Simple Summary
We studied the intestinal microbiota of Bufo tibetanus at different growth and development stages. Through 16S rRNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, significant differences were found in gut microbiota diversity (alpha and beta diversity) at different growth stages. The relative abundance of Firmicutes increased continuously with the growth of toads, reaching its maximum in the adult group, and Desulfobacterota was the most abundant phylum in the juvenile group. Bacillus and Succinispira had the highest relative abundance values at Gosner 18 to 31 stages. An LEfSe analysis identified specific gut microbiota at different stages, such as Proteobacteria at Gosner 18 to 31 stages, Desulfobacterota in the juvenile group, and Firmicutes in the adult group. A functional prediction analysis illustrated that the metabolic pathways and the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites were significant enrichment in all stages. These results indicated that the intestinal microbiota of B. tibetanus had adaptive changes at different growth stages, which provided insights for future research on the intestinal microbiota of amphibians.
Abstract
The intestinal microbiota is vital for host immunity and metabolism, and its changes are associated with the development stage of hosts. However, little is known regarding how growth and development of anurans affect the diversity of their microbiota, which has a complex life cycle. The Tibetan toad (Bufo tibetanus) is a wild population in the high-altitude area of southwest China, which has special adaptability to the environment. Here, the microbial community of the Tibetan toad at six developmental stages (from the tadpole at Gosner stage 18 to the 8-year-old adult) was assessed using high-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing. The alpha diversity index analysis showed that the Chao, Ace, and Shannon indices were highest at Gosner stage 32 and decreased as development progressed, and their alpha diversity remained unchanged over time in adult stages. Beta diversity revealed that the gut microbiota structure differed significantly from Gosner stages 18 to 31, and it became similar to adult toads from Gosner stages 45 to 46 and in juvenile groups. At the phylum level, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria were dominant phyla in tadpoles and adults. The relative abundance of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in the adult group was significantly higher and lower than that of tadpoles, respectively. The linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis identified seven phyla exhibiting significant differences during life stages: Verrucomicrobiota, Bacteroidota, and Proteobacteria (Gosner 18 to 31), Cyanobateria and Chloroflexi (Gosner 32 to 41), Actinobacteriota (Gosner 45 to 46), Desulfobacterota (juvenile group), and Firmicutes (adult group). A pathway enrichment analysis revealed that the metabolism and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites were significantly enriched across all developmental stages. This research unveiled variations in the intestinal microbiota composition during development in anurans. Factors such as developmental stage, habitat type and feeding habit jointly affected the gut microbial diversity and community composition in the Tibetan toad. The findings of this study can provide information for understanding the influence of historical developments on the intestinal microbiota and provide protection information for anurans.
1. Introduction
Gut microbiota is one of the main components of the intestinal ecosystem and can profoundly influence the biology of hosts, including digestive efficiency, metabolic processes, and immune regulatory processes [1,2]. In addition, a number of studies have established it contributes to the host’s ability to better adapt to changes in the environment, by aiding in the absorption of essential nutrients and maintaining organism balance [3,4,5,6]. It is well recognized that developmental changes in gut microbiota composition are mainly driven by host factors [7,8,9,10,11], such as the host genotype, gender, and diet [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Furthermore, the developmental stage of the host can also influence gut microbiota in animals, which has been confirmed in mammals [19,20,21,22], fish [23,24,25], shrimp [26], and artificially raised amphibians [27].
Anurans, noted for their unique life histories, are critical in ecosystems and exhibit enormous variations in life histories [28,29,30]. Many frogs and toads undergo metamorphosis, during which the external and internal body morphologies of tadpoles transform dramatically as they transition to a new ecosystem [31,32,33,34]. Meanwhile, the prey diet of tadpoles shifts from microalgae to insects [35]. In addition, the anurans can survive long winter by reducing the metabolic rate and reshaping the gut microbiota in cold regions, without food intake [36]. Thus, the unique life history of anurans leads to a unique microbial ecology in which gut microbiota can be reshaped by changes in morphological, physiological, environmental, and behavioral factors [27,37], making them an ideal model for examining differences in gut microbiota caused by different growth stages [27].
The intestinal microbial composition of anurans during the tadpole and adult stage is significantly different [37,38,39]. A study on Lithobates pipiens’s intestinal microbiota showed that the structure of the tadpole was similar to that of teleost fish, but the adult stage was similar to that of amniotic animals [32]. Moreover, the intestinal microbial richness and diversity in the adult stage were lower than those in the tadpole periods [32]. Further, studies on tadpoles in different regions had similar results [40]. The effects of food, habitat type, and specific life stages (such as metamorphosis and hibernation) on the gut microbial composition of some tadpoles and frogs have been reported [37]. In addition, there have also been many studies on the skin microbiota of amphibians [41,42,43,44,45]. However, systematic studies on the succession of microbiota are limited in anurans [2,38,46,47,48,49,50].
The Tibetan toad (Bufo tibetanus) belongs to the Bufonidae family and is endemic to southwestern China [51,52]. It is often found in grassland patches and farmlands, with an elevation range from 2400 to 4300 m asl [53]. The spawning period of this species extends from April to July, and the individuals spawn once in a year [53]. Thus, the toad can be classified as a prolonged breeder. Scientific research on the biology and ecology of B. tibetanus has been conducted on its skin structures, male call characteristics, populational age structure, and mitochondrial DNA [54,55,56,57,58]. B. tibetanus is a wild population in the high-altitude area of southwest China, which has special adaptability to the environment. Until now, little research on the succession of microbiota has been conducted in this toad. Here, we did so by examining the composition and structure of gut bacterial assemblages in the Tibetan toad across its life cycle. This study will help to expand the understanding of the effects of historical developments on the diversity and structure of intestinal microbial communities in wild anurans.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
All the samples were collected from Bomi town in Southeastern Tibet, China (29°53′ N, 95°41′ E, 2650 m asl), which is characterized by a humid subtropical climate. The tadpole, juvenile, and adult stage individuals were collected in July 2022. The developmental stage of each tadpole collected was determined using Gosner’s (1960) table [59]. The tadpoles were divided into 4 groups: T1 group (at 18–31 Gosner stages, n = 15), T2 group (at 32–41 Gosner stages, n = 15), T3 group (at 42–44 Gosner stages, n = 10), T4 group (at 45–46 Gosner stages, n = 11). The juveniles and adults were named J group (n = 6) and A group (n = 25), respectively.
All samples were transported to local laboratory facilities and euthanized by soaking in buffered MS-222 (10 g/L). Then, each animal was dissected, and the contents of the guts were collected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. In order to avoid contamination risks, all dissection instruments were wiped with 100% EtOH and flame-sterilized between each individual sample.
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
DNA was extracted from gut content samples using the MagAtrract PowerSoil Pro DNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and its quality was analyzed by agarose gel. The V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the primer sequences 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) for each gut sample. The amplicon products were gel-electrophoresed, purified using the AxyPrep DNA gel extraction kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA), and quantified using QuantiFluor™-ST (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Then, the purified amplicons were pooled at equal nanomolar concentration and sequenced on the Illumina MiSeq Sequencing Platform with paired-end read (2 × 300 bp) (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Using standard protocols, sequencing was performed by Majorbio Company (Majorbio, Shanghai, China).
Raw sequencing data were quality-filtered by fastq (version 0.19.6) and merged by FLASH (version 1.2.7) based on overlapping relationships to yield effective sequences. Representative sequences for each operational taxonomic unit (OTU) were obtained by QIIME1.9.1 software and were compared and annotated with the Silva (Release 138) database. Archaea, chloroplast, and mitochondria OTUs were removed following annotation. OTUs were clustered with a 97% similarity cutoff using UPARSE (version 7.1, http://drive5.com/uparse/ 6 September 2024), and chimeric sequences were identified and removed using UCHIME. The taxonomy of each 16S rRNA gene sequence was analyzed by the RDP Classifier algorithm (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/ 6 September 2024) against the Silva 16S rRNA database using a confidence threshold of 70%.
2.3. Biodiversity Analysis
Alpha diversity indices, including Chao and Ace indices (richness estimate) and Shannon index (diversity estimate) in the samples were analyzed from the sequencing data using Mothur software (version 1.30.2) to estimate the richness and diversity of microbial communities. The mean values of these indices were compared among groups using ANOVAs in R (version 3.3.1), followed by Tukey’s post hoc HSD test to obtain p-values for pairwise comparisons across each life stage. Rarefaction curves, the depth of sampling of a community compared with its total diversity, were constructed using R software (version 3.3.1). Beta diversity measurements, the differences in species composition between assemblages or regions, were visualized using R software (version 3.3.1) for the principal coordinate analysis (PCoA). The beta diversity distance matrix was calculated by QIIME (version 2020.2.0), and a hierarchical clustering analysis was performed according to the beta diversity distance matrix. The UPGMA (Unweighted Pair-group Method with Arithmetic Mean) was used to construct the tree structure, and then R was used to draw the tree to visualize the similarity or difference in community composition in different samples. The composition and abundance distribution tables of each sample at phylum and genus levels were obtained by QIIME software (version 1.9.1). For differences in microbial community composition across the six life stages, ANOSIMs in QIIME were performed. To determine which stages were most similar to one another, R values from each model were used. Here, all models were assessed with a permutation test (999 permutations), and FDR-corrected p-values were provided to correct for multiple comparisons. Linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) was performed to identify differentially abundant bacteria among different groups with a linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score threshold >4 [60]. The PICRUSt analysis was based on the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) to query protein sequences and predict gene functions. The predicted gene functions showed different abundance metabolic pathways between groups. An ANOVA was performed to determine the significant differences in KEGG pathways across groups. In this study, the bioinformatic analysis of the gut microbiota was carried out using the Majorbio Cloud platform (https://cloud.majorbio.com 6 September 2024).
3. Results
3.1. Summary of Sequencing Data
A total of 4,068,104 high-quality reads were obtained from all gut microbiota samples at six developmental stages. They were grouped into 2063 OTUs (>97% sequence similarity), which encompassed 30 phyla affiliated with 312 genera. Both rarefaction curves (Sobs rarefaction curve and Shannon index rarefaction curve) suggested that the sequencing depth was sufficient to cover most bacterial communities in all samples (Figure 1A,B).
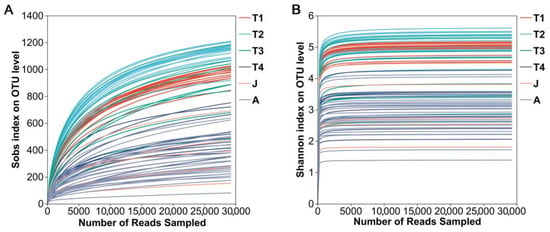
Figure 1.
Rarefaction curves of samples. (A): Sobs index; (B): Shannon index. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult.
3.2. Gut Microbial Diversity
3.2.1. Alpha Diversity of Gut Microbiota
Significant differences were observed among all developmental groups in terms of Chao, Ace, and Shannon indices values (ANOVA, all p < 0.001; Figure 2A–C). These three indices of the T2 group were the highest and decreased as development progressed, and all their values were the lowest in the A group (Figure 2A–C). The Chao, Ace, and Shannon indices were significantly decreased in the J group compared to the T2 group, whereas no significant differences existed between T4 and J and J and A groups (HSD’s test: all p > 0.05).
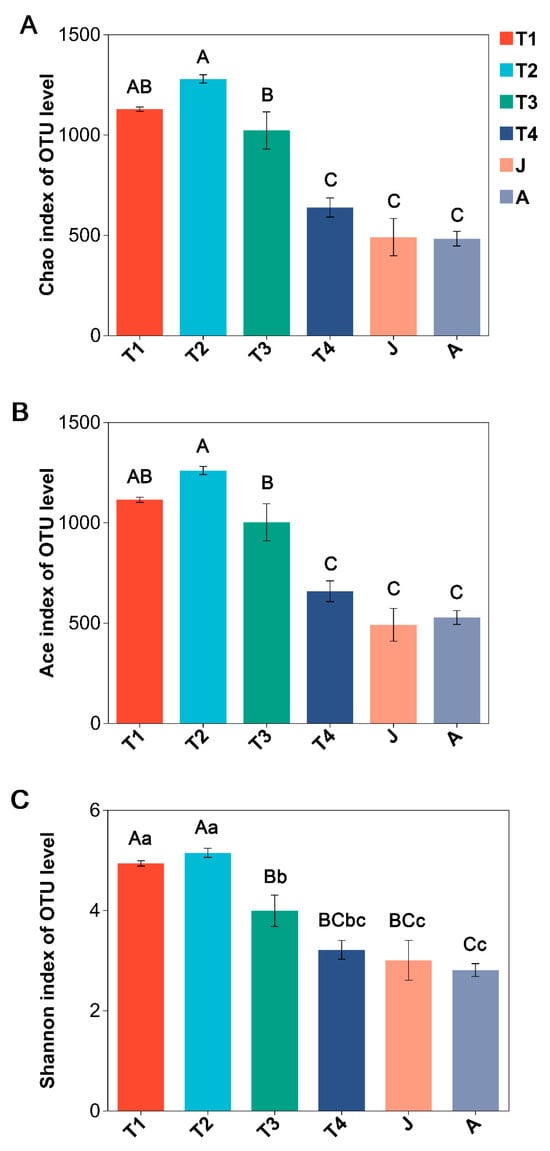
Figure 2.
Comparison of alpha diversity of intestinal microbiota at different growth stages of B. tibetanus. (A): Chao index; (B): Ace index; (C): Shannon index. Different letters indicate significant differences among groups. Capital letters represent extremely significant differences (p < 0.01), and lowercase letters represent significant differences (p < 0.05).
3.2.2. Beta Diversity Analysis
At the OTU level, a PCoA based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarities demonstrated most samples clustered according to development stages and significant differences in bacterial community structure for different groups (ANOSIM, R = 0.640, p = 0.001; Figure 3A). The results showed clear separations among the six groups with different developmental stages, except for many overlaps in the T2 and T3 groups. Further, the gut microbiota of the J group was similar to those of the T4 and A groups. Similar results were produced by hierarchical clustering (Figure 3B), implying that the distribution of gut microbiota in the toad became more similar after metamorphosis.
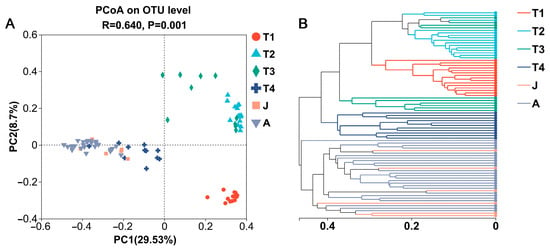
Figure 3.
PCoA plot based on Bray–Curtis distances (A) and hierarchical clustering tree (B) of gut microbes at different growth stages. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult.
3.3. Gut Microbial Composition
3.3.1. Community Composition of Gut Microbiota at the Phylum Level
There were 30 phyla detected from the gut microbiota of B. tibetanus in all developmental groups, with 7 phyla having a relative abundance of more than 1% (Figure 4A). For the T1 group, the gut microbiota was dominated by Firmicutes (39.2%), Proteobacteria (35.8%), Actinobacteria (9.3%), and Bacteroidetes (4.9%) (Figure 4A). Compared with the T1 group, the relative abundance of Bacteroidota in the T2 and T3 groups decreased by less than 0.2%. For the T2 group, the relative abundances of Firmicutes (from 39.2% to 49.6%), Actinobacteria (from 9.3% to 13.7%), and Cyanobacteria (from 2.0% to 2.7%) were increased compared to the T1 group, whereas that of Proteobacteria (from 35.8% to 21.4%) was decreased (Figure 4A). For the T3 group, the relative abundance of Firmicutes (from 49.6% to 63.8%) was increased compared to the T2 group, whereas those of Proteobacteria (from 21.4% to 16.3%), Actinobacteria (from 13.7% to 10.8%), and Cyanobacteria (from 2.7% to 1.6%) were decreased (Figure 4A). For the T4 group, the relative abundances of Firmicutes (from 63.8% to 71.7%) and Actinobacteria (from 10.8% to 14.8%) were increased compared to the T3 group, whereas those of Proteobacteria (from 16.3% to 8.3%) and Cyanobacteria (from 1.6% to 0.6%) were decreased (Figure 4A). For the J group, the relative abundances of Firmicutes (from 71.7% to 73.0%), Desulfobacterota (from 0.6% to 8.2%), and Bacteroidota (from 1.6% to 3.1%) were increased compared to the T4 group, whereas that of Actinobacteria (from 14.8% to 12.2%) was decreased (Figure 4A). For the A group, the relative abundance of Firmicutes (from 73.0% to 74.0%) was not significantly changed compared to that of the T4 group, whereas that of Proteobacteria (from 2.2% to 13.4%) and those of Actinobacteria (from 12.1% to 10.2%) and Bacteroidota (from 3.1% to 1.1%) were increased and decreased, respectively (Figure 4A).
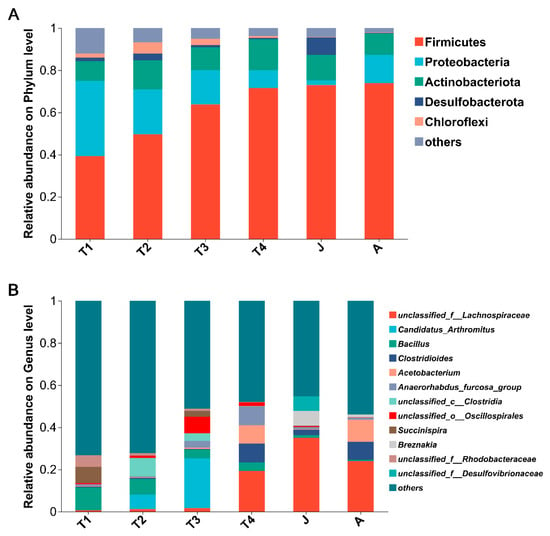
Figure 4.
Community barplot analysis showing the relative abundance at the phylum (A) and genus (B) level at different growth stages. Abundances of phyla or genera less than 1% were classified as “others”. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult.
At the phylum level, the composition of intestinal microbiota changed significantly with toad development. Twelve, or 40% of all the thirty phyla had high abundances (such as Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Chloroflexi, Desulfobacterota, Bacteroidota, and Cyanobacteria) and had significant differences among the different stages of development (all p < 0.01 except Actinobacteria). Seven significantly differentiated phyla were identified by the LEfSe analysis, namely, Verrucomicrobiota (T1 group), Bacteroidota (T1 group), Proteobacteria (T1 group), Cyanobacteria (T2 group), Chloroflexi (T2 group), Desulfobacterota (J group), and Firmicutes (A group) (LDA > 4, p < 0.05; Figure 5 and Figure 6).
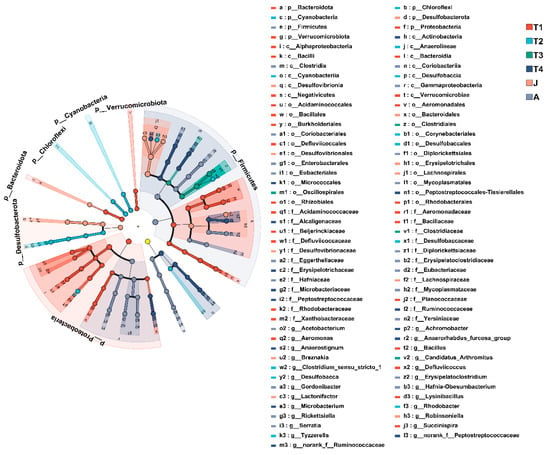
Figure 5.
Cladogram of LEfSe analysis showing differentially abundant bacterial taxa in the gut microbiota among groups. The yellow node represents no significant difference between the sample groups. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult.
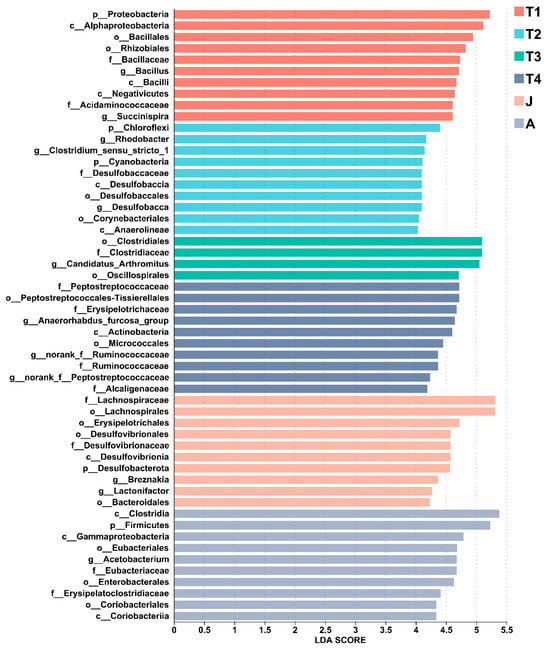
Figure 6.
LEfSe analysis of the top 10 gut microbiota in all groups. LDA scores of differentially abundant taxa in the gut microbiota of the six groups from the LEfSe analysis. The top 10 dominant taxa in each group are shown. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult.
3.3.2. Community Composition of Gut Microbiota at the Genus Level
There were 614 genera identified in all groups, with 20 genera having a relative abundance of more than 1% (Figure 4B). In the T1 group, the relative abundances of Bacillus (11.0%) and Succinispira (7.8%) were the highest. In the T2 group, the relative abundances of g__unclassified_c__Clostridia (from 0.03% to 8.7%) and Candidatus_Arthromitus (from 0.0% to 6.9%) were increased compared with those of the T1 group, whereas that of Bacillus (from 11.0% to 7.5%) was sharply decreased. In the T3 group, the relative abundances of Candidatus_Arthromitus (from 6.9% to 23.7%) and g__unclassified_o__Oscillospirales (from 1.0% to 7.8%) were increased compared with those of the T2 group, whereas that of Bacillus (from 7.5% to 4.1%) was decreased. In the T4 group, the relative abundances of g__unclassified_f__Lachnospiraceae (from 1.6% to 19.3%) and g__Anaerorhabdus_furcosa_group (from 3.3% to 9.0%) were increased compared with those of the T3 group, whereas those of Candidatus_Arthromitus (from 23.7% to 0.02%) and g__unclassified_o__Oscillospirales (from 7.8% to 1.7%) were decreased. In the J group, the relative abundances of g__unclassified_f__Lachnospiraceae (from 19.3% to 35.0%) and g__unclassified_o__Micrococcales (from 2.5% to 3.8%) were increased compared with those of the T4 group, whereas those of g__unclassified_o__Oscillospirales (from 1.7% to 0.4%) and g__Anaerorhabdus_furcosa_group (from 9.0% to 1.1%) were decreased. In the A group, the relative abundances of Acetobacterium (from 0.2% to 10.5%) and g__unclassified_f__Lachnospiraceae (from 35.0% to 24.1%) were increased and decreased compared with those of the J group, respectively.
At the genus level, LEfSe found significant enrichment of Succinispira, Aeromonas, and Defluviicoccus in the T1 group; Tyzzerella, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Rhodobacter, and Desulfobacca in the T2 group; Candidatus_Arthromitus in the T3 group; Anaerostignum, norank_f_Peptostreptococcaceae, norank_f_Ruminococcaceae, Anaerhabdus_furcosa_group, Microbacterium, and Achromobacter in the T4 group; Lactonifacter, Robinsoniella, and Breznakia in the J group; and Acetobacterium, Erysipelatoclostridium, and Gordonibacter in the A group (LDA > 4, p < 0.05; Figure 5 and Figure 6).
3.4. Microbiota Functional Prediction Analysis
KEGG pathways were used to predict the functions of the intestinal microbiota at different developmental stages. The enriched KEGG pathways illustrated that the metabolic pathways and the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites were significant enrichment in all stages (Figure 7). For KEGG pathway level 3, pathways associated with Microbial metabolism in diverse environments, Quorum sensing, Two-component system and Purine metabolism were significantly enriched in the T1 group, the pathway associated with Ribosome was more enriched in the T3 group, and pathways associated with ABC transporters and Carbon metabolism were more enriched in the T4 group.
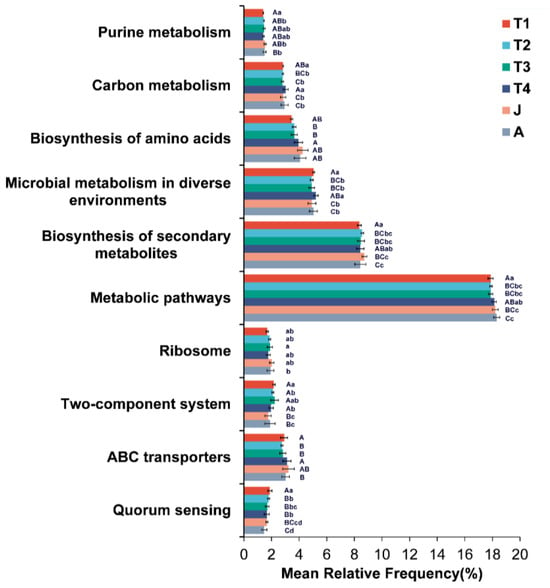
Figure 7.
Predicted functions of the intestinal microbiota on KEGG pathways. T1: Gosner 18–31; T2: Gosner 32–41; T3: Gosner 42–44; T4: Gosner 45–46; J: juvenile; A: adult. Different letters indicate significant differences among groups. Capital letters represent extremely significant differences (p < 0.01), and lowercase letters represent significant differences (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
There are few systematic studies on the ecological succession of intestinal microbiota during the development of anurans. Here, we provided a baseline description of the developmental succession of gut microbiota in the Tibetan toad by using a 16S rRNA sequencing analysis. The three alpha diversity indices were highest in the T2 group (Gosner 32 to 41), decreased as development progressed, and became stable at juvenile and adult stages. The developmental stage and feeding habitat could underlie this trend. Further, we found that the gut microbiota structure differed among different development stages of B. tibetanus and became relatively stable after metamorphosis. This developmental adaptation can be important for hosts grown with a change in habit use pattern.
Animal growth and development are tightly correlated with changes in intestinal microbiota [26,48,61]. Throughout the toad’s development, the intestinal microbiota of B. tibetanus undergoes changes. A higher alpha diversity was found in the T1 and T2 groups (Gosner 18 to 41), and its value decreased with the development of the toad, which was consistent with the results of Andrias davidianus in Brazil and Madagascar anuran faunas [40,62]. The intestinal microbiota of tadpoles is susceptible to external factors (e.g., growth, diet, temperature, drug, etc.), which cause it to be unstable, thus forming the characteristics of a high diversity [2,35,50,63,64,65]. In addition, the beta diversity analysis of the intestinal microbiota of B. tibetanus showed differences in different development stages of the toad. The intestinal microbiota of the T1 group was obviously separated from that of the other groups. However, the structure of the intestinal microbiota in the T2 and T3 groups tended to be similar, as well as that of the T4, juvenile, and adult groups. These results are similar to the research on Rana chensinensis, Bufo gargarizans, Andrias davidianus, and zebrafish gut microbiota with high-throughput sequencing [62,66,67,68]. Tadpoles during late developmental stages (T3 and T4 group, after Gosner stage 41) were in the metamorphosis period, and their functional traits exhibited significant changes to adapt switching from water to land [66,67]. In this process, the feeding of tadpoles was decreased, which had an impact on the colonization of intestinal microbiota [66,69,70,71,72]. Many studies have demonstrated that diet has a substantial impact on gut microbiota [73,74,75,76]. These changes in gut microbiota could be caused by the direct effect of diet composition [77]. In many animal taxa, intestinal microbiota undergo dynamic changes due to physical, morphological, and chemical changes concomitantly with the development of the digestive system [32,78]. The complex life history of most amphibians consists of an aquatic larval stage followed by terrestrial juvenile and adult stages [79]. In addition to diet, the structure and function of intestinal microbiota are more likely to be influenced by changes in the living environment [80,81].
The abundance of intestinal microbiota in different growth stages of B. tibetanus constantly changed. The dominant phyla of B. tibetanus tadpoles were Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, and Desulfobacterota, which were inconsistent with those of B. gargarizans, Rana pipiens and Rana dybowskii tadpoles [48,63,67]. The inconsistent results may be attributed to the diversity of the dietary habits of tadpoles [69,82,83]. B. tibetanus lives in meadow wetlands on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, where there are few phytoplankton and more benthic animal species [54,84,85,86]. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum in the gut of B. tibetanus, and it was enriched in the gut microbiota of the T1 group and gradually decreased with growth. Our results are consistent with those of Mirpuri et al., (2014) [87], who found that there was a transient dominance of Proteobacteria in newborn mice, and it was progressively lost with age. Similarly, a study on the intestinal microbiota of L. pipiens tadpoles showed that the proportion of Proteobacteria was high in the tadpole period [32]. Proteobacteria can participate in the decomposition of complex carbohydrates in animal intestines and convert them into small molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by animals [88,89,90]. At this stage, tadpoles grow rapidly, thus the enrichment of Proteobacteria is beneficial for them to access external nutrients.
Desulfobacterota was the most abundant phylum in the gut of B. tibetanus and was enriched in the gut microbiota of the J group by the LEfSe analysis. Desulfobacterota has the ability to reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide, which can help them to deal with some sulfur-containing compounds. The generated hydrogen sulfide can regulate the redox state in the intestine to a certain extent, and may participate in signal transmission in some physiological processes [91,92]. This may suggest this toad consumes more sulfur-containing foods in the juvenile stage, and being rich in Desulfobacterota can increase its ability to digest and help it adapt to the plateau environment [93,94]. In addition, Desulfobacterota is associated with a hypoxic environment [95]; therefore, it is more likely to evolve this characteristic to survive in the intestine.
Adult toads, compared to tadpoles, had a higher relative abundance of Firmicutes and a reduced abundance of Bacteroidetes. Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes are the predominant bacterial phyla colonizing the healthy intestinal of humans and animals. Studies have shown that Firmicutes accounted for a high proportion of the gut microbiota in many animals [7,96,97,98,99,100,101]. For example, research on Chinese giant salamanders has found that the abundance of Firmicutes increases at the ages of 3 and 4 [102]. Similar to our results, Firmicutes was most abundant in Polypedates megacephalus and L. pipiens [32,103]. Many studies have shown that dietary fiber is one of the key factors influencing gut Firmicutes [104,105,106]. It has been found that Firmicutes are important in maintaining gut homeostasis, as they possess many genes responsible for fermenting dietary fiber and could interact with the intestinal mucosa [107]. Some studies have demonstrated that gut Firmicutes can produce byproducts through fermentation, such as short-chain fatty acids, that are directly absorbed through the host bowel wall [35,108,109,110]. This process may promote their metabolism and increase energy intake. Firmicutes may play a crucial role in the growth and development of B. tibetanus. Therefore, the significant changes in the abundance of Firmicutes between adults and tadpoles were likely to be caused by diet change. However, the most enriched phyla in the intestines of Odorrana tormota, Odorrana graminea, and Amolops wuyiensis were inconsistent with ours [111]. The composition of gut microbiota in different species is affected by factors such as host genotype, individual development stage, gender, habitat, captivity, and seasonal differences [111,112], which may lead to inconsistent results. At present, the factors affecting the intestinal flora of amphibians are mainly biased towards the environment [40]. The results of this study suggest that the dynamics of intestinal microbiota in Tibetan toads may be potentially related to the physiological characteristics of the host, but the deeper mechanisms underlying the changes in gut microbiota still need further verification.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the developmental stages play a vital role in reshaping the structure and function of the intestinal microbiota of B. tibetanus. The reshaped intestinal microbiota could be due to the growth and diet of this toad. Future research will need to better determine the role and molecular mechanisms of the growth stages behind these effects. Understanding these changes can provide new ideas for the protection of anurans.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z.; methodology, L.Z. and K.H.; software, K.H., C.H., and C.L.; formal analysis, K.H.; investigation, K.H.; resources, K.H., C.H. and C.L.; data curation, K.H. and C.H.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Z. and K.H.; visualization, K.H., C.H., and C.L.; supervision, L.Z.; project administration, L.Z.; funding acquisition, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published versionversion of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Research Fund of Henan Normal University (No. 20210196) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32170424).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal-use protocol in this study was reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Henan Normal University, Henan, China, permission number: HNSD-2024-07-27.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data information is available in the NCBI sequence reads archive with number PRJNA955012.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, K.D.; Carey, H.V. A place for host–microbe symbiosis in the comparative physiologist’s toolbox. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3496–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrndorff, S.; Alemu, T.; Alemneh, T.; Lund Nielsen, J. The microbiome of animals: Implications for conservation biology. Int. J. Genom. 2016, 2016, 5304028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, C.S. Gut dysbiosis in animals due to environmental chemical exposures. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, N.; Noti, M. The aging gut microbiome and its impact on host immunity. Genes Immun. 2021, 22, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.K.; Kelly, S.A.; Legge, R.; Ma, F.; Low, S.J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Nehrenberg, D.; Hua, K. Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18933–18938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muegge, B.D.; Kuczynski, J.; Knights, D.; Clemente, J.C.; Gonzalez, A.; Fontana, L.; Henrissat, B.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Diet Drives Convergence in Gut Microbiome Functions Across Mammalian Phylogeny and Within Humans. Science 2011, 332, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeaMaster, B.; Walsh, W.; Brock, J.; Fujioka, R. Cold stress-induced changes in the aerobic heterotrophic gastrointestinal tract bacterial flora of red hybrid tilapia. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 50, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Bouvier, C.; Bouvier, T.; Troussellier, M.; Escalas, A.; Mouillot, D. Genetic difference but functional similarity among fish gut bacterial communities through molecular and biochemical fingerprints. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; van der Gast, C.J.; Yu, Y. Bacterial community assembly and turnover within the intestines of developing zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Maibunkaew, S.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Jiravanichpaisal, P.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Bacterial population in intestines of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) under different growth stages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Qu, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, H. Composition and diversity of gut microbiota in Pomacea canaliculata in sexes and between developmental stages. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Ngugi, D.K.; Stingl, U. Diet strongly influences the gut microbiota of surgeonfishes. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, I.; Coward, E.; Andersen, T.; Vadstein, O. Selection in the host structures the microbiota associated with developing cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.H.; Ochman, H. Rates of gut microbiome divergence in mammals. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, H.M.; Lundin, D.; Tolf, C.; Waldenström, J.; Zöttl, M. Environmental effects rather than relatedness determine gut microbiome similarity in a social mammal. J. Evol. Biol. 2023, 36, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, J.K.; Virgin, H.W. Transkingdom control of viral infection and immunity in the mammalian intestine. Science 2016, 351, aad5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevelline, B.K.; Moeller, A.H. Robustness of mammalian gut microbiota to humanization in captivity. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 9, 785089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Research progress of the gut microbiome in hybrid fish. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.R.; Ran, C.; Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.G. Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, L.-P.; Shen, Y.-Q. A systematic review of advances in intestinal microflora of fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X. Comparison of the intestinal microbiota during the different growth stages of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 696281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, R.R.; Sommer, S. The amphibian microbiome: Natural range of variation, pathogenic dysbiosis, and role in conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 763–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.; Hero, J.M. Geographic variation in life-history characteristics of amphibians: A review. J. Anim. Ecol. 2003, 72, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, N.; Nath, B. Role of Amphibians to Ecosystem Services: A Review. eJBio 2023, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sankararaman, V.; Miller, D. Life-history traits govern the habitat use of diverse amphibian assemblages in an agroforest landscape matrix. Anim. Conserv. 2024, 27, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, K.S.; Ismail, N.A.; Farinordin, F.A.; Izam, N.A.M. Frog Metamorphosis: A Review of Metamorphic Stages, Developmental Progression, and Influential Factors. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 1, 120–155. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, K.D.; Cary, T.L.; Karasov, W.H.; Dearing, M.D. Restructuring of the amphibian gut microbiota through metamorphosis. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.D.; Cai, L. Amphibian metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2007, 306, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.; Dodd, J. The biology of metamorphosis. Physiol. Amphib. 1976, 3, 467–599. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Huang, B.; Lin, S.; Huang, C.; Liao, P. Changes of diet and dominant intestinal microbes in farmland frogs. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoyama, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Takemura, N.; Ogasawara, T.; Watanabe, J.; Ito, H.; Morita, T. Response of gut microbiota to fasting and hibernation in Syrian hamsters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6451–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Cui, L.; Hu, Z.; Du, X.; Abid, H.; Wang, H. Environmental and host factors shaping the gut microbiota diversity of brown frog Rana dybowskii. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalvenzi, T.; Clavereau, I.; Bourge, M.; Pollet, N. Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages. Peer Community J. 2021, 5, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, M.L.; Bletz, M.C.; Haddad, C.F.; Vences, M. The intestinal microbiota of tadpoles differs from those of syntopic aquatic invertebrates. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vences, M.; Lyra, M.L.; Kueneman, J.G.; Bletz, M.C.; Archer, H.M.; Canitz, J.; Handreck, S.; Randrianiaina, R.-D.; Struck, U.; Bhuju, S. Gut bacterial communities across tadpole ecomorphs in two diverse tropical anuran faunas. Sci. Nat. 2016, 103, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueneman, J.G.; Parfrey, L.W.; Woodhams, D.C.; Archer, H.M.; Knight, R.; McKenzie, V.J. The amphibian skin-associated microbiome across species, space and life history stages. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, L.K.; Hughey, M.C.; Rebollar, E.A.; Umile, T.P.; Loftus, S.C.; Burzynski, E.A.; Minbiole, K.P.; House, L.L.; Jensen, R.V.; Becker, M.H. Panamanian frog species host unique skin bacterial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Bowers, R.M.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R.; Lauber, C.L. Co-habiting amphibian species harbor unique skin bacterial communities in wild populations. ISME J. 2012, 6, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, A.; Lee-Cruz, L.; Tripathi, B.; Waldman, B. Skin bacterial community reorganization following metamorphosis of the fire-bellied toad (Bombina orientalis). Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwis, R.E.; Haworth, R.L.; Engelmoer, D.J.; Ogilvy, V.; Fidgett, A.L.; Preziosi, R.F. Ex situ diet influences the bacterial community associated with the skin of red-eyed tree frogs (Agalychnis callidryas). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; Luo, S.; Chai, L. Cogrowth advantage: Intestinal microbiota analysis of Bufo gargarizans and Rana chensinensis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2025, 299, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, L.; Chang, Q.; Lu, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, L. The changes in the frog gut microbiome and its putative oxygen-related phenotypes accompanying the development of gastrointestinal complexity and dietary shift. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, R.W.; Kirschman, L.; Zeglin, L. Manipulation of gut microbiota reveals shifting community structure shaped by host developmental windows in amphibian larvae. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, T.J.; Jackson, C.R. Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3776–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Liu, X.N.; Hu, Z.F.; Ding, J.F.; Bie, J.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, J.T. Effects of captivity and season on the gut microbiota of the brown frog (Rana dybowskii). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duellman, W.E. Amphibian Species of the World: Additions and Corrections; Natural History Museum, University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Duellman, W.E.; Trueb, L. Biology of Amphibians; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Ye, C.; Jiang, J. Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians and Their Distributions; Sichuan Publishing Group: Chengdu, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Bufo tibetanus (Anura: Bufonidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y. Histological observation of Bufo tibetanus skin. Sichuan J. Zool. 2016, 35, 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tang, Y.; Cui, J. Song characteristics and auditory sensitivity of male Xizang toads. J. Zool. 2019, 54, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, P. Age, growth and other population characteristics of Bufo tibetanus in nyingchi city, Tibet. Sichuan J. Zool. 2022, 41, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, P.; He, Z.; He, K.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Age structure and body size of two Tibetan toad (Bufo tibetanus) populations from different elevations in China. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosner, K.L. A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 1960, 16, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, D.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; You, Y. Change in the intestinal bacterial community structure associated with environmental microorganisms during the growth of Eriocheir sinensis. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Deng, H.; Sun, H.; Si, W.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Huang, M.; Fan, W. Changes of intestinal microbiota in the giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) during growth based on high-throughput sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1052824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Cui, L.Y.; Bie, J.; Han, X.Y.; Hu, Z.F.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, J.T. Changes in the gut microbiota diversity of brown frogs (Rana dybowskii) after an antibiotic bath. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.S.; Novarro, A.J.; Kohl, K.D. Environmental temperature alters the digestive performance and gut microbiota of a terrestrial amphibian. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb187559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Park, W.B.; Do, Y. Tadpole growth rates and gut bacterial community: Dominance of developmental stages over temperature variations. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, R.; Meng, J.; Wang, H. Changes in intestinal microbial community of Rana chensinensis tadpoles during metamorphosis. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Dong, Z.; Chen, A.; Wang, H. Changes in intestinal microbiota of Bufo gargarizans and its association with body weight during metamorphosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, B.; Wang, C.; Shu, L.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, J. Host development overwhelms environmental dispersal in governing the ecological succession of zebrafish gut microbiota. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaña, C.G.; Silva, S.D.; Hagyari, D.; Wager, J.; Tiegs, L.; Sadeghian, C.; Schriever, T.A.; Schalk, C.M. Revisiting “what do tadpoles really eat?” A 10-year perspective. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, K.D.; Angert, E.R.; Montgomery, W.L.; Choat, J.H. Intestinal microbiota in fishes: What’s known and what’s not. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, J. Taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic beta diversity in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, D.D.; Oseen, K.L.; Wassersug, R.J. Ontogenetic changes in diet and intestinal morphology in semi-terrestrial tadpoles of Nannophrys ceylonensis (Dicroglossidae). Copeia 2007, 2007, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Marcos, J.A.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Camargo, A. The role of diet and intestinal microbiota in the development of metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, A.; Clinger, E.; Hao, L. Effect of diet and dietary components on the composition of the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Shah, B.R.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Zhan, F.; Geng, F.; Li, B. A critical review on interplay between dietary fibers and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, M.T. Altered gut microbiota: A link between diet and the metabolic syndrome. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2018, 16, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, D.R.; Toolson, E.C.; Takacs-Vesbach, C. Do diet and taxonomy influence insect gut bacterial communities? Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5124–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semlitsch, R.D.; Bodie, J.R. Biological criteria for buffer zones around wetlands and riparian habitats for amphibians and reptiles. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Tu, K.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the intestinal microbiota of several aquatic organisms and association with the surrounding environment. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Iftikhar, A.; Muzaffar, H.; Almatroudi, A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Navaid, S.; Saleem, S.; Khurshid, M. Biodiversity of gut microbiota: Impact of various host and environmental factors. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5575245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cui, Z.; Ning, M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, H. Variation in the intestinal microbiota at different developmental stages of Hynobius maoershanensis. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, A.; Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Xiao, G.; Feng, J. Changes in the gut microbiota during Asian particolored bat (Vespertilio sinensis) development. PeerJ. 2020, 8, e9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, J.R.; Schulte II, J.A.; Larson, A.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tuniyev, B.S.; Papenfuss, T.J. Phylogenetic relationships of toads in the bufo species group from the eastern escarpment of the Tibetan Plateau: A case of vicariance and dispersal. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1998, 9, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Weadick, C.J.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, Y. Phylogeographic analysis of the Bufo gargarizans species complex: A revisit. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Bufo gargarizans: What’s in a Name? Asian Herpetol. Res. 2023, 14, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpuri, J.; Raetz, M.; Sturge, C.R.; Wilhelm, C.L.; Benson, A.; Savani, R.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Proteobacteria-specific IgA regulates maturation of the intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.R.; Moss, M.O. Food Microbiology; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Satomi, M.; Vogel, B.F.; Gram, L.; Venkateswaran, K. Shewanella hafniensis sp. nov. and Shewanella morhuae sp. nov., isolated from marine fish of the Baltic Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.L.; Biggerstaff, J.; Eichhorn, A.; Ewing, E.; Shahan, R.; Soriano, D.; Stewart, S.; VanMol, K.; Walker, R.; Walters, P. Genomic characterization of three novel Desulfobacterota classes expand the metabolic and phylogenetic diversity of the phylum. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4326–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Tomás, B.; Lanzén, A.; Sánchez, P.; Estupiñán, M.; Sanz-Sáez, I.; Bilbao, M.E.; Rojo, D.; Mendibil, I.; Pérez-Cruz, C.; Ferri, M. Revisiting the mercury cycle in marine sediments: A potential multifaceted role for Desulfobacterota. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Permafrost temperatures and thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2010, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, D.W.; Chuvochina, M.; Pelikan, C.; Parks, D.H.; Yilmaz, P.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A.; Naganuma, T.; Nakai, R.; Whitman, W.B. Proposal to reclassify the proteobacterial classes Deltaproteobacteria and Oligoflexia, and the phylum Thermodesulfobacteria into four phyla reflecting major functional capabilities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5972–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yu, M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xue, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, P.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z. Microbial communities related to the sulfur cycle in the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01123–e01149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scupham, A.J.; Patton, T.G.; Bent, E.; Bayles, D.O. Comparison of the Cecal Microbiota of Domestic and Wild Turkeys. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 56, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K.; Gordon, J.I.; Secor, S.M.; Knight, R. Postprandial remodeling of the gut microbiota in Burmese pythons. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Benno, Y. Phylogenetic analysis of the human gut microbiota using 16S rDNA clone libraries and strictly anaerobic culture-based methods. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold, G.L.; Pryde, S.E.; Russell, V.J.; Furrie, E.; Flint, H.J. Assessment of microbial diversity in human colonic samples by 16S rDNA sequence analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suau, A.; Bonnet, R.; Sutren, M.; Godon, J.J.; Gibson, G.R.; Collins, M.D.; Doré, J. Direct analysis of genes encoding 16S rRNA from complex communities reveals many novel molecular species within the human gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4799–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gaughan, S.; Chang, Q.; Chen, H.; Lu, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, J. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.C.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, D. Functional analysis for gut microbes of the brown tree frog (Polypedates megacephalus) in artificial hibernation. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, H.L.; Campbell, B.J. Review article: Dietary fibre–microbiota interactions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndeh, D.; Gilbert, H.J. Biochemistry of complex glycan depolymerisation by the human gut microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; He, P. Clostridium species as probiotics: Potentials and challenges. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Xiang, H.; Yan, J.; He, L. Intestinal microbiota: A promising therapeutic target for hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 970036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, P.O.; Martin, J.C.; Lawley, T.D.; Browne, H.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Duncan, S.H.; O’Toole, P.W.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J. Polysaccharide utilization loci and nutritional specialization in a dominant group of butyrate-producing human colonic Firmicutes. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Commensal Clostridia: Leading players in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.H.; Qu, Y.F. Comparative study on gut microbiota in three Anura frogs from a mountain stream. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Do, Y. Combined effect of seasons and life history in an anuran strengthens the response and relationship between their physiology and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).