Abstract
The potential utilization of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as food or feed is interesting due to the nutritive value and the sustainability of the rearing process. In the present study, larvae and prepupae of H. illucens were reared at 20, 27, and 33 °C, to determine whether temperature affects the whole insect microbiota, described using microbiological risk assessment techniques and 16S rRNA gene survey. The larvae efficiently grew across the tested temperatures. Higher temperatures promoted faster larval development and greater final biomass but also higher mortality. Viable Enterobacteriaceae, Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter, Clostridium perfringens, coagulase-positive staphylococci, Listeriaceae, and Salmonella were detected in prepupae. Campylobacter and Listeriaceae counts got higher with the increasing temperature. Based on 16S rRNA gene analysis, the microbiota of larvae was dominated by Providencia (>60%) and other Proteobateria (mainly Klebsiella) and evolved to a more complex composition in prepupae, with a bloom of Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Bacilli, while Providencia was still present as the main component. Prepupae largely shared the microbiota with the frass where it was reared, except for few lowly represented taxa. The rearing temperature was negatively associated with the amount of Providencia, and positively associated with a variety of other genera, such as Alcaligenes, Pseudogracilibacillus, Bacillus, Proteus, Enterococcus, Pediococcus, Bordetella, Pseudomonas, and Kerstersia. With respect to the microbiological risk assessment, attention should be paid to abundant genera, such as Bacillus, Myroides, Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella, which encompass species described as opportunistic pathogens, bearing drug resistances or causing severe morbidity.
1. Introduction
Insects are promising protein sources for livestock and human diet and may represent a sustainable contribution for feeding the growing world population. Larvae and prepupae of Hermetia illucens (i.e., black soldier fly, BSF) are receiving increasing interest as potential food and feed source because of the high nutritional value and the low environmental impact of the rearing process [1]. In particular, insect meal of BSF was successfully utilized as an alternative protein source for poultry and aquaculture [2,3,4,5]. The utilization of mature larvae and prepupae in insect-based ingredients (e.g., powders, flours, protein bars, pasta, burgers, and nuggets) requires the development of cheap practices to produce and stabilize the insect biomass, providing a safe starting bulk product [6,7]. The ability of H. illucens to grow on a variety of solid organic matrices can be exploited to transform and valorize organic streams such as byproducts of the agroindustry, livestock manures, or urban solid wastes, reducing environmental pollution and converting organic wastes into biomass rich in protein and fat [8,9,10,11].
The possibility to rear H. illucens on different waste streams in a biorefinery approach requires attention to safety issues, both chemical and microbiological. The European Food Safety Authority reported the lack of data regarding microbiology, virology, parasitology, and toxicology of insects reared, addressing the potential hazards of nonprocessed insects in comparison with other nonprocessed sources of protein of animal origin [12]. Hygiene issues of edible insects can originate from the substrate but also from the microbial community of the insect gut and may be affected by processing steps linking farming and consumption.
Recent works reported the microbiota composition of BSF larvae and prepupae [3,13,14,15]. However, little attention has been paid to microbial dynamics associated with extrinsic parameters, such as the rearing temperature. From a bioeconomy perspective, the biotransformation of wastes toward new valuable compounds should be a low-energy process that can be exploited in different districts with good tolerance to temperature changes, minimizing the requirement of heating or cooling.
From this standpoint, BSF larvae were reared at different temperatures, to determine the effect of this parameter on the growth rate and the biomass yield of prepupae. Since temperature may be a primary driver of microbial population composition, the microbiota of prepupae reared at 20, 27, and 33 °C was characterized. To avoid biases due to the intrinsic different microbial communities of feed, the larvae were fed a basal substrate [16,17,18]. A survey of the 16S rRNA gene was utilized to determine the microbiota composition in samples of substrate, initial larvae, grown prepupae, and their frass (hereinafter referred to as S, L, PP, and F samples). To assess the risks associated with prepupae utilization as food and feed supplement/ingredient, the metagenomic approach was accompanied by standard microbiology quality control techniques targeting the most relevant food contaminants and pathogens [12,19,20,21]. The impact of rearing temperature on microbiota is expected to offer knowledge and tools to prevent microbiological hazards, protect the health and the welfare of the consumers, and promote the development of safe trade in food and feed products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hermetia illucens Rearing
The BSF larvae used in this study were obtained from a colony kept at the Applied Entomology Laboratory, BIOGEST-SITEIA (Reggio Emilia, Italy), originally established with prepupae purchased from CIMI srl (Cuneo, Italy). BSF larvae were routinely reared in a standard vegetable substrate (S), composed of 25% zootechnical use cornflour (mill waste), 15% wheat bran, 10% alfa-alfa flour, and 50% water [22]. The experiments were set up using second to third instar larvae that were obtained from eggs hatched in S and incubated in climatic chambers under controlled conditions of 27 ± 0.5 °C, 65% humidity, and 16:8 light/dark cycles. To compare the rearing temperatures, 100 small larvae (L) were collected and reared in glass containers (20 × 12 × 8 cm) containing 400 g of S within climatic chambers at 20 ± 0.5, 27 ± 0.5, or 33 ± 0.5 °C. Two independent experiments, starting with different batches of L, were carried out, where each rearing temperature was tested in triplicate. Test checks were performed every three days, starting from day seven until the end of the development period, when a minimum of 90% of the initial larvae became prepupae (PP) and the experiment was considered concluded. The time point presenting the highest PP appearance in a single control was registered as the peak of PP. At the end of the experiment, insects were collected from the frass (F). PP and the remaining larvae (Lfinal) were counted and weighed to determine total biomass weight, the mean growth rate of each insect, and larvae mortality, according to the following:
Throughout all the rearing phases, standard hygienic conditions were applied, without using surface disinfection of larvae, substrate sterilization or aseptic incubation. Samples of L, S, PP20 °C, PP27 °C, PP33 °C, F20 °C, F27 °C, and F33 °C from each experiment were frozen and maintained at –80 °C until analyzed.
2.2. Culture Dependent Microbiological Analyses
Samples consisting of 5 g of S, PP, or F were suspended (10% w/v) in buffered peptone water (BD Difco, Franklin Lake, NJ, USA) and homogenized by Ultra Turrax (T25 Ika, Staufen, Germany). Proper dilutions were spread on selective media provided by BD Difco (Franklin Lake, NJ, USA). Total mesophilic aerobes were counted on Plate Count Agar (PCA) after incubation at 30 °C for 72 h. Spore-forming aerobic bacteria were grown on plates of PCA supplemented with 2 g/L of starch incubated at 37 °C for 48 h, with samples heated at 80 °C for 10 min to inactivate vegetative bacteria. Lactic acid bacteria were detected on Lactobacilli MRS agar plates after incubation at 30 °C for 72 h under microaerophilic conditions (GasPack EZ, BD Difco). Enterobacteriaceae were enumerated on Violet Red Bile Agar plates incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Yeasts and molds were counted on Dichloran Rose Bengal Chloramphenicol agar after incubation at 25 °C for 5 d. Standard methodologies were utilized to detect and enumerate the following food pathogens: Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter spp.; Clostridium perfringens, Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria spp.; Salmonella spp.; and Staphylococcus aureus, and coagulase-positive staphylococci [23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Triplicate samples from the two rearing batches were analyzed (n = 6). Microbial contamination was compared with recommendations of international authorities [12,19,20].
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Profiling
For each rearing batch, triplicate samples of L, S, PP20 °C, PP27 °C, PP33 °C, and F20 °C, F27 °C, and F33 °C were pooled in equal weights. Approximately 2 g of material were 10-fold diluted in PBS and were homogenized by Ultra Turrax. Total DNA was isolated from the suspensions using the DNeasy Mericon Food Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), following the manufacturer’s standard protocol. The DNA was normalized to 5 ng/µL after quantification with a Qubit v. 3.0 fluorimeter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Partial 16S rRNA gene sequences were amplified using Probio_Uni/Probio_Rev primers, which targeted the V3 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Amplicons were sequenced using a MiSeq (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) platform according to Milani et al. [30]. The 16S rRNA gene sequences are available at NCBI repository with the BioProject ID: PRJNA573042.
Raw sequences were cleaned and filtered by size and quality using the software MOTHUR v. 1.25.0 [31]. Quality filtered sequences were processed with QIIME2 pipeline (v. 2019.1) for closed-reference picking of amplicon sequence variants (ASVs), taxonomy assignment, collapsing into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) [32,33]. Closed-reference picking and taxonomy assignation were carried out utilizing as reference SILVA SSU database release 132 (https://www.arb-silva.de/download/arb-files/) with the similarity threshold set at 0.97. The appropriate QIIME2 plugins were utilized to compute the alpha- (observed taxa, Chao1, Shannon, and Pielou’s evenness) and beta diversity (Jaccard, Bray–Curtis, Canberra, Unweighted Normalized UniFrac, and Weighted Normalized UniFrac) and to compare them within and between groups of samples (i.e., the Kruskal–Wallis test for alpha diversity; ANOSIM and PERMANOVA for beta diversity). Beta diversity distance/dissimilarity matrices were utilized for the hierarchical clustering of samples in UPGMA trees and the Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA), using QIIME2.
Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe, http://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/galaxy) algorithm was applied to discover distinctive taxonomic features characterizing the groups of samples [34]. In the analysis of the taxa characterizing the development stage, L and PP samples were entered as “classes”. In the comparison between frass and insects, F and PP were entered as “classes”. Spearman’s rank correlation was applied to identify the taxa in PP that positively or negatively correlated with the three temperatures. In both LEfSe and Spearman’s analysis, the alpha value for statistical significance was set at 0.05.
2.4. Statistics
Plate counts and growth parameters are presented as means ± SD (n = 6). ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test was carried out with the software SPSS Statistics (v. 21, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Differences were considered statistically significant for p < 0.05. Spearman’s rank correlation was utilized to estimate the correlation with temperature.
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance of Hermetia illucens at Different Temperatures
The growth parameters of H. illucens are presented in Table 1. The total development period was the longest at 20 °C (40 d), while it was approximately 24 d at 27 and 33 °C. Rearing at 20 °C resulted in both the lowest total biomass and mean growth rate (15.9 g and 4.1 mg/d). No significant differences were observed between 27 °C and 33 °C (approximately 21 g and 10 mg/d). The highest larval mortality (14.5%) was registered at 33 °C, whereas it was similar at 20 and 27 °C (3.8 and 5.5%, respectively). The temperature significantly affected the time point at which the peak of PP was observed. The higher the temperature, the earlier came the peak (30.0, 19.7, and 16.0 d at 20, 27, and 33 °C, respectively).

Table 1.
Growth parameters of H. illucens at the three temperatures tested (definitions in materials and methods). Within each line, values marked with different letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test, p < 0.05).
3.2. Culture Dependent Microbiological Analysis
The viable count of total mesophilic aerobes in PP positively correlated with temperature (ρ = 0.87, p < 0.05), being the lowest at 20 °C (7.4 Log10 cfu/g) and approximately one magnitude higher at both 27 and 33 °C (Table 2). Aerobic spore-forming bacteria were less abundant than total aerobes, at all the temperatures (p < 0.05). Lactic bacteria and Enterobacteriaceae lay in the range of 6.2–6.9 and 3.7–5.2 Log10 cfu/g, respectively, without any significant difference associated with temperature. A low load of cultivable yeasts and molds was observed, between 0.7 and 1.2 Log10 cfu/g, without significant influence of temperature.

Table 2.
Cultivable microorganisms observed in substrate (S) and grown prepupae (PP) grown at 20, 27 and 33 °C. Counts are expressed as Log10 CFU/g. For Salmonella spp. the number of positive samples out of six is reported.
Bacillus cereus, Campylobacter spp.; Clostridium perfringens, coagulase-positive staphylococci, and Listeriaceae were detected in PP reared at all the tested temperatures. The amount of Campylobacter and Listeriaceae was positively correlated to temperature (ρ > 0.87, p < 0.05). The former passed from 3.2 to 4.7 Log10 cfu/g and the latter from 4.8 to 5.8 Log10 cfu/g increasing the temperature from 20 to 33 °C. Coagulase-positive staphylococci, B. cereus, and C. perfringens (laying in the ranges of 3.7–4.2, 2.3–3.2, and 0.8–1.6 Log10 cfu/g, respectively) were not affected by the temperature. Salmonella spp. was found in 7 out of 18 samples. Among the positive samples, only one (PP grown at 20 °C) allowed the recovery of colonies by direct plating, at a concentration of 1.1 Log10 cfu/g.
The microbiological analysis of S revealed a mean viable charge of 4.5 Log10 CFU/g total mesophilic aerobes, 4.9 Log10 CFU/g aerobic spore-forming bacteria, 2.9 Log10 CFU/g lactic acid bacteria, and 3.4 Log10 CFU/g fungi, while Enterobacteriaceae, B. cereus, Campylobacter spp. C. perfringens, coagulase-positive staphylococci, and Salmonella spp. were absent.
3.3. Microbiota Composition by Metagenome Analysis
The 16S rRNA gene profiling of L, PP, S, and F yielded a total of 755,313 sequences, that were dereplicated into 3974 ASVs hitting a reference sequence in Silva database, and collapsed at the seventh level of taxonomic annotation (i.e., the species, if available) into 536 OTUs. Based on Bray–Curtis distance, the microbiota of L, PP, S, and F clustered in distinct groups (Figure 1) that had different centroids (PERMANOVA, p = 0.001) and intragroup permutational similarity significantly greater than the intergroup one (ANOSIM, p = 0.001). F represented an exception, the similarity within the group being comparable to that between F and PP (p > 0.05). Grouping was evident in the PCo1-PCo2 plot (describing the 49% of total variance), where F and PP were characterized by positive PCo1, L by positive Pco2, and S by negative PCo1. Both F and PP lay at progressively lower PCo2 with the increase of the rearing temperature. Main taxa positively contributing to PCo1 were Myroides, Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacillus, and Morganella, while Enterobacteriaceae weighted negatively. Positive PCo2 was strongly owed to Providencia, followed by Klebsiella and Myroides, and negative to Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and A. faecalis.
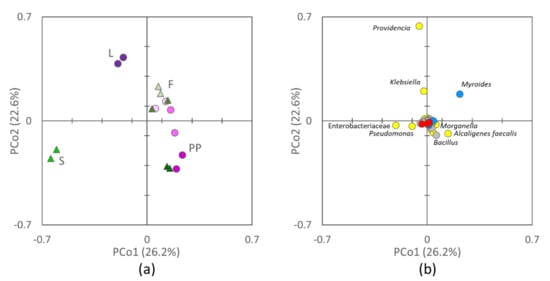
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional (2d) Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) visualization of microbiota beta diversity (Bray–Curtis) among initial larvae (L), S, PP, and frass (F): (a) scores of L (green circle), S (green triangles), PP (pink circles, with 20, 27, and 33 °C from the lightest to the darkest), and F (pink triangles, with 20, 27, and 33 °C from the lightest to the darkest), (b) contribution of the single bacterial taxa (Proteobacteria, yellow; Bacteroidetes, blue, Firmicutes, gray; Actinobacteria, red). Labels indicate taxa with the greatest contribution along PCo1 and PCo2.
The richness of the microbiota (evaluated as total no. of OTUs and Chao1 index) was similar in all the groups of samples, regardless of the rearing temperature (Supplementary Figure S1). The evenness (estimated in Shannon and Pielou metrics) was the highest in S samples, followed by PP and F, grouped regardless of the rearing temperature, and the lowest in L (Supplementary Figure S1).
A reduced dataset of 181 OTUs, occurring for more than 0.2% in at least one sample, still represented 99% of the reads. The distribution of the OTUs in the groups of samples is reported in the Venn diagram of Supplementary Figure S2. The bacterial composition of L, PP, S, and F is reported in Figure 2, showing the mean abundance of the main bacterial groups in the two experiments. The two experiments were not averaged for the analysis of the differential abundance of bacterial groups and the effect of temperature. The microbiota of L encompassed 98 of the 181 OTUs. It was dominated by Proteobacteria (87.4%), with remarkably high amounts of Providencia (64.1%) and Klebsiella (16.4%), followed by Firmicutes (9.3%), especially Bacillus (4.3%). The microbiota of PP included 156 OTUs, 95 of which shared with L. PP were poorer than L in Proteobacteria and richer in Bacteroidia, Actinobacteria, and Bacilli (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Providencia remained abundant in PP (from 6.4 to 26.1%, depending on the temperature), although it significantly decreased compared to L, likewise Klebsiella and other minor Enterobacteriaceae. The genera Morganella, Alcaligenes, Bordetella, and Kerstersia behaved in contrast to most Proteobacteria and were significantly enriched in PP. Morganella and Alcaligenes, in particular, reached remarkable levels (8.9 and 16.9%, respectively). The significant increase of Bacteroidia in PP was mainly due to Myroides, a Flavobacteriaceae that reached 30%. Bacilli also included several biomarkers characterizing PP, such as Planococcaceae, Paenibacillaceae, Pseudogracilibacillus, Oceanobacillus, and unclassified members of the genus Bacillus. Planococcaceae, Pseudogracilibacillus, and unclassified Bacillus reached 8.5, 5.9, and 13.1%, respectively. Within Actinobacteria, the main biomarkers characterizing PP were Micrococcales belonging to Brevibacterium, which increased up to 3.3%, and several minor genera.
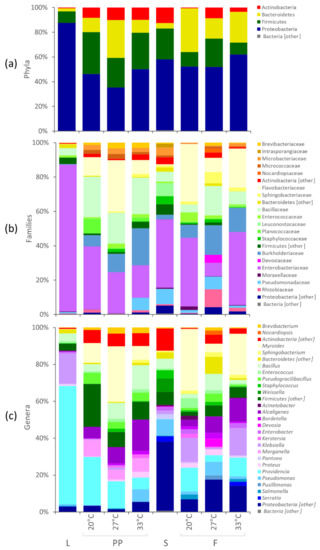
Figure 2.
Stacked bar-plot representation of microbiota composition in L, S, PP, and F with taxonomic features collapsed at the level of phyla (a), families (b), and genera (c). The mean values of the two independent experiments are reported. The phyla, families, and genera that remained unclassified or never occurred with abundance >2.0% are grouped as others.
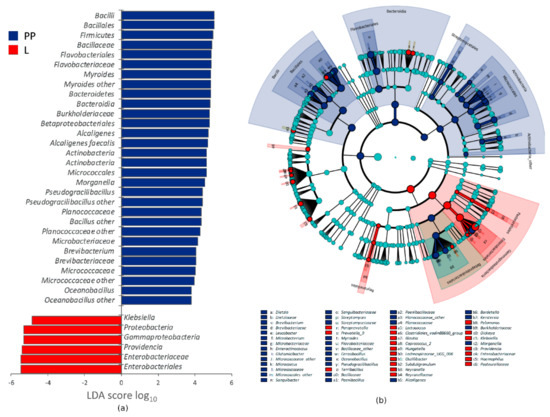
Figure 3.
Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) analysis of taxonomic features differentiating L (n = 2) and PP (n = 6), regardless of the growth temperature: (a) LDA logarithmic scores of taxonomic biomarkers exhibiting significant differential abundance (p < 0.05, logarithmic LDA logarithmic score ≥ 2.0) and appearing at least once with abundance >2.0%; (b) cladogram of all the taxonomic biomarkers.
The microbiota of S was characterized by 133 OTUs, 85 of which shared with L and 109 shared with PP. The remaining OTUs represented 6.3% of S microbiota, with only Rahnella being >1%. The microbiota of F encompassed 142 OTUs, 139 of which shared with PP. The composition of F differed from that of PP for being significantly richer in Proteobacteria (such as Klebsiella and Acinetobacter) and poorer in Actinobacteria (mainly Micrococcales, such as Brevibacterium), Firmicutes (Bacillales) and the Enterobacteriaceae Morganella (Supplementary Figure S3).
The increase of incubation temperature negatively correlated with the level of Enterobacteriaceae in PP, mostly due to the decrease of Providencia (Figure 4). Unlike Providencia, other Proteobacteria positively correlated with temperature, such as Kertersia, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Alcaligenes, and Bordetella. Pseudomonas was abundant only in PP reared at 33 °C (6.7%), whereas at the lower temperatures it accounted for less than 0.1%. Bacillus was also positively associated with increasing temperature and reached 13.1% at 33 °C. Increasing temperatures also favored the populations of other Actinobacteria (Brevibacterium), Bacilli (e.g., Enterococcus, Pediococcus, Paenibacillus, Pseudogracilibacillus), and Bacteroidetes (Sphingobacterium), although occurring in low amounts. The correlation of taxa with temperature is in agreement with their contribution in the PCoA biplot, resulting in PP samples being located at lower PCo1 values with the increase of the rearing temperature (Figure 1).
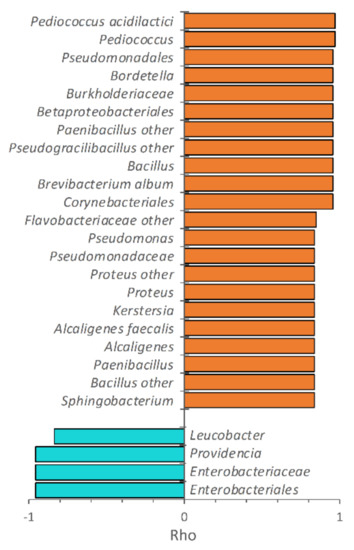
Figure 4.
Spearman’s rank correlation of the bacterial taxa in PP and the growth temperature. The correlation coefficient rho is reported only for the taxa exhibiting a positive (orange) or negative (cyan) significant correlation with temperature and appearing at least once with abundance >1.0% (n = 2, p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
In the present study, the larvae of H. illucens were reared at three different temperatures (20, 27, and 33 °C), utilizing a standard vegetal substrate, until reaching the PP stadium. The larvae efficiently grew across a range of temperatures, although with differences in the development rate, confirming the robustness of H. illucens. In the tropics, the development of H. illucens occurs yearlong, while it is restricted to a few generations per year in warm temperate regions [35], generally requiring temperatures above 26 °C [36]. Higher temperatures promoted faster larval development and greater final biomass but also higher mortality, in agreement with previous studies [37,38,39], suggesting that the best rearing temperature is 27 °C. The flexible rearing temperature enables the use of these insects also in developing countries, with minimal investment in energy-consuming devices for cooling or heating.
The first step of microbiological risk assessment in food or feed involves the collection of all information pertaining to potential pathogens that may exert any adverse effects on human or animal health. In the present study, the effect of rearing larvae at different temperatures on the microbiota of H. illucens was evaluated, with a focus on the viable load of the main food pathogens according to the Advisory Reports 2014/2372 and 2019/6200 [19,20]. The rearing temperature slightly affected the microbial load of PP, with only total mesophilic aerobes and Enterobacteriaceae significantly lower at 20 °C than at the higher temperatures. All the searched pathogens were detected in the whole set of PP samples and the counts of Campylobacter and Listariaceae got higher with the increasing temperature. Interestingly, the substrate was negative to all the pathogens except Listeriaceae. The larvae were not disinfected and were not reared under aseptic conditions, according to hygienic conditions that may be achieved in a production facility, where the substrate (e.g., a nonsterilized vegetal waste) is expected to be the main source of microbial contamination. It is likely that Enterobacteriaceae, B. cereus, Campylobacter spp., C. perfringens, coagulase-positive staphylococci, and Salmonella spp., laying below the limit of detection in S, were environmental contaminants or were introduced with small larvae. In any case, hygienic conditions must be kept under control throughout the multiple manufacturing processing stages, because the rearing of PP favored the blooming of the pathogens. Major attention has to be paid to microbiological optimization through the processes aimed at stabilizing the insects, such as powdering, heating, drying, UV treating, high-energy microwaving, pasteurizing, and acidifying, which are expected to contain the load of pathogens.
Metagenome analysis was complementary to the outcome of traditional microbiological approaches, providing more comprehensive information on ecological aspects. Previous studies determined the microbiota composition of H. illucens by 16S rRNA gene profiling, focusing on entire specimens, with or without any surface sterilization, or on the dissected gut, in some cases distinguishing specific gut sections [13,15,16,17,18,40]. These studies pointed toward a great variability of H. illucens microbiota, with the substrate, the stage of development of the insect, and the gut section being the major players shaping the structure and the diversity of the bacterial community. In some cases, the microbiota of H. illucens was dominated by Bacteroidetes, in others by Proteobacteria, accompanied by very variable amounts of Actinobacteria and Firmicutes [13]. However, the existence of a core composition, independent of the substrate and transmitted through the development stages, seems plausible. In particular, Providencia was reported as one of the most recurrent and abundant genera, occurring in insects reared on different substrates. Consistently, in the present study, the microbiota of L was dominated by Providencia (>60%) and other Proteobateria (mainly Klebsiella) and evolved to a more complex composition with insect development. A lower amount of Providencia was still present in the microbiota of PP, while Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Bacilli bloomed (Figure 2). Many taxa dominating the microbiota of PP (e.g., Providencia, Alcaligenes faecalis, Myroides, Morganella, Bordetella, and Kerstersia) occurred also in L and were not found or were negligible in S. These taxa took the most advantage from the interaction with the insect, exhibiting the greatest fitness relative to H. illucens. Other taxa, such as Pseudogracilibacillus and other unclassified Bacillaceae, that colonized PP were not found in either L or S. It is not clear whether they were contaminants of the rearing environment or they initially lay below the limit of detection in L and S.
For the first time, a significant effect of the rearing temperature on the microbiota composition of H. illucens is reported. The temperature was negatively associated with the amount of Providencia, which was the lowest at 33 °C. On the contrary, the temperature was positively associated with a variety of other genera, such as Alcaligenes, Pseudogracilibacillus, Bacillus, Proteus, Enterococcus, Pediococcus, Bordetella, Pseudomonas, and Kerstersia. Thus, the temperature has to be included among the main factors affecting the microbiota and may have contributed, together with the rearing substrate, to the wide differences in the structure of the microbial community associated with H. illucens reported in the literature.
The present study also indicates that H. illucens largely shares the microbiota with the medium where it is reared, except for a few lowly represented taxa. The main taxa constituting the microbiota of F and PP were the same, although some of them presented a differential abundance between the two environments, confirming that the insects and the medium shape the microbiota of each other [16].
With respect to the microbiological risk assessment, attention should be paid to the relevant abundance of some genera, such as Myroides, Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella, revealed by the 16S rRNA gene profiling. Species within these genera are not considered primary pathogens, although there is a vast literature describing them as opportunistic pathogens that may bear drug resistances and may cause severe morbidity [41,42,43,44,45]. Characterizing the species of Myroides, Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella harbored by H. illucens is recommended to establish whether they could be capable of causing adverse effects if present in the final product or throughout the production process.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/8/6/902/s1, Figure S1: Alpha diversity metrics of the microbiota in L, PP, S, and F; Figure S2: Distribution in the main 181 OTUs in L, PP, S, and F samples; Figure S3: LEfSe analysis of taxonomic features differentiating F and PP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R., M.R., L.M., and A.A.; software, F.C.; formal analysis, A.A. and F.C.; investigation, S.R., G.S., L.I.M., L.L., and F.C.; resources, L.M.; data curation, A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.R., M.R., and A.A.; visualization, A.A.; supervision, S.R., M.R., L.M., and A.A.; project administration, L.M.; funding acquisition, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Rural Development Plan 2014-2020 (Regione Emilia-Romagna, Op. 16.1.01—GO EIP-Agri - FA 5C) in the project “BIOECO-FLIES”, coordinated by CRPV (Cesena, Italy), and in part by ERDF Emilia-Romagna Regional Operational Programme 2014–2020, Italy, in the project “FLIES4VALUE” (grant number PG/2018/631984), coordinated by L. Maistrello.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wang, Y.S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrignelli, M.I.; Messina, M.; Tulli, F.; Randazzo, B.; Olivotto, I.; Gasco, L.; Loponte, R.; Bovera, F. Evaluation of an insect meal of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as soybean substitute: Intestinal morphometry, enzymatic and microbial activity in laying hens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Rimoldi, S.; Ascione, C.; Gini, E.; Ceccotti, C.; Gasco, L. Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gut microbiota is modulated by insect meal from Hermetia illucens prepupae in the diet. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisher. 2019, 29, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghit, I.; Liland, N.S.; Gjesdal, P.; Biancarosa, I.; Menchetti, E.; Li, Y.; Waagbø, R.; Krogdahl, Å.; Lock, E.J. Black soldier fly larvae meal can replace fish meal in diets of sea-water phase Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2019, 503, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Randazzo, B.; Truzzi, C.; Giorgini, E.; Marcellucci, C.; Vargas-Abúndez, J.A.; Zimbelli, A.; Annibaldi, A.; Parisi, G.; Tulli, F.; et al. A six-months study on Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) based diets in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truzzi, C.; Giorgini, E.; Annibaldi, A.; Antonucci, M.; Illuminati, S.; Scarponi, G.; Riolo, P.; Isidoro, N.; Conti, C.; Zarantoniello, M.; et al. Fatty acids profile of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens): Influence of feeding substrate based on coffee-waste silverskin enriched with microalgae. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 259, 114309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, L.; Pastorelli, R.; Viti, C.; Gasco, L.; Parisi, G. Characterisation of the intestinal microbial communities of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed with Hermetia illucens (black soldier fly) partially defatted larva meal as partial dietary protein source. Aquaculture 2018, 487, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan-Fonseca, K.B.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Nutritional value of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) and its suitability as animal feed—A review. J. Ins. Food Feed. 2017, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinnerås, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sust. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vanlaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Hadj Saadoun, J.; Foca, G.; Ulrici, A.; Bernini, F.; Malferrari, D.; Setti, L.; Ronga, D.; Maistrello, L. Hermetia illucens (L.) larvae as chicken manure management tool for circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Scientific Committee. Risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, J.; Wynants, E.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial community dynamics during rearing of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) and impact on exploitation potential. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02722-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Cardinali, F.; Roncolini, A.; Sabbatini, R.; De Filippis, F.; Ercolini, D.; Gabucci, C.; Petruzzelli, A.; et al. Revealing the microbiota of marketed edible insects through PCR-DGGE, metagenomic sequencing and real-time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 276, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Crauwels, S.; Verreth, C.; De Smet, J.; Sandrock, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Van Schelt, J.; Depraetere, S.; Lievens, B.; et al. Assessing the microbiota of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) reared on organic waste streams on four different locations at laboratory and large scale. Microbial. Ecol. 2018, 77, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; De Filippis, F.; Di Lelio, I.; Tettamanti, G.; Casartelli, M.; Ercolini, D.; Caccia, S. The Intestinal Microbiota of Hermetia illucens Larvae Is Affected by Diet and Shows a Diverse Composition in the Different Midgut Regions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01864-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.; Jeong, G.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.J. The intestinal bacterial community in the food waste-reducing larvae of Hermetia illucens. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Crippen, T.L.; Singh, B.; Tarone, A.M.; Dowd, S.; Yu, Z.; Wood, T.K.; Tomberlin, J.K. A survey of bacterial diversity from successive life stages of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) by using 16S rDNA pyrosequencing. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NVWA. Advisory Report on the Risks Associated with the Consumption of Mass-Reared Insects; NVWA/BuRO/2014/2372; Netherlands Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NVWA. Advice on Animal and Public Health Risks of Insects Reared on Former Foodstuffs as Raw Material for Animal Feed; TRCNVWA/2019/6200/EN; Netherlands Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski, N.T.; Klein, G. Microbiology of processed edible insect products—Results of a preliminary survey. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 243, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogsette, J.A. New diets for production of house-flies and stable flies (Diptera, Muscidae) in the laboratory. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Presumptive Bacillus Cereus—Colony-Count Technique at 30 Degrees C; ISO 7932:2004; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Clostridium perfringens—Colony-Count Technique; ISO 7937:2004; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feed—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 2: Enumeration by a Miniaturized Most Probable Number Technique; ISO/TS 6579-2:2012; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.—Part 2: Colony-Count Technique; ISO 10272-2:2017; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and of Listeria spp.—Part 2: Enumeration Method; ISO 11290-2:2017; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp.; ISO 6579-1:2017; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and other species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium; ISO 6888-1:1999/AMD 2:2018; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, C.; Hevia, A.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; Sanchez, B.; Martín, R.; Gueimonde, M.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA gene-based analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Chase, J.; Pitman, T.A.; Shiffer, A.; Mercurio, W.; Dillon, M.R.; Caporaso, J.G. An introduction to applied bioinformatics: A free, open, and interactive text. J. Open Source Educ. 2018, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Sheppard, D.C. Lekking behavior of the black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Fla. Entomol. 2001, 84, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Kim, W.T.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, Y.C.; Nho, S.K. Seasonal Pupation, Adult Emergence and Mating of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Artificial Rearing System. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2010, 21, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, metabolism and nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in relation to temperature and diet. J. Insects Food Feed 2018, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, L.M.; Tomberlin, J.K. Effects of temperature and diet on black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), development. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 266, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Adler, P.H.; Myers, H.M. Development of the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in Relation to Temperature. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelomi, M.; Wu, M.K.; Chen, S.M.; Huang, J.J.; Burke, C.G. Microbes associated with black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomiidae) degradation of food waste. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, C.E.; Mobley, H.L.T.; Pearson, M.M. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis infection. EcoSal Plus 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVergne, S.; Gaufin, T.; Richman, D. Myroides injenensis Bacteremia and Severe Cellulitis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnullina, L.F.; Pudova, D.; Shagimardanova, E.; Shigapova, L.; Sharipova, M.; Mardanova, A. Comparative genome analysis of uropathogenic Morganella morganii strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, C.M.; Brenner, F.W.; Miller, J.M. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Sharma, P.; Soni, P. First case report of Providencia rettgeri neonatal sepsis. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).