Abstract
Aspergillus fumigatus is an opportunistic fungal pathogen that causes serious lung diseases in immunocompromised patients. The lung surfactant produced by alveolar type II and Clara cells in the lungs is an important line of defense against A. fumigatus. The surfactant consists of phospholipids and surfactant proteins (SP-A, SP-B, SP-C and SP-D). The binding to SP-A and SP-D proteins leads to the agglutination and neutralization of lung pathogens as well as the modulation of immune responses. SP-B and SP-C proteins are essential for surfactant metabolism and can modulate the local immune response; however, the molecular mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated changes in the SP gene expression in human lung NCI-H441 cells infected with conidia or treated with culture filtrates obtained from A. fumigatus. To further identify fungal cell wall components that may affect the expression of SP genes, we examined the effect of different A. fumigatus mutant strains, including dihydroxynaphthalene (DHN)-melanin-deficient ΔpksP, galactomannan (GM)-deficient Δugm1 and galactosaminogalactan (GAG)-deficient Δgt4bc strains. Our results show that the tested strains alter the mRNA expression of SP, with the most prominent and consistent downregulation of the lung-specific SP-C. Our findings also suggest that secondary metabolites rather than the membrane composition of conidia/hyphae inhibit SP-C mRNA expression in NCI-H441 cells.
1. Introduction
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotrophic fungus and an opportunistic pathogen that produces thousands of small airborne spores (conidia) [1,2]. In immunocompetent persons, A. fumigatus conidia are cleared from the lung through different mechanisms including ciliary action of the epithelium and phagocytosis [3,4]. In immunocompromised patients, fungal conidia can survive, germinate and form a vegetative mycelium leading to a wide range of pulmonary diseases such as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, aspergilloma and even invasive pulmonary aspergillosis [3]. Despite current therapy, the mortality of pulmonary aspergillosis is reported to reach 30% to 80% [5].
The fungal cell wall is responsible for interacting with host cells. On one side, the cell wall provides a primary line of fungal defense against a hostile environment. On the other side, the cell wall components are often targets of the host’s immune system during fungal infections [6]. The cell wall of A. fumigatus is composed of polysaccharides (glucans), chitin and galactomannans (GMs) [7,8,9]. The outer layer of dormant A. fumigatus conidia has an additional rodlet layer containing hydrophobic RodA proteins and an underlying dihydroxynaphthalene (DHN)-melanin layer [7,10]. The DHN-melanin layer has been revealed to serve as a cover of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), including β-glucan and GM, and further protects fungi against UV irradiation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and microbial lytic enzymes [11,12]. It was shown that DHN-melanin-deficient mutants produce white hydrophilic spores with an altered surface structure and reduced virulence [12,13,14].
During conidial germination and fungal growth processes, the conidial surface undergoes major changes, the rodlet layer gets shed by aspartic proteases and the protective layer becomes porous, exposing possible PAMPs to the host’s immune system [10,15]. The formation of germ tubes is accompanied by the GM and galactosaminogalactan (GAG) exposure on the surface of A. fumigatus hyphae. GAG was shown to enhance the adherence of fungal hyphae to host cells [16,17]. Murine in vivo models demonstrated that GAG-deficient A. fumigatus strains do not produce biofilms and are less virulent during invasive aspergillosis [16,18].
Secondary metabolites of A. fumigatus such as degradative enzymes and mycotoxins also affect the host–pathogen interaction even though the molecular mechanisms remain largely unknown [19,20]. Culture filtrates obtained from A. fumigatus showed suppressive effects on alveolar macrophages and pulmonary leukocytes [21,22]. Extracellular enzymes, e.g., different proteases, cause damage to alveolar epithelial cells by inducing loss of focal contacts followed by cell detachment [23,24]. The treatment of cells with culture filtrates had a strong cytotoxic effect [25,26,27]: it induced cellular shrinkage, desquamation, actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and apoptosis [23,28].
Human lungs have several lines of defense against fungal pathogens. Among them, pulmonary surfactant plays an important role. A pulmonary surfactant is a lipoprotein complex composed of 90% lipids (mainly phospholipids) and 10% surfactant proteins (SP), including SP-A, SP-B, SP-C and SP-D [29]. Surfactant phospholipids decrease the surface tension at the air–water interface in the alveoli during inspiration and prevent alveolar collapse after expiration thus it is essential for gas exchange [30,31]. Furthermore, pulmonary surfactants are crucial for host defense against lung infections. Hydrophilic surfactant-associated proteins, SP-A and SP-D, belong to the family of innate immune proteins, named collectins [32]. SP-A and SP-D can bind surface structures expressed by pathogens and enhance their clearings by immune cells [32]. Hydrophobic proteins, SP-B and SP-C, are secreted along with surfactant phospholipids and are crucial for the surfactant lipid film dynamics [31]. Mutations in human SP-C and SP-B lead to severe chronic respiratory diseases such as chronic interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [33,34]. SP-B and SP-C were also suggested to be involved in the modulation of the local immune response, however, molecular mechanisms remain unclear [35].
Previous studies showed the impact of lung surfactants on the severity of pulmonary infections. The knockdown of SP-A, SP-C and SP-D genes resulted in significant impairment of host defense in murine models [36,37,38]. SP-C was shown to bind bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [39]. SP-A and SP-D were demonstrated to directly interact with A. fumigatus conidia: the CRD lectin domain of the SP binds sugar residues on the conidial surface and further increases conidia opsonization [8,40,41]. In addition, the binding of the hydrophilic SP led to agglutination of A. fumigatus conidia, preventing the dissemination of conidia, thus enhancing phagocytosis by macrophages and neutrophils [8,40]. It was observed that SP-D could directly bind both A. fumigatus conidia and hyphae, further inhibiting fungal growth [42].
Previous studies reported that A. fumigatus infection results in differential regulation of SP gene expression. Downregulation of the SP-C and SP-D mRNA was observed in human A549 cells infected with A. fumigatus conidia [43,44]. Altered gene and protein expressions of SP-A, SP-B, SP-C and SP-D were shown in mice models of A. fumigatus-induced allergic airway inflammation [36,45]. Our study aimed to investigate the effect of A. fumigatus culture filtrates as well as DHN-melanin-deficient, GAG-deficient and GM-deficient mutant strains of A. fumigatus on the mRNA expression of the SP in human lung cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
The human lung adenocarcinoma cell line NCI-H441 (ATCC-HTB-174) was obtained from LGC Standards (Wesel, Germany). NCI-H441 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with L-glutamine, 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 100 units/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin, which were all obtained from Capricorn Scientific (Ebsdorfergrund, Germany). For the infection experiments, an antibiotic-free medium was used overnight and during all experiments.
2.2. Fungal Strains
A. fumigatus DAL (=CBS144-89, [46]), ∆pksP, Δugm1 and ∆gt4bc strains were obtained from V. Aimanianda (Institut Pasteur, Université de Paris, CNRS, Unité de Mycologie Moléculaire, UMR2000, Paris, France). All strains were maintained at 37 °C in 25 cm2 culture flasks with filter cap (Biologix, Hallbergmoos, Germany) containing Sabouraud 4% glucose agar (15 g/L agar, 40 g/L D(+)-glucose, 10 g/L peptone; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) for 8–10 days. Conidia were collected using a spore buffer (0.9% NaCl (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and 0.01% Tween 80 (Fisher Scientific, Vienna, Austria)). To elude mycelial contamination, the conidial suspension was passed through a cell strainer (40 μm; Thermo Scientific, Vienna, Austria). Conidia swelling was controlled under the microscope, as discussed before [47].
2.3. Cell Treatments
Swollen conidia and culture filtrates were prepared as described before [42,47]. In short, to obtain swollen conidia, 108 freshly isolated conidia/mL were incubated in RPMI plus 3.45% MOPS (Fisher Scientific, Vienna, Austria) plus 2% glucose (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) on an environmental shaker–incubator ES-20/60 (BioSan, Riga, Latvia) at 37 °C and maintained at 160 rpm for 2 h. Swollen conidia were further diluted for experiments to the desired concentration, as stated below. To generate fungal culture filtrates, 108 conidia/mL were inoculated in 200 mL Sabouraud medium (40 g/L D(+)-glucose (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), 10 g/L peptone from casein (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany)) and kept on an environmental shaker–incubator ES-20/60 (BioSan, Riga, Latvia) for 24 h at 37 °C and 160 rpm. The suspension was further filtered using a sterile Whatman® paper filter (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), and mycelia were washed with double-distilled water, resuspended and incubated in 200 mL cell culture medium for 24 h at 37 °C and 160 rpm. The sterile culture filtrate medium was incubated in parallel as a control. After 24 h, the culture filtrate suspension was sterile-filtered with a 500 mL Nalgene™ Rapid-Flow™ sterile disposable filter unit with 0.2 µm PES membrane (ThermoScientific, Vienna, Austria) and stored in sterile 15 mL tubes (Corning GmbH, Kaiserslautern, Germany) at −20 °C.
For infection experiments, NCI-H441 cells were seeded into 6-well plates (Biologix, Hallbergmoos, Germany) with 106 cells per well and cultured for 26–28 h. Before infection with A. fumigatus conidia, cells were washed with serum- and antibiotic-free medium and incubated in this medium overnight. Then, 107 swollen conidia/mL were directly applied to the cells and incubated for 4 and 8 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Untreated cells were incubated in parallel as a control in each experiment. For the experiments with culture filtrates, filtrates diluted 1:5 in serum-free medium were applied on cells in 6-well plates (106 cells per well) and incubated for 4 and 8 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Cells treated with a control filtrate medium in the same dilution were incubated in parallel as a control.
2.4. Microscopy
The kinetics of the hyphal growth was examined by time-lapse video microscopy, as previously described [42]. In brief, 105 swollen conidia/mL were transferred to the 8-well Nunc™ Lab-Tek™ chamber slide system (Thermo Scientific, Vienna, Austria), and live imaging was performed in a cell incubator at 37 °C and 5% CO2 using an ioLight Portable Microscope (ioLight, Hampshire, UK) operated with the ioLight app (Vers.: 1.1.1.483) at 37 °C. Video sequences, tracking and quantification of the velocity of hyphal growth were prepared using Fiji software [48] and the “Manual Tracking” plug-in (developed at Institute Curie by F. Cordeli for ImageJ; Orsay, France). Figures were prepared using Fiji software (based on ImageJ 1.51n, maintained by the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USA) and Adobe Photoshop (Adobe Systems Incorporated, San José, CA, USA).
2.5. Real-Time qPCR
RNA was isolated using Tri Reagent™ Solution (Invitrogen, Vienna, Austria) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration was measured in duplicates using a NanoPhotometer NP80 (Implen, Munich, Germany). cDNA was prepared using the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, Vienna, Austria). TaqMan gene expression master mix and TaqMan gene expression assays were used.
Two genes, SP-A1 and SP-A2, encode SP-A1 and SP-A2 proteins in humans [49], and the following assays were used in our experiments: SP-A1 (Hs00831305_s1), SP-A2 (Hs04195463_g1), SP-B (Hs01090667_m1), SP-C (Hs00953663_g1) and SP-D (Hs01108490_m1), which were from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Vienna, Austria). RPLP0 (Hs99999902_m1) was used as the reference gene. For SP-A1, SP-A2, SP-B and RPLP0, RNA concentration of 50 ng was used, and for SP-C and SP-D, -100 ng was used for cDNA synthesis. The qPCR reaction was performed in 96-well plates (Biozym, Vienna, Austria). The following run method was used: Step 1, at 50 °C for 2 min; Step 2, at 98 °C for 10 min; Step 3, at 98 °C at 25 s; and Step 4, at 60 °C for 1 min. Steps 3 and 4 were repeated 40 times. (StepOnePlus RT-PCR cycler; Applied Biosystems, Vienna, Austria). Data obtained were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method to analyze relative changes in gene expression. As a calibrator for the 2−ΔΔCT method, the untreated NCI-H441 cells were used.
2.6. Statistics
All probes were isolated in three independent experiments with two technical repetitions; each experiment included an untreated control performed in the same experiment in parallel. For RT-qPCR experiments, technical duplicates were used for each probe. Data were further analyzed using a multiple unpaired T-test in GraphPad Prisma 9 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA). Only results with a p-value ≤ 0.05 were considered significant. RT-qPCR data were represented as fold change in gene expression normalized to RPLP0 rRNA expression and relative to untreated NCI-H441 cells (taken as one for each single biological and technical repetition).
3. Results
3.1. Kinetics of Fungal Growth
To exclude significant differences in fungal growth between the four A. fumigatus strains and better define time points for the infection experiments, we quantified conidial germination and hyphal growth dynamics and compared ΔpksP, Δugm1 and Δgt4bc to the DAL strain using time-lapse video microscopy. A total of 105 mL pre-swollen conidia were plated on LapTeck slides followed by imaging for 10 h. The start of conidial germination as well as the velocity of hyphal growth (defined as changes in hyphal length per minute) were quantified. Conidial germination started shortly after 5 h of imaging, and a small delay in gemination was detected in Δugm1 strain conidia (Figure 1a,b).
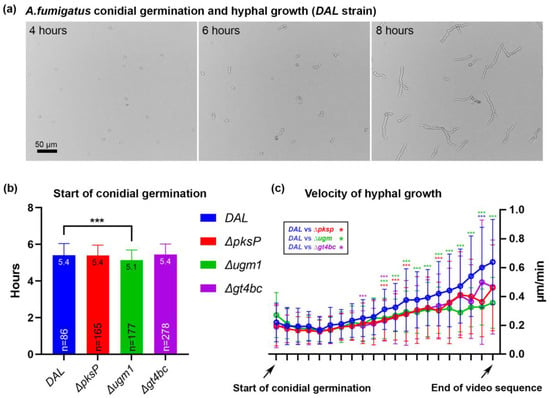
Figure 1.
Conidial germination and dynamics of hyphal growth. (a) Frames of a live-video sequence show examples of hyphal growth after 4, 6 and 8 h of imaging; (b) starting point of conidial germination in four tested A. fumigatus strains. Depicted are mean ± SD of mean as a column, mean as value and number of quantified conidia, n; (c) velocity of hyphal growth. For graphical representation, all germinating conidia were plotted to the first tick of the x-axis with 10 min between data points. Each tick depicts velocity mean ± SD of mean in µm/min. In (b,c) significant differences (p ≤ 0.001) between A. fumigatus strains are marked with *** according to the color scheme.
When we further tracked hyphal growth in individual conidia and quantified the velocity of hyphae growth, we observed that in the first 2 h after the start of germination, no significant differences in growth velocity were observed when comparing DAL (0.21 µm/min ± 0.03 SD) with ΔpksP (0.19 µm/min ± 0.02), Δugm1 (0.20 µm/min ± 0.04) and Δgt4bc (0.19 µm/min ± 0.01) strains. At later time points, the velocity of growth increased exponentially in all strains and reached 0.64 µm/min ± 0.29 (DAL), 0.46 µm/min ± 0.30 (ΔpksP), 0.36 µm/min ± 0.18 (Δugm1) and 0.47 µm/min ± 0.33 (Δgt4bc) at the end of the video sequence. We observed a slightly increased velocity at several time points when comparing the growth dynamics of DAL with ΔpksP, Δugm1 and Δgt4bc strains (marked with asterisks in Figure 1c); the most prominent difference was observed between the DAL and Δugm1 strain (green asterisks in Figure 1c). This observation is in line with previous studies showing a reduced growth phenotype for the Δugm1 mutant [50]. Based on the kinetics of fungal growth in our experiments, we defined two time points of special interest for the following RT-qPCR experiments: 4 h (conidia not yet germinated in any of strains) and 8 h (developed germ tubes in all tested strains).
3.2. Infection of Human NCI-H441 Cells with A. fumigatus Conidia
The lung adenocarcinoma human NCI-H441 cell line resembles bronchiolar epithelial Clara cells in phenotype. It was previously used to evaluate the protein and gene expression of SP [51,52]. In line with previous studies, we detected high levels of SP-A1, SP-A2 (Ct values < 19 in control samples) and SP-B (Ct < 23) and low levels of SP-C (Ct < 30) and SP-D (Ct < 29) gene transcripts [51].
Next, the relative gene expression of SP in cells separately infected with four A. fumigatus strains was measured (Figure 2). When cells were infected for 4 h, no significant changes were observed, as compared to the untreated controls, except for a slight elevation in the SP-D gene expression after infection with Δgt4bc strain conidia. However, when cells were infected for 8 h, a significant downregulation of the SP-C expression was observed in cells treated with DAL (fold change: 0.51 ± 0.19, p < 0.05), ΔpksP (0.57 ± 0.11, p < 0.01), Δugm1 (0.45 ± 0.10, p < 0.001) and Δgt4bc strain (0.58 ± 0.11, p < 0.01) conidia. Interestingly, the fungal infection had no significant effect on the SP-A1 and SP-D expression, except for a slight upregulation of SP-A2 by Δugm1 (fold change: 1.34 ± 0.12, p < 0.05,) and SP-D by the ΔpksP (fold change: 1.11 ± 0.02, p < 0.01). No significant differences were detected in the other samples (Figure 2, Table 1).
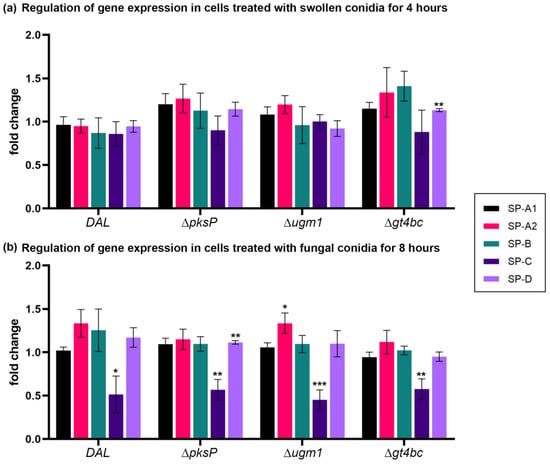
Figure 2.
Relative fold change of the mRNA expression levels of SP-A1, SP-A2, SP-B, SP-C and SP–D. All data are normalized with RPLP0 rRNA expression and given as relative to untreated control. Cells were treated with swollen conidia obtained from A.fumigatus strains for 4 h (a) and 8 h (b). Columns depict mean ± SE of the mean (* p ≤ 0.05), (** p ≤ 0.01), (*** p ≤ 0.001). See also Table 1.

Table 1.
Statistical analysis of RT-qPCR data.
3.3. Treatment of Human NCI-H441 Cells with A. fumigatus Culture Filtrates
Next, NCI-H441 cells were treated with culture filtrates collected from the DAL A. fumigatus strain. The treatment of cells with undiluted culture filtrates or 1:3 dilution with growth medium caused immediate cell detachment (data not shown). Furthermore, 1:5 dilution of filtrates in the growth medium was well tolerated by cells and, therefore, used in our experiments.
After 4 h of treatment with culture filtrates, a small downregulation of the SP-C gene expression was observed (0.82 ± 0.03, p-value < 0.001), while SP-A1, SP-A2, SP-B and SP–D mRNA were not regulated. However, treatment with culture filtrates for 8 h resulted in a moderate downregulation of all SP mRNA, with SP-C being the most significant (Figure 3, Table 1).
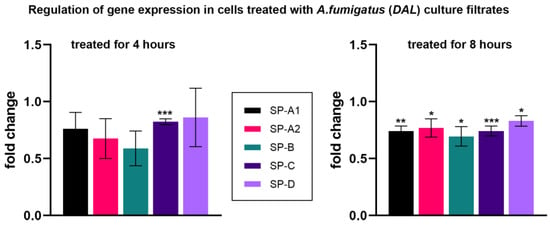
Figure 3.
Relative fold change of the mRNA expression levels of SP-A1, SP-A2, SP-B, SP-C and SP–D. All data are normalized with RPLP0 rRNA expression and given as relative to untreated control. Cells were treated with culture filtrates obtained from A. fumigatus DAL strain for 4 h (left graph) and 8 h (right graph). Columns depict mean ± SE of the mean (* p ≤ 0.05), (** p ≤ 0.01), (*** p ≤ 0.001). See also Table 1.
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the gene expression of the pulmonary SP (SP-A1, SP-A2, SP-B, SP-C and SP-D) in human NCI-H441 cells following an A. fumigatus infection. We tested the effect of DAL, DHN-melanin-deficient, GAG-deficient and GM-deficient mutant A. fumigatus strains as well as culture filtrates incubated with cells for 4 and 8 h.
Our results show that a short-term infection of NCI-H441 cells did not regulate the SP mRNA. Instead, 8 h of infection caused consistent downregulation of the SP-C gene. Within this time, conidial attachment, germination and hyphal growth took place [47,53]. Thus, in comparison to short-term experiments with conidia, NCI-H441 cells were exposed to another biochemical composition of the fungal cell wall when PAMPs, e.g., β-glucan, chitin, GM and GAG, were exposed to lung cells [10,15]. Surprisingly, we did not observe a significant downregulation of SP-A and SP-D mRNA and no difference was identified between infections with DHN-melanin-, GAG- and GM-deficient strains.
Previous studies demonstrated that infection with A. fumigatus caused the differential regulation of surfactant gene expression in vitro and in vivo. In line with our results, a downregulation of lung-specific SP-C mRNA was observed in cells and mouse models [36,43,44]. A study of A. fumigatus-induced allergic airway inflammation in mice showed decreased mRNA and protein expression of SP-B and SP-C that was accompanied by an upregulated SP-D protein expression without changes in mRNA levels [36]. Protein and mRNA levels of SP-A were not changed in this model [36]. Surprisingly, we did not identify significant differences between the four mutant strains: the downregulation of SP-C mRNA was independent of the fungal strain. A more recent report revealed the downregulation of SP-D mRNA in human alveolar A549 cells after 6 h of incubation with A. fumigatus conidia [44]. In our preliminary experiments, we tested a long-term culture model of A549 cells as a model to consider the deferential regulation of SP in infection settings. This model was shown to express increased levels of SP, as compared to regular A549 cell cultures [54]. Infection of these cells with A. fumigatus swollen conidia did not cause any consistent changes in SP-A and SP-D mRNA in our experiments (unpublished data).
Our data suggest that secondary metabolites of A. fumigatus, rather than contact/binding to the fungal cell wall polysaccharides, may alter the mRNA expression of SP. In line with this hypothesis, we observed that the treatment of NCI-H441 cells with culture filtrates resulted in a moderate decrease in gene expression of all SP mRNA when cells were incubated for 8 h. Short exposure to culture filtrates caused a small inhibition of SP-C mRNA, whereas changes in other SP genes were not statistically significant. Culture filtrates gained from A. fumigatus were previously shown to have a cytotoxic effect on alveolar cells [55] and inhibit a pulmonary immune response [21,56,57]. The effect of the filtrates on SP expression has not been reported before. Importantly, we used diluted filtrates that did not cause cell detachment or apoptosis and observed a moderate inhibiting effect on all tested SP genes.
The major function of SP-C is to reduce the surface tension at the air–liquid alveolar interface by regulating lipid adsorption and transfer of lipids between surfactant membranes, thus providing surfactant film stability [58]. Data from patients and mice models showed that SP-C has an important antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory function in the lung. Thus, patients with mutations in the SP-C gene developed familial interstitial lung disease [34]. Knockout of the SP-C gene in mice resulted in progressive lung inflammation [59]. These mice were also more susceptible to respiratory syncytial virus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and showed robust inflammation in the lungs after gram-negative bacterial infection [37,60]. The binding of SP-C to bacterial lipopolysaccharide has been observed in vitro [35,59,61]. Several studies showed that exogenous synthetic or natural surfactant treatment reduced symptoms of lung infection and improved bacterial clearance [62]. In vitro experiments demonstrated that treatment with Survanta (a natural surfactant product containing SP-B and SP-C and phospholipids) inhibited proinflammatory cytokine release from LPS-stimulated human alveolar macrophages [63]. Thus, decreased levels of SP-C may impair the resolution of lung inflammation and stimulate progressive interstitial disease [59]. The molecular mechanisms of SP-C inhibition by A. fumigatus observed in our study and by others remain unclear.
To summarize, our data show consistent downregulation of lung-specific SP-C mRNA in NCI-H441 cells caused by A. fumigatus. Further elucidating this inhibitory effect in more detail is important to better understand how potentially infectious pathogens overcome the defense mechanisms in the human lung. Moreover, data on the combinational use of pulmonary surfactants and antifungal agents against A.fumigatus have only started to arise [42,64] and should be investigated in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S.-M. and S.P.; methodology, L.H. and L.L.; validation and formal analysis, N.S.-M., L.H. and L.L.; investigation, L.L. and L.H.; resources, N.S.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.-M. and L.H.; visualization, N.S.-M., L.H. and L.L.; supervision, N.S.-M.; project administration, N.S.-M. and S.P.; funding acquisition, N.S.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by TWF Tirol Wissenschaftsfoerderung to Natalia Schiefermeier-Mach (grant number: F.33484/6-2021).
Data Availability Statement
All data and materials used in the analysis are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rhodes, J.C. Aspergillus fumigatus: Growth and virulence. Med. Mycol. 2006, 44 (Suppl. S1), S77–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Sugui, J.A. Aspergillus fumigatus—What Makes the Species a Ubiquitous Human Fungal Pathogen? PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.-P.; Chamilos, G. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00140-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osherov, N. Interaction of the pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus with lung epithelial cells. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases-Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, A.; Fernández-Molina, J.V.; Bikandi, J.; Ramírez, A.; Margareto, J.; Sendino, J.; Hernando, F.L.; Pontón, J.; Garaizar, J.; Rementeria, A. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2010, 27, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.; Fontaine, T.; Heddergott, C.; Robinet, P.; Aimanianda, V.; Beau, R.; Beauvais, A.; Mouyna, I.; Prevost, M.-C.; Fekkar, A.; et al. Biosynthesis of cell wall mannan in the conidium and the mycelium of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T.; Eggleton, P.; Kishore, U.; Strong, P.; Aggrawal, S.S.; Sarma, P.U.; Reid, K.B. Binding of pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia enhances phagocytosis and killing by human neutrophils and alveolar macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3171–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.-P.; Beauvais, A.; Chamilos, G. The Cell Wall of the Human Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Organization, Immune Response, and Virulence. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltussen, T.J.H.; Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Molecular Mechanisms of Conidial Germination in Aspergillus spp. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, A.; Fontaine, T.; Aimanianda, V.; Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus cell wall and biofilm. Mycopathologia 2014, 178, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinekamp, T.; Thywißen, A.; Macheleidt, J.; Keller, S.; Valiante, V.; Brakhage, A.A. Aspergillus fumigatus melanins: Interference with the host endocytosis pathway and impact on virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayry, J.; Beaussart, A.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Sharma, M.; Bansal, K.; Kniemeyer, O.; Aimanianda, V.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kaveri, S.V.; Kwon-Chung, K.J.; et al. Surface structure characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia mutated in the melanin synthesis pathway and their human cellular immune response. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, B.; Koch, A.; Schmidt, A.; Wanner, G.; Gehringer, H.; Bhakdi, S.; Brakhage, A.A. Isolation and characterization of a pigmentless-conidium mutant of Aspergillus fumigatus with altered conidial surface and reduced virulence. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 5110–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briard, B.; Muszkieta, L.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Galactosaminogalactan of Aspergillus fumigatus, a bioactive fungal polymer. Mycologia 2016, 108, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelat, F.N.; Beauvais, A.; Liu, H.; Lee, M.J.; Snarr, B.D.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Kravtsov, I.; Hoareau, C.M.Q.; Vanier, G.; et al. Aspergillus galactosaminogalactan mediates adherence to host constituents and conceals hyphal β-glucan from the immune system. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, D.C. Molecular mechanism of Aspergillus fumigatus adherence to host constituents. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, C.; Rambach, G.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Howell, P.L.; Sheppard, D.C. Galactosaminogalactan (GAG) and its multiple roles in Aspergillus pathogenesis. Virulence 2019, 10, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek-Ananth, R.P.; Mohanraj, K.; Vandanashree, M.; Jhingran, A.; Craig, J.P.; Samal, A. Comparative systems analysis of the secretome of the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus and other Aspergillus species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krappmann, S. How to invade a susceptible host: Cellular aspects of aspergillosis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Amitani, R.; Ikegami, Y.; Nawada, R.; Lee, W.J.; Kuze, F. Suppressive effects of Aspergillus fumigatus culture filtrates on human alveolar macrophages and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, K.; Shimada, H.; Kamaguchi, A.; Sakaguchi, O. Studies on the toxin of Aspergillus fumigatus. VII. Purification and some properities of hemolytic toxin (asp-hemolysin) from culture filtrates and mycelia. Microbiol. Immunol. 1977, 21, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, H.F.; Tomee, J.F.; van de Riet, M.A.; Timmerman, A.J.; Borger, P. Protease-dependent activation of epithelial cells by fungal allergens leads to morphologic changes and cytokine production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, H.; Amar, D.; Levdansky, E.; Mircus, G.; Shadkchan, Y.; Shamir, R.; Osherov, N. PrtT-regulated proteins secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus activate MAPK signaling in exposed A549 lung cells leading to necrotic cell death. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, K.; Watanabe, A. Aspergillus mycotoxins and their effect on the host. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. S1), S95–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Sekine, T.; Waku, M.; Nishimura, K.; Miyaji, M.; Kuriyama, T. Immunosuppressive substances in Aspergillus fumigatus culture filtrate. J. Infect. Chemother. 2003, 9, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitani, R.; Taylor, G.; Elezis, E.N.; Llewellyn-Jones, C.; Mitchell, J.; Kuze, F.; Cole, P.J.; Wilson, R. Purification and characterization of factors produced by Aspergillus fumigatus which affect human ciliated respiratory epithelium. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 3266–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.W.; Venaille, T.J.; Mendis, A.H.; McAleer, R. Allergens as proteases: An aspergillus fumigatus proteinase directly induces human epithelial cell detachment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, O.; Olmeda, B.; Alonso, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Lipid-Protein and Protein-Protein Interactions in the Pulmonary Surfactant System and Their Role in Lung Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, C.W.; Samaha, G.; Garcia-Arcos, I. Alveolar lipids in pulmonary disease. A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Mallampalli, R.K. The Role of Surfactant in Lung Disease and Host Defense against Pulmonary Infections. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouch, E.; Wright, J.R. Surfactant proteins a and d and pulmonary host defense. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selman, M.; Lin, H.-M.; Montaño, M.; Jenkins, A.L.; Estrada, A.; Lin, Z.; Wang, G.; DiAngelo, S.L.; Guo, X.; Umstead, T.M.; et al. Surfactant protein A and B genetic variants predispose to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hum. Genet. 2003, 113, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogee, L.M.; Dunbar, A.E.; Wert, S.E.; Askin, F.; Hamvas, A.; Whitsett, J.A. A mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with familial interstitial lung disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto, L.A.; Li, J.; Synguelakis, M.; Johansson, J.; Chaby, R. Structural basis for interactions between lung surfactant protein C and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23484–23492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haczku, A.; Atochina, E.N.; Tomer, Y.; Chen, H.; Scanlon, S.T.; Russo, S.; Xu, J.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Beers, M.F. Aspergillus fumigatus-induced allergic airway inflammation alters surfactant homeostasis and lung function in BALB/c mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 25, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, S.W.; Witt, T.L.; Senft, A.P.; Baatz, J.E.; Folger, D.; Maxfield, M.D.; Akinbi, H.T.; Newton, D.A.; Prows, D.R.; Korfhagen, T.R. Surfactant protein C-deficient mice are susceptible to respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L64–L72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T.; Reid, K.B.M.; Clark, H.; Singh, M.; Nayak, A.; Sarma, P.U.; Hawgood, S.; Kishore, U. Susceptibility of mice genetically deficient in SP-A or SP-D gene to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, L.; Le Blay, K.; Auger, G.; Blanot, D.; Chaby, R. Interaction of bacterial lipopolysaccharide with mouse surfactant protein C inserted into lipid vesicles. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L776–L785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliardo, R.; Pérez-Gil, J.; de Smedt, S.; Raemdonck, K. Pulmonary surfactant and drug delivery: Focusing on the role of surfactant proteins. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.S.W.; Rani, M.; Dodagatta-Marri, E.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Kishore, U.; Bayry, J.; Latgé, J.-P.; Sahu, A.; Madan, T.; Aimanianda, V. Fungal melanin stimulates surfactant protein D-mediated opsonization of and host immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus spores. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.S.W.; Dellière, S.; Schiefermeier-Mach, N.; Lechner, L.; Perkhofer, S.; Bomme, P.; Fontaine, T.; Schlosser, A.G.; Sorensen, G.L.; Madan, T.; et al. Surfactant protein D inhibits growth, alters cell surface polysaccharide exposure and immune activation potential of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell Surf. 2022, 8, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-S.; Shin, K.-S. Transcription Factor HSF1 Suppresses the Expression of Surfactant Protein D in Cells Infected with Aspergillus fumigatus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-S. Transcription Factor PU.1 Inhibits Aspergillus fumigatus Infection via Surfactant Protein-D. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochina, E.N.; Beers, M.F.; Tomer, Y.; Scanlon, S.T.; Russo, S.J.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Haczku, A. Attenuated allergic airway hyperresponsiveness in C57BL/6 mice is associated with enhanced surfactant protein (SP)-D production following allergic sensitization. Respir. Res. 2003, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thau, N.; Monod, M.; Crestani, B.; Rolland, C.; Tronchin, G.; Latgé, J.P.; Paris, S. rodletless mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4380–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefermeier-Mach, N.; Perkhofer, S.; Heinrich, L.; Haller, T. Stimulation of surfactant exocytosis in primary alveolar type II cells by A. fumigatus. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floros, J.; Wang, G.; Mikerov, A.N. Genetic complexity of the human innate host defense molecules, surfactant protein A1 (SP-A1) and SP-A2--impact on function. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2009, 19, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarre, C.; Beau, R.; Balloy, V.; Fontaine, T.; Wong Sak Hoi, J.; Guadagnini, S.; Berkova, N.; Chignard, M.; Beauvais, A.; Latgé, J.-P. Galactofuranose attenuates cellular adhesion of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucka, Z.; Vanhara, P.; Koutna, I.; Tesarova, L.; Potesilova, M.; Stejskal, S.; Simara, P.; Dolezel, J.; Zvonicek, V.; Coufal, O.; et al. Differential effects of insulin and dexamethasone on pulmonary surfactant-associated genes and proteins in A549 and H441 cells and lung tissue. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miakotina, O.L.; Goss, K.L.; Snyder, J.M. Insulin utilizes the PI 3-kinase pathway to inhibit SP-A gene expression in lung epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefermeier-Mach, N.; Haller, T.; Geley, S.; Perkhofer, S. Migrating Lung Monocytes Internalize and Inhibit Growth of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia. Pathogens 2020, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.R.; Abdullatif, M.B.; Burnett, E.C.; Kempsell, K.E.; Conforti, F.; Tolley, H.; Collins, J.E.; Davies, D.E. Long Term Culture of the A549 Cancer Cell Line Promotes Multilamellar Body Formation and Differentiation towards an Alveolar Type II Pneumocyte Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P.; Verhaegen, S.; Clynes, M.; Kavanagh, K. Culture filtrates of Aspergillus fumigatus induce different modes of cell death in human cancer cell lines. Mycopathologia 1999, 146, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, L.Y.; Sheppard, D.C.; Gravelat, F.N.; Patterson, T.F.; Filler, S.G. Aspergillus fumigatus stimulates leukocyte adhesion molecules and cytokine production by endothelial cells in vitro and during invasive pulmonary disease. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomee, J.F.; Wierenga, A.T.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Kauffman, H.K. Proteases from Aspergillus fumigatus induce release of proinflammatory cytokines and cell detachment in airway epithelial cell lines. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, S.; Beers, M.F. Surfactant protein C: Its unique properties and emerging immunomodulatory role in the lung. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, S.W.; Maxfield, M.D.; Ruetschilling, T.L.; Akinbi, H.T.; Baatz, J.E.; Kitzmiller, J.A.; Page, K.; Xu, Y.; Bao, E.L.; Korfhagen, T.R. Persistence of LPS-induced lung inflammation in surfactant protein-C-deficient mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, S.W.; Senft, A.P.; Whitsett, J.A.; Maxfield, M.D.; Ross, G.F.; Richardson, T.R.; Prows, D.R.; Xu, Y.; Korfhagen, T.R. Macrophage dysfunction and susceptibility to pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in surfactant protein C-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, L.A.; Synguelakis, M.; Espinassous, Q.; Lepoivre, M.; Johansson, J.; Chaby, R. Cellular antiendotoxin activities of lung surfactant protein C in lipid vesicles. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milad, N.; Morissette, M.C. Revisiting the role of pulmonary surfactant in chronic inflammatory lung diseases and environmental exposure. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, B.; Abraham, S.; Bonfield, T.L.; Malur, A.; Deb, A.; DiDonato, J.A.; Kavuru, M.S.; Thomassen, M.J. Surfactant blocks lipopolysaccharide signaling by inhibiting both mitogen-activated protein and IkappaB kinases in human alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwolf, K.K.; Hoertnagl, C.; Lass-Floerl, C.; Groll, A.H. Interaction in vitro of pulmonary surfactant with antifungal agents used for treatment and prevention of invasive aspergillosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).