Efficacy of Fosfomycin-Containing Regimens for Treatment of Bacteremia Due to Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
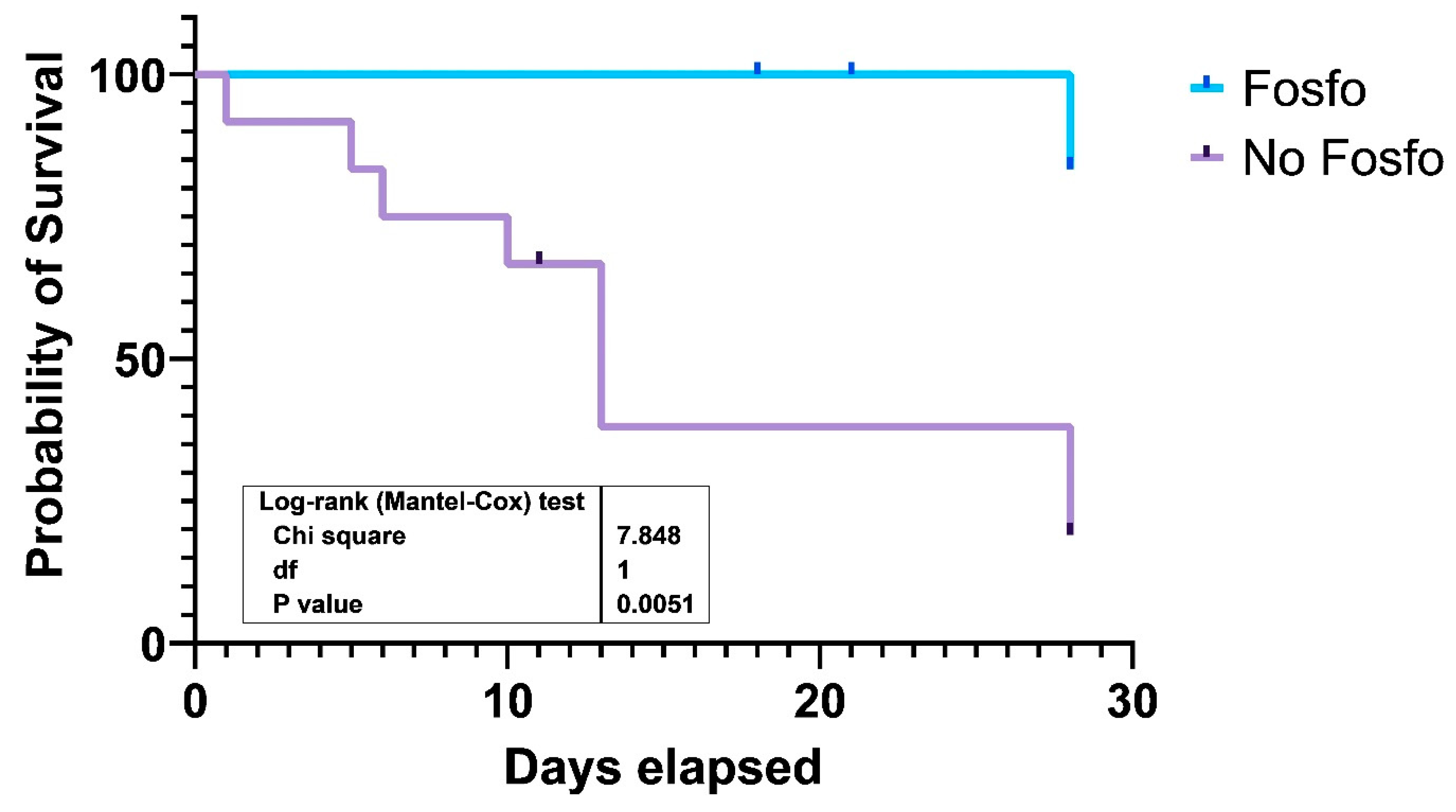
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowak, J.; Zander, E.; Stefanik, D.; Higgins, P.G.; Roca, I.; Vila, J.; McConnell, M.J.; Cisneros, J.M.; Seifert, H.; MagicBullet Working Group WP4. High incidence of pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates collected from patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia in Greece, Italy and Spain as part of the MagicBullet clinical trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3277–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polemis, M.; Mandilara, G.; Pappa, O.; Argyropoulou, A.; Perivolioti, E.; Koudoumnakis, N.; Pournaras, S.; Vasilakopoulou, A.; Vourli, S.; Katsifa, H.; et al. COVID-19 and Antimicrobial Resistance: Data from the Greek Electronic System for the Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance—WHONET-Greece (January 2018–March 2021). Life 2021, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Kritsotakis, E.I.; Gikas, A. Pandrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: A systematic review of current epidemiology, prognosis and treatment options. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Kritsotakis, E.I.; Gikas, A. Treatment options for K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii co-resistant to carbapenems, aminoglycosides, polymyxins and tigecycline: An approach based on the mechanisms of resistance to carbapenems. Infection 2020, 48, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Gikas, A.; Astrinaki, E.; Kritsotakis, E.I. Excess mortality due to pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 13.0. 2023. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Chuang, Y.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Sheng, W.H.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, S.C. Effectiveness of tigecycline-based versus colistin- based therapy for treatment of pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a critical setting: A matched cohort analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.; Chuang, Y.C.; Sun, H.Y.; Sheng, W.H.; Yang, C.J.; Liao, C.H.; Hsueh, P.R.; Yang, J.L.; Shen, N.J.; Wang, J.T.; et al. Excess Mortality Associated with Colistin-Tigecycline Compared with Colistin-Carbapenem Combination Therapy for Extensively Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremia: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Mei, H.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Tigecycline in 67 Infected Patients and a Population Pharmacokinetics/Microbiological Evaluation of A. baumannii Study. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 678165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; Corcione, S.; Lupia, T.; Shbaklo, N.; Olivieri, C.; Poggioli, M.; Pagni, A.; Colombo, D.; Roasio, A.; Bosso, S.; et al. The Burden of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in ICU COVID-19 Patients: A Regional Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballouz, T.; Aridi, J.; Afif, C.; Irani, J.; Lakis, C.; Nasreddine, R.; Azar, E. Risk Factors, Clinical Presentation, and Outcome of Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteremia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezza, F.C.; Arcari, G.; Alessi, F.; Valeri, S.; Curtolo, A.; Sacco, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Raponi, G.; Alessandri, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; et al. Clinical Impact of COVID-19 on Multi-Drug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli Bloodstream Infections in an Intensive Care Unit Setting: Two Pandemics Compared. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y. Treatment Options for Carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative Bacterial Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69 (Suppl. S7), S565–S575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.; Tansarli, G.S.; Falagas, M.E. Combination antibiotic treatment versus monotherapy for multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter infections: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Ioannou, P.; Samonis, G.; Kofteridis, D.P. Systematic Review of Antimicrobial Combination Options for Pandrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizbay, M.; Tozlu, D.K.; Cirak, M.Y.; Isik, Y.; Ozdemir, K.; Arman, D. In vitro synergistic activity of tigecycline and colistin against XDR-Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Ioannou, P.; Kofteridis, D.D. In search for a synergistic combination against pandrug-resistant A. baumannii; methodological considerations. Infection 2022, 50, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Samonis, G.; Vardakas, K.Z. Fosfomycin. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, R.M.; Principe, L.; Maraolo, A.E.; Viaggi, V.; Pol, R.; Fabbiani, M.; Montagnani, F.; Lovecchio, A.; Luzzati, R.; Di Bella, S. Fosfomycin as Partner Drug for Systemic Infection Management. A Systematic Review of its Synergistic Properties from in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sazlly Lim, S.; Heffernan, A.J.; Roberts, J.A.; Sime, F.B. Semi-mechanistic PK/PD modelling of fosfomycin and sulbactam combination against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kastoris, A.C.; Karageorgopoulos, D.; Rafailidis, P.I. Fosfomycin for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant non-fermenting Gram-negative bacilli: A systematic review of microbiological, animal and clinical studies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysert-Yildiz, P.; Özgen-Top, O.; Habibi, H.; Dizbay, M. Efficacy and safety of intravenous fosfomycin for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Chemother. 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirijatuphat, R.; Thamlikitkul, V. Preliminary Study of Colistin versus Colistin plus Fosfomycin for Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5598–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Bassetti, M.; Bellelli, V.; Bianchi, L.; Cattaneo, F.M.; Mazzocchetti, S.; Paciacconi, E.; Cottini, F.; Schiattarella, A.; Tufaro, G.; et al. Efficacy of a Fosfomycin-Containing Regimen for Treatment of Severe Pneumonia Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Prospective, Observational Study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient | AGE | SEX | CCI | COVID | APACHE II | Antibiotics Used | Microbiological Success | 28-day Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 65 | F | 3 | Yes | 15 | CST, TGC | Yes | No |
| 2 | 53 | M | 1 | Yes | 24 | CST, TGC | Yes | No |
| 3 | 64 | M | 2 | No | 22 | CST, SXT, FOS | Yes | No |
| 4 | 64 | M | 4 | No | 10 | CST, FOS | Yes | No |
| 5 | 28 | F | 0 | No | 7 | CST, AMS, FOS, AMK | Yes | No |
| 6 | 76 | M | 6 | No | 8 | CST, MEM | Yes | No |
| 7 | 72 | M | 9 | No | 13 | CST, TGC, FOS | Yes | No |
| 8 | 64 | F | 6 | No | 25 | TGC, AMS, FOS AMK | Yes | No |
| 9 | 71 | F | 7 | No | 19 | CST, TGC, FOS | Yes | No |
| 10 | 36 | F | 0 | Yes | 20 | CST, MEM, FOS, SXT, GEN | Yes | No |
| 11 | 53 | M | 1 | Yes | 11 | CST, TGC, AMS, SXT, AMK | Yes | Yes |
| 12 | 60 | M | 2 | Yes | 17 | CST, MEM, TGC, AMS | No | Yes |
| 13 | 71 | F | 4 | Yes | 38 | CST, TGC, FOS, AMK, SXT | Yes | Yes |
| 14 | 59 | M | 1 | Yes | 40 | CST, AMK | No | Yes |
| 15 | 78 | M | 3 | Yes | 39 | CST, PTZ | No | Yes |
| 16 | 70 | F | 5 | Yes | 26 | MEM, GEN | No | Yes |
| 17 | 55 | F | 4 | Yes | 20 | CST, MEM | No | Yes |
| 18 | 62 | F | 2 | Yes | 28 | MEM, AMS, TGC | No | Yes |
| 19 | 55 | F | 1 | Yes | 25 | CST, TGC, AMS | Yes | Yes |
| 20 | 93 | F | 8 | Yes | 12 | CST, MEM | Yes | Yes |
| 28-day Mortality | Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Survived (n = 10) | Died (n = 10) | p |
| Age years [Median (IQR)] | 64 (48–71) | 61 (55–72) | ns |
| Female Gender (%) | 5 (50) | 6 (60) | ns |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 3.1 | 3.1 ± 2.2 | ns |
| APACHE II mean ± SD | 16.3 ± 6.6 | 25.6 ± 10.8 | 0.032 |
| SOFA mean ± SD | 7.1 ± 3.8 | 11.4 ± 4.3 | 0.03 |
| Septic Shock (%) | 0 | 6 (60) | 0.003 |
| COVID (%) | 3 (30) | 10 (100) | 0.001 |
| ≥3 antibiotics combination regimen (%) | 6 (60) | 5 (50) | ns |
| Colistin containing regimen (%) | 9 (90) | 8 (80) | ns |
| Tigecycline containing regimen (%) | 5 (50) | 5 (50) | ns |
| Fosfomycin containing regiment (%) | 7 (70) | 1 (10) | 0.02 |
| Aminoglycoside containing regimen (%) | 3 (30) | 4 (40) | ns |
| Carbapenem containing regimen (%) | 2 (20) | 5 (50) | ns |
| Ampicillin-Sulbactam containing regimen (%) | 2 (20) | 4 (40) | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Karamouzos, V.; Eleftheriotis, G.; Lagadinou, M.; Bartzavali, C.; Kolonitsiou, F.; Paliogianni, F.; Fligou, F.; Marangos, M. Efficacy of Fosfomycin-Containing Regimens for Treatment of Bacteremia Due to Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series Study. Pathogens 2023, 12, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020286
Assimakopoulos SF, Karamouzos V, Eleftheriotis G, Lagadinou M, Bartzavali C, Kolonitsiou F, Paliogianni F, Fligou F, Marangos M. Efficacy of Fosfomycin-Containing Regimens for Treatment of Bacteremia Due to Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series Study. Pathogens. 2023; 12(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020286
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssimakopoulos, Stelios F., Vassilis Karamouzos, Gerasimos Eleftheriotis, Maria Lagadinou, Christina Bartzavali, Fevronia Kolonitsiou, Fotini Paliogianni, Fotini Fligou, and Markos Marangos. 2023. "Efficacy of Fosfomycin-Containing Regimens for Treatment of Bacteremia Due to Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series Study" Pathogens 12, no. 2: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020286
APA StyleAssimakopoulos, S. F., Karamouzos, V., Eleftheriotis, G., Lagadinou, M., Bartzavali, C., Kolonitsiou, F., Paliogianni, F., Fligou, F., & Marangos, M. (2023). Efficacy of Fosfomycin-Containing Regimens for Treatment of Bacteremia Due to Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients: A Case Series Study. Pathogens, 12(2), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12020286






