Abstract
Yersinia enterocolitica, widespread within domestic and wild-living animals, is a foodborne pathogen causing yersiniosis. The goal of this study was to assess a genetic similarity of Y. enterocolitica and Y. enterocolitica-like strains isolated from different hosts using Multiple Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis (MLVA) and Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) methods, and analyze the prevalence of virulence genes using multiplex-Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) assays. Among 51 Yersinia sp. strains 20 virulotypes were determined. The most common virulence genes were ymoA, ureC, inv, myfA, and yst. Yersinia sp. strains had genes which may contribute to the bacterial invasion and colonization of the intestines as well as survival in serum. One wild boar Y. enterocolitica 1A strain possessed ail gene implying the possible pathogenicity of 1A biotype. Wild boar strains, represented mainly by 1A biotype, were not classified into the predominant Variable-Number Tandem Repeats (VNTR)/PFGE profile and virulotype. There was a clustering tendency among VNTR/PFGE profiles of pig origin, 4/O:3, and virulence profile. Pig and human strains formed the most related group, characterized by ~80% of genetic similarity what suggest the role of pigs as a potential source of infection for the pork consumers.
1. Introduction
The genus Yersinia has been recently classified to Yersiniaceae family [1] and comprises of 19 species, i.e., Y. aldovae, Y. aleksiciae, Y. bercovieri, Y. enterocolitica, Y. entomophaga, Y. frederiksenii, Y. intermedia, Y. kristensenii, Y. massiliensis, Y. mollaretii, Y. nurmii, Y. pekkanenii, Y. pestis, Y. philomiragia, Y.pseudotuberculosis, Y. rohdei, Y. ruckeri, Y. similis, and Y.wautersii with a wide range of hosts (fish, insects, plants, mammals, and humans) [1,2,3]. Species. i.e., Y. pestis, Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis are pathogenic to humans. Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis cause human yersiniosis commonly reported in Europe [4]. All Y. pseudotuberculosis strains are considered pathogenic, while Y. enterocolitica includes both pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains according to the biotypes division (1A, 1B, and 2–5). The most common bioserotypes causing human yersiniosis in Europe are Y. enterocolitica 4/O:3 and 2/O:9 [5,6]. Strains belonging to biotype 1A are considered to be nonpathogenic because they lack significant virulence genes such as the chromosomal ail gene (attachment-invasion-locus) and the 70-kb virulence plasmid pYV. However, there are reports about potential enteropathogenicity of strains from 1A biotype [7,8,9,10,11]. Y. enterocolitica is most commonly found in pig meat and its products, in particular in raw or undercooked pork and pork products, but also in milk and other dairy products, plants, seafood, and drinking water. Food, especially pork, since fattening pigs are a symptomless reservoir, may be contaminated primarily or cross-contaminated by infected surface or equipment used during food processing. Other sources of possible Y. enterocolitica contamination include environment, poultry, cattle, sheep, goats, cats, dogs, and wild animals such as rodents, deer, and boars. Y. enterocolitica is present in pigs’ tongues, oral cavities, tonsils, lymph nodes, and feces. During the slaughter and processing of meat, Y. enterocolitica may be transferred from contaminated tissues onto the rest of the pig carcass and next persists in cooling conditions in pork products in retailers [12,13,14]. The risk factors of Y. enterocolitica transmission are poor hygiene after batch removal and the absence of cloth-boot change rooms at entrances to the facilities, straw on floors or mixing pig batches [15]. Furthermore, Y. enterocolitica strains are not detectable within the current pig meat inspection in EU [16]. The remaining species of the Yersinia genus were noted in the environmental samples, i.e., Y. pekkanenii was previously isolated from plants, water, and soil samples which indicates the environmental occurrence [17]. Y. kristensenii and Y. frederiksenii also tested within this work (listed in Table 1) have been isolated primarily from fresh water, sewage, soil, fish, wild rodents, domestic animals, foods, healthy and sick humans [18].

Table 1.
Yersinia spp. strains (n = 51) used in this study.
Many known virulence determinants are present in pathogenic biotypes of Y. enterocolitica. The most important for Yersinia sp. virulence are YadA (Yersinia adhesin A, outer membrane protein) conferring bacteria human serum resistance and ability to adhere to the intestinal epithelium; Ail (outer membrane protein) ensuring adhesive-invasive properties and invasin Inv (transmembrane protein) enabling rapid transcytosis through the intestinal epithelial layer. A thermostable enterotoxin Yst causes damage of the intestinal mucosa resulting in diarrhea in humans. An important chromosomal gene is ymoA (Yersinia-modulating protein) encoding the YmoA protein, which negatively regulates the expression of various genes, e.g., inv and ystA. Another virulence factor, a Myf antigen [8,19] is present in pathogenic biotypes and it possibly participates in the colonization of the gut, production of enterotoxin Yst, and protection against phagocytosis. The type III Yop effector proteins secretion system (T3SS) enables pathogenic Yersinia species to survive in the extracellular environment such as human intestine. A less-known type II secretion system (T2SS) probably plays a dual role for both the pathogenicity and the environmental survival of Y. enterocolitica. [20,21]. Due to this, in this work, the presence of the T2SS (Yts1) was screened in all tested Yersinia sp. More details on the other Yersinia sp. virulence factors can be found in [22,23,24,25].
Virulence genes such as myfA, invA and ymoA (Supplementary Table S1), characteristic of the pathogenic strains of Y. enterocolitica [8,26], have been detected in the genome of strains of 1A biotype [8]. This shows that the division of biotypes may not pertain the real pathogenicity within the Y. enterocolitica species. Due to this fact, the assessment of virulence profiles of Y. enterocolitica and Y. enterocolitica-like strains, i.e., Y. kristensenii or Y. frederiksenii and Y. pekkanenii is required.
The Y. enterocolitica occurrence in wild boars in Poland has so far been confirmed by Morka K. et al. in western Poland in 2018 [27], Syczyło et al. in 2016 [28] during 2011–2014 hunting seasons mainly in North-Eastern Poland, Syczyło et al. in 2018 [29] in 12 out of 16 Polish districts across Poland during the hunting seasons of 2013–2014, Bancerz-Kisiel et al. in 2015 [30] in North-East Poland during the 2013 hunting season and Bancerz-Kisiel et al. in 2015 [31] in two voivodeships of northern Poland, one voivodeship of central Poland and from two voivodeships of southern Poland. Only one paper, a published dissertation, indicated the endemic or alluvial origin of Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from people in the years 1996–2008 [32]. Nevertheless, data on the relatedness of Y. enterocolitica strains present among the animal reservoir or their similarities to human strains are still missing in Poland. The genetic comparison of Yersinia sp. strains isolated from pigs, wild animals, and humans will reveal the phylogenetic relationships between strains from varied origins.
The main object of this work was to determine the virulotypes and genetic profiles of Y. enterocolitica and Y. enterocolitica-like strains isolated from both humans and animals. To determine the genetic relationships between strains the gold standard PFGE (Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis) and MLVA (Multiple Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat Analysis) were used to generate a DNA fingerprint of a single bacterial isolate.
2. Results
2.1. Virulotyping
The presence of frequent Yersinia virulence genes was assessed in this study. In this work 20 different virulence profiles (designated from A to T) were determined among 51 Yersinia sp. strains (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The most common virulence gene present in all strains was ymoA, a Y. enterocolitica chromosomal gene modulating the expression of virulence functions (n = 51/51), followed by ureC coding the enzyme urease (n = 49/51), inv coding the invasive protein (n = 47/51), myfA coding Myf antigen involved in the colonization of the intestine (n = 39/51) and yst coding the enterotoxin (n = 35/51).
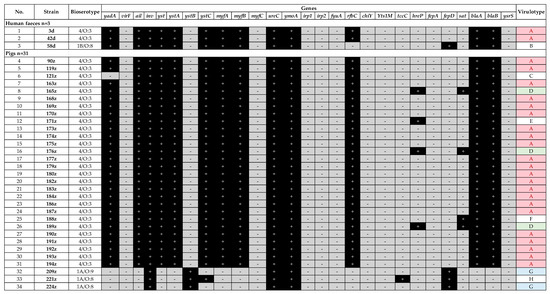
Figure 1.
Virulence profiles of Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from human feces and pigs.
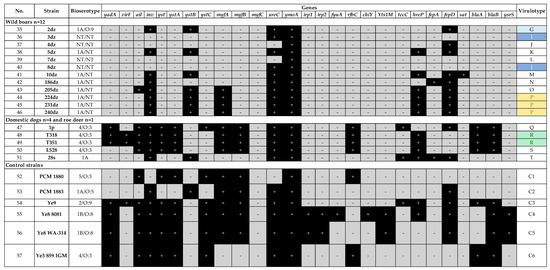
Figure 2.
Virulence profiles of Yersinia sp. strains isolated from wild boars, dogs, roe deer, and control strains.
The same profile A was observed for two out three human Y. enterocolitica strains (3d and 42d, 4/O:3, Figure 1). Another human strain (58d, 1B/O:8) lacked 4/O:3-specific rfbC gene, but possessed fepD gene coding enterochelin ABC transporter – profile B (Figure 1). This strain lacked the irp1, irp2, chiY, and Yts1M genes found in the reference strain of the same bioserotype 1B/O:8 (Figure 2).
Profile A was the most numerous within the pig Y. enterocolitica strains (n = 22/31, 71%) as among the human isolates. Virulotypes G and D were represented by 6.5% (n = 2/31) and 9.7% (n = 3/31) of pig strains, respectively; while each of the C, E, F, and H profiles was associated with only one pig strain (n = 1/31, 3.2%). The differences between profiles among pig strains were related to hreP (subtilisin/kexin-like protease), sat (streptogramin acetyltransferase), fepD (enterochelin ABC transporter) or ystB (enterotoxin YstIB of nonpathogenic biotype 1A) genes (Figure 1).
Nine virulotypes were noted within the wild boar Yersinia sp. strains, i.e., P (n = 3/12); I (n = 2/12) and L, J, G, K, M, O, N represented only by a single strain (n = 1/12). A very important observation is the presence of ail – adhesion-invasion and serum resistance-associated gene in Y. enterocolitica 205dz strain (1A biotype) (Figure 2).
The remaining Y. enterocolitica strains, which were isolated from dogs (4/O:3) and roe deer, were of different virulotypes, when compared to the other strains. Profiles Q and S were represented by single dog strains (n = 1/4), while profile R by two strains (n = 2/4). Roe deer 28s strain had profile T (Figure 2).
The less frequent genes among all tested strains were tccC, hreP, fepA, fepD, and sat (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Gene tccC coding an insecticidal toxin complex protein was present only in several isolates, i.e., 1A/O:8 pig (221z, n = 1/31), 4/O:3 dog (1p, n = 1/4) and in wild-living roe deer (28s) isolates. Gene hreP (subtilisin/kexin-like protease) was present within pig (n = 4/31), dog (n = 3/4), wild boar (n = 6/12) and one roe deer (28s) isolates. Gene fepD (enterochelin ABC transporter) was detected within one human 1B/O:8 isolate (n = 1/3), pig 4/O:3 isolates (n = 3/31), wild boar isolates (n = 9/12) and one roe deer isolate, while gene fepA was only present in wild boar 186dz isolate (n = 1/12) and roe deer isolate (28s). Gene sat (streptogramin acetyltransferase) was identified only in n = 4/31 pig 4/O:3 isolates and one n = 1/12 wild boar isolate.
2.2. Tracking Potential Variable-Number Tandem Repeats—VNTRs and Cluster Analysis
To characterize the group of n = 51 Yersinia sp. strains according to their genetic relationship the Tandem Repeats Finder was used to detect sequences containing VNTRs (variable-number tandem repeats) within the Y. enterocolitica 8081 genome. These VNTRs, met the criteria for easy handling, i.e., a repeat length greater than 20 nucleotides and at least 2 copies with a highly conserved repeated sequence (>90% matches). In this work only 5 of the 28 detected VNTRs loci (A-E) were selected for further analysis (Table 2). The number of tandem repeats was calculated based on previously described scheme in methodology and then used in clustering and listed in a phylogenetic tree.

Table 2.
VNTR sequences and primers used in this study.
Within the 53 tested Yersinia sp. strains (including two control strains) the total number of VNTR profiles was 19. According to the phylogenetic tree these profiles formed four main clusters. Cluster similarity cut-off value was set at least at 30% (Figure 3). The Simpson’s index of diversity for MLVA clustering was 0.6074. The same profile had twenty-eight 4/O:3 strains and one 2/O:9 control strain. Within this profile n = 23/28 strains were isolated from fattening pigs; n = 2/28 from domestic dogs; n = 2/28 from human feces and n = 1/28 was a control strain. The following profile represented by 4/O:3 bioserotype counted n = 5 strains isolated from fattening pigs and n = 1 from domestic dog. These two profiles shared 80% of genetic similarity and formed the M2 cluster (Figure 3). The M1 cluster consisted of wild animals (wild boar and roe deer) and pig strains being characterized by ~35% similarity, whereas M3 consisted of wild boar, human feces and dog strains sharing ~49% similarity. The last M4 cluster with ~41% similarity contained wild boar, pig, and control strains. (Figure 3).
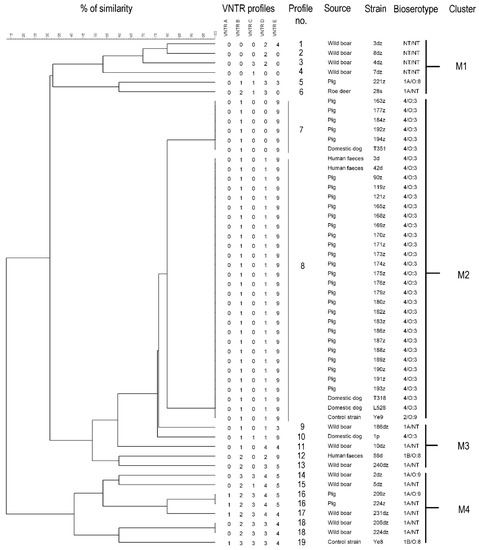
Figure 3.
Cluster analysis of MLVA profiles of Yersinia sp. with their corresponding origin and bioserotype. The tree was generated by the average linkage agglomeration method (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) based on the calculated number of tandem repeats using BioNumerics 7.6.2 (Applied Maths).
2.3. PFGE-CHEF (Contour-Clamped Homogeneous Electric Field)
Within the 51 tested Yersinia sp. strains the total number of PFGE profiles was 25. According to the phylogenetic tree these profiles formed three main clusters. Cluster similarity cut-off value was set at least at 60% The overall Simpson’s index of diversity for PFGE-CHEF clustering was 0.706 (Figure 4).
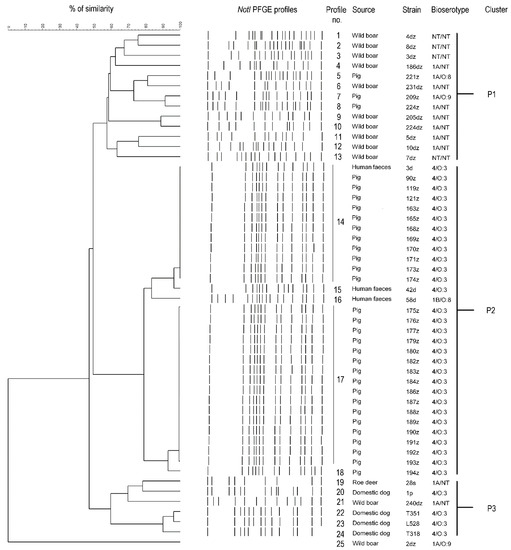
Figure 4.
Cluster analysis of PFGE profiles of Yersinia spp. with their corresponding origin and bioserotype. The tree was generated by the average linkage (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) based on the PFGE profiles using BioNumerics 7.6.2 (Applied Maths).
The P2 cluster with 80% genetic similarity included five PFGE profiles, i.e., n = 12 4/O:3 strains (isolated from pigs and human feces), n = 16 4/O:3 strains (isolated from pigs) and Y. enterocolitica 42d, 58d and 194z strains (Figure 4). Other profiles (n = 20/25) represented by a single wild animal, pig, roe deer and dog strains formed the P1 and P3 clusters with ~60% genetic similarity. The 2dz strain was not assigned to any of mentioned clusters however, it is shown on the phylogenetic tree as an unbound branch (Figure 4).
3. Discussion
The causative agent of yersiniosis is Yersinia enterocolitica, an important food- and water-borne enteropathogen, belonging to the Yersiniaceae family. Between 2014–2018 the number of yersiniosis cases in Poland has remained at constant levels (incidence rate between 0.4–0.6) [33]. In the years 2003–2019, the highest number of yersiniosis cases (n = 326) was recorded in 2009 [34]. Nevertheless, data on the number of cases can be underestimated due to low reportability and lack of bioserotyping as a part of routine diagnostics. In Poland prevalence of Y. enterocolitica and other species within Yersinia genus among animals was only studied in Northeast Poland [26,28,29,31,35]. High prevalence of Y. enterocolitica in the world, high pathogenicity of the 1B biotype, unusual psychrotrophic features and not much information on the occurrence of Yersinia sp. throughout the territory of Poland justify the study of Y. enterocolitica occurrence and its virulence genes. Except for Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis, there are also other species, ignored so far, which may be potentially pathogenic to humans or animals [18]. In the current work three Y. enterocolitica-like strains were included, i.e., Y. kristensenii, Y. frederiksenii and Y. pekkanenii.
The main source of Y. enterocolitica infection in humans is still pork and pork products, while Y. frederiksenii, Y. kristensenii and Y. pekkanenii have been isolated primarily from various environmental samples (water, sewage, soil), foods (milk, fruit, vegetables), domestic, and wild animals as well as healthy, and sick humans [17,18]. Y. enterocolitica is transmitted from slaughterhouses to meat-processing plants and then to retails via contaminated pig carcasses. It is facilitated by bacterial ability to multiply at low temperatures, even in frozen foods, and in a pH ranging from 4.2 to 9.0. Virulence factors such as pYV plasmid and YadA as well as ureC confer the resistance to low pH [36]. Due to the psychrotrophic feature and ability to produce the enterotoxin both at 37 °C (at pH 7.5) and at temperatures below 30 °C, Y. enterocolitica can survive cooling conditions and cause symptoms of diarrhea in humans after eating contaminated food [37].
A new tested reservoir for Y. enterocolitica includes wild animals such as wild boars or roe deer, which is reasonable considering that venison consumption is becoming increasingly popular [38]. The common assumption that only Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis are clinically relevant and the remaining species are environmental may have an impact on the identification of potential new hosts that can cause human disease. This also leads to overrepresentation of clinical Y. enterocolitica strains in databases and a limited number of representative Y. enterocolitica-like species in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALD)I Biotyper or VITEK® 2 Compact (bioMérieux) databases, which together require an application of several identification methods simultaneously, what was highlighted in a recently published paper [27].
In this study, virulence profiles and genetic relationships of strains derived from pig, wild boar, dog, roe deer, and human feces samples were investigated. The strains were screened for 27 virulence-associated genes, i.e., yadA, virF, ail, yst, ystA, ystB, ystC, ysrS, myfA, myfB, myfC, irp1, irp2, fyuA, Yts1M, chiY, inv, tccC, hreP, fepA, fepD, sat, blaA, blaB, rfbC, ureC, and ymoA. It was found that Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from pigs were characterized by less diversity of virulotypes and VNTR/PFGE profiles in contrast to wild boar group of strains. (Figure 1 and Figure 4). Most of the 4/O:3 strains isolated from fattening pigs slaughtered in west Poland carried virulence determinants and displayed the same virulence genes pattern between them, suggesting that pigs are an important reservoir of Y. enterocolitica 4/O:3 isolates (Figure 1). This observation is convergent with previous literature reports [39,40,41]. An exception for this remark was Y. enterocolitica 121z strain lacking yadA gene, which can be explained by the loss of pYV plasmid due to standard conditions for bacterial cultivation (incubation at 37 °C) [42,43]. Interestingly, in this paper there are some strains possessing additional genes such as sat (streptogramin acetyltransferase) and hreP (subtilisin/kexin-like protease) (Figure 1) previously reported as important virulence factors in Y. enterocolitica 1B and 1A biotypes, Y. pestis and Y. ruckeri [9]. The lack of virF gene in the majority of tested strains has been reported before [41,44].
This work described n = 12/51 1A Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from fattening pigs, wild boars and roe deer (Table 1) widely considered to be nonpathogenic to humans. However, in the last century, the first reports on nosocomial infections of Y. enterocolitica 1A were published [45,46]. Among the tested 1A group of strains, 11 had the ystB gene (Figure 1 and Figure 2). This gene is considered to be commonly present among nonpathogenic strains and its function is to control the production process of the heat stable enterotoxin. Although ystB gene does not encode an enterotoxin causing a damage to the intestinal epithelium there are reports demonstrating that Y. enterocolitica biotype 1A with the ystB gene is more often isolated from stool samples of patients suffering from diarrhea [37]. This information indicates that some strains of Y. enterocolitica biotype 1A are able to cause gastrointestinal symptoms after ingestion of contaminated food [8,9,10,11,47,48,49,50]. Altogether these findings indicate the role of the YstB toxin in the pathogenicity of Y. enterocolitica and suggest that biotype 1A cannot be considered completely nonpathogenic to humans. Despite the ystB gene, other genes had been detected within the tested Y. enterocolitica 1A isolates, i.e., ureC (12/12), fepD (12/12), tccC (2/12), sat (1/12), and hreP (7/12) (Figure 1 and Figure 2). The genes ureC and tccC enable bacteria to survive in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, sat confers resistance to streptogramins, which inhibit protein synthesis by ribosomes, while hreP is associated with early stage of 1B/O:8 infection [9,10].
It is noteworthy that Yersinia sp. strains (n = 12) isolated from wild boars harbor virulence-associated genes such as: inv, ystB, ureC, ymoA, hreP and fepD (Figure 2) and belong to 1A biotype. Moreover, one strain named 205dz (Table 1, 1A/NT) possessed ail gene, conferring bacteria human serum resistance and adhesive-invasive properties, characteristic of strains from pathogenic biotypes, what strongly supports an assumption about potential pathogenicity of 1A strains (Figure 2). Other papers also indicated the ail gene presence in 1A Y. enterocolitica strains [11,44,48,51,52,53]. One of them, recently published in Poland by Platt-Samoraj et al. [11] in 2017 proved that Y. enterocolitica 1A ail-positive strains are widely distributed in the environment. Batzilla et al. in 2011 confirmed that Y. enterocolitica 1A could be an emerging and opportunistic pathogen whose ability to cause an infection state seems to be dependent mainly on the host defense system [8]. These papers showed potential pathogenicity and ability of 1A strains to cause disease in humans. The presence of ail gene within nonpathogenic strains of 1A biotype could be recognized as the beginning of their acquisition of virulence-associated genes questioning biotypes division in terms of pathogenicity. On the other hand, Sihvonen et al. in 2011 compared the sequence of the ail gene from biotype 1A with ail derived from 1B indicating one point mutation—transition G2008088T and 99.7% of similarity, which according to the authors is the basis for studying the functionality of the ail gene in 1A strains. [48]. This suggests that molecular analyses of the pathogenicity should not be performed only based on possessing the virulence-associated ail gene. Taken together, the use of one method in determining potential pathogenicity may be insufficient, therefore, both virulotyping and bioserotyping seem to be worth an effort.
Currently, only limited data is available on the possible virulence, relatedness, and reservoir role of animals in human yersiniosis. Thus, the goal of this study was to analyze the genetic diversity of Yersinia sp. strains isolated from its reservoir—wild-living animals and fattening pigs and evaluate their genetic relationship with human Yersinia sp. strains. To reach this objective the multiplex-PCR, PFGE-CHEF, and MLVA were used. PFGE-CHEF is still a gold standard in epidemiological investigations while MLVA allows detection of more detailed differences. The advantage of PFGE is its adjustment to the specific tested microorganism. Despite this, Gilpin et al. claimed that PFGE has a very limited application for the discrimination of Y. enterocolitica biotypes 2, 3, and 4, but it is still valid for biotype 1A isolates [54]. It should be taken into account that current methods such as cgMLST or wgMLST, which, despite the high costs are less labor-intensive and more discriminatory techniques than PFGE or MLVA [54].
The presented study showed the clustering tendency among PFGE and VNTR profiles related to pig origin, 4/O:3 bioserotype and virulence profile and the similarity of PFGE and VNTR profiles between human and pig strains. Genetic and virulotype similarity between human and pig strains determined in this work strongly correlate with recognition fattening pigs and their meats as a main risk factor for transmission of Y. enterocolitica [55]. The same was shown in the studies conducted in Finland and Germany, which proved the genetic relationship of 81% and 83% of tested clinical strains with pig isolates in Finland and Germany, respectively [56,57]. Similar results were obtained by comparing the genetic relationship of strains isolated from humans, pigs, purchased pork, offal and domestic animals in Finland [56]. In contrast, there was no similarity between pig strains isolated in Finland and Germany, which was considered the effect of geographic distribution [57]. So far only Fredriksson-Ahomaa et al. proved significant differences between isolates from wild boars and slaughter pigs, which was also observed in our results—wild boar only represented biotype 1A while pig’s isolates mainly biotype 4/O:3 [58].
This work characterized Y. enterocolitica and Y. enterocolitica-like strains in terms of genetic similarity and virulence genes content. Presented results are certainly the basis for continuing research on the pathogenicity of Yersinia sp.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
A total of 51 tested Yersinia sp. strains originated from human stool (n = 3, Lower Silesia voivodship), wild boars (n = 12, Greater Poland voivodship), domestic dogs (n = 4, Lower Silesia voivodship), roe deer (n = 1, Lower Silesia voivodship) and fattening pigs (n = 31, Lower Silesia and Greater Poland voivodships), isolated in Poland during the years 2014–2018 were included in this study (Table 1). All tested strains were identified using MALDI TOF MS, VITEK®2 Compact (bioMérieux), PCR targeting 16S rRNA of Y. enterocolitica, 16S rRNA sequencing, and bioserotyped as previously described [27].
The Y. enterocolitica reference strains used as controls in this study were obtained from Polish Collection of Microorganisms (PCM, Wroclaw, Poland): PCM 1879 (4/O:3), PCM 1880 (5/O:3), PCM 1881 (4/O:3), PCM 1882 (1B), PCM 1883 (1A/O:5), PCM 1884 (2/O:8) and from Department of Applied Microbiology, Faculty of Biology, University of Warsaw, Poland: Y. enterocolitica 2/O:9, Y. enterocolitica WA-314, Y. enterocolitica 8081.
4.2. DNA Isolation
Bacteria were grown in Luria-Bertani Broth (Biocorp, Warszawa, Poland) for 16 h at 28 °C. Then 1 mL of bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm, for 10 min at room temperature. Extraction of genomic DNA was carried out using mini-columns from Genomic Mini kit (A&A Biotechnology, Gdańsk, Poland), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
4.3. Detection of Virulence-Associated Genes of Yersinia sp.
Several multiplex-PCRs based on gene grouping were used to detect virulence-associated determinants as: ail, ystB, and ymoA; blaA and blaB; chiY, ysrS, and yst1M; fepA and fepD; myfA, myfB and myfC; ureC and irp1; sat and hreP; rfbC and tccC; virF, invA and yst; irp2, ystA, and 16S; yadA and ystC; fyuA (Table S1). The 16S rDNA gene (amplified by following primers: AATACCGCATAACGTCTTCG and CTTCTTCTGCGAGTAACGTC) was used as a control specific for Y. enterocolitica [59].
The PCR mixtures consisted of 1 mM MgCl2, 1 × buffer, 0.2 mM dNTP, primers (Genomed, Warszawa, Poland) with a concentration in the range of 0.15 to 1.25 µM as indicated in Table S1, 1U of Taq polymerase, and 1 µL of template DNA. PCRs were performed with an initial denaturation step at 94 °C for 3 min, 35 cycles each of denaturation, annealing and extension as presented in Table S1 and a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. Amplicons were separated in 1.5% agarose gel containing 0.5 μg/mL ethidium bromide, at 120–130 V for 1 h and documented using GelDocXR System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) [35,60].
4.4. Multiple Locus Variable-Number Tandem Repeat (VNTR) Analysis—MLVA
The genome of the Y. enterocolitica subsp. enterocolitica 8081NC_008800 was scanned for tandem repeats using the Tandem Repeats Finder program (version 2.02 by Gary Benson) [61]. Five loci A, B, C, D, E were chosen for MLVA analysis. They were amplified by primers designed in this study (Table 2). PCRs were performed in a total volume of 25 µL containing 1.5 µL of 25 mM MgCl2, 2.5 µL of 10 × buffer, 0.5 µL of 10 mM dNTP, 0.1 µL of 100 µM primers (Genomed, Warszawa, Poland), 0.2 µL of Taq polymerase and 0.5 µL of DNA template. Thermocycling conditions included initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min and 35 cycles of: denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 60 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 120 s followed by final extension at 72 °C for 3 min. Amplification products were resolved in 2.5% agarose containing 0.5 μg/mL ethidium bromide in Tris-Acetate Electrophoresis 1× (TAE) buffer (pH 8.0), at 180 V for 2 h with cooling and documented using GelDoc XR System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Each product after electrophoresis was sequenced (Genomed, Warszawa, Poland). The number of repeats was calculated by dividing the difference of amplicon length and offsets size by the size of repeat, determined by BioNumerics 7.6.2 (Applied Maths). Dendrogram was generated using BioNumerics 7.6.2 (Applied Maths) by unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) clustering and categorical coefficient with a tolerance of 0%. The discriminatory power was calculated with the Simpson’s index of diversity [62].
4.5. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis—Contour-Clamped Homogenous Electric Field—PFGE-CHEF
The Yersinia sp. DNA plugs were prepared in Cell Suspension Buffer (CSB) according to PulseNet Yersinia pestis protocol with small modifications (www.pulsenetinternational.org/protocols) [63]. Briefly, the plugs were lysed for 2 h at 51 ± 2 °C in CLB/proteinase K (0.1 mg/mL) solution. The plugs were washed twice in pre-heated (50 °C) sterile water and four times in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer (pH 8.0) before restriction digestion. Bacterial DNA trapped in low melt 1.0% agarose (ABO, Gdańsk, Poland) was digested with 5U of NotI at 37 °C for 2 h. The restriction fragments were separated using 1.0% gel in 0.5 × TBE buffer with a CHEF Mapper XA system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The electrophoresis was carried out under following conditions: initial switch time: 3 s, final switch time: 30 s, voltage: 6 V/cm, included angle: 120°, run time: 20 h, temp. 14 °C. The gels were stained with ethidium bromide, destained with ultrapure water, and photographed with a Gel Doc EQ system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The DNA bands corresponded to specific PFGE profiles for each strain. Dendrogram was generated using BioNumerics 7.6.2 (Applied Maths) by Dice coefficient with optimization of 0.5% and an UPGMA clustering with a tolerance of 1.0%. The discriminatory power was calculated with the Simpson’s index of diversity [62].
5. Conclusions
The results of this study confirm that Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from pigs were less diverse in terms of virulotypes and VNTR/PFGE profiles in contrast to wild boar- derived group of strains. Wild boar strains represented only by biotype 1A and pig isolates mainly by biotype 4/O:3 were significantly different according to their genetic profiles. Pigs are an important host of Y. enterocolitica 4/O:3- carrying virulence determinants and this result has valuable implications in terms of food safety. Since fattening pigs are asymptomatic reservoirs (no clinical symptoms nor gross pathological lesions are visible) Y. enterocolitica strains are not detectable within the current pig meat inspection in EU. Additionally, Y. enterocolitica strains of biotype 1A can pose a risk of yersiniosis since they cannot be considered completely not virulent.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/10/1/65/s1. References [64,65,66,67] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.M., G.B.-P., J.B. (Jacek Bania); methodology, K.M., E.W.-Z., J.S., B.D., A.W.-B., M.K.; formal analysis, K.M., E.W.-Z., J.S., G.B.-P., J.B. (Jacek Bania); investigation, K.M.; resources, J.B. (Jacek Bania), J.B. (Jarosław Bystroń), G.B.-P., A.W.; writing—K.M.; writing—review and editing, K.M., J.B. (Jacek Bania), E.W.-Z., G.B.-P.; visualization, K.M.; supervision, G.B.-P., E.W.-Z., J.B. (Jacek Bania); funding acquisition, K.M., G.B.-P., J.B. (Jacek Bania) All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was prepared on the basis of a doctoral dissertation This research was partially funded by special-purpose grant of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education to carry out research or development work and tasks related to the development of young scientists and doctoral participants [Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Wroclaw, 0420/1404/16] (Main Investigator: Katarzyna Morka, Principal Investigator of the Team: Gabriela Bugla-Płoskońska).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank A. Korzeniowska-Kowal and A. Wzorek from the Polish Collection of Microorganisms and Professor Katarzyna Brzostek from Department of Applied Microbiology, University of Warsaw for sharing the control strains. We would like to thank G. Cieniuch, K. Kiejda and Kamila Korzekwa for their help during the isolating the strains.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Adeolu, M.; Alnajar, S.; Naushad, S.; Gupta, R.S. Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the “Enterobacteriales”: Proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5575–5599. [Google Scholar]
- LPSN—List of Prokaryotic Names with Standing in Nomenclature—Genus Yersinia. Available online: http://www.bacterio.net/yersinia.html#r (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Stenkova, A.M.; Bystritskaya, E.P.; Guzev, K.V.; Rakin, A.V.; Isaeva, M.P. Molecular Evolution of the Yersinia Major Outer Membrane Protein C (OmpC). Evol. Bioinform. 2016, 12, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, C.L.; Rosenzweig, J.A.; Kirtley, M.L.; Chopra, A.K. Pathogenesis of Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis in Human Yersiniosis. J. Pathog. 2011, 2011, 182051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skorek, K.; Raczkowska, A.; Dudek, B.; Miętka, K.; Guz-Regner, K.; Pawlak, A.; Klausa, E.; Bugla-Płoskońska, G.; Brzostek, K. Regulatory Protein OmpR Influences the Serum Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 by Modifying the Structure of the Outer Membrane. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79525. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Monitoring and identification of human enteropathogenic Yersinia spp.—Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Biological Hazards. EFSA J. 2007, 595, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Huovinen, E.; Sihvonen, L.M.; Virtanen, M.J.; Haukka, K.; Siitonen, A.; Kuusi, M. Symptoms and sources of Yersinia enterocolitica-infection: A case-control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Batzilla, J.; Heesemann, J.; Rakin, A. The pathogenic potential of Yersinia enterocolitica 1A. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 556–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, N.; Virdi, J.S. Distribution of virulence-associated genes in Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1A correlates with clonal groups and not the source of isolation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 266, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, N.; Virdi, J.S. The enigma of Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1A. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 37, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Platt-Samoraj, A.; Syczyło, K.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Jabłoński, A.; Łabuć, S.; Pajdak, J.; Oshakbaeva, N.; Szweda, W. Presence of ail and ystB genes in Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A isolates from game animals in Poland. Vet. J. 2017, 221, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents and Food-borne Outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3991. [Google Scholar]
- Latha, C.; Anu, C.J.; Ajaykumar, V.J.; Sunil, B. Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella enterica Typhimurium in meat and meat products using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Vet. World 2017, 10, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chlebicz, A.; Śliżewska, K. Campylobacteriosis, salmonellosis, yersiniosis, and listeriosis as zoonotic foodborne diseases: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 863–892. [Google Scholar]
- Fosse, J.; Seegers, H.; Magras, C. Prevalence and risk factors for bacterial food-borne zoonotic hazards in slaughter pigs: A review. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felin, E.; Hälli, O.; Heinonen, M.; Jukola, E.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Assessment of the feasibility of serological monitoring and on-farm information about health status for the future meat inspection of fattening pigs. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 162, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Murros-Kontiainen, A.; Johansson, P.; Niskanen, T.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Korkeala, H.; Björkroth, J. Yersinia pekkanenii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar]
- Sulakvelidze, A. Yersiniae other than Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. pestis: The ignored species. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gierczyński, R.; Jagielski, M.; Rastawicki, W. Evaluation of usefulness for selected virulence markers for identifying pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica strains. IV. Genes myfA and ureC. Med. Dośw. Mikrobiol. 2002, 54, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Brzostek, K. Mechanizmy regulacji czynników wirulencji Yersinia enterocolitica. Postępy Mikrobiol. 2009, 43, 7–38. [Google Scholar]
- von Tils, D.; Blädel, I.; Schmidt, M.A.; Heusipp, G. Type II secretion in Yersinia-a secretion system for pathogenicity and environmental fitness. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Pieczywek, M.; Łada, P.; Szweda, W. The most important virulence markers of Yersinia enterocolitica and their role during infection. Genes 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.; Williams, P. Yersinia virulence factors—A sophisticated arsenal for combating host defence. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Shehzad, A.; Raza, H.; Niazi, S.; Khan, I.M.; Akhtar, W.; Safdar, W.; Wang, Z. A comprehensive review on the prevalence, pathogenesis and detection of Yersinia enterocolitica. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41010–44102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Yersinia enterocolitica: Pathogenesis, virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szweda, W. Yersiniosis—A zoonotic foodborne disease of relevance to public health. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morka, K.; Bystroń, J.; Bania, J.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Korzekwa, K.; Guz-Regner, K.; Bugla-Płoskońska, G. Identification of Yersinia enterocolitica isolates from humans, pigs and wild boars by MALDI TOF MS. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syczyło, K.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Lipczyńska, K.; Jabłoński, A.; Procajło, Z.; Szweda, W. Monitoring of Yersinia enterocolitica strains from free-living animals using different methods. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syczyło, K.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Pajdak-Czaus, J.; Łabuć, S.; Procajło, Z.; Socha, P.; Chuzhebayeva, G.; Szweda, W. The prevalence of Yersinia enterocolitica in game animals in Poland. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Socha, P.; Szweda, W. Detection and characterisation of Yersinia enterocolitica strains in cold-stored carcasses of large game animals in Poland. Vet. J. 2016, 208, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Syczyło, K.; Szweda, W. The first pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica bioserotype 4/O:3 strain isolated from a hunted wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Poland. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierczyński, R. Genetyczna Struktura Populacji i Determinanty Chorobotwórczości Pałeczek Yersinia Enterocolitica Izolowanych z Materiału Klinicznego od Ludzi w Polsce w Latach 1996–2008. Habilitation Thesis, Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny, Warszawa, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Yersiniosis. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/AER_for_2018-yersiniosis-corrected.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Furman, S.; Napiórkowska, A.; Sadkowska-Todys, M. Yersiniosis in Poland in 2009. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2011, 65, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Socha, P.; Szweda, W. Bioserotypes and virulence markers of Y. enterocolitica strains isolated from roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) and red deer (Cervus elaphus). Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.L.; Hossain, M.A.; Isshiki, K.; Ukuku, D. Behavior of Yersinia enterocolitica in foods. J. Pathog. 2011, 2011, 420732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Virdi, J.S. Production of Yersinia stable toxin (YST) and distribution of yst genes in biotype 1A strains of Yersinia enterocolitica. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, A.; Battisti, E.; Zanet, S.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Ferroglio, E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Toxoplasma gondii in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) and red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Europe. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt-Samoraj, A.; Ugorski, M.; Szweda, W.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Wojciech, K.; Procajło, Z. Analysis of the presence of ail, ystA and ystB genes in Yersinia enterocolitica strains isolated from aborting sows and aborted fetuses. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2006, 53, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Szweda, W. Distribution of the ymoA and ystA genes and enterotoxins Yst production by Yersinia enterocolitica strains isolated from humans and pigs. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 15, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, R.; Moreno, L.Z.; Sena de Gobbi, D.D.; Raimundo, D.C.; Ferreira, T.S.; Spindola, M.G.; Hofer, E.; Falavina Dos Reis, C.M.; Matté, M.H.; Micke Moreno, A. Genotypic Characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica Biotype 4/O:3 Isolates from Pigs and Slaughterhouses Using SE-AFLP, ERIC-PCR, and PFGE. J. Pathog. 2013, 2013, 521510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bhaduri, S.; Magee, W.E. Maximizing plasmid stability and production of released proteins in Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1812–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Palmer, J.; Flint, S. Function of pYV plasmid on biofilm formation of Yersinia enterocolitica ERL032123 in the Presence of Ca2+. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, J.P.; Falcão, D.P.; Pitondo-Silva, A.; Malaspina, A.C.; Brocchi, M. Molecular typing and virulence markers of Yersinia enterocolitica strains from human, animal and food origins isolated between 1968 and 2000 in Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ratnam, S.; Mercer, E.; Picco, B.; Parsons, S.; Butler, R. A nosocomial outbreak of diarrheal disease due to Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 0:5, biotype 1. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 145, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, M.H.; Hooper, W.L. Excretion of Yersinia spp. associated with consumption of pasteurized milk. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 104, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, R.; Joutsen, S.; Hofer, E.; Säde, E.; Björkroth, J.; Ziegler, D.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strains isolated from patients and asymptomatic carriers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihvonen, L.M.; Hallanvuo, S.; Haukka, K.; Skurnik, M.; Siitonen, A. The ail gene is present in some Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strains. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, S.M.; Grant, T.H.; Robins-Browne, R.M. Pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 38, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Virdi, J.S. Interaction of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strains of diverse origin with cultured cells in vitro. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cheyne, B.M.; Van Dyke, M.I.; Anderson, W.B.; Huck, P.M. The detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in surface water by quantitative PCR amplification of the ail and yadA genes. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Michalczyk, M.; Szweda, W. Characterisation of ail-positive Yersinia enterocolitica of different biotypes using HRMA. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 269, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachelska, M.A. Identification of Pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica in Pig Tonsils Using the Real-Time PCR. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, B.J.; Robson, B.; Lin, S.; Hudson, J.A.; Weaver, L.; Dufour, M.; Strydom, H. The limitations of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for analysis of Yersinia enterocolitica isolates. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, J.; Keto-Timonen, R.; Virtanen, S.; Vilar, M.J.; Korkeala, H. Prevalence and dynamics of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica 4/O:3 among finnish piglets, fattening pigs, and sows. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Hallanvuo, S.; Korte, T.; Siitonen, A.; Korkeala, H. Correspondence of genotypes of sporadic Yersinia enterocolitica bioserotype 4/O:3 strains from human and porcine sources. Epidemiol. Infect. 2001, 127, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Stolle, A.; Siitonen, A.; Korkeala, H. Sporadic human Yersinia enterocolitica infections caused by bioserotype 4/O:3 originate mainly from pigs. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Wacheck, S.; Bonke, R.; Stephan, R. Different Enteropathogenic Yersinia Strains Found in Wild Boars and Domestic Pigs. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, H.; Hensel, A.; Aleksic, S.; Meyer, H. Identification of Yersinia enterocolitica within the genus Yersinia. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannet, W.J.B.; Reessink, M.; Brunings, H.A.; Maas, H.M.E. Detection of Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica by a Rapid and Sensitive Duplex PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4483–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC—PulseNet. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pulsenet/pathogens/index.html (accessed on 30 July 2018).
- Gierczyński, R. Evaluation of the usefulness of selected virulence markers for identification of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica strains. II. Genotypic markers associated with the pYV plasmid. Med. Dośw. Mikrobiol. 2000, 52, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharczuk, K. Investigation of molecular virulence factors of Yersinia enterocolitica 1B/08 human clinical isolates collected in Poland in 2009. Med. Dośw. Mikrobiol. 2013, 65, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Mittal, S.; Mallik, S.; Virdi, J.S. Molecular characterization of β-lactamase genes blaA and blaB of Yersinia enterocolitica biovar 1A. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 257, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtaz, H.; Rahimian, M.D.; Dehkordi, F.S. Identification and characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from raw chicken meat based on molecular and biological techniques. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).