Simple Summary
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) is the causative agent of Johne’s disease, affecting small and large ruminants and causing chronic diarrhea and severe emaciation. MAP is prevalent in many countries, including Saudi Arabia. Serological and molecular characterization of MAP and determination of the prevalent strains are essential for the control strategies. The results obtained from 31 herds showed that the sheep type (S-type) was the most prevalent MAP type and the molecular characterization revealed different strain profiles distributed among the sheep, goat, cattle, and camel herds in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
Abstract
The objectives of the present study were to characterize Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) infection using serological and molecular tools and investigate the distribution and molecular characterization of MAP strains (cattle (C) and sheep (S) types) in sheep, goat, cattle, and camel herds in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Serum and fecal samples were collected from all animals aged >2 years old in 31 herds (sheep = 8, goats = 6, cattle = 8 and camels = 9) from January to December 2019. Serum samples were tested by ELISA for the detection of MAP antibodies. Fecal samples were tested by PCR for the detection of MAP IS900 gene and the identification of MAP strains. MAP antibodies were detected in 19 (61.3%) herds. At the animal level, antibodies against MAP were detected in 43 (19.5%) sheep, 21 (17.1%) goats, 13 (19.7%) cattle and 22 (9.1%) camels. The IS900 gene of MAP was detected in 23 (74.2%) herds and was directly amplified from fecal samples of 59 (26.8%) sheep, 34 (27.6%) goats, 20 (30.3%) cattle and 36 (15.0%) camels. The S-type was the most prevalent MAP type identified in 15 herds, and all were identified as type-I, while the C-type was identified in only 8 herds. The IS900 sequences revealed genetic differences among the MAP isolates recovered from sheep, goats, cattle and camels. Results from the present study show that MAP was prevalent and confirm the distribution of different MAP strains in sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
1. Introduction
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) is a slow-growing, Gram-positive acid-fast bacterium that infects domestic and wild ruminants causing paratuberculosis or Johne’s disease [1,2]. Paratuberculosis is a chronic wasting disease that infects small and large ruminants causing chronic diarrhea, severe weight loss, emaciation and reduction in milk and wool production [3]. Infected animals have the ability to shed MAP in feces and milk for up to two years before the onset of clinical signs [4], which could transmit MAP to susceptible animals via fecal–oral route [5]. In humans, the MAP was related to Crohn’s disease, but this relationship remains controversial [6,7].
To reduce the risk of MAP infection, infected animals should be detected and culled at an early stage of infection [8]. There are currently several methods available for direct (i.e., bacterial culture and PCR) and indirect (i.e., ELISA and interferon-γ) detection of MAP infection. Bacterial culture is expensive, slow, takes up to 42 days or longer and not available in all laboratories [9]. However, PCR is more rapid and frequently used to remove high shedders from herds [10]. In addition, PCR could be used to directly diagnose MAP from fecal samples with sensitivity between 70% and 100% [11,12] and specificity of 100% [12,13]. The majority of previous studies that used PCR to detect MAP have targeted the IS900 gene, which represents approximately 17 copies of the MAP genome, thus providing a higher level of sensitivity [14].
Historically, MAP has been classified into cattle (C) and sheep (S) types based on the host from which MAP was first isolated [15]. Recently, phenotypic characteristics and molecular biology classified MAP into type-I, type-II and type-III [16,17,18]. MAP type-I was a slow grower, takes more than 16 weeks to achieve visible growth and was strongly associated with sheep. However, MAP type-II takes 4 to 16 weeks to grow and is commonly isolated from cattle [19]. MAP type-III or called “intermediate” was primarily thought to be different from C-type and S-type [19], but a recent study based on whole-genome sequence revealed that both types (I and III) are subgroups of S-type [20].
MAP infection has been reported in sheep [21], goats [22], cattle [23] and camels [24,25] in Saudi Arabia. However, to the author’s knowledge, there is limited information about the molecular characterization of MAP and the MAP types distributed in sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds in Saudi Arabia. Thus, the objectives of the present study were to (1) determine the MAP infection in sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds using serological and molecular tools and (2) investigate the distribution and molecular characterization of MAP strains (C-type and S-type) in sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
The present study was performed in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, which is located at 22°30′ N, 51°00′ E, at 390 km from the capital Riyadh (Figure 1). The Eastern Province is the third most populous province in Saudi Arabia, with varying climatic conditions from semi-desert to desert. The Eastern Province shares the borders with five countries (Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates), which may increase the risk of pathogen introduction to the country.
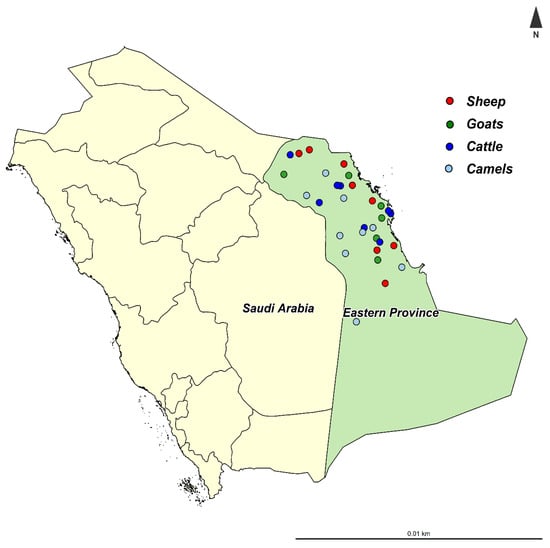
Figure 1.
The location of Eastern Province in Saudi Arabia and the location of sampled herds.
2.2. Samples Collection
A cross-sectional study was carried out from January to December 2019 to select herds with a previous history of Johne’s disease. A total of 31 herds were investigated (sheep = 8, goats = 6, cattle = 8 and camels = 9). Within herds, blood and rectal scrapings mixed with feces were collected from each animal aged >2 years old (Table 1). Blood samples were obtained from jugular venipuncture using vacuum tubes without anticoagulants; however, fecal samples were collected directly from the rectum into plastic containers. Samples were labeled with herd and animal ID, species and date of collection, then sent to the laboratory in ice pack containers and processed within 24 h.

Table 1.
The total number (n) of animals in each herd and number of animals (>2 years-old) sampled from each herd with a previous history of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
According to the local and national regulations, the Ethics Committee of Taif University has approved the study protocol (TURSP-2020-57). An informed consent (written in Arabic) was signed by all herd owners approving the use of their specimen samples for research purposes before enrolment in this study.
2.3. Serological Identification of MAP in Serum Samples
A commercial ELISA kit (mycobacterium paratuberculosis antibody test kit) from IDEXX (IDEXX, Hoofddorp, Netherlands) was used to detect antibodies against MAP in serum samples. Samples and controls were diluted 1:20 in dilutant containing mycobacterium phlei extract, then incubated at room temperature for 1 h to neutralize the cross-reactions with atypical mycobacteria. Briefly, a 100 µL/well of the diluted sample was loaded into the 96-well microtiter plate and then incubated at room temp for 45 mins. The conjugated and Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substate were added according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The addition of the stop solution stopped color development, and the optical density (OD) in each well was measured at 450 nm. Results were expressed as the ratio (S/P ratio) of the sample OD minus the mean of the negative control OD to the mean positive control OD minus the mean negative control OD. The sample was considered positive if the S/P ratio was ≥55%.
2.4. Molecular Identification of MAP in Fecal Samples
The DNA was extracted from each fecal sample according to Clark et al. [11] method with some modifications. Briefly, two grams of fecal sample were mixed with 4 mL sterile distilled water and vortexed vigorously for 15 s, then kept stand at room temperature for 10 min. Using a sterile pipette, 1.5 mL from the supernatant was transferred to a 2 mL tube containing 1 g zirconia/silica beads and centrifuged for 10 min at 13,000× g. After discarding the supernatant, the pellet was suspended in 400 µL distilled water and incubated at 95 °C for 10 min, then disrupted for 45 s at 6500 rpm using MagNA Lyser (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland). The sample was then centrifuged for 10 min at 13,000× g. The DNA was purified from the supernatant using QIAamp® PowerFecal® kit (QIAGEN, Courtaboeuf, France) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and the purified DNA was stored at froze temperature.
The template DNA was subjected to three different PCRs for molecular detection of MAP in fecal samples and identifying both cattle and sheep types. The purified DNA was amplified to detect the insertion sequence IS900 of MAP as described previously [17]. A specific PCR (DMC-PCR) to differentiate between cattle (C-type) and sheep (S-type) strains was performed according to Collins, et al. [26]. The size of the expected amplicon would be 310 bp for C-type and 162 bp for S-type. The representational difference analysis (RDA) fragments (pig-RDA10, pig-RDA20, and pig-RDA30) specific for sheep MAP type-I was amplified [27]. HotStartTaq® plus master mix kit (QIAGEN, Germantown, MD, USA) was used to amplify 2 µL of each purified genomic DNA, and PCR conditions were performed using I cycler PCR machine (BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA). The primers, annealing temperature, and expected DNA product size for each PCR conditions are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primers, annealing temperatures and product size used for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis identification in the present study.
The amplified IS900 product was purified (QIAquick PCR Purification Kit, QIAGEN GmbH—Hilden, Germany) and subsequently sequenced (3500 Genetic Analyzer, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The IS900 sequences were aligned with the IS900 elements of the reference MAP K-10 reference genome (GenBank accession no. AE016958).
2.5. Data Analysis
Data were introduced into R version 3.5.3 for visualization and descriptive data analysis. The proportions of MAP infections in each herd were calculated from the ratio of MAP positive samples to the total number of tested samples, with the exact binomial confidence interval of 95% (95% CI).
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Post-Mortem Lesions
From the 31 herds included in the study, only 7 (sheep = 2, goat = 2, cattle = 1 and camel = 2) herds showed one or more clinical signs of Johne’s disease, including chronic diarrhea and severe weight losses (Figure 2A). Necropsy findings in a single representative dead goat showed enlarged and edematous mesenteric lymph nodes (Figure 2B) and thickened and corrugated ileum (Figure 2C).
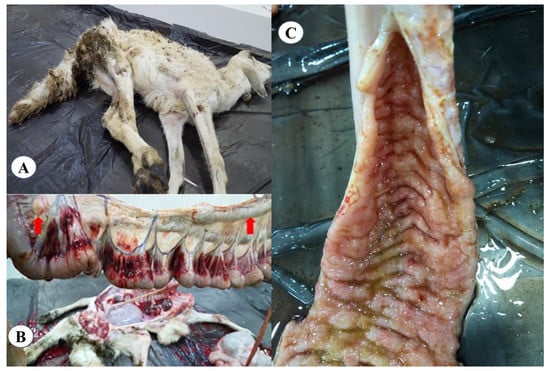
Figure 2.
Clinical and gross lesions of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infected goat. (A) dead goat with signs of diarrhea and emaciation; (B) mesenteric lymph nodes were enlarged and edematous; and (C) thickened and corrugated ileum.
3.2. Serological Detection of MAP
At the herd level, MAP antibodies were detected in 19 (61.3%) herds, including 6 sheep, 5 goat, 4 cattle and 4 camel herds. However, at the animal level, antibodies against MAP were detected in 43 (19.5%) sheep, 21 (17.1%) goats, 13 (19.7%) cattle and 22 (9.1%) camels (Table 3).

Table 3.
Number and percentage of ELISA and PCR positive animals in 31 herds examined for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
3.3. Molecular Detection of MAP
The IS900 gene of MAP was detected in 23 (74.2%) herds, including 6 sheep, 5 goat, 6 cattle and 6 camel herds. However, the IS900 gene of MAP was directly amplified from fecal samples of 59 (26.8%) sheep, 34 (27.6%) goats, 20 (30.3%) cattle and 36 (15.0%) camels (Table 3). Figure 3 shows the distribution of MAP S-type and C-type in sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds. The S-type was the most prevalent MAP type identified in 15 herds, including 5 sheep, 3 goats, 3 cattle and 4 camel herds. All S-types were identified as type-I based on RDA fragments PCR. The C-type was identified in 8 herds, including 1 sheep, 2 goats, 3 cattle and 2 camel herds.
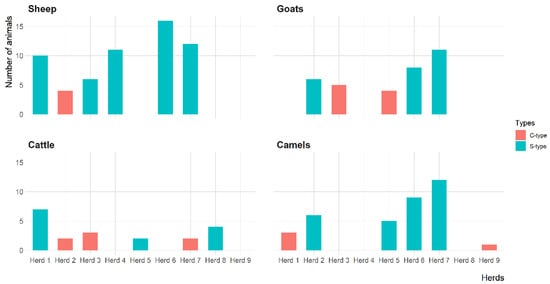
Figure 3.
The distribution of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains (C-type and S-type) in 31 herds with a previous MAP infection history in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
The differences in the IS900 gene sequences of MAP S-type and C-type identified in sheep, goat, cattle and camel are presented in Figure 4. All S-type sequences from sheep, cattle, goats and camels showed single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (G instead of A) at position 216 (GenBank accession no: MN928512, MT017587, MT017592 and MT017596). Additional SNP (C instead of G) was detected at position 235 in one S-type sequence from the camel (GenBank accession no: MT017595). However, the sequences of IS900 gene of C-type from sheep, goat, cattle and camel (GenBank accession no: MT017590, MT017591, MT017594 and MT017598) showed 100% identity to IS900 elements of MAP K10 strain. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (A instead of T) was detected at position 244 in C-type IS900 sequence from the camel (GenBank accession no: MT017594).
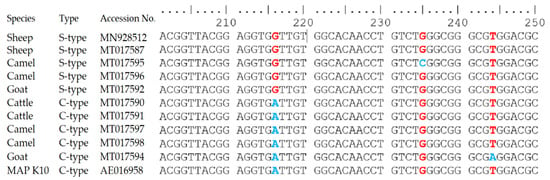
Figure 4.
The difference in the sequences of the IS900 gene of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains (C-type and S-type) recovered from sheep, goat, cattle and camel herds. The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in red and blue colours represent the differences between S-type and C-type at position 216, 235 and 244.
4. Discussion
Johne’s disease is a chronic contagious enteric disease with significant economic losses, particularly in the dairy industry around the world [28]. Early detection of MAP infection is essential for the successful control of Johne’s disease. Clinically, animals with Johne’s disease are classified under four categories based on the severity of clinical signs, the shedding of causative agents and the efficiency of diagnosis using existing laboratory techniques [29]. Animals up to 2 years of age are often in the early stage (silent infection) where no clinical signs and no cost-efficient screening tools can identify infection [30]. Bacterial culture of MAP from feces and tissues has been accepted as the reference standard for MAP infection diagnosis [31,32,33]. However, the long incubation time, the high expense and the need for a professional mycobacteriology laboratory are common disadvantages. Therefore, ELISA and PCR were commonly used as it rapid, simple, sensitive and cost-efficient tools for diagnosing MAP infection [34]. However, ELISA sensitivity is limited by the immune response to MAP infection, where antibodies can be detected at the late stage of infection and after fecal shedding has begun.
In the present study, herds with a previous history of MAP infection were selected, and animals aged over 2 years were sampled to increase the likelihood of serological and molecular detection of MAP [30,35]. The MAP antibodies were detected in sheep, goats, cattle and camels. However, the highest ELISA positive rate was in sheep (19.5%) and cattle (19.7%). Although the prevalence determination in the present study was biased due to the analysis of herds with previous MAP infection history, the calculated animal level prevalences were lower than those reported in European countries [36,37,38]. The proportion of ELISA positive sheep and goats was higher than the 6.3% reported in Italy [36] and lower than the 48.3% reported in Canada [39]. However, the proportion of ELISA positive detected in cattle was higher than the 0.4% recorded in Slovenia [37], lower than the 24.1% recorded in Germany [38] and similar to the 19% recorded in cattle in Australia [40]. In camel, 9.1% of the current study samples were ELISA positive, which was lower than the 30% previously reported in Saudi Arabia [25]. The variations in ELISA results in the diagnosis of MAP antibodies may be attributed to the delay of the humoral immune response of infected animals and the variability of antigens in commercial ELISA kits used in each country [30,31].
Animals in the present study were also tested by PCR for the detection of MAP IS900 gene. Several studies detected MAP infected animals through the detection of IS900 gene [11,41,42], which is highly specific and can detect 10-100 MAP per gram of feces or milk [43,44]. In the present study, the frequency of MAP infected animals detected by PCR was higher than ELISA. These results were similar to that reported by Clark et al. [11] and contradicted results reported by Wells et al. [45], who found that ELISA outperformed PCR in light and moderate shedding animals. The obtained result was not surprising because MAP-infected animals produce an immune response at the late stage of infection [39,46], whereas infected animals have the ability to shed the bacterium in feces and milk in an early stage of infection and about two years before the onset of clinical signs [4].
The phenotypic and genotypic differentiation of MAP provides essential information for molecular epidemiological analysis [47]. Several DNA-based techniques have been developed to examine the transmission of MAP among different animal species [16,48]. In the study area, S-type was the predominated MAP strain; it was identified by DMC-PCR in 15 herds, whereas the C-type was identified only in 8 herds. DMC-PCR was previously used to differentiate C-type from S-type [15]. The C-type is usually isolated from cattle; however, it shows no host specificity and can be isolated from a wide range of animals, including non-ruminants [49,50]. In the past, it was believed that S-type has a preference for sheep and goats. However, recently it has been isolated from cattle, deer and camelids [51]. A single nucleotide polymorphism was detected at position 216 after comparing the IS900 sequences of S-type with its ancients from MAP K10 strain, whereas the C-type showed 100% homology. Similar results were observed previously elsewhere [17,52,53,54].
It should be noted that our study has some limitations regarding the mycobacterial culture. We agree that fecal culture is the reference method for the detection of MAP. However, culture is expensive, slow and not widely available in Saudi Arabia. The direct fecal PCR used in the present study was sensitive (sensitivity ranged from 70% to 100% based on the MAP infection stage) and specific [11,12,13].
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the molecular characterization of MAP recovered from small and large ruminants in Saudi Arabia. The present study results showed that MAP was prevalent and confirm the distribution of different MAP strains in sheep, goat, cattle, and camel herds in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.E., M.F., and A.E.; methodology, I.E., M.F., M.A. and A.E.; software, I.E. and M.F.; validation, I.E., M.F., M.A. and A.E.; formal analysis, I.E., M.F. and A.E.; investigation, M.R., T.A-.M., F.A.A., A.S.A.A. and A.A.; resources, M.R., T.A.-M., F.A.A. and A.S.A.A.; data curation, I.E., M.R., T.A.-M., F.A.A., A.S.A.A. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, I.E. and M.F.; writing—review and editing, I.E., M.F, A.A. and A.E.; visualization, I.E., M.F. and A.E.; project administration, M.F. and M.A.; funding acquisition, M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/57), Taif University, P.O. Box 11099, Taif 21944, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
According to the local and national regulations, the Ethics Committee of Taif University has approved the study protocol (TURSP-2020-57). An informed consent (written in Arabic) was signed by all herd owners approving the use of their specimen samples for research purposes before enrolment in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Taif University Researchers Supporting Program (Project number: TURSP-2020/57), Taif University, Saudi Arabia for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Whittington, R.; Hope, A.; Marshall, D.; Taragel, C.; Marsh, I. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratu-berculosis: IS900 restriction fragment length polymorphism and IS1311 polymorphism analyses of isolates from animals and a human in Australia. JCM. 2000, 38, 3240–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, C.S.; De Jong, M.C.M.; Orsel, K.; De Buck, J.; Barkema, H.W. Quantifying transmission of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis among group-housed dairy calves. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.B.; Barletta, R.G. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in veterinary medicine. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.M.; Schukken, Y.; Koets, A.P.; Weber, M.; Bakker, D.; Stabel, J.R.; Whitlock, R.H.; Louzoun, Y. Differences in intermittent and continuous fecal shedding patterns between natural and experimental Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infections in cattle. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnaiah, G.; Zinniel, D.K.; Bannantine, J.P.; Stabel, J.R.; Gröhn, Y.T.; Collins, M.T.; Barletta, R.G. Pathogenesis, Molecular Genetics, and Genomics of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis, the Etiologic Agent of Johne’s Disease. Front. Veter Sci. 2017, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, M.A.; Kapur, V. The evidence for Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in Crohn’s disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 24, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, E.S. Could Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis cause Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis… and colorectal cancer? Infect. Agents Cancer 2018, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, I.A.; Nielsen, S.S.; Whittington, R.; Collins, M.T.; Bakker, D.; Harris, B.; Sreevatsan, S.; Lombard, J.E.; Sweeney, R.; Smith, D.R.; et al. Consensus-based reporting standards for diagnostic test accuracy studies for paratuberculosis in ruminants. Prev. Veter Med. 2011, 101, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, D.M.; Pearce, R.; Yearsley, D.; Ramovic, E.; Egan, J. Evaluation of three commercial PCR kits for the direct detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) in bovine faeces. Vet. J. 2018, 241, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.S.; Anderson, R.; Adaska, J.; Jiang, J.; Gardner, I. Association between Mycobacterium avium subspecies ++++ infection and milk production in two California dairies. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D., Jr.; Koziczkowski, J.; Radcliff, R.; Carlson, R.; Ellingson, J. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratubercu-losis: Comparing fecal culture versus serum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and direct fecal polymerase chain reaction. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logar, K.; Kopinč, R.; Bandelj, P.; Starič, J.; Lapanje, A.; Ocepek, M. Evaluation of combined high-efficiency DNA extraction and real-time PCR for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in subclinically infected dairy cattle: Comparison with faecal culture, milk real-time PCR and milk ELISA. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sting, R.; Hrubenja, M.; Mandl, J.; Seemann, G.; Salditt, A.; Waibel, S. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in faeces using different procedures of pre-treatment for real-time PCR in comparison to culture. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabel, J.R.; Bannantine, J.P. Development of a Nested PCR Method Targeting a Unique Multicopy Element, ISMap02, for Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Fecal Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4744–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.M.; Gabric, D.M.; De Lisle, G.W. Identification of two groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, K.; Hughes, V.M.; De Juan, L.; Inglis, N.F.; Wright, F.; Sharp, J.M. Molecular Characterization of Pigmented and Nonpigmented Isolates of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; De Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Rodriguez-Campos, S.; Romero, B.; Bezos, J.; Stevenson, K.; Mateos, A.; Domínguez, L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the IS900 Sequence of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Are Strain Type Specific. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, G.G.; Tripathi, B.N. Comparison of a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) with conventional PCR, bacterial culture and ELISA for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in sheep showing pathology of Johne’s disease. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Juan, L.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L.; Sharp, J.; Stevenson, K. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratu-berculosis isolates from goats detected by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.; Thibault, V.C.; Smith, D.G.E.; McLuckie, J.; Heron, I.; Sevilla, I.A.; Biet, F.; Harris, S.R.; Maskell, D.J.; Bentley, S.D.; et al. Phylogenomic exploration of the relationships between strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.H.; El-rahim, I.; Mohamed, A.M.; Ahmed, O.B. Clinical and molecular investigations of Johne’s disease among small ruminants in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Bioassays 2014, 3445–3451. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dubaib, M.A.; Mahmoud, O. Paratuberculosis of goats at Qassim region of Central Saudi Arabia. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2008, 11, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Shabana, I.I.; Aljohani, A.A. Sero-surveillance of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection in ruminants in Medina. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, K.B.; Al-Swailem, A.M.; Al-Dubaib, M.A.; Al-Yamani, E.; Al-Naeem, A.; Shehata, M.; Hashad, M.E.; Albusadah, K.A.; Mahmoud, O.M. Pathology and molecular diagnosis of paratuberculosis of camels. Trop. Anim. Heal. Prod. 2011, 44, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.A.; El-Deeb, W.M.; Zaghawa, A.A.; Housawi, F.M.; Alluwaimi, A.M. Investigation of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in Arabian dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius). Veter World 2019, 12, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.M.; De Zoete, M.; Cavaignac, S.M. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Strains from Cattle and Sheep Can Be Distinguished by a PCR Test Based on a Novel DNA Sequence Difference. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4760–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohmann, K.; Strommenger, B.; Stevenson, K.; De Juan, L.; Stratmann, J.; Kapur, V.; Bull, T.J.; Gerlach, G.-F. Characterization of Genetic Differences between Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Type I and Type II Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5215–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losinger, W.C. Economic impact of reduced milk production associated with Johne’s disease on dairy operations in the USA. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, R.H.; Buergelt, C. Preclinical and Clinical Manifestations of Paratuberculosis (Including Pathology). Veter Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pr. 1996, 12, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; VanLeeuwen, J.A.; McKenna, S.L.; Keefe, G.P.; Barkema, H.W. Johne’s disease in Canada: Part I: Clinical symptoms, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prevalence in dairy herds. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2006, 47, 874–882. [Google Scholar]
- Dargatz, D.A.; Byrum, B.A.; Barber, L.K.; Sweeney, R.W.; Whitlock, R.H.; Shulaw, W.P.; Jacobson, R.H.; Stabel, J.R. Evaluation of a commercial ELISA for diagnosis of paratuberculosis in cattle. J. Am. Veter Med Assoc. 2001, 218, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.; Keefe, G.; Barkema, H.W.; McClure, J.; VanLeeuwen, J.; Hanna, P.; Sockett, D. Cow-Level Prevalence of Paratuberculosis in Culled Dairy Cows in Atlantic Canada and Maine. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecteau, M.-E. Paratuberculosis in Cattle. Veter Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroudam, V.; Mohana Subramanian, B.; Praveen Kumar, P.; Dhinakar Raj, G. Paratuberculosis: Diagnostic methods and their constraints. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 4172. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, E.; Collins, M. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis: Pathogen, pathogenesis and diagnosis. Rev. Sci. Tech. l’OIE 2001, 20, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attili, A.-R.; Victor, N.N.; Preziuso, S.; Luciana, P.; Anastasia, D.; Vincenzo, C. Ovine Paratuberculosis: A Seroprevalence Study in Dairy Flocks Reared in the Marche Region, Italy. Veter Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocepek, M.; Pogačnik, M.; Logar, K.; Ferme, D.; Pate, M.; Krt, B. Seroprevalence of paratuberculosis in cattle in Slovenia. In Proceedings of the 10th International Colloquium on Paratuberculosis, Minneapolis, MI, USA, 9–14 August 2009; International Association for Paratuberculosis: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2009; pp. 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher, J.; Gangl, A. Mycobacterium avium ssp. Paratuberculosis–Combined Serological Testing and Classification of Individual Animals and Herds. J. Veter Med. Ser. B 2004, 51, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, C.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Jansen, J.; Kelton, D.; Menzies, P.I. Evaluation of fecal culture and fecal RT-PCR to detect Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis fecal shedding in dairy goats and dairy sheep using latent class Bayesian modeling. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, S.; Khol, J.L.; Stein, B.; Fuchs, K.; Gütler, S.; Baumgartner, W. Serological, Bacteriological and Molecularbiological Survey of Paratuberculosis (Johne’s Disease) in Austrian Cattle. J. Veter Med. Ser. B 2006, 53, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.M.; Cortabarria, N.; A Oguiza, J.; Aduriz, G.; A Juste, R. Use of a PCR method on fecal samples for diagnosis of sheep paratuberculosis. Veter Microbiol. 2000, 77, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikiz, S.; Bagcigil, A.; Ak, S.; Ozgur, N.; Lgaz, A. Paratuberculosis in cattle in Turkey detected by PCR. MED WETER 2005, 61, 881–883. [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini, R.J.; Hansen, D.; Whitlock, R.H. Council for agricultural science and technology-3 for agricultural science and technology. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2001, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, S.; Jayarao, B. Application of IS900 PCR for Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Directly from Raw Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, S.J.; Collins, M.T.; Faaberg, K.S.; Wees, C.; Tavornpanich, S.; Petrini, K.R.; Collins, J.E.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Whitlock, R.H. Evaluation of a Rapid Fecal PCR Test for Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Dairy Cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debroy, B.; Tripathi, B.; Sonawane, G.; Bind, R. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) in alco-hol-fixed tissues of sheep by ISMav2 gene PCR and its comparison with histopathology, bacterial culture and IS900 PCR. Small Rumin. Res. 2012, 105, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiwala, A.S.; Li, L.; Kapur, V.; Sreevatsan, S. Current understanding of the genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; Romero, B.; De Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Bezos, J.; Rodriguez-Campos, S.; Stevenson, K.; Mateos, A.; Domínguez, L. Polymorphisms in gyrA and gyrB Genes among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Type I, II, and III Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3439–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K.; Alvarez, J.; Bakker, D.; Biet, F.; De Juan, L.; Denham, S.; Dimareli-Malli, Z.; Dohmann, K.; Gerlach, G.-F.; Heron, I.; et al. Occurrence of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis across host species and European countries with evidence for transmission between wildlife and domestic ruminants. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.R.; Stevenson, K.; Greig, A.; Davidson, R.; Marion, G.; Judge, J. Infection of non-ruminant wildlife by Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. In Paratuberculosis: Organism, Disease, Control; Behr, M.A., Collins, D.M., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2010; pp. 188–200. [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo, C.; Pleydell, E.; Price-Carter, M.; Prattley, D.; Collins, D.; De Lisle, G.; Vogue, H.; Wilson, P.; Heuer, C. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolated from sheep, cattle and deer on New Zealand pastoral farms. Prev. Veter Med. 2014, 117, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.; Taragel, C.; Ottaway, S.; Marsh, I.; Seaman, J.; Fridriksdottir, V. Molecular epidemiological confirmation and circumstances of occurrence of sheep (S) strains of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in cases of paratuberculosis in cattle in Australia and sheep and cattle in Iceland. Veter Microbiol. 2001, 79, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, R.; Rhodes, G.; Arnott, S.; Sidi-Boumedine, K.; Bull, T.; Weightman, A.; Hurley, M.; Hermon-Taylor, J. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in the catchment area and water of the River Taff in South Wales, United Kingdom, and its po-tential relationship to clustering of Crohn’s disease cases in the city of Cardiff. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semret, M.; Turenne, C.Y.; Behr, M.A. Insertion Sequence IS900 Revisited. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).