Abstract
White spot disease, caused by the parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, is a significant threat to the freshwater fish farming industry worldwide, resulting in massive mortality and economic losses. Eliminating the free-swimming theronts from the culture environment is considered crucial for the control of I. multifiliis infection. It is well-documented that planktonic ciliates are valuable food resources for macro-zooplankton in aquatic ecosystems. In this study, we developed a fluorescence labeling method for alive theronts and found that cyclopoid copepods Thermocyclops taihokuensis, Mesocyclops spp., Macrocyclops sp., and Paracyclopina sp. present predation on the theronts in co-culture experiments. Laboratory challenge tests further confirmed that the presence of zooplankton in the culture water body significantly reduced the infection of I. multifiliis in goldfish (p < 0.01). Results from this study revealed that cyclopoid copepods have the potential to be used as biological control agents against white spot disease in aquaculture.
1. Introduction
The ciliated protozoan Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infests most freshwater fish, causing significant economic losses in aquaculture worldwide, including the ornamental fish [1]. The parasite invades the gills, skin, and fins of fish and establishes parasitism in the epithelium. Mature parasites cause hyperplasia of epithelial tissue, which was macroscopically visible as 0.5–1.0 mm white spots [2]. Severe infection by I. multifiliis results in numerous white spots and significantly affects the respiration and osmoregulation of fish hosts, leading to massive mortality [3].
Various chemical and physical interventions have been employed against white spot disease (ichthyophthiriasis) [2,4,5]. Historically, malachite green, mercurous acetate and their derivatives were used to control I. multifiliis due to the high efficacy against both the free-swimming stage (tomont and theront) of its life cycle in water and the parasitic stage (trophont) in fish host epithelium [4,6]. However, the carcinogenic and teratogenic effects of these chemicals led to bans on their use in aquaculture. On farms, formalin, copper sulphate, peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, sodium percarbonate, and plant extracts (Zingiber officinale and Capsicum annuum) are used to treat this ciliate disease. The treatments aim to eliminate the infection primarily by targeting the free-living tomonts and theronts. Repetitive use of chemicals is necessary to prevent the continuation of infection. However, repeated and prolonged treatments weaken and stress fish, increase the susceptibility to secondary bacterial infection, and may have negative environmental side-effects [7]. Meanwhile, these treatments face challenges in open aquaculture environments, such as cage-farming in rivers or reservoirs. There is an urgent need to discover novel, effective, and environmentally friendly methods for white spot disease.
In freshwater fish farming, fish in outdoor earthen ponds with abundant plankton are not susceptible to white spot disease, but those in indoor culture systems with clean water are more vulnerable. What is the potential biological mechanism behind this phenomenon? The life cycle of I. multifiliis involves three mainly different development stages: trophont, tomont, and theront [1,3]. Theronts are pelagic and highly motile ciliates free-swimming in water with a body size of 20–50 μm. They seek out their fish host in the water after being released from the tomonts [3,6]. In aquatic ecosystems, ciliates play an essential role in the microbial food web, effectively utilizing the production of bacteria and phytoplankton and transferring the energy and materials to larger zooplankton, such as copepods, cladocerans and rotifers [8,9,10,11]. Especially, the trophic link between ciliates and copepods has been well-documented in both marine and freshwater environments [9,10].
The predation of larger zooplankton on ciliates raises the hypothesis that free-swimming theronts of I. multifiliis could also be predated by copepods, cladocerans, or rotifers in aquatic ecosystems. According to the author’s knowledge, until now there was no information available about zooplankton predation on I. multifiliis. In this report, we conducted a series of indoor studies to identify the native predator of theronts by using a fluorescent tracer, and preliminarily studied the effect of larger zooplankton on the infection intensity of I. multifiliis in fish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Culture and Isolation
Ichthyophthirius multifiliis isolates were collected from goldfish purchased from a pet market in Wuxi, China. Following the methods described by Li et al. [12], an indoor recirculating water system was used to maintain I. multifiliis and fish host in a 100 L aquarium under water temperature 23 ± 1 °C, pH 7.1 ± 0.3, DO 5.0–7.0 mg/L. Naïve juvenile gibel carps (Carassius auratus gibelio) weighing 30–50 g were obtained from the experimental station of Freshwater Fisheries Research Center (FFRC), and used for maintaining I. multifiliis in vivo. Theronts of I. multifiliis were prepared following the method described by Clayton and Price [13]. Briefly, fish with visible white spots were immersed in aerated tap water in a 500 mL beaker and left for the trophonts to exit the fish and form tomonts. Tomonts from the bottom of the beaker were collected and transferred to a culture dish containing distilled water. After rinsing three times with distilled water to remove fish mucus, they were incubated at 23.5 ± 0.5 °C for 18–20 h. To determine the concentration of theronts, ten 2 μL droplets of the theront suspension were counted under a microscope, respectively.
2.2. Macro-zooplankton Collection and Identification
Macro-zooplankton samples were collected using a plankton net (64 μm) and divided into two parts: one was fixed immediately in neutral 1% Lugol’s solution (Yuanye, Shanghai, China), and the other was transferred to the lab with pond water for the following co-culture predation experiments. Farmed fish in the ponds were also collected and checked for I. multifiliis infection with a microscope. The date and location of each sample are listed in Table 1. The fixed samples were used for morphological identification of zooplankton species composition with the kind help of Professor Li Wu (School of Life Science, Hefei Normal University).

Table 1.
Information on macro-zooplankton samples collected in this study.
2.3. Fluorescent Labeling of Infective Theronts
5-(and 6)-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFDA-SE) is widely used as a cell stain in vivo for cell tracking and proliferation studies [14]. Based on the preliminary study, CFDA-SE was chosen and used to label and track the infective theronts of I. multifiliis in the following studies.
CFDA-SE solution (Bestbio, Shanghai, China) was added into the culture dish containing tomonts to a final concentration of 1 μM, and then the culture dish was kept in the dark at 23 °C for 3 h. A 40 μm cell strainer was used to isolate the tomonts from the staining solution. Tomonts were transferred to a new culture dish with distilled water and incubated at 23.5 ± 0.5 °C for 18–20 h. Analysis of theront labeling with CFDA-SE was performed using a fluorescence stereomicroscope (Nikon SMZ18, Tokyo, Japan). As a control, the culture solution without theronts was isolated using a 0.4 μm suction filtration.
2.4. Co-Culture and Predation Experiments
Approximately 2000 macro-zooplankton individuals and 10,000 fluorescence-labeled theronts were added in a plastic container with 1 L dechlorinated tap water. Containers with the same amount of macro-zooplankton and culture solution but without theronts served as controls. After 4 h co-culture under room temperature (23 ± 1 °C), macro-zooplankton were collected with cell strainers (100 μm) and observed under a fluorescence stereomicroscope. To reduce the swimming and jumping of zooplankton under microscopic view, several drops of alcohol were added to the dishes. Zooplankton individuals with fluorescent signals were handpicked individually using pipettes and stored in 95% alcohol. For each macro-zooplankton sample, the co-culture and predation trial was conducted in triplicate. Twenty positive individuals from each sample were randomly selected and coded. They were morphologically identified according to the description by Shen [15] and further confirmed with DNA identification.
2.5. Molecular Analyses
In total, 180 zooplankton individuals were collected and transferred to 0.2 mL PCR tubes, respectively. Genomic DNA was extracted using a lysis buffer for microorganism to direct PCR (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). According to the previous studies, the part of 28s rDNA was amplified with primers CopF2 and CopR1 [16]. PCR reaction contained 25 μL 2 × Taq Master Mix (Dye Plus) (Vazyme, Nanjing, China), 2 μL of each primer (10 μM), 4 μL DNA template and 17 μL ddH2O. The following thermocycler conditions were employed: 94 °C for 60 s; 35 cycles of 94 °C for 5 s, 61 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 30 s; and a final 72 °C extension step of 10 min. PCR products were purified and sequenced at Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). The obtained DNA sequencing chromatograms were checked in Chromas 2.6.6, and sequences were assembled with SeqMan (LaserGene package), aligned in Geneious [17]. Sequence similarity was searched against the GenBank database using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST), and the closest hit with a species identity was recruited. In phylogenetic analyses, 19 copepod sequences and Ceriodaphnia pulchella (DQ470627) retrieved from GenBank were aligned with sequences obtained in this study in MAFFT [18]. The phylogenetic relationship was inferred using the maximum likelihood (ML) method in IQ-TREE v1.6.12 [19].
2.6. Challenge and Infection Level Determination
Goldfish (Carassius auratus) weighing 4.2 ± 1.3 g were bought from a local fish market and acclimated for 2 weeks in a 100 L glass aquarium (water temperature 19.5–22.0 °C, pH 7.1 ± 0.3, DO 5.0–7.0 mg/L). Microscopic exams and PCR tests following the previous study [20] were carried out to ensure these fish did not carry I. multifiliis.
Macro-zooplankton were collected from an earthen pond in the experimental station of FFRC, and adjusted to a concentration of approximately 1000 ind./L. The zooplankton species compositions were counted under a microscope and identified as copepods, cladocerans, and rotifers (5:3:6).
One hundred eighty goldfish were divided into six groups with three replicates (Table 2), and the challenge test was conducted in two water sources, tap water (T) and pond water (P). Group T was set as null control, and fish were reared in plastic containers with 2 L aerated tap water without zooplankton and theronts. In group T+I, fish were reared in 2 L aerated tap water with theronts (final concentration, 50,000 cells). In group T+I+Z, fish were reared in tap water with zooplankton (1000 ind./L) and theronts (50,000 cells). Meanwhile, in group P, fish were reared in pond water filtrated with a plankton net (64 μm) set as control (without zooplankton). In group P+I, fish were reared in filtrated pond water (without zooplankton) with theronts. In group P+I+Z, fish were reared in pond water (with zooplankton) and theronts (Table 2). Four days later, fish were anesthetized with MS-222 and dissected. Trophonts on the first gill branch from the left side were counted under the microscope.

Table 2.
Experimental grouping of zooplankton intervention on I. multifiliis infection.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All infection intensity data were expressed as mean ± sem and analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Duncan test. The differences were considered significant at p < 0.01. Statistical analyses were performed in SPSS 23, and the graph was generated using OriginPro.
3. Results
3.1. Theronts Labeled with CFDA-SE
After 18 h of incubation, 90% of tomonts successfully released free-swimming theronts, and the theronts emerged from tomont cysts presenting a 100% fluorescent signal under microscopy (Figure 1). The viability of fluorescence-labeled theronts was similar to that of those not treated with CFDA-SE solution, and the fluorescent signal in theronts could persist over 6 h.
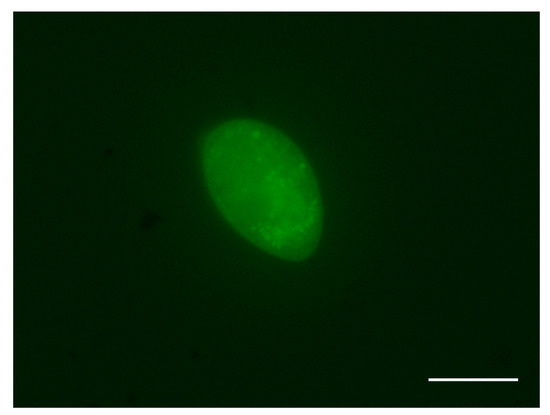
Figure 1.
Ichthyophthirius multifiliis theronts with a fluorescence label. Scale bar, 20 μm.
3.2. Predation of Copepods on Theronts
After 4 h co-culture, no fluorescent signal was detected from the zooplankton in the control group. In the group of fluorescence-labeled theronts, the fluorescence signal was mainly observed in copepods and few nauplii (Figure 2 and Figure 3); however, no signal was detected in cladocerans and rotifers. In the alimentary canal of copepods, several fluorescent points, similar in size to fluorescence-labeled theronts, were observed (Figure 3).
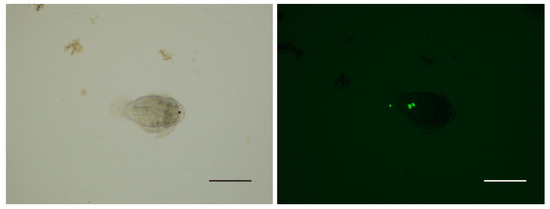
Figure 2.
Nauplius with fluorescence-labeled theronts. Scale bars, 200 μm.
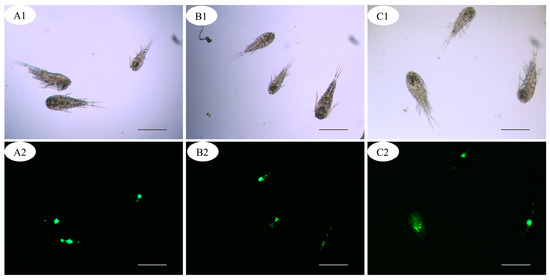
Figure 3.
(A1–C2) Copepods with fluorescence-labeled theronts. Scale bars, 500 μm.
3.3. Species of Zooplankton and Predators of Theronts
Zooplankton collected from six fish ponds and three wild water bodies had high species diversity and consisted of 11–18 species of copepods, cladocerans and rotifers (Table S1). Species compositions in the healthy fish ponds (NQ1, NQ2, NQ3), wild water bodies (LK1, LK2, LK3), and diseased ponds with I. multifiliis infection (YX1, YX2, YX3) were different.
Co-culture and predation experiments revealed that mature copepods were the main predators of free-swimming theronts of I. multifiliis, and only one copepod nauplii individual was observed with a fluorescence signal. The 28s rDNA sequences of 180 copepod individuals were amplified in this study; however, 96 (53.3%) were successfully obtained. Based on morphological characters and DNA sequence analysis, the copepod predators were identified as seven species or operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of the order Cyclopoida, including Thermocyclops taihokuensis, Mesocyclops sp1., Mesocyclops sp2., Paracvclopina sp., and Macrocyclops sp. (Table 3 and Figure 4). In the identified copepods, Thermocyclops taihokuensis and Mesocyclops sp1. were the dominant predators, comprising 62.5% (60/96) and 28.1% (27/96), respectively

Table 3.
Copepod predators of theronts of I. multifiliis discovered in this study.
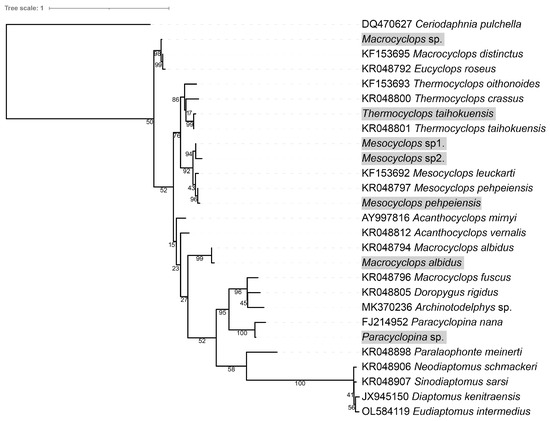
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of particular 28s rDNA of copepods. Ultrafast bootstrap support values are shown near the nodes. The species with gray shading are copepods, which prey on theronts in this study.
3.4. Intervention Effect of Macro-zooplankton on I. multifiliis Infection in Goldfish
Copepods grazing on the free-swimming theronts would decrease the abundance of theronts in water bodies and reduce the infection pressure of fish hosts. The authors here tried to assess the intervention effect of predators on I. multifiliis infection in goldfish using the macro-zooplankton collected in a fish pond (Table 2). The results indicated that predation of copepods on theronts significantly reduced the parasite burden on fish gills (p < 0.01) (Figure 5). In tap water, 84.93 ± 5.08 trophonts were detected on the first branch of the left gill in the group T+I (Figure 5); however, only 54.87 ± 2.31 trophonts were observed in the group T+I+Z with zooplankton. Similar results (p < 0.01) were seen in the groups raised in pond water (89.27 ± 4.61 to 58.93 ± 1.68). In control groups (T and P), no I. multifiliis was found in goldfish, and the water source had no influence on infection by I. multifiliis in this study.
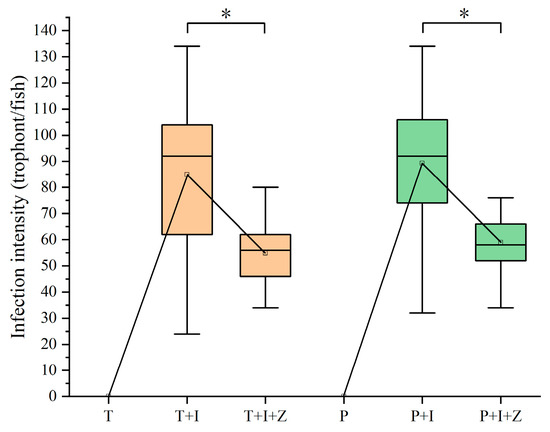
Figure 5.
Infection intensity changes of different treatments of goldfish post I. multifiliis infection. Significant differences (p < 0.01) are denoted by an asterisk (*).
4. Discussion
Fluorescent live cell dyes have been widely used to analyze cell vitality and perform cell tracking. However, until now, there was no report about live cells of I. multifiliis labeled with fluorescent dye. In the preliminary study, the authors tried using CM-Dil (Yeasen, China) to label tomonts and theronts of I. multifiliis. However, CM-Dil could not permeate through the cysts of tomonts and the densely packed cilia on the surface of theronts of I. multifiliis. In contrast, CFDA-SE could permeate the plasma membrane and become strongly fluorescence retaining in living cells over 6 h (Figure 1). Although CFDA-SE is toxic to cells to a certain extent [21], there was no significant effect on the survival and motility of theronts of I. multifiliis under the concentration (1 μM) used in this study.
In the life cycle of I. multifiliis, theronts are the infective stage to fish hosts. Therefore, killing or inhibiting theronts will prevent the invasion of fish which is essential to control white spot disease. Theronts, like most planktonic ciliates, are free-swimming in water. Although many studies revealed the top-down impact on ciliate community structure and biomass in the food webs by macro-zooplankton, especially cladocerans and copepods [22,23,24,25,26], until now, few reports have been published about the predation of copepods on I. multifiliis. However, most theronts, with a body size of 20–50 μm, fall within the prey size spectrum of macro-zooplankton. In the lab experiment of this study, the authors found that the live theronts labeled with fluorescence CFDA-SE were ingested by copepods, and strong fluorescent signals were observed in the alimentary canal (Figure 3). Furthermore, the challenge trials showed that the presence of zooplankton in the culture system could significantly mitigate the infection of I. multifiliis in goldfish (Figure 5). The results revealed that copepods could prey on the theronts of I. multifiliis. Therefore, eliminating theronts and disrupting the life cycle of I. multifiliis with copepods could be a potentially effective method for controlling white spot disease in aquaculture [2].
Planktonic ciliates are the main components of the microbial food web in both marine and freshwater ecosystems, and the abundance and species composition were significantly shaped by the different functional groups of macro-zooplankton predators [27]. Cladocerans, copepods and rotifers often co-occur in water and compete for limited food resources with different feeding behavior and efficiency. The feeding mechanism is strongly influenced by the availability of alternative food sources and by the motility, size and abundance of prey [28]. Most rotifers eat algal cells in the 4–17 μm range; most cladocerans are efficient filter feeders, ingesting suspended particles ranging in size from bacteria to algae and ciliates <30 μm [27]. In contrast, copepods selectively feed on larger prey and consume ciliates preferentially over alternative prey [29]. In this study, 11–18 species of copepods, cladocerans and rotifers were detected in the water samples; however, only mature copepods were found feeding on theronts of I. multifiliis. Meanwhile, one copepod nauplii individual was also found to be positive. Böttjer et al. [30] reported that Oithona spp. nauplii were important in controlling nanoplankton (3–20 μm) on the coast of Chile. Theronts of I. multifiliis are slightly larger in size, which may be difficult for nauplii to hunt.
Copepods can be divided into filter feeding, predatory feeding and scraping feeding species. Some species of copepods, called mix-feeding types, can filter and be predatory. Food availability and body size are major factors shaping copepod feeding rates. Most Calanoids are filter feeding and lack the ability to hunt free-swimming theronts of I. multifiliis. Additionally, most harpacticoids crawl along the bottom of the water body; therefore, they were not detected in the water samples. Cyclopoid copepods are exclusively ambush feeding species that hunt relatively large and mostly motile prey [15,27]. In this study, we discovered seven Cyclopoid copepods that preyed on theronts. According to a previous report [15], Macrocyclops albidus and Mesocyclops leuckarti engaged in predatory feeding on insect larvae, oligochaeta, cladocerans and copepods; Thermocyclops taihokuensis was a fierce copepod feeding on fish eggs and cladocerans; Microcyclops bicolor was a mix-feeding copepod grazing on algae, protozoa, rotifers and animal carcasses.
Notably, the cyclopoid T. taihokuensis comprised 62.5% of the copepods preying on theronts and were detected in all healthy ponds and lakes (NQ1, NQ2, NQ3 and LK1, LK2, LK3), but absent from samples collected from ponds where fish were heavily infected with white spot disease (YX1, YX2, YX3). Additionally, in all samples collected from NQ1, NQ2 and NQ3, T. taihokuensis was the only macro-zooplankton observed to eat fluorescence-labeled theronts. Therefore, we hypothesize that T. taihokuensis has a higher predation efficiency on theronts of I. multifiliis.
In challenge tests, the results showed that the infection intensity of I. multifiliis in goldfish was significantly lower in the water with zooplankton. Dhanker et al. [28] found that the ciliate consumption rate of Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda: Calanoida) was significantly lower in the presence of mixed algae. However, Acanthocyclops robustus (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) was found to be an effective biocontrol agent for eliminating the ciliate Sterkiella in cultures of the microalga Chlamydomonas without reducing microalgal production [31]. In this study, no significant difference (p > 0.01) was observed between the groups T+I and P+I or between the groups T+I+Z and P+I+Z, respectively. It suggests that zooplankton may preferentially feed on the theronts of I. multifiliis often over alternative prey, such as algae, smaller ciliates, in pond water. Furthermore, the results could well explain the phenomenon in aquaculture that fish in ponds with abundant plankton are less susceptible to white spot disease.
In conclusion, the present study determined the predation of cyclopoid copepods on theronts of I. multifiliis. The results indicate that seven species of copepods consumed fluorescence-labeled theronts, and the presence of zooplankton reduced the infection pressure of I. multifiliis on fish. This study uncovered a potential biological control method against white spot disease in aquaculture. However, further research is required to reveal the feeding efficacy of different copepod predators in the laboratory and field settings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens12070860/s1, Table S1: Species composition of macro-zooplankton collected from fish ponds and lakes in this study.
Author Contributions
Development or design of methodology, conducting a research and investigation process, writing original draft preparation, Z.-Y.C.; Sample preparation and structure fabrication, Q.-J.Z.; Conceptualization, commentary and revision, financial support, B.-W.X.; Technical support and data analysis, K.C.; Critical review and revision, J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-45) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (32073019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the protocols used on the experimental fish and followed the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China (Permit number: SYXK (Su) 2011-0036).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the manuscript and table.
Acknowledgments
Our sincere thanks to Li Wu (School of Life Science, Hefei Normal University) for the morphological identification of fixed samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dickerson, H.W.; Dawe, D.L. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans (Phylum Ciliophora). In Fish Diseases and Disorders. Volume 1: Protozoan and Metazoan Infections; Woo, P.T.K., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-85198-823-8. [Google Scholar]
- von Gersdorff Jørgensen, L. The Fish Parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis—Host Immunology, Vaccines and Novel Treatments. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, R.A. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet and Ichthyophthiriosis in Freshwater Teleosts. In Advances in Parasitology; Baker, J.R., Muller, R., Rollinson, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 59, pp. 159–241. [Google Scholar]
- Picón-Camacho, S.M.; Leclercq, E.; Bron, J.E.; Shinn, A.P. The Potential Utility of the Leopard Pleco (Glyptoperichthys gibbiceps) as a Biological Control of the Ciliate Protozoan Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieman, D.M.; Goodwin, A.E. Treatments for Ich Infestations in Channel Catfish Evaluated under Static and Flow-Through Water Conditions. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2001, 63, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Lee, L.S. Studies on the Morphology and Life Cycle of Ichthyophthirius nultifliis and Its Control, with a Description of a New Species. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1960, 2, 197–215. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Hafez, G.; Lahnsteiner, F.; Mansour, N.; Licek, E. Pathophysiology of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Chub (Leuciscus cephalus). J. Comp. Pathol. 2014, 151, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, A.S. Plankton. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R478–R483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiba, J.; Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Krztoń, W.; Strzesak, M.; Pociecha, A.; Walusiak, E.; Pudaś, K.; Szarek-Gwiazda, E. What Underpins the Trophic Networks of the Plankton in Shallow Oxbow Lakes? Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisse, T. Functional Diversity of Aquatic Ciliates. Eur. J. Protistol. 2017, 61, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Burton, G.A. Zooplankton Community Profiling in a Eutrophic Freshwater Ecosystem-Lake Tai Basin by DNA Metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bastos Gomes, G.; Zhao, W.; Hu, G.; Huang, K.; Yoshinaga, T.; Clark, T.G.; Li, W.; Zou, H.; Wu, S.; et al. Cultivation of Fish Ciliate Parasites: Progress and Prospects. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, G.M.; Price, D.J. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis: Standardization of the Infection-Response Model in Ameca splendens (Miller & Fitzsimons). J. Fish Dis. 1988, 11, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, C.; Stamm, I.; Taubert, A.; Lutz, K.; Zahner, H.; Menge, C. Fluorescent Eimeria bovis Sporozoites and Meront Stages In Vitro: A Helpful Tool to Study Parasite–Host Cell Interactions. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C. Fauna Sinica (Crustacea, Freshwater Copepoda); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bissett, A.; Gibson, J.A.E.; Jarman, S.N.; Swadling, K.M.; Cromer, L. Isolation, Amplification, and Identification of Ancient Copepod DNA from Lake Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2005, 3, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, K.; Xi, B.; Xie, J.; Pan, L.; Mao, Y. Establishment and Application of PCR and SYBR Green Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. J. Fish. China 2023, 1–9. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1283.S.20230109.1250.001.html (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Lašt’ovička, J.; Budinský, V.; Špíšek, R.; Bartůňková, J. Assessment of Lymphocyte Proliferation: CFSE Kills Dividing Cells and Modulates Expression of Activation Markers. Cell. Immunol. 2009, 256, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.J. The Effect of Daphnia Interference on a Natural Rotifer and Ciliate Community: Short-Term Bottle Experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, S.A.; Gilbert, J.J. Relative Vulnerabilities of Natural Rotifer and Ciliate Communities to Cladocerans: Laboratory and Field Experiments. Freshw. Biol. 1991, 26, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R.; Gifford, D.J.; Kirchman, D.L.; Wheeler, P.A.; Monger, B.C. Direct and Indirect Effects of Grazing by Neocalanus plumchrus on Plankton Community Dynamics in the Subarctic Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 1993, 32, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A. Subantarctic Copepods in an Oceanic, Low Chlorophyll Environment: Ciliate Predation, Food Selectivity and Impact on Prey Populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 130, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, D.; Hartmann, H.J. Contribution of Ciliated Microprotozoans and Dinoflagellates to the Diet of Three Copepod Species in the Bay of Biscay. Hydrobiologia 2001, 443, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Weisse, T. Top-down Control of Planktonic Ciliates by Microcrustacean Predators Is Stronger in Lakes than in the Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanker, R.; Kumar, R.; Tseng, L.C.; Hwang, J.S. Ciliate (Euplotes sp.) Predation by Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda: Calanoida) and the Effects of Mono-Algal and Pluri-Algal Diets. Zool. Stud. 2013, 52, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.V.; De Stasio, B.T., Jr.; Huizenga, K.N.; Silow, E.A. Trophic Coupling of the Microbial and the Classical Food Web in Lake Baikal, Siberia. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 64, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttjer, D.; Morales, C.E.; Bathmann, U. Trophic Role of Small Cyclopoid Copepod Nauplii in the Microbial Food Web: A Case Study in the Coastal Upwelling System off Central Chile. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Hue, N.T.; Deruyck, B.; Decaestecker, E.; Vandamme, D.; Muylaert, K. Biological Control of Ciliate Contamination in Chlamydomonas Culture Using the Predatory Copepod Acanthocyclops robustus. Algal Res. 2019, 37, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).