Simple Summary
Aeromonas veronii, an important aquatic bacterium, has been known to infect a variety of animals worldwide. However, there have been no reports of A. veronii infection in giant pandas. Here, we found that strain VGP was resistant to six antibiotics, carries a large number of resistance genes and virulence genes, and has strong pathogenicity in mice. These results suggest that infection with strain VGP could be one of the leading causes of death for this giant panda cub. Our study presents the first evidence that giant pandas could be infected by A. veronii.
Abstract
The objective of this study was to understand biological characteristics of one bacteria strain named as VPG which was isolated from multiple organs of a dead captive giant panda cub. Here, we use biochemical tests, 16S rRNA and gyrB genes for bacterial identification, the disk diffusion method for antibiotic resistance phenotype, smart chip real-time PCR for the antibiotic resistance genotype, multiplex PCR for determination of virulence genes, and the acute toxicity test in mice for testing the pathogenicity of isolates. The isolate was identified as A. veronii strain based on the biochemical properties and genetic analysis. We found that the strain carried 31 antibiotic resistance genes, revealed antimicrobial resistance phenotypically to several antibiotics including penicillin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amoxicillin, imipenem, and vancomycin, and carried virulence genes including aer, act, lip, exu, ser, luxs, and tapA. The main pathological changes in giant panda were congestion, necrotic lesions and a large number of bacteria in multiple organs. In addition, the LD50 in Kunming mice infected with strain VGP was 5.14 × 107 CFU/mL by intraperitoneal injection. Infection with strain VGP led to considerable histological lesions such as hemorrhage of internal organs, necrosis of lymphocytes and neurons in Kunming mice. Taken together, these results suggest that infection with strain VGP would be an important causes of death in this giant panda cub.
1. Introduction
Aeromonas veronii, a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, mesophilic, facultative anaerobic bacterium, is widely distributed in the aquatic environment [1,2]. As a common pathogen in aquaculture, A. veronii can infect a variety of aquatic animals, including sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus), crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) [3,4], Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis) [5], Yangtze finless porpoise (Neophocaena asiaeorientalis) [6] and soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) [7] and clinical symptoms are skin ulcers and visceral hemorrhages in these species. A. veronii can also cause visceral hemorrhage in ducks (Anatinae) [8]; diarrhea, lethargy, anorexia, and visceral hemorrhage in foxes (Vulpes sp.) [9]; diarrhea and hepatomegaly in wild yak (Bos mutus) [10]; coughing, sneezing and sniveling in rabbits (Leporidae sp.) [11]; and disease of Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus) [12]. It may be a potential pathogen of tawny owl (Strix aluco) and scarlet ibis (Eudocimus ruber) [13,14]. More seriously, it could cause gastroenteritis, bacteremia/septicemia and respiratory tract infections in humans [15]. In addition, wild waterfowl may carry pathogenic Aeromonas species in their intestine; therefore, the migration of waterfowl is a potential mechanism for the global distribution of Aeromonas [16].
As an iconic flagship species for wildlife conservation, the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) is considered a national treasure in China and is a Class 1 protected endemic species [17]. The giant panda is currently categorized as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), and faces continued threats from habitat fragmentation and infectious diseases in both the in situ and ex situ populations. Meanwhile, bacterial diseases, such as Escherichia coli [18,19], Klebsiella pneumoniae [20], Proteus mirabilis [21], Proteus vulgaris [22], Enterobacter cloacae [23], and Staphylococcus aureus [24], are more and more reported in the giant panda. So far, there is no report of infection and biological characteristics of A. veronii in the giant panda.
The objective of the present study investigated the cause of death of captive giant panda cubs and analyzed the identification, antibiotic sensitivity, virulence gene, and pathogenicity of the A. veronii isolated from the internal organs of a dead captive giant panda cub.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Organ Sampling and Bacterial Isolation
One dead captive one-day-old giant panda cub with no clinical symptoms was sampled in 2020, in Sichuan province, China. Brittle texture of liver and spleen, dark red liver with hemorrhagic spots and flatulence, pulmonary congestion and hemorrhage, pericardial effusion were found in autopsy. The heart, liver, lung, and kidney were collected for bacterial examination as a routine check. The samples were cultivated on 5% (v/v) sheep blood agar at 37 °C for 24 h and the bacterial colonies were purified by streaking onto the sheep blood agar plate twice. A single bacterial colony was selected and inoculated in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) medium at 37 °C for 24 h, and then preserved at −80 °C in the BHI medium containing 40% (v/v) sterile glycerol. The isolate was named as VGP (Aeromonas veronii in giant panda).
2.2. Histopathology of Giant Panda
To clarify the histopathological changes in dead giant panda, histopathology was performed on the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney under a light microscope (Leica DM4B optics) following 10% formalin fixation and hematoxylin–eosin staining.
2.3. Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Features
Staining characteristics of isolate VGP heart, liver, lung, and kidney were studied by light microscope. Biochemical features of isolate were performed by microbiochemical reaction tube including oxidase, lysine decarboxylase, citrate, indole, mannitol, sucrose, maltose, V-P, cellobiose, H2S production, L-lactate alkalinization, L-lactate alkalinization, and glycine arylamidase. The biochemical reactions were performed in three parallel groups. The biochemical features had been identified according to the Berger’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology.
2.4. Sequence Analysis of 16S rRNA and gyrB Genes
The genomic DNA of the isolate VGP were extracted using a TIANamp Bacterial DNA Kit (Tiangen-Biotech, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Genomic DNA was stored at −20 °C for analysis. The classic PCR of 16S rRNA gene (27 F: 5′-AGAGTTTGATYMTGGCTCAG-3′, 1492 R: 5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′, Product size: 1456 bp, Tm: 54 °C) and gyrB gene (3F: 5′-TCCGGCGGTCTGCACGGCGT-3′, 27R: 5′- TTGTCCGGGTTGTACTCGTC-3′, Product size: 1124 bp, Tm: 60 °C) were amplified by a pair of universal primers and gyrB gene primers [25,26]. Each PCR mixture was 25 µL in total volume consisting 12.5μL of Dream Taq Green PCR Master Mix (2×), 1 µL of each forward and reverse primer, 2 µL of template DNA and 8.5 µL of ddH2O. The reaction mixtures were subjected to start at 94 °C for 5 min prior to 30 cycles of amplification with 94 °C for 1 min, Tm for 1 min, 72 °C for 1 min; final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The sequences analysis was performed by BLAST in NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ accessed on 22 January 2020.). The phylogenetic trees were established using the Neighbor-joining method in the MEGA 7.0 software package.
2.5. Molecular Identification of Virulence Genes
Virulence genes including aer, act, ser, aha, lip, exu, luxs, tapA, and gcaT were detected by classic PCR using primers in previously published studies [2,3] (Table 1).The PCR Products were sequenced by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and sequences were analyzed by BLAST in NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ accessed on 22 January 2020.).

Table 1.
Primer pairs utilized for virulence gene detection.
2.6. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was carried out by a disk diffusion method (K-B method) recommended by the CLSI 2020 [27]. Forty-two antibiotics (Hangzhou Microbiological Reagent Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) were chosen, including penicillin (PEN), piperacillin (PIP), ampicillin (AMP), oxacillin (OX), amoxicillin (AMX), moxalactam (MOX), ceftazidime (CMZ), cefepime (FEP), cefotaxime (CTX), cephalexin (CA), cefazolin (CZ), ceftriaxone (CTR), cefoxitin (FOX), piperacillin/tazobactam (TZD), cefuroxime (CXM), cefaclor (CEC), ampicillin/sulbactam (AMS), cefoperazone (CFP), ceftizoxime (ZOX), aztreonam (AT), meropenem (MEM), imipenem (IPM), kanamycin (K), gentamicin (GM), streptomycin (S), enoxacin (ENX), ofloxacin (OFX), norfloxacin (NOR), lomefloxacin (FOX), fleroxacin (FOX), levofloxacin (LVX), ciprofloxacin (CIP), gatifloxacin (GAT), chloramphenicol (C), vancomycin (VA), azithromycin (AZM), doxycycline (DX), minocycline (MI), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), and trimethoprim (TMP). E. coli ATCC25922 was used as the quality control bacterial strain. The results were defined as susceptible (S), intermediate (I), and resistant (R) according to the CLSI 2020 breakpoints [27].
2.7. Molecular Identification of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs)
The genomic DNA of the isolate VGP were extracted using a TIANamp Bacterial DNA Kit (Tiangen-Biotech, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, the total genomic DNA was used as the template. The Wafergen smart chip real-time PCR system was used to analyze the VGP chromosome antibiotic resistance genes with a total of 97 primer sets (see Supplementary Materials Table S1) [28]. Each sample was repeated three times simultaneously. Following the initial activation of enzymes at 95 °C for 10 min, 30 cycles of the following procedure were used for amplification: denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, and annealing at 60 °C for 30 s. Then, the results were analyzed using smart chip qPCR software to exclude the wells with multiple melting peaks or amplification efficiency beyond the range (90–110%). The calculation method is based on the previous study [28,29]. Briefly, the mapping data in the relative copy number = copy number (gene)/copy number (16S), in which the copy number (gene) and the copy number (16S) belong to the same sample. Copy number = 10 (33 − CT)/(10/3), i.e., if the offline data have a CT value of null, the CT value is 33, and the copy number value is 1.
2.8. The Pathogenicity Testing in Kunming Mice
Female Kunming mice (aged 6 to 8 weeks old) were purchased from the Chengdu Dossy Experimental Animals Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China) and placed in polypropylene cages with sawdust bedding and kept under hygienic control. Forty-eight mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (8 mice per group). Bacterial isolate VGP were incubated overnight at 37 °C, and following the suspension in 0.9% endotoxin-free saline solution, animals were inoculated intraperitoneally with 500 µL of the bacterial suspension. Mice received bacterial concentration as follows: group 1: 5.01 × 109 CFU/mL, group 2: 1.05 × 109 CFU/mL, group 3: 5.01×108 CFU/mL, group 4: 1.58 × 108 CFU/mL, group 5: 5.01×107 CFU/mL, and group 6: Saline, The survival, psychological and nutritional status of each mouse was monitored every 2 h after injection for 24 h, once a day after, 7 days in total. On the seventh day, all remaining mice were euthanized. During the monitoring process, the mice that died were immediately necropsied to bacterial culture and the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney and brain were collected. Histopathology was performed on the aforementioned organs under a light microscope (Leica DM4B optics) following 10% formalin fixation and hematoxylin–eosin staining.
3. Results
3.1. Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Isolate
One bacterium was isolated from heart, liver, lung, and kidney of the dead giant panda cub and revealed Gram-negative rod morphology. Additionally, this isolate growth was characterized by grey—white, circular, umbilicate colonies showing β-hemolytic after 24 h (Figure 1). Biochemical analyses showed that the bacteria were positive for oxidase, lysine decarboxylase, citrate, indole, mannitol, sucrose, maltose, V-P, and cellobiose. Collectively, and negative to others such as H2S production, the physiological and biochemical results indicated that this isolate belonged to Aeromonas.

Figure 1.
Physiological characteristics of isolated isolate. Growth of isolate on sheep blood plates showed grey-white, circular, umbilicate colonies (A), and β-hemolysis (B). Gram staining of isolate showed typical Gram-negative, slightly curved, single or in pairs (C).
3.2. Histopathological Finding of Giant Panda
Short rod-shaped bacteria were in liver, spleen, and lung. Additionally, cardiomyocyte vacuolization, degeneration and necrosis were observed, congestion and scattered necrotic occurred in liver and spleen, cells necrosis and dissolution and a lot of hemoglobin imbibition occurred in Lung, granular degeneration occurred in epithelial cells of renal tubular. There was no significant change in the umbilical cord (Figure 2).
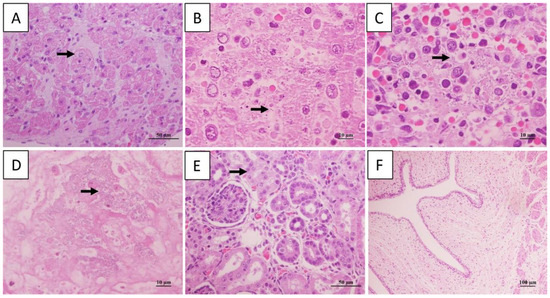
Figure 2.
Histopathological changes in dead giant panda. Cardiomyocyte vacuolization in heart (A). Rod-shaped bacteria and necrosis in hepatic (B), and spleen (C). Exudates with bacterial masses in the alveolar space (D). Granular degeneration in epithelial cells of renal tubular (E). No significant changed in umbilical cord (F). The arrow represents the location of the lesion.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses of the 16S rRNA and gyrB Genes of Isolated Bacterial
Amplification of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes revealed that the target band was 1500 bp and 1127 bp, respectively. The BLAST alignments of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes indicated that the isolated H, LI, LU, and K shared the same sequence and high homology with A. veroni (>99% homology). Therefore, this isolate was named as VGP. In addition, the phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA and gyrB sequences showed that isolate VGP were classified into the known strain species of A. veroni (Figure 3). Taken together, based on the physiology, biochemistry, and phylogenetic analysis, we identified isolate VGP as an A. veronii strain.
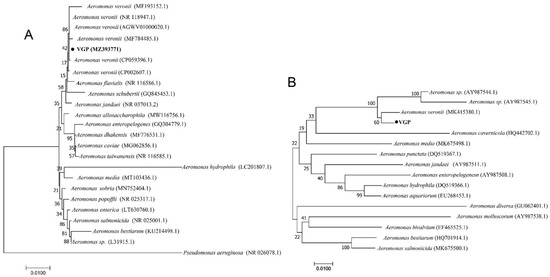
Figure 3.
Neighbor-Joining phylogenetic tree generated based on 16S rRNA (A) and gyrB (B) gene of the strain VGP and other sequences of A. veronii isolates detected in the present study and the other Aeromonas spp. from Genbank. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was used as an outgroup species. Bootstrap values out of 1000 repetitions were indicated above each branch. The scale bar represents 0.01-nucleotide change per nucleotide position.
3.4. The Pathogenicity Test in Mice
The pathogenicity test of the VGP strain in mice showed post-infection (p.i), except group 6, all challenged mice exhibited clinical symptoms, such as partial loss of appetite and coarse fur. The death of mice in each group were statistically analyzed (Figure 4). The results showed that the mortality of mice in group 1 was 8 (100%), which occurred at 4 h p.i (5 died) and 6 h p.i (3 died). The mortality of 8 mice (100%) in the group 2 occurred at 6 h p.i (4 died) and 8 h p.i (4 died). The mortality of mice in the group 3 was 8 (100%), all of which occurred at 10 h p.i. A total of 7 mice died in the group 4 (87.50%), which occurred at 12, 16, 18, 20, 22 h p.i, respectively (1, 2, 2, 1, 1 mice died, respectively) and then there are no more deaths. No deaths were observed in groups 5 and 6. The lethal dosage (LD50) of VGP in mice was determined to be 5.14 × 107 cfu by Kärber’s method. In addition, VGP was successfully re-isolated from the heart, liver, lung, kidney, and brain of the post-infected mice.
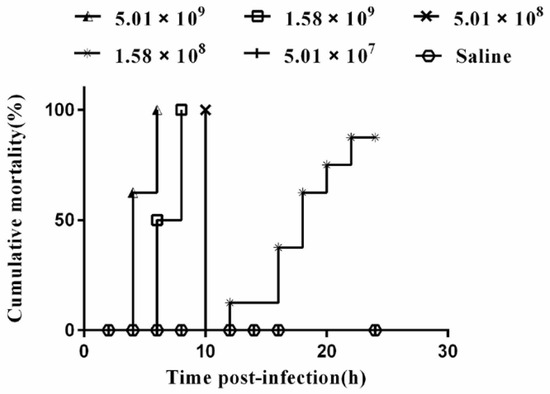
Figure 4.
The cumulative mortality of Kunming mice (n = 48) infection strain VGP in 24 h. Each line represents a different concentration of bacterial. The experiment was observed for 7 days. Since deaths do not occur after 24 h p.i, only deaths within 24 h p.i are shown.
3.5. Histopathology of the Inoculated Mice
Congestion is a common lesion of the liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and brain in all infected dead mice. Additionally basophilic granular aggregates consistent with bacteria were noticed in the hepatic sinuses, capsular thickening and lymphocytic necrosis were noticed in splenic. Interstitial thickening of lung were observed due to pulmonary hyperemia. Neuronal necrosis were observed in the brain and no significant lesions were observed in the heart (Figure 5).
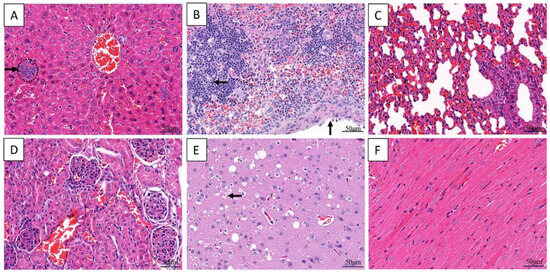
Figure 5.
Histological changes in the organs of Kunming mice inoculated with the strain VGP. Basophilic aggregates of bacteria (arrow) and congestion in the sinuses (A). Lymphocyte necrosis (horizontal arrow) and capsular thickening (vertical arrow) in spleen (B). Congestion in lung (C) and in kidney (D). Neuronal necrosis and congestion in brain (E). No significant changes in heart (F).
3.6. Virulence Gene Analyses of the Strain VGP
In this study, we screened nine virulence genes by PCR and the results indicated that strain VGP was positive for seven of the genes (aer, act, lip, exu, ser, luxs, and tapA), while the remaining two genes, aha and gcaT, were not detected (Figure 6).
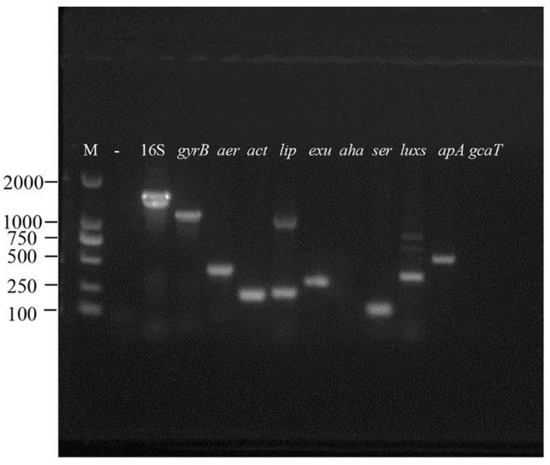
Figure 6.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of nine virulent genes (aer, act, lip, exu, aha, ser, luxs, tapA, gcaT) and house-keeping genes (16S rRNA and gyrB) in the strain VGP. M: DNA molecular weight standard; “-”: negative control.
3.7. Antibiotic Resistance of the Strain VGP
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing results showed that strain VGP was resistant to six antibiotics, namely penicillin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amoxicillin, imipenem, and vancomycin. On the other hand, it was sensitive to 36 antibiotics, including ceftizoxime, kanamycin, and ofloxacin (Table 2), which can be used as candidate drugs for the clinical treatment of A. veronii infection.

Table 2.
Antibiotic resistance of the strain VGP.
3.8. ARGs Analyses of the Strain VGP
Among all the 96 unique ARGs, including mobile genetic elements (MGEs), a total of 31 unique ARGs were present in strain VGP. The resistance genes aac, tetA-02 and tnpA-05 were the most abundant, followed by aacC and aadA2-02. These 31 ARGs had the potential to confer resistance to a range of antibiotics, such as β-lactamase resistance (32%), aminoglycosides resistance (22%), vancomycin resistance (19%), tetracycline resistance genes (10%) and sulfonamide resistance (6%) (Figure 7).
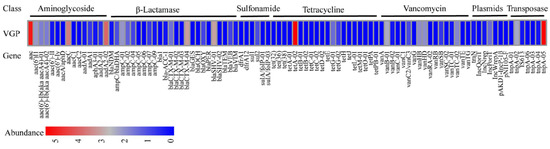
Figure 7.
Antimicrobial resistance genes abundance in strain VGP.
4. Discussion
A. veronii is a pathogen that has a broad host range, infecting hundreds of aquatic animals, waterfowl, and several mammalian species [9,10,11,15]. In clinical practice, the pathogen causes human biliary sepsis and diarrhea [15]. A. veronii infections have been reported in a wide variety of animals; however, there have been no reports of A. veronii infection in giant pandas.
The physiological and biochemical characteristics of the isolate VGP showed that it was Gram-negative, β-hemolytic, and positive to oxidase, lysine decarboxylase. This is consistent with the characteristics of Aeromonas. Due to the wide variety of Aeromonas species, molecular methods are necessary to distinguish different species. 16S rRNA and gyrB are commonly used to identify A. veronii [25,29]. In this study, the phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes demonstrated that isolate VGP belong to A. veronii.
Our study presents the first evidence that giant pandas could be infected by A. veronii. Histopathological analysis of captive giant panda cub showed rod-shaped bacteria in liver, spleen, and lung (This is consistent with the pathological characteristics of bacterial infection.). Then, A. veronii strain VGP was subsequently isolated from the heart, liver, lung, and kidney of the panda cub, that means A. veronii may be the causative factor of death. Furthermore, Kunming mice infection experiment results showed the time of death for Kunming mice infected with A. veronii was concentrated within 24 h, This indicated that strain VGP had pathogenicity. At the same time, a large number of virulence genes were detected in the strain VGP, which also proved this. The main histopathological results of infected mice were multi-organ congestion and bacterial infection. Additionally, bacteria masses were observed and A. veronii was isolated from the organs of Kunming mice infected with the strain VGP, this pathological feature is basically consistent with that of giant panda. Currently, the source of A. veronii infection in the giant panda cub is unknown and requires further investigation.
The pathogenicity of A. veronii is related to the expression of virulence factors [26]. One of the most important and abundant virulence factors is Aer, which is a cytotoxic pore-forming enterotoxin. Aer-positive A. veronii exhibited significantly higher mortality than Aer-negative A. veronii [30]. The Act gene plays a crucial role in A. hydrophila and significantly reduces the capacity to evoke fluid secretion [30], while Lip plays a common role in the pathogenicity of Aeromonas spp, which is secreted into the environment through the secretion system together [3]. The pili are well-established virulence factors for many bacteria [31]. TapA is mainly associated with host adherence and virulence [32], lacking tapA could result in a reduced ability to invade and survive within the host [33]. Luxs is one of the quorum sensing genes and encodes another autoinducer synthetase [34]. Lip plays an essential role in adhesion and integration, as well as in the pathogenesis of Aeromonas spp. [2]. Ser is an additional class of potential virulence factors related to the pathology and mortality of salmonid fish [34,35]. Exu is an important virulence factor that has been detected in diseased Gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) [36]. The number of virulence genes carried by A. veronii may be positively correlated with its pathogenicity [2]. Our results showed that strain VGP carried seven virulence genes (aer, act, lip, exu, ser, luxs, and tapA). Previous research has suggested that the more virulence genes the strain carried, the smaller the LD50 and the stronger the pathogenicity [2], which may be related to A. veronii’s strong pathogenicity. As an important aquatic zoonotic agent, the potential pathogenesis of A. veronii should be further monitored.
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics has significant effects on animal, environmental, and human health [37]. Our results showed that A. veronii from the giant panda cub was resistant to six antibiotics (penicillin, ampicillin, oxacillin, amoxicillin, imipenem and vancomycin). Previous studies showed that A. veronii isolated from duck resistant to tetracycline, doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole [8], isolated from fox resistance to tetracycline, rifampicin, penicillin, norvancomycin, bacitracin, oxacillin, clindamycin, ampicillin, novobiocin [9], Isolated from rabbit resistance to ampicillin (3/4), amoxicillin (2/4), streptomycin (4/4), tobramycin (3/4), tmikacin (2/4), gentamicin (1/4), neomycin (2/4), polymyxin B (4/4) [11], isolated from wild yak resistance to cefalexin, amoxicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, tetracyclin, erythromycin [12]. It can be seen that non-aquatic animal-derived A. veronii has universal drug resistance to ampicillin, which is contrary to the results in aquatic animals [38]. The resistance of A. veronii to other antibiotics is different, which may be related to the different selection and frequency of antibiotic use in different species.
ARGs are the primary reason for bacteria development of drug resistance [39]. In this study, 31 unique ARGs were positively detected in strain VGP. The β-lactam ARGs were detected which was consistent with the phenotype. At the same time, the emergence of ARGs such as blaCTX-M-04, blaCTX-M-01, blaSHV-01, blaOXY which related to extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBLs) should be taken seriously. Whether the emergence of these resistance genes is related to ESBL-producing E. coli [40] and ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae [41] of giant panda origin needs to be confirmed by further studies, while some ARGs showed a high abundance but there is no phenotype associated with it such as aminoglycoside resistance genes aac, aaC, aadA2-02, and tetracycline gene tetA-02, which may be related to the expression of these resistant genes.
The main lesions of the autopsy were congestion of the lung and liver. In most animals, the main symptoms of A. veronii infection are congestion or bleeding in internal organs, such as duck [8], fox [9], wild yaks [10], and rabbits [11]. Some will have gastrointestinal symptoms such as fox [9] and wild yaks [10]. Cold-blooded animals also show skin congestion or ulcers, etc. [3,4]. Their pathogenicity tests on mice all showed congestion or bleeding in multiple organs. This is basically consistent with our results. Congestion or bleeding of internal organs are the main clinical symptoms of animal diseases caused by A. veronii.
5. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first report that an A. veronii could infect giant pandas. We successfully isolated the pathogen of A. veronii from the internal organs of a deceased captive giant panda cub by bacterial culture, with identification by PCR methods. Additionally, detection of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes was performed by PCR methods. Our results revealed that A. veronii is resistant to six antibiotics, including penicillin, ampicillin and oxacillin, and carried seven virulence genes (aer, act, lip, exu, ser, luxs and tapA). The main pathological changes in giant panda were the large number of bacteria in multiple organs. Using artificial infection, A. veronii caused pathological damage to the heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney of Kunming mice, including degeneration, necrosis, and hemorrhage. This new study reporting this potential bacterial disease in giant pandas provides insights into understanding the pathogenicity of A. veronii towards its host. Further epidemiological investigations and exploration of the relationship between pathogenic bacteria and the host are needed.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani13172779/s1, Table S1. The primers of high-throughput real-time PCR.
Author Contributions
X.S. and M.Y., conceptualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition, methodology, investigation, validation, project administration, resources, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, and project administration; Y.L., methodology and formal analysis; X.Y., investigation; C.Y., resources; L.L., software; D.Z. and R.H., methodology and funding acquisition; S.L. and J.E.A., writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2023NSFSC1926) and the Chengdu Giant Panda Breeding Research Foundation (2021CPB-B15).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The methods, use of materials and all experimental procedures involving animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Chengdu Research Base of Giant Panda Breeding protocol #2018017. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations under the Law of the People’s Republic of China.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary Materials files.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all of the animal husbandry staff.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tekedar, H.C.; Kumru, S.; Blom, J.; Perkins, A.D.; Griffin, M.J.; Abdelhamed, H.; Karsi, A.; Lawrence, M.L. Comparative genomics of Aeromonas veronii: Identification of a pathotype impacting aquaculture globally. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Raza, S.H.A.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, W.; Qian, A.; Wang, C.; Kang, Y.; Shan, X. Aeromonas veronii Infection in Commercial Freshwater Fish: A Potential Threat to Public Health. Animals 2020, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Mao, C.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, B.; Gu, Q.; Su, Y. A First Report of Aeromonas veronii Infection of the Sea Bass, Lateolabrax maculatus in China. Front. Veter- Sci. 2021, 7, 600587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Yang, X.; Xian, J.A.; Lv, A.; Hu, X.; Shi, H. Isolation, Identification and Characteristics of Aeromonas veronii From Diseased Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Dong, N.; Chen, S.; Shu, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Chan, E.W.; Gu, D. Detection and genetic characterization of the colistin resistance gene mcr-3.3 in an Aeromonas veronii strain isolated from alligator faeces. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zheng, A.F.; Chen, M.M.; Lian, Y.X.; Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, S.Z.; Yu, D.; Li, J.K. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from a dead Yangtze finless porpoise. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2018, 132, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xiao, Z.; Li, B.; Xue, M.; Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Chen, P.; Qi, F.; Kong, X.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of Aeromonas veronii from Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Trionyx sinensis). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, T.; Chen, S.; Peng, D. Isolation an identification of Aeromonas veronii from duck and preliminary study on its pathogenicity. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 42, 191–194. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Kang, K.; Chen, M. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from fox. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 34, 289–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Ze, M.; Tang, C.; Yue, H. Isolation and identification of Aeromonas veronii from yak. J. Grass Forage Sci. (In Chinese). 2021, 3, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Calleja, J.; García-López, I.; García-López, M.; Santos, J.; Otero, A. Rabbit meat as a source of bacterial foodborne pathogens. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najera, F.; Grande-Gomez, R.; Pena, J.; Vazquez, A.; Palacios, M.J.; Rueda, C.; Corona-Bravo, A.I.; Zorrilla, I.; Revuelta, L.; Gil-Molino, M.; et al. Disease Surveillance during the Reintroduction of the Iberian Lynx (Lynx pardinus) in Southwestern Spain. Animals 2021, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, C.; Borges, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simoes, M. Biofilm formation and multidrug-resistant Aeromonas spp. from wild animals. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 12, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelo-Branco, D.S.; Silva, A.L.; Monteiro, F.O.; Guedes, G.M.; Sales, J.A.; Oliveira, J.S.; Maia Junior, J.E.; Miranda, S.A.; Sidrim, J.J.; Alencar, L.P.; et al. Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species from scarlet ibis (Eudocimus ruber) and their environment: Monitoring antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bravo, A.; Figueras, M.J. An Update on the Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Epidemiology, and Pathogenicity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviad-Shitrit, S.; Izhaki, I.; Arakawa, E.; Halpern, M. Wild waterfowl as potential vectors of Vibrio cholerae and Aeromonas species. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2018, 23, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Carr, M.; Booher, C.R.; Pointer, A.M.; Mitchell, B.M.; Smith, N.; Calnan, K.; Montgomery, G.M.; Ogada, M.; Kramer, D.B. Characteristics that make trophy hunting of giant pandas inconceivable. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zou, W.; Xie, S.; Kong, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, G.; Qin, Y.; et al. Serotype and Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia Coli Isolated from Feces of Wild Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda Melanoleuca) in Sichuan Province, China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhu, L.; Jia, M.; Wang, T.; Liang, B.; Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, X. Detection of Multi-Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli in a Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) with Extraintestinal Polyinfection. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Su, X.; Gen, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Bai, M.; Chen, Z. A Case of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Proteus mirabilis Infection in Giant Panda(Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Chin. J. Wildl. 2020, 41, 1013–1019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, D.; Tang, C.; Deng, L.; Huang, Z.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y. A case of giant panda reproductive tract infection with Proteus mirabilis. Sichuan J. Zool. 2007, 26, 167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Chi, X.; Xiu, Y.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, C. Isolation, identification and pathogenicity analysis of a strain of Proteus vulgaris from giant panda. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2020, 50, 1379–1388. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Wu, H.; Deng, L.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. A case of Enterobacter cloacae respiratory tract infection in giant panda. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2013, 45, 64–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Lan, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, X. A Subadult Giant Panda Case of Staphylococcus aureus Resparatory Tract Infection. Sichuan J. Zool. 2005, 24, 593. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Soler, L.; Yanez, M.A.; Chacon, M.R.; Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Catalan, V.; Figueras, M.J.; Martinez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54 Pt 5, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksal, F.; Oguzkurt, N.; Samastı, M.; Altas, K. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Aeromonas strains isolated from drinking water samples in istanbul, Turkey. Chemotherapy 2007, 53, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards For Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twenty—Fourth Informational Supplement CLSI Document M100-S24; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Su, X.; Ren, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Yue, C.; Yang, M.; Deng, H.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. High Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance and Integron Gene Cassettes in Multi-Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates From Captive Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 801292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, H.J.; Denner, E.; Lubitz, W. Classification and identification of bacteria: Current approaches to an old problem. Overview of methods used in bacterial systematics. J. Biotechnol. 1996, 47, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Qin, C.; Xie, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Fu, X.; et al. Aeromonas veronii and aerolysin are important for the pathogenesis of motile aeromonad septicemia in cyprinid fish. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3442–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonson, A.B.; Normark, S.; Rhen, M. Fimbriae, pili, flagella and bacterial virulence. Contrib. Microbiol. 2005, 12, 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J. Aeromonas spp. whole genomes and virulence factors implicated in fish disease. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, J.M.; Dacanay, A.; Knickle, L.C.; Touhami, A.; Brown, L.L.; Jericho, M.H.; Johnson, S.C.; Reith, M. Contribution of type IV pili to the virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reith, M.E.; Singh, R.K.; Curtis, B.; Boyd, J.M.; Bouevitch, A.; Kimball, J.; Munholland, J.; Murphy, C.; Sarty, D.; Williams, J.; et al. The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449, insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipond, R.; Bricknell, I.R.; Durant, E.; Bowden, T.J.; Ellis, A.E.; Smith, M.; MacIntyre, S. Defined deletion mutants demonstrate that the major secreted toxins are not essential for the virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Lin, L. Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Mao, C.; Liu, G.; Xu, L.; Cheng, C.; Bei, L.; Feng, J. Prevalence and distribution of antibiotic resistance in marine fish farming areas in Hainan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wang, K.Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, E.L.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.F.; Lai, W. Multidrug-Resistant Aeromonas veronii Recovered from Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) in China: Prevalence and Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone Resistance. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; An, X.; Li, H.; Su, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.G. Long-term field application of sewage sludge increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in soil. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Sun, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, W.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y. Molecular Characteristics of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Diseased Captive Giant Pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in China. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Geng, Y.; Su, F.; Yue, C.; Hou, R.; Liu, S. Identification of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (CTX-M)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to ST37, ST290, and ST2640 in captive giant pandas. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).