Abstract
In this paper, an intelligent simulation method for chloride ion diffusion behavior in marine concrete is established based on a physical information neural network. The dimensionless constraint equation is constructed to solve the influence of different physical parameter dimensions on the generalization ability of the model. The performance of the simulation method is verified by field measured data. The influence of different exposure ages and chloride ion diffusion coefficients on chloride ion diffusion behavior is quantified. The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of chlorine ion (C) in concrete under a multi-dimensional diffusion state are analyzed, and the reliability model is further constructed to evaluate the degradation law of the service performance of marine concrete. The results show that the dimensionless physical information neural network model can effectively simulate the diffusion behavior and spatial–temporal distribution of C in marine concrete. The maximum error between the predicted value and the experimental value obtained by the method proposed in this paper is less than 15%. The dimension problem of high-order nonlinear equations can be solved by Non-PINN, with the maximum error value less than 5%. The spatial–temporal distributions of C on different exposed surfaces under a multi-dimensional diffusion state are independent of each other. The service performance of marine concrete will increase with an increase in slag content and protective layer thickness, and decrease with an increase in surface chloride ion concentration.
1. Introduction
The designed functions of concrete structures are expected to be significantly shorter than their design lifespan, influenced by the diffusion of ions [,,]. Therefore, scholars have begun to pay attention to the durability of the components [,,]. Studies have shown that corrosion is a major factor influencing the service life of structures. Chloride ions, through diffusion and other reactions, reach the steel surface, compromising the passivation film. Once the C on the steel surface exceeds the critical threshold (Cr), corrosion of the steel bar will lead to structural damage. The process of C entering concrete contains a variety of complex mechanisms, such as diffusion, penetration, binding, convection, and electromigration [,,]. In these mechanisms, the diffusion behavior of C is the main role of C entering concrete. Therefore, exploring the diffusion behavior of chlorides in concrete is an important prerequisite for predicting the corrosion time of steel bars in marine concrete. Homan et al. [] analyzed the diffusion behavior of C under multi-field coupling by fitting the water transfer rate and chloride ion diffusion coefficient. Song et al. [] introduced ‘contact duration’ to analyze the time-varying behavior of chloride diffusion coefficient. Zhang et al. [] quantified the effects of the water-binder ratio and curing time on chloride ion concentration on the surface of steel bars. However, the diffusion behavior of C will be affected by the coupling of surface chloride ion concentration, age, diffusion coefficient, and other factors, and the diffusion behavior changes significantly at an early age, which makes it difficult for the traditional theoretical model to analyze the effect of multiple features on the diffusion behavior of C at the same time [,,]. Yu et al. [] proposed the evaluation model for marine structures. Xia et al. [] proposed a reliability assessment model for concrete structures, including multiple parameters such as concrete type. However, the existing models are mainly based on theoretical analysis methods, which significantly consume computing resources.
Machine learning has been widely used in the prediction of chloride ion diffusion in concrete due to its better multivariate system analyzing functions [,,]. Hoang et al. [] used gene programming and multivariate adaptive regression to predict chloride ion diffusion behavior in cement mortar. Guo et al. [] used multiple machine learning algorithms to predict the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of compressed concrete. However, machine learning models usually require a large amount of training data to achieve high-quality-prediction performance. Additionally, the lack of interpretable black box models and small sample data of engineering tests lead to more limitations in the application of data-driven models to chloride ion diffusion simulation [,,]. Different from the traditional machine learning algorithm, the physical information neural network uses the physical constraint equation to constrain the distribution of the effective solution, which can make the model satisfy the data law and also satisfy the physical law. In recent years, scholars have used PINN to intelligently simulate physical fields with complex boundary conditions, such as fatigue, structural response, and parameter identification []. Wan et al. [] used inverse PINN to predict the diffusion coefficient. The results show that when the noise data is 5%, the PINN model can estimate the unknown parameters of the chloride ion diffusion equation. However, the model only considers the chloride ion diffusion behavior in a one-dimensional state and does not consider the time-varying behavior of the chloride ion coefficient.
Based on this, this paper proposes a dimensionless physical information neural network (Non-PINN) to simulate the diffusion behavior and service performance degradation of chloride under real service conditions (Figure 1). Considering the limitation of experimental data, this paper attempts to use Non-PINN without experimental data input to simulate the spatial and temporal diffusion behavior of chlorides. Based on the intelligent simulation results, a reliability model of service performance of marine concrete is constructed to quantify the service performance degradation of parameters such as slag content and surface chloride ion concentration. The core contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) Combining the chloride ion migration law based on Fick’s second law with PINN: the spatial and temporal distribution of C in concrete at different ages is simulated with high precision. (2) A dimensionless parameter equation is proposed to solve the influence of different parameter dimensions on the accuracy of the model. (3) The difference of the chloride ion diffusion mechanism in concrete under different dimensions is quantified. (4) The effects of different concrete cover thickness: the slag content (rslag) on the service performance of marine concrete structures is quantified.
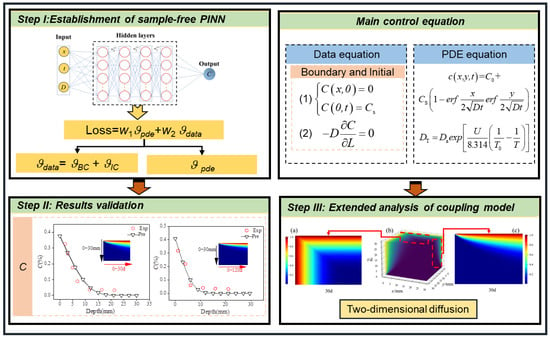
Figure 1.
The proposed framework for chloride ion evaluation using PINN.
2. The Diffusion Model Based on Non-PINN
2.1. Model Theory
The physical information neural network integrates the physical control equation into the neural network, and the control equation is mainly in the form of partial differential engineering. The main form of PINN can be obtained as follows:
where u is the solution of the equation, F[u] is a linear or nonlinear operator, IC[u] is an initial condition operator, FIC(u) is an initial condition, BC[u] is the boundary condition operator, FBC(u) is the initial condition, and M is the domain.
In this paper, time t and space x are used as input variables, and chloride ion concentration c is used as an output variable (Figure 2). Therefore, the loss of PINN established in this paper is mainly composed of physical constraint (ϑpde(θ)), boundary loss (ϑBC(θ)), and initial condition loss (ϑIC(θ)):
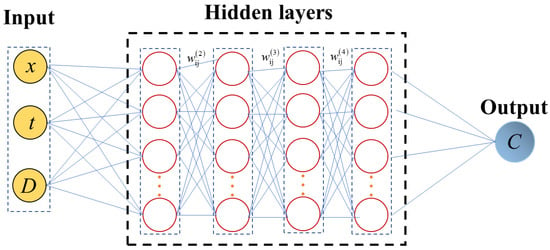
Figure 2.
Chloride ion diffusion model based on physical information neural network.
To describe the physical process of diffusion, PINN must satisfy the constraints of boundary, PDE, and initial conditions. NIC, NBC, and Npde represent the number of training points used to calculate the initial loss, boundary loss, and PDE loss, respectively. The LOSS obtained after each iteration is expressed as follows:
where u(θ,xi,ti) is the predicted value of PINN; F(u(xi,ti)) is the theoretical value for network parameters.
The forward calculation of PINN can be realized through the above steps, and the loss function (LOSS) is minimized and the parameters are optimized through multiple iterations. It should be noted that this paper uses the mean square error as the indicator of LOSS:
2.2. Chloride Ion Diffusion Equation
The one-dimensional and two-dimensional forms of the chloride ion diffusion equation based on Fick’s second law are:
where t is the diffusion time, D is the chloride diffusion coefficient, x and y represent spatial variables, respectively, and C(x, t) represents the chloride ion concentration at x at time t.
Assuming that there is no chloride ion in the concrete at the initial stage, the boundary conditions can be defined as follows:
where Cs is the surface concentration.
Under the two-dimensional state, when x and y = L, the chloride ion does not diffuse, and the boundary conditions are considered to obey the Neumann boundary conditions:
When D is a fixed value, the numerical equation of chloride ion diffusion can be simplified to an equation with analytical solution, which can be used to verify the accuracy of the PINN model proposed in this paper:
where erf is the error function, and C0 represents the chloride ion concentration in concrete at the initial time.
2.3. Dimensionless Equation
The PINN constructed in most studies uses the original control equation without considering the influence of parameter dimensions. Therefore, a large number of grid points and a large amount of calculation time are needed to ensure the convergence of the model. However, this method is applicable to simple conditions because the governing equations involve fewer physical parameters. Considering that when using PINN to solve the physical field, the dimensional problem will significantly increase the computational cost and convergence performance of the model. Therefore, it is necessary to propose a dimensionless PINN to solve the influence of dimension on the accuracy of the model.
For the dimension and time parameters, the feature length xmax and the feature tmax are selected as the feature length and the feature time, respectively. The characteristic parameters of the chloride ion field model are as follows: (1) Diffusion coefficient: Considering that the unit of chloride ion diffusion coefficient is mm2/s, the dimensionless chloride ion diffusion coefficient Dnon can be obtained by multiplying the diffusion coefficient by the characteristic time and dividing it by the square of the characteristic length. (2) Chloride ion concentration: The chloride ion concentration inside the concrete can be divided by the surface chloride ion concentration to achieve dimensionlessness.
2.4. Service Performance Degradation Model
In this paper, the service performance evaluation model of marine concrete structure is proposed. Chloride ions in concrete exist in two states: (1) free chloride ions in the pore solution, and (2) chloride ion adsorption. Given that the concentration of free chloride ions is a crucial factor influencing the corrosion in concrete, the calculation model of free chloride ion content (Equation (12)) proposed by Nilsson et al. [] is used in this paper. The influence of temperature on the diffusion coefficient was analyzed by using the model proposed by Ref. []:
where Da is the content of free chloride ion, R is the activation energy, DT is the diffusion coefficient, T0 represents the reference temperature, and the recommended value is 10 °C.
On this basis, the deterioration coefficient K is added into the model by substituting Equations (12) and (13) into Equation (10):
The expected function of structures is determined by the probability of these structures. To assess this, a reliability model is proposed to evaluate the expected function of the structure. Firstly, the resistance of the model is determined by the Cr, and the loading effect is the free chloride ion concentration c(x,y,t) on the surface of the steel bar. Therefore, the function of the model is Z = G(Cr, c(x,y,t)) = cr − c(x,y,t). The failure probability [] of the structure is as follows:
2.5. PINN Model Parameter Selection
In this paper, python3.9.1 is used for programming, and the Adam and L-BFGS optimizers are used. This is because the Adam optimizer adjusts the learning rate of the model by analyzing the first-order matrix of the gradient, which can help the model converge quickly in the early stage and avoid gradient explosion. The L-BFGS optimizer updates the parameters by calculating the second-order matrix, which is more suitable for the case where the loss function is locally optimal, so the optimizer is more suitable for accurately adjusting the parameters. For the model parameters, this paper uses four hidden layers, an L-BFGS optimizer with a learning rate of 0.0001, and a Tanh function with better activation function performance. The specific parameter settings are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of PINN model.
2.6. Service Performance Parameters
The failure probability [] of concrete in the Qingdao tidal zone is analyzed. The effect of uncertain features is evaluated. It is worth noting that the material features and environmental parameters of concrete adopt the measured data. The Cr also adopts the advised value of the literature. The thickness of concrete cover (xk), chloride binding capacity (R), and deterioration coefficient (K) adopt following distribution model (Table 2).

Table 2.
Selection of uncertain parameters.
3. Model Discussion
3.1. Diffusion Behavior Evaluation
In this paper, the model is verified by the measured data of marine concrete carried out by Xue et al. []. In the literature, the concrete mixed with fly ash and mineral powder was exposed in the ocean tidal zone for 30, 120, 180, and 720 days, respectively. The specific parameters of the specimen are as follows (Table 3).

Table 3.
Long-term exposure test parameters of the specimen.
Figure 3 compares and analyzes the experimental values of chloride ion diffusion in concrete under different exposure ages with the simulated values of Non-PINN. When the exposure age is 30 d, the experimental values of chloride ion distribution along the concrete are 0.326, 0.264, 0.176, and 0.070, respectively, and the predicted values are 0.303, 0.274, 0.209, and 0.073, respectively. When the exposure age is 120 d, the test values of C distributed along the concrete are 0.317, 0.209, and 0.060, and the predicted values are 0.345, 0.181, and 0.078, respectively. When the exposure age is 180 d, the test values of C distributed along the concrete are 0.366, 0.244, and 0.143, respectively, and the predicted values are 0.361, 0.248, and 0.166, respectively. When the exposure age is 720 d, the test values of C along the internal distribution of concrete are 0.611, 0.532, 0.489, and 0.421, and the predicted values are 0.591, 0.519, 0.473, and 0.403, respectively. This shows that the intelligent model can simulate the diffusion behavior of C considering different exposure ages, and can also effectively simulate the diffusion law of C when the concrete tends to be saturated.
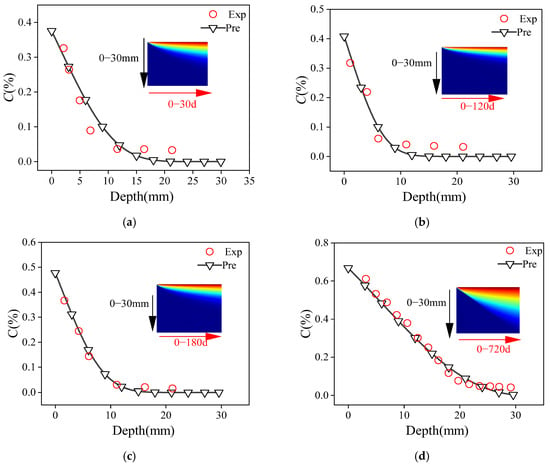
Figure 3.
Comparison of chloride ion diffusion test results and predicted results under different exposure ages: (a) 30 d, (b) 120 d, (c) 180 d, and (d) 720 d.
3.2. Results Validated with Numerical Data
In order to verify the effectiveness of the PINN framework proposed in this paper in solving high-order nonlinear equations, the Matlab2025b PDE toolbox is used to construct the finite element model, and the test conditions in Section 3.1 are used as the corresponding working conditions. The convergence of the PINN program is verified by setting the corresponding boundary conditions and comparing the PINN and numerical simulation results. Figure 4 shows the grid distribution of the numerical simulation set in this paper, and the grid growth rate is set to 1.3.
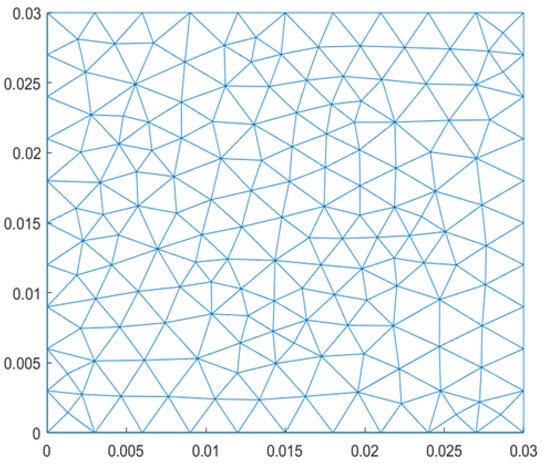
Figure 4.
Grid setting of numerical model.
The numerical model is subsequently used to simulate the chloride ion diffusion in concrete at 30 d, 120 d, 180 d, and 720 d, and the results were compared with the PINN simulation outcomes (Figure 5). Specifically, for a diffusion time of 30 days and distances of 2 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, and 10 cm from the diffusion surface, the chloride concentration values obtained via PINN (numerical simulation) were 0.31 (0.33), 0.27 (0.26), 0.20 (0.16), and 0.07 (0.05), with a maximum error of 0.04. For a diffusion time of 120 days and distances of 1 mm, 4 mm, 6 mm, and 10 cm from the diffusion surface, the corresponding values were 0.34 (0.32), 0.18 (0.21), 0.09 (0.06), and 0.03 (0.04), with a maximum error of 0.03. For a diffusion time of 180 days and distances of 1 mm, 4 mm, 6 mm, and 10 cm, the PINN (numerical simulation) results were 0.41 (0.39), 0.25 (0.26), 0.17 (0.16), and 0.05 (0.04), with a maximum error of 0.02. Finally, for a diffusion time of 720 days and distances of 1 mm, 4 mm, 6 mm, and 10 cm, the values obtained from PINN (numerical simulation) were 0.64 (0.63), 0.58 (0.59), 0.54 (0.52), and 0.35 (0.34), with a maximum error of 0.02.
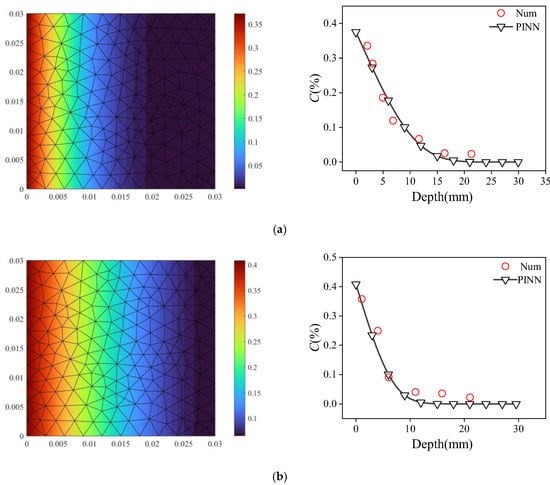
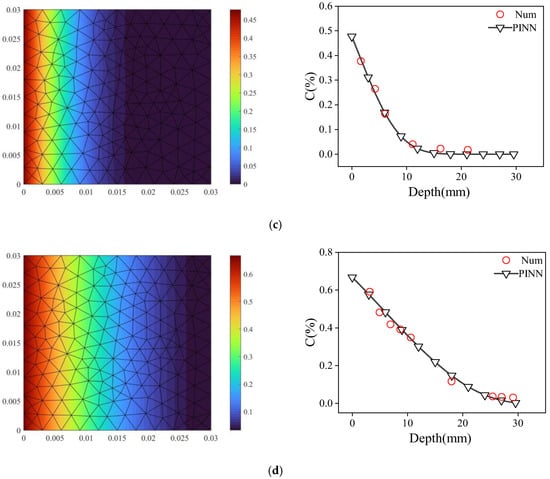
Figure 5.
The comparison between numerical results and PINN: (a) 30 d, (b) 120 d, (c) 180 d, and (d) 720 d.
3.3. The Effect of Non-Dimensionalization
By configuring various activation functions and time step settings, the model was trained to a fixed number of iterations (10,000), enabling a systematic comparison of the computational efficiency between the proposed Non-PINN framework and the conventional PINN approach (Table 4). The results demonstrate that the Tanh activation function yields the highest prediction efficiency. Specifically, when the time step is set to 1000, the loss values of Non-PINN and PINN using Tanh are reduced by 52.2% and 63.5%, respectively, compared to the second-best performing Sigmoid function. Furthermore, the Non-PINN framework significantly enhances computational efficiency, with the maximum reduction in computation time reaching 59.2%.

Table 4.
Comparison of model parameters.
3.4. Chloride Diffusion Coefficient
Figure 6 compares and analyzes the diffusion of C in concrete under different chloride ion diffusion coefficients. In the example, the specimen with the exposure age of 30 d in Section 2.1 is used. The chloride diffusion coefficients were set to 1.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, 2.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, and 3.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, respectively. It can be found that the chloride ion concentration in concrete increases significantly with the increase in the chloride ion diffusion coefficient. When x = 15 mm and D is 1.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, 2.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, and 3.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, respectively, the chloride ion concentration is 0.087, 0.115, and 0.137, respectively. Compared with D is 1.254 × 10−12 mm2/s, the chloride ion concentration increases by 32.2% and 57.4%, respectively, when D is 2.254 × 10−12 mm2/s and 3.254 × 10−12 mm2/s. This is because the concrete with higher chloride ion diffusion coefficient tends to have larger porosity and looser pore structure, resulting in faster accumulation of C in the concrete.
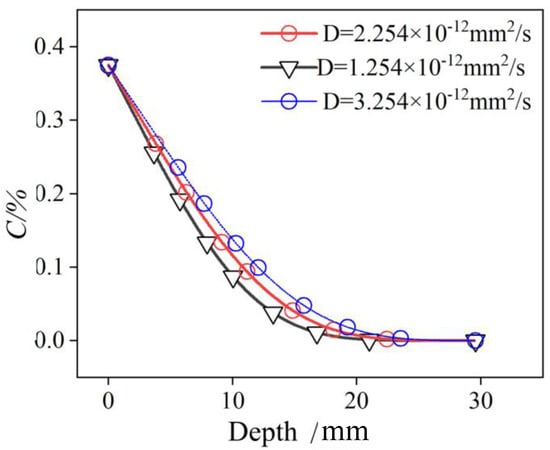
Figure 6.
Effect of D on chloride diffusion behavior.
3.5. Two-Dimensional Diffusion
In the actual service environment, it is necessary to consider the chloride ion transfer of concrete at different locations. One-dimensional diffusion often occurs on the surface of the component, and two-dimensional diffusion occurs at the edge of the structure. When multi-dimensional diffusion occurs, the steel corrosion in concrete is more serious. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the distribution of chloride ion field under multi-dimensional diffusion. Considering the limited experimental research on the distribution of chloride ion field under multi-dimensional diffusion, this paper uses the verified Non-PINN to analyze the chloride ion field under two-dimensional diffusion. It should be noted that the simulation parameters used are the parameters in Section 2.1 when the exposure age is 30 days. In addition, it should be emphasized that the initial governing equation is still based on the one-dimensional case, and only the boundary conditions and PDE governing equations are modified to adapt to the two-dimensional diffusion equation (Equation (7)). Figure 7 shows the diffusion behavior and concentration distribution of C in concrete under two-dimensional diffusion. It can be known that the Non-PINN can analyze the diffusion of C in concrete under the two-dimensional diffusion state. Figure 7a gives the distribution of C in the concrete when the exposure age is 30 d. When both sides of the concrete are exposed, the distribution of C along the exposed surface is symmetrical. Figure 7c shows the concentration distribution of C in concrete under one side of the exposed surface. It can be found that the result is consistent with Figure 7a, which indicates that the diffusion behavior of C under this exposed surface will not be affected by the other exposed surface.
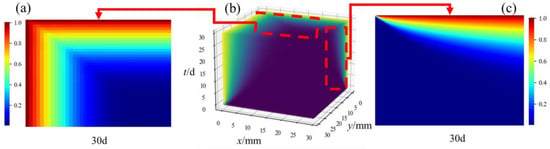
Figure 7.
Distribution of chloride ion diffusion in two-dimensional state (a–c).
3.6. Service Performance Evaluation
In this paper, Monte Carlo (MC) is used to randomly generate samples of uncertain variables. It should be noted that the high-quality prediction results of MC depend on the number of iterations of random samples, while it also leads to computing resources and iteration time problems. This paper analyzes the sampling number N from the perspective of Pf: N = 10,000/Pf. Therefore, this paper sets the N = 10,000 > 100/5% = 2000. It can be found that service life (S) decreases with the increase in xk (Figure 8a). When xk is 6, 6.5, 7, and 7.5 cm, the S of the structure is 48.3, 54.7, 58.4, and 61.9 years, respectively. This is because with the increase in xk, the chloride ion diffusion path becomes larger. Compared with xk = 6 cm, the S of the structure with xk = 6.5, 7, and 7.5 cm increased by 10.3%, 18.7%, and 23.1%, respectively, indicating that with the increase of xk, the growth rate of the S of the structure decreased. The results in Figure 8b show that S decreases with the increase of rslag. When the rslag is 20, 30, 40, and 50%, the S is 55.1, 63.2, 67.1, and 70.4 years. Compared with an rslag of 20%, the service life of an rslag of 30%, 40%, and 50% increased by 11.9%, 19.3%, and 23.7%, respectively.
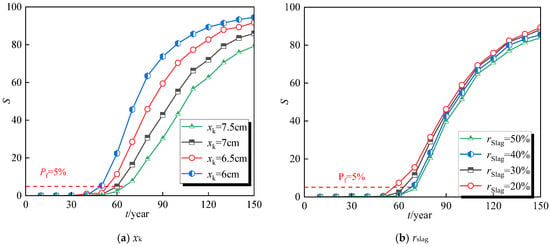
Figure 8.
The effect of model parameters on S.
4. Conclusions
This paper proposed an intelligent simulation method of chloride ion diffusion based on a dimensionless physical information neural network. Fick’s second law is taken as the physical constraint equation into the method to carry out physical constraints, and then the spatial and temporal distribution of C in concrete is simulated with high precision. The main conclusion are follows:
(1) The accuracy of the proposed method is verified by the field measured data, with a maximum error of less than 15%. The effects of different exposure ages and chloride ion diffusion coefficients on the diffusion behavior of concrete were quantified.
(2) PINN effectively solves the dimension problem of high-order nonlinear equations, and the maximum difference between the obtained results and the numerical simulation results is 0.03.
(3) The chloride ion field diffusion behavior in a multi-dimensional state can be realized by changing the physical constraint equation. The chloride ion distribution on one side of the exposed surface of concrete under a two-dimensional diffusion state is not affected by the exposed surface on the other side.
(4) The evaluation model based on Non-PINN and uncertainty simulation can analyze the influence of materials and spatial–temporal factors. The Pf of the structure decreases with the increase in xk and rslag.
(5) This study proposes a PINN-based framework for chloride ion diffusion, which effectively addresses poor convergence. In the future, this framework can be used to quantitatively investigate the influence of spatiotemporal heterogeneity and concrete material parameters across different regions on chloride ion diffusion behavior, thereby validating the superiority of the proposed approach.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W. and B.Z.; methodology, F.G.; software, H.C.; validation, F.G.; formal analysis, S.W. and P.K.; investigation, H.C., P.K. and B.Z.; resources, P.K.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W.; writing—review and editing, B.Z.; visualization, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific Research Fund of the Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (Y202352850).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Peihan Kong was employed by the The fourth construction co, Ltd of construction eighth engineering division, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Z.; Gong, F.; Maekawa, K. Multi-scale and multi-chemo-physics lifecycle evaluation of structural concrete under environmental and mechanical impacts. J. Intell. Constr. 2023, 1, 9180003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, H.; Nie, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, C. A method to analyze the long-term durability performance of underground reinforced concrete culvert structures under coupled mechanical and environmental loads. J. Intell. Constr. 2023, 1, 9180011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Abe, H.; Hayashi, D.; Tanaka, H. Behavioral characteristics of RC beams with non-uniform corrosion along the reinforcement. J. Intell. Constr. 2023, 1, 9180019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, S.; Shen, L. Application of high-performance cementitious composites in steel–concrete composite bridge deck systems: A review. J. Intell. Constr. 2024, 2, 9180012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.S.; Medepalli, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ishida, T. Effect of microstructure differences on the thermal and mechanical behaviors of porous cementitious composites using phase change materials. J. Intell. Constr. 2025, 3, 9180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Gong, F.; Xia, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, B. Service life evaluation of marine concrete structures considering spatial and temporal characteristics: A framework based on multi training-MCS-NLS. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Tian, D.; Dong, M.; Lv, M.; Yang, X.; Lu, S. Effects of interlayer-modified layered double hydroxides with organic corrosion inhibiting ions on the properties of cement-based materials and reinforcement corrosion in chloride environment. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Lu, S.; Kan, L.; Xia, X.; Huang, C. Machine learning prediction of compressive strength of concrete with resistivity modification. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, F. A damage constitutive model for intermittent jointed rocks under cyclic uniaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 103, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, L.; Ababneh, A.N.; Xi, Y. The effect of moisture transport on chloride penetration in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Influence of cation type on diffusion behavior of chloride ions in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 99, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luzio, G.D.; Alnaggar, M. Coupled multi-physics simulation of chloride diffusion in saturated and unsaturated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 292, 123394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Y.; Gao, N.; Lv, Y.; Niu, D. Effect of non-uniform freeze-thaw damage on the stress-strain curves of concrete under repeated loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-T.; Zhu, J.-X.; Weng, K.-F.; Li, V.C.; Dai, J.-G. Ultra-high-strength engineered/strain-hardening cementitious composites (ECC/SHCC): Material design and effect of fiber hybridization. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 129, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Gong, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, B. Insights on the multiple ions distribution in concrete under stray current: From experiments to multi-field simulation. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Da, B.; Ma, H.; Dou, X.; Wu, Z. Service life prediction of coral aggregate concrete structure under island reef environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wu, R.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Min, W.-L.; Chen, K.-Y.; Jin, W.-L. Systematic framework for handling uncertainty in probabilistic failure analysis of corroded concretes. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 156, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xia, P.; Gong, F.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, P. A Bayesian-physical informed conditional tabular generative adversarial network framework for low-carbon concrete data augmentation and hyperparameter optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 152, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xia, P.; Chen, K.; Gong, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, W. Prediction and optimization model of sustainable concrete properties using machine learning, deep learning and swarm intelligence: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, T.; Xie, X.; Gao, B.; Xiang, P. Strain distribution prediction in UHPC beams using deep learning model. Struct. Concr. 2025, 26, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.-D.; Chen, C.-T.; Liao, K.-W. Prediction of chloride diffusion in cement mortar using Multi-Gene Genetic Programming and Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Measurement 2017, 112, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Dong, Y. Dynamic Bayesian network for durability of reinforced concrete structures in long-term environmental exposures. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 142, 106821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussallem, I.; Jörissen, J.; Kunz, U.; Pinnow, S.; Turek, T. Chlor-alkali electrolysis with oxygen depolarized cathodes: History, present status and future prospects. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Tong, J.-Z.; Li, Q.-H.; Xu, S.-L.; Gao, W.; Liu, X. Flexural behavior of novel profiled steel-UHTCC assembled composite bridge decks. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 212, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-Q.; Tong, G.-S.; Tong, J.-Z.; Zhang, J.-W.; Li, X.-G.; Xu, S.-L. Experimental and numerical study on seismic performance of L-shaped multi-cellular CFST frames. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 213, 108360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karumuri, S.; Tripathy, R.; Bilionis, I.; Panchal, J. Simulator-free solution of high-dimensional stochastic elliptic partial differential equations using deep neural networks. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 404, 109120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y. Identification of chloride diffusion coefficient in concrete using physics-informed neural networks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, L.-O. Models for Chloride Ingress—An Overview. In Benchmarking Chloride Ingress Models on Real-Life Case Studies—Marine Submerged and Road Sprayed Concrete Structures: State-of-the-Art Report of the RILEM TC 270-CIM; Koenders, E., Imamoto, K.-i., Soive, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 7–23. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Pérez, B.; Pantazopoulou, S.J.; Thomas, M.D.A. Numerical solution of mass transport equations in concrete structures. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, O.P.; Gong, K.; Severson, K.A.; Chen, J.; Gregory, J.R.; Ghosh, S.; Goodwin, R.T.; Olivetti, E.A. Bayesian design of concrete with amortized Gaussian processes and multi-objective optimization. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 177, 107406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Jin, Z.; Wang, X. Chloride ion penetration into concrete exposed to marine environment for a long period. Ocean Eng. 2015, 33, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).