Silver Nanoparticles from Hermetia illucens Biomass Are Antibacterial Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Caenorhabditis elegans Maintenance
2.2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
2.3. Chemical Synthesis of AgNPs
2.4. Extraction of Hermetia illucens Polyphenols and Green Synthesis of AgNPs
2.5. Characterization of AgNPs
2.6. Caenorhabditis elegans Infection Assay
2.7. Antimicrobial Effect of Chemically and Green-Sinthesized AgNPs Against P. aeruginosa
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
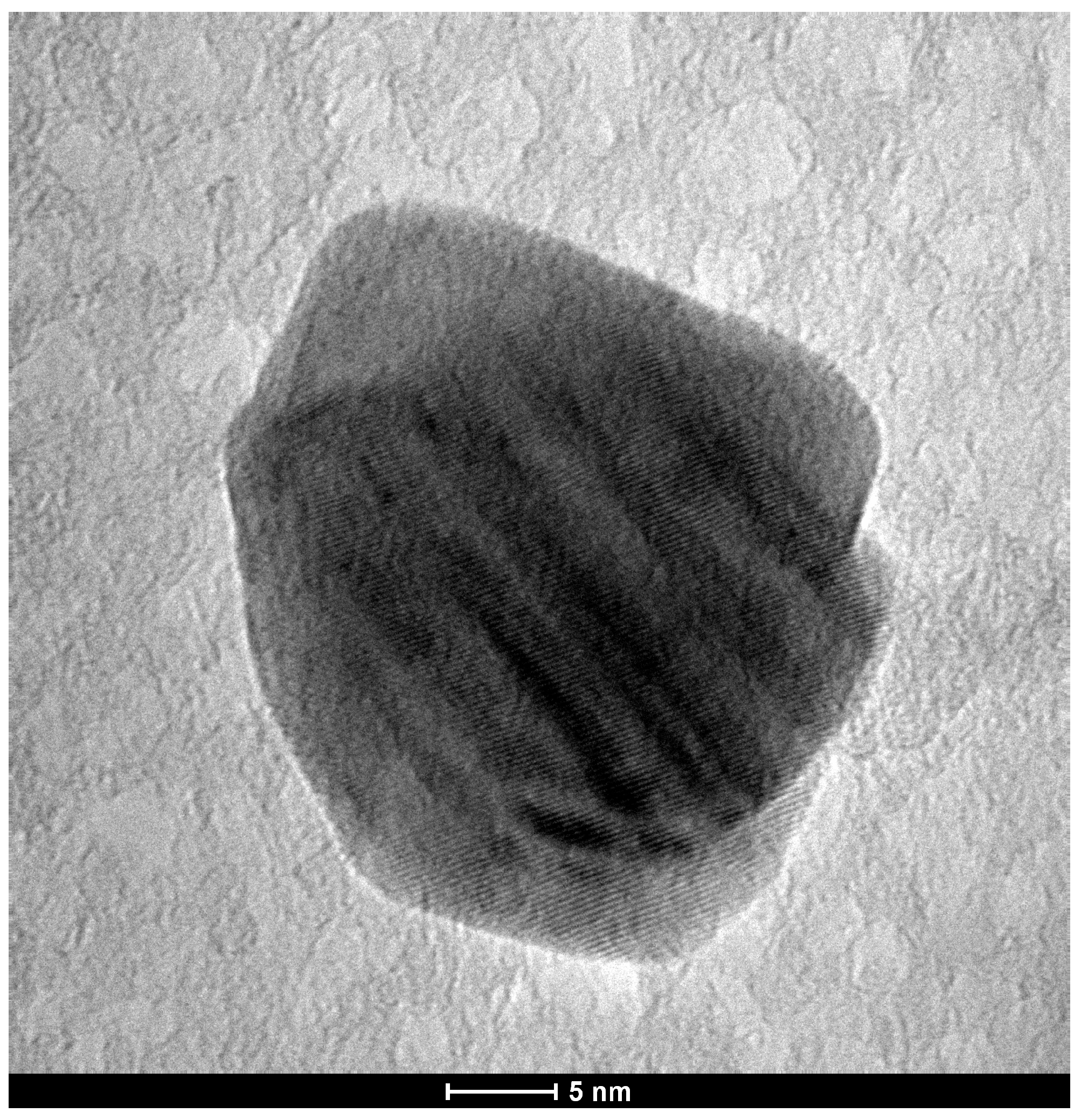
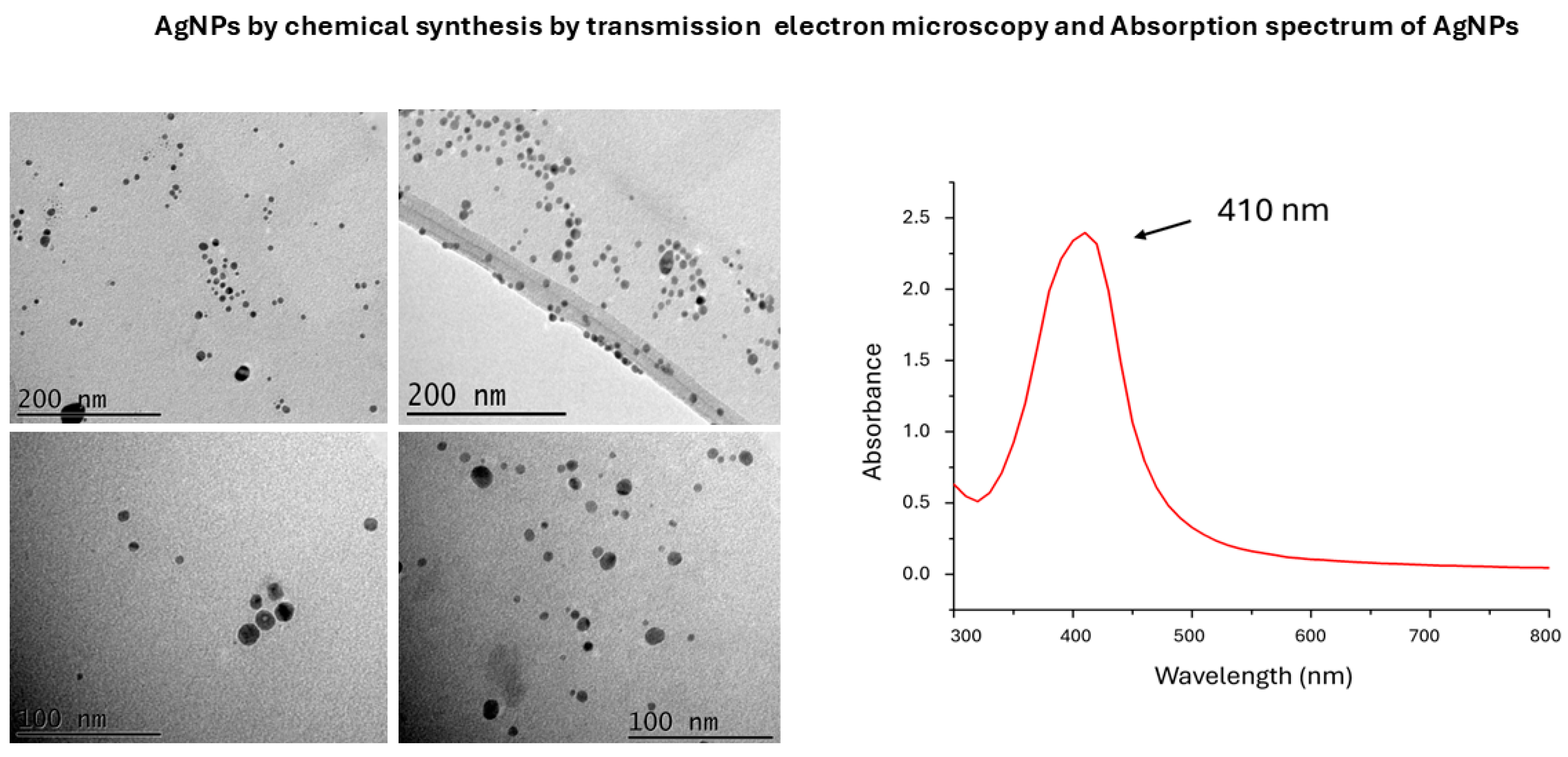
3.1. Characterization of AgNPs
3.2. Total Polyphenols and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity from Hermetia illucens Extract
3.3. Zeta Potential of AgNPs from Chemical and Green Synthesis
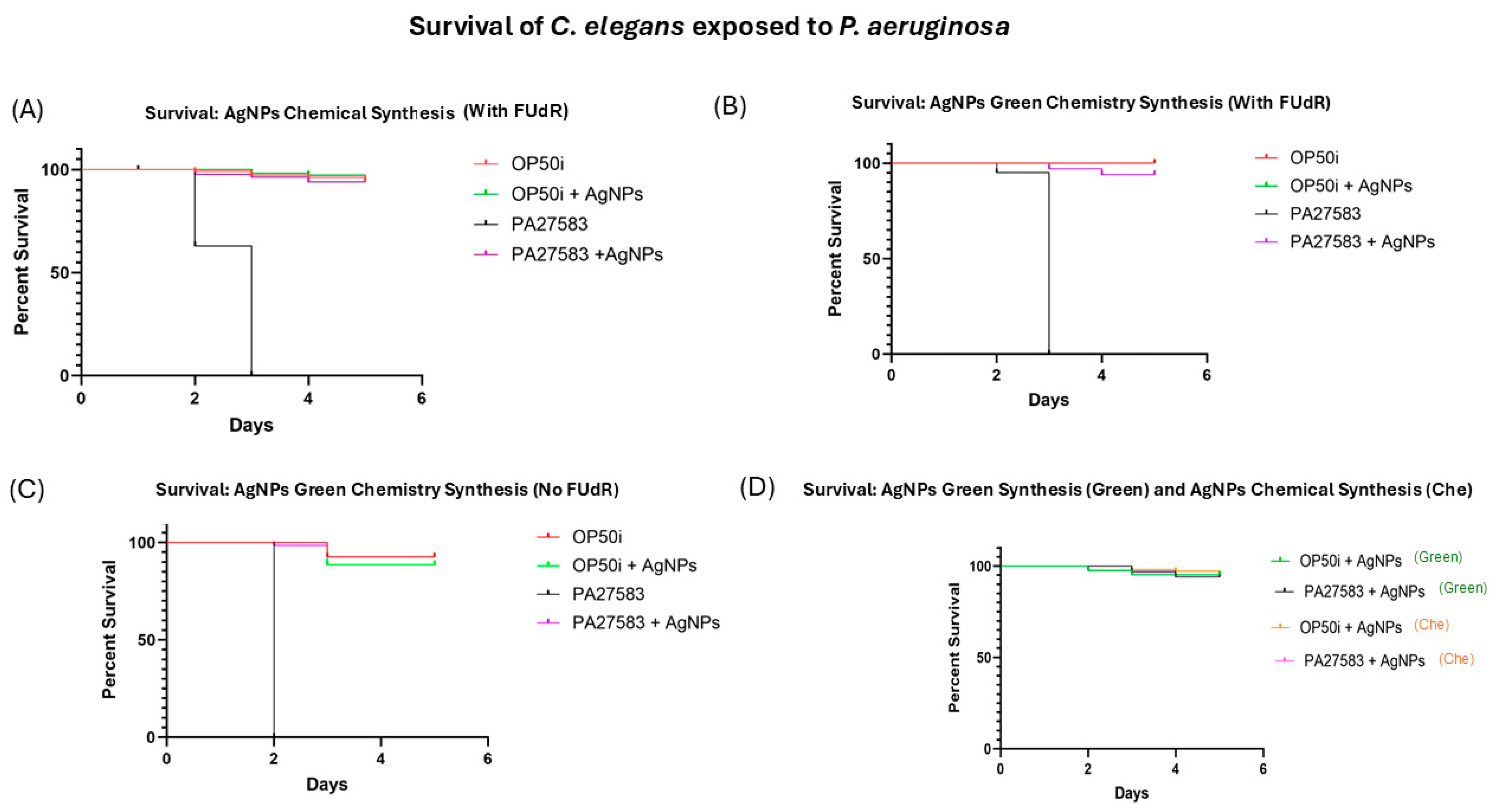
3.4. Survival of C. elegans to P. aeruginosa
3.5. Antimicrobial Efficacy of AgNPs Against P. aeruginosa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Ibraheem, D.R.; Hussein, N.N.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Khan, R.A.; Al Rugaie, O. Ciprofloxacin-loaded silver nanoparticles as potent nano-antibiotics against resistant pathogenic bacteria. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Yasmin, R.; Asif, R.; Ambreen, A.; Mustafa, M.; Umbreen, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), structural characterization, and their antibacterial potential. Dose-Response 2022, 20, 15593258221088709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumavat, S.R.; Mishra, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization, and applications. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayech, A.; Josende, M.E.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Ruas, C.; Gelesky, M.A.; Ale, A.; Cazenave, J.; Galdopórpora, J.M.; Desimone, M.F.; Duarte, M.; et al. Toxicity evaluation of nanocrystalline silver-impregnated coated dressing on the life cycle of worm Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, N.S.; Alsubhi, N.S.; Felimban, A.I. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using medicinal plants: Characterization and application. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2022, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.P.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.M. Caenorhabditis elegans: A model organism in the toxicity assessment of environmental pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39273–39287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewenza, S.; Charron-Mazenod, L.; Giroux, L.; Zamponi, A.D. Feeding behaviour of Caenorhabditis elegans is an indicator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Virulence. Peer J. 2014, 2, e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.-J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, G.; Wu, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Chang, B.S.; Yoe, S.M. Detection of antimicrobial substances from larvae of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The Genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josende, M.E.; Nunes, S.M.; Müller, L.; dos Santos Francisco, W.; Gelesky, M.A.; Monserrat, J.M.; Ventura-Lima, J. Multigenerational Effects of ecotoxicological interaction between arsenic and silver nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.L. Determination of total phenolics. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2002, 6, I1.1.1–I1.1.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicari, V.; Pellicanò, T.M.; Laganà, V.; Poiana, M. Use of orange by-products (dry peel) as an alternative gelling agent for marmalade production: Evaluation of antioxidant activity and inhibition of HMF formation during different storage temperature. J. Food Process Preserv. 2018, 42, e13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NANoREG D4.12 SOP Probe Sonicator Calibration for Ecotoxicological Testing.pdf. 2015. Available online: https://www.rivm.nl/sites/default/files/2018-11/NANoREG%20D4.12%20SOP%20Probe%20Sonicator%20Calibration%20for%20ecotoxicological%20testing.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Manohar, P.; Loh, B.; Elangovan, N.; Loganathan, A.; Nachimuthu, R.; Leptihn, S. A Multiwell-Plate Caenorhabditis elegans assay for assessing the therapeutic potential of bacteriophages against clinical pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certa, U. A Method for Fractionating C. elegans Populations by Size Using Filtration Through Nylon Nets. In Worm Breeder’s; Gazette 4; WormBook: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 16. Available online: http://dev.wormbook.org/wli/wbg4.1p16/ (accessed on 21 January 2025).
- Lau, K.Y.; Zainin, N.S.; Abas, F.; Rukayadi, Y. Antibacterial and sporicidal activity of Eugenia polyantha wight against Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Loya, J.; Lerma, M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Dynamic light scattering and its application to control nanoparticle aggregation in colloidal systems: A review. Micromachines 2024, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anith, J.R.; Devina, D.; Arulananth, T.S.; Shaik, N. Characterization analysis of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Chaetoceros calcitrans. J. Nanomater. 2022, 1, 4056551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, Z.; Sajab, M.S.; Abdul, P.M.; Ding, G. A novel chitinous nanoparticles prepared and characterized with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) using steam flash explosion treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Age-dependent effects of floxuridine (FUdR) on senescent pathology and mortality in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.; Klang, I.; Sivapatham, R.; Mark, K.; Zucker, D.; Bhaumik, D.; Lithgow, G.J.; Andersen, J.K. A DNA synthesis inhibitor is protective against proteotoxic stressors via modulation of fertility pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging 2013, 5, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirienko, N.V.; Cezairliyan, B.O.; Ausubel, F.M.; Powell, J.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 pathogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Pseudomonas Methods Protoc. 2014, 1149, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkabti, A.B.; Issi, L.; Rao, R.P. Caenorhabditis elegans as a model host to monitor the candida infection processes. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.M.; Buitrago, J.R.; Colombo, G.M.; Pereira, A.C.; Roselet, F.; Ramos, D.F.; Bernardi, F.; Monserrat, J.M. Biofloc residue conversion from shrimp production: Optimizing polyphenol extraction for silver nanoparticles synthesis with antibacterial and antibiofilm properties. Aquaculture 2024, 585, 740719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, F.-G.; Dai, Y.; Chen, X. Polyphenol-containing nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and therapeutic delivery. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Xu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, C.; He, R.; et al. Recent insight on edible insect protein: Extraction, functional properties, allergenicity, bioactivity, and applications. Foods 2022, 11, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Sowbhagya, R.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Almalik, A.I.; Ahmad, W.; Tripathi, T.; Elderdery, A.Y. Polyphenols and their nanoformulations: Protective effects against human diseases. Life 2022, 12, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayech, A.; Hollmann, G.; Gomes, R.M.M.; Rodrigues, B.A.; Engers, V.K.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Nornberg, S.D.; Ramos, D.F.; Zimmer, K.R.; Monserrat, J.M. Silver Nanoparticles from Hermetia illucens Biomass Are Antibacterial Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061277
Ayech A, Hollmann G, Gomes RMM, Rodrigues BA, Engers VK, Gonçalves RS, Nornberg SD, Ramos DF, Zimmer KR, Monserrat JM. Silver Nanoparticles from Hermetia illucens Biomass Are Antibacterial Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061277
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyech, Alinne, Gabriela Hollmann, Robson M. Marreiro Gomes, Belisa A. Rodrigues, Vanessa K. Engers, Rafael S. Gonçalves, Sandro Daniel Nornberg, Daniela F. Ramos, Karine Rigon Zimmer, and José M. Monserrat. 2025. "Silver Nanoparticles from Hermetia illucens Biomass Are Antibacterial Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061277
APA StyleAyech, A., Hollmann, G., Gomes, R. M. M., Rodrigues, B. A., Engers, V. K., Gonçalves, R. S., Nornberg, S. D., Ramos, D. F., Zimmer, K. R., & Monserrat, J. M. (2025). Silver Nanoparticles from Hermetia illucens Biomass Are Antibacterial Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Caenorhabditis elegans. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061277






