Novel Cu-Rich Nano-Precipitates Strengthening Steel with Excellent Antibacterial Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
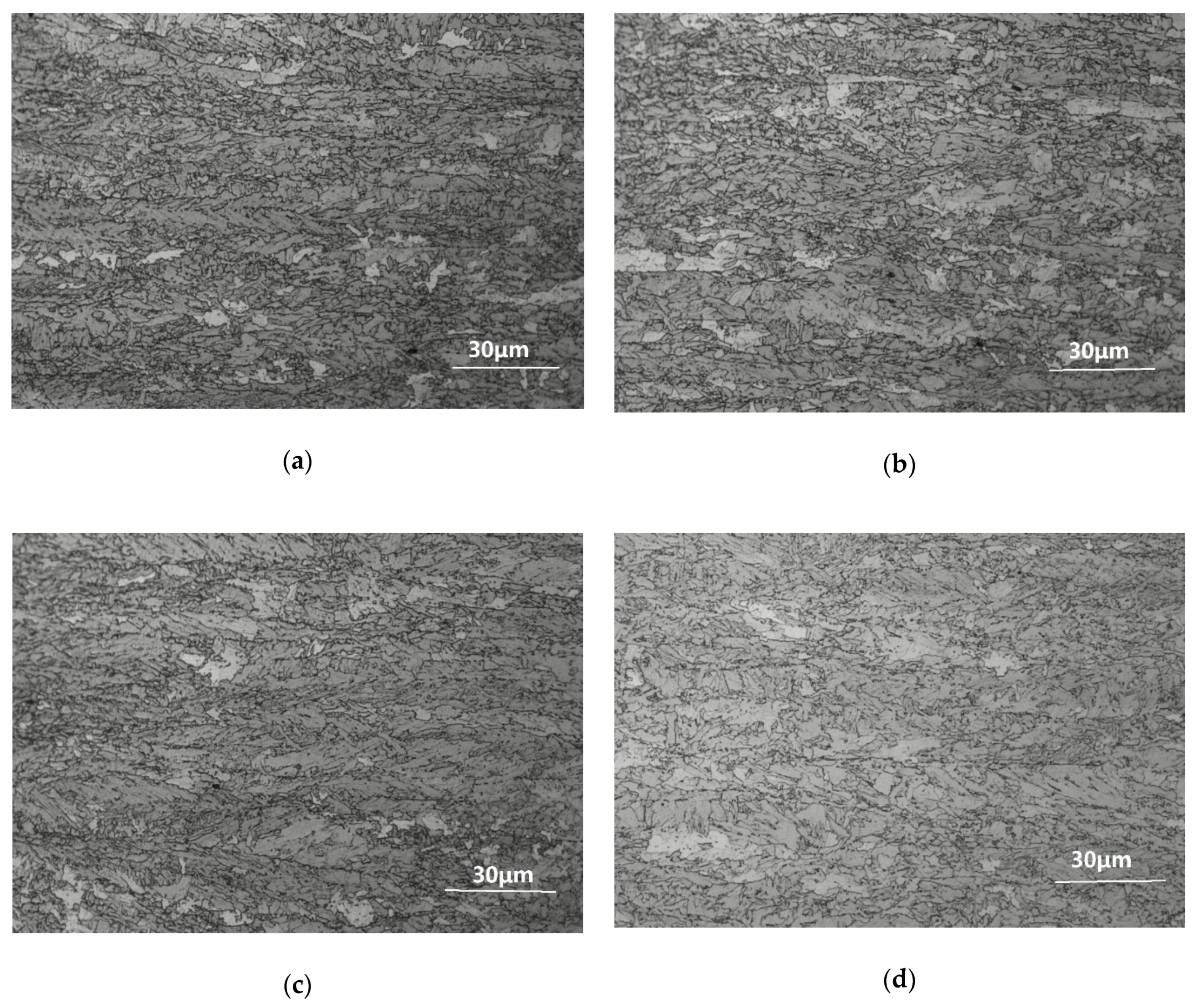
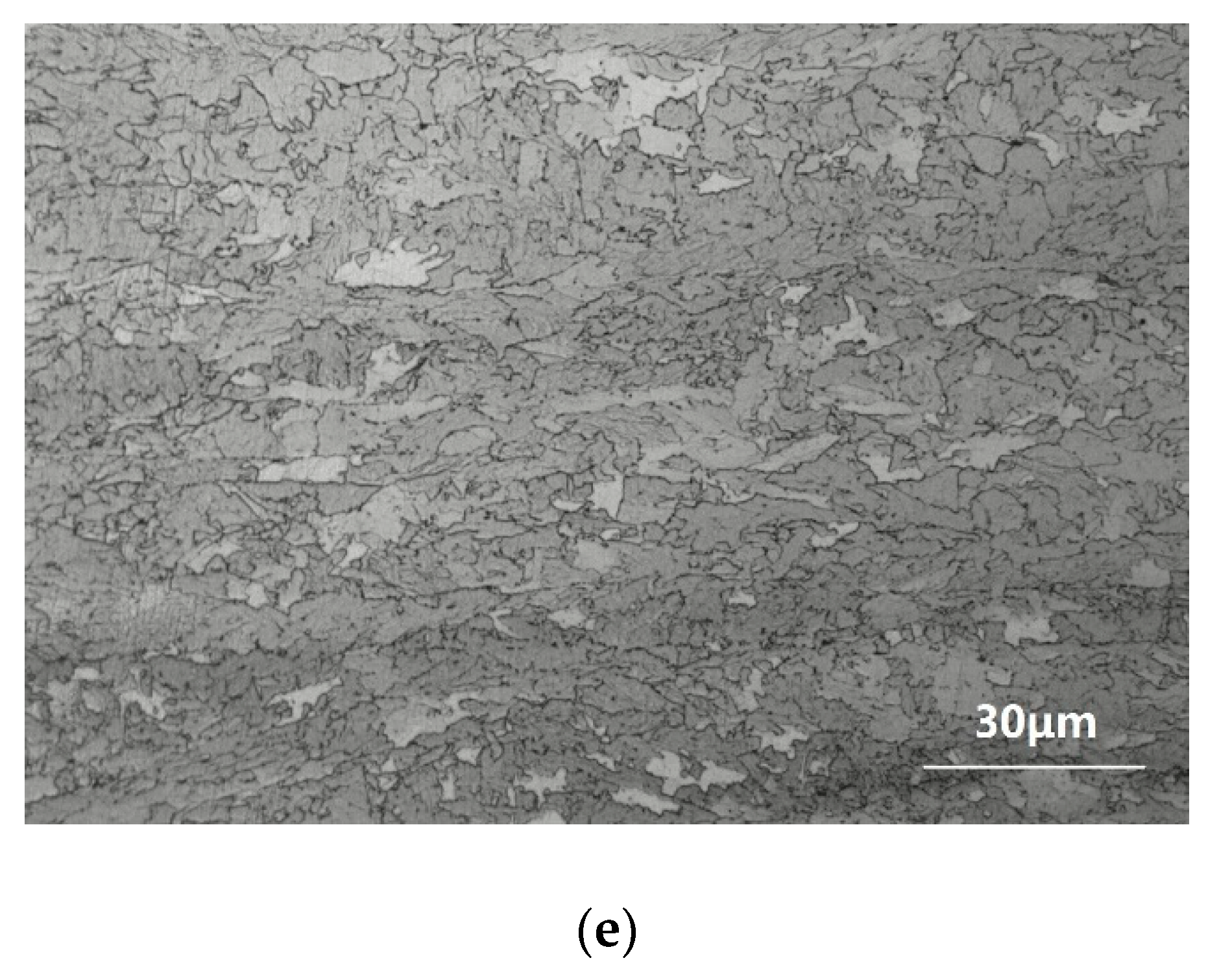
3.1. Microstructure
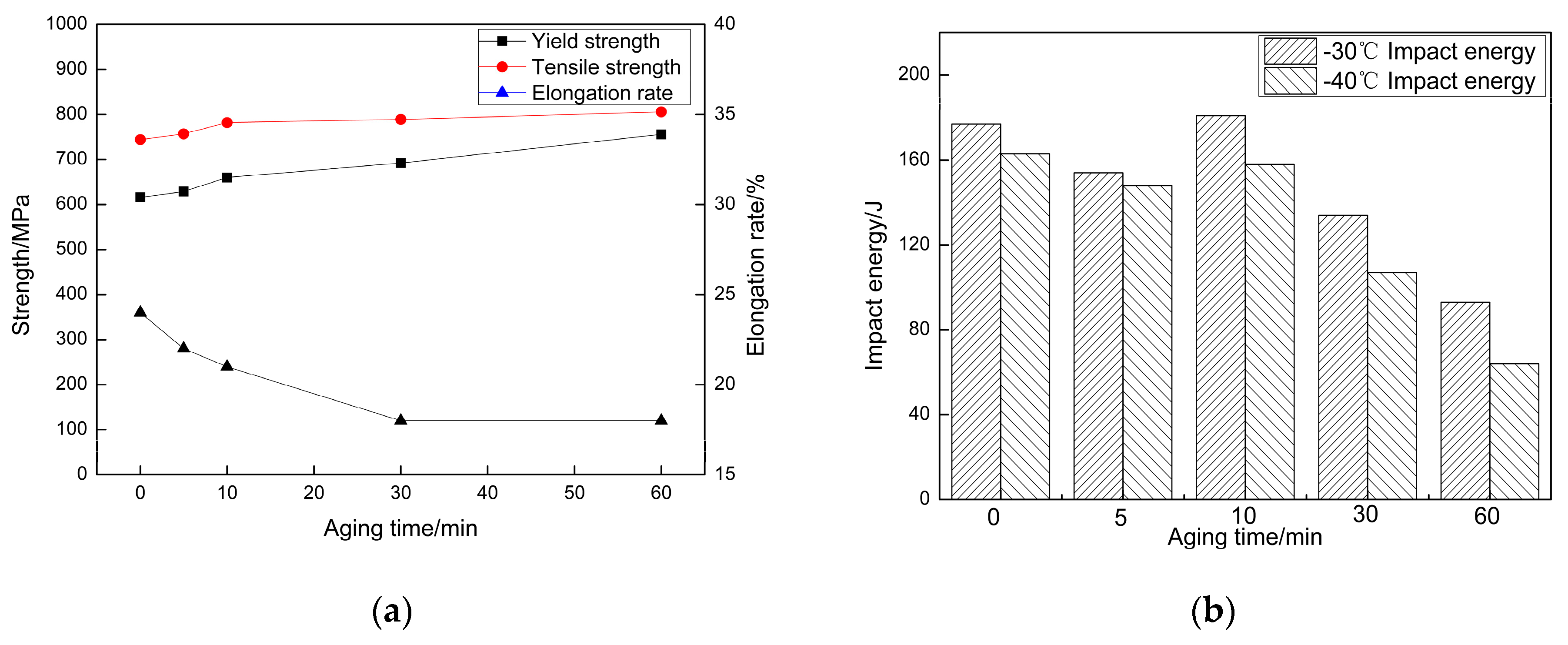
3.2. Tensile Properties and Microhardness
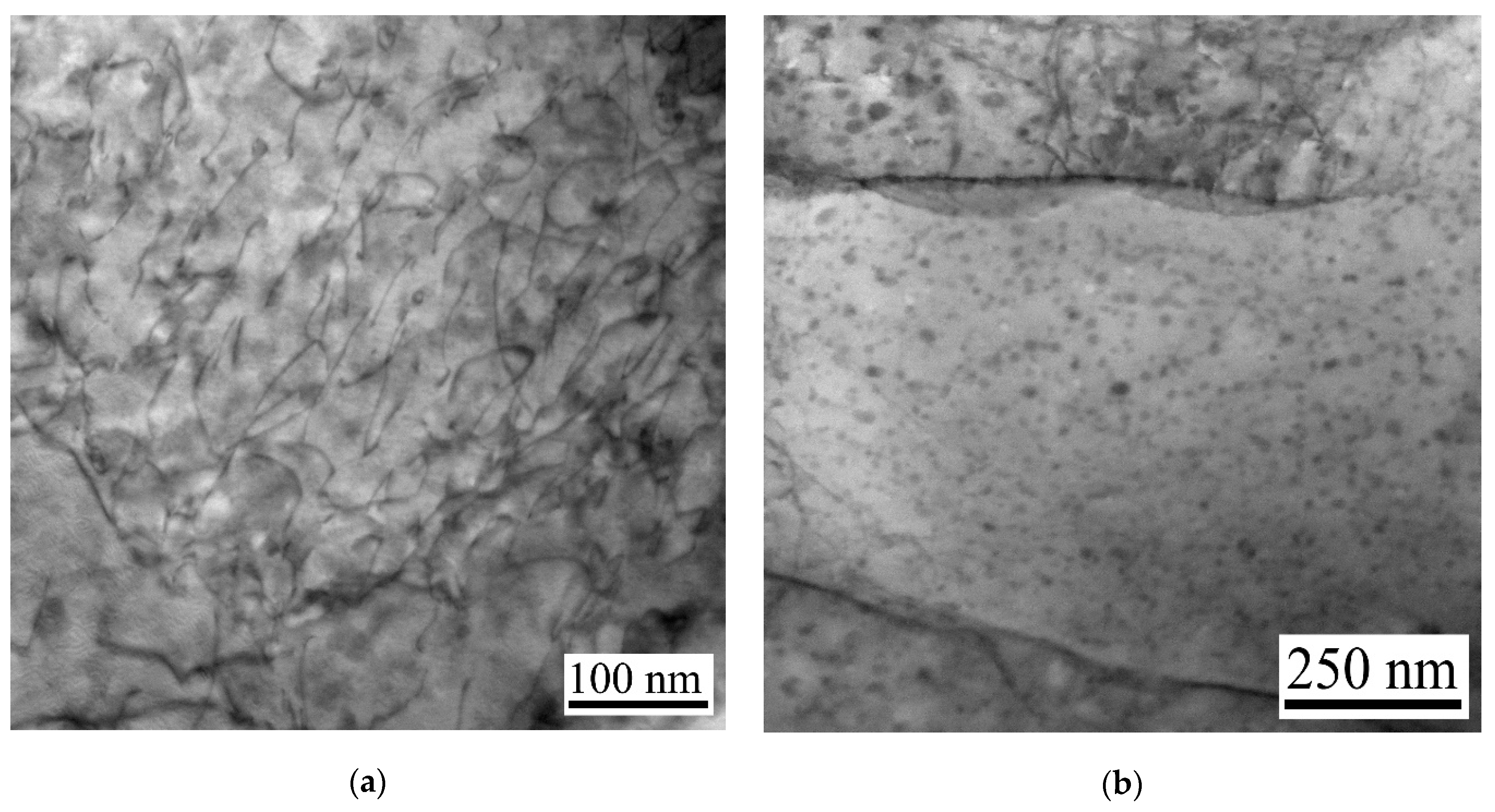
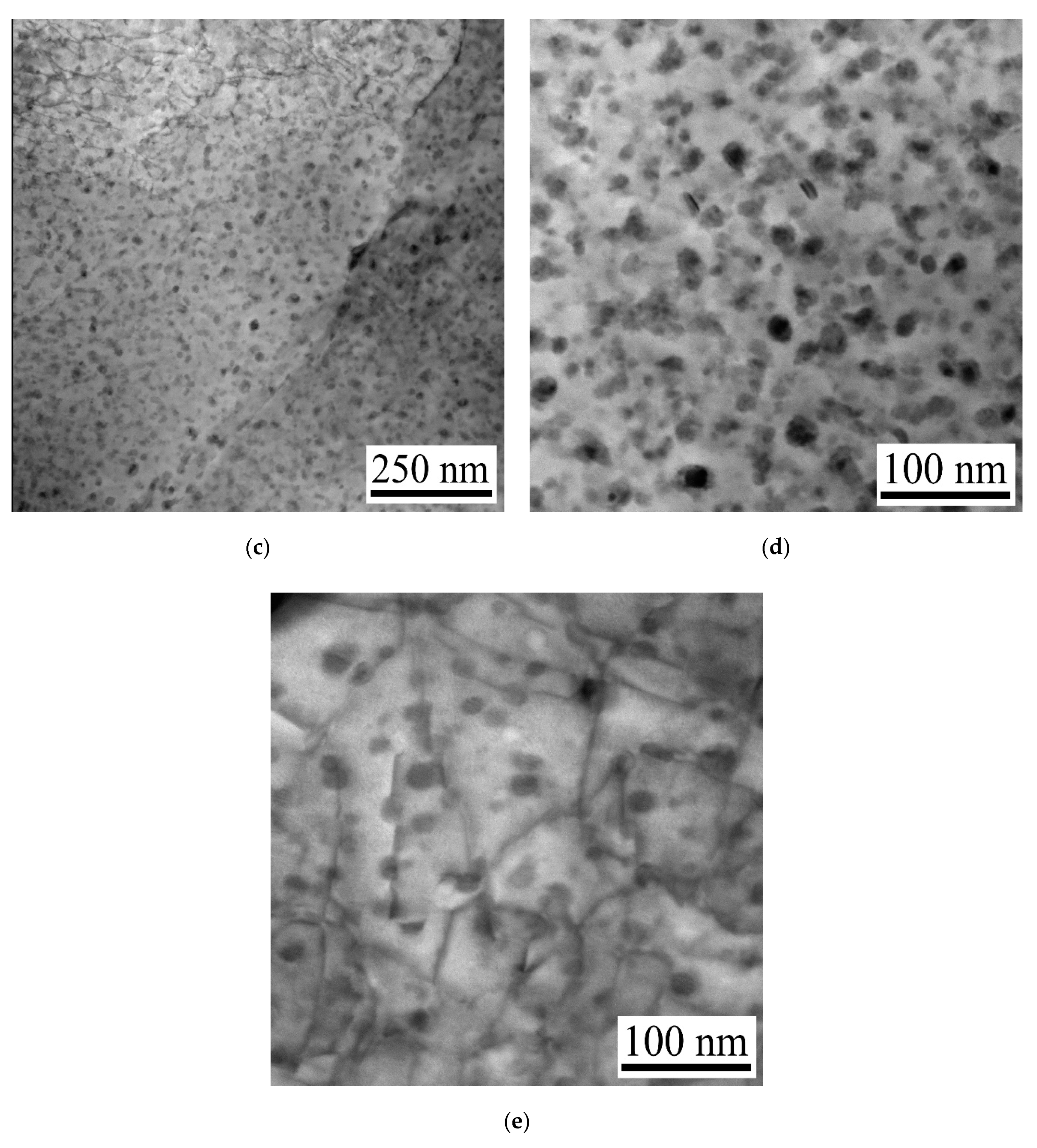
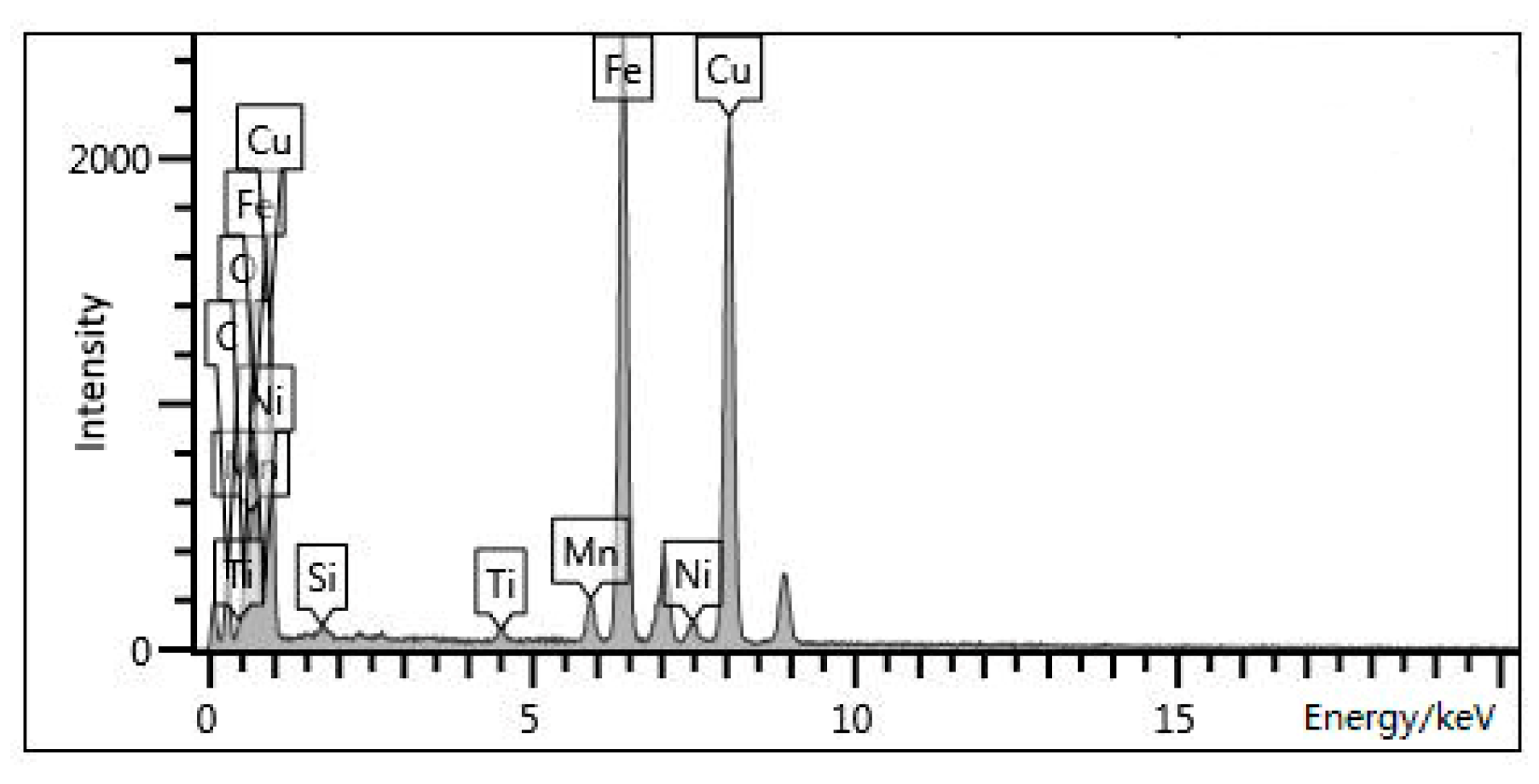
3.3. Precipitation
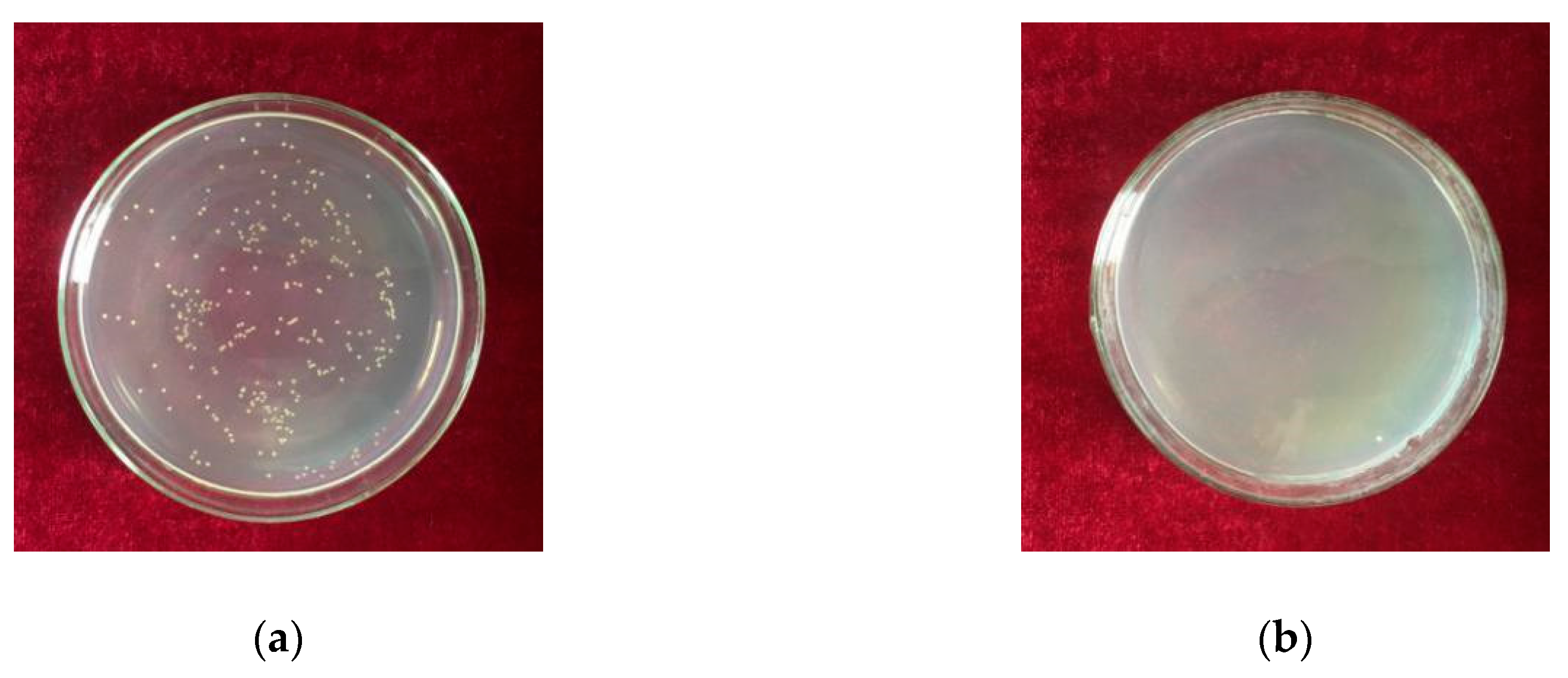
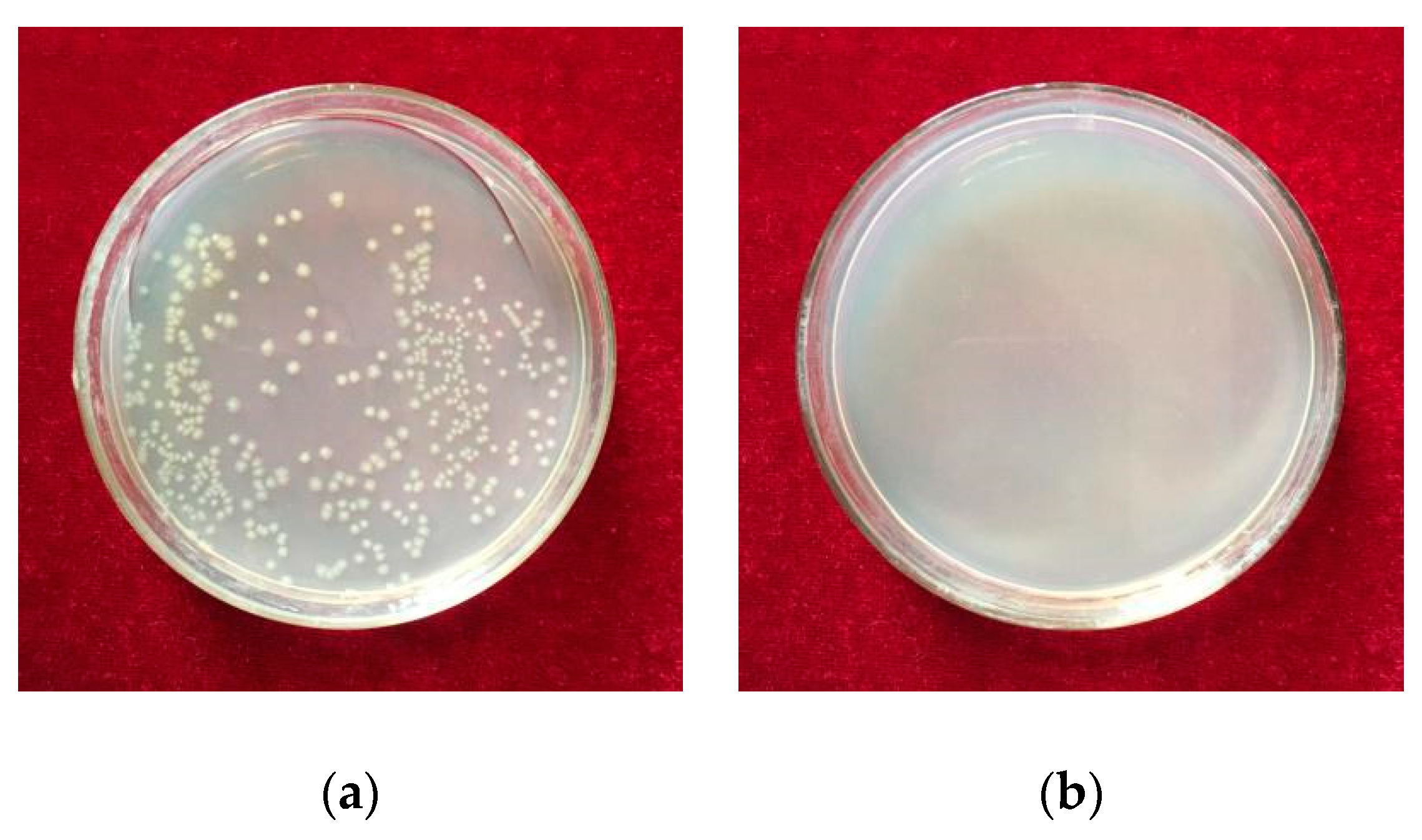
3.4. The Antibacterial Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argon, A.S. Strengthening Mechanisms in Crystal Plasticity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.B.; Hong, S.G.; Park, C.G.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.H. Influence of Mo on precipitation hardening in hot rolled HSLA steels containing Nb. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Iino, M. Microstructural refinement by Cu addition and its effect on strengthening and toughening of sour service line pipe steels. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.H.; Zhen, L.; Guo, B. Influence of Mo content on microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength pipeline steel. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 723–728. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, S.U.; Lee, J.M.; Yang, B.Y.; Kim, K.Y. Effect of molybdenum and chromium addition on the susceptibility to sulfide stress cracking of high-strength, low-alloy steels. Corrosion 2007, 63, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Li, M.Y.; Wei, G. Controlled Rolling and Controlled Cooling, 1st ed.; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.W. Research development of high strength low alloy (HSLA) steels. Mater. China 2016, 35, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Czyryca, E.J.; Vassilaros, M.G. Advances in Low Carbon, High Strength Ferrous Alloys. Key Eng. Mater. 1993, 34, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Asfahani, R.; Tither, G. International symposium on low-carbon steels for the 90’s. Mater. Soc. 1993, 1, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Vaynman, S.; Fine, M.; Ghosh, G.; Bhat, S. Materials for the new millennium. In Proceedings of the Fourth Materials Engineering Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hattestrand, M.; Andren, H.O. Influence of strain on precipitation reactions during creep of an advanced 9% chromium steel. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaynman, S.; Isheim, D.; Kolli, R.P.; Bhat, S.P.; Seidman, D.N.; Fine, M.E. High-strength low-carbon ferritic steel containing Cu-Fe-Ni-Al-Mn precipitates. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.D.; Seidman, D.N. Nanoscale co-precipitation and mechanical properties of a high-strength low-carbon steel. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Rivera-Diaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J.; Yan, W.; Yang, K.; Martin, D.S.; Kestens, L.A.I.; Van Der Zwaag, S. A new ultrahigh-strength stainless steel strengthened by various coexisting nanoprecipitates. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Liu, C.T.; Wang, X.L.; Ma, D.; Chen, G.; Williams, J.R.; Chin, B.A. Effects of proton irradiation on nanocluster precipitation in ferritic steel containing fcc alloying additions. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 3034–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.B.; Luan, J.H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Miller, M.K.; Ma, W.B.; Liu, C.T. Synergistic effects of Cu and Ni on nanoscale precipitation and mechanical properties of high-strength steels. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5996–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Caron, J.L.; Babu, S.S.; Lippold, J.C.; Isheim, D.; Seidman, D.N. Characterization of microstructural strengthening in the heat-affected zone of a blast-resistant naval steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5596–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Xu, D.K.; Wu, Y.N.; Yang, K.; Liu, H.F. Research progress in corrosion of steels induced by sulfate reducing bacteria. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol 2015, 27, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Videla, H.A. Manual of Biocorrosion, 1st ed.; CRC-Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 24–26.3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.B.; Xu, D.K.; Yan, M.C.; Yan, W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Study on Microbiologically influenced corrosion behavior of novel Cu-bearing pipeline steels. Acta Metall. Sin. 2017, 53, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Xu, D.K.; Nan, L. Study on mechanisms of microbiologically influenced corrision of metal from the perspective of bio-electrochemistry and bio-energetics. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 30, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.L.; Chen, Q.J.; Wang, K.L.; Sun, H.; Yu, H. Heattreatment techniques research of 700 MPa low carbon bainite steel. Tran. Mater. Heat Treat. 2005, 26, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, S.R.; Brenner, S.S.; Low, J.R. An FIM-atom probe study of the precipitation of copper from lron-1.4 at. pct copper. Part II: Atom probe analyses. Metall. Trans. 1973, 4, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isheim, D.; Kolli, R.P.; Fine, M.E.; Seidman, D.N. An atom-probe tomographic study of the temporal evolution of the nanostructure of Fe-Cu based high-strength low-carbon steels. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, R.P.; Seidman, D.N. Comparison of compositional and morphological atom-probe tomography analyses for a multicomponent Fe-Cu steel. Microsc. Microanal. 2007, 13, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolli, R.P.; Mao, Z.; Seidman, D.N.; Keane, D.T. Identification of a Ni0.5(Al0.5−xMnx) B2 phase at the heterophase interfaces of Cu-rich precipitates in an α-Fe matrix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, R.P.; Seidman, D.N. The temporal evolution of the decomposition of a concentrated multicomponent Fe-Cu-based steel. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2073–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, M.D.; Seidman, D.N. Multiple dispersed phases in a high-strength low-carbon steel: An atom-probe tomographic and synchrotron X-ray diffraction study. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Liu, C.T.; Miller, M.K.; Wang, X.; Wen, Y.R.; Fujita, T.; Hirata, A.; Chen, M.W.; Chen, G. A nanoscale co-precipitation approach for property enhancement of Fe-base alloys. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, R.P.; Seidman, D.N. Co-Precipitated and Collocated Carbides and Cu-Rich Precipitates in a Fe–Cu Steel Characterized by Atom-Probe Tomography. Microsc. Microanal. 2014, 20, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Studies on Aging Behavior of Cu-Enriched Nano Cluster Strengthened HSLA Steels. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.G.; Xu, D. Effect of heat treatment on antibacterial performance of 3Cr13MoCu martensitic stainless steel. Acta Metall. 2014, 50, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, H.; Shamaila, S.; Zafar, N.; Sharif, R.; Nazir, J.; Rafique, M.; Ghani, S.; Saba, H. Antibacterial behavior of laser-ablated copper nanoparticles. Acta Metall. 2016, 29, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.X. Copper Precipitation Mechanism and Performance Control of Ferritic Antibacterial Stainless Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, C.P. Alcamo’s Fundamentals of Microbiology, 9th ed.; Jones and Bartlett Publishers: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 57–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, T.D.J.A.; Okamoto, R.T.; Traple, M.A.L.; Lourenco, F.R. Development and validation of microbiological assay for ceftriaxone and its application in photo-stability study. Current Pharmaceutical Analysis. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 9, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Malathi, S.; Ramya, V.; Ezhilarasu, T.; Abiraman, T.; Balasubramanian, S.J. Green Synthesis of Novel Jasmine Bud-Shaped Copper Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 1, 34–40. [Google Scholar]


| C | Si | Mn | S | P | Cu + Ni + Nb + Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 0.2 | 1.73 | 0.004 | 0.005 | <3.0 |
| Elements in Precipitates | C | O | Si | Ti | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content/% | 7.16 | 2.68 | 0.34 | 0.6 | 2.81 | 33.43 | 1.4 | 51.58 | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, H. Novel Cu-Rich Nano-Precipitates Strengthening Steel with Excellent Antibacterial Performance. Metals 2019, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010052
Fan Y, Ma C, Li S, Zhang H. Novel Cu-Rich Nano-Precipitates Strengthening Steel with Excellent Antibacterial Performance. Metals. 2019; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yanqiu, Changwen Ma, Shaopo Li, and Hai Zhang. 2019. "Novel Cu-Rich Nano-Precipitates Strengthening Steel with Excellent Antibacterial Performance" Metals 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010052
APA StyleFan, Y., Ma, C., Li, S., & Zhang, H. (2019). Novel Cu-Rich Nano-Precipitates Strengthening Steel with Excellent Antibacterial Performance. Metals, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9010052





