Simple Summary
The black soldier fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomydiae) is an important resource and environmental protection insect with a large biomass, a high food conversion efficiency, and a high reproductive rate. H. illucens can be applied in environmental ecology and as an effective treatment for organic waste. Due to its broad feeding range, many types of organic waste (such as kitchen waste, livestock excrement, deteriorated fruits and vegetables, crop waste, and food-processing waste) can be converted into proteins, lipids, peptides, amino acids, chitin, vitamins, and polypides. The proteins and amino acids have been used to produce aquaculture feed and feedstuffs with high digestibility. In addition, the grease from H. illucens digestion has been successfully used as a raw material for biodiesel with good performance. Furthermore, the antimicrobial peptides and chitin extracted from H. illucens have high medicinal value. For the full development and utilization of this resource, studies of the biological characteristics of the H. illucens, its resource utilization of proteins and grease, and its environmental applications are crucial.
Abstract
The black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), is a saprophytic insect that can digest organic wastes, such as animal manure, plant residues, and food and agricultural wastes. In the degradation process, organic wastes are converted into protein, grease, and polypeptides, which can be applied in medicine, the refining of chemicals, and the manufacturing of feedstuffs. After their conversion by the H. illucens, organic wastes not only become useful but also environmentally friendly. To date, the H. illucens has been widely used to treat food waste and to render manure harmless. The protein and grease obtained via this insect have been successfully used to produce livestock feed and biodiesel. In this article, the biological characteristics, resource utilization of protein and grease, and environmental functions of the H. illucens are summarized. This article provides a theoretical basis for investigating potential applications of the H. illucens.
1. Introduction
H. illucens, was thought to originate from the South American savannah. It is widely distributed in temperate, subtropical, and tropical regions [1]. However, the recent discovery of a larva of H. illucens larva in the sarcophagus of Isabella d’Aragona (1470–1524) shows how the geographical origin and spread of this insect still represent an intriguing topic [2]. The H. illucens inhibits multiplication of the housefly [3], but unlike the housefly it does not invade human living environments, pollute the environment, spread diseases, or harm crops [4,5]. Research has identified the larvae of this insect as a type of saprophytic insect that feeds on industrial, agricultural, and household organic waste or plant and animal remains [6]. The larvae can digest harmful and pernicious bacteria, such as Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli, in the process of organic waste decay [7,8,9], thereby reducing the harmful effect of such waste on the environment [7]. In early research, Sheppard and Tomberlin discussed the factors that influence H. illucens oviposition, which provided technical support for the artificial breeding of H. illucens [10,11] and subsequent development of the resource value of the H. illucens. Due to its wide dietary range, the H. illucens has been widely used to treat and render harmless food waste, manure [8], and diseased or dead livestock. H. illucens has been studied and utilized in many fields to favorable effect. A complete list of substrates that have been tested as feeding substrates for H. illucens larvae and the corresponding outcomes are provided in the table. It can be seen from the Table 1 that the effects on the development of the H. illucens vary among substrates. In additional to substrate type, environmental factors are key factors affecting the development of the H. illucens, contributing to variation among studies. In general, substrates rich in nutrients (protein and oil), are more suitable for the development of the H. illucens.

Table 1.
Complete list of tested substrates as feed for H. illucens larvae (NA: not available).
Organic wastes are converted by biotransformation into organic matter comprising polypeptide-containing proteins, lipids, peptides, amino acids, chitin, and vitamins. Therefore, H. illucens is regarded as a non-pest and beneficial insect. Insects are regarded as an important source of protein for the 21st century [26]. The digestibility of insect-derived protein can reach more than 70%, which approaches the digestibility of fish and meat protein and is significantly higher than that of vegetable protein. In addition, much progress has been made in research on the replacement of fodder with H. illucens protein [27,28,29]. Several studies have indicated that H. illucens can be induced to produce antimicrobial peptides, that have activity against many bacteria [30,31,32,33], and that chitin can be extracted from H. illucens puparium to produce chitosan [34]. Furthermore, H. illucens grease has substantial future potential in the development of high-tech products, such as biodiesel. Because of its abundant nutritional value, H. illucens offers considerable potential for exploitation. However, breeding on a scale appropriate for modern industrialization remains under-researched. Although studies have been conducted on, the application of chitin in the field of biomedicine; the industrial application of grease; and the efficient extraction of proteins, amino acids, peptides, and grease for the development of later high value-added products; detailed research on the feeding of H. illucens using agricultural waste as the primary raw material has not been reported. In this article, the development value and resource utilization of H. illucens and the use of this insect to treat and render harmless manure, agricultural wastes, and domestic wastes are summarized. This article provides a theoretical basis for research on the future ecological treatment of organic waste and other potential uses for H. illucens.
2. Biological Morphology
2.1. Morphological and Biological Characteristics
The H. illucens was first recorded by Linnaeus in 1738 and is mostly distributed between approximately 45° N and 40° S in the Americas [35]. H. illucens has been recorded in Beijing, Tianjin, Henan, Hebei, Shandong, Fujian, Sichuan, Yunnan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and other provinces or cities in China [36]. H. illucens possesses four distinct developmental stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. In nature, H. illucens lays its eggs in dry areas near wet, rotting organisms. Temperature, humidity, and light intensity are the main environmental factors affecting adult mating and egg laying [10]. The incubation time of the eggs is typically 4–14 days and varies with season, region, and temperature [37]. According to Kim, there are six instars in the larval phase [38,39], and the larvae range in size from 1.8 mm to 20 mm, with 20-mm larvae being referred to as mature larvae. H. illucens initiate feeding immediately upon hatching, with consumption rates increasing greatly after the 3rd instar. When the larvae reach the 6th instar, they cease feeding and initiate pupation, subsequently becoming adults. Adult females initiate egg laying approximately 2–3 days after mating, and female fecundity can reach 900 eggs/female [37]. The performance and nutrition of the H. illucens vary with substrate, and substrates rich in protein and oil are more conducive to the accumulation of protein and grease in this insect [40,41,42,43].
2.2. Ecological Characteristics and Environmental Stressors of Hermetia illucens
Natural ecological factors, such as parasites, microorganisms, hormone analogues, heavy metals, acid–base compounds, corrosive substances, and salt, affect the growth and development of insects [44,45,46,47]. Heavy metals in organic waste accumulate in H. illucens, which can affect the developmental period of this insect, increase larval mortality, and reduce the rates of pupation and emergence [48,49,50,51]. Studies indicate that different concentrations of Zn2+ have different effects on the developmental period of larvae, which mainly involve changes in weight, enzyme activity, total amounts of small molecule proteins and hemolymph levels of hormones in larvae [52,53]. Similarly, the weight, enzyme activities, levels of hormones, and, in particular, the contents of total sugars, proteins, and grease of larvae are affected by Cu2+. In addition, as Cu2+ accumulation in the larvae appears with high levels of the Cu2+ stress [54], the tolerance characteristics of mature larvae and pre-pupae can be affected by stress from alcohol toxicity, oxygen, and high osmotic pressure. Mature larvae and pre-pupae have been found to exhibit good resistance to these stresses, and their average mortality rates were found to decrease when the concentration of each stress factors (i.e., ethanol, mineral oil, and sodium chloride) is lower than 20–60%. In particular, at high levels of alcohol and osmotic pressure and low concentrations of oxygen, the development of larvae is threatened [55]. In addition, research has revealed that the Cd and Cr contents in the pupal shell are significantly higher than those in the pupa. This distribution pattern may be informative for studying the migration process of heavy metals in H. illucens [56]. Insect growth and development are also affected by temperature, light, and humidity. Certain appropriates temperature (27.5–37.5 °C) [57,58], light levels [59,60] and humidity (70%) [61] are more conducive to spawning, emergence, and conversion of organic waste in this insect. Several studies have found that hydrolytic proteins and organophosphates from Bacillus subtilis are present in the gut and skin of H. illucens larvae [62,63]. Bacillus has been reported to be a common microorganism that plays an important role in the intestinal tract of insects [64]. For example, a Bacillus strain exists in the gut of Apis cerana japonica (Japanese honeybee) that can inhibit Paenibacillus, which in the American honeybee can cause larvae to emit an unpleasant odor [65]. Bradley observed a Trichopria sp (Hymenoptera: Hamiidae) that can parasitize and lay eggs on the pupae of H. illucens, which likely affects development in H. illucens [66]. Although, the gut microbial communities (fungal and bacterial) in H. illucens larvae varies with substrate [63,67,68], identified communities in the gut of H. illucens have been found to be unique relative to those of other insects [69]. These unique communities, by possessing certain metabolic properties might be key in the conversion and digestion of complex organic waste by the H. illucens [70,71,72,73]. Thus, the gut microbiome in the larvae may play an important role in the conversion of organic waste.
2.3. Research on Artificial Breeding on Hermetia illucens
According to Tomberlin and Sheppard, the number of matings is proportional to the intensity of illumination in the range of 400–700 nm, and when the intensity of illumination is greater than 200 μ mol m−2s−1, the mating rate reaches 75%. However, at less than 63 μ mol m−2s−1, no mating behavior was observed [10]. In addition, the number of matings gradually decreases with time between 8:00–17:00, particularly before 15:00. Tomberlin and Sheppard achieved the highest mating rate with irradiation with an iodine tungsten lamp at a power of 500 W and an illumination intensity of 135 μ mol m−2s−1 under a temperature of 22 °C and a relative humidity of 60–70% The adult longevity (females: approximately 8–9 days; males: approximately 6–7 days) and hatching period of H. illucens are affected by morphological, biological, ecological factors, and environmental stress. Therefore, the density of H. illucens in the wild is low. In the 1970s, to promote resource utilization and large-scale production of H. illucens, Sheppard and Tomberlin started systematic research on the artificial breeding of H. illucens. They determined the ecological factors that affect mating and spawning and identified and summarized the that affect the survival rate of larvae and the development of the pupa prophase [10,17]. There were no significant effects of artificial feeding on the development and survival of pre-pupal H. illucens. However, the number of adults bred under fodder feeding was significantly lower than under natural feeding, and there were differences in the proportions of males and females. Therefore, to increase mating rates under artificial feeding, it is necessary to achieve the proportions observed in nature [74]. When peanut bran was used to feed the larvae, the effective conversion rate was 28.9%, this information was valuable for the standardization, scale expansion, and industrialization of the artificial breeding of H. illucens [75]. With the successful development of scientific, large-scale breeding of the H. illucens, the production of insect protein and oil has become possible [76,77]. Furthermore, organic wastes have been recycled and treated in an environmentally friendly way [78,79].
3. Resource Value of Hermetia illucens
Insects possess economic, ecological, and scientific value because their bodies (e.g., as food, medicine, or ornaments), products (e.g., secretions, excrement), behaviors (e.g., pollination, parasitism, preying on other organisms), cells and intracellular activities, and structures and functions (e.g., bionomics) can be used directly or indirectly by humans as resources. H. illucens is a resource insect with respect to its proteins, fats, and ability to convert organic waste. Current, research on H. illucens is primarily focused on its resource value and ecological value. The salivary glands and intestines of H. illucens can secrete digestive enzymes, and their digestive activities are significantly higher those of the enzymes secreted by houseflies [74,80]. Among these digestive enzymes, trypsin plays decisive roles in the digestion and transformation of organic wastes [81]. The gut microbiome in the larvae plays an important role in the conversion of organic waste [69,82]. The gut microbial communities (bacterial and fungal communities) in H. illucens are diverse and abundant, and they vary significantly with substrate [83], Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, and Actinobacteria are the predominant bacterial taxa [63,68], and Pichia, Geotrichum, and Trichosporon are the predominant fungal taxa [67]. The functional and biological characteristics of H. illucens vary with variation in the compositions of the gut microbial communities [84]. These characteristics include oviposition, hatchability, longevity, conversion, and utilization efficiency of organic waste, and nutritional value [85,86].
Due to the abundance of enzymes and microbes in the intestine of H. illucens, the larvae have a wider range of potential sources of food than do other saprophytic insects. The larvae can effectively digest and convert organic matter; therefore, high-quality fertilizers and organic matter can be acquired. Organic matter contains 20–70% protein, 30–60% amino acids, 10–50% fat, and 2–10% sugar. It also contains fatty acids, minerals elements, vitamins and other active substances that possess health functions for humans [87]. The nutritional value of H. illucens has been studied in the fields of industry, medicine, health care, and feed processing and has strong development potential. The protein derived from larvae has been used as animal feed [88,89] and as a substitute for soy flour or fish meal in formula feed for chickens, pigs, and fish [90]. The grease of the larvae has been used as raw material in the extraction of biodiesel [91,92]. Furthermore, H. illucens can be used as a raw material for the extraction of antimicrobial peptides [31,32,33]. The amino acid content of dried larvae, soybean meal, and fish meal [93,94], and the nutrient contents of different insects, soybean meal, and fish meal [95,96,97,98,99] are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 respectively.
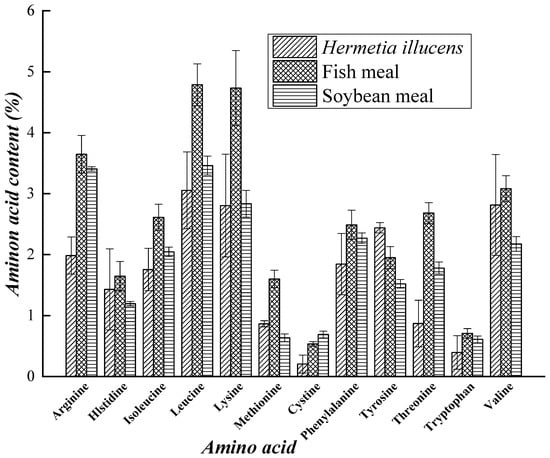
Figure 1.
Amino acid contents of dried larvae, soybean meal and fish meal.
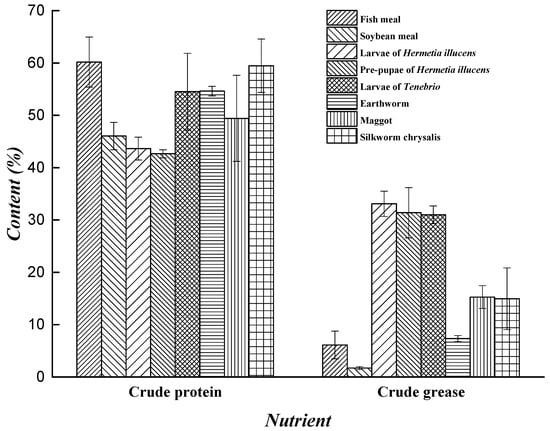
Figure 2.
Nutrient contents of different insects, soybean meal and fish meal.
3.1. Resource Value of Hermetia illucens Proteins and Minerals
The larvae of H. illucens are rich in amino acids and minerals. The nutritional value of larvae varies according to the type of organic waste the larvae are fed [96]. The H. illucens has been reported, as a good source of proteins and minerals [19,100]. Essential amino acids are abundant in the protein obtained from black soldier fly larvae. According to Sheppard and Newton, the leucine, isoleucine and valine contents of pre-pupa powder are much higher than those of fish meal, and the contents of all other amino acids except tryptophan are higher in pre-pupa powder than in soybean meal (Figure 1) [93]. Regarding mineral contents, the Fe, Mn, and Al contents of pre-pupa powder are much higher those in fish meal and soybean meal. The contents of some other minerals (Na, Mg, Zn) are also higher in pre-pupa powder than in fish meal and soybean meal, but those of K and Cu are slightly lower [93]. Compared with other insects, soybean meal and fish meal, the crude protein contents of the larvae and pre-pupae of H. illucens are slightly lower.
With the rapid development of stock breeding, an urgent need for protein feed has emerged. The protein from H. illucens can be used as feed or an additive for livestock and in aquaculture [89,101,102]. H. illucens has been validated as a feed additive or alternative for livestock and in aquaculture, and there has been much research on this application [103,104]. April Hari Wardhana has successfully harvested H. illucens as a protein substitute for animal feed [105]. Based on an analysis of the growth performance, serum indicators, and nutrient digestibility of pigs, Zhang et al. reported that larvae powder can be added as a protein feed or can replace fish meal and soybean meal in pig feed. When the larvae were used in broiler chicks feed, body weight gain was improved, and frequency of CD4+ T lymphocytes, serum lysozyme activity, and spleen lymphocyte proliferation were increased. These findings indicted that as feed, the larvae have prophylactic properties, stimulating non-specific immune responses and reducing the burden of S. gallinarum [106]. The nutritional value of the protein is greatly affected by the drying method, Huang et al. reported that conventional drying (60 °C) yielded a higher digestible indispensable amino acid score and better digestibility than did microwave drying [107]. It is necessary to identify improved methods to obtain protein and ensure its nutritional value and digestibility.
3.2. Resource Value of Hermetia illucens Grease
Although the grease content in H. illucens larvae is greatly affected by the rearing substrate [19,108,109,110], crude grease content is much higher in these larvae than in other insects, soybean meal, and fish meal (Figure 2) [95,96,97,98,99].
The resource value of the grease of H. illucens larvae has been demonstrated [18,111]. A total of 1200 H. illucens larvae can digest 1248 g of fresh cow dung by bioconversion in 21 days, and 15.8 g of biodiesel can be extracted from the grease of such larvae. When larvae were used to convert 1 kg of chicken manure, 1 kg of pig manure and 1 kg of cow dung, the amount of crude grease extracted by petroleum ether was 95.5 g, 60.4 g, and 38.2 g, respectively, which accounted for 30.1%, 29.1%, and 29.9% of the total biomass of the H. illucens larvae, respectively. The physicochemical properties of the crude grease of larvae are as follows: lodine value (the amount of unsaturation in fatty acids), 96 ± 2.4 gL/100 g; acid value, 8.7 ± 0.4 mg KOH/g; saponification value, 157.5 ± 6.2 mg KOH/g; melt point, 5 ± 0.3 °C; and peroxide value, 0.03 ± 0.01 meq/kg grease [112]. The physical and chemical fuel properties of biodiesel largely depend on the fatty acid distribution of the triglycerides used in the production. The fatty acid composition of larvae fed cow dung is enriched in myristic acid, palmitoleic acid, palmitic acid, oleinic acid, linolenic acid, stearic acid, and other acids [112]. Compared with biodiesel converted from rapeseed oil [112] and with reference to the EU biodiesel standard (EN14214), the parameters of the biodiesel converted from the crude grease of larvae fed on chicken manure, cow dung, pig manure, dairy manure, and restaurant waste met the standard and exhibited higher oxidation resistance [15,18,111]. Seven days after feeding 1000 larvae 1 kg kitchen waste, 64.9 g of larvae dry matter was obtained. After subsequent refining, 23.6 g of biodiesel with an ester content of 96.9% was obtained, and the fuel performance of this biodiesel almost met the EU biodiesel standard [113]. Experimental studies have indicated that H. illucens can effectively convert kitchen waste and rice straw into organic matter containing polypeptides by co-biotransformation and that the resulting crude grease can be refined into biodiesel that meets the EU biodiesel standard [16]. The grease from larvae has been used to replace traditional grease sources in feed formulations without adverse effects on animal performance and product quality [94,114,115]. When the grease of this insect was used to substitute soybean oil in the diets for broiler chickens, the productive performance, carcass traits, and overall meat quality were found to be satisfactory [116,117]. Similarly, when grease from H. illucens was provided as dietary grease to juvenile Jian carp, satisfactory results were obtained except for a decrease in lipid deposition in the intraperitoneal fat tissue of Jian carp [118].
Compared with typical energy-resource plants, H. illucens has advantages of high fertility and a short life cycle. In addition, H. illucens can convert livestock excrement and domestic waste into clean energy, which results in the resource utilization of organic waste. In addition, glucose and xylose have been shown to contribute to the accumulation of lipids in larvae, yielding a lipid content of 34.60% [119]. These findings indicate that, lignocellulose is a useful substance for lipid accumulation in larvae and that the H. illucens is a very promising organism for the conversion of lignocellulose [120,121]. Therefore, the conversion of organic waste into grease by H. illucens has substantial potential and research value.
3.3. Other Hermetia illucens Resource Values
The larvae and pre-pupae can be developed not only as sources of insect protein and grease but also as high-value resource materials for the extraction of antimicrobial peptides, chitin, and chitosan [122]. Osama Elhag et al. reported seven new gene fragments of three types of antimicrobial peptides obtained from H. illucens [123]. The induction and extraction of antimicrobial peptides from H. illucens revealed that the best period for induction and production was the 5th instar. In one study, the abdomens of 5th instar H. illucens larvae were punctured with needles dipped in Escherichia coli solution (3 × 1012 individuals/mL) and then soaked in Escherichia coli solution for 60 s. After larval feeding for 24 h the activity of antimicrobial peptides against Escherichia coli was better than that induced by ultrasound of 100 W for 20 min [124]. The hemolymph of larvae can be induced to produce antimicrobial peptide DPL4 [30,31], which exhibits antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, and the immunity of the larvae can be promoted. The active antimicrobial peptide induced by methanol solution has strong inhibitory effects on many bacteria. The crude antimicrobial peptide can inhibit Staphylococcus aureus well after purification, as evidenced from high-performance liquid chromatography. Compared with natural conditions, needle stimulation has been shown to result in stronger antimicrobial activity and a broader antibacterial spectrum of the antimicrobial peptide [30,31]. In addition, the antimicrobial peptide derived from H. illucens larvae has been shown to possess greater thermal stability than antimicrobial peptides derived from other insects and to exhibit good performance after repeated freezing and thawing. Storage time can reach 96 h at room temperature, and the suitable pH range is 5–9, which indicates good biological stability [125].
Chitin derived from crustaceans is a linear biological biopolymer [126] and has been widely used in the textiles industry, papermaking, agriculture and forestry, food, medicine, environmental protection, bio-engineering, and other fields [127,128]. The resource value of insects derives not only from their protein, grease, and antimicrobial peptides but also from their chitin. In recent years, chitosan has been successfully extracted from the pupa shell of silkworms, maggots, and pine caterpillars [129]. White or yellowish chitin was extracted from the pupa shell of H. illucens and successfully transformed into chitosan by Xu Qiyun for the first time. The extraction rates of chitin and chitosan were 12.3–14.3% and 83.2–86.3%, respectively, and the degree of deacetylation of the chitosan was 82.8%. Waśko and Bulak reported the physicochemical properties of chitin extracted from larvae and imagoes of H. illucens. The surface morphologies of the two chitin types were separately analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, and the crystalline index values of the chitins extracted from the imagoes and larvae were 24.9% and 35%, respectively. Compared with the crystallinity indexes (CrI) of chitin from other insects, those of chitin extracted from H. illucens were much lower. Low-crystallinity chitin has desirable adsorption properties [130], and chitin with a low CrI index exhibits high heavy-metal-removal efficiency due to its low diffusion resistance [131]. The chitin extracted from H. illucens larvae has unique physicochemical traits, suggesting H. illucens as a new source of this biopolymer for biotechnological applications [34]. Therefore, the resource value of the antibacterial peptides and chitin of H. illucens may become a topic of further investigation in the biomedical field.
3.4. Ecological Value of the Treatment of Organic Waste by Hermetia illucens
The treatment of organic waste by H. illucens larvae is gaining attention [69,110,132,133,134,135]. In addition, other types of waste are being explored as potential substrates for the sustainable use of H. illucens larvae biomass as food for humans and other animals [43,136,137].
Previous research has revealed that the ecological characteristics of H. illucens are similar to those of houseflies and that the two species appear to compete with one another. H. illucens fly has been shown to inhibit the breeding of houseflies [3,93]. In 1997, Sheppard successfully developed the first system for excrement treatment using H. illucens. Subsequently, research on the treatment of livestock excrement and domestic waste has been ongoing. In 1997, Dr. Oliver of the United States Environmental Technology and Engineering Corporation invented a H. illucens larvae biotransformer for domestic use. The biotransformer has been successfully used to treat municipal solid waste. In 2007, Dr. Xincheng An of the Guangdong Institute of Entomology designed a bioconversion system for the efficient large-scale treatment of organic waste; the system achieved satisfactory reduction, decontamination, and recycling of waste. Kitchen waste, livestock excrement, deteriorated fruits and vegetables, crop waste, and food-processing waste can be quickly and effectively converted by H. illucens larvae because of this insect’s wide range of potential foods. The converted waste then forms the biomass of H. illucens larvae itself, such that H. illucens larvae can be applied in environmental ecology and as an effective treatment for organic waste [138,139].
Environmental safety assessment has shown that H. illucens consumes only small amounts of plant juice and does not carry human pathogens. Therefore, H. illucens has important ecological value, appears not to harm human beings or their environment, and poses no threat to crops.
3.4.1. Research on the Treatment of Excrement by Hermetia illucens
The accumulation of livestock excrement that cannot be promptly and effectively treated leads to environmental pollution, primarily through air, water, and soil pollution [140,141]. At present, the methods of converting or utilizing livestock excrement are mainly restricted to excrement use in high-temperature compost, as an energy source, and in feedstuff production [142]. In the late 1970s, H. illucens larvae began to replace houseflies in the bioconversion of livestock excrement, and substantial progress rapidly followed [94,143]. Recently, a model for converting livestock excrement by H. illucens larvae has been piloted and promoted for sustainable agricultural production in the United States. In 1994, Professor Sheppard of the University of Georgia (USA) established an efficient, low-cost a manure treatment system using H. illucens larvae. The system converted half the manure into protein (42%) and grease (35%) as evidenced by the characteristics of H. illucens, and the nitrogen content and the abundance of E. coli were significantly reduced [7,17]. Fermented and fresh pig manure was also converted by H. illucens larvae, with conversion rates of 23% and 28%, respectively. After conversion, the content of organic matter in the manure was 71.9%, the total nutrient content (N + P2O5 + K2O) was 8.76%, and the pH value was 7.3. These nutrient values fully met the standard for organic fertilizer [144]. With the amounts of fecal accumulation and metallic elements (except iron) being significantly reduced [145]. Cow dung, swine manure and chicken manure converted by H. illucens larvae can be used as high-quality organic fertilizer and produce no offensive smell. In particular, cow dung converted by this insect becomes less solid, and when as an organic fertilizer, can increase the growth of pasture. In addition, the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents of pig manure were found to decrease by 55.1%, 44.1%, and 52.8%, respectively, following conversion, and organic matter formed. These observations indicate that H. illucens larvae offers significant economic and environmental benefits in the treatment and conversion of livestock excrement [111]. In addition, the treatment system has been adopted to the treatment of waste from animal farming and has achieved satisfactory results [146,147,148,149]. H. illucens larvae can effectively convert human feces from source separation toilets or fecal sludge from onsite sanitation systems [9,150,151]. Research has shown that after conversion, the pH of human feces increases, the total amounts of solid and total volatile solids and the abundance of Salmonella significantly decrease, and the level of total ammonia nitrogen improves. No significant effect of such treatment has been observed on enterococci, phage 174, or Ascaris eggs. These outcomes indicate the environmental and ecological value of such treatment [12].
3.4.2. Research on the Treatment of Other Organic Waste by Hermetia illucens
In addition to excrement, kitchen waste, coffee grounds, palm seed meal, agricultural waste, and other organic waste can be effectively converted by H. illucens larvae [152]. Kitchen waste contains not only large amounts of organic components, such as starch and cellulose, but also fat, salt, and abundant trace elements. This form of organic waste continuously affects the environment. Another common form of organic waste is fruit and vegetable waste from food companies or markets. At present, treatment methods for organic waste primarily include incineration, landfills, fodder, anaerobic digestion, aerobic composting, and earthworm compost [153]. However, these treatment methods cannot satisfy the requirements of environmental protection and a high degree of resource utilization. H. illucens larvae has been applied to the conversion of kitchen, fruit and vegetable waste [13,20,146,147,154,155]. Research has shown that among the larval instars of H. illucens, 6th instar larvae exhibited the highest survival rate and the highest conversion rate in converting kitchen residue, particularly when the moisture level was 60%. Regarding the dry matter of old mature larvae, values of 44.7% protein and 37.2% grease were obtained [113]. In addition, the NH4+ of the kitchen waste was 5–6 times higher following treatment than before treatment; such conversion has the potential to offset the nitrogen accumulation caused by fertilization [156]. Therefore, there are substantial prospects for the conversion and treatment of kitchen, fruit and vegetable wastes by H. illucens larvae. More importantly, effective treatment and conversion of municipal organic solid waste and industrial organic waste by larvae has been achieved [43,154,157,158]. These advances provide a basis for the large-scale cultivation of H. illucens and the large-scale treatment of organic wastes [136]. In 2015, based on the effective conversion of organic wastes by H. illucens larvae, a specialized H. illucens larvae breeding base was established in Tieyong Town, Huidong County, Guangdong Province. In the same year, the output and the kitchen waste treatment capacity were 1.3 t/day and 7.8 t/day, respectively. The bioconversion of a mixture of rice straw and kitchen waste was investigated. A total of 2000 H. illucens larvae were used to convert 1.0 kg of an organic waste mixture (30% rice straw; 70% kitchen waste). After 10 days, 65.5% of the cellulose, 56.3% of the hemicellulose, 8.8% of the lignin, 91.6% of the protein, and 71.6% of the fat had been digested by H. illucens larvae and converted into their own biomass. Therefore, the transformation of agricultural waste using H. illucens larvae has excellent prospects.
3.4.3. Ecological Value of Hermetia illucens for the Treatment of Organic Waste
After the conversion of organic waste by H. illucens larvae, organic waste accumulation is reduced, and pollution and harm to the environment are decreased. In its ecology, H. illucens fly is similar to the housefly. However, the larvae of H. illucens fly can produce pheromones that are repellent to houseflies, which results in no oviposition or breeding of houseflies in excrement. Similar effects of H. illucens fly against other noxious insects, such as Tenebrio molitor, have been observed [3,93]. Following the inoculation of chicken manure with labelled E. coli and Salmonella enterobacter, the use of H. illucens larvae to convert the manure was found to reduce the abundances of these pathogens by more than 2000 times [7]. The larvae not only inhibited Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella but also displayed the ability to escape the symbiotic matrix with Salmonella, especially at a temperature of 27 °C. In addition, the larvae affected the growth of E. coli in cow dung and showed good antibacterial properties. Furthermore, it has been shown that during conversion, some organic pollutants, such as antibiotics and pesticides, are degraded [159], the accumulation of metals in the organic waste is decreased [48,160,161,162,163], and the abundances of pathogens and harmful microorganisms are reduced [7,8,164,165] by the larvae. In addition, the conversion of organic waste by H. illucens larvae results in no accumulation of antibiotics, pesticides, dioxins, polychlorinated biphenyls or polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the insect body; only heavy metal accumulation has been observed [159,161,166,167]. Thus, in addition having saprophytic characteristics, H. illucens larvae is an important insect for environmental protection because it has the ability to digest or decompose harmful bacteria in the environment and reduce the harmful effects of waste on the environment.
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Due to its biological characteristics, the H. illucens has been widely used for the environmentally friendly treatment of common organic waste, such as excrement, kitchen waste, domestic waste, and agricultural waste. Importantly, such treatment not only converts the organic waste to useful and harmless forms but also results in the conversion of the nutriment to insect biomass. The proteins and grease of this insect have been applied to the breeding industry and the fine chemical engineering industry. In addition, the antimicrobial peptides and chitin obtained from H. illucens are important raw materials for biology, medicine, and food production. However, the biological characteristics and resource value of this insect have not been used effectively or sufficiently because of the low level of industrialization. Although this insect has been applied to the treatment of organic wastes and the feed industry, the industrialized, large-scale breeding of H. illucens remains in the exploratory stage. Reports on the detailed process and mechanism of conversion are lacking, although some research on the gut microbial communities of the larvae has been performed. Crop straw is an important source of biomass energy, but its utilization efficiency is low, and its processing is challenging due to its physicochemical properties. The bioconversion of agriculture waste by H. illucens is in very early stages, and studies of the mechanisms of the bioconversion and degradation of crop straw by H. illucens in cooperation with microorganisms are needed.
With the rapid development of intensive and modern industry, agriculture and livestock farming, problems related to food, the environment and energy will be aggravated. Research on the comprehensive resource utilization of waste using the H. illucens will receive increasing attention. Studies of the process and mechanism of conversion, including the interactions with microorganisms, are needed, as are studies of the acquisition and safety evaluation of nutrients from this insect. The results of such efforts might encourage the development of industrialized, large-scale breeding and a processing industry based on H. illucens as well as the safe and useful treatment of organic wastes. These developments will play an important role in agriculture, industry and human health.
Author Contributions
C.W. and H.Y. contributed to the conception and design. C.L. wrote the manuscript. H.Y. and C.W. contributed to the revision of the manuscript. H.Y. and C.W. secured funding. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41525002), and the Collaborative Innovation Center of Catalysis Materials of Hubei Province.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that none of the authors have a conflict of interest.
References
- James, M.T. The genus Hermetia in the United States (Dipt, Stratiomyidae). Bull. Brooklyn Entomol. Soc. 1935, 30, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Benelli, G.; Canale, A.; Raspi, A.; Fornaciari, G. The death scenario of an Italian Renaissance princess can shed light on a zoological dilemma: Did the black soldier fly reach Europe with Columbus? J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 49, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.W.; Sheppard, D.C. House fly oviposition inhibition by larvae of Hermetia illucens, the black soldier fly [Musca domestica, allomone]. J. Chem. Ecol. 1984, 10, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Oliveira, F.; Doelle, K.; Smith, R.P. External morphology of Hermetia illucens Stratiomyidae: Diptera (L.1758) based on Electron microscopy. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2016, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranshaw, W.; Shetlar, D. Garden Insects of North. America: The Ultimate Guide to Backyard Bugs; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondari, K.; Sheppard, D.C. The soldier fly Hermetia illucens L., as feed for channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque), and blue tilapia, Oreochromis aureus (Steindachner). Aquac. Res. 1987, 18, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.C.; Islam, M.; Sheppard, C.; Liao, J.; Doyle, M.P. Reduction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in chicken manure by larvae of the black soldier fly. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Brady, J.A.; Sanford, M.R.; Yu, Z. Black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae reduce Escherichia coli in dairy manure. Env. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Magri, M.E.; Zurbrügg, C.; Lindström, A.; Vinnerås, B. Faecal sludge management with the larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens)—From a hygiene aspect. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, D.C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Joyce, J.A.; Kiser, B.C.; Sumner, S.M. Rearing methods for the black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Sheppard, D.C. Factors influencing mating and oviposition of black soldier flies (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in a colony. J. Entomol. Sci. 2002, 37, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae: Establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Manag. Res. J. Int. Solid Wastes Public Clean. Assoc. Iswa 2009, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Broekhoven, S.; van Huis, A.; van Loon, J.J.A. Feed conversion, survival and development, and composition of four insect species on diets composed of food by-products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, P.; Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Rojo, S. The effects of larval diet on adult life-history traits of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). EJE 2013, 110, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Yu, Z.N. Double the biodiesel yield: Rearing black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens, on solid residual fraction of restaurant waste after grease extraction for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Hou, Y.F.; Wu, L.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z.N. Biodiesel production from rice straw and restaurant waste employing black soldier fly assisted by microbes. Energy 2012, 47, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, D.C.; Newton, G.L.; Thompson, S.A.; Savage, S. A value added manure management system using the black soldier fly. Bioresour. Technol. 1994, 50, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, N.; Cai, H.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z. Bioconversion of dairy manure by black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for biodiesel and sugar production. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Ottoboni, M.; Klootwijk, C.; Ovyn, A.; Deboosere, S.; De Meulenaer, B.; Michiels, J.; Eeckhout, M.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on different organic waste substrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, C.; Erba, D.; Leonardi, M.G.; Lupi, D.; Savoldelli, S. Assessment of vegetable and fruit substrates as potential rearing media for Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, S.; Khanikor, B.; Sarma, R. Potentiality of essential oil from Citrus grandis (Sapindales: Rutaceae) against Culex quinquefasciatus Say (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 803–809. [Google Scholar]
- Hem, S.; Toure, S.; Sagbla, C.; Legendre, M. Bioconversion of palm kernel meal for aquaculture: Experiences from the forest region (Republic of Guinea). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduh, M.Y.; Manurung, R.; Faustina, A.; Affanda, E.; Siregar, I.R.H. Bioconversion of Pandanus tectorius using black soldier fly larvae for the production of edible oil and protein-rich biomass. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 803–809. [Google Scholar]
- Abduh, M.Y.; Jamilah, M.; Istiandari, P.; Manurung, S.; Manurung, R. Bioconversion of rubber seeds to produce protein and oil-rich biomass using black soldier fly larva assisted by microbes. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Manurung, R.; Supriatna, A.; Esyanthi, R.R.; Putra, R.E. Bioconversion of rice straw waste by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.): Optimal feed rate for biomass production. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, V.C.; Rawles, S.D.; Thompson, K.R.; Velasquez, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hager, J.; Webster, C.D. Evaluation of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal as partial or total replacement of marine fish meal in practical diets for Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, M.; Sánchez-López, A.; Leal, R.S.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) pre-pupae meal as a fish meal replacement in diets for European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2017, 476, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranghers, T.; Michiels, J.; Vrancx, J.; Ovyn, A.; Eeckhout, M.; Clercq, P.D.; Smet, S.D. Gut antimicrobial effects and nutritional value of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) prepupae for weaned piglets. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 235, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Chang, B.S.; Yoe, S.M. Detection of antimicrobial substances from larvae of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Kim, J.W.; Yoe, S.M. Purification and characterization of a novel antibacterial peptide from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Yoe, S.M. A novel cecropin-like peptide from black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens: Isolation, structural and functional characterization. Entomol. Res. 2017, 47, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Müller, A.; Heckel, D.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional immunology: Diversification and diet-dependent expression of antimicrobial peptides in the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waśko, A.; Bulak, P.; Polak-Berecka, M.; Nowak, K.; Polakowski, C.; Bieganowski, A. The first report of the physicochemical structure of chitin isolated from Hermetia illucens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callan, E.M. Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera, Stratiomyidae), a cosmopolitan American species long established in Australia and New Zealand. Entomol. Mon. Mag. 1974, 109, 232–234. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Cheng, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tomberlin, J.K. Inoculating poultry manure with companion bacteria influences growth and development of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae. Env. Entomol. 2011, 40, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, B.M. The occurrence in New Zealand and the life-history of the soldier fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Nzj Sci. 1961, 4, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araujo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbo, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.J. Modulation of nutrient composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae by feeding seaweed-enriched media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.T.; Bae, S.W.; Park, H.C.; Park, K.H.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, Y.C.; Han, S.M.; Koh, Y.H. The larval age and mouth morphology of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2010, 21, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- Belghit, I.; Liland, N.S.; Waagbø, R.; Biancarosa, I.; Pelusio, N.; Li, Y.; Krogdahl, Å.; Lock, E.-J. Potential of insect-based diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2018, 491, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. The Impact of Diet Protein and Carbohydrate on Select Life-History Traits of The Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects 2017, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; Loon, J.J.A.v. Influence of larval density and dietary nutrient concentration on performance, body protein, and fat contents of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 166, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.Y.; Tanga, C.M.; Osuga, I.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Khamis, F.M.; Salifu, D.; Sevgan, S.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Niassy, S.; van Loon, J.J.A.; et al. Effects of waste stream combinations from brewing industry on performance of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). PeerJ 2018, 6, e5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camenzuli, L.; Van Dam, R.; de Rijk, T.; Andriessen, R.; Van Schelt, J.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.I. Tolerance and Excretion of the Mycotoxins Aflatoxin B₁, Zearalenone, Deoxynivalenol, and Ochratoxin A by Alphitobius diaperinus and Hermetia illucens from Contaminated Substrates. Toxins 2018, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, L.; Ceballos, S.J.; Johnson, P.C.; Niemeier, D.; Pitesky, M.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Cultivation of black soldier fly larvae on almond byproducts: Impacts of aeration and moisture on larvae growth and composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5893–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneguz, M.; Gasco, L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Impact of pH and feeding system on black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens, L.; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larval development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, G.; Fels-Klerx, H.J.v.d.; Rijk, T.C.d.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. Aflatoxin B1 Tolerance and Accumulation in Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Yellow Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor). Toxins 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens and effects on its life cycle. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumble, J.T.; Jensen, P.D. Ovipositional response, developmental effects and toxicity of hexavalent chromium to megaselia scalaris, a terrestrial detritivore. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Studt Solano, N.M.; Roa Gutiérrez, F.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Biological treatment of municipal organic waste using black soldier fly larvae. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2011, 2, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nursita, A.I.; Singh, B.; Lees, E. The effects of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc on the growth and reproduction of Proisotoma minuta Tullberg (Collembola). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Dan, J.L.; Zhu, W.; Liao, Y.; Yu, G.H.; Chen, Y.F. Effects of Zinc on the growth and development of black soldier fly Hermetia illucens L. (Dipetra: Stratiomyidae). J. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 35, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y. Accumulation of Zn2+ in the Hemolymph of Larvae of Hermetia Illucens L. and Its Preliminary Effects on the Enzyme Activity and Protein of Hemolymph; Zunyi Medical College: Zuiyi, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xia, Q. Research progresses about the effect of copper pollution on the growth and reproduction of insects. J. Environ. Entomol. 2016, 38, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, Q.Y.; An, X.C. The study of stress resistance for larva and pre-pupa stage of black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens. J. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 34, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Lei, C.; Zhu, F. Influences of chromium and cadmium on the development of black soldier fly larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 8637–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.C.; Sheppard, C. Oviposition of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae): Eggs, Masses, Timing, and Site Characteristics. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumo, M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; van Huis, A.; Borgemeister, C. Influence of Temperature on Selected Life-History Traits of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Two Common Urban Organic Waste Streams in Kenya. Animals (Basel) 2019, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; He, J.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Li, J.; Lei, C.; Sun, M.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. An artificial light source influences mating and oviposition of black soldier flies, Hermetia illucens. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heussler, C.D.; Walter, A.; Oberkofler, H.; Insam, H.; Arthofer, W.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M. Influence of three artificial light sources on oviposition and half-life of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae): Improving small-scale indoor rearing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Vanlaerhoven, S.L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Substrate effects on pupation and adult emergence of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; Niu, C.Y.; He, B.G.; Zhou, L.; Xia, Q.; CHeng, P. Isolation and identification of bacteria producing enzymes from gut and skin of black soldier fly. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2010, 47, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Crippen, T.L.; Singh, B.; Tarone, A.M.; Dowd, S.; Yu, Z.; Wood, T.K.; Tomberlin, J.K. A survey of bacterial diversity from successive life stages of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) by using 16S rDNA pyrosequencing. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth-Prestia, C.; Hirshfield, I.N. Isolation of plasmid-harboring serratia plymuthica from facultative gut microflora of the tobacco hornworm, manduca sexta. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1988, 54, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiyama, M.; Kimura, K. Bacteria in the gut of Japanese honeybee, Apis cerana japonica, and their antagonistic effect against Paenibacillus larvae, the causal agent of American foulbrood. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 102, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, S.W.; Booth, D.C.; Sheppard, D.C. Parasitism of the black soldier fly by trichopria sp. (Hymenoptera: Diapriidae) in poultry houses. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotto Boccazzi, I.; Ottoboni, M.; Martin, E.; Comandatore, F.; Vallone, L.; Spranghers, T.; Eeckhout, M.; Mereghetti, V.; Pinotti, L.; Epis, S. A survey of the mycobiota associated with larvae of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) reared for feed production. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Jeong, G.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.J. The intestinal bacterial community in the food waste-reducing larvae of Hermetia illucens. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, J.; Wynants, E.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial Community Dynamics during Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) and Impact on Exploitation Potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Seo, S.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Hahn, B.S.; Sim, J.S.; Koo, B.S.; Lee, C.M. Identification of a novel alkaline amylopullulanase from a gut metagenome of Hermetia illucens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Seo, S.H.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Hahn, B.S.; Sim, J.S.; Koo, B.S. Screening and characterization of a novel cellulase gene from the gut microflora of Hermetia illucens using metagenomic library. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; Oh, H.W.; Jeong, W.J.; Kim, H.; Park, H.Y.; Bae, K.S. A culture-based study of the bacterial communities within the guts of nine longicorn beetle species and their exo-enzyme producing properties for degrading xylan and pectin. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Warnecke, F.; Luginbuhl, P.; Ivanova, N.; Ghassemian, M.; Richardson, T.H.; Stege, J.T.; Cayouette, M.; McHardy, A.C.; Djordjevic, G.; Aboushadi, N.; et al. Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 2007, 450, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Sheppard, D.C.; Joyce, J.A. Selected life-history traits of black soldier flies (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) reared on three artificial diets. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2002, 95, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Long, J.C.; Ye, M.Q.; An, X.C.; Han, S.C. Development rate and food conversion efficiency of black soldier fly. J. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 36, 561–564. [Google Scholar]
- DeFoliart, G.R. Edible insects as minilivestock. Biodivers. Conserv. 1995, 4, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; Bosch, G. Insects: A protein-rich feed ingredient in pig and poultry diets. Anim. Front. 2015, 5, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, R.; Saija, G.; Mondello, G.; Giannetto, A.; Fasulo, S.; Savastano, D. Environmental impact of food waste bioconversion by insects: Application of Life Cycle Assessment to process using Hermetia illucens. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, R.; Green, T.R. Using black soldier fly larvae for processing organic leachates. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, H.M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Lambert, B.D.; Kattes, D. Development of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae fed dairy manure. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Bae, S.; Park, K.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Han, S.; Koh, Y. Biochemical characterization of digestive enzymes in the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; De Filippis, F.; Di Lelio, I.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M.; Ercolini, D.; Caccia, S. The Intestinal Microbiota of Hermetia illucens Larvae Is Affected by Diet and Shows a Diverse Composition in the Different Midgut Regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01864-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, M.; Bruno, D.; Caccia, S.; Sgambetterra, G.; Cappellozza, S.; Jucker, C.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M. Structural and Functional Characterization of Hermetia illucens Larval Midgut. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetti, C.; Samayoa, A.C.; Hwang, S.Y. Effects of Feeding Adults of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) on Longevity, Oviposition, and Egg Hatchability: Insights into Optimizing Egg Production. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Van Miert, S.; Geeraerd, A.; Claes, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Risks related to the presence of Salmonella sp. during rearing of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) for food or feed: Survival in the substrate and transmission to the larvae. Food Control 2019, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoliart, G.R. Insect fatty acids: Similar to those of poultry and fish in their degree of unsaturation, but higher in the polyunsaturates. Food Insects News Lett. 1991, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; Loon, J.J.A.V. Nutritional value of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and its suitability as animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, A.; Marco, M.D.; Martínez, S.; Dabbou, S.; Renna, M.; Madrid, J.; Hernandez, F.; Rotolo, L.; Costa, P.; Gai, F. Nutritional value of a partially defatted and a highly defatted black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) meal for broiler chickens: Apparent nutrient digestibility, apparent metabolizable energy and apparent ileal amino acid digestibility. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Sheppard, C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Irving, S.; Newton, L.; Mcguire, M.A.; Mosley, E.E.; Hardy, R.W.; Sealey, W. Fly Prepupae as a Feedstuff for Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Liang, S.H.; Doan, T.T.; Su, C.H.; Yang, P.C. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of biodiesel from black soldier fly (Hermetica illucens): Optimization by using response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 145, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qian, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Deng, Z.; Yang, F.; Xiong, J.; Feng, W. Exploring the potential of lipids from black soldier fly: New paradigm for biodiesel production (I). Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C. House fly and lesser fly control utilizing the black soldier fly in manure management systems for caged laying hens. Environ. Entomol. 1983, 12, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.L.; Booram, C.V.; Barker, R.W.; Hale, O.M. Dried Hermetia illucens larvae meal as a supplement for swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 44, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.M.; Liu, L.E.; Lv, Q.J.; Wu, Y.J. Analysis of nutrition composition on silkworm pupa. J. Zhengzhou Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2009, 44, 638–641. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Yu, Z.N.; Cheng, P. Research progression on the larvae and prepupae of black soldier fly Hermetia illucens used as animal. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2009, 46, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Nutritional components of the larvae of Tenebrio molitor L. and its control. Kun Chong Zhi Shi 1999, 36, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, G.Y. Experiment on growing-finishing pigs fed on earthworm meal instead of fish meal. Hunan J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2006, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Chen, M.; Peng, W.F. Study on the nutritional value of the housefly larva fed with pig manure. J. Guiyang Med. Coll. 2001, 26, 377–379. [Google Scholar]
- Caligiani, A.; Marseglia, A.; Leni, G.; Baldassarre, S.; Maistrello, L.; Dossena, A.; Sforza, S. Composition of black soldier fly prepupae and systematic approaches for extraction and fractionation of proteins, lipids and chitin. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, M.; Martínez, S.; Hernandez, F.; Madrid, J.; Gai, F.; Rotolo, L.; Belforti, M.; Bergero, D.; Katz, H.; Dabbou, S.; et al. Nutritional value of two insect larval meals (Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens) for broiler chickens: Apparent nutrient digestibility, apparent ileal amino acid digestibility and apparent metabolizable energy. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 209, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Zotte, A.; Singh, Y.; Michiels, J.; Cullere, M. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) as Dietary Source for Laying Quails: Live Performance, and Egg Physico-Chemical Quality, Sensory Profile and Storage Stability. Animals 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hori, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Hirayasu, H.; Iwase, S.-I.; Hashizume, A.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T.; et al. Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Pre-Pupae Raised on Household Organic Waste, as Potential Ingredients for Poultry Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwaniki, Z.; Neijat, M.; Kiarie, E. Egg production and quality responses of adding up to 7.5% defatted black soldier fly larvae meal in a corn-soybean meal diet fed to Shaver White Leghorns from wk 19 to 27 of age. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhana, A.H. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as an Alternative Protein Source for Animal Feed. WARTAZOA. Indones. Bull. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2016, 26, 069–078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, Y.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Jung, B.G.; Lee, B.J. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae enhances immune activities and increases survivability of broiler chicks against experimental infection of Salmonella Gallinarum. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Feng, W.; Xiong, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F. Impact of drying method on the nutritional value of the edible insect protein from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae: Amino acid composition, nutritional value evaluation, in vitro digestibility, and thermal properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.Y.; Kutty, S.R.; Malakahmad, A.; Tan, C.K. Feasibility study of biodiesel production using lipids of Hermetia illucens larva fed with organic waste. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Cranfill, K.; McGuire, M.A.; Mosley, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Newton, L.; Sealey, W.; Sheppard, C.; Irving, S. Fish Offal Recycling by the Black Soldier Fly Produces a Foodstuff High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Animal Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Garza, E.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S. From organic waste to biodiesel: Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens, makes it feasible. Fuel 2011, 90, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M.; Sanli, H. Biodiesel production from various feedstocks and their effects on the fuel properties. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zheng, L.Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.L.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Yu, Z.N. Conversion process and resource utilization of restaurant waste by black soldier fly. ChemBioEng Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealey, W.M.; Gaylord, T.G.; Barrows, F.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; McGuire, M.A.; Ross, C.; St-Hilaire, S. Sensory Analysis of Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, Fed Enriched Black Soldier Fly Prepupae, Hermetia illucens. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teotia, J.S. Fly pupae as a dietary ingredient for starting chicks. Poult. Sci. 1973, 52, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, A.; Cullere, M.; De Marco, M.; Meneguz, M.; Biasato, I.; Bergagna, S.; Dezzutto, D.; Gai, F.; Dabbou, S.; Gasco, L.; et al. Partial or total replacement of soybean oil by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) fat in broiler diets: Effect on growth performances, feed-choice, blood traits, carcass characteristics and meat quality. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, A.; Dabbou, S.; De Marco, M.; Cullere, M.; Biasato, I.; Biasibetti, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Bergagna, S.; Dezzutto, D.; Meneguz, M.; et al. Black soldier fly larva fat inclusion in finisher broiler chicken diet as an alternative fat source. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2018, 12, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ji, H.; Zhang, B.; Tian, J.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H. Influence of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae oil on growth performance, body composition, tissue fatty acid composition and lipid deposition in juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Aquaculture 2016, 465, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, M.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Q. Simultaneous utilization of glucose and xylose for lipid accumulation in black soldier fly. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Yao, H.; Qiu, Q.; Chapman, S.J. High turnover rate of free phospholipids in soil confirms the classic hypothesis of PLFA methodology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rehman, K.U.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. Insect biorefinery: A green approach for conversion of crop residues into biodiesel and protein. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhao, Q.F.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Guo-Hui, Y.U.; Chen, Y.F.; Song, M.Y. Black soldier fly antimicrobial peptides induced conditions optimization and research of crude extracts activity. J. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 35, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, O.; Zhou, D.; Song, Q.; Soomro, A.A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Screening, Expression, Purification and Functional Characterization of Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Genes from Hermetia illucens (L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.F. Preliminary Research on Functional Roles in Antimicrobial Peptides from Crude Extracting in Black Soldier Fly; Zunyi Medical College: Zunyi, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Zhao, Q.F.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yu, G.H.; Chen, Y.F. Biological stability observation of antibacterial peptides in black soldier fly. Shandong Med. J. 2013, 53, 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tharanathan, R.N.; Kittur, F.S. Chitin—The undisputed biomolecule of great potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gades, M.D.; Stern, J.S. Chitosan supplementation and fat absorption in men and women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuoka, K.; Ishihara, M.; Asazuma, T.; Hattori, H.; Matsui, T.; Takase, B.; Kanatani, Y.; Fujita, M.; Saito, Y.; Yura, H. The interaction of chitosan with fibroblast growth factor-2 and its protection from inactivation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3277–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemtsev, S.V.; Zueva, O.Y.; Khismatullin, M.R.; Albulov, A.I.; Varlamov, V.P. Isolation of chitin and chitosan from honey bees. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2004, 40, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, E.S.; Nagy, K.S.; Elsabee, M.Z. Extraction and characterization of chitin and chitosan from local sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranaz, I.; Mengibar, M.; Harris, R.; Panos, I.; Miralles, B.; Acosta, N.; Galed, G.; Heras, A. Functional Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2009, 3, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Diener, S.; Zurbrugg, C.; Mathys, A. Decomposition of biowaste macronutrients, microbes, and chemicals in black soldier fly larval treatment: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohri, C.R.; Diener, S.; Zabaleta, I.; Mertenat, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Treatment technologies for urban solid biowaste to create value products: A review with focus on low- and middle-income settings. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2017, 16, 81–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurbrügg, C.; Dortmans, B.; Fadhila, A.; Vertsappen, B.; Diener, S. From pilot to full scale operation of a waste-to-protein treatment facility. Detritus 2018, 1, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čičková, H.; Newton, G.L.; Lacy, R.C.; Kozánek, M. The use of fly larvae for organic waste treatment. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.Y.; Tanga, C.M.; Khamis, F.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Salifu, D.; Sevgan, S.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Niassy, S.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M.; et al. Threshold temperatures and thermal requirements of black soldier fly Hermetia illucens: Implications for mass production. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetana, S.; Schmitt, E.; Mathys, A. Sustainable use of Hermetia illucens insect biomass for feed and food: Attributional and consequential life cycle assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohri, C.R.; Rajabu, H.M.; Sweeney, D.J.; Zurbrügg, C. Char fuel production in developing countries—A review of urban biowaste carbonization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 59, 1514–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.R.; He, F.; Mo, W.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, G.X.; Sun, Y.P. The feeding value of black soldier fly Hermetia illucens larvae for feeding different organic wastes. China Feed 2017, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Khan, S.; Yao, H.; Wang, J. Biochars reduced the bioaccessibility and (bio)uptake of organochlorine pesticides and changed the microbial community dynamics in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, H.; Yao, H. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Air-Conditioning Systems in Hospitals, Farms, and Residences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.L. Characterization and Comparison Study on Energy and Fertilizer Related Properties of Animal Manure in China; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, O.M. Dried Hermetia illucens larvae (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) as a feed additive for poultry. Ga Entomol. Soc. J. 1973, 8, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, L.; Sheppard, C.; Watson, D.W.; Burtle, G.; Dove, R. Using the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens, as a value-added tool for the management of swine manure. Anim. Poult. Waste Manag. Cent. North. Carol. State Univ. Raleigh NC 2005, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, G.; Sheppard, D.; Watson, D.; Burtle, G.; Dove, C.; Tomberlin, J.; Thelen, E. The black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens, as a manure management/resource recovery tool. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the State of the Science of Animal Manure and Waste Management, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–7 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nyakeri, E.M.; Ogola, H.J.; Ayieko, M.A.; Amimo, F.A. An open system for farming black soldier fly larvae as a source of proteins for smallscale poultry and fish production. J. Insects Food Feed 2016, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Rehman, A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, X.; Somroo, A.A.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Conversion of mixtures of dairy manure and soybean curd residue by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Huis, A.v.; Loon, J.J.A.v. Nutrient utilisation by black soldier flies fed with chicken, pig, or cow manure. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Influence of resources on Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larval development. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakeri, E.M.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Ayieko, M.A.; Amimo, F.A. Valorisation of organic waste material: Growth performance of wild black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) reared on different organic wastes. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, I.J.; Gibson, W.T.; Cameron, M.M. Growth rates of black soldier fly larvae fed on fresh human faeces and their implication for improving sanitation. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Field, L.M.; Michaelson, L.V. Using Hermetia illucens to process Ugandan waragi waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.C. Reliability Analysis about Technology for Using Black Soldier Fly on Bioconversion from Food Waste to Entomic Protein. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 41, 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tinder, A.C.; Puckett, R.T.; Turner, N.D.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K. Bioconversion of sorghum and cowpea by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.)) larvae for alternative protein production. J. Insects Food Feed 2017, 3, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lim, J.-W.; Mah-Hussin, M.-I.-A.; Uemura, Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Ramli, A.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Tham, L. Optimization of self-fermented period of waste coconut endosperm destined to feed black soldier fly larvae in enhancing the lipid and protein yields. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.R.; Popa, R. Enhanced Ammonia Content in Compost Leachate Processed by Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschirner, M.; Simon, A. Influence of different growing substrates and processing on the nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae destined for animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods (Basel, Switzerland) 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.; Senecal, J.; Gros Calvo, M.; Ahrens, L.; Josefsson, S.; Wiberg, K.; Vinneras, B. Fate of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in fly larvae composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Camenzuli, L.; van der Lee, M.K.; Oonincx, D.G. Uptake of Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic by Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens from Contaminated Substrates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purschke, B.; Scheibelberger, R.; Axmann, S.; Adler, A.; Jager, H. Impact of substrate contamination with mycotoxins, heavy metals and pesticides on the growth performance and composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for use in the feed and food value chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2017, 34, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaldina, O.; Peräniemi, S.; Sorvari, J. Ants and their nests as indicators for industrial heavy metal contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancarosa, I.; Liland, N.S.; Biemans, D.; Araujo, P.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.-J.; Amlund, H. Uptake of heavy metals and arsenic in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae grown on seaweed-enriched media. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.H.; Hill, G.B.; Vinnerås, B. Hygienic quality of faeces treated in urine diverting vermicomposting toilets. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinnerås, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Dickinson, M.; Wakefield, M.E.; Fitches, E.; Kenis, M.; Han, R.; Zhu, F.; Kone, N.; Grant, M.; Devic, E.; et al. Exploring the chemical safety of fly larvae as a source of protein for animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canteri de Souza, P.; Custódio Caloni, C.; Wilson, D.; Sergio Almeida, R. An Invertebrate Host to Study Fungal Infections, Mycotoxins and Antifungal Drugs: Tenebrio molitor. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).