rice two times per year, most of the respondents often use two local rice varieties as a way in which to adapt to local natural conditions. In particular, these two types of rice are also grown in two different ways and at different times. The first rice variety (mùa) is planted in June and harvested at the end of November. Meanwhile, the second variety (ba trăng) is cultivated and harvested one month earlier than the first rice variety. Regarding acacia cultivation, they also have two different cultivation methods at different times. The first type of acacia cultivation is planted by seed at the end of March, after weeding and cleaning the fields in January and February. In contrast, the second type of acacia cultivation is grown by the transplanting method. This happens at the end of May and takes up to 4 months before weeding, and cleaning of the fields is done. A technique of burning is also used in this process. These agricultural practices are derived from the farmer’s experience and knowledge.
In the past 10 years, based on their observation in many years on changes of top soil layers, out of the 84 respondents, 64.28% experienced a decrease in the frequency of soil erosion, with 15.46% who experienced a significant decrease. Less than 5% of the respondents did not experience an annual increase in soil erosion events and 13/84 of respondents did not notice a change in the frequency of erosion. However, it is worth noting that while most farmers agreed that soil erosion is on a declining trend, they stated that the impact of soil erosion seems to be more severe than previously, as was corroborated by 32.14% and 14.28% of households who agreed that soil erosion intensity had increased and those in later the percentile had noted extreme increases. They also stated that the impact of soil erosion in NIK farming system areas on top soil layer is more serious than those in comparison to IK farming system.
3.2.2. Adaptation Strategies in Responding to Climate Change
Farmers mentioned several private AMs as their current responses toward perceived soil erosion. We selected a variety of these, both at the household level and at the community level. When AMs were identified in the interview process, we then asked the farmers to highlight which measures they were using and subsequently we recorded their explanations. Based on results from FGDs and in-depth interviews, these were grouped into four categories: (1) adjusting planting calendars, (2) adjusting planting techniques, (3) using native varieties, and (4) diversifying crops and varieties (see Table 7 for details).

Table 7.
Private adaptation measures (AMs) used in the farming system.
The farmers in our sample were able to plausibly justify their adaptive responses. For instance, to avoid storms and flood seasons (October and November), they use native rice variety “ba trăng” with shortened growing seasons and earlier harvesting of cassava and wet rice. In addition, local rice varieties were intercropped with acacia during the early stages of acacia growth. They use the rice variety of “ba trăng” when intercrop with the seed-planting of acacia at the same time (end of March). The planting of “mùa” rice variety is combined with transplanting of acacia in the same fields, but at different times. Normally, acacia trees will be transplanted in May, then farmers will sow rice seeds “mùa” when intercropping with acacia fields after a two-week periods. In the past, farmers produced local rice in one season annually as a system of monoculture; and subsequently the land would be left for periods of time to allow for soil rejuvenation. Later, during the relaxed time after harvesting the rice, farmers started growing maize and cassava to prevent soil erosion caused by heavy rain. However, this method was inefficient because of low yield and because of the duration of time that was required. Subsequently, some farmers adopted acacia intercropping with local rice during the early growth of acacia. In this way, they have been able to expand the acacia area because the mono-rice fields have been replaced with acacia fields. However, they can still produce rice to meet their daily needs. This approach was an initiative of the “Co Tu” ethnic minority people that began around 10 years ago. In addition, a new finding in the study area is that the “Co Tu” people do not use any pesticides or fertilizers, even organic fertilizers such as cow manure. There are two reasons for this, the first relates to their agricultural culture, where they consider rain itself to be a sufficient fertilizer, the second reason is because of the lack of economic resources. Because of the fact that most households have a low collective income, their financial resources are used up in everyday concerns of shelter and survival, namely that of buying daily food. Hence, there is very little money left for investing in agricultural production.
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Erosion Risk and Indigenous Farming System
The soil erosion rate in the research area at each location is very different. This can be explained by the specific terrain and land use type. Our findings indicate that the areas where natural forests are the dominant land cover, soil erosion rates are greater and more serious. As has been noted by some previous research concerning the same natural conditions [9], the grade of slope length is considered to be the main reason for an increased rate of soil erosion in the natural forest. This also has to do with the degradation of these forested areas. The overlapping result of the land use map and the map showing the ratio of sloping indicates that the average slope in the natural forest is 24°. By comparison, the average sloping of cultivated acacia areas and other agricultural land-use areas are 20° and 17°. In relation to other studies in Vietnam [9,86], the slope of our research site is significantly higher. It could be considered to be the main reason why there is dramatically high rate of soil erosion. DEMs with different resolutions and accuracies can generate varied topographic and hydrological features, which can, in turn, affect predictions by soil erosion models. Some researchers [87,88] stated that the LS value grew with the increase of the resolution of DEM data. Another research [89] made a comparison in the changes of LS factor with some DEM resolution from 0.5 m to 100 m and found that the LS with DEM resolution of 30 m is the highest. Our research used the DEM of 30 m. This source could be considered biased in leading to the inference of a very high soil erosion rate.
Our findings indicated that the C factor values of IK farming systems are significantly lower than those of NIK at the confidence level of 95% (p-value < 0.05) (Table 4). This showed that the IK farming systems can prevent soil erosion rates more effectively than NIK (Table 5).
One other benefit of IK farming systems is that when growing acacia, the planting of seeds directly, or with the use of regenerated seeds, other trees and plants species are able to coexist within the naturally acacia plantation. This method leads to a greater health and resilience of that planting area because of increased biodiversity. By contrast, using the method of transplanting seedlings, the farmers are required to initially clear the land of all other species. That form of “clear-cutting” results in imbalances within the ecosystem and reduces the symbiotic health of the area. As a result, the biodiversity of the area where IK farming systems has been applied is more abundant and influences an increased quality of vegetation than in NIK-farmed areas. It may be noted that our findings coincided with other such studies on biodiversity and indigenous farming systems [90,91,92]. The variety of species thus will have an anti-erosion effect through the mechanisms that alter rainfall properties [93].
Another consideration is that, the density of acacia plantations by IK and NIK also contributes to the different influences of the C factor on the soil erosion rate. We found that the acacia plantations that are planted with IK method are denser than those areas that were sown with NIK method.
The importance of plant cover in controlling water erosion is widely accepted [94]. The planting calendar also has an effect on soil erosion rates [95]. For the IK method, local farmers often sow the seeds right after harvesting which maintains some holding mechanism for the soil. In contrast, using the transplanting method for acacia, the land is laid bare for months at a time, which increases the conditions by which the soil will erode. This negative factor is also increased by the burning of previous plant covers, clearing the grasses, and the digging of holes. Another point in favor of IK methods is that the acacia planted by seed have life cycles longer than that of the NIK farming system by one to two years. As a result, the land where acacia is planted by seed has better land surface cover, and less soil erosion, than the NIK farming system.
4.2. From Perception to Adaptive Measures Regarding the Soil Erosion Risk
Although the populations of these mountainous areas are impoverished and significantly lacking in opportunities for formal mainstream education, our findings showed that these farmers are highly aware of soil erosion and of how they can deal with the negative impacts of climate change on their agricultural practices. Indeed, the awareness of soil erosion and its impacts has positively influenced the adoption of AMs within the local agriculture. This is consistent with the numerous earlier studies regarding the interplay between local perception and AMs in agricultural techniques not only in Vietnam [21,34], but also such countries as Tanzania [96], Thailand [97], Canada, the USA, Australia, and New Zealand [98]. Our findings indicated that most of the farmers are already adapting quite extensively to these new environmental concerns by using their innate instinctual capacity to implement cultural initiatives. It has been previously shown that they cannot hope to rely on outside sources which will to help them cope with these climatic effects upon their land. Despite government incentives suggesting the production of hybrid crops including maize and rice, many native varieties continue to be cultivated in these areas. Native rice as well as other native crops are well-known to “Co Tu” farmers, these crops also thrive under local conditions, and continue to match dietary preferences. This is consistent with numerous earlier studies, for example, in describing the IK of the ethnic minorities in North Vietnam. Son et al. [21] concluded that farmers do not have to rely on government guidelines which may not be appropriate to the complex topography and diverse microclimates of mountainous regions. Similarly, a survey of another study in Mekong delta, Vietnam claimed that agricultural extension programs and education geared toward a specific area may not be appropriate in other areas of the country [34].
Our findings indicated that most of the farmer’s adaptive strategies are derived from their culture, especially the cultural considerations regarding agricultural production. For example, it is traditional for these farmers not to use any pesticides or fertilizers on their farmlands. Similarly, despite being opposed by local authorities, these farmers continue to apply local rice varieties as an important adaptation method of their own. The local people recognized the advantages of crop combinations, such as acacia with local rice, in terms of improved incomes and reduction of soil erosion as well as helping to stop the general degradation of their soil. The cultivation of rice yield quick returns, providing income within 6 months of planting (from April to September and from June to November in case of “ba trăng” and “mùa” respectively). On the other hand, a financial income derived from the planting of acacia does not manifest until 5 years or longer after planting, and this is dependent upon the conditions of fields in which they are planted. Local cultural beliefs and practices are an essential element in understanding the motivations behind the people’s responses to soil erosion and soil degradation [99]. Many farmers indicate strong concerns related to their ability to learn from other farmers, adhering to a kind of communal knowledge, as it were. So AMs are applied in relation to their familiarity with local knowledge and group experience of the geographical features of their environment [100]. A strong social network is a prominent feature of the “Co Tu” people, and it helps them in their cultural survival. The farmers’ willingness to adapt and to diversify adaptation strategies is implemented largely because of the quality of their social networks and social communication [96]. One of our survey results indicated that 15.48% of respondents did not receive any formal education from outside their communities. It showed that their agricultural knowledge is based on their strong social cohesion.
The provision of tailor-made courses and training, as well as the mediated communication between peers, friends, neighbors, cooperatives, etc., will increase social learning and will strengthen the people’s resilience and capacity to adapt [100]. It is also important to consider that agricultural adaptation does not only depend on making changes in agronomic practices and attitudes, but also on supportive functions provided by other farm enterprises and institutions both at micro and macro levels [101]. These institutions including local government, non-governmental organizations, and universities not only play an essential part in improving the capacity of these local communities, but they also play a key role in eliminating the obstacles to farming adaptation practices [102]. To achieve these goals, it is required for the local government bodies to organize training courses around these adaptation measures (i.e., cultivation techniques, breeding techniques), and this is also where government extension officers play such an important part. It is necessary for government extension officers to communicate more often with local farmers. Considered within the purpose and function of these extension officers, is the need to put a strong emphasis on fostering good relationships with these indigenous peoples, which will result in increased trust among all parties. Further efforts to integrate local adaptation strategies within local and district government policy will increase the adaptive capacity of the local people, while also contributing to the wider sustainable development goals of the region [100]. According to Pham et al. [99] to facilitate scientific applications in farming activities that include the implementation of innovative farming methods, extension officers are considered to be the connecting link between the scientific community and farmers. However, a word of caution is needed here, that it is necessary for these relationships to be reciprocal between all the various parties involved. It requires a balance in listening, and a respect of different forms of knowledge [100,103]. Different cultural groups will act differently to the severe impacts of modern changes in climate, even within the same geographical region [104]. Here it is matter of achieving a balance between IK and modern scientific techniques. In these times of extreme climatic change, it is also necessary for young researchers and technical professionals to develop good monitoring systems. This can aid in the dissemination of appropriate farming techniques among the different ethnic groups. With increased research and monitoring new ways can be introduced to improve yields, to improve market access, and thus to improve family incomes. Appropriate local knowledge can be brought into the design of soil erosion prevention projects with the farmer’s full participation in planning, implementing, and maintaining conservation measures [105]. In improving the success of adaptation strategies in agriculture, motivating the farmers to do so is a primary consideration [104].
5. Conclusions
The combination of USLE model with GIS and remote sensing is a suitable approach for soil erosion estimation, especially in the area where ground-based observation is difficult. The spatial distribution of different erosion prone areas can be easily identified based on the selection functions of GIS. Moreover, the USLE with five factors and GIS tools will help land users to determine the main causes of soil erosion on their land and from that they will have the most effective response measures.
IK farming systems are effective in the prevention of soil erosion rates through the improvement of land surface cover. The AMs used in IK-based farming systems include the cultivation of biodiversity, the consideration planting density, and the ongoing modification of the annual planting. All of these factors have a significant impact on the vegetation index. The resulting C factor of IK farming systems is significantly higher than the NIK farming system.
From the above insights, this study brings to light some aspects that should be included in future agricultural policies for this region. These future policies should not only focus on technical aspects, but also on the social dimensions of the area. A vital part of this is to include the perceptions and experience of smallholder farmers in the design and implementation of future agricultural projects. This also infers the participation of local people in managing soil erosion. There are some historic barriers to overcome, but conscientious collaboration is essential in order to achieve good stewardship of the agricultural land that is specific to each individual area. Our study found that while most farmers have previous knowledge and experience that is relevant in the prevention of serious soil erosion, other members of the community have very little awareness of this. There are socio-economic factors and resource constraints in applying AMs, but also there are psychological factors within the local culture that need to be further considered in regard to how they might enhance or impede the adaptation process. We support the views that there should be a combination of local knowledge and the introduction of new scientific technologies in order to deal with these concerns in the most effective way. In order to achieve this, attention should be given to improving the co-operative communication between scientists, public officials, and the local indigenous people.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.V.H., T.G.P., T.Q.N., L.H.K.N., P.T.T., Q.N.P.L., and M.T.H.N.; methodology, C.V.H., T.G.P., and T.Q.N.; software, T.G.P., L.H.K.N., and P.T.T.; validation, C.V.H. and T.G.P.; investigation, C.V.H., T.G.P., T.Q.N., L.H.K.N., P.T.T., Q.N.P.L., and M.T.H.N.; resources, L.H.K.N., P.T.T., Q.N.P.L., and M.T.H.N.; data curation, C.V.H., T.G.P., and T.Q.N.; writing—original draft preparation, C.V.H., T.G.P., and T.Q.N.; writing—review and editing, C.V.H., T.G.P., T.Q.N., and L.H.K.N.; visualization, T.G.P.; supervision, C.V.H.; project administration, C.V.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam; grant number B2019-DHH-02.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam for their financial support. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which greatly improved our paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jarraud, M.; Steiner, A. Summary for Policymakers, 1st ed.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 9781107025, ISBN 9781139177245. [Google Scholar]
- Bruun, O. Sending the right bill to the right people: Climate change, environmental degradation, and social vulnerabilities in Central Vietnam. Weather Clim. Soc. 2012, 4, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Laplante, B.; Meisner, C.; Wheeler, D.; Yan, J. (Eds.) The Impact of Sea Level Rise on Developing Countries: A Comparative Analysis; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R. Community-based climate change adaptation in Vietnam: Inter-linkages of environment, disaster, and human security. In Multiple Dimension of Global Environmental Changes; Sonak, S., Ed.; TERI Publication: New Delhi, India, 2006; pp. 521–547. [Google Scholar]
- McElwee, P. The Social Dimensions of Adaptation of Climate Change in Vietnam: The Social Dimensions of Adaptation of Climate Change in Vietnam; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Margaret, W. The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture, Land Resources, Water Resources, and Biodiversity in the United States. Available online: https://www.usda.gov/oce/climate_change/SAP4_3/CCSPFinalReport.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Bautista, R. Agriculture-based development: A SAM perspective on Central Vietnam. Dev. Econ. 2001, 39, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, V.; Fink, A.; Ngo, D.; Trinh, T.; Pinto, J.; Van der Linden, R.; Schubert, D. Observed climate variations and change in Vietnam. In EWATECCOAST: Technologies for Environmental and Water Protection of Coastal Zones in Vietnam. Contributions to 4th International Conference for Environment and Natural Resources, ICENR 2014; Meon, G., Pätsch, M., Phuoc, N., Quan, N., Eds.; Cuvillier-Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.G.; Degener, J.; Kappas, M. Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture in Vietnam. Strengthening Capacities to Enhance Coordinated and Integrated Disaster Risk Reduction Actions and Adaptation to Climate Change in Agriculture in the Northern Mountain Regions of Viet Nam; FAO: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- El Jazouli, A.; Barakat, A.; Ghafiri, A.; El Moutaki, S.; Ettaqy, A.; Khellouk, R. Soil erosion modeled with USLE, GIS, and remote sensing: A case study of Ikkour watershed in Middle Atlas (Morocco). Geosci. Lett. 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelagay, H.S.; Minale, A.S. Soil loss estimation using GIS and Remote sensing techniques: A case of Koga watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Soares, D.; Cunha, M. Assessing soil erosion risk using RUSLE through a GIS open source desktop and web application. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Risse, L.M.; Nearing, M.A. Nearing evaluation of WEPP and its comparison with USLE and RUSLE. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Kumar, U. Integrated approach of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil loss risk assessment in Upper South Koel Basin, Jharkhand. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Koubouris, G.C.; Karatzas, G.P.; Metzidakis, I. Assessing water erosion in Mediterranean tree crops using GIS techniques and field measurements: The effect of climate change. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.; Woomer, P. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savo, V.; Lepofsky, D.; Benner, J.P.; Kohfeld, K.E.; Bailey, J.; Lertzman, K. Observations of climate change among subsistence-oriented communities around the world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Hoa Sen, L.; Bond, J. Agricultural adaptation to flood in lowland rice production areas of Central Vietnam: Understanding the ‘regenerated rice’ ratoon system. Clim. Dev. 2017, 9, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle, S.; Turner, S. The weather is like the game we play: Coping and adaptation strategies for extreme weather events among ethnic minority groups in upland northern Vietnam. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2016, 57, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.N.; Chi, D.T.L.; Kingsbury, A. Indigenous knowledge and climate change adaptation of ethnic minorities in the mountainous regions of Vietnam: A case study of the Yao people in Bac Kan Province. Agric. Syst. 2019, 176, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.; Shizha, E. Indigenous Knowledge and Learning in Asia/Pacific and Africa, 1st ed.; Kapoor, D., Shizha, E., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan US: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-349-38311-5. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, P. Indigenous Knowledge, Ecology, and Evolutionary Biology (Indigenous Peoples and Politics); Routledge: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-203-84711-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rautela, P.; Karki, B. Weather forecasting: Traditional knowledge of the people of Uttarakhand Himalaya. J. Geogr. Environ. Earth Sci. Int. 2015, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkomwa, E.C.; Joshua, M.K.; Ngongondo, C.; Monjerezi, M.; Chipungu, F. Assessing indigenous knowledge systems and climate change adaptation strategies in agriculture: A case study of Chagaka Village, Chikhwawa, Southern Malawi. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2014, 67–69, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.; Rasmussen, K.; Leisz, S.; Folving, R.; Quang, N.V. The effects of land tenure policy on rural livelihoods and food sufficiency in the upland village of Que, North Central Vietnam. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeyune, V.; Turner, S. Yielding to high yields? Critiquing food security definitions and policy implications for ethnic minority livelihoods in upland Vietnam. Geoforum 2016, 71, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, C. (Ed.) Voices from the Forest: Integrating Indigenous Knowledge Into Sustainable Upland Farming; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781936331840. [Google Scholar]
- Mairura, F.S.; Mugendi, D.N.; Mwanje, J.I.; Ramisch, J.J.; Mbugua, P.K.; Chianu, J.N. Integrating scientific and farmers’ evaluation of soil quality indicators in Central Kenya. Geoderma 2007, 139, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklu, E.; Gezahegn, A. Indigenous knowledge and practices for soil and water management in East Wollega, Ethiopia. In Technological and Institutional Innovations for Sustainable Rural Development: International Research on Food Security, Natural Resource Management and Rural Development; Book of Abstracts; Wollny, C., Deininger, A., Bhandari, N., Maass, B., Manig, W., Muuss, U., Brodbeck, F., Howe, I., Eds.; Georg-August-Universität: Göttingen, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3-9808714-3-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yeshambel, M. Indigenous knowledge practices in soil conservation at Konso People, South Western Ethiopia. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ajibade, L. Indigenous approach to the control of soil erosion among small scale farmers in Asa L.G.A., Kwara State, Nigeria. Ethiop. J. Environ. Stud. Manag. 2008, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudat, B.; Bloemertz, L.; Kuhn, N.J. Local soil quality assessment of north-central Namibia: Integrating farmers’ and technical knowledge. SOIL 2018, 4, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Dang, H.; Li, E.; Nuberg, I.; Bruwer, J. Farmers’ perceived risks of climate change and influencing factors: A study in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, L.T.M.; Stringer, L.C. Multi-scale assessment of social vulnerability to climate change: An empirical study in coastal Vietnam. Clim. Risk Manag. 2018, 20, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- People’s Committee of Dong Giang District. Statistical Annual Report of Dong Giang District; Quangnam Statistical Publishing House: Quangnam, Vietnam, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam Academy of Social Sciences; Ministry of Labour; Invalids and Social Affairs; United Nations Development Programme. Multidimensional Poverty in Vietnam. Reducing Poverty in All Its Dimensions to Ensure a Good Quality Life for All; Ministry of Labour, Invalids and Social Affairs of Vietnam: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2018.
- Ty, P.H. Dilemmas of Hydropower Development in Vietnam: Between Dam-Induced Displacement and Sustainable Development; Eburon: Delft, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 978-90-5972-959-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; van Huynh, C.; Nguyen, H.K.L.; Tran, T.P.; Nguyen, T.H.M.; Pham, G.T.; Le, N.P.Q.; Tran, T.A.T.; van Truong, T. Effectiveness of agriculture-land use of Co Tu ethnic minority in mountainous areas of Quang Nam province. Hue Univ. J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2019, 128, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Natural Resources and Environment Department of Dong Giang District. Land Use Map of Dong Giang District (2017, Update 2019); Dong Giang Statistical Publishing House: Dong Giang District, Vietnam, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, A.L.; Rzotkiewicz, A.; Mwita, E.; Lopez, M.C.; Zwickle, A.; Richardson, R.B. Participatory mapping of environmental resources: A comparison of a Tanzanian pastoral community over time. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvini, G.; Ligtenberg, A.; van Paassen, A.; Bregt, A.K.; Avitabile, V.; Herold, M. REDD+ and climate smart agriculture in landscapes: A case study in Vietnam using companion modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 172, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, R. The origins and practice of participatory rural appraisal. World Dev. 1994, 22, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R. Participatory rural appraisal (PRA): Challenges, potentials and paradigm. World Dev. 1994, 22, 1437–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorothy, G. Participatory methods in community practice. In The Handbook of Community Practice; Weil, M., Reisch, M., Ohmer, M.L., Eds.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 327–343. ISBN 978-1412987851. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.; Smith, D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses. A Guide to Conservation Planning: Agriculture Handbook No.537; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning With Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-16-048938-5.
- Gitas, I.Z.; Douros, K.; Minakou, C.; Silleos, G.N.; Karydas, C.G. Multi-temporal soil erosion risk assessment in N. Chalkidiki using a modified USLE raster model. In Proceedings of the EARSeL 33rd General Assembly and 29th annual Symposium, Chania, Greece, 15–18 June 2009; European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories (EARSeL): Hanover, Germany, 2009; pp. 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.A.; Bryant, R.B.; Schwager, S.J.; Smith, S.D. Predicting rainfall erosivity in Honduras. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, D.; Borselli, L.; Guzzetti, F.; Calzolari, M.C.; Bazzoffi, P.; Ungaro, F.; Bartolini, D.; Salvador Sanchis, M.P. Italy. In Soil Erosion in Europe; Boardman, J., Poesen, J., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 245–261. ISBN 9780470859209. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, C. Evaluation of Relationship Between the RUSLE R Factor and Mean Annual Precipitation. Available online: https://www.engr.colostate.edu/~pierre/ce_old/Projects/linkfiles/Cooper-R-factor-Final.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Nguyen, T. Identify the Factors Effect to Soil Erosion and Forecast Soil Erosion on Slope Land. Ph.D Thesis, Thuy Loi University, Hanoi, Vietnam, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.-S.; Chen, C.-K.; Thomas, K.; Hsu, C.-K.; Ho, H.-C. Improvement of the K-Factor of USLE and soil erosion estimation in Shihmen reservoir watershed. Sustainability 2019, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, V.; Ceddia, M.; Antunes, M.; Carvalho, D.; Anache, J.; Rodrigues, D.; Oliveira, P. USLE K-Factor method selection for a tropical catchment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H. Application Usle and Gis tool to predict soil erosion potential and proposal land cover solutions to reduce soil loss in Tay Nguyen. In Proceedings of the Bridging the Gap Between Cultures: FIG Working Week 2011 & 6th National Congress of ONIGT, Marrakech, Morocco, 18–22 May 2011; International Federation of Surveyors FIG: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vietnam National Institute of Agricultural Planning and Projection. Soil Type Map of Quang Nam Province (Scale 1:500.000); Agricultural Academy Publishing House: Hanoi, Vienam, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.I.; Wilson, P.J. Length slope factor for the revised universal soil loss equation: Simplified method of solution. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 47, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Mitas, L. Multiscale soil erosion simulations for land use management. In Landscape Erosion and Evolution Modeling; Harmon, R.S., Doe, W.W., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 321–347. ISBN 978-1-4615-0575-4. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fohrer, N.; Hörmann, G.; Kiesel, J. Suitability of S factor algorithms for soil loss estimation at gently sloped landscapes. CATENA 2009, 77, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Moore, D.; He, P.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.; Mueller, T.; Rienzi, E.; Neelakantan, S.; Mijatovic, B.; Karathanasis, T.; Rodrigues, M. Terrain Analysis for locating erosion channels: Assessing LiDAR data and flow direction algorithm. In Gully Erosion in Southeastern Nigeria: Role of Soil Properties and Environmental Factors; Godone, D., Ed.; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0839-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bircher, P.; Liniger, H.P.; Prasuhn, V. Comparing different multiple flow algorithms to calculate RUSLE factors of slope length (L) and slope steepness (S) in Switzerland. Geomorphology 2019, 346, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabalíková, M.; Janeček, M. Comparison of different approaches to LS factor calculations based on a measured soil loss under simulated rainfall. Soil Water Res. 2017, 12, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Tresch, S.; Meusburger, K. Modification of the RUSLE slope length and steepness factor (LS-factor) based on rainfall experiments at steep alpine grasslands. MethodsX 2019, 6, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nearing, M.A. A single, continuous function for slope steepness influence on soil loss. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Gai, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. An improved method for calculating slope length (λ) and the LS parameters of the revised universal soil loss equation for large watersheds. Geoderma 2017, 308, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.A.; Jetten, V.; Baffaut, C.; Cerdan, O.; Couturier, A.; Hernandez, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Nichols, M.H.; Nunes, J.P.; Renschler, C.S.; et al. Modeling response of soil erosion and runoff to changes in precipitation and cover. CATENA 2005, 61, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K.T.; Sekiyama, A.; Mihara, M. Determining C factor of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) based on remote sensing. Int. J. Environ. Rural Dev. 2016, 7, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Schönbrodt, S.; Saumer, P.; Behrens, T.; Seeber, C.; Scholten, T. Assessing the USLE crop and management factor C for soil erosion modeling in a large mountainous watershed in Central China. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 21, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-T.; Chou, W.-C. Soil erosion prediction and sediment yield estimation: The Taiwan experience. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 68, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaburun, A.C. Estimation of C factor for soil erosion modeling using NDVI in Buyukcekmece watershed. Ozean J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 3, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Durigon, V.L.; Carvalho, D.F.; Antunes, M.A.H.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Fernandes, M.M. NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.I. Revised universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, M.K.; Das, D. Estimation of sediment yield and areas of soil erosion and deposition for watershed prioritization using GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 2091–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamage, F.; Zhang, C.; Kayiranga, A.; Shao, H.; Fang, X.; Ndayisaba, F.; Nahayo, L.; Mupenzi, C.; Tian, G. USLE-Based Assessment of soil erosion by water in the Nyabarongo river catchment, Rwanda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of land use changes on soil erosion in a fast developing area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G. The Analysis of Soil Erosion Analysis in Watershed Using GIS. Ph.D. Thesis, Gang-won National University, Gangwon-do, Korea, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sabine, L.; Brian, S.E. A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using SPSS; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, P.C.; Cardon, D. Plant Resources for Tropical Africa 3. Dyes and Tannins; Backhuys Publisher: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005; ISBN 90-5782-159-1. [Google Scholar]
- Berkman, E.; Reise, S. One- and two-sample t-tests. In A Conceptual Guide to Statistics Using SPSS; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- USGS Landsat Enhanced Vegetation Index. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/land-resources/nli/landsat/landsat-enhanced-vegetation-index?qt-science_support_page_related_con=0#qt-science_support_page_related_con (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Ho, K. Soil Erosion and Accumulation Evaluation on Some Popular Farming Systems on Steep Land in Huong River Catchment, Thua Thien Hue Province; University of Ha Noi Agriculture: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Penížek, V.; Zádorová, T.; Kodešová, R.; Vaněk, A. Influence of elevation data resolution on spatial prediction of colluvial soils in a Luvisol region. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.R.; George, J.; Raghavendra, S.; Kumar, S.; Agrawal, S. Effect of DEM resolution on LS factor computation. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-5, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Xiaomei, Y.; Lingtong, G.; Viollette, G. Influence of terraced area DEM resolution on RUSLE LS factor. In Proceedings of the Geophysical Research Abstracts, EGU General Assembly 2017, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maitima, J.M.; Mugatha, S.M.; Reid, R.S.; Gachimbi, L.N.; Majule, A.; Lyaruu, H.; Pomery, D.; Mathai, S.; Mugisha, S. The linkages between land use change, land degradation and biodiversity across East Africa. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 310–325. [Google Scholar]
- Baul, T.K.; McDonald, M.A. Agro-biodiversity management: Using indigenous knowledge to cope with climate change in the middle-hills of Nepal. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, G.S. Traditional agriculture: A climate-smart approach for sustainable food production. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 296–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geißler, C.; Nadrowski, K.; Kühn, P.; Baruffol, M.; Bruelheide, H.; Schmid, B.; Scholten, T. Kinetic energy of throughfall in subtropical forests of SE China—Effects of tree canopy structure, functional traits, and biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e49618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Zuazo, V.H.; Rodríguez Pleguezuelo, C.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.H.; Fischer, G.; Antoine, J. Agro-Ecological Land Resources Assessment for Agricultural Development Planning. A Case Study of Kenya Resources Data Base and Land Productivity; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Below, T.B.; Mutabazi, K.D.; Kirschke, D.; Franke, C.; Sieber, S.; Siebert, R.; Tscherning, K. Can farmers’ adaptation to climate change be explained by socio-economic household-level variables? Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereenonchai, S.; Arunrat, N. Practical agricultural communication: Incorporating scientific and indigenous knowledge for climate mitigation. Kasetsart J. Soc. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfer, E.; Ford, J.D.; Maillet, M. Representation of Indigenous peoples in climate change reporting. Clim. Chang. 2017, 145, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.T.T.; Nong, D.; Garschagen, M. Farmers’ decisions to adapt to flash floods and landslides in the Northern Mountainous Regions of Vietnam. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, L.T.H.; Biesbroek, G.R.; Sen, L.T.H.; Wals, A.E.J. Understanding smallholder farmers’ capacity to respond to climate change in a coastal community in Central Vietnam. Clim. Dev. 2018, 10, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyanga, P.H.; Johnsen, F.H.; Aune, J.B.; Kalinda, T.H. Smallholder farmers’ perceptions of climate change and conservation agriculture: Evidence from Zambia. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesbroek, G.R.; Klostermann, J.E.M.; Termeer, C.J.A.M.; Kabat, P. On the nature of barriers to climate change adaptation. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, F. Evolution of co-management: Role of knowledge generation, bridging organizations and social learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N.; Barnett, J.; Brown, K.; Marshall, N.; O’Brien, K. Cultural dimensions of climate change impacts and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, D.K.N.T.; Phuong, L.T.V.; Douglas, I.; Van De, N.; Mcmorrow, J.; Lindley, S.; Van, T.T.; Thanh, L.H.; Tho, N. Local knowledge and economic realities affecting soil erosion in the Rach Rat catchment, Vietnam. Geogr. Res. 2008, 46, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).