Abstract
Copepods dominate marine zooplankton in abundance and play key roles in pelagic food webs. These small crustaceans show high taxonomic and functional diversity. Although there has been considerable research on their taxonomy, only a few studies have focused on their functional traits. In this study, we analyzed the functional traits of 95 copepod species, considering their body size, trophic regime, feeding behavior, and spawning strategy. Based on samples collected during two surveys (autumn 2020 and summer 2021) located in the coastal waters of three gulfs (Gaeta, Naples, and Salerno) in the highly populated Campania region (the central Tyrrhenian Sea, NW Mediterranean), we identified nine functional groups of copepods with different characteristics. The group that comprised herbivorous copepods with feeding currents and a broadcast strategy was the most abundant in both seasons and all gulfs. This group was dominated by Acartia clausi, Centropages typicus, Temora stylifera, and the Paracalanus parvus complex. The other functional groups showed differences in their temporal and spatial distribution. Our study reports the functional diversity of copepods along the Campania coast, thus contributing to advancing our knowledge of the planktonic trophic structure in a region of considerable importance due to its marine resources and services.
1. Introduction
Zooplanktonic communities play a vital role in marine ecosystems [1]. They are mainly represented by copepods, which are the dominant taxonomic group both in terms of their diversity and abundance of individuals [2] and account for more than 80% of the total abundance of mesozooplankton (0.2–2.0 mm) [3]. Copepods represent the key link within pelagic food webs, as they are the main pathway of energy transfer from primary producers to fish [1,4] and contribute substantially to the functioning of the biological pump [5,6]. Furthermore, copepods also show enormous diversity in functional terms: they can obtain food through ambushing, filter feeding, or cruising behavior and can feed on particles and aggregates [7]. Copepods can select their prey based on size [8,9] and motility [10], as well as mechanical and/or chemical cues [11,12]. Since the role of planktonic copepods in the marine ecosystem is influenced by their diversity and phenotypic characteristics [13], studying the functional traits of these organisms is a fundamental step toward understanding the overall ecosystem functioning [14].
Functional traits, defined as phenotypic attributes that shape the physical form of an organism, delineate species based on their physiological functions and the interactions displayed in the abiotic and biotic environment [15]. Functional traits are characteristics that, at the species or organism level, influence their fitness and have been related to survival, feeding, growth, and reproduction [14,16]. Functional traits are useful for categorizing species that show similar traits into certain functional groups (FGs) [17,18]. The categorization approach based on similarity in functional traits rather than taxonomic classification allows diversity to be summarized in distinct and parsimonious groups. These groups have the potential to improve the representation of zooplankton in ecosystem models, as FGs enrich the description of ecological functionality without introducing additional diversity and taxonomic complexity.
Few studies have been conducted on zooplankton functional diversity in marine and estuarine environments (e.g., [19,20]) and in marine plankton ecology [18,21], and most of them are focused on copepods, given their high abundance, as well as great functional and morphological complexity [22]. Several studies, both at the regional and global scales, have used the study of functional traits to group species with similar traits into FGs [17,18] to describe zooplankton diversity [23,24], with the aim of analyzing community responses to environmental disturbances [21,25] or describing marine food webs with a higher level of detail [26,27].
Although functional trait analyses have been carried out in the Mediterranean Sea [21,28], similar studies are still lacking in the Tyrrhenian Sea, which is considered the most oligotrophic region in the western Mediterranean [29]. The coastal areas of the Tyrrhenian Sea have represented globally crucial ecosystems over the last few decades [30,31], but they are constantly exposed to increasing anthropogenic pressures, which have intensified over time [32,33]. One of the areas overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea is Campania, a region with three main gulfs, which are, from north to south, the Gulf of Gaeta, the Gulf of Naples, and the Gulf of Salerno (Figure 1). The entire coast of Campania, and particularly the metropolitan area of Naples, is severely exposed to anthropogenic pressure [34] and extensive agriculture, livestock farming, and industrial activities [35]. In addition, coastal waters may also be subject to natural forcings that act at the seasonal or multi-year scale (e.g., periods of drought/rain), as well as short-term episodic disturbances (e.g., floods, storms) [36]. Monitoring these environments is important for understanding the risks imposed by anthropogenic and natural impacts on coastal marine habitats.
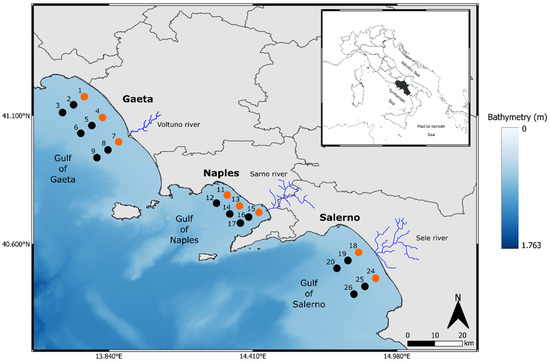
Figure 1.
Study area (Campania region) and sampling stations. Orange circles represent inner shelf stations (<20 m depths), and black circles represent mid shelf stations (50–150 m depths).
In particular, the Gulf of Naples has been extensively studied thanks to the presence of the Long-Term Ecological Research site MareChiara (LTER MC), established in 1984 [37,38] to monitor the physical [39] and chemical [40] characteristics of the water column and the dynamics of plankton [41,42,43]. In contrast, the Gulf of Gaeta and the Gulf of Salerno have received less attention. Studies in the Gulf of Gaeta have primarily focused on assessing the effects of the Garigliano and Volturno river flows on coastal dynamics [44], while studies on both the physical [44] and biological aspects [45] of the Gulf of Salerno are scant [45].
In this study, we present a complete and detailed overview of copepods’ functional traits and of their spatial distribution in the Campania region. Statistical analyses were conducted to define the copepods’ FGs, based on specific biological and ecological information obtained during two oceanographic surveys (autumn 2020 and summer 2021) conducted along the Campania coast. We also discuss the spatial distribution of copepod functional traits considering local environmental conditions, such as trophic resource availability, and inputs from the land. This study aims to contribute to a better understanding and trophic characterization of the pelagic system, while providing important background information for future studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Environmental Data
We carried out two surveys along the Campania coast (central Tyrrhenian Sea, NW Mediterranean Sea) on board R/V Vettoria in the autumn of 2020 (9 September–9 October) and summer 2021 (29 June–15 July). During each survey, we sampled a total of 22 stations among the Gulf of Gaeta (9 stations), the Gulf of Naples (7 stations), and the Gulf of Salerno (6 stations) (Figure 1). The stations were located along transects from the inner (<20 m depth) to mid (50–100 m depth) shelf waters (Table S1).
The three gulfs have different geomorphological characteristics and are influenced by different anthropogenic factors. The Gulf of Gaeta (41°06′ N 13°30′ E) is heavily urbanized, hosts fish and shellfish farms [46,47], and is placed at the mouth of one of the main rivers in southern Italy, i.e., Volturno, which is highly polluted due to discharges from local factories, sewers, and agricultural drains [48]. Volturno River has a seasonal influence on the coasts; in fact, in winter, it manifests a plume oriented more offshore, therefore without interacting with the coastal waters, while in summer, the plume is oriented both north and south of the estuary, influencing the coastal waters [49,50].
The Gulf of Naples (40°44′ N 14°16′ E) is characterized by heavy land runoff from a very densely populated area due to the Sarno River’s outflow, though it is also influenced by typical Tyrrhenian oligotrophic waters due to its bottom topography and general physiography [35,51]. The Sarno River is considered the most polluted river in Europe due to heavy metal contamination from industrial activities along its course [52]. From a physical point of view, the Gulf of Naples [53,54] shows a period of stratification in July–August and a period when the water column is close to completely mixing from December to January, followed by surface re-stratification in February. Similar detailed knowledge about the water stratification processes is not available for the Gulfs of Gaeta or Salerno.
The Gulf of Salerno (40°31′ N 14°42′ E) is characterized by oligotrophic conditions and exposed to the influence of Tyrrhenian waters [45,55]. Here, the Sele River is responsible for transporting pollutants into the sea due to the presence of manufacturing companies from the textile and leather industries and agroindustry along its banks [56,57]. In general, the Gulf of Salerno has been described as a spatially homogeneous system without areas of enrichment, with its coastal influence limited to a restricted inner shelf area [45].
All three gulfs are influenced by upwelling processes, which bring nutrient-rich waters to the surface. Along the Campania coast, these processes occur due to strong winds and the presence, in the Gulf of Gaeta and Naples, of the Cuma Canyon and the Dohrn Canyon, respectively [58,59].
For each sampling site, temperature (°C), salinity (PSU), and turbidity (transmittance) profiles were acquired using a multi-parameter probe (Sea-Bird 911 Plus). In addition, the total chlorophyll a was analyzed at selected depths (0, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 m) using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography analysis (HPLC—Agilent 100, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). These environmental values were integrated into the surface layer (0–10 m) and the deep layer (10 m—zooplankton sampling depth) (Table S1).
2.2. Mesozooplankton Sampling and Analysis
Mesozooplankton samples were collected using vertical hauls from 5 m above the bottom to the surface using a double WP2 net (57 cm Ø, 0.25 m2 mouth area of each net, 200 µm mesh size) equipped with a flowmeter and towed at 0.7–1 m s−1. One of the two samples was used to estimate the mesozooplankton abundance and taxonomic composition, and the other was used to investigate the gelatinous zooplankton taxonomy. We consider here only the first series of the samples, which were transferred from the cod-end into 500 mL plastic jars, gently concentrated on a gauze (100 µm mesh size), and then fixed in ethanol 96% in 100 mL plastic jars.
In the laboratory, each sample was resuspended in a bowl with distilled water to a final volume of 200 mL. The sample was accurately stirred with a graduated pipette, which was also used to collect two aliquots of 5 mL each that were analyzed for zooplankton identification and enumeration under a stereomicroscope (Leica MZ12.5) in a 10 mL Bogorov counting chamber. The rest of the sample was checked to account for the presence of rare species. The taxonomic identification was performed down to the species level whenever possible, following the proper literature (e.g., [60,61,62,63]). The copepods were further identified according to gender and developmental stage (adult females and males, copepodites). To allow for comparison of records collected in water columns of different depths, the abundance was expressed as the number of individuals in a square meter (ind. m−2) (Tables S2 and S3).
2.3. Copepod Functional Traits
Functional traits represent various aspects of copepod ecology related to competition and habitat use. In this work, functional traits were attributed to copepod species based on their (i) mean body length (<1 mm, 1–2 mm, >2 mm), (ii) feeding strategy (FS) (ambush feeding, current feeding, cruise feeding), (iii) spawning strategy (SS) (broadcast spawners, egg sacs), and (iv) trophic regime (TR) (carnivore, omnivore, omnivore–detritivore, and omnivore–herbivore). Transitional groups were established to separate species that, while being technically omnivorous, showed a relative preference for herbivory or detritivory [23]. Information on copepod functional traits was obtained from the literature [18,63,64,65,66] and from the knowledge of experts in the field. Concerning the feeding strategy, three different categories have been considered: the ambush strategy, in which copepods encounter and intercept prey and capture them with active attacks; current feeding, in which copepods are able to generate a feeding current and convey prey to their mouth appendages; cruise feeding, in which copepods navigate through the water, catching individual prey [64].
A binary matrix of functional traits was created including all the recorded taxa, assigning 1 when a trait was present in the specific taxon or conversely 0 when a trait was absent. When it was not possible to allocate specific traits to a copepod species owing to little or no information in the literature, the category NA (Not Assigned) was used (Table S4).
2.4. Data Analysis
A dissimilarity matrix (with Jaccard distance) was calculated based on the binary matrix of functional traits, and then agglomerative hierarchical clustering analysis (Ward’s method) was used to identify different FGs. For this analysis, only feeding strategy, spawning strategy, and trophic regime were considered as traits. The number of FGs was determined by using the K-means values as a cut-off level, and the “Elbow method” was applied [67] to determine the optimal number of FGs.
To test the significance of seasonal and spatial differences in terms of the abundance of functional groups (data transformed by log(x + 1)) and environmental parameters (data normalized), a two-way permutational multivariate analysis (used Hellinger and Euclidian distances for biological and environmental data, respectively) of variance (PERMANOVA, p < 0.05), followed by a pairwise test for significant terms, was performed on three fixed factors: “Season” (two levels: autumn 2020 and summer 2021), “Gulf” (three levels: Gulf of Gaeta, Gulf of Naples, and Gulf of Salerno), and “Distance” (two levels: inner and mid shelf stations). All the analyses were performed and plots generated using the R Studio software v.4.3.2 (‘factoextra’, ‘vegan’, ‘Rstatix’, and ‘tidyverse’ packages) [68].
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables
The environmental conditions, defined by temperature, salinity, turbidity, and chlorophyll a, appeared to be significantly different between the inner and mid shelf stations (p < 0.001) in both seasons. Only during the summer did significant differences emerge among the three gulfs, particularly between the Gulf of Naples and the Gulf of Salerno (p < 0.01).
The overall sea water temperature was not significantly different between the three gulfs (Figure 2). In the Gulf of Salerno, the integrated temperature was significantly higher in autumn as compared to summer, while no significant difference was recorded between seasons in the other gulfs.
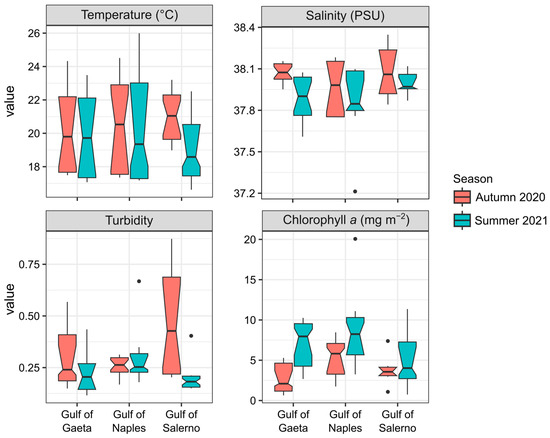
Figure 2.
Box plots showing the depth-integrated values of environmental variables recorded during the autumn (red) and summer (blue) seasons in the three gulfs of the Campania region. The midline indicates the median value, the vertical line represents the minimum and maximum values, and the black dots indicate the outliers.
The lowest values for depth-integrated temperature were recorded in summer in the Gulfs of Salerno (19.1 °C) and Gaeta (19.8 °C), and the highest values in autumn were recorded in the Gulf of Salerno (21 °C) (Figure 2). In both autumn and summer, the average sea surface temperature was higher in the upper 10 m (24.5 ± 0.98 °C and 25.7 ± 1 °C, respectively) than in deeper waters (19.1 ± 2.6 °C in both seasons) (Table S1). Salinity was consistent across regions, with the highest values recorded in the Gulf of Salerno in autumn and the lowest in the Gulf of Gaeta in summer. The seasonal distributions were not significantly different, except for in the Gulf of Gaeta, where the salinity in autumn was significantly higher than that in summer (Figure 2). Turbidity varied between 0.12 and 0.87, with the highest depth-integrated values in the Gulf of Salerno, where turbidity was significantly higher in the autumn (up to 0.48) as compared to the summer (Figure 2). In summer, the surface turbidity was higher in the Gulf of Naples (0.51) than in Gaeta and Salerno (~0.22), while in the deep layers, it was similar in all three gulfs (~0.25) (Table S1). Chlorophyll a peaked in summer (highest concentrations in the Gulf of Naples, 9.1 µg L−1) and was lower in autumn (minimum in the Gulf of Gaeta, 2.9 mg m−2), with significant seasonal differences in the Gulfs of Gaeta and Naples (Figure 2). The chlorophyll a concentration was higher in the Gulf of Naples in both autumn and summer, with surface concentrations of 3.19 mg m−2 in autumn and 6.62 mg m−2 in summer, than in Gaeta and Salerno (<2 mg m−2). Even in the deeper layers, the concentration of chlorophyll a was highest in the Gulf of Naples (5.25 mg m−2 in autumn and 9.07 mg m−2 in summer), while in Gaeta and Salerno, it was around 4.7 mg m−2 (Table S1).
3.2. Copepod Functional Groups
In autumn, the total mesozooplankton abundance was on average 3 × 106 ind. m−2, 52.6% of which was represented by copepods, followed by cladocerans, which were less represented in the Gulfs of Gaeta and Naples (7%) than in the Gulf of Salerno (19%) (Figure 3). Calanoids were overall the most abundant copepod group (on average, 81% of the total copepod abundance), with Temora stylifera being the dominant species, particularly in the Gulf of Naples (3% of total copepod abundance), as opposed to the Gulf of Gaeta and Salerno, where it represented 21% and 13% of the total copepods, respectively. The Paracalanus parvus complex, the second dominant copepod taxon, represented 13% of the total copepod abundance in all three gulfs. In summer, the total mesozooplankton abundance was on average 1.62 × 106 ind. m−2, of which 44.9% was represented by copepods, followed by cladocerans, which, also in this season, were particularly abundant in the Gulf of Salerno (14% of the total zooplankton). In summer, calanoids were the main copepod group (81%) (Figure 3) and were dominated by the Paracalanus parvus complex (22.6%) and Centropages spp. (11.2%), with both taxa present with a relatively similar abundance in all three gulfs (Tables S2 and S3).
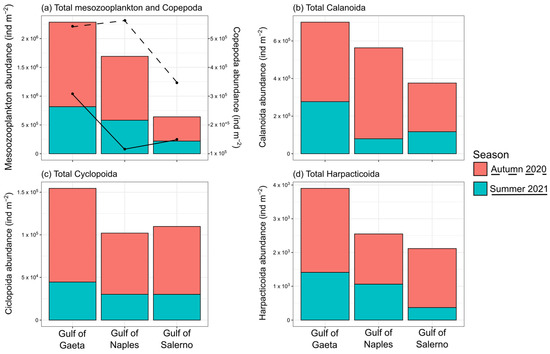
Figure 3.
Bar plot showing the total abundance (ind. m−2) during autumn (in red) and summer (in blue) of mesozooplankton and copepods (a), where the dashed lines refer to the total abundance of copepods in autumn 2020 and the solid lines to summer 2021. (b) Total abundance of Calanoida, (c) Cyclopoida, and (d) Harpacticoida.
We identified nine functional groups (FGs) in the overall copepod assemblage, represented by 95 species (Figure 4). FG1 encompassed the highest number of species and included broadcast, current-feeding taxa, with a tendency toward herbivory. Moreover, this assemblage included different body sizes, among them small (e.g., Calocalanus spp. and Paracalanus spp.) and medium-sized (Acartia spp., Temora stylifera) calanoids. FG2 included medium-sized, cruising, broadcasting species (Scaphocalanus and Scolecitrichidae). FG3 was represented by small (Diaixis pygmaea), medium-sized (Isias clavipes and Pontellidae), and large (Labidocera wollastoni) omnivorous species, which produce feeding currents and have a broadcasting reproductive strategy. FG4 included the cyclopoid family of Corycaeidae, small–medium-sized carnivore species, ambush feeders, and sac-spawners. FG5 grouped all the Oithona species, which are small, omnivorous, ambush-feeding cyclopoids and carry egg sacs. FG6 consisted mainly of large (Haloptilus spp., Heterorhabdus spp.) to medium-sized (Candacia spp.) cruising carnivores with a broadcast reproductive strategy. FG7 grouped small to medium-sized species of the genera Clausocalanus and Macrosetella, which feed by cruising and carry egg sacs. FG8 consisted mainly of large carnivores (e.g., the genus Copilia, members of the family Euchaetidae, and species of the genus Sapphirina), with a cruising feeding strategy and a reproductive strategy using egg sacs. FG9 included small cruising detritivores (Oncaea spp., Microsetella spp.) that use a sac-spawning strategy.
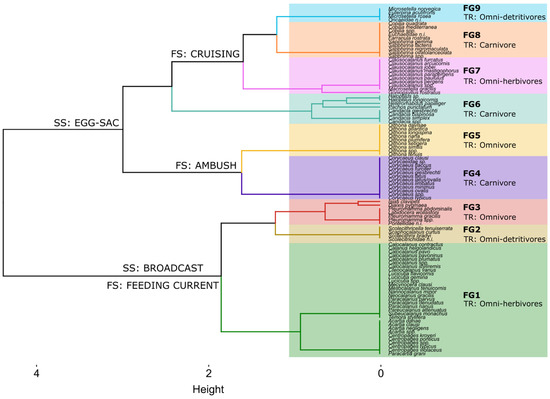
Figure 4.
Functional dendrogram obtained from hierarchical clustering using Ward’s method, showing nine functional groups (FGs) of the 95 analyzed copepod species (FS: Feeding Strategy; TR: Trophic Regime; SS: Spawning Strategy).
The occurrence of copepod FGs differed significantly (p < 0.01) between seasons and between the inner and mid stations. When considering the three gulfs, differences were found in autumn between Gaeta and Salerno (p < 0.001), whereas in summer, they were found between Gaeta and Naples (p < 0.001) and between Naples and Salerno (p < 0.01).
The prevalent group was FG1 (Figure 5a,b), more abundant in summer (69%) than in autumn (54%). In autumn, FG1 was more represented in the Gulfs of Gaeta and Naples (~65% for both) than in Salerno (34%). In summer, FG1 was more represented in the Gulf of Gaeta (83%), while it decreased in the Gulfs of Naples and Salerno (59% and 66%, respectively). In both seasons, FG1 was on average more represented at the inner shelf stations (76%) than at the mid shelf stations (62%). In autumn, the second most represented group was FG7, particularly abundant in the Gulf of Salerno (41%) as compared with Gaeta (15%) and Naples (21%), with an even distribution from the inner shelf to mid shelf stations (~23%). In summer, FG7 was poorly represented (7%). The third group in ranked order of relative abundance was FG5, which showed a similar percentage during both the summer and autumn (~12%) and higher relative abundance at the mid shelf (13%) than at the inner shelf (7%) stations. In autumn, FG5 was more represented in the Gulfs of Gaeta and Naples (16% and 12%, respectively) than in Salerno (7%), whereas in summer, it accounted for similar percentages (~13%) in the three gulfs. The other functional groups (FGs 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 9) were poorly represented in the three gulfs in both seasons, as they overall accounted for less than 5% of the total mesozooplankton abundance (Figure 5a,b and Table S5).
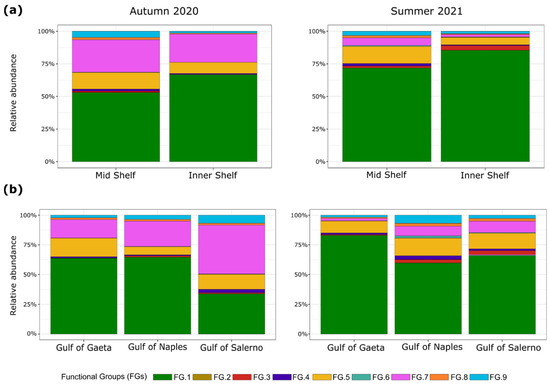
Figure 5.
Bar plots of the relative abundance (%) of nine functional groups (FGs) found through cluster analysis, during the autumn and summer seasons at the mid and inner shelf stations (a) and in the three gulfs (b).
4. Discussion
This study presents the functional traits of copepods along the Campania coast, allowing for a better understanding of the patterns of the variability in and functioning of zooplankton communities in an important Mediterranean region. Our results identified nine different functional groups, which differed in their spawning and feeding strategies and trophic habits. These groups have consistently been found in other studies conducted at both the regional [18,28] and global scales [17,19,65].
Overall, we observed that the spawning strategy, represented by egg sac and broadcast spawners, was the trait distinguishing the two main copepod assemblages characterizing the Campania coast (Figure 2). Carrying egg sacs is considered an energetic strategy that reduces egg mortality, at the expense of individual fecundity and hatching rate, while egg broadcasting is a form of adaptation to protect the eggs [69]. Broadcast spawners are mostly calanoid copepods, while cyclopoids and harpacticoids mainly carry egg sacs, employing cruising and ambush feeding strategies.
Ambush feeding is frequently observed in small copepods, whereas it is less common in larger species, which tend to acquire food while cruising, probably due to differences in metabolic requirements linked to body size [70]. Ambush feeders encounter prey passively and require less energy than cruising predators, who must actively search for prey [7]; this strategy reduces metabolic costs and predation risk, although at the expense of feeding efficiency [64,71].
Our results showed that both summer and autumn were dominated by omni–herbivorous copepods, i.e., FG1. The species in this group represent the main food of many pelagic fish [72,73] and zooplanktonic predators [74,75]. Based on long-term observations, omni–herbivorous copepods, i.e., Acartia clausi, Centropages typicus, the Paracalanus parvus complex, and Temora stylifera, are the most abundant copepods in the Gulf of Naples. These species are present and consistently reproduce all year round [76] but with a succession of their peak of seasonal abundance. For the former three species, the populations begin to increase at the onset of the stratification period and reached peaks during the shallowest stratification period [43]. We observed that FG1 was more abundant under the conditions of a high chlorophyll a concentration, which typically characterize inner shelf stations during summer [77,78]. This seasonal preference could be possibly explained by the feeding strategy of the FG1 species, which feed through currents carrying phytoplanktonic cells and tending to reach high abundance along the inner shelf, where rivers provide a greater supply of nutrients. Considering the high concentration of contaminants and potentially toxic compounds accumulated along the Campania coast due to river runoff [34], the success of FG1 in this area could be also explained by the high capacity of some species in this group (such as Acartia) to tolerate eutrophicated and polluted areas [79,80].
The mid shelf stations explored in our study host a higher abundance of Clausocalanus species (FG7), which constitute an important numerical component of copepod communities throughout the year [81]. Clausocalanus in our study dominated the autumn period, when C. furcatus largely prevailed over the other congeners, and the autotroph biomass was much lower than in summer. In the Gulf of Naples, this species, which is reported to prefer oligotrophic conditions, where it reproduces better, is mainly found in the upper 40 m of the water column [81].
The presence of small omnivorous copepods, such as the cyclopoids Oithona (FG5) and Oncaeidae (FG9), was observed in both summer and autumn in all the gulfs. Oithona is considered one of the most abundant genera in the oceans and acts as an important link in the trophic network between the microbial loop and higher trophic levels [82]. Oithona spp. can adopt a predatory ambush strategy, preferring mobile prey such as flagellates, ciliates, and dinoflagellates [83,84]. This strategy reduces the risk of predation [85] and metabolic costs [86,87], while increasing tolerance to starvation due to lower energy demands [85]. These adaptations enable the genus Oithona to thrive in both oligotrophic and eutrophic environments [85,86], like the Gulf of Naples, which is highly intermittent in terms of the trophic resources originating from the coastline [88].
FG9 comprises detritivorous species, such as Oncaea, which mainly consume detritus originating from discharged appendicuralian houses and copepod nauplii [89,90] and use gelatinous zooplankton (e.g., thaliaceans and chaetognaths) as a potential substrate for survival [91], contributing to the recycling of organic matter [92]. Our analyses showed that FG9 was more represented in the Gulf of Salerno in autumn. This is probably due to a rise in turbidity caused by increased river runoff, sediment resuspension, and coastal erosion [93,94] but also by the increase in gelatinous zooplankton (such as thaliaceans and chaetognaths) observed in these area [43]. These conditions may also expose Oncaea to pollutants originating from urban areas. In fact, both Oncaea and Oithona species, thanks to their adaptation strategies, in particular their low metabolic rate and ability to feed on a wide range of prey [86,95], are copepods tolerant or insensitive to pollution [2,96,97].
Two-thirds of the carnivorous copepods appearing during our surveys (FG4 and FG8) were sac-spawners, and only FG6 showed a broadcast spawning strategy. Within these groups, we find species belonging to the families Corycaeidae (FG4), Candaciidae (FG6), and Sapphirinidae (FG8), which have very diversified diets, ranging from the consumption of microalgae [98,99] to small copepods [74,100], meroplankton [101,102], and gelatinous zooplankton, such as thaliaceans, appendicularians, and chaetognaths [102,103]. The low relative abundance of FG4, FG6, and FG8 in the Campania gulfs (Figure 4) is probably due to the use of a sampling method that fails to capture larger zooplanktonic organisms [104,105]. In general, our results show that only in the Gulf of Naples, during the summer, are relatively large carnivores present. This is probably due to an increase in available prey, which may include meroplankton larvae, showing a peak in the early summer [43] likely favored by the abundant presence of microalgae (indicated by the increase in chlorophyll a). The presence of these available prey could also be due to the presence of nutrient-rich water from upwelling processes due to the presence of the Dohrn Canyon [59]. The appearance of typical offshore species (i.e., Candacia) is probably due to the surface circulation of the Tyrrhenian Sea, which arrives more regularly within the Gulf of Naples at this time of year [44,106], from oligotrophic Tyrrhenian to coastal waters [76].
5. Conclusions
Our results highlighted the spatial and temporal functional diversity of copepods along the Campania coast, which can be related to local environmental characteristics, thus improving our knowledge of the ecological roles of Mediterranean coastal zooplankton. Herbivorous species dominated in all the three gulfs and in both seasons, detritivorous species were observed most in autumn in the Gulf of Salerno, while carnivorous groups were most represented in summer in the Gulf of Naples. Our study represents a base for successive holistic studies to integrate the information acquired in this work with other biological, physical, and chemical data to increase our understanding of the functional complexity of plankton communities. Our study corroborates the view that functional traits in a community can be used as indicators of environmental characteristics, thus allowing for inference of ecosystem functions, such as energy transfer in the food web and nutrient cycling. Future studies should therefore focus on integrating a wider range of functional traits with multiple environmental factors and ecosystem functions to obtain a more complete and accurate view of the ecological dynamics of planktonic systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments11060113/s1. Table S1: Sampling stations and environmental data; Table S2: Abundance of mesozooplankton community (ind. m−2) found in the sample during the autumn season (2020); Table S3: Abundance of mesozooplankton community (ind. m−2) found in the sample during the summer season (2021); Table S4: Functional traits for each species found in the sample (the number of references is present in the main text); Table S5: Abundance of the functional groups (FGs) (ind. m−2) found through cluster analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B., M.G.M., D.D. and P.L.; methodology, D.B., M.G.M. and P.L.; software, D.B.; validation, D.B., M.G.M., P.L. and D.D.; formal analysis, D.B.; investigation, D.B., M.G.M. and P.L.; resources, D.B., J.V., M.S., A.B., M.G.M. and P.L.; data curation, D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B., M.G.M., P.L. and D.D.; writing—review and editing, D.B., M.G.M. and D.D.; visualization, D.B. and L.R.; supervision, M.G.M., P.V., P.L. and D.D.; project administration, M.G.M., P.L. and D.D.; funding acquisition, D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the project ISSPA—PO FEAMP Campania 2014–2020 (DRD n. 35 of 15th March 2018). This study was also partially supported by a project funded under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.4—Call for tender No. 3138 of 16 December 2021, rectified by Decree No. 3175 of 18 December 2021 of the Italian Ministry of University and Research, funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU, and Award Number/Project code CN_00000033, Concession Decree No. 1034 of 17 June 2022, adopted by the Italian Ministry of University and Research, CUP C63C22000520001, Project title “National Biodiversity Future Center—NBFC”. Daniele Bellardini was supported by a Ph.D. fellowship co-funded by the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn and the University of Genoa (Ph.D. in Marine Sciences and Technologies, University of Genoa). Luca Russo was supported by the BiOcean5D project (ID: 101059915).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article and supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the crew of the R/V Vettoria for the sampling and the Marine Research Infrastructure of the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn for acquiring, processing, and managing the environmental data. The three anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Buitenhuis, E.; Le Quéré, C.; Aumont, O.; Beaugrand, G.; Bunker, A.; Hirst, A.; Ikeda, T.; O’Brien, T.; Piontkovski, S.; Straile, D. Biogeochemical Fluxes through Mesozooplankton. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Shiganova, T.; Christou, E.D.; Kamburska, L.; Gubanova, A.; Konsulov, A.; Musaeva, E.; Skryabin, V.; Khoroshilov, V. Mesozooplankton Communities in the Aegean and Black Seas: A Comparative Study. Mar. Biol. 2004, 144, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, M.G.; Siokou, I.; Tirelli, V.; Bandelj, V.; Fernandez de Puelles, M.L.; Örek, Y.A.; de Olazabal, A.; Gubanova, A.; Kress, N.; Protopapa, M.; et al. Regional and Seasonal Characteristics of Epipelagic Mesozooplankton in the Mediterranean Sea Based on an Artificial Neural Network Analysis. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 135, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Terol, S.; Novotny, A.; Winder, M. Molecular Evidence of Host-Parasite Interactions between Zooplankton and Syndiniales. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.K.; Landry, M.R. Zooplankton and the Ocean Carbon Cycle. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 413–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.T. Zooplankton Fecal Pellets, Marine Snow, Phytodetritus and the Ocean’s Biological Pump. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 130, 205–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T. What Makes Pelagic Copepods so Successful? J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggreen, U.; Hansen, B.; Kiørboe, T. Food Size Spectra, Ingestion and Growth of the copepodAcartia Tonsa during Development: Implications for Determination of Copepod Production. Mar. Biol. 1988, 99, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.W. Effects of Size and Concentration of Food Particles on the Feeding Behavior of the Marine Planktonic Copepod Calanus Pacificus1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P.; Tiselius, P. Feeding Behaviour, Prey Detection and Capture Efficiency of the Copepod Acartia Tonsa Feeding on Planktonic Ciliates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 60, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMott, W.R. Feeding Selectivities and Relative Ingestion Rates of Daphnia and Bosmina1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teegarden, G. Copepod Grazing Selection and Particle Discrimination on the Basis of PSP Toxin Content. Grad. Sch. Oceanogr. Fac. Publ. 1999, 181, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.D.; Pershing, A.J.; Litchman, E.; Record, N.R.; Edwards, K.F.; Finkel, Z.V.; Kiørboe, T.; Ward, B.A. The Biogeography of Marine Plankton Traits. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.-L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the Concept of Trait Be Functional! Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Cabido, M. Vive La Différence: Plant Functional Diversity Matters to Ecosystem Processes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchman, E.; Ohman, M.D.; Kiørboe, T. Trait-Based Approaches to Zooplankton Communities. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, É.C.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; de Macedo-Soares, L.C.P.; Costa Brandão, M.; Santarosa Freire, A. Latitudinal Gradient of Copepod Functional Diversity in the South Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 199, 102710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Gasparini, S.; Ayata, S.-D. Identifying Copepod Functional Groups from Species Functional Traits. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerleau, C.; Sastri, A.R.; Beisner, B.E. Evaluation of Functional Trait Diversity for Marine Zooplankton Communities in the Northeast Subarctic Pacific Ocean. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, L.K.; Leskinen, E.; Lehtonen, H.; Nurminen, L. Spatial Patterns of Littoral Zooplankton Assemblages along a Salinity Gradient in a Brackish Sea: A Functional Diversity Perspective. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Ayata, S.-D.; Irisson, J.-O.; Adloff, F.; Guilhaumon, F. Climate Change May Have Minor Impact on Zooplankton Functional Diversity in the Mediterranean Sea. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, M.; Calbet, A. Zooplankton Ecology. In Marine Ecology; Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS): Paris, France, 2003; Volume I, pp. 295–318. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, A.J.; Finlay, K.; Beisner, B.E. Functional Diversity of Crustacean Zooplankton Communities: Towards a Trait-Based Classification. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 796–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.J.; Peres-Neto, P.R.; Beisner, B.E. Using Functional Traits to Investigate the Determinants of Crustacean Zooplankton Community Structure. Oikos 2013, 122, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veríssimo, H.; Patrício, J.; Gonçalves, É.; Moura, G.C.; Barbosa, J.E.L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Functional Diversity of Zooplankton Communities in Two Tropical Estuaries (NE Brazil) with Different Degrees of Human-Induced Disturbance. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 129, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulot, F.D.; Lacroix, G.; Lescher-Moutoué, F.; Loreau, M. Functional Diversity Governs Ecosystem Response to Nutrient Enrichment. Nature 2000, 405, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, P.; Bellardini, D.; Castellano, M.; Dapueto, G.; Povero, P. Structure and Functionality of the Mesozooplankton Community in a Coastal Marine Environment: Portofino Marine Protected Area (Liguria). Diversity 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Vogt, M.; Righetti, D.; Guilhaumon, F.; Ayata, S.-D. Do Functional Groups of Planktonic Copepods Differ in Their Ecological Niches? J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ortenzio, F.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. On the Trophic Regimes of the Mediterranean Sea: A Satellite Analysis. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, E.R.; Hole, D.G.; Allison, E.H.; Arkema, K.K.; McKinnon, M.C.; Chu, J.; De Sherbinin, A.; Fisher, B.; Glew, L.; Holland, M.B.; et al. Mapping Global Human Dependence on Marine Ecosystems. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Silliman, B.R. Climate Change, Human Impacts, and Coastal Ecosystems in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. CB 2019, 29, R1021–R1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (Program). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-59726-040-4. [Google Scholar]
- Crain, C.M.; Halpern, B.S.; Beck, M.W.; Kappel, C.V. Understanding and Managing Human Threats to the Coastal Marine Environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1162, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appolloni, L.; Sandulli, R.; Vetrano, G.; Russo, G.F. A New Approach to Assess Marine Opportunity Costs and Monetary Values-in-Use for Spatial Planning and Conservation; the Case Study of Gulf of Naples, Mediterranean Sea, Italy. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 152, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, V.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. Contamination by Hazardous Substances in the Gulf of Naples and Nearby Coastal Areas: A Review of Sources, Environmental Levels and Potential Impacts in the MSFD Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 820–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Dennis, R.L.; Whitall, D.R. Atmospheric Deposition of Nitrogen: Implications for Nutrient over-Enrichment of Coastal Waters. Estuaries 2002, 25, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Conversano, F.; Corato, F.; Licandro, P.; Mangoni, O.; Marino, D.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Modigh, M.; Montresor, M.; Nardella, M.; et al. Seasonal Patterns in Plankton Communities in a Pluriannual Time Series at a Coastal Mediterranean Site (Gulf of Naples): An Attempt to Discern Recurrences and Trends. Sci. Mar. 2004, 68, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingone, A.; D’Alelio, D.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Sarno, D.; Team, L.-M. Time Series and beyond: Multifaceted Plankton Research at a Marine Mediterranean LTER Site. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 34, 273–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, F.; Saviano, S.; Botte, V.; Iudicone, D.; Zambianchi, E.; Cianelli, D. Gulf of Naples Advanced Model (GNAM): A Multiannual Comparison with Coastal HF Radar Data and Hydrological Measurements in a Coastal Tyrrhenian Basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiotta, F.; Balestra, C.; Buondonno, A.; Casotti, R.; D’Ambra, I.; Di Capua, I.; Gallia, R.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Merquiol, L.; Pepi, M.; et al. Do Plankton Reflect the Environmental Quality Status? The Case of a Post-Industrial Mediterranean Bay. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 160, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montresor, M.; Prisco, C.D.; Sarno, D.; Margiotta, F.; Zingone, A. Diversity and Germination Patterns of Diatom Resting Stages at a Coastal Mediterranean Site. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 484, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingone, A.; Tortora, C.; D′Alelio, D.; Margiotta, F.; Sarno, D. Assembly Rules Vary Seasonally in Stable Phytoplankton Associations of the Gulf of Naples (Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Ecol. 2023, 44, e12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, M.G.; Di Capua, I.; Kokoszka, F.; Margiotta, F.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M.; Sarno, D.; Zingone, A.; Licandro, P. Coastal Mesozooplankton Respond to Decadal Environmental Changes via Community Restructuring. Mar. Ecol. 2023, 44, e12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruggiero, P.; Esposito, G.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Pierini, S.; Zambianchi, E. Modelling the Marine Circulation of the Campania Coastal System (Tyrrhenian Sea) for the Year 2016: Analysis of the Dynamics. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 210, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragosta, M.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Macchiato, M. Differentiation of Copepod Assemblages in Coastal Waters of the Tyrrhenian Sea. Oceanol. Acta 1995, 18, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Careddu, G.; Costantini, M.L.; Calizza, E.; Carlino, P.; Bentivoglio, F.; Orlandi, L.; Rossi, L. Effects of Terrestrial Input on Macrobenthic Food Webs of Coastal Sea Are Detected by Stable Isotope Analysis in Gaeta Gulf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Calizza, E.; Careddu, G.; Rossi, D.; Orlandi, L.; Jona-Lasinio, G.; Aguzzi, L.; Costantini, M.L. Space-Time Monitoring of Coastal Pollution in the Gulf of Gaeta, Italy, Using δ15N Values of Ulva Lactuca, Landscape Hydromorphology, and Bayesian Kriging Modelling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triassi, M.; Nardone, A.; Giovinetti, M.C.; De Rosa, E.; Canzanella, S.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Montuori, P. Ecological Risk and Estimates of Organophosphate Pesticides Loads into the Central Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, the River of the “Land of Fires” Area, Southern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, C.; Lega, M.; Fusco, G.; Bishop, P.; Endreny, T. Characterization of Terrestrial Discharges into Coastal Waters with Thermal Imagery from a Hierarchical Monitoring Program. Water 2017, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iermano, I.; Liguori, G.; Iudicone, D.; Buongiorno Nardelli, B.; Colella, S.; Zingone, A.; Saggiomo, V.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. Filament Formation and Evolution in Buoyant Coastal Waters: Observation and Modelling. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 106, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianelli, D.; Uttieri, M.; Buonocore, B.; Falco, P.; Zambardino, G.; Zambianchi, E. Dynamics of a Very Special Mediterranean Coastal Area: The Gulf of Naples. Mediterr. Ecosyst. Dyn. Conserv. 2012, 7, 129–150. [Google Scholar]
- Baldantoni, D.; Bellino, A.; Lofrano, G.; Libralato, G.; Pucci, L.; Carotenuto, M. Biomonitoring of Nutrient and Toxic Element Concentrations in the Sarno River through Aquatic Plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, F.; Conversano, F.; Iudicone, D.; Ferron, B.; Bouruet-Aubertot, P. A Turbulence Survey in the Gulf of Naples, Mediterranean Sea, during the Seasonal Destratification. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, F.; Le Roux, B.; Iudicone, D.; Conversano, F.; Ribera d’Alcalá, M. Long-Term Variability of the Coastal Ocean Stratification in the Gulf of Naples: Two Decades of Monitoring the Marine Ecosystem at the LTER–MC Site, between Land and Open Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2023, 44, e12725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, M.G. Mesozooplankton Abundance and Species Composition in the Gulf of Naples and the Gulf of Salerno in March 1987. Part 2 [dataset]. Stazione Zool. Anton Dohrn 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghan, W.; Stefano, A.; Annamaria, L.; Claudia, C.; Antonio, C.; Wanjun, L.; Marco, S.; Angela, D.; Benedetto, D.V. Compositional Analysis and Pollution Impact Assessment: A Case Study in the Gulfs of Naples and Salerno. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 160, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, E.; Montuori, P.; Triassi, M.; Masucci, A.; Nardone, A. Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System. Toxics 2022, 10, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ruggiero, P.; Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Pierini, S.; Spezie, G. A Baroclinic Coastal Trapped Wave Event in the Gulf of Naples (Tyrrhenian Sea). Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciannelli, L.; Cannavacciuolo, A.; Konstandinidis, P.; Mirasole, A.; Wong-Ala, J.A.T.K.; Guerra, M.T.; D’Ambra, I.; Riginella, E.; Cianelli, D. Ichthyoplankton Assemblages and Physical Characteristics of Two Submarine Canyons in the South Central Tyrrhenian Sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 2022, 31, 480–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M. Faune de France, N°26: Copépodes Pélagiques. Available online: https://www.abebooks.it/1933-Faune-France-N%C2%B026-Cop%C3%A9podes-P%C3%A9lagiques/31096854703/bd (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Trégouboff, G.; Rose, M. MANUEL DE PLANCTONOLOGIE MEDITERRANEENNE. Available online: https://doris.ffessm.fr/Bibliographie/MANUEL-DE-PLANCTONOLOGIE-MEDITERRANEENNE (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Castellani, C.; Edwards, M. Marine Plankton: A Practical Guide to Ecology, Methodology, and Taxonomy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-19-183569-8. [Google Scholar]
- Razouls; Desreumaux; Kouwenberg; de Bovée Marine Planktonic Copepods: Home Page. Available online: https://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en/ (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Kiørboe, T. How Zooplankton Feed: Mechanisms, Traits and Trade-Offs. Biol. Rev. 2011, 86, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Wydler, J.; Vogt, M. Copepod Functional Traits and Groups Show Divergent Biogeographies in the Global Ocean. J. Biogeogr. 2023, 50, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Payne, M.R.; Kiørboe, T. A Trait Database for Marine Copepods. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, R.; Chen, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z. Functional Diversity and Groups of Crustacean Zooplankton in the Southern Yellow Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kiørboe, T.; Sabatini, M. Reproductive and Life Cycle Strategies in Egg-Carrying Cyclopoid and Free-Spawning Calanoid Copepods. J. Plankton Res. 1994, 16, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T.; Hirst, A.G. Shifts in Mass Scaling of Respiration, Feeding, and Growth Rates across Life-Form Transitions in Marine Pelagic Organisms. Am. Nat. 2014, 183, E118–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Someren Gréve, H.; Almeda, R.; Kiørboe, T. Motile Behavior and Predation Risk in Planktonic Copepods. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1810–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borme, D.; Tirelli, V.; Palomera, I. Feeding Habits of European Pilchard Late Larvae in a Nursery Area in the Adriatic Sea. J. Sea Res. 2013, 78, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalago, D.; Garrido, S.; Palomera, I. Comparison of the Feeding Apparatus and Diet of European Sardines Sardina Pilchardus of Atlantic and Mediterranean Waters: Ecological Implications. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 86, 1348–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.T. The Importance of Small Planktonic Copepods and Their Roles in Pelagic Marine Food Webs. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Tönnesson, K.; Tiselius, P. Diet of the Chaetognaths Sagitta Setosa and S. Elegans in Relation to Prey Abundance and Vertical Distribution. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 289, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, M.G.; Dubroca, L.; García-Comas, C.; Capua, I.D.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. Stability and Resilience in Coastal Copepod Assemblages: The Case of the Mediterranean Long-Term Ecological Research at Station MC (LTER-MC). Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 97–100, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Sanders, R.W.; Moeller, R.E.; Stutzman, P.L. Utilization of Subsurface Food Resources for Zooplankton Reproduction: Implications for Diel Vertical Migration Theory. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan-Nhu, H.; Nguyen, T.-V.; Do-Huu, H.; Montoya, J.P.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L. Copepods Key Traits in Diverse Habitats of Tropical Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2022, 44, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Papathanassiou, E. Differentiation of Zooplankton Populations in a Polluted Area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 76, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, I.; Villate, F. Differences in the Abundance and Distribution of Copepods in Two Estuaries of the Basque Coast (Bay of Biscay) in Relation to Pollution. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peralba, À.; Mazzocchi, M.G. Vertical and Seasonal Distribution of Eight Clausocalanus Species (Copepoda: Calanoida) in Oligotrophic Waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2004, 61, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornils, A.; Wend-Heckmann, B.; Held, C. Global Phylogeography of Oithona Similis s.l. (Crustacea, Copepoda, Oithonidae)—A Cosmopolitan Plankton Species or a Complex of Cryptic Lineages? Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 107, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, E.; Griffell, K.; Calbet, A.; Isari, S. Feeding Rates and Prey: Predator Size Ratios of the Nauplii and Adult Females of the Marine Cyclopoid Copepod Oithona Davisae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Akiba, T.; Omura, T.; Tanaka, Y. On the Foraging and Feeding Ability of Oithona Davisae (Crustacea, Copepoda). Hydrobiologia 2014, 741, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeda, R.; van Someren Gréve, H.; Kiørboe, T. Prey Perception Mechanism Determines Maximum Clearance Rates of Planktonic Copepods. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 2695–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, C.; Robinson, C.; Smith, T.; Lampitt, R.S. Temperature Affects Respiration Rate of Oithona Similis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 285, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeda, R.; Alcaraz, M.; Calbet, A.; Saiz, E. Metabolic Rates and Carbon Budget of Early Developmental Stages of the Marine Cyclopoid Copepod Oithona Davisae. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianelli, D.; D’Alelio, D.; Uttieri, M.; Sarno, D.; Zingone, A.; Zambianchi, E.; Ribera d’Alcalà, M. Disentangling Physical and Biological Drivers of Phytoplankton Dynamics in a Coastal System. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.T. Zooplankton Feeding Ecology: Contents of Fecal Pellets of the Cyclopoid Copepods Oncaea Venusta, Corycaeus Amazonicus, Oithona Plumifera, and O. Simplex from the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. 1986, 7, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiang, P.; Chen, X.; Xing, B. Research Advance in the Taxonomy and Ecology of Oncaeidae Giesbrecht, 1893. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 919877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger-Schnack, R.; Schnack, D.; Weikert, H. Biological Observations on Small Cyclopoid Copepods in the Red Sea. J. Plankton Res. 1989, 11, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishida, H.; Harimoto, T.; Furusawa, K.; Suzuki, S.; Ishizaka, J.; Ikeda, T.; Takahashi, M.M. Community and Trophic Structures of Pelagic Copepods down to Greater Depths in the Western Subarctic Pacific (WEST-COSMIC). Deep Sea Res. Part Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.A.; Daming, W.S. Estimation of Coastal Waters Turbidity Using Sentinel-2 Imagery. Geod. Cartogr. 2023, 49, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Folkard, A.R. Factors Affecting Turbidity in the Southern North Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1969, 32, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffenhöfer, G.-A. On the Ecology of Marine Cyclopoid Copepods (Crustacea, Copepoda). J. Plankton Res. 1993, 15, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi-Trabelsi, N.; Guermazi, W.; Leignel, V.; Al-Enezi, Y.; Karam, Q.; Ali, M.; Ayadi, H.; Belmonte, G. Effects of Eutrophication on Plankton Abundance and Composition in the Gulf of Gabès (Mediterranean Sea, Tunisia). Water 2022, 14, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besiktepe, S.; Kucuksezgin, F.; Besiktepe, S.T.; Eronat, C.; Gonul, T.; Kurt, T.T.; Sayın, E.; Gubanova, A. Variations in Copepod Composition and Diversity in Relation to Eutrophication and Hydrology in İzmir Bay, Aegean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, K.R.; Thistle, D. Microbial Food Partitioning by Three Species of Benthic Copepods. Mar. Biol. 1985, 88, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleppel, G.S.; Pieper, R.E. Phytoplankton Pigments in the Gut Concents of Planktonic Copepods from Coastal Waters off Southern California. Mar. Biol. 1984, 78, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R.; Lehner-Fournier, J.M.; Fagerness, V.L. Predatory Feeding Behavior of the Marine Cyclopoid Copepod Corycaeus Anglicus. Mar. Biol. 1985, 85, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, S.; Onbé, T. Evidence of Selective Feeding on Larvaceans by the Pelagic Copepod Candacia Bipinnata (Calanoida: Candaciidae). J. Plankton Res. 1989, 11, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battuello, M.; Sartor, R.M.; Brizio, P.; Nurra, N.; Pessani, D.; Abete, M.C.; Squadrone, S. The Influence of Feeding Strategies on Trace Element Bioaccumulation in Copepods (Calanoida). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Urrutia, Á.; Harris, R.P.; Smith, T. Predation by Calanoid Copepods on the Appendicularian Oikopleura Dioica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, J.D.; Baird, M.E.; Buchanan, P.; Bulman, C.; Davies, C.; Downie, R.; Griffiths, C.; Heneghan, R.; Kloser, R.J.; Laiolo, L.; et al. Modeling What We Sample and Sampling What We Model: Challenges for Zooplankton Model Assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, M.C.; Benedetti, F.; Martini, S.; Soviadan, Y.D.; Irisson, J.-O.; Romagnan, J.-B.; Elineau, A.; Desnos, C.; Jalabert, L.; Freire, A.S.; et al. Macroscale Patterns of Oceanic Zooplankton Composition and Size Structure. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, S.; Simioli, A. A Wind-Driven Circulation Model of the Tyrrhenian Sea Area. J. Mar. Syst. 1998, 18, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).