Simple Summary
Sarcocystis spp. are heteroxenous protozoan parasites, which form sarcocysts in muscle tissue of intermediate hosts and sporocysts in the intestinal mucosa of definitive hosts. It has previously been discovered that rodents of the genus Meriones, commonly known as jirds or gerbils, can be infected by two Sarcocystis species, S. hoarensis and S. dirumpens. However, there is a lack of studies reporting on the role of rodents as intermediate hosts of these parasites in the Middle East. In the current study, a new species of Sarcocystis, named Sarcocystis meriones, was described in the Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) from Kuwait. Microscopic sarcocysts of the parasite were found in the thigh muscles of four of the jirds studied. The unique wall structure of S. meriones was determined to have protrusions resembling thuja or a cylinder and having lateral microvilli. DNA analysis showed the new species is closely related to similar parasites that infect mice and rats. The study suggests that predatory mammals preying on jirds likely serve as the definitive hosts for S. meriones.
Abstract
Sarcocystis is a genus of heteroxenous, globally distributed coccidian parasites. Limited research has been conducted on the natural infection of Sarcocystis in rodents in the Middle East. In this study, the Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) was identified as the natural intermediate host of the new species Sarcocystis meriones, based on morphological and molecular data. Microscopic sarcocysts were detected in the thigh muscles of 8.5% (4/47) of Libyan jirds captured from a semi-desert area in Amghara, Eastern Kuwait. Under the light microscope, sarcocysts were filamentous with blunt ends and thin walls, measuring 1550 × 89 µm. Transmission electron microscopy analysis showed the densely packed protrusions measure 1.2 × 0.5 µm and resemble thuja or a cylinder and having lateral microvilli, while the ground substance layer was 0.5–0.6 µm thick and type 22-like. Based on four genetic loci (18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1), S. meriones was genetically most similar to S. myodes and S. ratti, infecting voles and mice of the genus Apodemus and black rats (Rattus rattus), respectively. Phylogenetic results suggest predatory mammals as potential definitive hosts of S. meriones. Further studies are needed to reveal host specificity, geographical distribution, and the impact of the parasite on the host’s health of the newly described Sarcocystis species.
1. Introduction
Sarcocystis parasites belonging to the order Apicomplexa are worldwide distributed protists having an obligatory two-host prey–predator life cycle [1]. Typically, sarcocysts develop in the muscles and central nervous system (CNS) of the intermediate host (IH), while oocysts sporulate in the small intestine of the definitive host (DH). More than 220 species of Sarcocystis spp. have been described in reptiles, birds, and mammals [1,2]. Sarcocystis species found in rodents are a highly diversified group of tissue cyst-forming coccidia, where the exact number of these parasites is not known. Rodents are natural or experimental IHs of over 40 Sarcocystis species [1,3]. Members of the family Muridae serve as IHs for half of the known Sarcocystis spp. found in rodents. Experimental infections have established that rodents of the genus Meriones can act as IHs for two Sarcocystis species, S. hoarensis and S. dirumpens [4,5,6,7]. Notably, no natural infections with Sarcocystis have been reported in Meriones spp. Sarcocystis species are generally more host-specific to their IHs than for their DHs [2,5,8]. For example, species such as S. muris, S. muriviperae, and S. singaporensis have been attempted to be transmitted to the Mongolian jird (Meriones unguiculatus), the Tristram’s jird (Meriones tristrami), and the Shaw’s jird (Meriones shawi), resulting in no success [5,9,10].
Rodents constitute 40% of mammals on the earth, with the identification of 220 species in 29 families, of which the family Muridae encompasses all small rodents, e.g., mice, rats, gerbils, and jirds [11]. Jirds of the genus Meriones are omnivores feeding on plants and insects [12]. In their habitats, they could be predators of desert insects, e.g., beetles and ants; on the other hand, they are preyed upon by wild mammals and reptiles. The Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) is distributed in North Africa and the Middle East and extends far east to Mongolia and China [13]. This wild rodent is widespread in the desert and steppes of northern and eastern Arabia, including Kuwait [14]. In the Middle East and North Africa, most previous studies have investigated rodents, including Libyan jirds, for their helminth biodiversity in Kuwait, Tunisia, and Iran [12,15,16]. As humans and grazing animals are portions of semi-desert and desert ecosystems, pathogens potentially carried by jirds (Meriones spp.) could be candidates for spillover to humans and livestock. For example, zoonotic helminths, e.g., Hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta, were reported in Libyan jirds and Sundevall’s jirds (Meriones crassus) in Kuwait [15] and Capillaria hepatica in the Persian jird (Meriones persicus) from Iran [17]. Meriones spp. were found to be reservoirs of some zoonotic protozoa, e.g., Toxoplasma gondii [18] and Leishmania major [19]. Various bacteria, such as Anaplasma ovis, Rickettsia spp., and Bartonella spp., were detected in Shaw’s jird [20], and Anaplasma bovis was identified in Libyan jird [21]. These pathogens could be a potential threat to humans and animals in wildlife.
The primary morphological diagnostic criterion for the description and differentiation of Sarcocystis species found in IHs is the structure of the sarcocyst wall, as examined by light and electron microscopy. Therefore, a detailed morphological characterization of sarcocysts is essential when describing a new Sarcocystis species [1]. Nevertheless, morphological analyses alone are insufficient to differentiate closely related Sarcocystis species that share similar structural traits. Nowadays, Sarcocystis spp. are described in IHs based on a combination of morphological and genetic characterization of the parasites. Sequencing of nuclear 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and mitochondrial-encoded cox1 is most widely used for the genetic analysis of Sarcocystis spp. [22]. It should be noted that there are no universal genetic loci for the discrimination of all species of the genus Sarcocystis [23]. Therefore, new nuclear, mitochondrial, and apicoplast DNA markers are increasingly suggested [24,25,26].
Very little work has been carried out on Sarcocystis infection in rodents in the Middle East. Using a digestion technique, Rahdar et al. [27] detected Sarcocystis bradyzoites in 50% of domestic mice (Mus musculus) and in 25% of brown rats (Rattus norvegicus), while Indian gerbils (Tatera indica) were free from infection. However, the Sarcocystis species was not identified in the study. More recently, S. cymruensis was found in the thigh muscles of 13 brown rats from Kuwait [24]. This study reports a new Sarcocystis species in Libyan jirds trapped from a semi-desert area in Kuwait based on light microscopy, ultrastructural analysis, and genetic characterisation of the parasite in four loci.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The study area is a semi-desert region surrounding the Veterinary Laboratories (Coordinates: 29°17′49.62″ N, 47°46′45.09″ E), located in the Amghara district, Al-Jahra Province, Eastern Kuwait (Figure 1). The area contains edible trees, such as date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) and Christi’s thorn-jujube (Ziziphus spina-christi), and is bordered by a hedgerow of green buttonwood bushes (Conocarpus erectus). Some parts of the study area have been left uncultivated and are covered with natural herbs and grasses, e.g., saltlover (Halogeton glomeratus) and cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum). Beyond the study area lies an open, sandy desert.
Figure 1.
Location of the study area in the Amghara district, Al-Jahra Province, Eastern Kuwait. The area surrounds the veterinary laboratories (coordinates: 29°17′49.62″ N, 47°46′45.09″ E).
As part of an epidemiological study of rodent parasites in Kuwait, Libyan jirds were trapped alive from the study area using 10 special steel wire traps (38 cm L × 23 cm W × 19 cm H). Traps were placed at selected sites at the entrance of their barrows and under trees in the evening and visited the next morning. Trapped rodents were placed in plastic bags and transferred to the necropsy laboratory of Public Authority of Agriculture and Fish Resources (PAAFR) within a few hours for analysis. Libyan jirds were identified according to [15,28]. The captured Libyan jirds were euthanized using chloroform (CHCl3). These rodents were treated carefully without stress in adherence to the guidelines issued by the Norwegian Committee for Research Ethics in Science and Technology [29]. This study was carried out according to the regulations set by PAAFR for conducting research work and with the approval of technical committee of the Animal Resources sector.
2.2. Morphological Examination
For the detection of sarcocysts of Sarcocystis spp., fragments of thigh muscle tissue (~1–3 mm) were pressed between two slides and examined under stereo- (Kern OZL-463 stereo microscope (Kern, Germany)) and light microscopes (Nikon ECLIPSE 80i light microscope with the INFINITY3 image analysis (Nikon Instruments Inc., New York, NY, USA, JAV)). Prevalence of Sarcocystis was evaluated in fresh-squashed muscle samples. In addition, pieces of muscle were fixed in 10% formalin prior to histopathological examination by embedding in paraffin, then sectioned at 4 µm thickness, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and examined by the light microscope (LM).
For the detailed morphological and molecular analysis of observed sarcocysts, muscle samples of infected Libyan jirds were stored at −20 °C until delivery to the Laboratory of Molecular Ecology, State Scientific Research Institute Nature Research Centre, Vilnius, Lithuania. Sarcocysts were excised from fresh-squashed thigh muscles with the help of two preparation needles. These sarcocysts were morphologically characterized by LM, analysing the size and shape of the sarcocyst and describing the sarcocyst wall and bradyzoites located in the cyst. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis was performed as previously described in [24]. One sarcocyst isolated from the same Libyan jird was examined via TEM.
2.3. Molecular Analysis
Three sarcocysts isolated from three individual Libyan jirds were subjected to molecular examination. The isolation of genomic DNA was carried out from individual sarcocysts using GeneJet Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania).
Using previously developed primers (Table 1), we attempted to amplify 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA (rRNA), internal transcribed spacers 1 and 2 (ITS1 and ITS2), cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (cox1), cytochrome b (cytb), and apicoplast RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpob). Each PCR was carried out in a 25 μL volume consisting of 12.5 μL of Vazyme 2 × Taq Master Mix (Vazyme, Nanjing, China), 0.5 μM of each primer, 7.5 μL of nuclease-free water, and 4 μL of template DNA. The PCR was initiated with an initial hot start at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 45 s at 94 °C, 60 s at 54–60 °C depending on the annealing temperature of primers, 70 s at 72 °C, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. Positive (DNA of S. rileyi) and negative (nuclease-free water instead of DNA template) controls were used for each amplification with different primers. Visualization and evaluation of PCR products were conducted using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The amplified products were purified enzymatically with the help of ExoI and FastAP (Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, Vilnius, Lithuania).

Table 1.
The oligonucleotides used in this study and their characteristics.
Purified PCR products were subjected to directional Sanger sequencing using the same forward and reverse primers as for the PCR. Sequencing reactions were carried out using the BigDye® Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit and the 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For the evaluation of interspecific genetic variation and selection of sequences for phylogenetic analyses, the obtained sequences were compared with those of various taxa representing the Sarcocystidae family using the Nucleotide BLAST 2.17.0 (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 5 August 2025) sequence similarity search algorithm [34].
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
Phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA11 (version 11.0.13) software [35]. Multiple sequence alignments of partial sequences of 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1 were obtained using the MUSCLE algorithm. The final alignments of 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and ITS1 contained 1666, 1498, and 887 nucleotide positions, including gaps, respectively, while the cox1 alignment consisted of 1015 nucleotide positions. The reconstruction of phylogenetic relationships was carried out using the maximum likelihood method. Evolutionary models for each sequence data set were chosen based on the lowest values of the Bayesian Information Criterion. As a result, the Tamura-Nei + G + I, HKY + G + I, HKY + G, and GTR + G nucleotide substitution models were selected for 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1, respectively. Two species, Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii, representing the Sarcocystidae family, were set as outgroups for 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and cox1. While S. rileyi was used as an outgroup for the highly variable ITS1. The bootstrap method with 1000 repetitions was used for testing the reliability of the phylogeny.
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence and Morphological Characterisation of Sarcocysts
Sarcocystis spp. sarcocysts were detected in the thigh muscles of 8.5% (4/47) of Libyan jirds from Kuwait. Sarcocysts detected in all four rodents were morphologically similar and most likely represented one species.
Sarcocysts detected in tight muscles of the Libyan jird were microscopic and filamentous with blunt ends and measured 1560 × 89 μm (900–2450 × 75–124 μm) (Figure 2A). In H&E-stained sections, insignificant pathological changes with very scanty leukocytic infiltration were observed. Additionally, in fresh squash preparations, the sarcocyst wall was thin and reached up to 1.5 μm in thickness (Figure 2B). Septa divided sarcocysts into compartments filled with lancet-shaped bradyzoites, 7.7 × 2.2 μm (6.1–9.0 × 1.2–3.0 μm) in size (Figure 2C). TEM analysis revealed that the villar protrusions (vp) of the sarcocyst wall have a proximal, sharply conical base and a distal segment that is thuja-like. The densely packed vp extending from the surface of the cyst were 1.2 × 0.5 µm in size, resembling a thuja or a cylinder and having lateral microvilli. The ground substance layer measured 0.5–0.6 μm in thickness (Figure 2D). The sarcocyst wall corresponds to type 22-like of the Dubey et al. [1] classification.
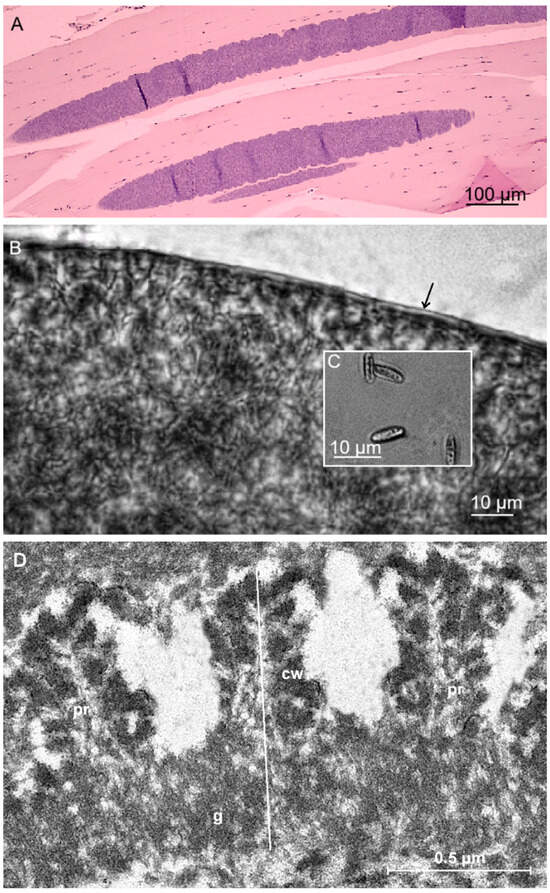
Figure 2.
Morphology of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp. from muscle tissue of the Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) from Kuwait. (A) H&E-staining. LM micrograph showing spindle-shaped sarcocysts with thin cyst wall. (B,C) Light micrographs. Fresh preparations. (B) Fragment of sarcocyst. Note a thin and apparently smooth cyst wall (marked with arrow). (C) Lancet-shaped bradyzoites. (D) TEM micrograph; fragment of cyst wall (cw) with thuja or a cylinder protrusion and having lateral microvilli (pr); ground substance (g).
3.2. Molecular Characterisation of the Novel Sarcocystis Species
We were able to genetically characterise three isolates of Sarcocystis meriones within 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and cox1 and one isolate of parasite species within ITS1. Whereas the amplification using primers targeting rpoB, cytb, and ITS2 was unsuccessful. All three isolates of S. meriones, showed 100% identity within 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and cox1. Based on four genetic loci, sequences of S. meriones demonstrated the highest similarity with those of S. ratti from the black rat (Rattus rattus) and S. myodes from the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) (Table 2). Furthermore, relatively high similarity was observed comparing our sequences of S. meriones with those of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 isolated from two vole species, common vole (Microtus arvalis) and tundra vole (Alexandromys oeconomus), showing 99.2% similarity within cox1 and 97.7% similarity within 28S rRNA. However, the cox1 and 28S rRNA sequences of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 available were relatively short, 619 bp and 735 bp in length, respectively. Therefore, these sequences of Sarcocystis sp. Rod1 were not included in further phylogenetic analysis.

Table 2.
The genetic comparison of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp. with other Sarcocystis species.
Comparing the 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, and cox1 sequences of S. meriones with those of S. ratti, S. myodes, and Sarcocystis sp. Rod1, the obtained genetic similarity values were ≥97.7%. However, within 28S rRNA and cox1, S. meriones showed relatively high differences from other Sarcocystis spp., exceeding 4.5%. When the 665 bp partial ITS1 sequence of S. meriones was analysed using BLAST, significant genetic similarity was obtained only with sequences of S. myodes and S. ratti, and the values of genetic similarity were in the range of 78.2–78.7%.
The genetic variability between sequences of S. meriones, S. myodes, and S. ratti within 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1, and ITS1 is provided in Table 3. At cox1 these three species differed by 4–8 SNPs; at 18S rRNA, and 28S rRNA from seven to 28 SNPs and up to a single indel were determined between species pairs; and finally, at ITS1 the number of indels (47–81) and SNPs (74–101) was very high. Thus, based on four analyzed genetic loci, S. meriones showed significant genetic differences from other Sarcocystis spp.

Table 3.
The genetic variability between sequences of S. meriones, S. myodes, and S. ratti.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the New Sarcocystis Species
The phylogenetic analyses using four genetic loci (18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1) showed the placement of S. meriones with two Sarcocystis species, S. myodes and S. ratti (Figure 3). Based on all genetic loci examined, S. meriones was most closely related to S. ratti; however, significant clustering of these two species was supported by significant bootstrap values only in cases of 28S rRNA and cox1. Furthermore, S. meriones, S. myodes, and S. ratti formed a sister clade to S. cymruensis and S. muris (Figure 3C). Other Sarcocystis species with rodents as IHs and birds (S. jamaicensis and S. strixi), opossums (S. speeri), or snakes (S. muricoelognathis and S. pantherophisi) as their DHs, and which were included in phylogenetic analyses, were placed in other clusters.
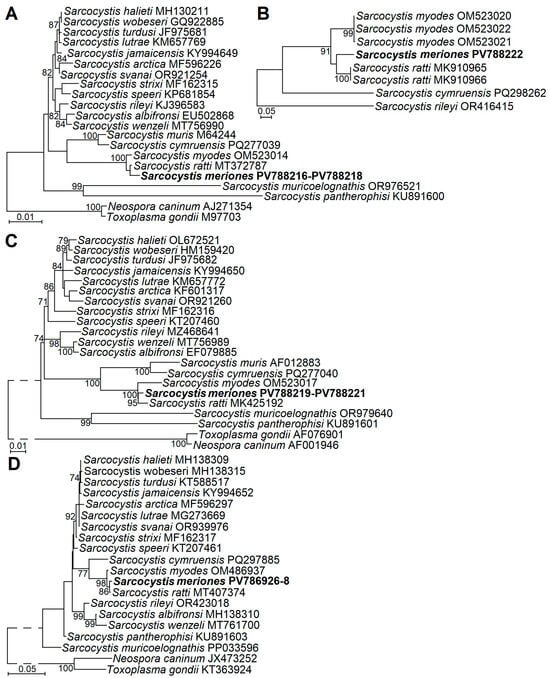
Figure 3.
The phylogenetic placement of Sarcocystis meriones sp. n. from Lybian jird based on sequences of 18S rRNA (A), ITS1 (B), 28S rRNA (C), and cox1 (D). Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii (A,B,D) or Sarcocystis rileyi (C) were used as outgroup species. Bootstrap values ≥ 70% are displayed next to branches.
3.4. Description of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp.
The Sarcocystis parasite discovered in the present study was recovered from the tight muscles of the Libyan jird in Amghara district, Al-Jahra Province, Eastern Kuwait. The newly discovered parasite species was morphologically distinct by LM and TEM from S. dirumpens and S. hoarensis, found in rodents of the genus Meriones (Table 4). Based on TEM results, the sarcocyst wall of S. meriones was most similar to that of S. villivillosi found in muscles of laboratory rats and prior transmission of this Sarcocystis species to related rodent hosts was unsuccessful. However, villar protrusions of S. villivillosi were with a sharply conical base and a distal segment that is cocklebur-like with short, radiating projections, while the densely packed villar protrusions of S. meriones resembled thuja or a cylinder and had lateral microvilli (Table 4). The newly discovered parasite species was genetically characterised at four loci most commonly used for the differentiation of Sarcocystis spp. The comparison of sequences obtained in the present study and phylogenetic analysis revealed that S. meriones was genetically most similar to S. ratti, S. myodes, and Sarcocystis sp. Rod1, which form sarcocysts in the muscles of rodents. In comparison with the most closely related Sarcocystis species, small but significant genetic differences were observed in cox1 (0.4–0.8%), 18S rRNA (0.6–0.7%), and 28S rRNA (1.1–2.3%). By contrast, the ITS1 sequence of S. meriones showed less than 80% similarity with those of other Sarcocystis species, clearly confirming the genetic distinctiveness of the newly identified parasite. Based on results of TEM and molecular analysis, sarcocysts detected in thigh muscles of Libyan jirds from Kuwait were described for the first time and named as Sarcocystis meriones n. sp.

Table 4.
Morphological comparison of S. meriones n. sp. from the Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) with two Sarcocystis species previously detected in Meriones jirds and with S. villivillosi, which forms sarcocysts most similar in morphology to those described in the present study.
- Taxonomy summary of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp.
- Type intermediate host: Libyan jird (Meriones libycus).
- Definitive host: Unknown. Based on phylogenetic results, predatory mammals are suspected to serve as DHs.
- Localit:y Amghara district, Al-Jahra Province, Eastern Kuwait.
- Morphology of sarcocysts: By LM, sarcocysts were microscopic, filamentous with blunt ends, 1560 × 89 μm (900–2450 × 75–124 μm) in size with a thin (up to 1.5 μm) sarcocyst wall. Lancet-shaped bradyzoites measured 7.7 × 2.2 μm (6.1–9.0 × 1.2–3.0 μm). By TEM, densely packed protrusions of the sarcocyst wall were 1.2 × 0.5 µm in size, resembling a thuja or a cylinder and having lateral microvilli; the ground substance layer measured 0.5–0.6 μm; type 22-like
- Genetic characteristics: The new species was characterised by almost complete 18S rRNA, partial 28S rRNA, partial ITS1, and partial cox1. Obtained sequences showed ≤99.6%, ≤99.4%, ≤98.9%, and ≤78.7% genetic similarity to those of other Sarcocystis spp. within cox1, 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA and ITS1, respectively.
- Type specimen: Hapantotype 1 slide toluidine bluestained (NRCP00004) is deposited in the State Scientific Research Institute Nature Research Centre, Vilnius, Lithuania.
- Sequences are available: In the NCBI GenBank database under the accession numbers PV788216-PV788218 (18S rRNA), PV788219-PV788221 (28S rRNA), PV788222 (ITS1), and PV786926-PV786928 (cox1).
- Etymology: The Latin name of the genus Meriones is used for the species name.
- ZooBank registration: The Life Science Identifier (LSID) of the article is urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1EE58E69-1A28-4C44-BDA6-3A45A46C5B16. The LSID for the new name Sarcocystis meriones is urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:C12B8541-B611-4FAD-8372-A969D8105079.
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological Differentiation of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp. from Other Sarcocystis Species
In the present work, sarcocysts detected in tight muscles of Libyan jirds were microscopic and filamentous with blunt ends and measured 900–2450 × 75–124 μm. The sarcocyst wall was thin and reached up to 1.5 μm in thickness under LM and bradyzoites were lancet-shaped and 6.1–9.0 × 1.2–3.0 μm in size. By TEM, the sarcocyst wall corresponds to type 22-like (Figure 2). Previously, cyst wall type 22 was identified exclusively for sarcocysts of S. villivillosi found in the muscles of the laboratory rat from the USA [1,37], and the DH of this Sarcocystis species is the boid snake (Python reticulatus) [37]. However, attempts to transmit S. villivillosi to other rodents, including jirds (Apodemus agrarius, Apodemus flavicollis, Microtus arvalis, Gerbillus perpallidus, and Meriones unguiculatus, etc.), were unsuccessful [5]. Furthermore, compared to S. meriones, S. villivillosi had striated sarcocyst walls and fusiform bradyzoites, 5 µm in length and 1 µm in width [37]. Moreover, the villar protrusions of S. villivillosi have a proximal, sharply conical base and a distal segment that is cocklebur-like, with short, radiating projections. Cross-sections of the distal segment of the projections resemble cogwheels. Meanwhile, the villar protrusions of S. meriones have a proximal, sharply conical base and a distal segment that resembles a thuja or a cylinder, with lateral microvilli (Table 4).
Previously, two Sarcocystis species, S. hoarensis and S. dirumpens, have been experimentally established in the muscle of the genus Meriones [5,6,7,36]. The macroscopically visible white sarcocysts of S. hoarensis were detected in the eyelids, the connective tissue of the snout, the tongue, the subcutis, and the connective tissue of the ears, as well as in the subcutis and connective tissue of the scrotum, anus, the base of the tail, and the soles of the feet of experimentally infected rodents [6]. Sarcocysts of S. hoarensis were seen with the naked eye and reached diameters of up to 2.5 mm. Meanwhile, the cyst wall of this species was smooth, and bradyzoites were approximately 11–12 µm in length and 2 µm in width [6]. Dubey et al. [1] assigned the wall of sarcocysts of S. hoarensis to type 42. Whereas S. dirumpens developed in the musculature of jirds experimentally exposed to sporocysts collected from a naturally infected butterfly viper (Bitis nasicornis) [5,6,36]. Sarcocysts of this species, two years post-infection, were macroscopic, measuring approximately 100–400 µm in width and up to 2.5 cm in length, depending on the muscles parasitized. The cyst wall of the septated sarcocysts appeared thin and smooth under LM; bradyzoites measured approximately 8–9 µm in length and 2 µm in width [6]. Dubey et al. [1] assigned the wall of sarcocysts of S. dirumpens to type 1b. Sarcocysts of S. hoarensis and S. dirumpens were found in jirds, gerbils, hamsters, and mice [6]. Thus, sarcocysts detected in our work differ significantly in morphology from those of S. hoarensis and S. dirumpens previously reported in rodents of the genus Meriones.
4.2. Potential Definitive Hosts of Sarcocystis meriones n. sp.
On the basis of 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1, Sarcocystis meriones n. sp. clustered in phylogenetic analyses with four Sarcocystis spp. (S. cymruensis, S. muris, S. myodes, and S. ratti) that employ rodents as IHs [24,38,39,40]. Specifically, S. cymruensis and S. ratti form sarcocysts in brown rats and black rats, respectively; S. muris infects domestic mice, and IHs of S. myodes are voles and mice of the genus Apodemus [38,40,41,42,43]. Domestic cats (Felis catus) have been shown to serve as DH of S. cymruensis and S. muris in transmission experiments [40,41]. The DHs of S. myodes and S. ratti have not yet been found, but phylogenetic evidence suggests that they could be predatory mammals [38,39]. The ecological conditions and landscape of the study area in Kuwait favor the thriving of Libyan jirds, as well as the presence of reptilian predators and wild carnivores, such as the desert monitor lizard (Varanus griseus), false cobra (Malpolon moilensis), and the red fox (Vulpes vulpes). As these predators coexist with Libyan birds, it is thought that one of them may be the DH of the new species. Based on phylogenetic results, the red fox could be suggested as DH of the new Sarcocystis species; however, this hypothesis should be confirmed by the transmission experiments. The present study may encourage further investigations of the new Sarcocystis species in other countries where Libyan jirds are present, to better understand its geographical distribution. Additionally, further research on other wild rodents in the semi-desert and desert regions of Kuwait is necessary to clarify the host specificity of S. meriones.
5. Conclusions
For the first time sarcocysts of Sarcocystis were detected in thigh muscles of the Libyan jird (Meriones libycus) collected from a semi-desert area in Eastern Kuwait. Based on microscopical (LM and TEM) and molecular examinations using four genetic loci (18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, ITS1, and cox1), the new species S. meriones was described. The phylogenetic results of the present study suggest that predatory mammals are potential DHs of S. meriones. Future investigations are required to elucidate the host specificity, geographical distribution, and pathological effects of this newly described Sarcocystis species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; methodology, F.A.M.A., O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; software, O.M.E.E.-A., E.J.-N. and P.P.; validation, O.M.E.E.-A., D.B. and P.P.; formal analysis, F.A.M.A., O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; investigation, O.M.E.E.-A., E.J.-N., D.Š., L.M.A.T. and P.P.; resources, O.M.E.E.-A., D.B. and P.P.; data curation, O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.A.M.A., O.M.E.E.-A., E.J.-N., D.Š., L.M.A.T., D.B. and P.P.; writing—review and editing, F.A.M.A., O.M.E.E.-A., E.J.-N., D.Š., L.M.A.T., D.B. and P.P.; visualization, O.M.E.E.-A., E.J.-N. and P.P.; supervision, O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; project administration, O.M.E.E.-A. and P.P.; funding acquisition, O.M.E.E.-A., D.B. and P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This work was conducted according to the regulations set by PAARF for conducting research and received ethical approval from technical committee of Animal Resources Sector (reference no. 021111, date 28 November 2019, Deputy Director General for Animal Resources). Also, the study received ethics approval from Ministry of Health to trap and examine rodents for zoonotic parasitic diseases (Reference no. 2021-658-4, date 21 January 2021, Deputy Minister). The research of the current study was conducted under the approval guidelines of the Ethics Committee of Nature Research Centre (no. GGT-9).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The 18S rRNA, 28S rRNA, cox1, and ITS1 sequences generated in the present study were submitted to the GenBank database under accession numbers PV786926–PV786928, PV788216–PV788222.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dubey, J.P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Speer, C.A.; Fayer, R. Sarcocystosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayer, R. Sarcocystis spp. in Human Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Ortega-Perez, P.; Wibbelt, G.; Lakim, M.B.; Ginting, S.; Khoprasert, Y.; Wells, K.; Hu, J.; Jäkel, T. A Cyst-Forming Coccidian with Large Geographical Range Infecting Forest and Commensal Rodents: Sarcocystis muricoelognathis sp. nov. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschka, F.R. The African Bitis nasicornis (Shaw 1802) as Final Host of an Unknown Sarcocystis Species. Salamandra 1979, 15, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, U.; Frank, W. Host Specificity and Host Range of the Genus Sarcocystis in three Snake Rodent Life Cycles. Zentralblatt Für Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. 1. Abt. Orig. A Med. Mikrobiol. Infekt. Parasitol. 1986, 256, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschka, F.R.; Häfner, U. Cyclic Transmission of an African Besnoitia Species by Snakes of the Genus Bitis to Several Rodents. Z. Parasitenkd. 1984, 70, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschka, F.R.; Mehlhorn, H.; Abd-Al-Aal, Z. Replacement of Besnoitia Matuschka and Häfner 1984 by Sarcocystis hoarensis. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 74, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, U.; Matuschka, F.R. Life Cycle Studies on Sarcocystis dirumpens sp. n. with Regard to Host Specificity. Z. Parasitenkd. 1984, 70, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschka, F.R.; Heydorn, A.O.; Mehlhorn, H.; Abd-Al-Aal, Z.; Diesing, L.; Biehler, A. Experimental Transmission of Sarcocystis muriviperae n. sp. to Laboratory Mice by Sporocysts from the Palestinian viper (Vipera palestinae): A Light and Electron Microscope Study. Parasitol. Res. 1987, 73, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, T.; Burgstaller, H.; Frank, W. Sarcocystis singaporensis: Studies on Host Specificity, Pathogenicity, and Potential use as a Biocontrol Agent of Wild Rats. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, M.A.; Treuting, P.M.; Rothenburger, J.L.; Rodentia. Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, H.; Jrijer, J.; Neifar, L.; Nouira, S. A Survey Study on the Helminth Parasites of two Wild Jirds, Meriones shawi and M. libycus (Rodentia: Cerbillinae), in Tunisian Desert Areas. Euro. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Granjan, L. Meriones libycus; (Errata Version Published in 2017). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: eT131b4A115110005. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/13164/115110005 (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Abu Boker, M.A.; Buhadi, Y.A.; Alenezi, A.; Amr, Z.S. Mammals of the State of Kuwait; IUCN and Kuwait. State of Kuwait, Environment Public Authority: Gland, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Behbenani, B. Studies on Helminth Parasites of Rodents from Kuwait. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 1999; p. 507. [Google Scholar]
- Moradpour, N.; Borji, H.; Darvish, J.; Moshaverinia, A.; Mahmoudi, A. Rodents Helminth Parasites in Different Region of Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2018, 13, 275–284. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Kai, E.B.; Shahryary-Rad, E.; Mohebali, M.; Mahmoudi, M.; Mobedi, I.; Zahabiun, F.; Zarei, Z.; Miahipoor, A.; Mowlavi, G.H.; Akhavan, A.A.; et al. Endoparasites of Rodents and their Zoonotic Importance in Germi, Dashte-Mogan, Ardabil Province, Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2010, 5, 15–20. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Seifollahi, Z.; Sarkari, B.; Motazedian, M.H.; Asgari, Q.; Ranjbar, M.J.; Khabisi, S.A. Protozoan Parasites of Rodents and their Zoonotic Significance in Boyer-Ahmed District, Southwestern Iran. Vet. Med. Int. 2016, 3263868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, Z.; Kalantari, M.; Mohammadib, J.; Daliri, S.; Mehrabani, D.; Azizi, K. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran: A Review of Epidemiological Aspects, with Emphasis on Molecular Findings. Parasite 2022, 29, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmi, R.; Belkahia, H.; Dhibi, M.; Abdelaali, H.; Lahmar, S.; Ben Said, M.; Messadi, L. Zoonotic Vector Borne Bacteria in Wild Rodents and Associated Ectoparasites from Tunisia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 95, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Cui, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Tang, L.; Tan, W.; Wang, Y. Anaplasma bovis and Bartonella spp. in Libyan jirds (Meriones libycus) from China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2024, 60, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazmand, A.; Moradi, L.; Almasi, P.; Nabavi, R.; Prakas, P. First Report of Sarcocystis halieti in Asia: The Genetic Confirmation in Muscles of the Eurasian sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus) from Iran. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Dubey, J.P. Sarcocystis Infection in Domestic and Wild Avian Hosts: Inseparable Flight Partners. Vet. Parasitol. 2025, 335, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryan, F.A.M.; Prakas, P.; Juozaitytė-Ngugu, E.; Šneideris, D.; Abd-Al-Aal, Z.; Alhoot, A.A.A.; El-Kabbany, A.I.; Tahrani, L.M.A.; El-Azazy, O.M.E. Sarcocystis cymruensis in the Brown Rat (Rattus norvegicus) from an Urban District in Kuwait: Detailed Morphologic and Molecular Characterization. Acta Parasitol. 2025, 70, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J. Infection of the Asian Gray Shrew Crocidura attenuata (Insectivora: Soricidae) with Sarcocystis attenuati n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) in China. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Gupta, A.; de Araujo, L.S.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Khan, A.; Rosenthal, B.M. Sarcocystis cruzi (Hasselmann, 1923) Wenyon, 1926: Redescription, Molecular Characterization and Deposition of Life Cycle Stages Specimens in the Smithsonian Museum. Parasitology 2023, 150, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahdar, M.; Roointan, E.; Vazirianzadeh, B.; Alborzi, A. Study of Internal Parasites of Rodents in Ahvaz, South-Weast of Iran. Jundishapur J. Health Sci. 2016, 19, e29067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.T.; Xie, Y.; Hoffmann, R.S.; Lunde, D.; Mackinnon, J.; Wilson, D.E.; Wozencraft, W.E. A Guide to the Mammals of China; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 249–250. [Google Scholar]
- NENT. Guidelines for Research Ethics in Science and Technology. 2016. Available online: https://www.forskningsetikk.no/en/about-us/our-committees-and-commission/nent/guidelines-nent/ethical-guidelines-for-the-use-of-animals-in-research/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Kutkienė, L.; Prakas, P.; Sruoga, A.; Butkauskas, D. The Mallard Duck (Anas platyrhynchos) as Intermediate Host for Sarcocystis wobeseri sp. nov. from the Barnacle Goose (Branta leucopsis). Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Molecular Characterisation of Sarcocystis rileyi from a Common Eider (Somateria mollissima) in Norway. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, B. Phylogenetic Relationships among Sarcocystis species in Cervids, Cattle and Sheep Inferred from the Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit I Gene. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendte, J.M.; Miller, M.A.; Lambourn, D.M.; Magargal, S.L.; Jessup, D.A.; Grigg, M.E. Self-mating in the Definitive Host Potentiates Clonal Outbreaks of the Apicomplexan Parasites Sarcocystis neurona and Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 8, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, U.; Frank, W. Morphological Studies on the Muscle cysts of Sarcocystis dirumpens (Hoare 1933) Hafner and Matuschka 1984 in Several Host Species Revealing Endopolygeny in Metrocytes. Z. Pasrasitenkd. 1986, 72, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, P.C.; Maleckar, J.R. Sarcocystis singaporensis Zaman and Colley, (1975) 1976, Sarcocystis villivilliso sp. n., and Sarcocystis zamani sp. n.: Development, Morphology, and Persistence in the Laboratory Rat, Rattus norvegicus. J. Parasitol. 1981, 67, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Kirillova, V.; Gavarāne, I.; Grāvele, E.; Butkauskas, D.; Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Kirjušina, M. Morphological and Molecular Description of Sarcocystis ratti n. sp. from the Black Rat (Rattus rattus) in Latvia. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudaitytė-Lukošienė, E.; Jasiulionis, M.; Balčiauskas, L.; Prakas, P.; Stirkė, V.; Butkauskas, D. Morphological and Molecular Description of Sarcocystis myodes n. sp. from the Bank Vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) in Lithuania. Biology 2022, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Frenkel, J.K. Recognition of Cyclic Transmission of Sarcocystis muris by Cats. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 133, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes Murata, F.H.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Thompson, P.C.; Tiwari, K.; Mowery, J.D.; Verma, S.K.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sharma, R.N.; Dubey, J.P. Sarcocystis cymruensis: Discovery in Western Hemisphere in the Brown rattus Rattus norvegicus) from Grenada, West Indies: Redescription, Molecular Characterization, and Transmission to IFN-γ Gene Knockout Mice via Sporocysts from Experimentally Infected Domestic Cat (Felis catus). Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakas, P.; Stirkė, V.; Šneideris, D.; Rakauskaitė, P.; Butkauskas, D.; Balčiauskas, L. Protozoan Parasites of Sarcocystis spp. in Rodents from Commercial Orchards. Animals 2023, 13, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakas, P.; Gudiškis, N.; Kitrytė, N.; Bagdonaitė, D.L.; Baltrūnaitė, L. Detection of three Sarcocystis Species (Apicomplexa) in Blood Samples of the Bank Vole and Yellow-necked Mouse from Lithuania. Life 2024, 14, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).