Cloning and Expression of Col10a1 Gene and Its Response to Wnt/TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Ethical Declaration
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Preparation
2.3. Cloning of the Col10a1 Gene
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Col10a1
2.5. Expression Analysis of the Col10a1 Gene in Different Tissues of M. reevesii
2.6. Treatment of M. reevesii Carapace Cells with Salinomycin Sodium Salt and Oxymatrine
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the M. reevesii Col10a1
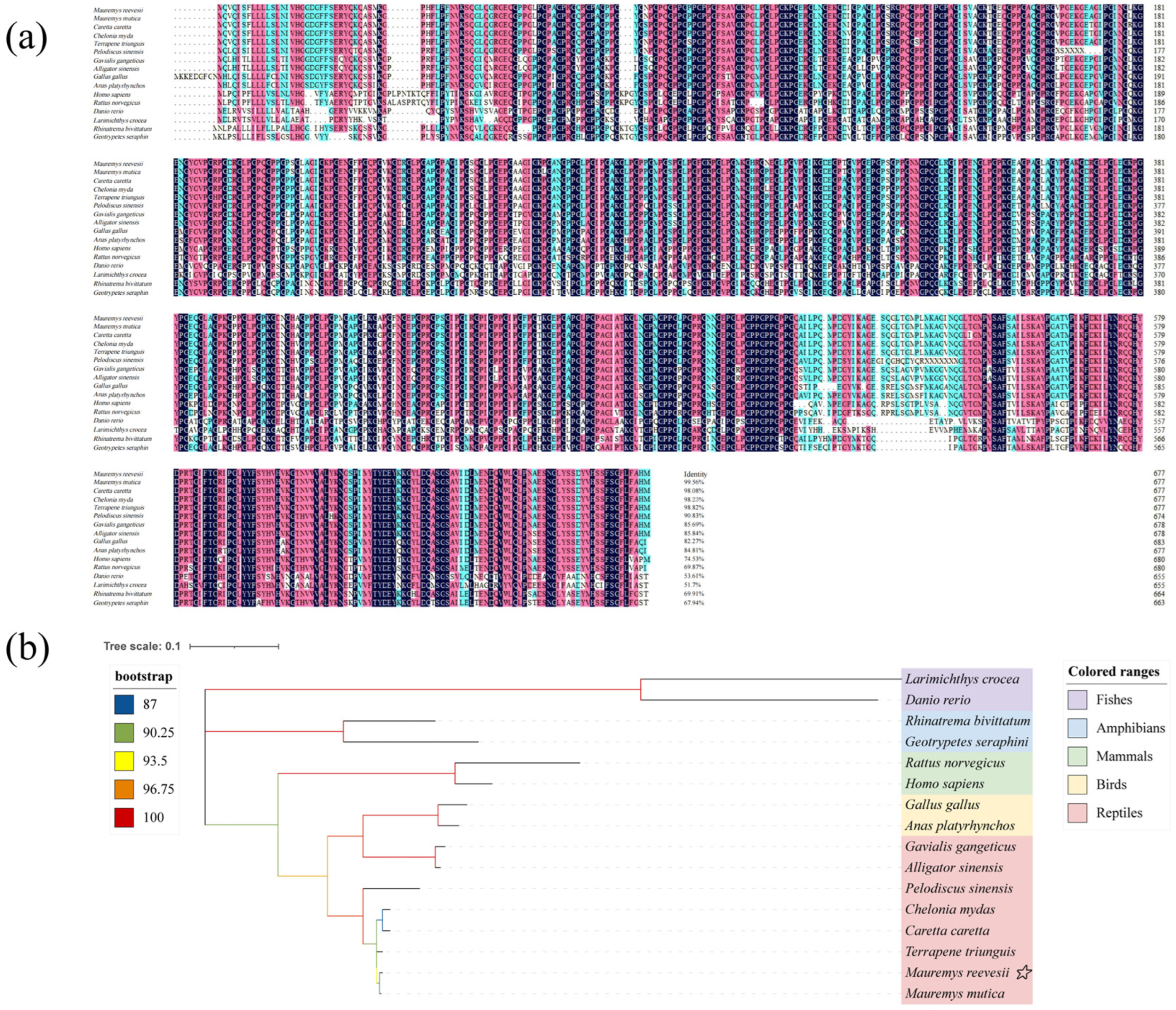
3.2. Amino Acid Similarity Analysis of Col10a1 Protein and Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
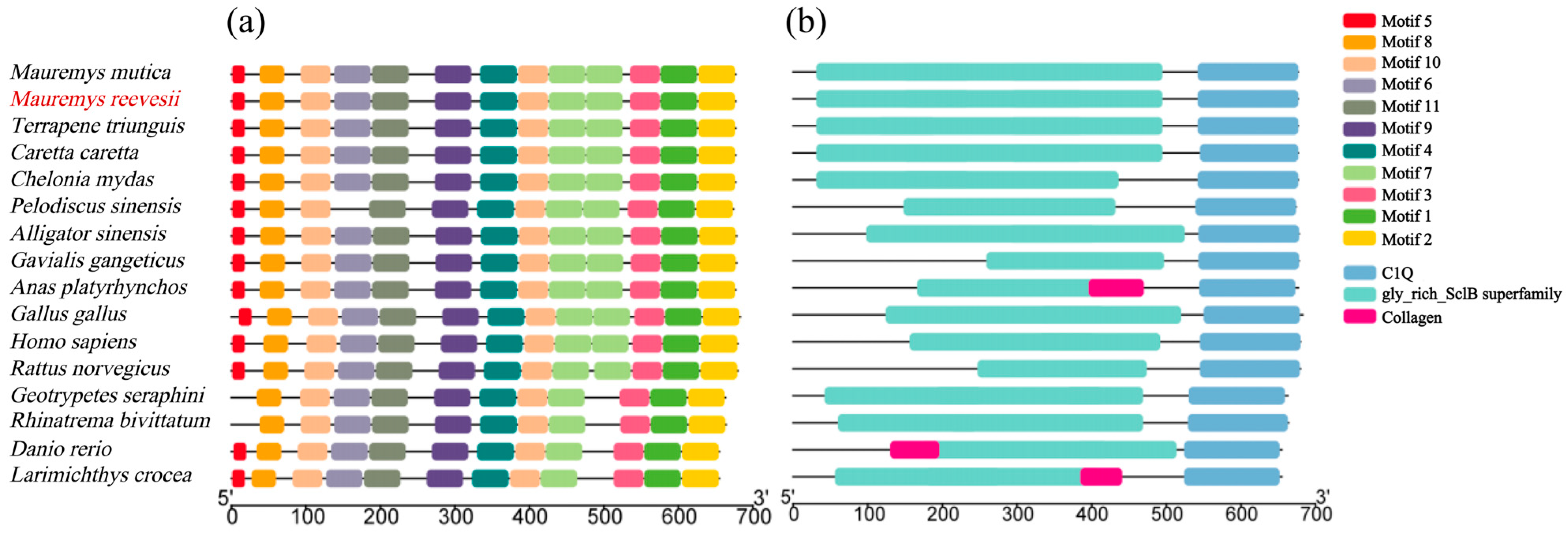
3.3. Conserved Motifs and Structural Domain Analysis of Col10a1 Proteins Across Different Species
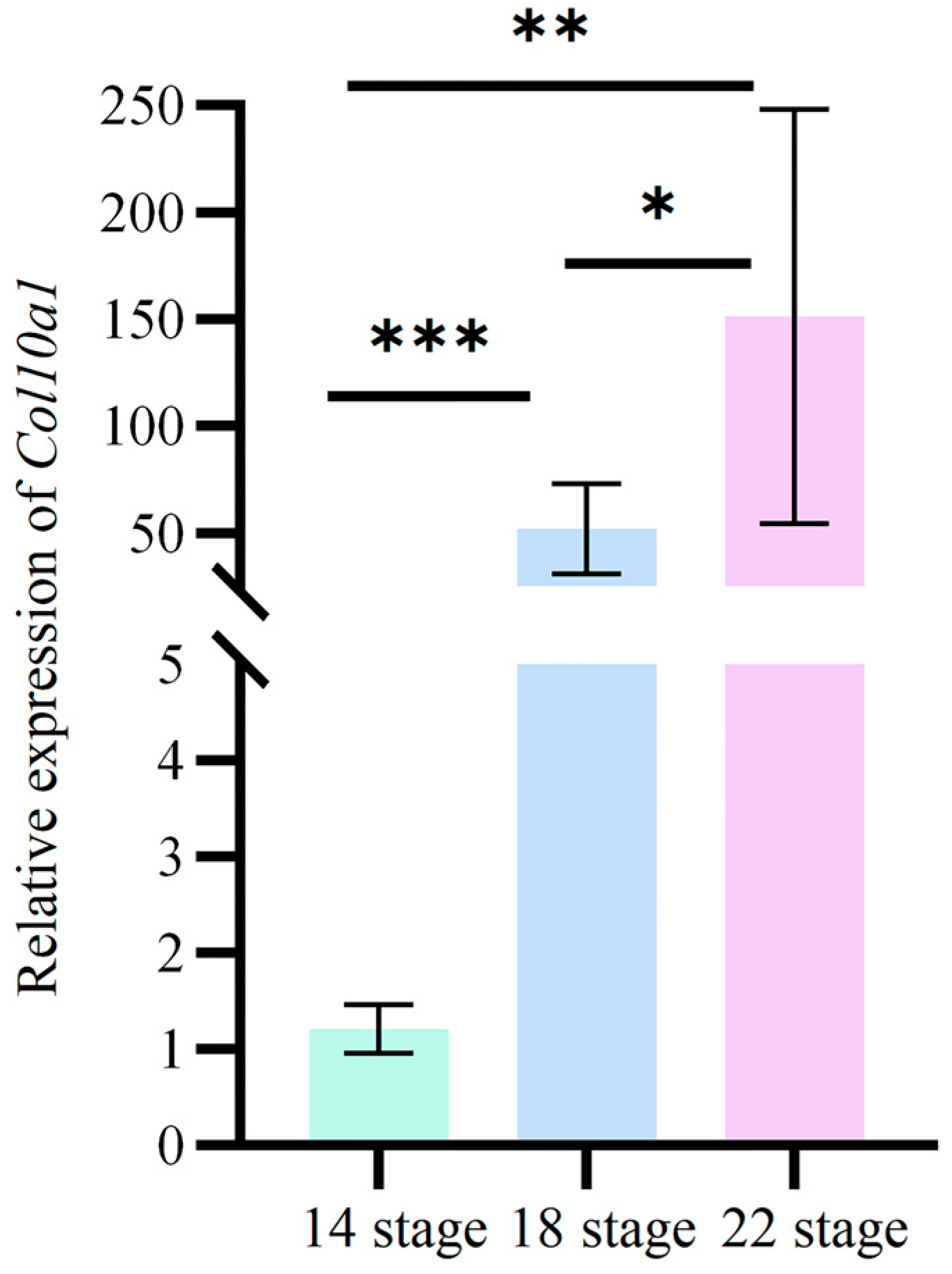
3.4. Expression Changes in Col10a1 in the Carapace of M. reevesii Embryos During Development
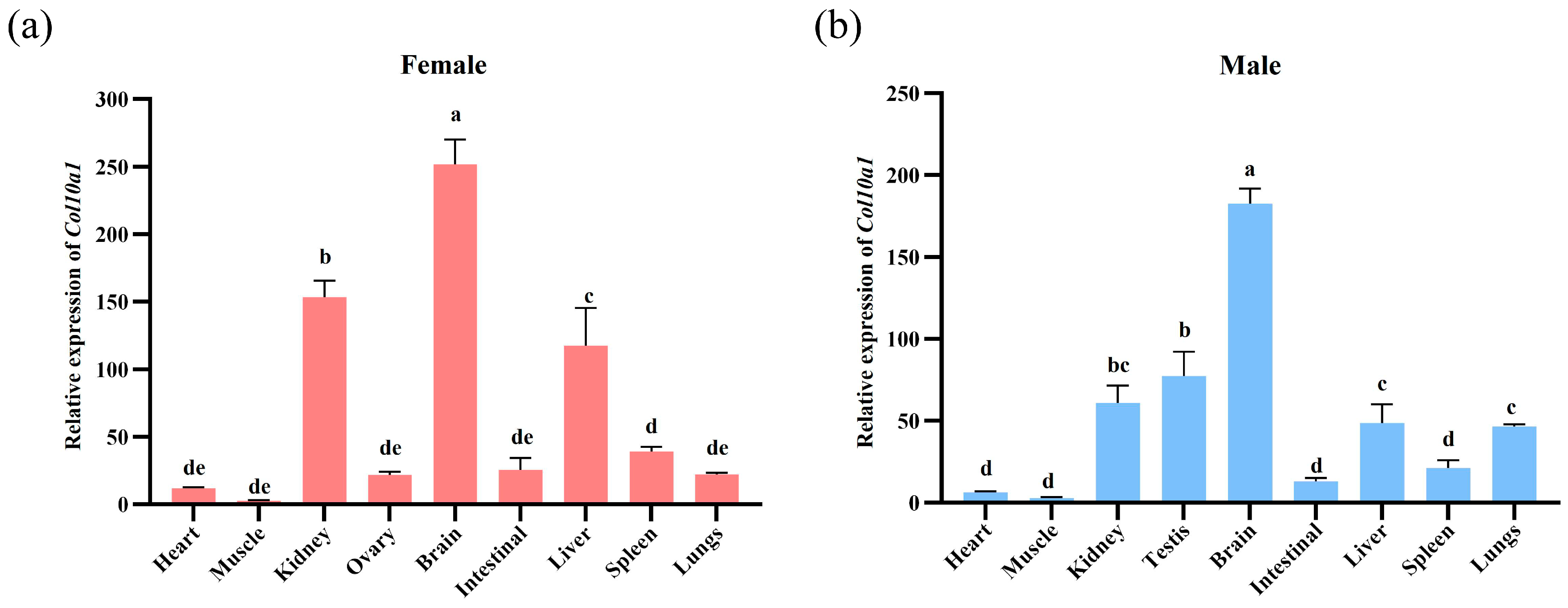
3.5. Expression Profile of the Col10a1 in Adult M. reevesii Tissues
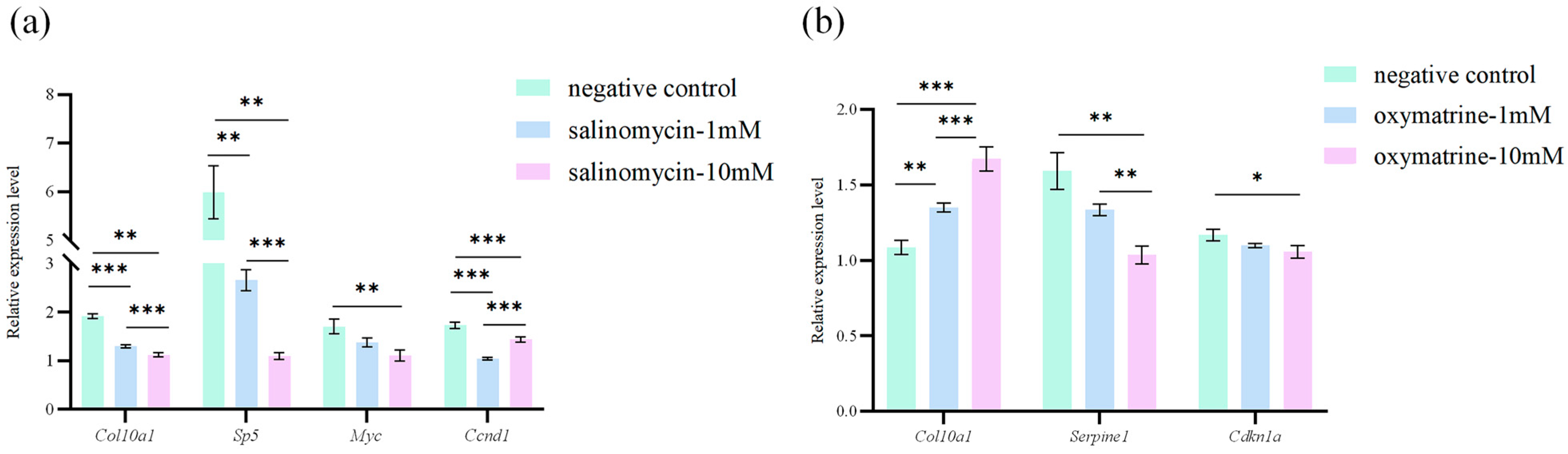
3.6. Effects of Salinomycin Sodium Salt and Oxymatrine on Gene Expression in MRCCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Takagi, Y.; Zhang, X. Properties of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) Collagen and Gel for Application in Biomaterials. Gels 2022, 8, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampitiya, A.G.D.M.; Gonapinuwala, S.T.; Fernando, C.A.N.; De Croos, M.D.S.T. Extraction and Characterisation of Type I Collagen from the Skin Offcuts Generated at the Commercial Fish Processing Centres. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelse, K. Collagens—Structure, Function, and Biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ookawa, M.; Tan, Y.; Ura, K.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Biochemical Characterisation and Assessment of Fibril-Forming Ability of Collagens Extracted from Bester Sturgeon Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sionkowska, A.; Lewandowska, K.; Adamiak, K. The Influence of UV Light on Rheological Properties of Collagen Extracted from Silver Carp Skin. Materials 2020, 13, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, M.; Ojagh, S.M.; Latifi, A.M.; Esmaeili, M.; Udenigwe, C.C. Biochemical and Structural Characterization of Sturgeon Fish Skin Collagen (Huso huso). J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, P. Extraction, Characterization and Osteogenic Activity of a Type I Collagen from Starfish (Asterias amurensis). Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, N.M.H.; Yusoff, F.M.; Jamilah, B.; Basri, M.; Maznah, I.; Chan, K.W.; Armania, N.; Nishikawa, J. Improved Collagen Extraction from Jellyfish (Acromitus hardenbergi) with Increased Physical-Induced Solubilization Processes. Food Chem. 2018, 251, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, D.; Peng, J.; Fang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Cloning, Expression and Antioxidant Activity of a Novel Collagen from Pelodiscus sinensis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M. Research on Industrialized Farming and All-Female Seed Breeding Technology of Mauremys reevesii. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Hu, L.; Lu, J.; Zhu, L. Effects of Incubation Temperature on Embryonic Development Rate, Sex Ratio and Post-Hatching Growth in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle, Chinemys reevesii. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Lu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lin, L.; Lu, H.; Wan, Q.; Jiang, S. Comparison between High-Pressure Steam and Vinegar Stir-Frying on Grinding Characteristics and Nutrient Components of Turtle Shells: Difference between Carapace and Plastron. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tong, Q. Analysis of the Research and Development of Tortoise Shell Glue. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 43, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Song, L.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Chen, T.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Z. Effect of Guiling Jelly in Treating Excess Fire from Yin Deficiencyin Model Rats by Nourishing Yin and Purging Fire. J. Guangxi Univ. Chin. Med. 2022, 25, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, J. Research Progress on Collagen. Life Sci. Res. 2016, 20, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, T.M.; Linsenmayer, T.F. Immunohistochemical Localization of Short Chain Cartilage Collagen (Type X) in Avian Tissues. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, T.M.; Linsenmayer, T.F. Developmental Acquisition of Type X Collagen in the Embryonic Chick Tibiotarsus. Dev. Biol. 1985, 1072, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, F.; Qiao, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Borgia, J.A.; Deng, Y.; Lei, G.; Zheng, Q. Identification and Characterization of the Novel Col10a1 Regulatory Mechanism during Chondrocyte Hypertrophic Differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G. The Role of Type X Collagen in Facilitating and Regulating Endochondral Ossification of Articular Cartilage. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2005, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuth, C.; Andres Sastre, E.; Fahy, N.; Witte-Bouma, J.; Ridwan, Y.; Strabbing, E.; Koudstaal, M.; Van De Peppel, J.; Wolvius, E. Collagen Type X Is Essential for Successful Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Cartilage Formation and Subsequent Endochondral Ossification. Eur. Cells Mater. 2019, 38, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Jacenko, O. Phenotypic and Biochemical Consequences of Collagen X Mutations in Mice and Humans. Matrix Biol. 1998, 17, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Kneissel, M. WNT Signaling in Bone Homeostasis and Disease: From Human Mutations to Treatments. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, K.; Ten Dijke, P.; Janssens, S.; Van Hul, W. Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 to the Bone. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 743–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L. Research on the Epigenetics of Mauremys reevesii Sex Determination System and Early Gonadal Development and Adult Function Maintenance. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M.; Kuratani, S. Normal Embryonic Stages of the Chinese Softshelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis (Trionychidae). Zool. Sci. 2001, 18, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, E. A Standardized Series of Embryonic Stages for the Emydid Turtle Trachemys scripta. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 1350–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Shao, F.; Yu, J.; Gilbert, E.; Gu, Z. Molecular Cloning, Tissue Expression and Polymorphism Analysis of the Caveolin-3 Gene in Ducks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.K. CLOURE: Clustal Output Reformatter, a Program for Reformatting ClustalX/ClustalW Outputs for SNP Analysis and Molecular Systematics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3501–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lian, C.; Lyu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Molecular Cloning, Tissue Expression and Bioinformatics Analysis of socs1 Gene in Zhongshan Ma Duck. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 61, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant Improvements in Protein Secondary Structure Prediction by Consensus Prediction from Multiple Alignments. Bioinformatics 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Weng, Z.; Zheng, H.; Jin, M.; Bao, C.; Su, S.; et al. Gene Regulation during Carapacial Ridge Development of Mauremys reevesii: The Development of Carapacial Ridge, Ribs and Scutes. Genes 2022, 13, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Choi, M.Y.; Yu, J.; Castro, J.E.; Kipps, T.J.; Carson, D.A. Salinomycin Inhibits Wnt Signaling and Selectively Induces Apoptosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13253–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zeng, W.; Jiang, M.; Qin, J.; Xu, H. Effect of Oxymatrine on the TGFbeta-Smad Signaling Pathway in Rats with CCl4-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Hong, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, W. Molecular Characteristics of Dkkl1 Gene in Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) and Its Response to Exogenous Hormone Treatment. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, A.; Kadler, K.E.; Thomas, J.T. The Fibrillar Collagens, Collagen VIII, Collagen X and the Clq Complement Proteins Share a Similar Domain in Their C-Terminal Non-Collagenous Regions. FEBS Lett. 1992, 303, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Ho, M.P.; Cheah, K.E. Aberrant Signal Peptide Cleavage of Collagen X in Schmid Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7992–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Weng, Y.M.; Hocking, A.M.; Golub, S.; McQuillan, D.J.; Bateman, J.F. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Human Type X Collagen. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13566–13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischholz, S.; Beier, F.; Girkontaite, I.; Wagner, K.; Pöschl, E.; Turnay, J.; Mayer, U.; Von Der Mark, K. Characterization of Human Type X Procollagen and Its NC-1 Domain Expressed as Recombinant Proteins in HEK293 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, V.; Bhattaram, P. Vertebrate Skeletogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2010, 90, 291–317. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, K.M.; Pang, M.K.M.; Zhou, S.; Cowan, S.K.; Kong, R.Y.C.; Pfordte, T.; Olsen, B.R.; Sillence, D.O.; Tam, P.P.L.; Cheah, K.S.E. Abnormal Compartmentalization of Cartilage Matrix Components in Mice Lacking Collagen X: Implications for Function. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 136, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamakura, T.; Jin, Y.; Nishio, M.; Nagata, S.; Fukuda, M.; Sun, L.; Kawai, S.; Toguchida, J. Collagen X Is Dispensable for Hypertrophic Differentiation and Endochondral Ossification of Human iPSC-derived Chondrocytes. JBMR Plus 2023, 7, e10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, R. Collagenous Proteins of Blood Vessels. Arterioscler. Off. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Inc. 1986, 6, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilling, T.; Korte, D.; Hoheisel, D.; Galla, H. Basement Membrane Proteins Influence Brain Capillary Endothelial Barrier Function In Vitro. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nirwane, A.; Yao, Y. Basement Membrane and Blood–Brain Barrier. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2019, 4, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabkin, S.W. Collagen Type IV as the Link between Arterial Stiffness and Dementia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Su, Q.; Wang, H.; Shi, S.; Liu, L.; Lv, J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H. Genetic Variants of the COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5 Genes Contribute to Thinned Glomerular Basement Membrane Lesions in Sporadic IgA Nephropathy Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 34, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülow, R.D.; Boor, P. Extracellular Matrix in Kidney Fibrosis: More than Just a Scaffold. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2019, 67, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C. Krüppel-like Factor 4 Modulates the miR-101/COL10A1 Axis to Inhibit Renal Fibrosis after AKI by Regulating Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2316259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, J.; Steixner-Kumar, A.A.; Gabler, S.; Motyka, M.; Rippmann, J.F.; Brosa, S.; Boettner, D.; Schönberger, T.; Lempp, C.; Frodermann, V.; et al. Diverse Potential of Secretome from Natural Killer Cells and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Activating Stellate Cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1232070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hong, L. Research Progress on Signaling Pathways Related to Collagen Metabolism. China Med. Her. 2017, 14, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Hamburg-Shields, E.; DiNuoscio, G.J.; Mullin, N.K.; Lafyatis, R.; Atit, R.P. Sustained Β-catenin Activity in Dermal Fibroblasts Promotes Fibrosis by Up-regulating Expression of Extracellular Matrix Protein-coding Genes. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhu, X.; Pang, J.; Xu, Q.; Jin, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, B.; Huang, D. Transforming Growth Factor β: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target of Ventricular Remodeling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53780–53790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Nakazato, K.; Song, H.; Ishii, N. TGF-β1 and TNF-α Are Involved in the Transcription of Type I Collagen α2 Gene in Soleus Muscle Atrophied by Mechanical Unloading. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Chen, L. LncRNA SNHG12 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Hepatic Progenitor Cells via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 32, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Lai, R.; Zheng, C.; Lu, J.; Jiang, X.; He, F.; Yang, C.; Li, K. Salinomycin Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression via Inhibiting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 112, 109225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Shi, L.; Xu, Y.P.; Qin, X.Y.; Wang, Q.Z. Oxymatrine Inhibits Renal Fibrosis of Obstructive Nephropathy by Downregulating the TGF-Β1-Smad3 Pathway. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lou, X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N. Oxymatrine Protects against the Effects of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation via Modulation of the TGF-Β1/Smad3 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4747–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.; Lekven, A.C. Divergent Functions of the Evolutionarily Conserved, yet Seemingly Dispensable, Wnt Target, Sp5. Differentiation 2025, 141, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Sparks, A.B.; Rago, C.; Hermeking, H.; Zawel, L.; Da Costa, L.T.; Morin, P.J.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Identification of C-MYC as a Target of the APC Pathway. Science 1998, 281, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsu, O.; McCormick, F. B-Catenin Regulates Expression of Cyclin D1 in Colon Carcinoma Cells. Nature 1999, 398, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinuma, D.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kamimura, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Miyazawa, K.; Sunamura, M.; Imamura, T.; Miyazono, K.; Aburatani, H. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation on Microarray Analysis of Smad2/3 Binding Sites Reveals Roles of ETS1 and TFAP2A in Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.K.; Blake, M.C.; Moses, H.L. Regulation of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Expression by Transforming Growth Factor-β-Induced Physical and Functional Interactions between Smads and Sp1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40014–40019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, R.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 664168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Soung, D.Y.; Schwarz, E.M.; O’Keefe, R.J.; Drissi, H. Wnt Induction of Chondrocyte Hypertrophy through the Runx2 Transcription Factor. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 208, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, H. TGF-β/SMAD Signaling Inhibits Intermittent Cyclic Mechanical Tension-induced Degeneration of Endplate Chondrocytes by Regulating the miR-455-5p/RUNX2 Axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 10415–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.N.; Batschkus, S.; Schimmel, S.; Bode, C.; Schminke, B.; Miosge, N. The Influence of TGF-Β3, EGF, and BGN on SOX9 and RUNX2 Expression in Human Chondrogenic Progenitor Cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2019, 67, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, X.; Mao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhang, C.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Z. MicroRNA-455-3p Promotes TGF-β Signaling and Inhibits Osteoarthritis Development by Directly Targeting PAK2. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Primer Sequences (5′—3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Col10a1-F | CACTGCATGCCAGCGTATCT | cDNA cloning |
| Col10a1-R | ATCCTCACTTCCCCTTTGTGG | |
| Col10a1-qF | AAGCAATACTCCCACAGATGCCAGA | Real-time fluorescence quantification |
| Col10a1-qR | GGTAGGCTTTGGAGAGAATGGCAGAG | |
| Sp5-qF | CCCACCTTCCATGATCGCA | |
| Sp5-qR | TGGGTGTGCAGGAAAGGTC | |
| Myc-qF | GGGCCAAGATCTCACCCTTT | |
| Myc-qR | CTGGTGCCTGCTTTTGGAAG | |
| Ccnd1-qF | AAGGTCTACGGCAAGACCTCG | |
| Ccnd1-qR | TTGAGCTTCTTGTTCTGATGGGTC | |
| Serpine1-qF | ACGGGGAGCGCATATAAGG | |
| Serpine1-qR | CCACGTTACGATCTGGGGAC | |
| Cdkn1a-qF | ACGGGGAGCGCATATAAGG | |
| Cdkn1a-qR | CCACGTTACGATCTGGGGAC | |
| Gapdh-F | TGGGATACACCGAGGACC | Reference genes |
| Gapdh-R | CATACCAGGAGACCAGTTTGAC |
| Species | NCBI Accession Number |
|---|---|
| Mauremys mutica | XP_044865908.1 |
| Caretta caretta | XP_048700688.1 |
| Chelonia mydas | XP_007057487.3 |
| Terrapene triunguis | XP_026509269.1 |
| Pelodiscus sinensis | XP_025040541.1 |
| Gavialis gangeticus | XP_019375611.1 |
| Alligator sinensis | XP_025062835.1 |
| Gallus gallus | XP_046768794.1 |
| Anas platyrhynchos | XP_071892193.1 |
| Homo sapiens | NP_001411035.1 |
| Rattus norvegicus | NP_037272.1 |
| Danio rerio | NP_001077296.1 |
| Larimichthys crocea | XP_010745936.1 |
| Rhinatrema bivittatum | XP_029451094.1 |
| Geotrypetes seraphini | XP_033795657.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ren, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Hong, X.; Wei, C.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; et al. Cloning and Expression of Col10a1 Gene and Its Response to Wnt/TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). Animals 2025, 15, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223315
Li Y, Zhu J, Ren T, Liu X, Chen C, Ji L, Hong X, Wei C, Chen H, Zhu X, et al. Cloning and Expression of Col10a1 Gene and Its Response to Wnt/TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). Animals. 2025; 15(22):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yue, Junxian Zhu, Tong Ren, Xiaoli Liu, Chen Chen, Liqin Ji, Xiaoyou Hong, Chengqing Wei, Haigang Chen, Xinping Zhu, and et al. 2025. "Cloning and Expression of Col10a1 Gene and Its Response to Wnt/TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii)" Animals 15, no. 22: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223315
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhu, J., Ren, T., Liu, X., Chen, C., Ji, L., Hong, X., Wei, C., Chen, H., Zhu, X., Li, W., & Dang, L. (2025). Cloning and Expression of Col10a1 Gene and Its Response to Wnt/TGF-β Signaling Inhibitors in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). Animals, 15(22), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223315






