Abstract
Physical inactivity among older adults is a major public health concern linked to various chronic conditions. Digitally delivered physical activity (PA) programs offer a promising solution to overcome traditional barriers. This scoping review aimed to explore the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement factors of these programs for older adults. A comprehensive search was conducted on PubMed, Embase (OVID), and Scopus on 22 May 2024, adhering to PRISMA guidelines. Inclusion criteria targeted older adults (≥60 years) engaged in healthy digital PA interventions. Data analysis was guided by the FAME Framework, TSQ, and the COM-B model. A total of 16 studies met the inclusion criteria, involving 901 older adults. Most studies reported moderate to high adherence rates with programs being well-received. However, several implementation challenges were found, such as inadequate digital literacy, concerns regarding program quality, participant safety, and lack of perceived relevance. Despite these implementation challenges, they may be overcome using the TAM and UTAUT frameworks for technology acceptance and usage to address digital literacy, ensuring high-quality interactions and participant safety, and incorporating social support. Future interventions should leverage similar theoretical frameworks to enhance design and implementation.
1. Introduction
Physical inactivity is a major public health concern globally, particularly among older adults. The World Health Organisation (WHO) identifies physical inactivity as the fourth leading risk factor for global mortality, contributing to an estimated 3.2 million deaths annually (Bull et al. 2020). In older adults, sedentary behaviour is associated with increased risks of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis, as well as mental health issues like depression and cognitive decline (Lee et al. 2012). Conversely, engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for older adults, including improved cardiovascular health, better weight management, enhanced mental health, and reduced risk of falls and fractures (Liguori 2020). Exercise can also improve muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and endurance, which are essential for maintaining independence and quality of life in older age. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends that older adults engage in at least 150 min of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, or 75 min of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week (Liguori 2020).
2. Barriers to Physical Activity
Despite the well-documented benefits of physical activity, older adults face several barriers to participating in traditional exercise programs. These barriers include physical limitations, such as arthritis or mobility issues, lack of transportation, financial constraints, and limited access to fitness facilities (Bethancourt et al. 2014). Additionally, psychological factors, such as fear of injury and lack of confidence, can deter older adults from engaging in physical activity (Allison et al. 2020; Wilson et al. 2021). Social isolation and lack of social support further compound these challenges, making it difficult for older adults to maintain regular exercise routines (Gell et al. 2015).
3. Digital Alternatives
The advent of digital technology presents a novel solution to overcoming many of the barriers associated with traditional exercise programs. Digitally delivered physical activity programs offer the flexibility and convenience needed to engage older adults in regular physical activity while being accessible at home (Wilson et al. 2021; Cimperman et al. 2013; Cimperman et al. 2016). Digital platforms also enable opportunities for social interaction, which are critical for maintaining motivation and adherence in older adults (Cimperman et al. 2013; Bethancourt et al. 2014). Thus, understanding the factors that influence the adoption and effective use of digitally delivered PA programs is essential for their successful implementation.
4. Theoretical Frameworks
The increasing prevalence of physical inactivity among older adults is a global concern, contributing to heightened risks of chronic illnesses and reduced quality of life (Lee et al. 2012). Digitally delivered physical activity (PA) programs have emerged as innovative solutions to address traditional barriers such as limited mobility, geographic constraints, and social isolation. However, their effectiveness hinges on understanding key factors that influence adoption and sustained engagement, such as digital literacy, access to technology, and subjective individual motivations. While theoretical frameworks such as the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis and Davis 1989) and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh et al. 2003) provide a critical lens for examining the usability and perceived utility of digital interventions from the perspective of the users, these frameworks do not account for behavioural determinants of engagement, which are critical in maintaining adherence to PA programs. Previous studies (Gell et al. 2015; Wilson et al. 2021) have highlighted the role of digital infrastructure and social support in promoting engagement in digital health interventions. Yet a detailed exploration of these factors in digitally delivered PA programs remains underdeveloped. This review seeks to fill this gap by systematically examining the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement variables within these programs, integrating insights from these theoretical frameworks to provide actionable recommendations for practice and policy.
5. Review Questions
Given the potential benefits and challenges of digitally delivered PA programs for older adults, this study aimed to explore their feasibility, acceptability, and engagement factors by examining the following review questions:
What factors influence the feasibility of digitally delivered PA programs for older adults, specifically related to technology access, participant safety, and cost-effectiveness?
How acceptable are these programs to older adults, considering satisfaction, perceived quality, and user experience?
What engagement variables facilitate or hinder adherence to these programs, including intrapersonal and environmental factors?
6. Methods
This scoping review was conducted following the scoping review framework proposed by Arksey and O’Malley (2005), and adhered to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines (Moher et al. 2009) for reporting. The process involved five key stages: identifying the research questions, searching for relevant studies, selecting studies based on predefined criteria, charting the data, and collating, summarising, and reporting the results. This review was registered with the Open Science Framework (OSF) Centre for Open Science Registry database [https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9EGW4].
6.1. Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria, displayed in Table 1 below, were determined based on the PICOS (Population, Interest, Comparisons, Outcomes) Framework (Methley et al. 2014).

Table 1.
PICOS criteria.
6.2. Search Strategy
A comprehensive search was performed on 22 May 2024 using the following databases: PubMed (Medline), Embase (OVID), and Scopus. The search strategy, depicted in Table 2, included a combination of Title, Abstract, keywords, and MeSH terms (if available), related to physical activity, digital interventions, older adults, and feasibility, acceptability or engagement.

Table 2.
Sample search strategy of Title, Abstract, keywords, and MeSH terms (if available).
6.3. Study Selection
All identified records from the database searches were exported to EndNote 20 for duplicate removal. Titles and abstracts of the identified studies were then screened against the predetermined eligibility criteria. Studies that potentially met the inclusion criteria were retrieved and full-text screening was conducted independently by two researchers. Discrepancies between researchers were discussed until a consensus was reached and the final list of included studies was compiled.
6.4. Data Extraction and Transformation
Articles were extracted onto a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet in a matrix format as recommended by Garrard (2020). The extracted data included study characteristics (author, year, country, study design), participant demographics (age, gender, health status), intervention details (type of exercise, duration, frequency, digital delivery method), and outcome measures (feasibility, acceptability, engagement). The data extraction process was verified independently by a second reviewer using the same Microsoft Excel spreadsheet to extract data from the included articles. Reviewers were blinded to each other’s decisions. A third reviewer was consulted for any articles where a consensus could not be reached.
7. Data Synthesis and Integration
Due to the lack of a specific framework for assessing digitally delivered PA programs at the point of time in writing, data synthesis was guided by three frameworks: The Joanna Briggs Institute’s FAME (Feasibility, Appropriateness, Meaningfulness, Effectiveness) framework for evaluating interventions (Pearson et al. 2005), the Telemedicine Satisfaction Questionnaire (TSQ) (Yip et al. 2003), and the COM-B (Capability, Opportunity, Motivation-Behaviour) Framework for behavioural analysis (Michie et al. 2011). The feasibility aspect of FAME assessed the practicality of implementation, including technology requirements, participant safety, and cost-effectiveness. The FAME framework was chosen for its comprehensive approach to the assessment of various dimensions of intervention implementation and outcomes, and its validity has been established in numerous studies across different healthcare contexts (Pearson et al. 2005). Acceptability sub-themes were designed based on the TSQ, which was selected for its validated constructs in evaluating user satisfaction with telehealth services (Yip et al. 2003). The TSQ includes measures such as quality of care, similarity with face-to-face programs, and communication experiences, making it particularly suitable for assessing the nuanced perceptions of older adults and their PA providers engaging in digital PA programs. Both Feasibility and Acceptability data were further categorised according to their relevance for participants or providers. For participant engagement, the COM-B model provides a comprehensive approach to understanding the intrapersonal (Capability and Motivation) and environmental (Opportunity) behavioural aspects influencing engagement with digital PA programs (Michie et al. 2011). This model categorises the factors affecting behaviour change into three components: Capability (both physical and psychological), Opportunity (both social and physical), and Motivation (both reflective and automatic). The validity of the COM-B model has been supported in various behavioural studies related to PA, demonstrating its effectiveness in identifying and addressing barriers to behaviour change (Teo et al. 2022). Subsequently, a narrative synthesis approach was employed to integrate findings from qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method studies, highlighting common themes and discrepancies.
8. Results
Referring to Figure 1, the initial database search resulted in the identification of 622 records. After various screening steps, 16 articles were included in the review.
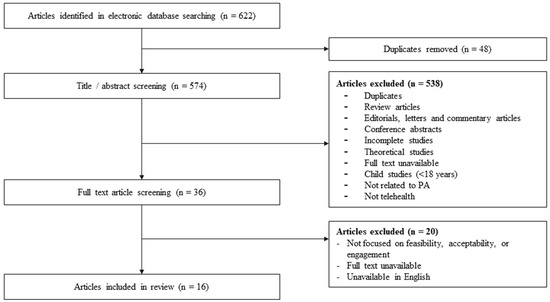
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of scoping review methodology.
8.1. Included Studies
Referring to Table 3, a total of 16 studies were included in this review. Seven studies were quantitative (Li et al. 2022; Daly et al. 2021; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022), three were qualitative (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Bosco et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019), and six were mixed-method studies (Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; Hong et al. 2014; Pischke et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021). Study locations included the United States (Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Li et al. 2022; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; Hong et al. 2014; Wu and Keyes 2006; Thompson et al. 2023), Australia (Daly et al. 2021), Germany (Pischke et al. 2022; Mikolaizak et al. 2022), the United Kingdom (Bosco et al. 2022), Brazil (da Silva et al. 2022) The Netherlands (Cabrita et al. 2019; Mikolaizak et al. 2022), Norway (Mikolaizak et al. 2022), Canada (Granet et al. 2023), and Israel (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021). The majority of digital programs reported either high (≥80%) participation rates (Daly et al. 2021; Li et al. 2020; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Granet et al. 2023) or moderate (≥70%) participation rates (Bosco et al. 2022; Li et al. 2022; Saquib et al. 2016; Wu and Keyes 2006; Thompson et al. 2023). One program had a low (≤60%) participation rate (Pischke et al. 2022).

Table 3.
Details of included studies (n = 16).
8.2. Participant Demographics
A total of 901 older adults (Mean age = 68.6 ± 5.8 years; Female = 626; Male = 275) were included in the 16 reviewed articles, as displayed in Table 3. Participants were generally of good health, with one study involving participants with mild cognitive impairment (Li et al. 2022), and another focused on postmenstrual older women (Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015).
9. Program Dosage
Referring to Table 3, nine studies (Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Bosco et al. 2022; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; Hong et al. 2014; Pischke et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019) had participants self-administer their own exercise sessions throughout the study, which ranged from 2 to 36 weeks. Four studies had set daily or weekly goals for the self-administered exercise participants, such as a minimum required daily step count (Cabrita et al. 2019; Li et al. 2020) or a total duration of 150 min of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week (Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Saquib et al. 2016). Seven studies (Li et al. 2022; Daly et al. 2021; Thompson et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Wu and Keyes 2006) had delivered a fixed digital exercise program structure ranging from 30 min to 60 min per session (Mean = 46 ± 14 min), for 2 to 5 times per week (Mean = 3 ± 1), and a range of 8 to 36 weeks (Mean = 16 ± 10).
10. Exercise Programs
Referring to Table 4, seven out of 16 studies delivered a combination of different types of physical activities, while the remaining 9 focused on a single type. The majority of studies (75%) involved cardiovascular exercise (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Bosco et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Cabrita et al. 2019; Daly et al. 2021; Saquib et al. 2016; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Hong et al. 2014; Pischke et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2022), followed by resistance exercises (41%) (Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Pischke et al. 2022; Li et al. 2020; da Silva et al. 2022), balance exercises (44%) (Pischke et al. 2022; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; da Silva et al. 2022), flexibility exercises (31%) (Pischke et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; da Silva et al. 2022), and Tai Chi (20%) (Li et al. 2022; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Wu and Keyes 2006). The majority of studies (63%) focused on delivering programs to the individual participant (Bosco et al. 2022; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cabrita et al. 2019; Daly et al. 2021; Saquib et al. 2016; Li et al. 2020; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Hong et al. 2014), while six studies (38%) involved group digital PA programs (Pischke et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Li et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2022).

Table 4.
Intervention components of included studies.
11. Digital Delivery Methods
Referring to Table 5, out of the 16 included studies, the majority of studies (69%) utilised mobile applications or online web platforms (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019; Li et al. 2020; Pischke et al. 2022; Hong et al. 2014; Daly et al. 2021; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2022) to deliver digital PA programs. Several studies (44%) also supplemented their exercise programs with wearable technology (Daly et al. 2021; Saquib et al. 2016; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cabrita et al. 2019; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Pischke et al. 2022), such as pedometers and accelerometers, to monitor PA frequency among participants. Other methods used included phone calls (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Daly et al. 2021; Saquib et al. 2016), DVD recordings of PA programs (Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023), and the use of videoconferencing software (Li et al. 2022; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Granet et al. 2023; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Five studies had a pre-intervention education session for participants on technology usage (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Li et al. 2020).

Table 5.
Digital components of included studies.
Table 6 displays the Feasibility variables to digital PA program implementation extracted from the reviewed literature.

Table 6.
Feasibility data extracted from reviewed literature 1.
11.1. Technological Requirements
Digital literacy was found to be a common hurdle for older adults commencing a digital PA program in some but not all studies (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Li et al. 2020; Hong et al. 2014; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006). In those where it was identified as a barrier, it was reported that many older adults were found to struggle with understanding the required procedures and handling the necessary equipment for digital technologies. Older adults were reported to need additional time at the beginning of the intervention to learn the procedures to receive telehealth, with some continuing to struggle with technology use throughout the study (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021). Other studies had noted digital literacy to not be an issue for older adults or their PA providers, with some reporting that older adults were able to develop the necessary skills to handle digital technologies quickly after some usage (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Li et al. 2022; Daly et al. 2021; Saquib et al. 2016; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Hong et al. 2014; Granet et al. 2023). Both older adults and providers may also have issues with access to the necessary hardware or infrastructure (e.g., devices for videoconferencing, suitable internet connection, etc.) for participating in digital programs (Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Granet et al. 2023; Lyons and Lewis 2014).
11.2. Safety Concerns
Two studies (Li et al. 2022; Daly et al. 2021) reported adverse events occurring during intervention delivery. Li et al. (2022) reported a total of 11 cases of adverse events during intervention delivery (11/69; 16% of participants). Five were classified as moderate events unrelated to the intervention, instead due to medical surgeries or health conditions. Six were classified as mild, four of which were suspected to be intervention-related events—one participant in the main intervention group reported a hernia pain caused by the exercise; three participants complained about muscular discomfort or pain. Of these 11 cases of adverse events, only 3 successfully proceeded with and completed the assigned intervention. From the study of Daly et al. (2021), two participants reported mild adverse events that were possibly intervention-related. One participant reported musculoskeletal knee pains from a pre-existing condition but was able to continue with the PA using a modified program. The second participant suffered a strained calf injury and sought treatment, subsequently withdrawing from the study. No intervention-related adverse events were reported by other studies (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Li et al. 2020; Hong et al. 2014; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Cadmus-Bertram et al. 2015; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Bosco et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019; Saquib et al. 2016; Pischke et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2022).
11.3. Cost Effectiveness
Participants and providers noted reduced costs of sessions and travel (Granet et al. 2023; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006). Providers also highlighted reduced costs of physical infrastructure required (Granet et al. 2023). There was no reported data on issues regarding cost-effectiveness.
12. Acceptability
Table 7 below displays the acceptability factors extracted from the reviewed literature.

Table 7.
Acceptability data extracted from reviewed literature 1.
12.1. Quality of Care Provided
In some studies, participants (Thompson et al. 2023; Hong et al. 2014; Saquib et al. 2016) and providers (Granet et al. 2023) had reservations regarding the quality of care and overall experiences using telehealth. However, participants (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Li et al. 2022; Daly et al. 2021; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; Pischke et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022) and providers (Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Li et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023) from 11 studies were satisfied with quality of services provided.
12.2. Comparison with Face-to-Face Delivery
When compared with face-to-face delivery, the scepticism of both participants (Thompson et al. 2023; Granet et al. 2023) and providers (Granet et al. 2023) mainly pertained to a perceived decrease in the ability to view another individual through a digital medium, compared with in-person encounters. Providers specifically mentioned limited feedback and monitoring of participants as an issue when it came to using digital delivery (Granet et al. 2023). However, these perceptions were not universal and the participants and providers from several studies felt the level of interaction and support were similar to that of face-to-face sessions (Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023). Older adults showed positive interest in the use of digital alternatives (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Daly et al. 2021; Pischke et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006) and many expressed further interest in continuing the use of digital alternatives post intervention (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Daly et al. 2021; Hong et al. 2014; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023). Specifically, several participants mentioned the convenience appeal of a digitally delivered PA program (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Daly et al. 2021).
12.3. Digital Communication
The majority of studies did not mention issues with digital communication, with several studies noting participants appreciated the instantaneous feedback and information exchange (Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Granet et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022).
13. Engagement
Table 8 displays the extracted engagement factors categorised according to the COM-B Framework.

Table 8.
Engagement factors categorised according to the COM-B Framework.
13.1. Capability
In terms of psychological capability, some studies reported a lack of digital literacy regarding the use of required digital technologies as a barrier to older adult engagement (Bosco et al. 2022; Hong et al. 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Daly et al. 2021; Granet et al. 2023; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Mikolaizak et al. 2022). A lack of understanding of PA requirements (e.g., recommended frequency of PA for older adults) was also noted to be a barrier for some older adults (Bosco et al. 2022). Improvements in technology access through pre-program education or employing user-friendly platforms assisted with the facilitation of engagement (Li et al. 2020; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Hong et al. 2014; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006). Providing relevant educational materials to participants to raise general health knowledge on the importance of healthy PA and the benefits of the intervention also facilitated engagement (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Bosco et al. 2022). The development of behavioural regulation skills, such as incorporating the use of pedometers, scheduling, logging progress, and activity planning, enabled older adults to develop habits and facilitate engagement (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Saquib et al. 2016; Bosco et al. 2022). Physical capability barriers identified were primarily negative health conditions that affected the ability to participate in activities in general, such as cognitive or physical impairments and chronic disease (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006).
13.2. Opportunity
Older adults appreciated the opportunity to partake in PA from the safety of their homes, which facilitated participation in their digital interventions (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Granet et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Thompson et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022). The convenience and timing flexibility of receiving digital programs was also well-received by older adults (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Technical access support (e.g., Technology education lessons, use of user-friendly interfaces, ongoing technical assistance etc.) provided during the study aided in facilitating adherence (Li et al. 2020; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Hong et al. 2014; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Assessing and maintaining the required hardware for digital delivery was noted as a potential barrier (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Mikolaizak et al. 2022). Participants frequently cited having online social interactions with peers to greatly influencing their willingness to engage with the digital alternatives (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Hong et al. 2014; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Additionally, social support from friends, family, and their PA providers aided in program engagement (Bosco et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022). Conversely, a lack of social interaction and social support was noted to be barriers to engagement (Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006).
13.3. Motivation
High perceived relevance was associated with increased program engagement in multiple studies (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Saquib et al. 2016; Cabrita et al. 2019; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Reasons for increased personal relevance were highly varied and included: perceiving the program to have a positive impact on their health (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006), feeling that the program was suitable and age-appropriate (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006), being able to socially interact with other participants (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Hong et al. 2014; Granet et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006), overcoming loneliness and boredom (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Bosco et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023), and enjoyment (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Granet et al. 2023; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). Using a participatory approach to program design also aided in program facilitation by improving participants’ perceived relevance (Bosco et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019). On the other hand, participants who perceived the program to be incongruent with their needs had lower levels of engagement (Li et al. 2022; Bosco et al. 2022; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Granet et al. 2023).
Technology access support to minimise digital literacy requirements was found to facilitate motivational engagement, as older adults were less hesitant to try utilising new technologies (Li et al. 2020; Lyons and Lewis 2014; Saquib et al. 2016; Granet et al. 2023; Hong et al. 2014; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; da Silva et al. 2022). On the other hand, an aversion to trying new technologies was associated with lower levels of digital self-efficacy and lower levels of engagement (Bosco et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023).
An online group exercise program reported higher participant engagement related to the social aspects of a group setting (Bosco et al. 2022; Pischke et al. 2022; Cabrita et al. 2019; Granet et al. 2023; da Silva et al. 2022). However, several participants were concerned about group-related issues such as peer pressure and a lack of privacy, leading to unwarranted anxiety or demotivation (Bosco et al. 2022; Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021).
Reinforcement through the use of goal setting (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Cabrita et al. 2019; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023) was highlighted by multiple studies as a facilitator for motivation. The use of periodic reminders and motivational messaging (e.g., the use of text prompts, phone calls, inspirational messaging, etc.) also facilitated participation (Lyons and Lewis 2014; Li et al. 2020; Thompson et al. 2023; Granet et al. 2023).
Several studies highlighted that the role of the PA provider was important for facilitating participation (Bosco et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006). A PA provider who could provide positive support and encouragement was seen as important for older adults (Bosco et al. 2022; Granet et al. 2023; Mikolaizak et al. 2022; Wu and Keyes 2006).
With regards to automatic motivation, developing and maintaining a daily routine that led to habit development was cited as a facilitator by participants (Cohen-Mansfield et al. 2021; Thompson et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006). Individual intrinsic sources of autonomous motivation were reported to be the major source for continued engagement as well as sustained long-term adherence post-program completion (Daly et al. 2021; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016).
14. Discussion
This scoping review synthesised data from 16 studies to investigate the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement of digitally delivered physical activity (PA) programs for older adults. In terms of feasibility for initial implementation, significant barriers in digital literacy were identified with many older adults struggling to use the necessary technology. With proper precautions, safety concerns were minimal, and the programs proved to be cost-effective by reducing travel and infrastructure expenses. Acceptability was mixed, with some scepticism about the quality of care but overall high satisfaction due to convenience and flexibility. Engagement factors highlighted the importance of digital literacy support, social interactions, perceived program relevance, and behavioural regulation.
Findings regarding digital literacy from this review supported previous literature highlighting the need for addressing digital literacy among older adults (Kienle et al. 2021; Cimperman et al. 2013; Cimperman et al. 2016; Wilson et al. 2021). Furthermore, studies highlighted the need for additional time and support at the beginning of interventions to help participants develop the required skills (Granet et al. 2023; Wu and Keyes 2006; Li et al. 2020; Saquib et al. 2016). However, these studies reported that older adults could quickly adapt to the technology after initial use, suggesting that with adequate support and preparation, digital literacy issues can be overcome. This finding aligns with previous literature, such as the work by Wilson et al. (2021) and Cimperman et al. (2016), which emphasised the importance of tailored support to improve digital literacy among older adults. Although access to digital tools and equipment was not found to be an issue, this finding may be due to the studies having provided the necessary hardware setup for the participants in their respective studies. Previous literature shows that different populations of older adults may face varying levels of access to technology, leading to differences in technology usage (Gell et al. 2015; Wilson et al. 2021). While the majority of studies in this review had not reported cases of adverse events, a study involving healthcare professionals and PA providers by Kienle et al. (2021) revealed concerns regarding the safety of participants engaging in remote digital PA programs. Furthermore, chronic health conditions and decreased physical capacity are valid concerns when considering the safety of older adults (Bethancourt et al. 2014). Hence, it is recommended that future programs consider incorporating safety management measures while designing digital PA programs for older adults.
Digital PA program acceptability was high amongst participants of reviewed studies. Nonetheless, these findings may be skewed due to the selection requirements for participants. The majority of included studies recruited participants who already had access to, or had been provided access to, resources to participate in digital PA studies. A study conducted by de Veer et al. (2015) on the determinants of intention to use e-Health presented the differences in online usage between participants as a result of technology familiarity and digital literacy. de Veer et al. (2015) showed that participants who had perceived the use of online health services as beneficial and had reported minimal difficulties regarding ease of use were more likely to express interest in using e-Health. It should also be noted that many older adults from the studies included in the review both expressed interest in the use of digital delivery and cited appreciating the benefits of these programs. Previous literature has also found that older adult technology usage was negatively impacted by physical (e.g., visual, cognitive, auditory) impairments that made it difficult to communicate online, especially without the appropriate equipment (Wilson et al. 2021; Gell et al. 2015). These findings were consistent with technology acceptance frameworks regarding perceived ease of use and perceived benefits, such as the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis and Davis 1989). As a result, these review findings may not be indicative of the number of older adults expressing acceptance towards the use of digital delivery methods but may provide greater insight into the factors facilitating acceptance, primarily perceived benefits from the use of digital technologies and perceived ease of use. Future studies may consider incorporating the TAM to better understand factors affecting acceptability.
Participant engagement findings related to digital PA programs from this review generally aligned with that of previous research on engagement with in-person PA programs, with social support, program relevance, reinforcement, PA provider support, and the development of behavioural control and regulation, being highlighted as influences on participation (Bethancourt et al. 2014). However, several notable differences were exclusive to digital PA programs. The theme of digital literacy was a prevalent influence identified in both intra-personal (Capability and Motivation) and environmental (Opportunity) factors. Previous studies found similar results regarding digital literacy issues with older adults facing a significant barrier in the uptake of digital PA programs, emphasising the need for consideration while designing online programs (Wilson et al. 2021; de Veer et al. 2015; Cimperman et al. 2013; Cimperman et al. 2016). Moreover, an aversion of older adults to utilising digital technologies was noted in previous literature but was only briefly mentioned in two studies in this review (Bosco et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2023). Older adults of different sociodemographic and health statuses expressed varying reasons for a reluctance to use novel technologies, such as disbelief in digital delivery efficacy, lack of perceived need to change, and high perceived usage difficulties (Cimperman et al. 2016; Wilson et al. 2021; de Veer et al. 2015; Allison et al. 2020; Gell et al. 2015; Nymberg et al. 2019). The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh et al. 2003) further validates the need for addressing these factors exclusively affecting behavioural intentions towards engaging in digital PA programs.
15. Research Implications
Table 9 displays a summary of the implementation recommendations based on the findings of this review and the recommendations of previous literature. These recommendations were guided by the TAM and UTAUT (Davis and Davis 1989; Venkatesh et al. 2003). These technology acceptance and behavioural intent frameworks were selected due to the relevance of the various digital-related factors found in this review to affect the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement of digital PA programs.

Table 9.
Program implementation recommendations.
15.1. Addressing Digital Literacy
Providing comprehensive, user-friendly training sessions at the beginning of digital PA programs may enhance participants’ ability to engage with the technology, thereby decreasing their aversion towards participating in an online program. This approach is supported by the TAM and UTAUT, which emphasise the importance of ease of use of digital technologies (Davis and Davis 1989; Venkatesh et al. 2003). Thus, comprehensive digital literacy training should be implemented as part of the program orientation. These training sessions can cover basic technology use, navigation of digital platforms, and troubleshooting common issues. Such sessions can be conducted in various formats, including in-person workshops, online tutorials, and one-on-one support. Moreover, ongoing technical support should be made available throughout the program to ensure ongoing smooth program delivery.
15.2. Ensuring High-Quality Interactions
Perceptions towards performance, benefits, and ease-of-use, were found to contribute significantly towards intentions and acceptance of digital technologies (Venkatesh et al. 2003). As such, ensuring high-quality interactions through effective PA provider communication, personalised program feedback and seamless real-time communication may enhance older adults’ perceptions of digitally delivered PA programs, resulting in greater acceptance and usage. Physical activity providers are recommended to learn the appropriate communication skills to effectively deliver PA or exercise online, such as focusing on verbal cues rather than visual to guide participants (Kienle et al. 2021). Moreover, personalised feedback online is crucial for maintaining participant motivation and engagement, aligning with previous findings highlighting the importance of personalised and engaging content in PA interventions online and in-person (Liguori 2020; Wilson et al. 2021). Incorporating motivational messaging, goal-setting features, and regular progress tracking may enhance the quality of interactions, such as regularly scheduled virtual check-ins with exercise providers to assist participants with staying on track and adjusting their goals as needed (Wilson et al. 2021). Furthermore, ensuring access to the necessary hardware and a stable internet connection is critical to allow for seamless real-time feedback, especially to older adults with limitations in seeing, hearing, or processing information (Allison et al. 2020; Wilson et al. 2021; Kienle et al. 2021). However, some studies highlighted barriers related to technology access, suggesting that providing devices or subsidies for internet costs could be beneficial. This approach is supported by previous studies that have shown improved outcomes when participants are provided with the necessary technological infrastructure (Gell et al. 2015; Wilson et al. 2021). Programs can partner with community organisations, libraries, and local governments to provide devices or offer subsidies for internet services. Establishing technology-lending libraries or offering low-cost rental options may help overcome financial barriers while providing access to adequate digital tools for high-quality videoconferencing.
15.3. Ensuring Participant Safety
Safety is a paramount concern for older adults engaging in physical activity. This review showed that safety considerations were relevant. Participants could provide an emergency contact list to their PA provider in the case of emergencies. Adequate physical space was a requirement for PA programs, especially for older and more vulnerable participants to minimise the risk of tripping and head-on collisions with peripheral objects (Kienle et al. 2021). Furthermore, programs must ensure that exercises are safe and suitable for participants with varying levels of fitness and health conditions. Programs should provide guidance on creating a safe exercise space at home, such as offering checklists and instructional videos on setting up a safe exercise area, including recommendations on appropriate footwear, removing tripping hazards, and ensuring adequate lighting.
15.4. Incorporating Social Support
The importance of social support in promoting usage of digital PA programs is well-documented in the literature and supported by the UTAUT (Allison et al. 2020; Gell et al. 2015; Venkatesh et al. 2003), with this review similarly showing that participants who had received encouragement from friends, family, and PA providers were more likely to remain engaged. Digital PA programs should therefore include mechanisms to facilitate either physical or online social interaction, such as offering family-friendly exercise routines. Additionally, incorporating social interaction elements, such as virtual group exercises and online forums, may reduce feelings of isolation and increase motivation, resulting in increased acceptability and engagement.
16. Strengths and Limitations
This scoping review adhered to PRISMA guidelines to systematically synthesised data from a diverse range of studies, providing a comprehensive overview of digitally delivered PA programs for older adults, providing novel insights into the implementation factors of digital PA programs for older adults. While previous reviews had investigated the implementation factors of either PA programs or the use of e-health, this review was the first to focus on the use of digital methods for healthy PA for older adults living within the community. The use of established theoretical frameworks, such as the FAME framework (Pearson et al. 2005), TSQ (Yip et al. 2003), and the COM-B model (Michie et al. 2011), enhanced the robustness and applicability of the findings. The review incorporated a wide array of study designs, including qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods studies, allowing for a nuanced understanding of various factors affecting digital PA program implementation and participation. Practical recommendations for improving the design and implementation of these interventions were also provided. Despite these strengths, the review faced several limitations. Participants in the reported studies were volunteers and thereby had an existing interest in PA and perhaps an existing amenability for digital delivery. Therefore, they may not be a true representative sample of the wider spectrum of older adults. Moreover, the participants may not be indicative of populations with limited access to digital technologies, which may have differing implementation barriers. This review also identified a lack of longitudinal evaluations within the included studies, limiting insights into the long-term effectiveness and sustainability of digital PA programs.
17. Future Research Recommendations
While this review focused on key factors influencing the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement of digitally delivered PA programs for older adults, the authors acknowledge that there may be other variables that play a significant role in participation in digital PA programs but lacked sufficient data to be properly captured and evaluated. For instance, included studies varied in program delivery mode (i.e., self-administered, guided exercise programs, etc.), program dosage, types of PA (i.e., resistance exercise, aerobic exercise, flexibility, etc.), and types of technology (i.e., videoconferencing platforms, mobile applications, computer programs, wearable technologies, etc.) used. Perceived program relevance, digital literacy, and digital self-efficacy were highlighted as key findings in this review; thus program structure may be an important consideration for future studies to evaluate to better understand their relationship towards participation. Moreover, review findings also highlighted the importance of having program access convenience and flexibility while needing strategies for reinforcing behaviour and facilitating routine building for sustained engagement. However, there was insufficient evidence to compare differences between self-administered exercise programs and guided exercise programs between studies. Future research should include measures to evaluate the effects of program structure on participation and explore the optimal balance between structured exercise guidance and self-administered exercise programs for participant autonomy. Additionally, future studies should include follow-up assessments to determine the participation in PA post-interventions.
18. Conclusions
In conclusion, this scoping review highlighted the potential of digitally delivered PA programs for older adults to overcome traditional barriers such as mobility limitations, access to facilities, and social isolation. Despite growing interest in the use of digital delivery methods, the findings underscore the importance of addressing digital literacy, ensuring high-quality interactions and participant safety, and incorporating social support, to enhance the feasibility, acceptability, and engagement of these interventions among both older adults and their PA providers. By utilising theoretical frameworks such as the TAM and UTAUT models, future digital PA programs may be more effectively designed to cater to the needs of the older adult population, ultimately contributing to improved public health outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.T., Z.Z., S.R.B.; methodology, J.L.T., Z.Z., S.R.B.; software, J.L.T.; validation, Z.Z., S.R.B., K.B.-H.; formal analysis, J.L.T.; investigation, J.L.T.; data curation, J.L.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.T.; writing—review and editing J.L.T., Z.Z., S.R.B., K.B.-H.; visualization, J.L.T.; supervision, Z.Z., S.R.B., K.B.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable as this was a review study.
Informed Consent Statement
This study entailed the analysis of publications/data available in the public domain, it did not include direct human material or data.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article. Original data files and analyses are stored in accordance with the authors’ institution’s data storage and management policy, and are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Allison, Matthew, Jonathan Patterson, Stephen Burton, Dhiren Patel, and Kelly Jean Brassil. 2020. Digital engagement preferences of individuals aged 65 and older with cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 38: 289–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, Hilary, and Lisa O’Malley. 2005. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology 8: 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethancourt, Hilary J., Dori E. Rosenberg, Tara Beatty, and David E. Arterburn. 2014. Barriers to and facilitators of physical activity program use among older adults. Clinical Medicine & Research 12: 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bosco, Alessandro, Lisa McGarrigle, Dawn A. Skelton, R. M. E. Laventure, Bex Townley, and Chris Todd. 2022. Make Movement Your Mission: Evaluation of an online digital health initiative to increase physical activity in older people during the COVID-19 pandemic. Digital Health 8: 20552076221084468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, Fiona C., Salih S. Al-Ansari, Stuart Biddle, Katja Borodulin, Matthew P. Buman, Greet Cardon, Catherine Carty, Jean-Philippe Chaput, Sebastien Chastin, and Roger Chou. 2020. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. British Journal of Sports Medicine 54: 1451–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrita, Miriam, Monique Tabak, and Miriam M. R. Vollenbroek-Hutten. 2019. Older adults’ attitudes toward ambulatory technology to support monitoring and coaching of healthy behaviors: Qualitative study. JMIR Aging 2: e10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus-Bertram, Lisa A., Bess H. Marcus, Ruth E. Patterson, Barbara A. Parker, and Brittany L. Morey. 2015. Randomized trial of a Fitbit-based physical activity intervention for women. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 49: 414–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimperman, Miha, Maja Makovec Brenčič, and Peter Trkman. 2016. Analyzing older users’ home telehealth services acceptance behavior—Applying an Extended UTAUT model. International Journal of Medical Informatics 90: 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimperman, Miha, Maja Makovec Brenčič, Peter Trkman, and Mateja de Leonni Stanonik. 2013. Older adults’ perceptions of home telehealth services. Telemedicine Journal and e-Health 19: 786–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Mansfield, Jiska, Aline Muff, Guy Meschiany, and Shahar Lev-Ari. 2021. Adequacy of web-based activities as a substitute for in-person activities for older persons during the COVID-19 pandemic: Survey study. Journal of Medical Internet Research 23: e25848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, Wagner Albo, Valéria Feijó Martins, Aline Nogueira Haas, and Andréa Kruger Gonçalves. 2022. Online Exercise Training Program for Brazilian Older Adults: Effects on Physical Fitness and Health-Related Variables of a Feasibility Study in Times of COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19: 14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, Robin M., Jenny Gianoudis, Travis Hall, Niamh L. Mundell, and Ralph Maddison. 2021. Feasibility, usability, and enjoyment of a home-based exercise program delivered via an exercise app for musculoskeletal health in community-dwelling older adults: Short-term prospective pilot study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 9: e21094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, Fred, and Fred Davis. 1989. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly 13: 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veer, Anke J. E., José M. Peeters, Anne E. M. Brabers, Francois G. Schellevis, Jany J. D. J. M. Rademakers, and Anneke L. Francke. 2015. Determinants of the intention to use e-Health by community dwelling older people. BMC Health Services Research 15: 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrard, Judith. 2020. Health Sciences Literature Review Made Easy. Burlington: Jones & Bartlett Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Gell, Nancy M., Dori E. Rosenberg, George Demiris, Andrea Z. LaCroix, and Kushang V. Patel. 2015. Patterns of technology use among older adults with and without disabilities. Gerontologist 55: 412–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granet, Jordan, Eva Peyrusqué, Fabien Ruiz, Fanny Buckinx, Lilia Ben Abdelkader, Thien Thanh Dang-Vu, Marie-José Sirois, Jean-Philippe Gouin, Benjamin Pageaux, and Mylène Aubertin-Leheudre. 2023. Web-Based Physical Activity Interventions Are Feasible and Beneficial Solutions to Prevent Physical and Mental Health Declines in Community-Dwelling Older Adults During Isolation Periods. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 78: 535–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Yan, Daniel Goldberg, Deborah Vollmer Dahlke, Marcia G. Ory, Jessica S. Cargill, Rachel Coughlin, Edgar Hernandez, Debra K. Kellstedt, and S. Camille Peres. 2014. Testing usability and acceptability of a web application to promote physical activity (iCanFit) among older adults. JMIR Human Factors 1: e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienle, Gunver Sophia, Paul Werthmann, Birgit Grotejohann, Theodor Hundhammer, Claudia Schmoor, Ch Stumpe, Sebastian Voigt-Radloff, and Roman Huber. 2021. Addressing COVID-19 challenges in a randomised controlled trial on exercise interventions in a high-risk population. BMC Geriatrics 21: 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I-Min, Eric J. Shiroma, Felipe Lobelo, Pekka Puska, Steven N. Blair, and Peter T. Katzmarzyk. 2012. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 380: 219–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Fuzhong, Peter Harmer, Kathleen Fitzgerald, and Kerri Winters-Stone. 2022. A cognitively enhanced online Tai Ji Quan training intervention for community-dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A feasibility trial. BMC Geriatrics 22: 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Junxin, Nancy Hodgson, M. Melanie Lyons, Ker-Cheng Chen, Fang Yu, and Nalaka S. Gooneratne. 2020. A personalized behavioral intervention implementing mHealth technologies for older adults: A pilot feasibility study. Geriatr Nurs 41: 313–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, Gary. 2020. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, Elizabeth. J., and Zakkoyya H. Lewis. 2014. An activity monitor and mobile device intervention is feasible among older adults. Clinical and Translational Science 7: 254–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methley, Abigail M., Stephen Campbell, Carolyn Chew-Graham, Rosalind McNally, and Sudeh Cheraghi-Sohi. 2014. PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: A comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Services Research 14: 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michie, Susan, Maartje M. Van Stralen, and Robert West. 2011. The behaviour change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implementation Science 6: 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolaizak, A. Stefanie, Kristin Taraldsen, Elisabeth Boulton, Katharina Gordt, Andrea Britta Maier, Sabato Mellone, Helen Hawley-Hague, Kamiar Aminian, Lorenzo Chiari, Anisoara Paraschiv-Ionescu, and et al. 2022. Impact of adherence to a lifestyle-integrated programme on physical function and behavioural complexity in young older adults at risk of functional decline: A multicentre RCT secondary analysis. BMJ Open 12: e054229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, David, Alessandro Liberati, Jennifer Tetzlaff, Douglas G. Altman, and Prisma Group. 2009. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicince 6: e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymberg, Veronica Milos, Beata Borgström Bolmsjö, Moa Wolff, Susanna Calling, Sofia Gerward, and Magnus Sandberg. 2019. ‘Having to learn this so late in our lives…’ Swedish elderly patients’ beliefs, experiences, attitudes and expectations of e-health in primary health care. Scandinavian Journal of Primary Health Care 37: 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, Alan, Rick Wiechula, Anthea Court, and Craig Lockwood. 2005. The JBI model of evidence-based healthcare. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare 3: 207–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, Claudia R., Claudia Voelcker-Rehage, Tiara Ratz, Manuela Peters, Christoph Buck, Jochen Meyer, Kai von Holdt, and Sonia Lippke. 2022. Web-based wersus print-based physical activity intervention for community-dwelling older adults: Crossover randomized trial. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 10: e32212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquib, Juliann, Abby C. King, Cynthia M. Castro, Lesley F. Tinker, Stacy Sims, James M. Shikany, Jennifer W. Bea, Andrea Z. Lacroix, Linda Van Horn, and Marcia L. Stefanick. 2016. A pilot study combining Go4Life® materials with an interactive voice response system to promote physical activity in older women. Journal of Women & Aging 28: 454–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Junsheng L., Zhen Zheng, and Stephen R. Bird. 2022. Identifying the factors affecting ‘patient engagement’ in exercise rehabilitation. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation 14: 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, Christian, Kathryn N. Porter Starr, Elizabeth Chmelo Kemp, June Chan, Emily Jackson, and Justin Phun. 2023. Feasibility of Virtually Delivering Functional Fitness Assessments and a Fitness Training Program in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20: 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, Viswanath, Michael G. Morris, Gordon B. Davis, and Fred D. Davis. 2003. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly 27: 425–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, Jessica, Milena Heinsch, David Betts, Debbie Booth, and Frances Kay-Lambkin. 2021. Barriers and facilitators to the use of e-health by older adults: A scoping review. BMC Public Health 21: 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. E., and Lawrence Malcolm Keyes. 2006. Group tele-exercise for improving balance in elders. Telemedicine Journal and e-Health 12: 561–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M. P., Anne M. Chang, Juliana Chan, and Ann E. Mackenzie. 2003. Development of the Telemedicine Satisfaction Questionnaire to evaluate patient satisfaction with telemedicine: A preliminary study. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare 9: 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).