Abstract
Background: Members of Micobacterium. abscessus complex comprises three subspecies (M. abscessus subsp. Abscessus, M. abscessus subsp. Bolletii, and M. abscessus subsp. Massiliense) and are a rapid-growing nontuberculous mycobacteria present in different aquatic habitats and soil. It often causes a wide spectrum of infections involving pulmonary infections, surgical wound infections, and infections related to mesotherapy, catheters, hemodialysis devices, endocarditis, and disseminated infections in immunocompromised individuals. Methods: In this article we comment on the most relevant aspects of nine patients with skin lesions caused by M. abscessus subsp. massiliense infection. Clinical characteristics, histopathology, and molecular identification were performed. Results: The patients in the clinical cases presented a history of trauma, tattoos, and physical therapy techniques. The most common treatments were minocycline and clindamycin, doxycycline, ceftriaxone, cephalexin, moxifloxacin, rifampicin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The evolution of the treated patients was acceptable, except for one patient, who showed a partial improvement. M. massiliense were identified in all clinical cases using a species-specific PCR. Conclusion: Our series consisted of nine cases of skin biopsies recorded in different years; for this reason, we do not have all the data necessary for a complete description, in particular in four cases, causing limitations in the manuscript, especially in the therapy used and the evolution of patients due to lack of follow-up.
1. Introduction
Microorganisms that form the Mycobacterium abscessus complex are considered saprophytes and can be found in soil, water, mud, organic matter, animal feed deposits, sediments, and vegetables, for which the environment is the main source of infection. The importance of studying these microorganisms lies in their ability to survive in the absence of nutrients, grow at a wide range of temperatures, form biofilms, and resist the action of chlorinated disinfectants and glutaraldehyde [1,2]. They have been implicated as causal agents of wound and soft tissue infections [3], especially in immunocompromised patients and after invasive procedures, such as acupuncture and surgery [4,5].
Members of M. abscessus complex comprises three subspecies: M. abscessus subsp. abscessus; M. abscessus subsp. bolletii and M. abscessus subsp. massiliense. Taxonomy classification has been controversial due to the close relationship between M. abscessus subsp. bolletii and M. abscessus subsp. massiliense. However, whole-genome sequencing based phylogenetic analysis confirmed their differentiation in three distinct subspecies [6]. This differentiation is important because the treatment varies depending on the causal agent.
Skin and soft tissue infection by M. abscessus subsp. massiliense is difficult to differentiate from a skin infection by other nontuberculous mycobacteria or Nocardia because the clinical presentation is similar (persistence of subcutaneous nodules, erythema, and infected wounds) [7,8].
Here, we report nine clinical cases of cutaneous infection due to M. abscessus subsp. massiliense in Mexican patients and one Spanish patient. Due to the history of the treatments to which the patients were subjected, the lack of response to usual antibacterials, and the heterogeneity of the clinical manifestations, a granulomatous reaction associated with a foreign body was intentionally sought. Clinical characteristics, histopathology, and molecular identification were performed.
2. Material and Methods
Nine cases with cutaneous mycobacteriosis infection were processed. For all patients, skin biopsies were obtained. The histopathology study including hematoxylin-eosin and Ziehl-Neelsen staining. The biopsy samples were also processed for bacterial molecular identification. Briefly, genomic DNA was isolated from paraffin-embedded tissue samples using a DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions before preliminary removal of paraffin by extraction with the xylene protocol [9]. Molecular identification was achieved using 16S rRNA and mass_3210 gene amplification. For multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, a set of primers previously reported to identify all mycobacterial species (506 bp of 16S rRNA gene), 5′-GAGATACTCGAGTGGCGAAC-3′ and 5′-CAACGCGACAAACCACCTAC-3′, were used. For M. abscessus subsp. abscessus and M. abscessus subsp. Massiliense identification a set of primers of mass_3210 gene were applied (5′-GCTTGTTCCCGGTGCCACAC-3′ and 5′-GGAGCGCGATGCGTCAGGAC-3′) to amplify a 310 bp for M. abscessus subsp. abscessus and 1145 bp for M. abscessus subsp. massiliense [9]. The PCR products were visualized in a 1.5% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide.
3. Results
Data were collected from nine patients and sociodemographic and clinical characteristics are described in Table 1. The mean age of patients was 35.5 ± 16.6 years, ranging from 18 months to 60 years. Most of our patients were men (66.5%). The time of evolution was 12.1 ± 21.3 months, with a range of 0.1 months to 60 months. Two patients were HIV-positive, and one received anti-TNF-α biological treatment. We emphasize that most patients had a history of trauma, tattoos, electromagnetic girdle, or anti-TNF-α biological drugs, while three patients did not have information on the origin of the infection. Following the morphological patterns, the most frequent presentations were erythema and infiltration (Figure 1 and Figure 2), followed by nodules and ulcers (Figure 3). Gum, shrink scars, and fistulas were observed (Figure 4). The histopathological studies showed that the most frequent lesion was suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis, followed by a fistulous tract and abscess.

Table 1.
Clinical and sociodemographic characteristics of the patients.
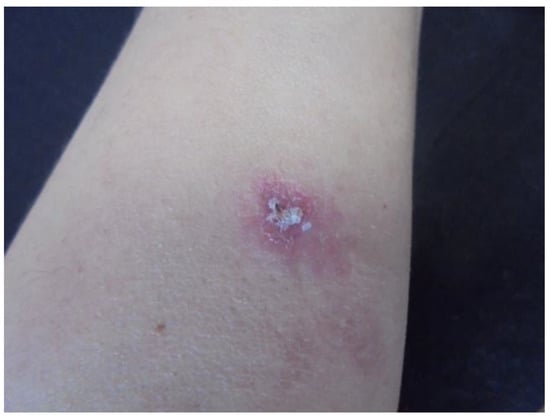
Figure 1.
Erythema and infiltration in the left forearm (Patient 1).
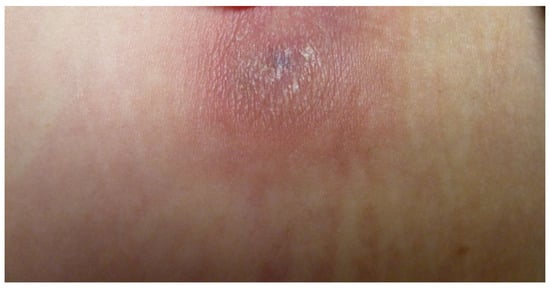
Figure 2.
Infiltrated lesions in the abdomen (Patient 8).
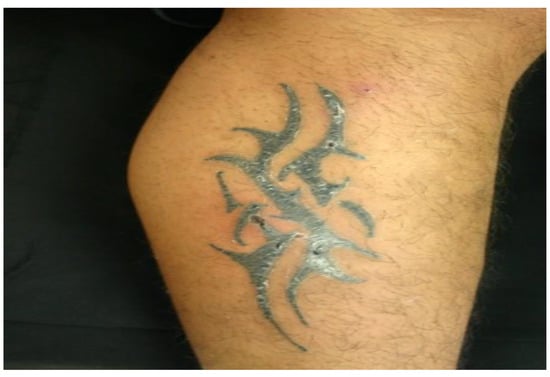
Figure 3.
Nodular lesion on the right leg under a tattoo (Patient 3).
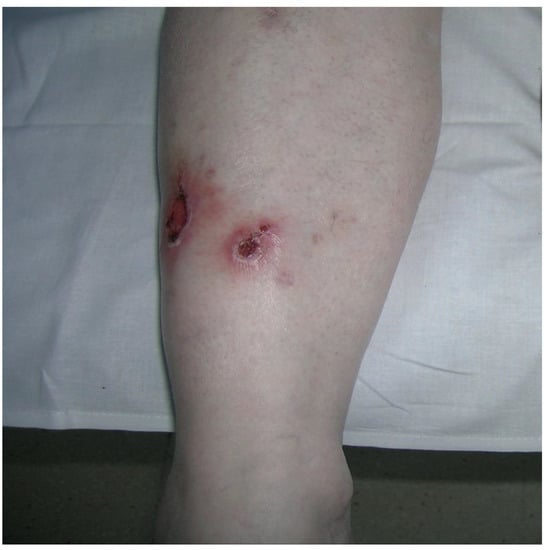
Figure 4.
Erythema and shrink scars located throughout the lower of the right leg (Patient 9).
The molecular identification showed that the nine samples amplified a 506 bp product and a 1145 bp product, corresponding to M. abscessus subsp. massiliense (Figure 5).
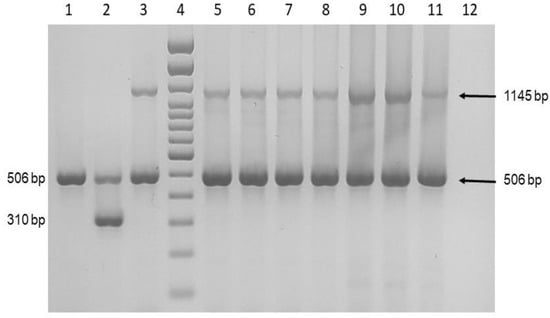
Figure 5.
Molecular identification of M. abscessus. Multiplex PCR for the amplification of Mycobacterium spp., M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, and M. abscessus subsp. masiliense. Lane 1: M. tuberculosis 322; Lane 2: M. abscessus subsp. abscessus GEA-Ped1; Lane 3: M. abscessus subsp. massiliense GEA-Mic1; Lane 4; 100 bp DNA ladder; Lanes 5–11: Patient 1–7; Lane 12: Negative control.
With respect to the treatment in four patients, we did not have results on the treatment and the evolution, due to not being able to carry out the follow-up of the patients. The most common treatments were minocycline and clindamycin, followed by doxycycline, ceftriaxone, cephalexin, moxifloxacin, rifampicin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The evolution of the treated patients was generally acceptable, except for one patient, who showed only a partial improvement.
4. Discussion
Mycobacterial species are ubiquitous in the environment in water and soil habitats and can be classified according to growth characteristics: the group of non-tuberculous mycobacteria belonging to fast-growing mycobacteria and the slow-growing mycobacteria. Currently, M. abscessus complex comprises three closely related subspecies: M. abscessus subsp. abscessus, M. abscessus subsp. massiliense, and M. abscessus subsp. bolletii. M. abscessus subsp. abscessus is more frequently associated with pulmonary infections; however, M. abscessus subsp. massiliense is more predominant in skin or underlying soft tissue infection [9,10,11].
During the last three decades, the frequency of diseases caused by the M. abscessus complex has increased by diverse factors: greater virulence of mycobacteria; increase in immunocompromised patients, especially patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), patients with organ transplants, and widespread use of antineoplastic drugs in interventional therapies and cancer treatment; use of biological drugs for the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases, and progresses in methods or techniques to detect and identify these pathogen [12]. In our cases, we observed two immunosuppressed patients with HIV infection (Cases 1 and 7), an important comorbidity for M. abscessus subsp. massiliense infection.
Cases of infection by M. abscesses complex have been reported in patients with a history of laser myopia correction surgery, mesotherapy sessions, or breast implants [4,9,13]. Case 8 describes a patient with a history of mesotherapy, which is related to risk factors for developing the disease. The same occurs in patients with a history of surgical procedures, injections, minor trauma, and immunosuppressive treatment [3]. In cases 2, 3, 6 and 9, the patients had a history of minor trauma due to contact with thorns, tattoos, electromagnetic girdle, and acupuncture, respectively.
The clinical presentation of skin and soft tissue infections is variable and includes pyogenic subcutaneous abscesses with an acute inflammatory reaction, violaceous erythematous nodules, dermatitis, cellulitis, folliculitis, ulcers, and chronic inflammatory reactions with fistula formation. These infections are characterized by a late onset of symptoms between 2 and 14 weeks after the history of inoculation [12,14,15]. In our clinical cases, patients present skin manifestations characterized by the presence of nodules, ulcers, erythema and infiltration, gums, fistulas, and shrink scars and the most histopathological lesion was suppurative and granulomatous dermatitis.
Regarding treatment, we must consider the extension, anatomical site, and the immunological status of the host. Due to the resistance observed in the treatments used, the use of combinations of these and extraction of foreign bodies or debridement of the lesions is recommended. An important characteristic of M. abscessus complex is the presence of macrolide resistance observed in M. abscessus subsp. Abscessus, and M. abscessus subsp. bolletti due to functional inducible erythromycin ribosome methyltransferase (erm (41)), generating a resistant phenotype. However, in M. abscessus subsp. massiliense the erm (41) gene is not functional, generating a profile susceptible to macrolides and useful as a treatment for this microorganism [8,16]. Tigecycline and moxifloxacin are also more effective against M. abscessus subsp. massiliense than against M. abscessus subsp. abscessus [10,17].
Some authors have reported successful treatment of M. abscessus complex with a combination use of macrolides with amikacin, fluoroquinolones, imipenem/cilastatin, or cefoxitin [18,19,20,21,22]. In addition, a few cases were successfully treated with oral clarithromycin as monotherapy [23,24]. In our patients, the treatments were similar, using the same type of antibiotics; however, in four clinical cases, the treatment and evolution data were not available (Table 1). The evolution of the treated patients was generally acceptable, except for one patient, who showed only a partial improvement.
For M. abscessus subsp. massiliense identification, conventional culture methods for bacterial isolation needs at least 7 days of incubation and in many times presenting a low level of success. The use of biochemical tests is not useful because they are not able to differentiate the members of M. abscessus complex. The histopathologic findings of M. abscessus complex are not specific, which may represent a diagnostic problem to the unexperienced pathologist [11]. The use of molecular techniques allows a rapid and more accurate identification of M. abscessus complex and are a fundamental tool for the control of Mycobacterium infections.
For exact identification of M. abscessus complex species, sequencing analysis of 16S rRNA subunit, the internal transcription spacer 16S-23S (ITS-1), and hsp65 and rpoB genes are recommended [8]. To carry out the identification, we used a previously described PCR end point, designed from the whole-genome sequence analysis, which can differentiate the species of M. abscessus complex. Among these specific genes, mass_3210 (879 bp) is specific to M. abscessus subsp. massiliense and is located between mass_3209 and mass_3211, which correspond to mab_3265c and mab_3266c genes, respectively, in the M. abscessus subsp. abscessus genome. This insertion gene region can be used to differentiate M. abscessus subsp. abscessus and M. abscessus subsp. bolletti from M. abscessus subsp. Massiliense by designing primers to sites flanking mass_3210, to positions in mab_3265c/mass_3209 and mab_3266c/mass_3211 genes [12,25]. In this sense, the correct identification of species or subspecies in relatively short times will allow improved patient management and therapeutic treatments, as well as epidemiological actions.
5. Conclusions
Our series consisted of nine cases of skin biopsies recorded in different years; for this reason we do not have all the data necessary for a complete description, in particular in four cases, causing several limitations in the work, especially in the therapy used and the evolution of patients due to lack of follow-up. We carried out the molecular identification of M. abscessus subsp. massiliense as the etiological agent of various skin infections using a PCR capable of differentiating M. abscessus complex members. The accurate identification of M. abscessus complex is important because antibiotic susceptibility and treatment outcomes differ according to the etiologic M. abscessus complex members. In addition, in the case of the Spanish patient, the finding of M. abscessus subsp. massiliense was associated with treatment with an anti-TNF drug, this is remarkable because we have not found any similar cases in the literature reviewed.
Author Contributions
C.R.-C., R.H.-C., A.M.-R. and C.D.S.-C. conceived, designed, and reviewed the manuscript. S.T.-C. and C.A.-D. provided the ideas and contributed to writing the manuscript. R.A. addressed the questions related to bibliographies and summaries. E.M.-H. reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) Hospital General Dr. Manuel Gea Gonzalez, Mexico City, Mexico (27 September 2019; IRB No. 177-2019) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thomson, R.; Tolson, C.; Sidjabat, H.; Huygens, F.; Hargreaves, M. Mycobacterium abscessus isolated from municipal water-a potential source of human infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.R.; Kim, H.J.; Koh, W.J.; Ki, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, J.M.; Lee, D.Y. Cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense infection of the sole of the feet. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.S.; Yang, C.H.; Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Chao, A.S.; Leu, H.S.; Wu, T.L.; Lin, C.S.; Griffith, D.E.; Chiu, C.H. Postcesarean section wound infection caused by Mycobacterium massiliense. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsao, S.M.; Liu, K.S.; Liao, H.H.; Huang, T.L.; Shen, G.H.; Tsao, T.C.; Lee, Y.T. The clinical management of cesarean section-acquired Mycobacterium abscessus surgical site infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Johansen, M.D.; Herrmann, J.L.; Kremer, L. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria and the rise of Mycobacterium abscessus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victoria, L.; Gupta, A.; Gómez, J.L.; Robledo, J. Mycobacterium abscessus complex: A Review of Recent Developments in an Emerging Pathogen. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 659997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopeman, R.C.; Harrison, J.; Desai, M.; Cox, J.A. Mycobacterium abscessus: Environmental Bacterium Turned Clinical Nightmare. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Sheng, W.H.; Hung, C.C.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, L.N.; Hsueh, P.R. Mycobacterium abscessus Complex Infections in Humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.J. Nontuberculous Mycobacteria-Overview. Microbiol. Spectrum. 2017, 5, 5-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Cheng, A.; Ku, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, J.T.; Hsieh, T.W.; Sheng, W.H.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, U.I. Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense exhibit distinct host and organ specificity: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Infect. Diseases 2022, 116, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardiña, L.A.; Kaw, U.; Jour, G.; Knabel, D.; Dyck, R.M.; Procop, G.W.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Harrington, S.; Demkowicz, R.; Piliang, M.P. Diagnosis of Mycobacterium abscessus/chelonae complex cutaneous infection: Correlation of tissue culture and skin biopsy. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.; Han, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Ki, C.S.; Huh, H.J.; Yong, D.; Koh, W.J.; Shin, S.J. Development of a one-step multiplex PCR assay for differential detection of major Mycobacterium species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2736–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, R.S.; Lourenço, M.C.S.; Fonseca, L.D.S.; Leão, S.C.; Amorim, E.D.L.T.; Rocha, I.L. Epidemic of postsurgical infections caused by Mycobacterium massiliense. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanaga, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Era, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Kanazawa, Y.; Tomita, A.; Furuta, M.; Washizu, M.; Makino, M.; Ishii, N. Multiple cases of cutaneous Mycobacterium massiliense infection in a “hot spa” in Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingen, J.v.; Zwaan, R.D.; Dekhuijzen, R.P.N.; Boeree, M.J.; Soolingen, D.v. Clinical relevance of Mycobacterium chelonae-abscessus group isolation in 95 patients. J. Infect. 2009, 59, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.E.; Shin, S.J.; Won, C.J.; Min, K.N.; Oh, T.; Hahn, M.Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Daley, C.L.; Kim, S.; et al. Macrolide treatment for Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense infection and inducible resistance. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, Y. In vitro activity of clarithromycin in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium massiliense. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmon, K.E.; Pounder, J.I.; Greene, J.N.; Walsh, F.; Anderson, C.M.; Cohen, S. Identification of an emerging pathogen, Mycobacterium massiliense, by rpoB sequencing of clinical isolates collected in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, M.; Barkan, D. Alternative and Experimental Therapies of Mycobacterium abscessus Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessar, R.; Cambau, E.; Reyrat, J.M.; Murray, A.; Gicquel, B. Mycobacterium abscessus: A new antibiotic nightmare. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Shahraki, A.; Mirsaeidi, M. Phage Therapy for Mycobacterium abscessus and Strategies to Improve Outcomes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Tsai, H.Y.; Cheng, A.; Liu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Liao, C.H. Otitis media and otomastoiditis caused by Mycobacterium massiliense (Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. bolletii). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3754–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rominski, A.; Roditscheff, A.; Selchow, P.; Böttger, E.C.; Sander, P. Intrinsic rifamycin resistance of Mycobacterium abscessus is mediated by ADP- ribosyltransferase MAB_0591. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.J.; Jeon, K.; Shin, S.J. Successful treatment of Mycobacterium massiliense lung disease with oral antibiotics only. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1098–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Yi, H.; Chun, J.; Cho, S.N.; Daley, C.L.; Koh, W.J.; Shin, S.J. The genome sequence of ‘Mycobacterium massiliense’ strain CIP 108297 suggests the independent taxonomic status of the Mycobacterium abscessus complex at the subspecies level. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).