Simple Summary
Milk or mammary tissue swab samples were collected from both defective and normal udder halves in three different studies to identify the bacterial species involved. Samples were collected at different physiological time points: pre-mating, throughout lactation, at weaning and post-weaning. Numerous bacterial species were identified, with Staphylococcus species, Mannheimia haemolytica and Streptococcus being the most frequently isolated. Bacteria were isolated from at least one third (udder lumps) or more than half (hard udder) of defective udder halves, whereas no bacteria were isolated from more than two thirds of normal udder halves. Frequently isolated bacterial species tended to persist longer, whereas less frequently isolated bacterial species showed less stability over time. Bacterial species more frequently identified from defective udder halves and which appear more stable over time should be considered as a factor for making culling decisions.
Abstract
The objectives of these studies were to identify associations between udder half defects (hard or lump) and bacteria isolated from milk or mammary tissue swabs, to compare with samples from normal udder halves at different physiological time points and to compare bacterial species isolated via milk and swabs of mammary tissue from within the same udder halves. A total of 1054 samples were aseptically collected from each udder half of 199 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes from three different studies (Study A, n = 77; Study B, n = 74; and Study C, n = 48). Conventional bacterial culture and MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry were used for bacterial identification. Of the 225 samples from which bacteria were isolated, Mannheimia haemolytica and Streptococcus uberis were the dominantly identified species from defective udder halves, whereas coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CNS) species, mostly Staphylococcus simulans and Staphylococcus chromogenes, were more frequently isolated from normal udder halves. The ongoing presence of bacterial species over time was variable, although less frequently identified species showed less stability over time. A very high agreement (91.5%) of bacterial species identified was observed between the mammary tissue swab and udder half milk samples during post-weaning. In summary, palpable udder half defects were associated with bacterial positivity, and the ongoing presence of the bacteria over time was dependent on the species involved. Hence, culling ewes with palpable udder half defects that had more stable bacterial species could contribute to reducing the recurrence of palpable defects or mastitis.
1. Introduction
Udder defects have been associated with reduced milk production and changes in milk composition in both dairy and non-dairy ewes [1,2,3]. Further, low survival rates [4] and reduced live weight gains [5] have been observed in pre-weaned lambs reared by ewes with udder defects. These defects can be associated with mild to clinically noticeable changes in milk production and udder structure [6]. Studies from Canada, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom (UK) and New Zealand have reported that a range of bacterial species have been isolated from either milk or in abscesses from defective udders, with Staphylococci (S. aureus and coagulase-negative isolates) and Mannheimia haemolytica (M. haemolytica) being the most frequently reported isolates [6,7,8,9,10]. These studies also reported isolation of other relatively less frequently isolated bacterial species such as Streptococci, Enterobacteria, Corynebacterium and Pseudomonas. Over the past five decades in New Zealand, a small number of studies investigating bacterial species isolated from defective udders and teats have reported isolation of these and related bacterial species from clinically mastitic milk [7,8,11,12]. These studies were undertaken either shortly after lambing or during the post-weaning period and in most cases involved taking milk samples at a single point in time from ewes whose history of udder defects was unknown.
Upon palpation of an udder, any detectable mass of different consistency from the rest of the gland tissue or diffuse change in consistency of the whole mammary gland can be considered as a palpable udder defect [4]. A diffuse hard consistency of the whole mammary gland is a unilateral or bilateral udder defect with no to a small amount of milk excretion from the gland [8,13]. Authors from New Zealand, UK and Greece have reported that this defect type can be observed during both lactation and the dry or the pregnancy period [4,14,15]. Recently, Ridler et al. [7] reported at least seven different bacterial species from milk samples collected from udder halves categorised as hard, one week after weaning in non-dairy ewes in New Zealand. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was identified as the dominant bacterial species in that study, although 19.4% (7/36) of the udder halves categorised as hard yielded no bacteria.
Udder lumps have been described as intramammary masses (IMMs) that can vary in size, consistency and location [4,15]. Smith et al. [10], in the UK, collected mammary gland samples with lumps (abscesses) and reported that S. aureus was the most frequently detected bacterial species. Ridler et al. [7], in New Zealand, reported various species of bacteria isolated from milk samples from udder halves that contained lumps, including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Mannheimia. Distinct subcutaneous lumps immediately cranial or sometimes caudal to the udder have been reported in some ewes at weaning or shortly thereafter [7]. Such lumps were described by Saratsis et al. [15] as bacterial negative cysts filled with milk-like fluid.
Previous studies have shown changes in the percentage of palpable udder defects in repeated examinations within the same flock, indicating the dynamic nature of palpable udder defects [4,14]. Further, Ridler et al. [7] reported changes in udder defect status (defective to normal, defective to other defect category (e.g., hard to lump) or normal to defective) across two visits four to six weeks apart following weaning. A recent study by Zeleke et al. [16] reported that udder half defects, either hard or lump, change over time across different physiological time points. However, there has been no research evaluating bacterial isolation in defective udder halves over time.
Combined, the data indicate that while there has been research on bacterial isolation from udders with palpable udder defects in non-dairy ewes, most were undertaken during the short period between weaning and mating. Moreover, the association between bacterial isolation and udder half defect category or changes in defect category over time has not been studied. Therefore the objectives of the current studies were, firstly, to identify aerobic bacteria species isolated from milk and mammary tissue swab samples collected from normal udder halves and those with palpable defects at different physiological times (pre-mating, early lactation, weaning and post-weaning); secondly, identify associations between udder half defect and bacterial isolation; thirdly, assess changes in bacterial isolation from the same udder halves over time; and lastly, compare bacterial isolation from udder halves sampled via milk samples compared with swabs of mammary tissue.
2. Materials and Methods
This manuscript comprises data collected during three separate studies described as studies A, B and C below.
2.1. Animal Selection and Management
Study A: Ewes were part of a three-year longitudinal study from 2016 to 2018 at Massey University’s Riverside Farm, Wairarapa, New Zealand. The ewes were managed under standard commercial New Zealand conditions on pasture. A total of 77 Romney ewes aged four to five years were selected based on the following: 1. a history of having had udder half defects in the previous three years (24 ewes); 2. a history of no udder half defects in the previous three years but having an udder half defect identified at weaning on 5 December 2018 (38 ewes); 3. a history of no udder half defects in the previous three years and with no udder half defect at weaning on 5 December 2018 (15 ewes). At weaning on 5 December 2018, milk samples were collected from each udder half for bacterial identification from all 77 ewes.
Study B: Seventy-four Romney ewes that had been culled by the owner due to udder defects were obtained from a single commercial farm in North Canterbury, South Island, New Zealand and were transported to Massey University’s Tuapaka Farm, Palmerston North on 10 May 2019. The ewes remained at Tuapaka Farm for a week under standard commercial pasture grazing conditions. During this time, the udder and teats of each ewe were scored using the system described by Griffiths et al. [4]. Ewes were then slaughtered either at a local abattoir (n = 70) or, if deemed unfit for transportation to slaughter, were humanely euthanised at Massey University (n = 4). In all cases, the whole udder was collected, transported to Massey University and a mammary gland tissue swab was collected from each udder half within three to six hours (see below for further detail).
Study C: Forty-six ewes joined this study from a three-year (2016 to 2018) longitudinal study at Massey University’s Riverside Farm, Wairarapa, New Zealand based on udder defect history and udder defect status on the selection day. This study comprised lactating ewes with both normal and defective udder halves. Milk samples were collected from each udder half six times during lactation (on approximately days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42 of lactation), at weaning (29 November 2019) and three weeks after weaning (18 December 2019). Two ewes were culled at day 42 due to routine farm management, and four ewes missed day 42 milk sample collection. Udder halves were scored immediately prior to sample collection on all sampling days. On 21 December 2019, all ewes were slaughtered through a commercial abattoir, and udders were collected for mammary tissue swab sampling (see Section 2.3 below).
2.2. Udder Scoring
Each udder half was scored according to Griffiths et al. [4] and categorised into hard, lump or normal. Ewes were restrained and each udder was assessed in a sitting (shearing) position. Initially, each udder half was scored in 7-category score, where scores 1 and 2 describe a “normal” and scores 3 to 6 comprise an udder half with various sizes and consistency of udder lumps. Score 7 was palpated as diffusely hard consistency of the whole udder half. Udder halves categorised as “hard” or “lump” were considered defective.
2.3. Post-Mortem Udder Collection
Immediately post-slaughter (Studies B and C), the whole udder was removed, transported to Massey University and washed and thoroughly cleaned.
Mammary Swab Sample Collection
A swab sample was collected (Studies B and C) from each udder half (gland) using a sterilized blade to incise the udder skin at the base of teat and at the gland cistern, to expose the whole gland cistern. Several dissections were made using new sterilized blades to check the presence of lumps in the different parts of the udder (cranial or caudal to gland cistern). In each udder half, the gland cistern and/or contents of defects found were swabbed using a transport swab (Fort Richard Laboratories, Auckland, New Zealand). The ewes’ identification number, site of collection, nature of the contents and number of samples were recorded for each udder half independently. The swab samples were cultured immediately or kept for a maximum of 12 h in the refrigerator (4 °C) until culturing.
2.4. Milk Sampling
An aseptic milk sampling procedure was conducted to collect milk samples from each udder half (Studies A and C) from live ewes. Before sampling, teats were thoroughly cleaned with 70% ethanol and wiped with commercial teat wipes (Zoetis Mediwipes, Zoetis New Zealand Limited, Auckland, New Zealand). The first three milk squirts were discarded, and then 3–4 mL of milk was collected from each udder half into sterile tubes for bacteriological testing. Milk samples were cultured (see Section 2.5 below) in less than one hour after collection or kept for a maximum of 12 h in the refrigerator (4 °C) until culturing.
2.5. Bacterial Culture and Identification
Milk and swab samples were processed at the Massey University School of Veterinary Science bacteriology laboratory. The medium used was Colombia blood agar with 5% sheep blood, which was incubated aerobically at 37 °C for 48 h. Swabs were streaked directly onto the plate. Milk samples (10 µL) were put on a plate using micropipettes and streaked with a sterilized inoculation loop. Cultures with three or more morphologically distinct colonies on a single sample plate were considered positive, and morphological characteristics were assessed [17]. Cultures with three or more different colony types without a dominant colony type were considered contaminated. For all the isolates, single distinct colonies were picked further for sub-culture, Gram stain and catalase and coagulase testing. Purified isolates were then stored at −80 °C until tested using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-ToF) mass spectrometry to identify isolates.
2.6. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight (MALDI-ToF) Mass Spectrometry Identification
MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry was used to identify isolates [18]. All bacterial isolates were analysed using the direct transfer method, by directly smearing bacterial colony to a target plate (Bruker MALDI Biotyper) at SC Bio Limited, Auckland, New Zealand, and Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand. An extended direct method with addition of 1 μL of 70% formic acid or ethanol extraction method was applied for isolates that could not be identified by the direct method. MALDI-TOF results were interpreted based on three categories: high confidence identification (range 2.0–3.0), low confidence identification (range 1.70–1.99) and unidentified (less than 1.70) [19]. Unidentified isolates either at genus or species level were described based on their Gram staining and morphological characteristics.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Chi-squared/Fisher’s test of independency was used to assess associations between udder half defect and bacterial positivity or bacterial species at weaning (Study A), pre-mating (study B) and lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), weaning and post-weaning (Study C). Udder halves with no milk excretion and contaminated culture samples from Study A were excluded from these analyses. However, exclusion of these udder halves did not change the defective to normal proportion difference (p > 0.05). The strengths of these associations were measured by Cramer’s V Coefficient [20]. The coefficient ranges from 0 (no association at all) to 1 (perfect association), where high (>0.5), moderate (0.3–0.5), low (0.1–0.3) and little (0–0.1) indicate the range in between.
Multinomial logistic regression was applied to assess the association of time and bacterial positivity using “nnet” package in R statistical software (R-studio 2020 version 4.0) [21]. A lasagna plot was used to visualize longitudinal bacterial positivity (positive/negative or no milk excretion) in an individual udder half across six times in the first six weeks of lactation, at weaning and three weeks post-weaning. In addition, descriptive frequency was used to summarize the ongoing presence of each bacterial species identified in an individual udder half over eight repeated occasions (six times in the first six weeks of lactation, at weaning and three weeks post-weaning). The frequencies were described in three categories: occurrence of only once in an individual udder half, two to three times in an individual udder half or more than four in an individual udder half in those udder halves that excreted milk at least seven times.
The agreement between milk and swab samples from the same udder halves (Study C) was analysed using Cohen’s Kappa [22]. The strength of the Kappa agreement is described as follows: poor (<0.00), slight (0.00–0.20), fair (0.21–0.40), moderate (0.41–0.60), substantial (0.61–0.80) and almost perfect (0.81–1.00).
3. Results
3.1. Study A: Bacterial Species Identified from Ewes’ Milk Samples Collected at Weaning and Their Association with Udder Defects
In Study A, of the 154 udder halves (from 77 ewes) where attempts were made to collect milk samples, 23 udder halves did not excrete milk (Table 1). No milk was excreted from 3/7 (43%), 11/39 (28%) and 9/108 (8%) of udder halves categorised as hard, lumpy and normal, respectively. Of those that did excrete milk, 41 udder halves were positive for bacteria, 67 had no growth of bacteria and 23 had three or more bacterial colony types with no dominant species and were considered contaminated. All culture-positive udder halves grew a single colony type, except one udder half that grew Escherichia coli and Mannheimia haemolytica. Bacterial species identified were coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CNS) species, Mannheimia haemolytica, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis and others (Table 1).

Table 1.
Frequency of bacterial species identified from milk samples collected at weaning (Study A, n = 77 ewes) and swab samples collected at pre-mating (Study B; n = 74 ewes) from udder halves categorised as hard, lump and normal in non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes.
Chi-squared testing of independence between bacterial positivity (positive/negative) and udder half defect (hard, lump or normal) was significantly (p < 0.05) associated, but the strength of the association was low (Cramer’s V = 0.26, Table 2). In udder halves that excreted milk and with no contamination of bacterial culture, bacteria were isolated from 3/3 (100%) udder halves categorised as hard and 19/25 (76%) udder halves categorised as lump (Table 2). In contrast, 62 out of 81 (76.5%) normal udder halves yielded no bacteria. M. haemolytica and Streptococcus species were predominantly isolated from defective udder halves, whereas the majority of CNS species were isolated from normal udder halves. S. aureus was isolated from both normal and udder halves categorised as lump. Association between udder half defect and bacterial species was observed, but the strength was weak (p = 0.039, Cramer’s V = 0.20, Table 2).

Table 2.
Association between udder half defects (hard, lump or normal) and bacteria identified from 108 udder half milk samples collected at weaning (Study A, 5 December 2018) from 77 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes.
3.2. Study B: Bacterial Species Identified from Mammary Swab Samples Collected during Pre-Mating and Their Association with Udder Defects
From a total of 148 udder half (from 74 ewes) mammary swab samples cultured from commercial ewes prior to mating, 91 (61.5%) were culture-negative (Table 1). Eleven udder halves grew three or more dissimilar colony types and were categorised as contaminated. The remaining 46 (31.1%) udder halves were identified as bacterial culture-positive with 43 having a single colony type and three udder halves that yielded two colony types (Table 1). S. aureus, M. haemolytica and S. uberis were the dominant bacterial species identified and were isolated from udder halves categorised as hard, lump and normal (Table 1).
The association between udder half defect and bacterial positivity (positive or negative) was significant (p < 0.05), although the strength of the association was weak (Cramer’s V = 0.24; Table 3). Eleven of fourteen (78.6%) udder halves categorised as hard were bacterial culture-positive and one third of the udder halves categorised as lump were culture-positive, whereas most (69.3%) udder halves categorised as normal were culture-negative (Table 3). However, the association between udder half defect and bacterial species was not significant (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Association between udder half defect (hard, lump or normal) and bacteria identified from 148 udder half swabs of mammary tissue from 74 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes at pre-mating (Study B, 10 May 2019).
As in the case of Study A, M. haemolytica and Streptococcus species were the major bacterial species isolated from defective udder halves (Table 1). S. aureus and Staphylococcus simulans (S. simulans) were isolated in comparable numbers from both normal and defective udder halves. Trueperella pyogenes (T. pyogenes) was isolated in lower frequency and only from defective udder halves. A weak association was seen between udder half defect and bacterial species involved (p < 0.05, Cramer’s V = 0.24; Table 3).
3.3. Study C: Bacterial Species Identified from Milk Samples Collected from Ewes during Lactation, Weaning and Post-Weaning at Keeble Massey University Farm
Udder half milk excretion status and bacterial positivity varied throughout six occasions during lactation, at weaning and at post-weaning in 96 udder halves (48 ewes; Figure 1 and Figure 2). The number of udder halves that did not excrete milk varied from 39 on day 7 to 44 at post-weaning. Udder halves categorised as hard, lump and normal were observed on all eight occasions except at weaning when no udder halves were categorised as hard (Figure 1). The frequency of udder halves that were bacterial culture-positive became less frequent as time went on: it was highest at day 7 of lactation and lowest at weaning (Figure 1). From 752 potential udder half milk sampling occurrences, on 339 occasions no sample was able to be obtained. Of the 413 milk samples collected, 5 were contaminated and 270 grew no bacteria, while at least 19 different bacterial species were isolated from the 138 samples that grew bacteria (Table 4). The most commonly isolated bacteria were coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CNS) species, in particular S. simulans, S. chromogenes, S. xylosus and S. haemolyticus. M. haemolytica and Streptococcus species recorded a reasonably high frequency of occurrence, while the rest of the bacterial species identified were found at low frequency (Table 4).
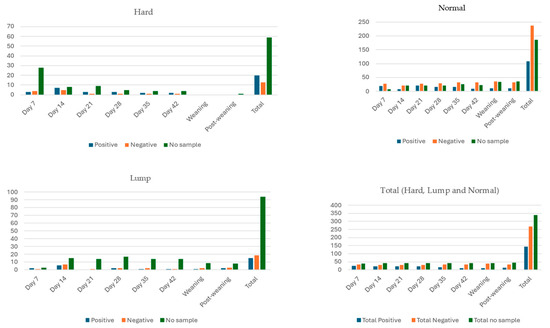
Figure 1.
Bacterial positivity of milk samples collected from udder halves categorised as hard, lump or normal from 48 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes, during the first six weeks of lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), at weaning and three weeks post-weaning (Study C). Note: No data were collected from four ewes on day 42 and two ewes at weaning and three weeks post-weaning.
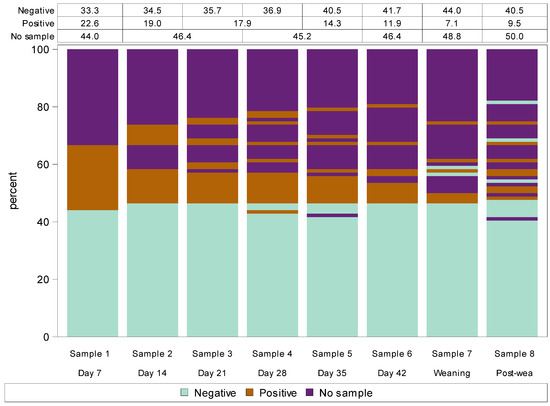
Figure 2.
Lasagna plot of bacterial culture positivity (negative, positive or no sample) from eight repeated milk samples collected from each udder half over the first six weeks of lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), at weaning and three weeks post-weaning in 46 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes (Study C). Note: Each bar shows a different udder half milk collection (i.e., time) while the different colours within each bar represent the bacterial culture result (positive, negative or no sample). The data in the table at the top of the plot designate the percentage of each bacterial culture result at each event, which corresponds to the percentage of each colour at each event. Change in bacterial positivity over time of each udder half can be tracked by following longitudinal transitions across the udder scoring events of stacked bars.

Table 4.
Bacterial species identified from milk samples collected from non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes in the first six weeks of lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), at weaning and three weeks post-weaning (Study C).
Multinomial logistic regression analysis of association between udder half bacterial positivity and time (day 7 of lactation through to post-weaning) was only significant (p < 0.05) at weaning compared to day 7. The relative risk ratio (±SE) of an udder half being bacterial culture-positive at weaning was 0.39 (±0.45) times compared with day 7 of lactation (the reference).
3.4. Study C: Udder Half Bacterial Positivity and Species Identified over Time during Lactation, Weaning and Post-Weaning at Keeble Massey University Farm
Figure 2 describes the repeated culture result from each udder half over the eight milk sampling occasions. The plot demonstrates that udder halves that were bacterial culture-negative on day 7 of lactation almost always remained negative throughout lactation, at weaning and at post-weaning. In the one udder half which did subsequently present a culture-positive result, this only occurred at one sampling time. In contrast, almost all udder halves that were bacterial culture-positive at day 7 either remained positive through to and including post-weaning or subsequently no milk sample was able to be obtained (Figure 2). Most udder halves that did not excrete milk during early lactation continued to not excrete milk until post-weaning; for those that did excrete some milk, it was generally bacterial positive (Figure 2).
To investigate the ongoing presence of bacterial species over time, individual udder halves from which specific bacterial species were isolated were classified into three categories based on how many times they were culture-positive on the eight sampling occasions: single, two to three or more than four occasions. Of the total bacterial species identified, more than six species occurred on only a single occasion in an individual udder half. Staphylococcus aureus, S. uberis and CNS species such as S. similans, S. chromogenes, S. auricularis, S. haemolyticus and S. warneri were observed on both one occasion as well as on more than two occasions in an individual udder half. However, M. haemolytica, S. xylosus and S. pluranimalium were only isolated from an individual udder half on more than four occasions, indicating the apparent ongoing presence of these organisms over time (Table A1). Table A1 includes those udder halves that excreted milk on at least six occasions (n = 71). M. haemolytica (2), S. chromogenes (2), S. aureus (1), S. uberis (1), S. simulans (1) and no growth (2) were detected in those udder halves that excreted milk on only one or two occasions (n = 9).
3.5. Study C: Association of Udder Half Defect and Bacterial Isolation over Lactation, Weaning and Pre-Mating
The association between udder half defect (hard/lump/normal) and bacterial culture positivity (positive/negative) at each time point (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42 of lactation, weaning and post-weaning) was not significant (p > 0.05). However, M. haemolytica, Streptococcus uberis and Staphylococcus aureus were more frequently isolated (descriptively) from defective udder halves (hard/lump), whereas CNS species were more frequently identified from normal udder halves (Table 5).

Table 5.
Frequency of bacterial species identified from udder halves categorised as hard, lump or normal from 46 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes, during the first six weeks of lactation, at weaning and three weeks post-weaning (Study C).
3.6. Study C: Bacterial Species Identified from Udder Half Mammary Tissue Swab Samples Collected Post-Weaning and Their Association with Udder Half Defect
Swab samples were taken from 92 udder halves (from 46 ewes) at slaughter three weeks after weaning, and only 17 (18%) showed bacterial growth. Four of sixteen udder halves categorised as lump (25%) and 13 of 78 (16.7%) udder halves categorised as normal grew bacteria. There was only one udder half categorised as hard at this time. Fifteen samples grew a single species of bacteria while two udder halves grew two species of bacteria. The bacterial species identified were Staphylococcus aureus (2), S. simulans (4), Streptococcus uberis (2), Streptococcus pluranimalium (1), Acinetobacter indicus (1), Trueperella pyogenes (1), M. haemolytica (1), S. epidermidis (1), Staphylococcus xylosus (1), Acinetobacter schindlerim (1) and unidentified Gram-positive rods (2). The association between udder half defect and bacterial positivity was not significant (p > 0.05).
From a total of 43 udder halves (nine ewes with both halves and 25 single udder halves) that did not excrete milk on at least six occasions, a culture-positive result was observed from seven udder halves from swab samples post-weaning. No significant (p > 0.05) association was observed between udder half defect and bacterial positivity. Swab samples from normal udder halves grew Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, Streptococcus mitis and Staphylococcus simulans, while Trueperella pyogens and Streptococcus uberis were isolated from lumps.
3.7. Study C: Comparison of Bacterial Isolation from Ewes’ Udder Half Milk and Swab Samples Collected at Post-Weaning
From a total of 92 udder halves from which milk sampling was attempted three weeks post-weaning, 46 (50%) did not excrete milk. Thus, the agreement analysis of bacterial isolation from milk and mammary tissue swabs could only be undertaken for the 46 udder halves from which both types of samples were collected. All udder halves that had culture-positive milk samples also had culture-positive swab samples. However, four udder halves with bacterial culture-positive milk samples were bacterial culture-negative from the swab samples. These bacterial species identified from these four milk samples were S. simulans, S.warneri and S. capitis. Udder half swab and milk sampling methods showed a substantial strength of agreement with a k-coefficient of 0.724 (p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Overall, more than 30 bacterial species of 10 genera were identified during this study. The type and range of bacteria isolated were similar among populations of sheep and time points of sampling (pre-mating, lactation, weaning and post-weaning). CNS (mainly S. simulans and S. chromogens), M. haemolytica, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus uberis were the most frequently isolated bacterial species. Previous studies have similarly reported Staphylococcus aureus, M. haemolytica and CNS as the most frequently isolated bacterial species in non-dairy ewes in New Zealand [7,8,11] and internationally [6,23,24,25].
A significant but weak association between udder half defect and bacterial culture positivity was observed at weaning and pre-mating, whereas no association was found during lactation. Across these three studies, bacteria were isolated from 50–78% of udder halves categorised as hard. Similarly, Ridler et al. [7] isolated bacteria from 28/36 (78%) udder halves categorised as hard. Other authors have also isolated various bacterial species from defective udder halves including those udder halves categorised as hard [8,15]. Bacteria were isolated from 33–61% of udder halves categorised as lump across the three studies. Likewise, in a study undertaken at weaning, 30% of udder halves categorised as lump isolated bacteria [2]. Smith et al. [10] reported identification of several bacterial species from lumps (abscesses), but some failed to grow bacteria. No bacteria were isolated from 69–85% of normal udder halves in the current three studies which is comparable to the 75% previously reported by Ridler et al. [7]. The bacteria isolated from normal udder halves (15–31%) could be due to subclinical mastitis or opportunistic normal skin or environmental microbial flora such as CNS [26]. Marogna et al. [27] analysed the correlation between bacterial positivity and clinical findings such as visible abscesses, nodules and milk abnormalities and reported that ewes with such clinical findings were 105 to 317% more likely to be bacterial culture-positive compared to samples from udders/milk with no abnormalities.
Combining these current studies shows that a considerable percentage of udder halves categorised as either hard or lump isolated no bacteria, while a small percentage of normal udder halves did isolate bacteria. This variation in the association between udder half defect and bacterial positivity might be due to differences in bacterial species pathogenicity (i.e., infection with some species may be more likely to result in palpable defects) or ongoing presence over time with the dynamic nature of the defects [9]. In many cases, the defects were likely to have been chronic and, while they are most likely to have been initiated by bacterial infection, the bacteria may have been cleared from the mammary gland over time. It is possible the negative culture results could also be due to low accuracy of traditional bacterial culture [28]. Overall, the association between palpable udder defects and bacterial culture positivity indicates the effect of aerobic bacteria; however, the weakness of the association could also be suggestive of involvement of pathogens other than aerobic bacteria such as anaerobic bacteria, rickettsial organisms, viruses or sterile cysts [29,30]. Mycoplasma species have been reported to cause contagious agalactia in dairy sheep and goats overseas [31], but this condition has not been reported in sheep in New Zealand, nor have any of the four Mycoplasma species implicated in this condition been isolated from New Zealand sheep. In the present study, Mycoplasma organisms were not tested for.
Among the commonly identified bacterial species in the present studies, M. haemolytica and S. uberis were predominantly isolated from defective udder halves (hard or lump) during lactation, weaning, post-weaning and pre-mating. Similarly, in previous studies, M. haemolytica and S. uberis were isolated from hard udder halves or udder halves with lumps in the post-weaning period [7,10]. These bacterial species have also been described as an important and highly frequent bacterial species isolated from clinically mastitic milk in non-dairy breed ewes [6,32,33,34]. Watkins and Jones [35] suggested that M. haemolytica was equally important or more significant than S. aureus, the latter of which is the most identified bacteria from the udders of dairy ewes [36], possibly due to transmission of the bacteria via lamb suckling. M. haemolytica resulted in a higher SCC response than S. aureus, which showed the pathogenicity of the pathogen in non-dairy ewes [37]. Experimental infection of ewe udders with M. haemolytica has been associated with small nodules with thin-walled abscesses [35] and serious pathological changes with little or no milk excretion in later stages of lactation [38]. Streptococcus uberis is a common pathogen found in the milk of both dairy cows and dairy sheep and is known to form mammary gland abscesses in sheep [10,39]. The isolation of this bacterium from udder halves with palpable udder defects in the present study may have been due to the chronicity of the defects, which provided extended time to develop abscesses.
Staphylococcus aureus has been reported to be the most commonly identified bacterial species in both dairy and non-dairy ewes with subclinical mastitis [23,24], acute clinical mastitis or chronic mastitic udders with lumps or abscesses [10] and defective udders with lumps, diffuse hardness, nodules or open abscess [15]. In the present study, S. aureus was isolated in comparable numbers from defective (lump or hard) and normal udder halves at weaning, pre-mating and isolated predominantly from defective udder halves during lactation. Ridler et al. [7] and Smith et al. [10] isolated the most S. aureus from udder halves categorised as hard or lump during the dry period. S. aureus have been reported to be less frequent in subclinical infection [6]. Nevertheless, the comparable number of S. aureus isolated from udder halves with or without clinically identifiable or palpable udder half defects during the dry period in the present study might be because some of the udder halves categorised as normal in the present studies had a previous history of udder defects.
It has been reported that CNS species are the most prevalent bacteria isolated in clinically normal or subclinical mammary infection [26,36,37]. In the present study, CNS species were predominantly isolated from normal udder halves with no palpable defects, which agrees with [7]. However, CNS species were also isolated from udder halves categorised as either hard or lump, which could suggest potential pathogenicity of some CNS species (such as S. simulans and S. chromogens) to be associated with clinically noticeable changes, as was observed in experimental infection with S. simulans in non-dairy ewes [1]. CNS species have been isolated from up to 20% of clinical mastitis cases in cows and have been referred to as emerging mastitis pathogens [40,41]. Trueperella pyogenes was only isolated from swab samples collected at pre-mating and post-weaning from udder halves categorised as hard or lump but not during lactation or from milk samples at weaning. Similarly, this bacterium has been associated with dry period mastitis [15].
Individual udder halves that were bacterial culture-negative at the start of lactation almost always remained negative in repeated milk samples across the first six weeks of lactation, weaning and post-weaning. However, udder halves that were bacterial culture-positive in the first week of lactation almost always either had ongoing presence with positivity or resulted in no excretion of milk at later stages. M. haemolytica, S. xylosus and S. pluranimalium had an ongoing presence observed over four or more weeks in an individual udder half. S. aureus and other CNS species were either present for a short period or remained stable for four or more weeks. The other less frequently identified bacterial species mostly occurred for a very short period. This finding agrees with a previous study which reported M. haemolytica as being stable in its presence over a three-week period in lactation, but S. aureus and CNS were only moderately stable [9]. While udder half defects change over time as described by Zeleke et al. [16] (e.g., defective udder halves changed to normal as days in lactation advanced), the ongoing presence of these commonly identified bacterial species in an udder half may indicate the stability of these bacterial species even after a defective udder half changed to normal. This could cause future defect recurrence in these udder halves or be a potential source of infection for other ewes in the flock.
As expected, those udder halves that did not excrete milk at sample collection in the early weeks of lactation had less chance of excreting milk at later stages of lactation or at post-weaning. However, in those udder halves that did excrete small amounts of milk at later stages, the samples were bacterial culture-positive. In these cases, M. haemolytica, S. chromogenes, S. uberis, S. aureus and S. simulans were identified, which may imply the ongoing presence or severity of these species. In those udder halves that did not excrete milk at all during lactation, 83% were bacterial culture-negative in post-mortem swab samples, collected three weeks post-weaning. It is possible that these udder halves were bacterial culture-negative throughout lactation, but it is more likely that they were positive at some time in lactation and then resolved by three weeks post-weaning. In chronic mammary inflammation, the mammary immunity can clear or reduce bacterial load to below limits of detection by bacterial culture at post-weaning [42] and therefore be reported as culture-negative. In those udder halves that did not excrete milk, therefore, assessing the bacterial status while the udder was detected with either diffusely hard or lump during lactation, before changing into normal or another defect category, may provide a satisfactory explanation.
Bacteria identified from mammary swab and milk samples collected in individual ewes post-weaning were almost always (91.3%) in agreement. The only difference occurred in four udder halves that had swab-negative cultures, but the milk sample was positive. The agreement between milk and tissue swab bacterial species identified was higher compared to a previous report by Smith et al. [10]. This might be because most of the lumps in this study were in the gland cistern area and were not capsulated or closed; therefore, if bacteria were present in the lump, they were also present in milk. Alternatively, the three CNS species found only in the milk could be opportunists from the teat skin or environment or possibly transferred to milk by suckling from the mouth of the lamb [42,43]. Nearly all the swab samples collected from palpable udder defects (abscess) in the current studies showed one distinct colony type on culture. Overseas authors have reported that mammary abscesses are often polymicrobial [10,44]. It is possible that not only the presence of abscesses but also the location and degree of capsulation of abscesses may play a role in the bacterial diversity of the abscesses and/or agreement between mammary abscess swab and milk samples. Overall, the very high agreement of bacterial species isolated from milk and mammary tissue swabs indicates that identifying bacterial species in udder halves by milk sampling can be a reliable and practical method.
In the current studies, commonly identified pathogenic bacterial species were associated with udder halves categorised as hard or lump, confirming the most likely cause of these palpable udder half defects. Bacterial species such as M. haemolytica were stable over time, which could result in future recurrence of udder defects or act as a source of infection for other ewes. However, in the present study, the number of bacterial species identified to assess ongoing presence over time in an individual udder half was not large enough to undertake statistical analysis; hence, the descriptive analysis should be interpreted with caution. To more accurately describe the bacterial species’ changes over time, a higher number of isolates would be needed for each bacterial species, which would require a greater number of ewes than the current study.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, common bacterial species that were isolated from udder halves categorised as either lump or hard were M. haemolytica and Streptococcus uberis, whereas CNS species were more commonly isolated from normal udder halves. S. aureus was isolated from both defective and normal udder halves in comparable numbers with combined high frequency at pre-mating and weaning but predominantly from defective udder halves during lactation. Udder half milk bacterial positivity was stable in repeated assessment across lactation, weaning and post-weaning; however, the stability over time varied among the species involved. M. haemolytica, S. xylosus and S. pluranimalium had ongoing presence, while Staphylococcal species including S. aureus stability were variable in their ongoing presence. Mammary tissue swab and udder half milk methods of bacteria sampling presented a very high agreement of bacterial positivity and species identified at post-weaning. Hence, identifying ewes with bacterial species predominantly identified from udder halves categorised as hard or lump and which appear more stable over time could contribute to making culling decisions and minimize future recurrence of palpable defects or mastitis. Future research is required to further explore the role of specific bacterial species and other pathogens and their relationship to udder defects and changes over time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.Z., P.R.K., K.J.F. and A.L.R.; data curation, M.M.Z., K.J.F. and N.V.; formal analysis, M.M.Z.; funding acquisition, A.L.R.; investigation, M.M.Z. and A.L.R.; methodology, M.M.Z., K.J.F., N.V. and A.L.R.; project administration, A.L.R.; supervision, P.R.K., D.A., S.J.P. and A.L.R.; visualization, M.M.Z. and A.L.R.; writing—original draft, M.M.Z.; writing—review and editing, P.R.K., K.J.F., D.A., S.J.P., N.V. and A.L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by Beef and Lamb New Zealand Ltd., project number 16MU07.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures involving the use of live animals were undertaken in accordance with animal welfare standards and approved by the Massey University Animal Ethics Committee (application numbers: MUAEC 15/105 and 18/99).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data utilised by this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Alex Grinberg, Elizabeth Burrows, Geoff Purchas, Dean Burnham, Catriona Jenkinson and Sam Peterson for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Frequency of isolation of bacterial species from milk samples collected from individual udder halves on eight occasions during the first six weeks of lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), at weaning and three weeks post-weaning, from 40 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes (Study C).
Table A1.
Frequency of isolation of bacterial species from milk samples collected from individual udder halves on eight occasions during the first six weeks of lactation (days 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42), at weaning and three weeks post-weaning, from 40 non-dairy breed (Romney) ewes (Study C).
| Bacterial Species | Number of Individual Udder Halves | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Occasion | Two or Three Occasions | Four or More Occasions | |
| A. viridans | 1 | ||
| C. lipophiloflavum | 4 | ||
| E. coli | 1 | ||
| K. carniphila | 2 | ||
| S. petrasii | 2 | ||
| Psychrobacter spp. | 1 | ||
| A. viridans and S. simulans | 1 | ||
| S. auricularis and S. parasanguinis | 1 | ||
| Contaminated | 4 | ||
| Gram-positive bacilli | 1 | ||
| S. aureus | 1 | 1 | |
| S. capitis | 1 | ||
| CNS-unidentified | 3 | 1 | |
| S. simulans | 2 | 6 | |
| S. warneri | 1 | 1 | |
| S. haemolyticus | 1 | 1 | |
| S. auricularis | 1 | 1 | |
| S. chromogenes | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| S. uberis | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| M. haemolytica | 1 | ||
| S. xylosus | 2 | ||
| S. pluranimalium | 1 | ||
Note that this table only includes data from udder halves where milk samples were collected on six or more occasions.
References
- Fthenakis, G.; Jones, J. The effect of inoculation of coagulase-negative staphylococci into the ovine mammary gland. J. Comp. Pathol. 1990, 102, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, O.M.; Logan, C.; Ridler, A.; Greer, A. Investigation into udder characteristics, mastitis and milk production in crossbred sheep. N. Z. J. Anim. Sci. Prod. 2018, 78, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Saratsis, P.; Alexopoulos, C.; Tzora, A.; Fthenakis, G. The effect of experimentally induced subclinical mastitis on the milk yield of dairy ewes. Small Rumin. Res. 1999, 32, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Ridler, A.; Compton, C.; Corner-Thomas, R.; Kenyon, P. Investigating associations between lamb survival to weaning and dam udder and teat scores. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, K.; Ridler, A.; Compton, C.; Corner-Thomas, R.; Kenyon, P. Associations between lamb growth to weaning and dam udder and teat scores. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, J.; Dubreuil, P.; Higgins, R.; Bélanger, D. Risk factors and impacts of clinical and subclinical mastitis in commercial meat-producing sheep flocks in Quebec, Canada. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008, 87, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridler, A.L.; Rout-Brown, G.; Flay, K.J.; Velathanthiri, N.; Grinberg, A. Defects and bacterial pathogens in udders of non-dairy breed ewes from New Zealand. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2022, 65, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.; Nieper, B.; Collett, M.; Grinberg, A. BRIEF COMMUNICATION: An investigation of mastitis in a hill-country sheep flock. In Proceedings of the New Zealand Society of Animal Production, Rotorua, New Zealand, 28–30 June 2017; pp. 114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Crommenacker-Konings, L.W.; van Dam, P.; Everts, R.; Shittu, A.; Nielen, M.; Lam, T.J.; Koop, G. Dynamics of intramammary infections in suckler ewes during early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 5979–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Willis, Z.N.; Blakeley, M.; Lovatt, F.; Purdy, K.J.; Green, L.E. Bacterial species and their associations with acute and chronic mastitis in suckler ewes. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7025–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlivan, T. Survey observations on ovine mastitis in New Zealand stud Romney flocks: 2. The bacteriology of ovine mastitis. N. Z. Vet. J. 1968, 16, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, M. Characteristics of some organisms causing ovine mastitis. In Proceedings of the Society of Sheep and Beef Cattle Veterinarians of the NZVA, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 9–11 June 1972; pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Skyrme, H. Hard udders in ewes. N. Z. Vet. J. 1970, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Smith, E.M.; Green, L.E. A longitudinal study of factors associated with acute and chronic mastitis and their impact on lamb growth rate in 10 suckler sheep flocks in Great Britain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 127, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratsis, P.; Leontides, L.; Tzora, A.; Alexopoulos, C.; Fthenakis, G. Incidence risk and aetiology of mammary abnormalities in dry ewes in 10 flocks in Southern Greece. Prev. Vet. Med. 1998, 37, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeleke, M.M.; Flay, K.J.; Kenyon, P.R.; Aberdein, D.; Pain, S.J.; Ridler, A.L. Assessment of Changes in Udder Half Defects over Time in Non-Dairy Ewes. Animals 2023, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, P.; Middleton, J.; Fox, L.; Pighetti, K.; Petersson-Wolfe, C. Laboratory Handbook on Bovine Mastitis; National Mastitis Council: New Prague, MN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alatoom, A.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Ihde, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.; Patel, R. Comparison of direct colony method versus extraction method for identification of Gram-positive cocci by use of Bruker Biotyper matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2868–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuzara, M.; Barberis, C.; Velázquez, V.R.; Ramirez, M.S.; Famiglietti, A.; Vay, C. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) as a reliable tool to identify species of catalase-negative gram-positive cocci not belonging to the Streptococcus genus. Open Microbiol. J. 2016, 10, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.L. The chi-square test of independence. Biochem. Medica 2013, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. In Proceedings of the R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 28 June 2016; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, G.; Rietman, J.; Pieterse, M. Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in Texel sheep associated with suckling twins. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogianni, V.; Fthenakis, G. Clinical, bacteriological, cytological and pathological features of teat disorders in ewes. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2007, 54, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omaleki, L.; Barber, S.R.; Allen, J.L.; Browning, G.F. Mannheimia species associated with ovine mastitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3419–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spuria, L.; Biasibetti, E.; Bisanzio, D.; Biasato, I.; De Meneghi, D.; Nebbia, P.; Robino, P.; Bianco, P.; Lamberti, M.; Caruso, C. Microbial agents in macroscopically healthy mammary gland tissues of small ruminants. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marogna, G.; Rolesu, S.; Lollai, S.; Tola, S.; Leori, G. Clinical findings in sheep farms affected by recurrent bacterial mastitis. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 88, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, R.N.; Tassi, R.; Martin, E.; Holopainen, J.; McCallum, S.; Gibbons, J.; Ballingall, K.T. Comparison of bacteriological culture and PCR for detection of bacteria in ovine milk—Sheep are not small cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeff, A.; Du Preez, J. Simultaneous isolation of anaerobic bacteria from udder abscesses and mastitic milk in lactating dairy cows. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1985, 56, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Minguijón, E.; Reina, R.; Pérez, M.; Polledo, L.; Villoria, M.; Ramírez, H.; Leginagoikoa, I.; Badiola, J.; García-Marín, J.F.; De Andrés, D. Small ruminant lentivirus infections and diseases. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, S.; Puleio, R.; Nicholas, R.A.; Loria, G.R. Mycoplasma agalactiae: The sole cause of classical contagious agalactia? Animals 2021, 11, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omaleki, L.; Browning, G.F.; Allen, J.L.; Barber, S.R. The role of Mannheimia species in ovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, S.; Allen, J.; Mansell, P.; Browning, G. Mastitis in the ewe. In Proceedings of the Australian Sheep Veterinarians 2006 Conference, Eight Mile Plains, Australia, January 2006; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Omaleki, L.; Browning, G.F.; Allen, J.L.; Markham, P.F.; Barber, S.R. Molecular epidemiology of an outbreak of clinical mastitis in sheep caused by Mannheimia haemolytica. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 191, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, G.; Jones, J. The effect of the intra-mammary inoculation of lactating ewes with Pasteurella haemolytica isolates from different sources. J. Comp. Pathol. 1992, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelasakis, A.; Mavrogianni, V.; Petridis, I.; Vasileiou, N.; Fthenakis, G. Mastitis in sheep–The last 10 years and the future of research. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, Y.; Nyman, A.-K.; Söderquist, L.; Tomic, N.; Waller, K.P. Intramammary infections and somatic cell counts in meat and pelt producing ewes with clinically healthy udders. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 156, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Masannat, E.; Jones, J.; Scott, M. The experimental production of mastitis in sheep by intramammary inoculation of Pasteurella haemolytica. J. Comp. Pathol. 1991, 105, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, N.M.; Agnoletti, F.; Lollai, S.; Tola, S. Comparison of PCR-RFLP, API® 20 Strep and MALDI-TOF MS for identification of Streptococcus spp. collected from sheep and goat milk samples. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 180, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S. Coagulase-negative staphylococci—Emerging mastitis pathogens. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, K.P.; Aspán, A.; Nyman, A.; Persson, Y.; Andersson, U.G. CNS species and antimicrobial resistance in clinical and subclinical bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragkou, I.; Papaioannou, N.; Cripps, P.; Boscos, C.; Fthenakis, G. Teat lesions predispose to invasion of the ovine mammary gland by Mannheimia haemolytica. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogianni, V.; Cripps, P.; Fthenakis, G. Bacterial flora and risk of infection of the ovine teat duct and mammary gland throughout lactation. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 79, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, I. Microbiology of polymicrobial abscesses and implications for therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).