Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
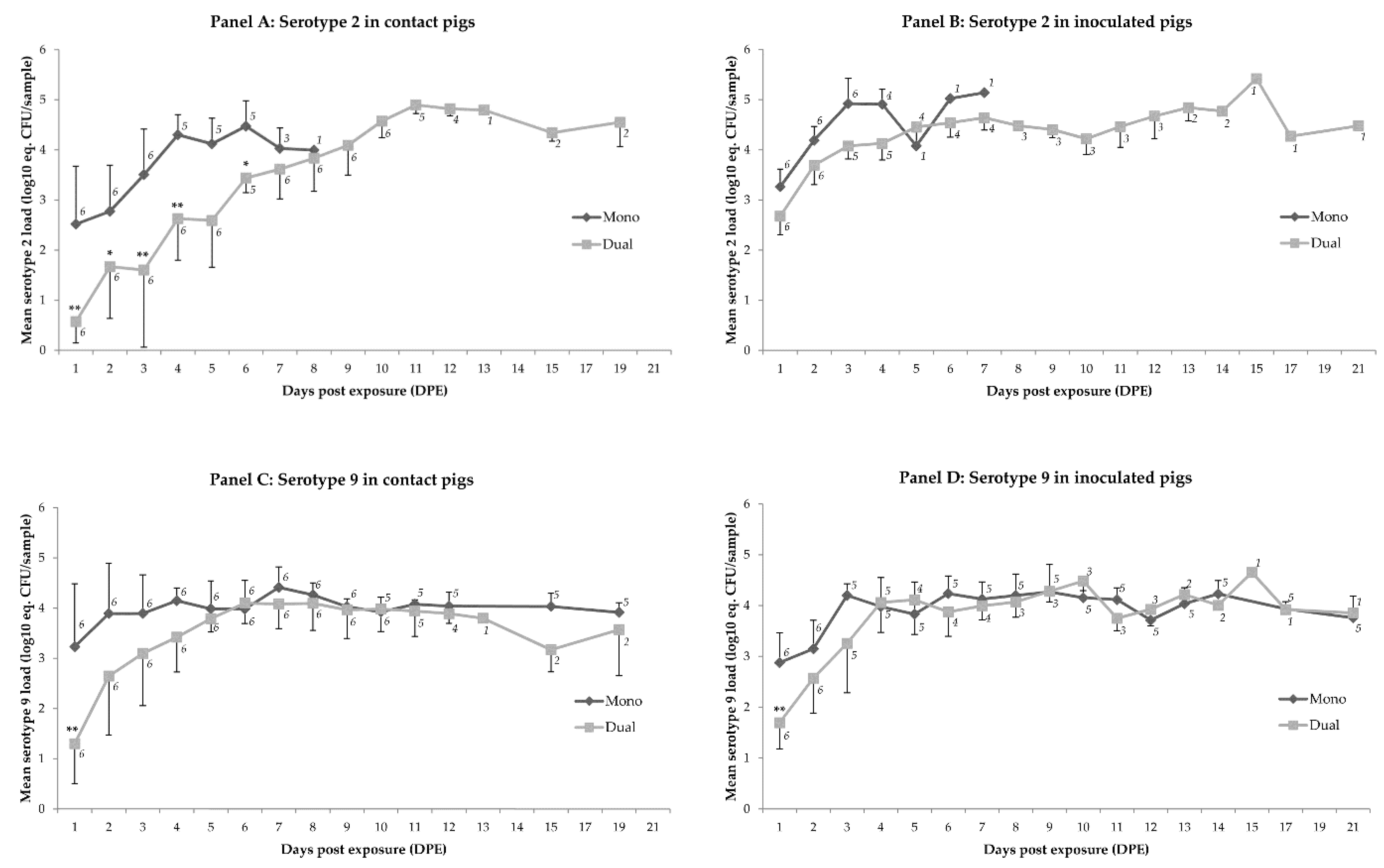
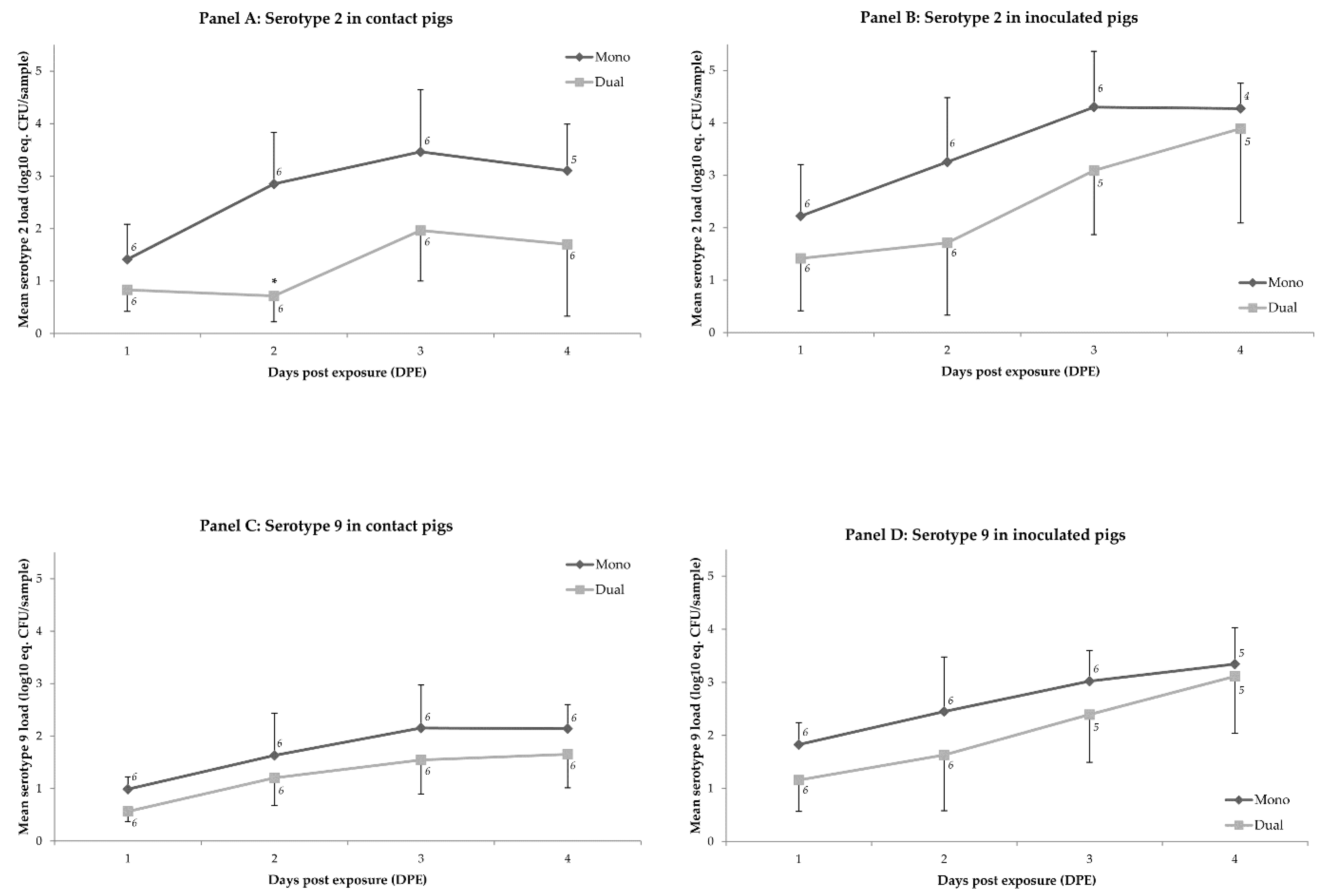
2.1. Colonization
2.2. Transmission
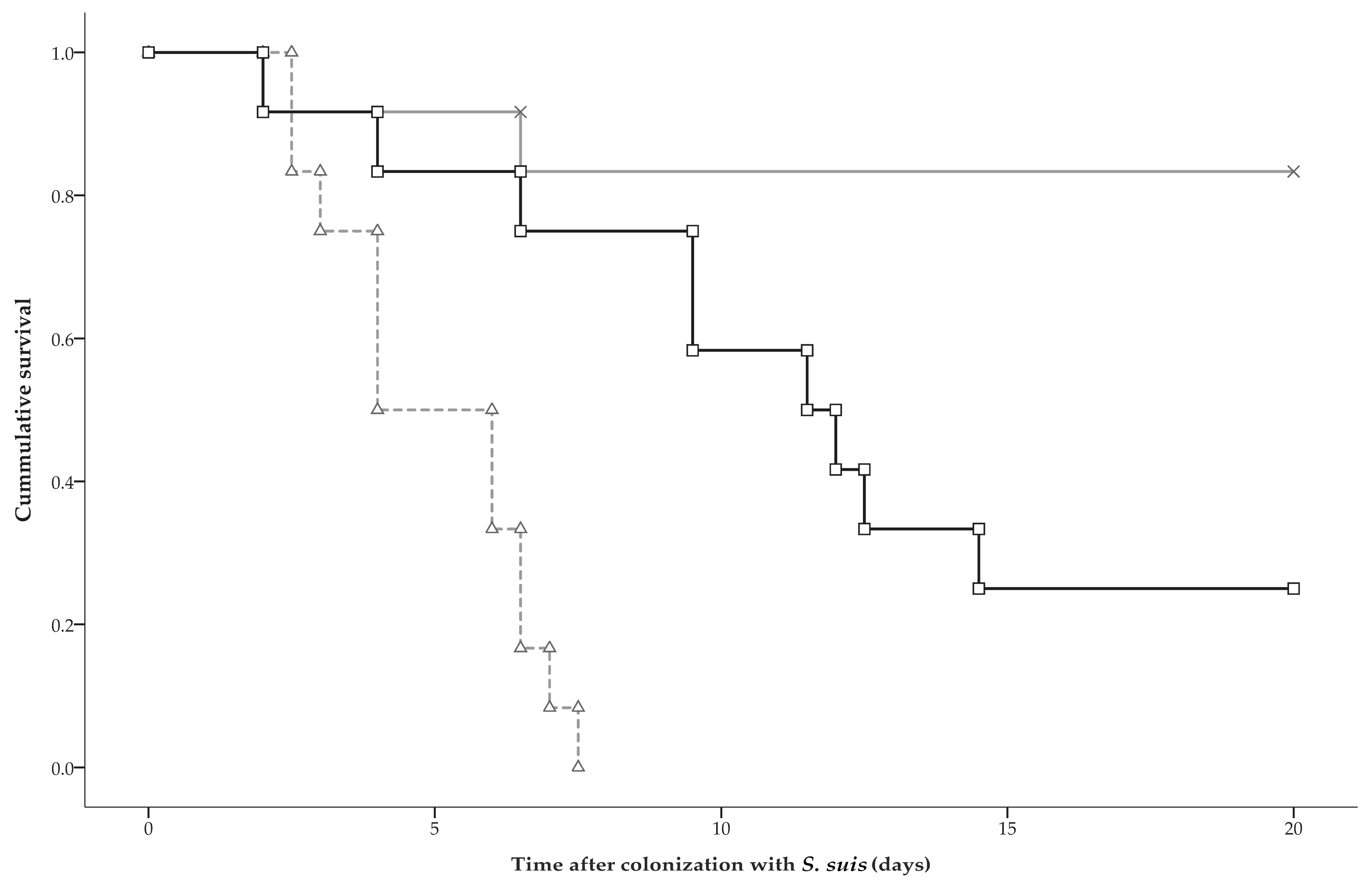
2.3. Clinical Disease and Mortality
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inoculum
4.2. Pigs
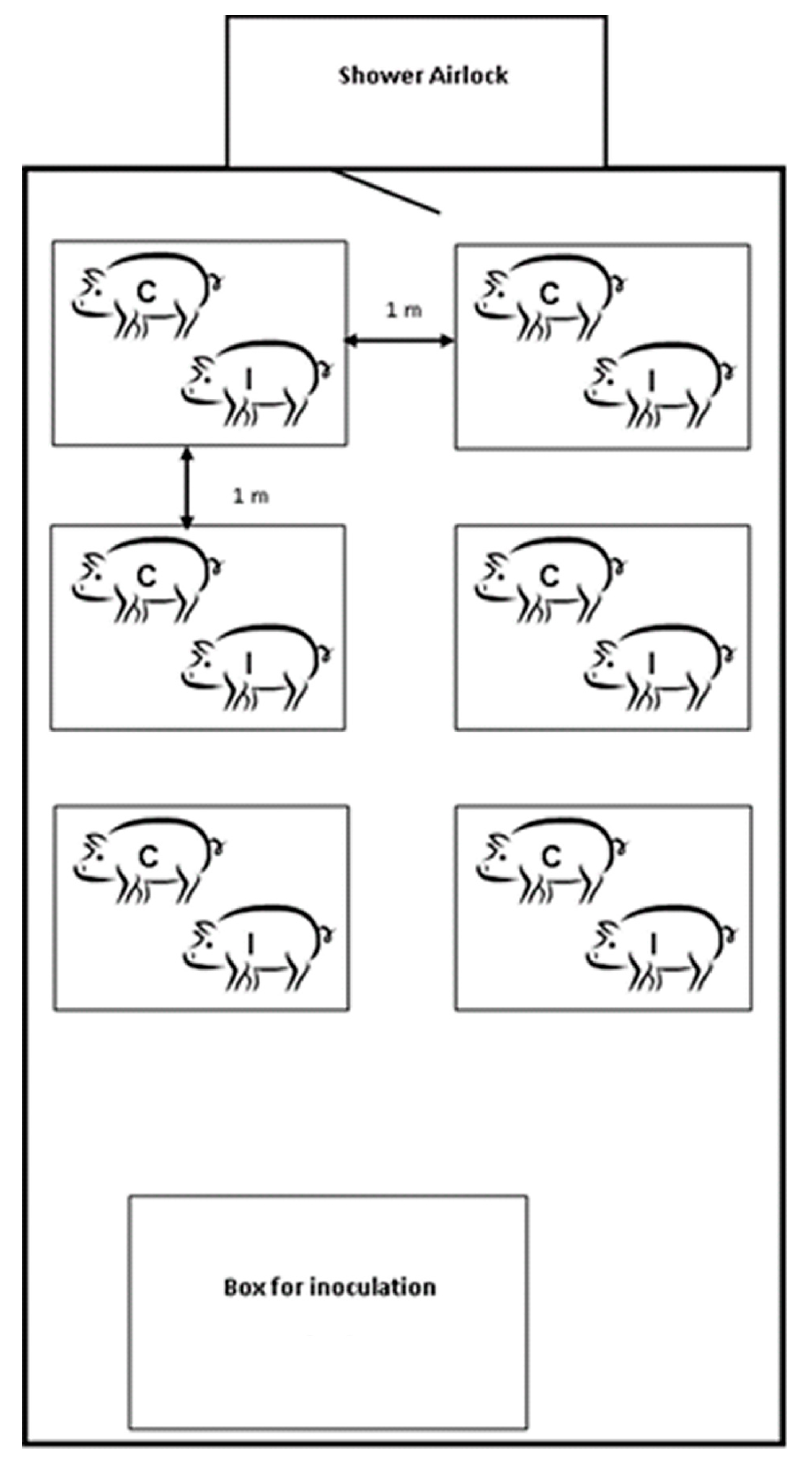
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Clinical Inspection
4.5. Sampling
4.6. Laboratory Tests
4.6.1. Bacterial Examination
4.6.2. Multiplex Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.7.1. S. suis Colonization
4.7.2. Animal Survival
4.7.3. Transmission
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottschalk, M. Streptococcosis. In Diseases of Swine, 10th ed.; Zimmerman, J., Karriker, L., Ramirez, A., Schwarz, K., Stevenson, G., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: West Sussex, UK, 2012; pp. 841–855. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, M.; Xu, J.; Calzas, C.; Segura, M. Streptococcus suis: A new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic pathogen? Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, M.; Calzas, C.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Initial steps of the pathogenesis of the infection caused by Streptococcus suis: Fighting against nonspecific defenses. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3772–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent—An update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Ji, S.; Liu, Z.; Lan, R.; Huang, Y.; Bai, X.; Gottschalk, M.; Xu, J. Eight Novel Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis Gene Loci Identified in Nontypeable Streptococcus suis Isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Ma, J.; Dong, W.; Song, W.; Wang, K.; Lu, C.; Yao, H. Novel variant serotype of Streptococcus suis isolated from piglets with meningitis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, J.L.; Higgins, R.; D’Allaire, S.; Charette, R.; Boudreau, M.; Gottschalk, M. Distribution of the different capsular types of Streptococcus suis in nineteen swine nurseries. Can. Vet. J. 1993, 34, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Joosten, J.J.; Smith, H.E. Multiplex PCR assays for simultaneous detection of six major serotypes and two virulence-associated phenotypes of Streptococcus suis in tonsillar specimens from pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2922–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, M.; Lacouture, S. Canada: Distribution of Streptococcus suis (from 2012 to 2014) and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (from 2011 to 2014) serotypes isolated from diseased pigs. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heath, P.J.; Hunt, B.W. Streptococcus suis serotypes 3 to 28 associated with disease in pigs. Vet. Rec. 2001, 148, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Jorsal, S.E.; Jensen, N.E. Serological characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus suis isolates from diagnostic samples in Denmark during 1995 and 1996. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 60, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarradas, C.; Perea, A.; Vela, A.I.; Goyache, J.; Dominguez, L.; Fernández-Garaizabal, J.F.; Borge, C.; Huerta, B.; Luque, I. Distribution of serotypes of Streptococcus suis isolated from diseased pigs in Spain. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, A.A.; van den Berg, A.J.; Baars, J.C.; Nielsen, B.; Johannsen, L.W. Production of suilysin, the thiol-activated haemolysin of Streptococcus suis, by field isolates from diseased pigs. Vet. Rec. 1995, 137, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Smith, H.E.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Peperkamp, K.; Vecht, U. Distribution of capsular types and production of muramidase-released protein (MRP) and extracellular factor (EF) of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased pigs in seven European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultsz, C.; Jansen, E.; Keijzers, W.; Rothkamp, A.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van der Ende, A. Differences in the population structure of invasive Streptococcus suis strains isolated from pigs and from humans in the Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, I.; Tarradas, C.; Arenas, A.; Maldonado, A.; Astorga, R.; Perea, A. Streptococcus suis serotypes associated with different disease conditions in pigs. Vet. Rec. 1998, 142, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, C.; Pena, J.; Suarez, P.; Imaz, M.; Castro, J.M. Isolation and distribution of Streptococcus suis capsular types from diseased pigs in Spain. Zentralbl. Veterinarmed. B 1993, 40, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela, A.I.; Goyache, J.; Tarradas, C.; Luque, I.; Mateos, A.; Moreno, M.A.; Borge, C.; Perea, J.A.; Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F. Analysis of genetic diversity of Streptococcus suis clinical isolates from pigs in Spain by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auranen, K.; Mehtälä, J.; Tanskanen, A.S.; Kaltoft, M. Between-strain competition in acquisition and clearance of pneumococcal carriage—Epidemiologic evidence from a longitudinal study of day-care children. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erästö, P.; Hoti, F.; Granat, S.M.; Mia, Z.; Mäkelä, P.H.; Auranen, K. Modelling multi-type transmission of pneumococcal carriage in Bangladeshi families. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, S.D.; Frey, P.; Aebi, S.; Hinds, J.; Mühlemann, K. Multiple colonization with S. pneumoniae before and after introduction of the seven-valent conjugated pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitch, M.; Abdullahi, O.; D’Amour, O.A.; Xie, W.; Weinberger, D.M.; Tchetgen Tchetgen, E.; Scott, J.A.G. Estimating rates of carriage acquisition and clearance and competitive ability for pneumococcal serotypes in Kenya with a Markov transition model. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitch, M.; Dykes, J.K.; Johnson, S.E.; Ades, E.W.; King, J.; Briles, D.E.; Carlone, G.M. Competition among Streptococcus pneumoniae for intranasal colonization in a mouse model. Vaccine 2000, 18, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.R.; Reddinger, R.M.; Hakansson, A.P. High levels of genetic recombination during nasopharyngeal carriage and biofilm formation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. MBio 2012, 3, e00200–e00212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawid, S.; Roche, A.M.; Weiser, J.N. The blp bacteriocins of Streptococcus pneumoniae mediate intraspecies competition both in vitro and in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzciński, K.; Li, Y.; Weinberger, D.M.; Thompson, C.M.; Cordy, D.; Bessolo, A.; Malley, R.; Lipsitch, M. Effect of serotype on pneumococcal competition in a mouse colonization model. MBio 2015, 6, e00902–e00915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swildens, B. Detection and Transmission of Extracellular Factor Producing Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Strains in Pigs. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 17 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wichgers Schreur, P.J.; van Weeghel, C.; Rebel, J.M.; Smits, M.A.; van Putten, J.P.; Smith, H.E. Lysozyme resistance in Streptococcus suis is highly variable and multifactorial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawei, G.; Liping, W.; Chengping, L. In vitro biofilm forming potential of Streptococcus suis isolated from human and swine in China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W. Introduction to biofilm. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1999, 11, 217–221,237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuzeville, S.; Auger, J.P.; Dumesnil, A.; Roy, D.; Lacouture, S.; Fittipaldi, N.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Serotype-specific role of antigen I/II in the initial steps of the pathogenesis of the infection caused by Streptococcus suis. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, L.J.; Maddocks, S.E.; Larson, M.R.; Forsgren, N.; Persson, K.; Deivanayagam, C.C.; Jenkinson, H.F. The changing faces of Streptococcus antigen I/II polypeptide family adhesins. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreur, P.J.; Rebel, J.M.; Smits, M.A.; van Putten, J.P.; Smith, H.E. Differential activation of the Toll-like receptor 2/6 complex by lipoproteins of Streptococcus suis serotypes 2 and 9. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijerink, M.; Ferrando, M.L.; Lammers, G.; Taverne, N.; Smith, H.E.; Wells, J.M. Immunomodulatory effects of Streptococcus suis capsule type on human dendritic cell responses, phagocytosis and intracellular survival. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melancon, D.; Grenier, D. Production and properties of bacteriocin-like inhibitory substances from the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4482–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Weinberger, D.M.; Thompson, C.M.; Trzciński, K.; Lipsitch, M. Surface charge of Streptococcus pneumoniae predicts serotype distribution. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 4519–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathaway, L.J.; Brugger, S.D.; Morand, B.; Bangert, M.; Rotzetter, J.U.; Hauser, C.; Graber, W.A.; Gore, S.; Kadioglu, A.; Mühlemann, K. Capsule type of Streptococcus pneumoniae determines growth phenotype. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, T.J.; Bouma, A.; Daemen, A.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Stegeman, A.; Klinkenberg, D. Association between transmission rate and disease severity for Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae infection in pigs. Vet. Res. 2013, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Labrie, J.; Tremblay, Y.D.; Oropeza-Navarro, R.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Auxotrophic Actinobacillus pleurpneumoniae grows in multispecies biofilms without the need for nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NAD) supplementation. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.H.; Meng, F.; Seitz, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Herrler, G. Sialic acid-dependent interactions between influenza viruses and Streptococcus suis affect the infection of porcine tracheal cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greeff, A.; van Selm, S.; Buys, H.; Harders-Westerveen, J.F.; Tunjungputri, R.N.; de Mast, Q.; van der Ven, A.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; de Jonge, M.I.; Smith, H.E. Pneumococcal colonization and invasive disease studied in a porcine model. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greeff, A.; Wisselink, H.J.; de Bree, F.M.; Schultsz, C.; Baums, C.G.; Thi, H.N.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smith, H.E. Genetic diversity of Streptococcus suis isolates as determined by comparative genome hybridization. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velthuis, A.G.; Bouma, A.; Katsma, W.E.; Nodelijk, G.; De Jong, M.C. Design and analysis of smallscale transmission experiments with animals. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 135, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthelot-Hérault, F.; Gottschalk, M.; Labbé, A.; Cariolet, R.; Kobisch, M. Experimental airborne transmission of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 82, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, N.; Bouma, A.; Daemen, I.; Klinkenberg, D.; van Leengoed, L.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Stegeman, A. Effect of spatial separation of pigs on spread of Streptococcus suis serotype 9. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, A.; Van Nes, A.; de Jong, M.C.; Bolder, F.W. Assessment of the effectiveness of vaccination against pseudorabies in finishing pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouma, A. Determination of the effectiveness of pseudorabies marker vaccines in experiments and field trials. Biologicals 2005, 33, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baums, C.G.; Bruggemann, C.; Kock, C.; Beineke, A.; Waldmann, K.H.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Immunogenicity of an autogenous Streptococcus suis bacterin in preparturient sows and their piglets in relation to protection after weaning. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beineke, A.; Bennecke, K.; Neis, C.; Schröder, C.; Waldmann, K.H.; Baumgärtner, W.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. Comparative evaluation of virulence and pathology of Streptococcus suis serotypes 2 and 9 in experimentally infected growers. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 128, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, C.N.; Bouma, A.; Daemen, A.J.; van Leengoed, L.A.; Jonker, F.H.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Stegeman, J.A. Homologous whole bacterin vaccination is not able to reduce Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain 7997 transmission among pigs or colonization. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Reek, F.H.; Vecht, U.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smits, M.A.; Smith, H.E. Detection of virulent strains of Streptococcus suis type 2 and highly virulent strains of Streptococcus suis type 1 in tonsillar specimens of pigs by PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 67, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriese, L.A.; Ceyssens, K.; Hommez, J.; Kilpper-Balz, R.; Schleifer, K.H. Characteristics of different Streptococcus suis ecovars and description of a simplified identification method. Vet. Microbiol. 1991, 26, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, N.; Daemen, I.; Verstappen, K.; de Greeff, A.; Smith, H.; Duim, B. Simultaneous Quantification and Differentiation of Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 by Quantitative Real-Time PCR, Evaluated in Tonsillar and Nasal Samples of Pigs. Pathogens 2016, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, T.J.; Bouma, A.; Klinkenberg, D.; Daemen, A.J.; Stegeman, J.A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Duim, B. Detection of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in pigs by real-time quantitative PCR for the apxIVA gene. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.E.; Damman, M.; van der Velde, J.; Wagenaar, F.; Wisselink, H.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smits, M.A. Identification and characterization of the cps locus of Streptococcus suis serotype 2: The capsule protects against phagocytosis and is an important virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dohoo, I.; Martin, W.; Stryhn, H. Veterinary Epidemiologic Research, 2nd ed.; AVC Inc.: Charlottetown, PE, Canada, 2007; 706p, ISBN 978-0-919013-41-4. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Development Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models; R Package Version 3.1-103; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, N.G. Analysis of Infectious Disease Data, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1989; pp. 139–174. ISBN 978-0412309908. [Google Scholar]
- Kroese, A.H.; De Jong, M.C.M. Design and analysis of transmission experiments. In Proceedings of the Meeting for the Society for Veterinary Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands, 28–30 March 2001; pp. xxi–xxxvii. [Google Scholar]
- Velthuis, A.G.; De Jong, M.C.; Kamp, E.M.; Stockhofe, N.; Verheijden, J.H. Design and analysis of an Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae transmission experiment. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 60, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1989; 506p, ISBN 978-0412317606. [Google Scholar]
| Inoculated Pigs | Contact Exposed Pigs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (DPE) 1 | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value |
| 1 | 0.64 | 0.352 | 1.57 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 0.46 | 0.873 | 1.40 | 0.004 |
| 3 | 0.79 | 0.158 | 1.72 | <0.001 |
| 4 | 0.82 | 0.158 | 1.76 | <0.001 |
| 5 | −0.06 | 0.999 | 0.87 | 0.351 |
| 6 | 0.55 | 0.999 | 1.48 | 0.012 |
| 7 | 0.31 | 0.999 | 1.24 | 0.078 |
| 8 | −0.64 | 0.999 | 0.29 | 0.999 |
| Inoculated Pigs | Contact Exposed Pigs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (DPE) 1 | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value |
| 1 | 1.61 | 0.004 | 1.72 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 0.86 | 0.361 | 0.96 | 0.240 |
| 3 | 0.79 | 0.361 | 0.90 | 0.227 |
| 4 | 0.29 | 0.999 | 0.40 | 0.999 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 0.999 | 0.00 | 0.999 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 0.999 | 0.09 | 0.999 |
| 7 | 0.13 | 0.999 | 0.24 | 0.999 |
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.999 | 0.13 | 0.999 |
| Inoculated Pigs | Contact Exposed Pigs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (DPE) 1 | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value |
| 1 | 0.94 | 0.233 | 0.67 | 0.709 |
| 2 | 0.98 | 0.203 | 0.71 | 0.620 |
| 3 | 0.72 | 0.650 | 0.45 | 0.999 |
| 4 | 0.48 | 0.999 | 0.21 | 0.999 |
| Inoculated Pigs | Contact Exposed Pigs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (DPE) 1 | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value | Mean load ‘Mono’ Minus Mean Load ‘Dual’ (log10 eq. CFU/sample) 2,3 | p-Value |
| 1 | 0.73 | 0.999 | 1.29 | 0.352 |
| 2 | 1.63 | 0.157 | 2.19 | 0.013 |
| 3 | 1.15 | 0.566 | 1.70 | 0.133 |
| 4 | 1.06 | 0.747 | 1.61 | 0.170 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dekker, N.; Bouma, A.; Daemen, I.; Vernooij, H.; Van Leengoed, L.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Stegeman, A. Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality. Pathogens 2017, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6040046
Dekker N, Bouma A, Daemen I, Vernooij H, Van Leengoed L, Wagenaar JA, Stegeman A. Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality. Pathogens. 2017; 6(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleDekker, Niels, Annemarie Bouma, Ineke Daemen, Hans Vernooij, Leo Van Leengoed, Jaap A. Wagenaar, and Arjan Stegeman. 2017. "Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality" Pathogens 6, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6040046
APA StyleDekker, N., Bouma, A., Daemen, I., Vernooij, H., Van Leengoed, L., Wagenaar, J. A., & Stegeman, A. (2017). Effect of Simultaneous Exposure of Pigs to Streptococcus suis Serotypes 2 and 9 on Their Colonization and Transmission, and on Mortality. Pathogens, 6(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6040046





