Simple Summary
Birds and their parasites have evolved over millions of years, forming complex relationships that shape biodiversity. Until now, little was known about the mites living inside the feathers of Euphoninae birds, which includes Euphonia and Chlorophonia species found in Central and South America. Previously, only one species of these mites was recorded in this bird group. In our study, we discovered 4 species of quill mites living in the feathers of 15 bird species, significantly expanding our knowledge of their diversity and host associations. Our findings suggest that the evolutionary history of these birds has influenced which mite species they host. Some mites are found in both Euphonia and Chlorophonia, while others appear restricted to only one of these genera. Additionally, our findings suggest that different mite species occupying the same ecological niche tend to avoid co-infesting the same bird species, likely as a strategy to minimise competition. The mite material collected from museum bird collections provides valuable insights into host–parasite relationships, helping scientists better understand biodiversity, evolution, and species interactions in nature.
Abstract
Quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) are highly specialised avian ectoparasites that inhabit feather quills. Despite their widespread occurrence, their diversity, distribution, and host associations remain poorly understood. This study examined the diversity and ecological interactions of syringophilid mites parasitising Euphoninae hosts. We analysed 298 dry bird skins representing 25 species deposited in the Bavarian State Collection for Zoology in Munich, Germany. Quill mite infestations were detected in 15 host species, identifying 4 mite species, including 2 newly described taxa: Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. and Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n. Infestation prevalence ranged from 2% to 25%. Quill mite–host interactions exhibited high specialisation and niche differentiation, with no co-occurring species sharing the same microhabitat. Network analysis indicated moderate connectance (0.35) and significant host specificity (H2′ = 0.77, p = 0.007). Biogeographic history suggests that divergence from Carduelinae and subsequent evolutionary events shaped syringophilid diversity in Euphoninae. These findings underscore the importance of museum collections in uncovering cryptic parasite diversity and provide new insights into host–parasite co-evolutionary dynamics.
Keywords:
acari; aves; biodiversity; birds; ectoparasites; euphoninae; fringillidae; syringophilidae 1. Introduction
The subfamily Euphoninae, belonging to the family Fringillidae (order Passeriformes), represents a group of birds native to the tropical and subtropical regions of Central and South America [1,2,3]. This subfamily comprises two genera, Euphonia and Chlorophonia, encompassing 35 species characterised by their striking plumage and specialised dietary habits [1,4]. Members of Euphoninae are predominantly frugivorous, although occasional insect consumption has been reported. Their role as seed dispersers is ecologically significant, contributing to the maintenance and regeneration of tropical forests. Morphologically, species within Euphonia and Chlorophonia exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males often adorned in vibrant combinations of yellow, blue, and green, while females display more subdued hues that aid in camouflage. These birds inhabit various forested environments, from lowland rainforests to montane cloud forests, where they form small social groups or pairs [1].
Quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Cheyletoidea) are highly specialised avian parasites inhabiting feather quills [5]. Quill mites demonstrate high specificity toward their hosts, with most syringophilid species being either monoxenous or oligoxenous parasites. They also show distinct preferences for the specific habitats they colonise [5,6]. The Syringophilidae family includes approximately 400 species across 63 genera, associated with 27 bird orders [7,8]. Until recently, new species of the family Syringophilidae were described rather randomly, without much reference to host groups. It is only in recent years that intensive studies on quill mite fauna have begun, focusing on entire bird families or orders [9,10,11,12,13].
Up to now, the acarofauna of mites from the family Syringophilidae parasitising Euphoninae birds comprised only a single record—Syringophilopsis stawarczyki Skoracki et al., 2010 described from Chlorophonia cyanocephala in Brazil [14]. This limited record highlights the significant knowledge gap regarding the diversity, distribution, and host-parasite interactions of Syringophilidae mites in Euphoninae. This study addresses this gap by expanding the knowledge of Syringophilidae mites associated with Euphoninae and exploring their potential implications for host and parasite ecology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mites Collection, Preparation, Description, and Deposition
Mite material used in this study was collected from dry bird skins housed in the Bavarian State Collection for Zoology (SNSB-ZSM) in Munich, Germany. For each bird specimen, approximately ten contour feathers near the cloacal region, two under-tail coverts, two upper-tail coverts, and one secondary wing covert were selected. These feathers were subsequently examined for the presence of quill mites belonging to the family Syringophilidae.
Infested quills were placed in Nesbitt’s solution for three days at room temperature to soften the mites inside. Each quill was then carefully opened along its length using fine-tipped forceps. The mites were rinsed in 70% ethanol and subsequently mounted on permanent microscope slides using Hoyer’s medium [15]. Slide-mounted mites were examined using a ZEISS Axioscope light microscope (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with differential interference contrast (DIC) optics and a camera lucida.
Descriptions of idiosomal setation follow the system established by Grandjean [16], as adapted for Prostigmata by Kethley [17]. The nomenclature for leg chaetotaxy adheres to Grandjean’s proposal [18], while the morphological terminology is based on the works of Kethley [5] and Skoracki [6]. All measurements are reported in micrometres, with ranges for paratypes provided in brackets following the holotype data.
All mite specimens analysed in this study are deposited in two institutions: Adam Mickiewicz University, Poznan, Department of Animal Morphology (AMU), and the Bavarian State Collection for Zoology, Munich, Germany (SNSB-ZSM).
2.2. Statistics
Descriptive statistics were calculated using Quantitative Parasitology v.3.0 on the Web [19,20,21]. To analyse the host–parasite ecological two-way web, we employed the “bipartite” package in R version 4.3.1 [22,23], quantifying the ecological relationships between parasites and their hosts. In this analysis, parasite prevalence served as a quantitative index. First, we calculated connectance, a measure of the ratio of actual connections in the bipartite network to the maximum possible connections. Next, we assessed the C-score, a metric that quantifies the tendency of species pairs to avoid co-occurrence. A high C-score suggests that species rarely share the same host, which may indicate competition or niche differentiation, whereas a low value implies frequent co-occurrence, suggesting random or overlapping associations. To evaluate whether parasites were generalists or specialists, we used the H2′ metric, a network-wide specialisation index. H2′ ranges from 0 (complete generalisation, where all species interact with many partners) to 1 (complete specialisation, where each species interacts with only a single partner or a very restricted set). This metric provides a standardised way to compare specialisation across different networks. The null.t.test was applied to determine whether the observed H2′ values significantly deviated from random expectations [23], helping to assess whether the observed level of specialisation is ecologically meaningful. In the next step, we calculated nestedness, which describes the degree of order in the network, where parasites with fewer host interactions tend to share hosts with parasites with more interactions. Finally, to measure the functional diversity of parasites, we calculated d′, which represents how unique a species interaction pattern is relative to the entire network. The metric d′ is normalised between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates that a species interacts similarly to other species in the network (low functional diversity), while 1 represents a highly unique interaction pattern, suggesting a high degree of specialisation.
2.3. Bird Systematics and Zoogeographical Regions
The scientific names and taxonomy of birds are based on Winkler et al. [1] and Clements et al. [24]. Host species distribution follows BirdLife International [25]. Zoogeographical regions are defined according to Holt et al. [26] and Ficetola et al. [27].
3. Results
3.1. Systematics
Family Syringophilidae Lavoipierre, 1953
Subfamily Syringophilinae Lavoipierre, 1953
3.1.1. Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. (Figure 1 and Figure 2)
Female, holotype. Total body length 465 (460–475 in nine paratypes). Gnathosoma. Infracapitulum apunctate. Each medial branch of peritremes has two chambers; each lateral branch has five chambers. Stylophore 130 (130–140) long; exposed portion of stylophore apunctate, 100 (100–105) long. Idiosoma. Propodonotal shield rectangular in shape, apunctate, bearing bases of setae ve, si, c1, and se. Length ratio of setae ve:si 1:1. Setae se and c1 situated at same transverse level. Setae c1 1.2 times longer than se. Length ratio of setae d2:c1 1:1.2. Hysteronotal shield fused to pygidial shield, weakly sclerotised, apunctate, bases of setae d1 and e2 situated near this shield. Setae f2 3–3.5 times longer than f1. Setae h2 4–4.4 times longer than f2. Agenital setae ag1 1.3–1.7 longer than ag2. Genital plate absent. Both pairs of genital setae subequal in length. All coxal fields apunctate. Setae 3c 2.8 times longer than 3b. Legs. Fan-like setae p’ and p″ of legs III and IV with five or six tines. Lengths of setae: ve 15 (15–20), si 20 (15–20), se 160 (160–180), c1 190 (190–210), c2 155 (150–165), d1 20 (15–20), d2 165 (130–165), e2 15 (15–20), f1 20 (20–25), f2 70 (70–80), h1 20 (20–25), h2 310 (270–320), ps1 20 (15–20), g1 and g2 20 (20–25), ag1 65 (65–85), ag2 50 (40–50), ag3 105 (105–110).
Male. Total body length 260–270 in two paratypes. Gnathosoma. Infracapitulum apunctate. Each medial branch of peritremes has two chambers; each lateral branch has five or six chambers. Stylophore 100–105 long; exposed portion of stylophore apunctate, 80 long. Idiosoma. Propodonotal shield invisible in posterior part, apunctate, bearing bases of setae ve, si, and c1, bases of setae se on or near this shield. Length ratio of setae ve:si 1:1. Bases of setae se situated anterior to level of setae c1. Setae c1 and se subequal in length. Setae d2 short but twice as long as d1 and e2. Hysteronotal and pygidial shields absent. Setae h2 3–4 times longer than f2. Two pairs of agenital setae present, ag1 2–2.5 times longer than ag2. All coxal fields apunctate. Lengths of setae: ve 5–10, si 5–10, se 20, c1 20, c2 10–15, d1 10, d2 5, e2 5, f2 10, h2 30–40, ag1 20–25, ag2 10.
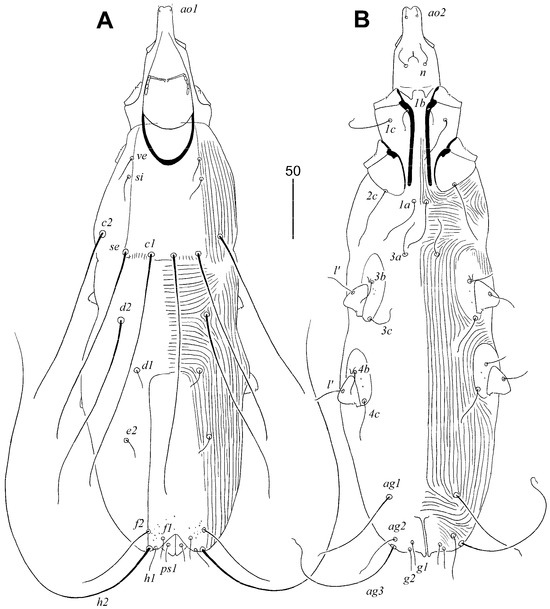
Figure 1.
Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n., female. (A) Dorsal view; (B) ventral view.
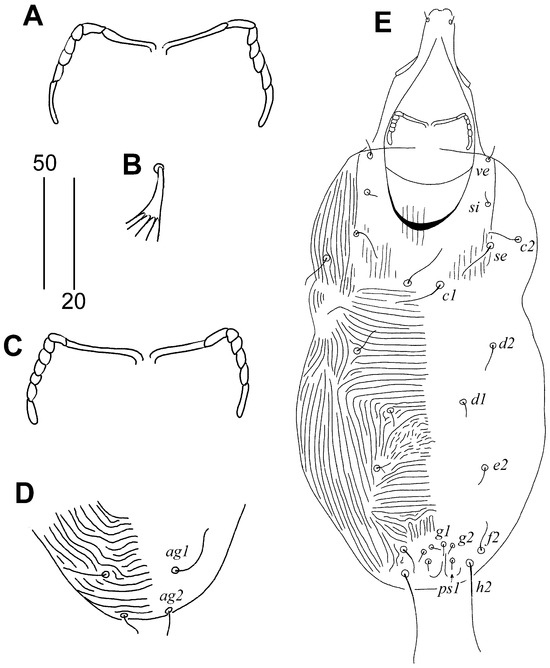
Figure 2.
Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n., female (A,B): (A) Peritremes; (B) fan-like seta p’III. Male (C,D): (C) Peritremes; (D) opisthosoma in ventral view. (E) Body in dorsal view. Scale bars (A–C) = 20 µm, (D,E) = 50 µm.
Type Material
Female holotype, nine female paratypes, and two male paratypes from the Blue-naped Chlorophonia Chlorophonia cyanea (Thunberg) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 30.96); Venezuela: Carabobo State, Valencia, 1928, coll. P. C. Vogl.
Type Material Deposition
Holotype and most paratypes deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250001) except two female paratypes and one male paratype in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-012).
Additional Material
Ex type host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 27.1872); Bolivia: Santa Cruz Province, Buena Vista, August 1926, coll. M. Kiefer—three females and two males deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250002), one female and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-010). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 10.2153); Venezuela: Carabobo State, Valencia, 9 February 1910, coll. S. M. Klages—two females deposited in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-013). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2281); Venezuela: Sucre State, Bermúdez, March 1897, coll. E. Andre—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-014).
Ex the Lesser Antillean Euphonia Chlorophonia flavifrons (Sparrman) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2291); Guadeloupe (Lesser Antillean Creole): 16 January 1896, coll. Chazalie—three females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250003), one female and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-034).
Ex the Golden-rumped Euphonia Chlorophonia cyanocephala (Vieillot) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2314); Colombia: Bogota, 1896, no other data—three females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250004), one female in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-037).
Ex the Scrub Euphonia Euphonia affinis (Lesson) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 15.941); Colombia: Bogotá D.C., Bogota, no other data—three females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250005), one female and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-016). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.5215) and locality—two females deposited in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-015).
Ex the Velvet-fronted Euphonia Euphonia concinna Sclater (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2356); Colombia: no other data—one female deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250006), one female in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-023). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 03.767); Colombia: Cauca Valley, 1903, coll. J.H. Batty—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-024).
Ex the Yellow-crowned Euphonia Euphonia luteicapilla (Cabanis) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.5337); Panama: Chiriquí Province, 17 February 1905, coll. H. Watson—three females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250007), two females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-025).
Ex the Tawny-capped Euphonia Euphonia anneae Cassin (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2303); Costa Rica: Guanacaste Province, Puerto Carrillo, 21 November 1897, coll. C.F. Underwood—three females and two males deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250008), one female and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-043).
Ex the Orange-bellied Euphonia Euphonia xanthogaster Sundevall (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 16.304); Peru: Carabaya Andes, Puno Region, Chaquimayo, 2 June 1910, coll. Watkins—four females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250009), two females in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-047). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 16.303) and locality, 18 June 1910, coll. Watkins—two females in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-048).
Ex the White-lored Euphonia Euphonia chrysopasta Sclater & Salvin (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2364); Venezuela: Río Caura, coll. E. Andre—three females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250010), two females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-041).
Ex the Golden-sided Euphonia Euphonia cayennensis (Gmelin) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 1909/275); French Guiana: 1907, coll. Le Moult—three females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250011), three females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-050).
Differential Diagnosis
Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. is morphologically similar to A. fringillus Skoracki, 2011 recorded from the Common Chaffinch Fringilla coelebs Linnaeus and the Eurasian Linnet Linaria cannabina (Linnaeus) [6,28]. In females of both species, the propodonotal shield is rectangular and bears bases of setae ve, si, se, and c1; the hysteronotal shield is fused with the pygidial shield; setae c1 are 1.2–1.5 longer than se; and setae e2 and d1 are subequal in length. This new species differs from A. fringillus as follows: in females of A. neotropicalis sp. n., the propodonotal shield is apunctate; the coxal fields III and IV are sparsely punctate; the lengths of setae se, c1, c2, and d2 are 160–180, 190–210, 150–165, and 130–165 respectively. In females of A. fringillus, the propodonotal shield is punctate on the whole surface; the coxal fields III and IV are apunctate; the lengths of setae se, c1, c2, and d2 are 120–125, c1 140–165, c2 90–100, and 80–90 respectively.
Etymology
The species name “neotropicalis” reflects the Neotropical origin of its hosts.
3.1.2. Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n. (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5)
Female, holotype. Total body length 980 (950–1040 in three paratypes). Gnathosoma. Hypostomal apex with one pair of small and sharp-ended protuberances. Infracapitulum apunctate. Stylophore 250 (230–250) long; exposed portion of stylophore apunctate, 205 (200–205) long. Length of movable cheliceral digit 145 (145–150). Each medial branch of peritremes has 2 or 3 chambers, each lateral branch with 12 chambers. Idiosoma. Propodonotal shield concave on anterior margin, sculptured laterally, and sparsely punctate near bases of setae ve and si, bearing bases of setae vi, ve, si, and c1; bases of se situated on the margin of this shield. Bases of setae se and c1 situated at same transverse level. Bases of setae c2 situated posterior to level of si setal bases. Length ratio of setae vi:ve:si 1:1.5–2:3.5–4. Hysteronotal shields absent. Pygidial shield weakly sclerotised in anterior part, apunctate. Genital setae ag2 3.8–4 times longer than genital setae g1 and g2. Setae ag1 and ag2 long and subequal in length. Coxal fields I–II sparsely punctate, III–IV densely punctate. Apodemes I fused to apodemes II in anterior part of apodemes II. Coxal setae 3c twice as longer as 3b. Lengths of setae: vi 90 (90–95), ve 140 (150–180), si 315 (350–355), se 335 (370–390), c1 320 (375–380), c2 325 (350), d1 320 (370–410), d2 320 (360), e2 300 (375–400), f1 longer than 250, f2 400, h1 290 (315–345), h2 430 (415–470), ps1 and ps2 30 (25–35), g1 and g2 50 (35–45), ag1 195 (230–295), ag2 190 (230–235), ag3 230 (230–300), l’RIV 60 (40–60), tc’III–IV 65 (65–70), 3b 80 (100–110), 3c 160 (150).
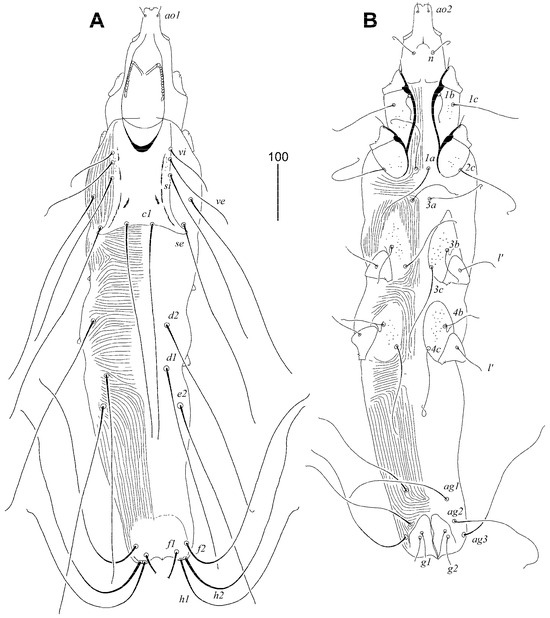
Figure 3.
Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n., female. (A) Dorsal view; (B) ventral view.
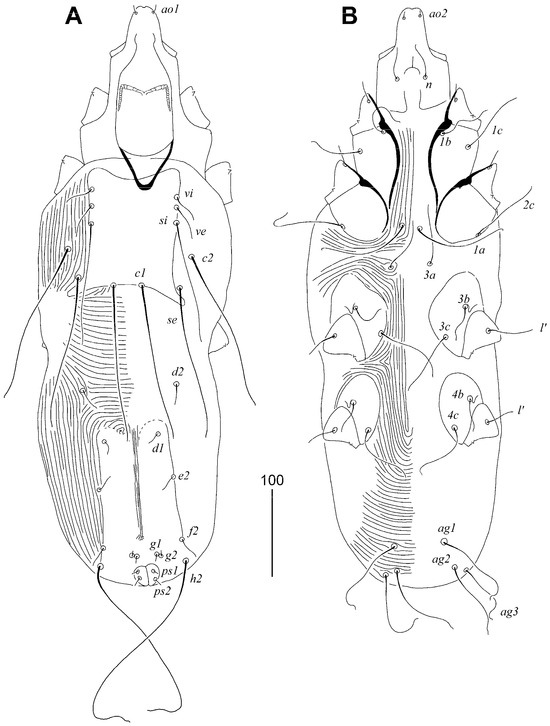
Figure 4.
Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n., male. (A) Dorsal view; (B) ventral view.
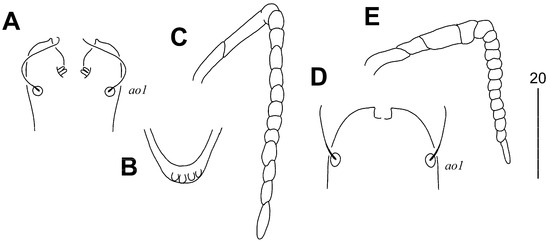
Figure 5.
Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n., female (A–C): (A) Hypostomal apex; (B) posterior part of stylophore; (C) peritreme. Male (D,E): (D) Hypostomal apex; (E) peritreme.
Male, paratype. Total body length 670. Gnathosoma. Hypostomal apex without protuberances. Infracapitulum apunctate. Stylophore 200 long; exposed portion of stylophore apunctate, 160 long. Each medial branch of peritremes with 5–6 chambers, each lateral branch with 12 chambers. Idiosoma. Propodonotal shield rectangular in shape, concave on anterior margin, apunctate, bearing bases of setae vi, ve, si, and c1; bases of setae se situated on the margin of this shield. Bases of setae se and c1 situated at same transverse level. Bases of setae c2 situated posterior to level of si setal bases. Hysteronotal shield fused to pygidial shield, divided longitudinally, apunctate, bearing bases of setae d1, bases of setae e2, f2, and h2 situated on the margin of this shield. Three pairs of agenital setae present, all subequal in length. Coxal fields I–IV apunctate. Apodemes I fused to apodemes II in middle part of apodemes II. Lengths of setae: vi 30, ve 40, si 140, se 170, c1 170, c2 175, d1 20, d2 30, e2 20, f2 35, h2 245, ag1 90, ag2 95, ag3 100, l’RIII 50, 3b 60, 3c 85.
Type Material
Female holotype, three female paratypes and one male paratype from the Trinidad Euphonia Euphonia trinitatis Strickland (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2381); Venezuela: Bermúdez, Andes of Cumaná, March 1897, coll. E. Andre.
Type Material Deposition
Holotype and two female paratypes are deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250012), one female paratype and one male paratype in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-018B).
Additional Material
Ex the Orange-bellied Euphonia Euphonia xanthogaster Sundevall (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 16.304); Peru: Carabaya Andes, Puno Region, Chaquimayo, 2 June 1910, coll. Watkins—two females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250013), two females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-047). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 16.303) and locality, 18 June 1910, coll. Watkins—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. AMU-MS-24-1025-048B). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 12.587); Peru: Puno Region, Carabaya Province, Yahuarmayo, 4 December 1910, coll. Watkins—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-046). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 12.588); Peru: Puno Region, Carabaya Province, Yahuarmayo, 4 December 1910, coll. Watkins—two females deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-049).
Ex the White-vented Euphonia Euphonia minuta Cabanis (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 67.122); Colombia: Antioquia Department, Mutatá, 120 m a.s.l., 13 August 1966, coll. J. Haffer—two females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250014), one female in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-045). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2352); Colombia: 1896, no other data—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-044).
Differential Diagnosis
Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n. belongs to the elongatus species-group [6]. Within this group, it is morphologically similar to S. nucifragus Skoracki, 2011, which has been recorded from the Spotted Nutcracker Nucifraga caryocatactes (Linnaeus) (Passeriformes: Corvidae) from Europe [6]. In females of both species, setae vi are shorter than 160 µm, the hysteronotal shields are absent, and agenital setae ag2 are distinctly longer (3–4 times) than genital setae (g1 and g2). The new species, S. euphonicus sp. n., can be distinguished by the following features: in females of S. euphonicus sp. n., the hypostomal apex is ornamented with a single pair of small and sharp-ended protuberances; the length of setae vi is 90–95 µm; the coxal fields I–II are sparsely punctate, while III–IV are densely punctate. In contrast, in females of S. nucifragus, the hypostomal apex is ornamented with two pairs of short protuberances; the length of setae vi is 150–200 µm; all coxal fields are apunctate. Furthermore, S. euphonicus sp. n. can be easily distinguished from other Syringophilopsis species parasitising fringillid birds, such as S. kirgizorum and S. fringillae, by the length of setae f1 and h1. In females of S. euphonicus sp. n., setae f1 and h1 are long, exceeding 250 µm; in S. kirgizorum, setae f1 and h1 measure only 80 µm; in S. fringillae, setae f1 are 185–190 µm long while setae h1 measure 340–350 µm.
Etymology
The species name “euphonicus” is taken from the generic name of the hosts.
3.1.3. Syringophiloidus stawarczyki Skoracki, 2004
This species was previously recorded on Euphoninae host, the Golden-rumped Euphonia Chlorophonia cyanocephala in Brazil [14], and two hosts from the family Thraupidae: the White-lined Tanager Tachyphonus rufus (Boddaert) and the Blue Dacnis Dacnis cayana (Linnaeus). Below, we present eight newly identified host species for this quill mite belonging to the Chlorophonia and Euphonia genera.
New Material Examined
Ex Blue-naped Chlorophonia Chlorophonia cyanea (Thunberg) (host uncatalogued); Brazil: Rio de Janeiro State, Rio de Janeiro, 20 July 1818, coll. J. Hatterer—fifteen females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250015), five females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-009). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2278); Colombia: Bogotá D.C., Bogota, 1896, coll. C. Dalmas—six females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250016), six females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-011).
Ex Velvet-fronted Euphonia Euphonia concinna (Sclater) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 15.933); Colombia: Bogotá D.C., Bogota, no other data—ten females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250017), six females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-022).
Ex White-lored Euphonia Euphonia chrysopasta (Sclater & Salvin) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2363); Venezuela: Bolívar State, Río Caura, November 1897, coll. E. Andre—six females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250018) and two females in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-042). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 27.1850); Bolivia: Santa Cruz Province, Buena Vista, August 1926, coll. M. Kiefer—ten females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250019), seven females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-039). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 27.1849) and other data—two females deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-040).
Ex Violaceous Euphonia Euphonia violacea (Linnaeus) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2373); Trinidad and Tobago: Trinidad Island, Santa Cruz, January 1897, coll. R. de Dalmas—four females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250020) and two females in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-026).
Ex Thick-billed Euphonia Euphonia laniirostris (d’Orbigny & Lafresnaye) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2335); Venezuela: Sucre state, hills between Bermúdez and Cumaná, March 1897, coll. E. Andre—five females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250021), four females and two males in the (reg. no. MS-24-1025-031).
Ex Purple-throated Euphonia Euphonia chlorotica (Linnaeus) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 32.1013); Paraguay: Apa Highlands (Apa Bergland) near Serranía San Luis National Park, Department of Concepción, 18 September 1931, coll. M. Kiefer—ten females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250022), four females and two males in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-020).
Ex Golden-rumped Euphonia Chlorophonia cyanocephala (Vieillot) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 36.109); Paraguay: Dept. Itapúa, Cambyretá, 14 July 1936, coll. A. Neunteufel—ten females deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250023), eight females and one male in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-038). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2316); Colombia: Bogotá D.C., Bogota, 1896, no other data—three females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250024), two females and one male (reg. no. MS-24-1025-036). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09/2313) and other data—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-035).
3.1.4. Picobia chloris Bochkov, Mironov & Kravtsova, 2000
This species was considered a monoxenous parasite, as it was previously known only from European Greenfinch Chloris chloris (Linnaeus) (Passeriformes: Fringillidae) in Kyrgyzstan [29]. Below, we report a new host species for this parasite.
New Material Examined
Ex Violaceous Euphonia Euphonia violacea (Linnaeus) (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.12); Brazil: Bahia State, no other data—three females and one male deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250025), two females (PF) and two males in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-030). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 09.2366); French Guiana: Cayenne, 1896, coll. Petit—one female deposited in the SNSB-ZSM (reg. no. ZSMA20250026) and one female in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-027). From the same host species (host reg. no. SNSB-ZSM 12.1682); Trinidad and Tobago: Trinidad Island, Caparo, 27 July 1912, coll. S. M. Klages—one female deposited in the AMU (reg. no. MS-24-1025-028).
3.2. Prevalence, Host Specificity and Bipartite Network Analysis
Data from 298 euphonine individuals belonging to 25 species were included in this study. Out of these, 15 host species were found to be parasitised by 4 quill mite species from 4 genera belonging to the 2 subfamilies. Infestation prevalences ranged from 2% to 25% in particular host species (Table 1). Among the analysed material, 44 specimens belonging to 10 species were not infested by quill mites (Table 2). The syringophilid mites—Euphoninae bipartite network (Figure 6) exhibited a moderate value of connectance (Con = 0.35). It means that 35% of all possible connections between birds and quill mites are observed in the network. A value of C.score = 0.675 indicates a moderate tendency for non-co-occurrence, but a value of H2′ = 0.77 indicates moderate to high specialisation in the network. A comparison between H2′ and null model values revealed significant differences (mean H2′ for null model = 0.775; t = 0.006; p = 0.007), indicating a statistically significant deviation from randomness. Temperature of nestedness = 32.39 indicates moderate nestedness, i.e., the network is not perfectly nested but shows significant structure. The normalised specialisation level (d′) ranged from 0.62 to 0.91, indicating a network dominated by moderate to highly specialised interactions. This means that each of these parasite species generally has unique ways of interacting with the host in the network.

Table 1.
Birds of the subfamily Euphoninae (Fringillidae) parasitised by quill mites of the family Syringophilidae with prevalence and distribution.

Table 2.
Euphonine host species not infested by quill mites.
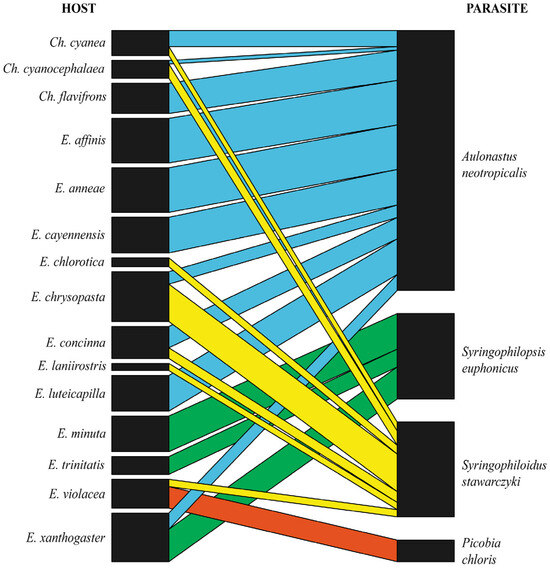
Figure 6.
Bipartite network graph of interactions between Euphoninae hosts (left) and their quill mite species (right); edge thickness is correlated with prevalence.
4. Discussion
The fauna associated with birds of the subfamily Euphoninae includes four species belonging to four genera and two subfamilies. Mites of the genera Aulonastus and Syringophilopsis, present on fringillid birds, are not exclusively associated with Euphoninae but have also been recorded on birds from the other two subfamilies, Fringillinae and Carduelinae [6,29,30,31,32,33]. The remaining two genera, Syringophiloidus and Picobia, are present on members of Euphoninae and Carduelinae but have not been found on representatives of Fringillinae [6,14,28,29,34,35]. Interestingly, despite a relatively large sample size (298 specimens belonging to 25 species), no representatives of the genera Aulobia and Neopicobia, which appear to be exclusively associated with members of Carduelinae [28,36,37,38,39], nor the genus Torotrogla, which inhabits birds belonging to both Fringillinae and Carduelinae [6,40,41], were found on Euphoninae (Table 3).

Table 3.
Quill mite genera associated with birds of the family Fringillidae; number of mite species/number of host species and distribution in the brackets.
Molecular dating suggests that Euphoniinae diverged from Carduelinae approximately 13.8 million years ago, with the crown age of Euphoniinae estimated at 7.1 million years ago [42]. The subfamily Euphoninae includes only two genera, Chlorophonia and Euphonia [1,2], both of which originated relatively recently. The crown age of Euphonia is estimated at 6.5 million years, while Chlorophonia is estimated around 3.8 million years ago [42]. The recent analysis revealed that the ancestral lineage of Euphoninae likely migrated to the Neotropics from North America, eventually diversifying in South America after crossing the Isthmus of Panama. In the Neotropics, the formation of the Western Amazon basin and the Northern Andean uplift during the Miocene likely triggered vicariance events that drove the divergence of the Chlorophonia and Euphonia lineages. As a result, Chlorophonia adapted to the Andean region, while Euphonia established itself in the Amazon basin [3,42]. This biogeographical history likely shaped the distribution and diversity of their associated syringophilid mites.
Among quill mites, the species Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. and Syringophiloidus stawarczyki have been recorded on hosts from both genera and should be classified as mesostenoxenous parasites (more than one genus of hosts, but restricted to one family [39]). These species were likely present on the last common ancestor of the Chlorophonia + Euphonia lineage. In contrast, the species Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n. exclusively inhabits birds of the genus Euphonia and should be regarded as an oligoxenous parasite (more than one host, but restricted to one genus). Likely, this species was also present on the last common ancestor of the Chlorophonia + Euphonia lineage but during the divergence of the two genera, it failed to colonise Chlorophonia hosts. This could be attributed to the “missing the boat” phenomenon, in which a parasite present in an ancestral host fails to establish itself in one of the newly diverging lineages. Such failure may result from ecological constraints, host specialisation, or competition. In this case, S. euphonicus sp. n. may have been unable to compete with Syringophiloidus stawarczyki, which occupies the same habitat on Euphoninae hosts. The last recorded species of quill mites, Picobia chloris, has been found on only one host species of Euphoninae, i.e., Euphonia violacea. Interestingly, this species has also been recorded on Chloris chloris, a member of the subfamily Carduelinae [29]. In the case of Euphonia violacea, P. chloris was found on 3 individuals (out of 26 examined, prevalence = 12%) from three distinct localities: Brazil, French Guiana, and Trinidad and Tobago. It suggests that the mite forms a stable association with this host and should not be regarded as an incidental infestation. Unfortunately, the prevalence of P. chloris infestation in Chloris chloris remains unknown.
The analyses demonstrated that the quill mites—Euphonias network exhibits moderate specialisation, with connectance = 0.35. Within this system, all quill mite species, except P. chloris, interact with multiple hosts, yet there is still a notable degree of specialisation, as indicated by H2′ = 0.77 and d′ values ranging from 0.62 to 0.91. Generalists (in this case mesostenoxenous parasites), such as Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. and Syringophiloidus stawarczyki, infest a broad spectrum of birds belonging to both genera Euphonia and Chlorophonia. In contrast, specialists (oligoxenous parasites) are more selective, e.g., Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n., which is restricted to representatives of Euphonia. On the other hand, each host species has a unique parasite fauna, indicating that host–parasite interactions are not random but rather are shaped by evolutionary processes (e.g., co-speciation). Such a high degree of specialisation aligns with the structured interactions commonly observed in quill mites–birds relationships [9,10,11,12,13] and in other co-evolved warm-blooded vertebrates and obligatory parasitic mites [43,44,45,46,47,48]. The analyses also revealed that the C-score value of 0.675 is relatively high, suggesting that quill mites tend to avoid sharing the same hosts. Conversely, host species often harbour distinct parasite communities with minimal overlap. In this study, no single host species was infested by different quill mite species inhabiting the same niche. For instance, Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n. and Syringophiloidus stawarczyki, found in wing coverts, or Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. and Picobia chloris, inhabiting contour feathers, were never observed on the same host specimen or even host species. In cases where a host species was infested by multiple quill mite species, niche differentiation was always observed, with syringophilids occupying distinct ecological niches (types of feathers) on the same host to avoid competition. For example, Chlorophonia cyanea, Ch. cyanocephala, Euphonia chrysopasta, and E. concinna were infested by two different mite species occupying different habitats, with A. neotropicalis sp. n. always found in contour feathers and S. stawarczyki exclusively in wing coverts. It implies competitive exclusion among parasites, where quill mites avoid co-occurrence to minimise competition for resources on the same host. This strategy is frequently observed in host species infested by two, three, or even four syringophilid mite species [5,6].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we identified 4 species of quill mites parasitising 15 host species of Euphoninae, whereas previously, only a single quill mite species had been recorded from a single Euphoninae host. This significantly expands our understanding of syringophilid mite diversity in this bird group and highlights the complexity of their host–parasite associations. The phylogenetic and biogeographical history of Euphoninae has likely played a key role in shaping the distribution and specialisation of their associated parasites. While some species, such as Aulonastus neotropicalis sp. n. and Syringophiloidus stawarczyki, exhibit broad oligoxenous parasitism and were likely present on the last common ancestor of Chlorophonia and Euphonia, others—like Syringophilopsis euphonicus sp. n.—show a more restricted host association. The absence of S. euphonicus sp. n. in Chlorophonia may be attributed to the “missing the boat” phenomenon or competitive exclusion by Syringophiloidus stawarczyki. Network analysis of quill mite–Euphoninae interactions revealed a moderately specialised system, with most mites exploiting multiple hosts while maintaining distinct ecological preferences. The observed values suggest that quill mites tend to avoid sharing the same host, likely due to competitive exclusion and niche differentiation. The lack of co-occurrence among species occupying similar microhabitats, such as wing coverts or contour feathers, further supports this pattern. These findings align with broader host–parasite co-evolutionary trends, where specialisation and competition drive structured interactions within parasite communities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, B.S., M.S. and M.U.; methodology, M.S., B.S. and M.U.; validation, B.S., M.S. and M.U.; formal analysis, B.S., M.S., M.U. and M.H.; investigation, B.S., M.S., M.U. and M.H.; material collection, M.S. and M.U.; data curation, B.S. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S., M.S., M.U., R.R.M., S.F. and M.H.; writing—review and editing, B.S., M.S., M.U., R.R.M., S.F. and M.H.; visualisation, M.S.; supervision, B.S. and M.S.; project administration, B.S., M.S., R.R.M., S.F. and M.H.; funding acquisition, B.S., M.S., R.R.M. and M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the SNSB collection panel (project 808: “New species from old collections”), Slovak Research and Development Agency under the contract APVV-22-0440, the Excellence Initiative Program “Mobility” of the UAM Research University—UAM ID-UB 146/07/POB1/0013 (to M.S.) and UAM ID-UB 146/07/POB1/0012 (to B.S.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The ethics was not applied. The research was conducted solely and exclusively on dry bird skins deposited in the ornithological collection of the museum.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All necessary data are available in the text.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Claudia Weidner and Burcin Yurdakul (ZSM) for their assistance during the research. The correspondence authors (B.S. and M.S.) expressed their gratitude to the SNSB—Bavarian State Collections of Natural History administration for invaluable support during research tenure at the ZSM. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their critical review of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Winkler, D.W.; Billerman, S.M.; Lovette, I.J. Finches, Euphonias, and Allies (Fringillidae). In Birds of the World; Version 1.0; Billerman, S.M., Keeney, B.K., Rodewald, P.G., Schulenberg, T.S., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccon, D.; Prys-Jones, R.; Rasmussen, P.C.; Ericson, P.G.P. The phylogenetic relationships and generic limits of finches (Fringillidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 62, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-López, M.; Ramírez-Barrera, S.M.; Terrones-Ramírez, A.K.; Robles-Bello, S.M.; Nieto-Montes de Oca, A.; Ruegg, K.; Hernández-Baños, B.E. Biogeographic factors contributing to the diversification of Euphoniinae (Aves, Passeriformes, Fringillidae): A phylogenetic and ancestral areas analysis. ZooKeys 2024, 1188, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesser, R.T.; Billerman, S.M.; Burns, K.J.; Cicero, C.; Dunn, J.L.; Hernández-Baños, B.E.; Kratter, A.W.; Lovette, I.J.; Mason, N.M.; Rasmussen, P.C.; et al. Sixty-second Supplement to the American Ornithological Society’s Check-list of North American Birds. Ornithology 2021, 138, ukab037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kethley, J.B. A revision of the family Syringophilidae (Prostigmata: Acarina). Contrib. Am. Entomol. Inst. 1970, 5, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M. Quill mites (Acari: Syringophilidae) of the Palaearctic region. Zootaxa 2011, 2840, 1–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowska, E.; Chrzanowski, M.; Kaszewska, K. Checklist of the quill mites (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) of the World. Zootaxa 2015, 3968, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmudzinski, M.; Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B. An Updated Checklist of Quill Mites of the Family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata). 2023. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/An_updated_checklist_of_quill_mites_of_the_family_Syringophilidae_Acariformes_Prostigmata_/16529574 (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Sikora, B.; Unsoeld, M.; Melzer, R.R.; Friedrich, S.; Hromada, M. Revealing the Complexity of Host-Parasite Relationships Between Syringophilid Mites and Sunbirds in Their Global Range. Animals 2025, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcisova, I.; Skoracki, M.; Patan, M.; Hromada, M.; Sikora, B. Quill Mites of the Subfamily Syringophilinae (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) Parasitising Starlings (Passeriformes: Sturnidae). Animals 2024, 14, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, B.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Patan, M.; Marcisova, I.; Hromada, M.; Skoracki, M. Diversity and Interactions between Picobiine Mites and Starlings. Animals 2024, 14, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak-Musial, N.; Skoracki, M.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Unsöld, M.; Sikora, B. Host-parasite relationships of quill mites (Syringophilidae) and parrots (Psittaciformes). Diversity 2023, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszewska-Gilas, K.; Kosicki, J.Z.; Hromada, M.; Skoracki, M. Global Studies of the Host-Parasite Relationships between Ectoparasitic Mites of the Family Syringophilidae and Birds of the Order Columbiformes. Animals 2021, 11, 3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoracki, M. A review of quill mites of the genus Syringophiloidus Kethley, 1970 (Acari: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae) parasitising quills of passeriform birds, with descriptions of four new species. Genus 2004, 15, 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, D.E.; Krantz, G.W. Collecting, rearing, and preparing specimens. In A Manual of Acarology; Krantz, G.W., Walter, D.E., Eds.; Texas Tech University Press: Lubbock, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F. Les segments post-larvaires de l’hystérosoma chez les Oribates (Acariens). Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 1939, 64, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kethley, J.B. Acarina: Prostigmata (Actinedida). In Soil Biology Guide; Dindal, D.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 667–756. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F. Observations sur les Acariens de la famille des Stigmaeidae. Arch. Sci. Phys. Nat. 1944, 26, 103–131. [Google Scholar]
- Reiczigel, J.; Rozsa, L.; Reiczigel, A.; Fabian, I. Quantitative Parasitology (QPweb). 2021. Available online: http://www.zoologia.hu/qp/qp.html (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Rozsa, L.; Reiczigel, J.; Majoros, G. Quantifying parasites in samples of hosts. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiczigel, J.; Marozzi, M.; Fábián, I.; Rózsa, L. Biostatistics for parasitologists—A primer to Quantitative Parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Dormann, C.F.; Fründ, J.; Blüthgen, N.; Gruber, B. Indices, graphs and null models: Analysing bipartite ecological networks. Open Ecol. J. 2009, 2, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.F.; Rasmussen, P.C.; Schulenberg, T.S.; Iliff, M.J.; Fredericks, T.A.; Gerbracht, J.A.; Lepage, D.; Spencer, A.; Billerman, S.M.; Sullivan, B.L.; et al. The eBird/Clements Checklist of Birds of the World. 2024. Available online: https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- IUCN 2025. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Holt, B.G.; Lessard, J.P.; Borregaard, M.K.; Fritz, S.A.; Araújo, M.B.; Dimitrov, D.; Fabre, P.H.; Graham, C.H.; Graves, G.R.; Jønsson, K.A.; et al. An update of Wallace’s zoogeographic regions of the World. Science 2013, 339, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.; Mazel, F.; Thuiller, W. Global determinants of zoogeographical boundaries. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmudzinski, M.; Unsoeld, M. Quill mites (Acariformes: Syringophilidae) parasitising birds in Germany: New host records and descriptions of two new species from Limosa lapponica (L.) (Aves: Scolopacidae). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 24, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Mironov, S.V.; Kravtsova, N.T. Two new syringophilid mites (Acari: Syringophilidae) from the Greenfinch Carduelis chloris (Passeriformes: Fringillidae) from Kirghizia. Genus 2000, 11, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch, W. Die milbengattung Syringophilus Heller, 1880 (subordo Trombidiformes, Fam. Myobiidae Megnin, 1877). Zool. Jahrb. Syst. 1958, 86, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Mironov, S.V. Quill mites of the family Syringophilidae Lavoipierre, 1953 (Acariformes: Prostigmata) parasitic on birds (Aves) of the fauna of the former USSR. Acarina 1998, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Glowska, E.; Skoracki, M.; Khourly, F. A new species and new records of syringophilid mites (Acari: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae) from birds of Jordan. Zootaxa 2007, 1635, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M. Quill mites of the genus Syringophilopsis (Acari, Syringophilidae) from passeriform birds of Poland with descriptions of five new species. Acta Parasitol. 2004, 49, 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Apanaskevich, D. Two new species of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Cheyletoidea) from passeriform birds collected in the Altai. Folia Parasitol. 2001, 48, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Fain, A.; Skoracki, M. New quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Cheyletoidea). Syst. Parasitol. 2004, 57, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Bochkov, A.V. Quill mites from Kazakhstan. Zootaxa 2010, 2546, 52–68. [Google Scholar]
- Skoracki, M.; Hendricks, S.; Spicer, G.S. Systematics of the ectoparasitic quill mites of the genus Aulobia Kethley, 1970 (Acari: Syringophilidae) with the description of a new species. Zootaxa 2010, 2399, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hendricks, S.; Spicer, G.S. Four new species of Aulonastus Kethley, 1970 (Acari: Syringophilidae) from North American passerines. Syst. Parasitol. 2010, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Sikora, B.; Spicer, G.S. A review of the subfamily Picobiinae Johnston and Kethley, 1973 (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Syringophilidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4113, 1–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Mironov, S.V. New quill mite species of the family Syringophilidae (Acari: Cheyletoidea) from the European part of Russia. Acarina 1999, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov, A.V.; Flannery, M.E.; Spicer, G.S. Mites of the Genus Torotrogla (Prostigmata: Syringophilidae) from North American passerines. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imfeld, T.S.; Barker, F.K.; Brumfield, R.T. Mitochondrial genomes and thousands of ultraconserved elements resolve the taxonomy and historical biogeography of the Euphonia and Chlorophonia finches (Passeriformes: Fringillidae). Auk 2020, 137, ukaa016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Hromada, M.; Zmudzinski, M.; Unsoeld, M.; Sikora, B. Parasitic quill mites of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) associated with sub-Saharan sunbirds (Passeriformes: Nectariniidae): Species composition and host-parasite relationships. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierocka, K.; Izdebska, J.N.; Rolbiecki, L. The Co-Occurrence of Demodecidae and Psorergatidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) in the Yellow-Necked Field Mouse Apodemus f lavicollis (Rodentia: Muridae) with a Description of Two New Species and a NewHostRecord. Diversity 2024, 16, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracki, M.; Zabludovskaya, S.A.; Bochkov, A.V. A review of Prostigmata (Acariformes: Trombidiformes) permanently associated with birds. Acarina 2012, 20, 67–107. [Google Scholar]
- Izdebska, J.N.; Rolbiecki, L. The Biodiversity of Demodecid Mites (Acariformes: Prostigmata), Specific Parasites of Mammals with a Global Checklist and a New Finding for Demodex sciurinus. Diversity 2020, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajfer, M. Acari (Chelicerata)—Parasites of reptiles. Acarina 2012, 20, 108–129. [Google Scholar]
- Deunff, J. Observations on Spinturnicidae of occidental Paleartic region (Acarina, Mesostigmata)—Specificity, distribution and repartition. Acarologia 1977, 18, 602–617. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).