Studying the Shape Variations of the Back, the Neck, and the Mandibular Angle of Horses Depending on Specific Feeding Postures Using Geometric Morphometrics
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Horses and Management
Hay Net Features
2.2. Study Setup
2.2.1. Feeding Positions
- -
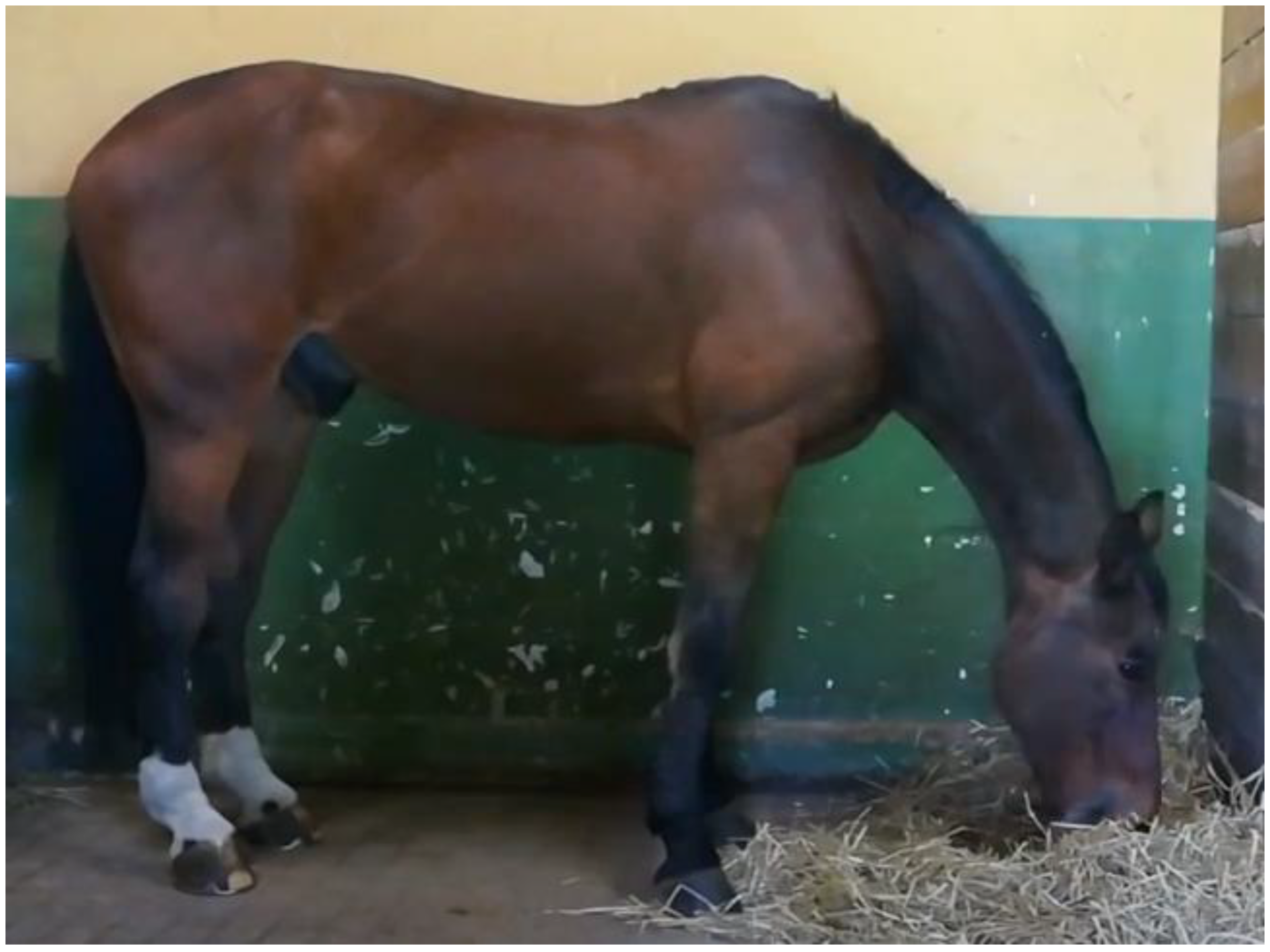
- Control position (CP): the hay was offered on the ground, and was considered the natural feeding position (Figure 1).
- -
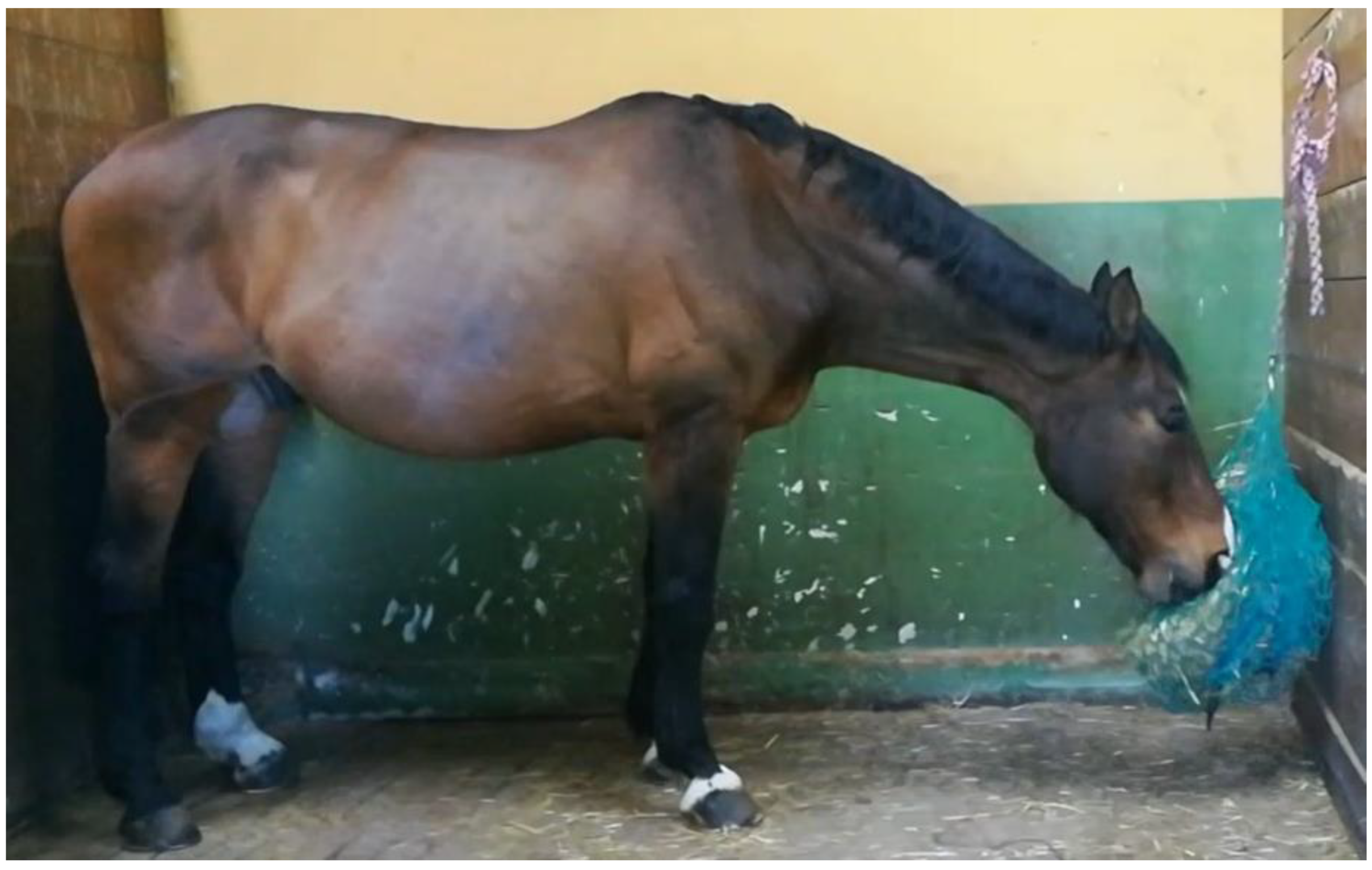
- Low hay net position (LP): the bottom edge of the hay net was level with the mid-point of the cannon bone (Figure 2). In this way, as the horse fed from the net, the neck was slightly below the withers.
- -
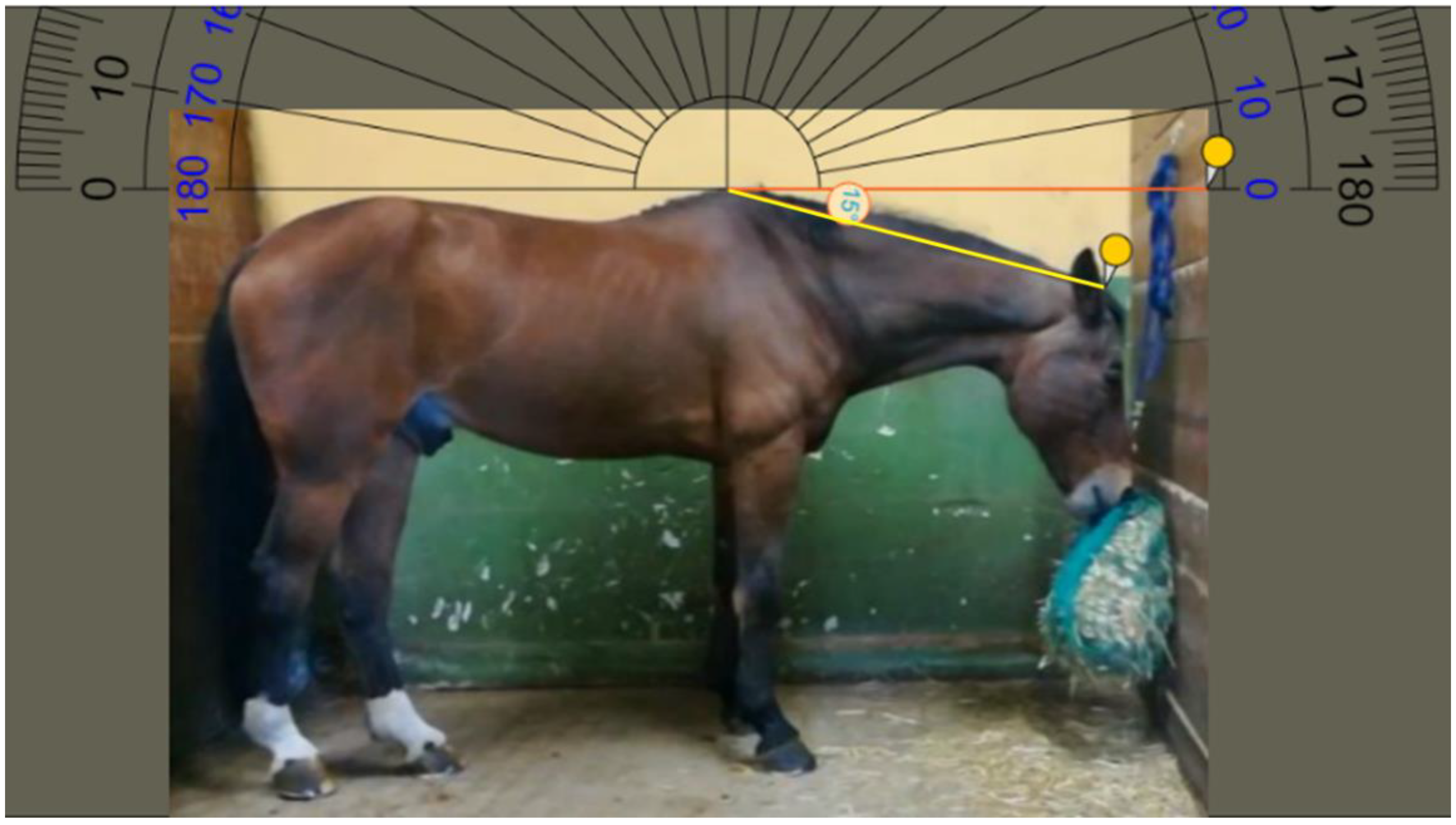
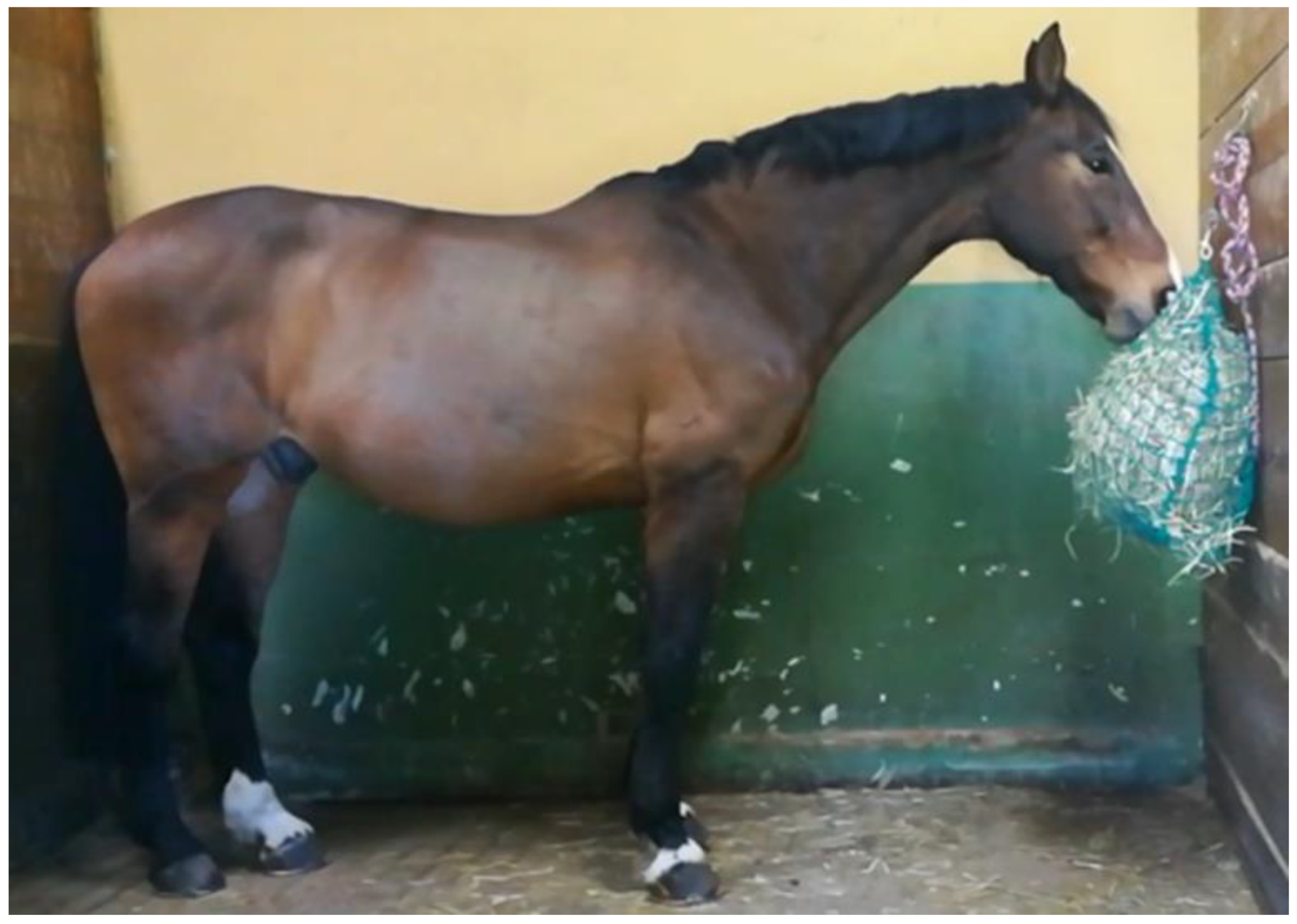
- High hay net position (HP): the bottom edge of the hay net was level with the horse’s elbow (Figure 3). In this position, the horse was required to hold his neck slightly above withers height.
2.2.2. Video Recordings
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3.2. Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA)
2.3.3. Partial Least Squares (PLS)
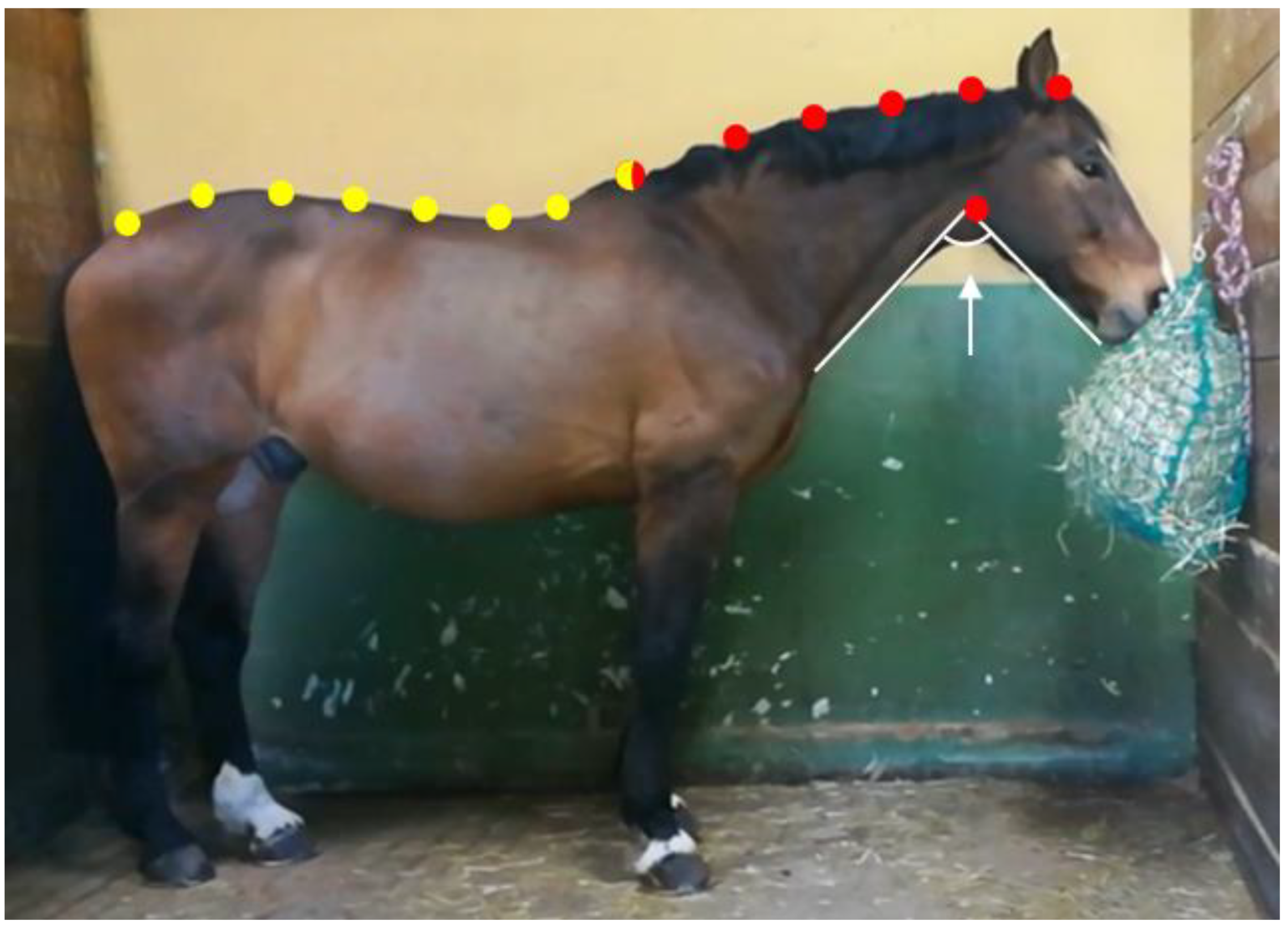
2.3.4. Magnitude of the Mandibular Angle
3. Results
3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.2. MANOVA
3.3. Partial Least Squares (PLS)
3.4. Magnitude of the Mandibular Angle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duncan, P. Time-budgets of Camargue horses. II. Time-budgets of adult horses and weaned sub-adults. Behaviour 1979, 72, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, L.E.; Carbonaro, D.A.; Houpt, K.A. The 24-Hour Time Budget of Przewalski Horses. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1988, 21, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, S.; Campbell, E.P.; Qazamel, M.; Owen, H.; Ellis, A.D. Effects of traditional versus novel feeding management on 24 h time budget of stabled horses. EAAP Sci. Ser. 2012, 132, 319–322. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, N.; Harris, P. Nutrition and Welfare. In The Welfare of Horses; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 45–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wageningen UR Livestock Research Welfare Monitoring System-Assessment Protocol for Horses. Available online: http://edepot.wur.nl/238619 (accessed on 13 May 2019).
- Swiss Federal Council Animal Welfare Ordinance. The Swiss Federal Council. Animal Welfare Ordinance, 455.1. (English Version) 1–152. 2008. Available online: https://www.tierschutz.uzh.ch/dam/jcr:ffffffff-eb0a-0d29-ffff-ffff8b68fdea/animal_welfare_ordinance_455_1.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2019).
- Merritt, A.M.; Julliand, V. Gastrointestinal physiology. In Equine Applied and Clinical Nutrition; E-Book: Health, Welfare and Performance; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Durham, A.E. The Role of Nutrition in Colic. Vet. Clin. NA Equine Pract. 2009, 25, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, D.; Weary, D.M.; Pajor, E.A.; Milligan, B.N. A Scientific Conception of Animal Welfare that Reflects Ethical Concerns. Anim. Welf. 1997, 6, 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Waran, N.K. Can studies of feral horse behaviour be used for assessing domestic horse welfare? Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesimple, C.; Poissonnet, A.; Hausberger, M. How to keep your horse safe? An epidemiological study about management practices. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 181, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspa, F.; Tarantola, M.; Bergero, D.; Bellino, C.; Mastrazzo, C.M.; Visconti, A.; Valvassori, E.; Vervuert, I.; Valle, E. Stocking Density Affects Welfare Indicators in Horses Reared for Meat Production. Animals 2020, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhajali, H.; Richard-Yris, M.-A.; Leroux, M.; Ezzaouia, M.; Charfi, F.; Hausberger, M. A note on the time budget and social behaviour of densely housed horses A case study in Arab breeding mares. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 112, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspa, F.; Tarantola, M.; Bergero, D.; Nery, J.; Visconti, A.; Mastrazzo, C.M.; Cavallini, D.; Valvassori, E.; Valle, E. Time-Budget of Horses Reared for Meat Production: Influence of Stocking Density on Behavioural Activities and Subsequent Welfare. Animals 2020, 10, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunk, E.C.; Hathaway, M.R.; Weber, W.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Martinson, K.L. The effect of hay net design on rate of forage consumption when feeding adult horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2014, 34, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, K.; Wilson, J.; Cleary, K.; Lazarus, W.; Thomas, W.; Hathaway, M. Round-bale feeder design affects hay waste and economics during horse feeding1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.D.; Redgate, S.; Zinchenko, S.; Owen, H.; Barfoot, C.; Harris, P. The effect of presenting forage in multi-layered haynets and at multiple sites on night time budgets of stabled horses. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2015, 171, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.J.; Albentosa, M.J. Behavioural adaptation in the domestic horse: Potential role of apparently abnormal responses including stereotypic behaviour. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 92, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, V.; Ellis, A.D. Preference of forage feeding position in stabled horses: A pilot study. In The Impact of Nutrition on the Health and Welfare of Horses, 5th ed.; Ellis, A.D., Longland, A.C., Coenen, M., Miraglia, N., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 128, p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Rochais, C.; Henry, S.; Hausberger, M. “Hay-bags” and “Slow feeders”: Testing their impact on horse behaviour and welfare. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2018, 198, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fureix, C.; Hausberger, M.; Seneque, E.; Morisset, S.; Baylac, M.; Cornette, R.; Biquand, V.; Deleporte, P. Geometric morphometrics as a tool for improving the comparative study of behavioural postures. Naturwissenschaften 2011, 98, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imogen Gmel, A.; Druml, T.; Portele, K.; von Niederhäusern, R.; Neuditschko, M.; Loor, J.J. Repeatability, reproducibility and consistency of horse shape data and its association with linearly described conformation traits in Franches-Montagnes stallions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202931. [Google Scholar]
- Sénèque, E.; Lesimple, C.; Morisset, S.; Hausberger, M. Could posture reflect welfare state? A study using geometric morphometrics in riding school horses. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignon, O.; Baylac, M.; Vigne, J.D.; Eisenmann, V. Geometric morphometrics and the population diversity of Late Glacial horses in Western Europe (Equus caballus arcelini): Phylogeographic and anthropological implications. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, I.; Baumung, R.; Molina, A.; Druml, T.; Gutiérrez, J.P.; Sölkner, J.; Valera, M. Size and shape analysis of morphofunctional traits in the Spanish Arab horse. Livest. Sci. 2009, 125, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansson, T.; Bjornsdottir, S.; Sigurdsson, A.; Crevier-Denoix, N.; Pourcelot, P.; Arnason, T. Objective quantification of conformation of the Icelandic horse based on 3-D video morphometric measurements. Livest. Sci. 2013, 158, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, K.; Burt de Perera, T.; Carere, C.; Carter, T.; Hailey, A.; Hubrecht, R.; Jennings, D.; Metcalfe, N.; Pitcher, T.; Peron, F.; et al. Guidelines for the treatment of animals in behavioural research and teaching. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Henneke, D.R.; Potter, G.D.; Kreider, J.L.; Yeates, B.F. Relationship between condition score, physical measurements and body fat percentage in mares. Equine Vet. J. 1983, 15, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocco, C.; Roggero, A.; Rolando, A.; Palestrini, C. Interspecific shape divergence in Aphodiini dung beetles: The case of Amidorus obscurus and A. immaturus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea). Org. Divers. Evol. 2011, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestrini, C.; Roggero, A.; Nova, L.K.H.; Giachino, P.M.; Rolando, A. On the evolution of shape and size divergence in Nebria (Nebriola) ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. The tps series of software. Hystrix 2015, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. The Method of Random Skewers. Evol. Biol. 2017, 44, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. Statistics at the Bench: A Step-by-Step Handbook for Biologists. By M. Bremer and R. W. Doerge. Cold Spring Harbor (New York): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. $59.00 (spiral). ix + 167 p.; ill.; index, index to Worked Examples, and index to Excel C. Q. Rev. Biol. 2011, 86, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C.; James Rohlf, F.; Slice, D.E. Italian Journal of Zoology Geometric morphometrics: Ten years of progress following the “revolution” Geometric morphometrics: Ten years of progress following the “revolution”. Ital. J. Zool. 2004, 71, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesimple, C. Indicators of Horse Welfare: State-of-the-Art. Animals 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, A. Don’t fence me in: Managing psychological well being for elite performance horses. Taylor Fr. 2007, 10, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutzner-Mulligan, J.; Eisemann, J.; Siciliano, P.; Smith, J.; Hewitt, K.; Sharlette, J.; Pratt-Phillips, S. The effect of different feed delivery methods on time to consume feed and the resulting changes in postprandial metabolite concentrations in horses1. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 3772–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.; Kjellberg, L.; Karlsson Budde, L.; Kjell, E.; Ryman, M. Pilot study on work load management and feed intake time when feeding horses with small mesh haynets. Livest. Sci. 2016, 186, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, M.G.; Rodrigues e Silva, C.F.; Dias, L.A.; da Silva Rocha Junior, S.; Thomes, F.R.; Alberto do Lago, L.; de Mattos Carvalho, A.; Faleiros, R.R. Welfare benefits after the implementation of slow-feeder hay bags for stabled horses. J. Vet. Behav. 2020, 38, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesimple, C.; Fureix, C.; De Margerie, E.; Sénèque, E.; Menguy, H.; Hausberger, M. Towards a Postural Indicator of Back Pain in Horses (Equus caballus). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, C.B.G.; Rhodin, M.; Bobbert, M.F.; Meyer, H.; Weishaupt, M.A.; Johnston, C.; Van Weeren, P.R. The effect of head and neck position on the thoracolumbar kinematics in the unridden horse. Equine Vet. J. 2006, 38, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.; Holmt, K.; Faber, M.; Erichsen, C.; Eksell, P.; Drevemo, S. Effect of conformational aspects on the movement of the equine back. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 2002, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sénèque, E.; Morisset, S.; Lesimple, C.; Hausberger, M. Testing optimal methods to compare horse postures using geometric morphometrics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffcott, L.B. Disorders of the thoracolumbar spine of the horse-a survey of 443 cases. Equine Vet. J. 1980, 12, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussler, K.K. The lower back and pelvis of performance horses receive a closer look. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 1996, 16, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weeren, P.R.; McGowan, C.; Haussler, K.K. Development of a structural and functional understanding of the equine back. Equine Vet. J. 2010, 42, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, H.H.F.; Savelberg, H.H.C.M.; Schamhardt, H.C.; Barneveld, A. Inertial properties of dutch warmblood horses. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebisch, A.; May, A.; Reese, S.; Gehlen, H. Effects of different head-neck positions on the larynges of ridden horses. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


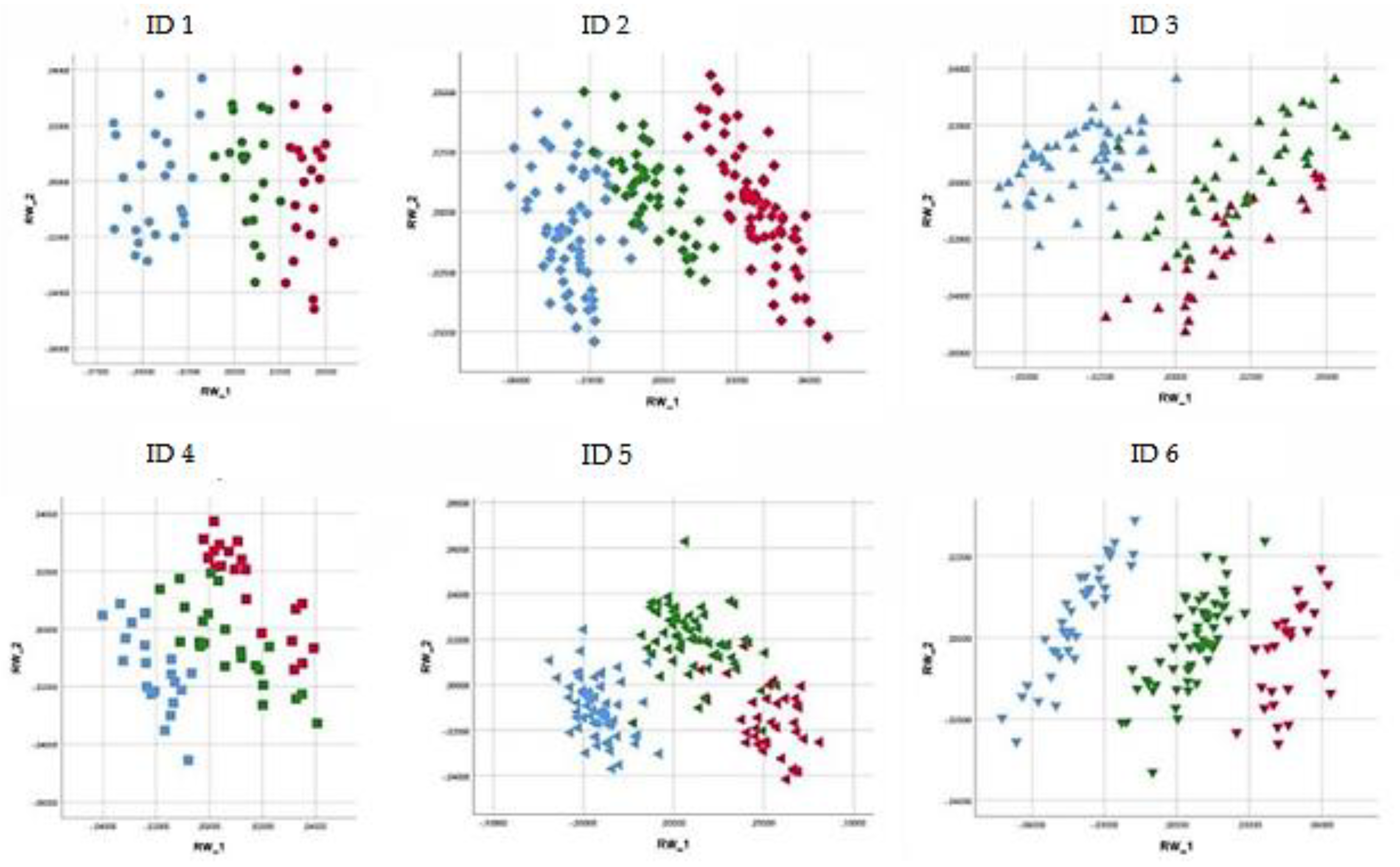
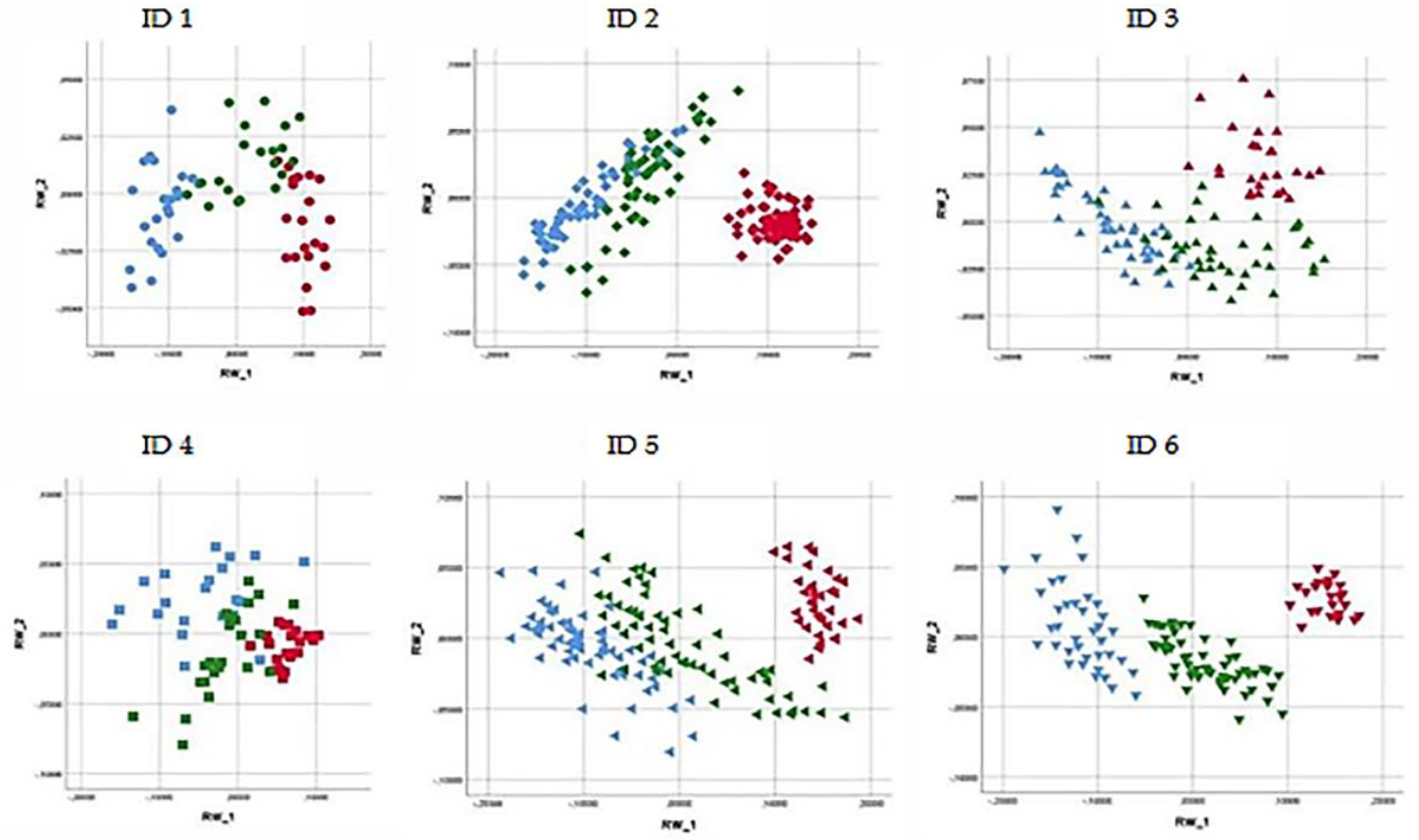
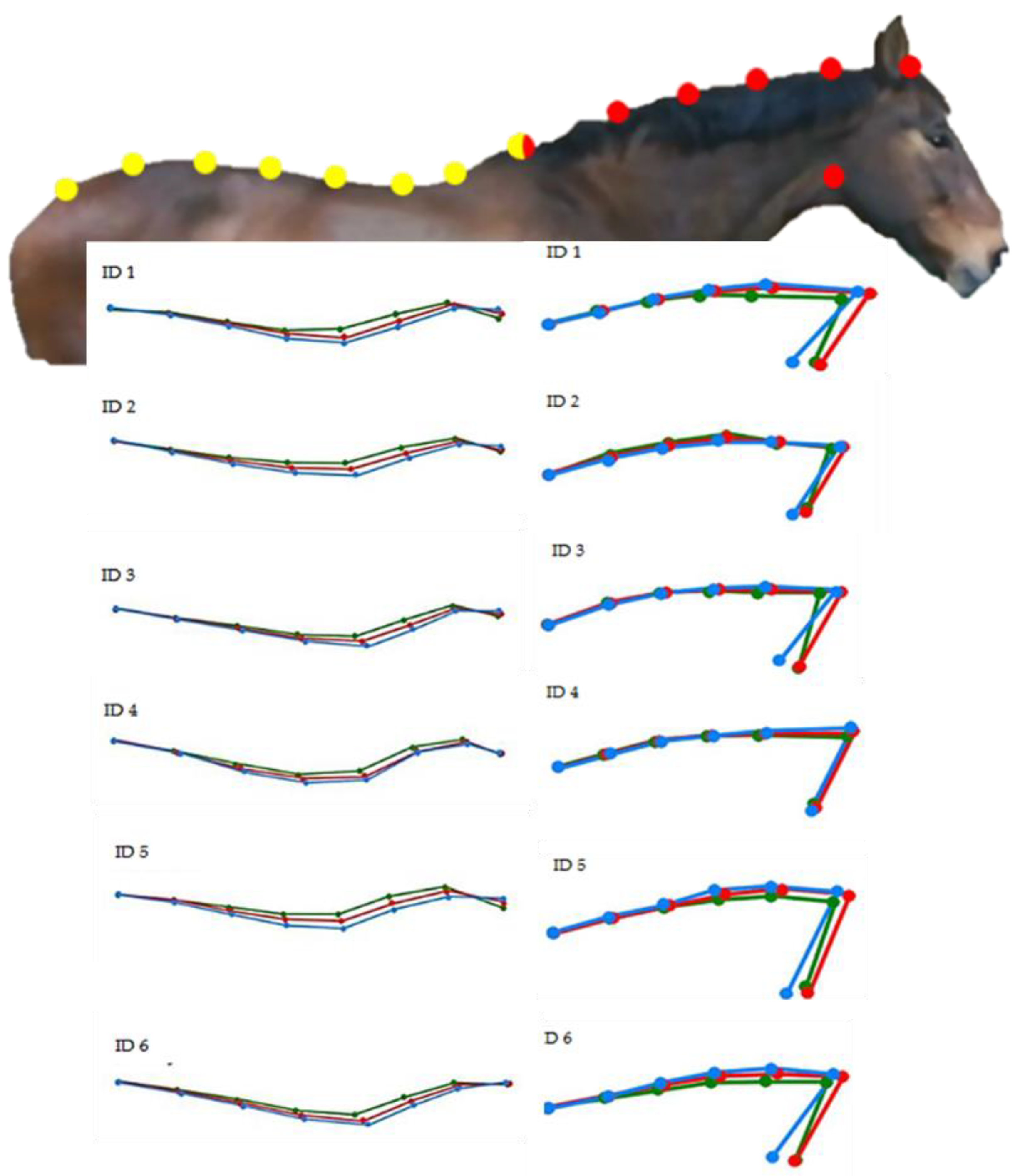
| Results for Back Postures (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse | CP | LP | HP | Total |
| ID 1 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 97 |
| ID 2 | 98 | 100 | 87 | 95 |
| ID 3 | 96 | 85 | 100 | 94 |
| ID 4 | 100 | 91 | 100 | 97 |
| ID 5 | 94 | 95 | 98 | 96 |
| ID 6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Dataset Total | 76 | 66 | 92 | 78 |
| Results for Neck Postures (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse | CP | LP | HP | Total |
| ID 1 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 94 |
| ID 2 | 100 | 100 | 88 | 96 |
| ID 3 | 100 | 85 | 96 | 93 |
| ID 4 | 95 | 91 | 86 | 91 |
| ID 5 | 100 | 92 | 98 | 96 |
| ID 6 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Dataset Total | 96 | 83 | 82 | 86 |
| Horse | r * | Cross Set Analysis (%) a | Permutation Tests (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID 1 | 0.93 | 99.60 | 0.10 |
| ID 2 | 0.93 | 99.80 | 0.10 |
| ID 3 | 0.86 | 99.70 | 0.10 |
| ID 4 | 0.82 | 93.70 | 0.10 |
| ID 5 | 0.85 | 99.50 | 0.10 |
| ID 6 | 0.92 | 99.60 | 0.10 |
| Feeding Positions | Median (25–75° Quantiles) | SEM $ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 153.25 (145.67–161.43) A | 0.0003 | <0.001 * |
| LP | 113.12 (110.78–121.23) B | ||
| HP | 97.74 (91.11–102.91) C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raspa, F.; Roggero, A.; Palestrini, C.; Marten Canavesio, M.; Bergero, D.; Valle, E. Studying the Shape Variations of the Back, the Neck, and the Mandibular Angle of Horses Depending on Specific Feeding Postures Using Geometric Morphometrics. Animals 2021, 11, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030763
Raspa F, Roggero A, Palestrini C, Marten Canavesio M, Bergero D, Valle E. Studying the Shape Variations of the Back, the Neck, and the Mandibular Angle of Horses Depending on Specific Feeding Postures Using Geometric Morphometrics. Animals. 2021; 11(3):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030763
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaspa, Federica, Angela Roggero, Claudia Palestrini, Martina Marten Canavesio, Domenico Bergero, and Emanuela Valle. 2021. "Studying the Shape Variations of the Back, the Neck, and the Mandibular Angle of Horses Depending on Specific Feeding Postures Using Geometric Morphometrics" Animals 11, no. 3: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030763
APA StyleRaspa, F., Roggero, A., Palestrini, C., Marten Canavesio, M., Bergero, D., & Valle, E. (2021). Studying the Shape Variations of the Back, the Neck, and the Mandibular Angle of Horses Depending on Specific Feeding Postures Using Geometric Morphometrics. Animals, 11(3), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030763








