Abstract
Plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) of Ti-15Mo alloys conducted in electrolytes containing Ca and P compounds can be an efficient process with which to obtain bioactive coatings. This paper reports on the influence of the nature of the electrolyte, its concentration, and PEO process parameters on the properties of anodized layers on Ti-15Mo. A wide range of Ca- and P-containing alkaline and acidic solutions was employed to incorporate Ca and P ions into the anodized layer. The efficiency of the incorporation was evaluated by the Ca/P ratio in the coating as compared to that in the electrolyte. It was found that alkaline solutions are not suitable electrolytes for the formation of good quality, uniform PEO coatings. Only acidic electrolytes are appropriate for obtaining well-adherent homogeneous layers on Ti-15Mo. However, the maximum Ca/P ratios reached in the coatings were rather low (close to 1). The variation of electrical signal (negative-to-positive current ratio, frequency) and time of electrolysis do not result in a substantial change of this value. The processing time, however, did influence the coating thickness. Despite their low Ca/P ratio, the anodized layers demonstrate good biological activity, comparable to pure microrough titanium.
1. Introduction
Titanium alloys are widely applied in implantology [1]. Ti-6Al-4V alloy is one of the most used alloys due to its high corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and mechanical properties. However, its elastic modulus (E = 100 GPa) is significantly higher than that of bone (5–40 GPa), which results in a stress at the bone-implant interface. Furthermore, this alloy contains aluminium, an element that is harmful to the human body. For these reasons, alternative titanium alloys without Al are considered for biomedical applications [2]. In this respect, β-phase Ti alloys are of particular interest owing to their low elastic modulus [3]. For example, Ti-15Mo alloy has high corrosion and wear resistance, low elastic modulus, and good ductility. Molybdenum is a safe alloying element and stabilizes the β-phase. Increasing the amount of β-phase leads to a decrease of elastic modulus and, therefore, to a better mechanical compatibility with the natural bone [4].
Several attempts have been made to further improve the biocompatibility of Ti-15Mo alloy by the incorporation of Ca- and P-ions in the surface layer [5,6]. In order to achieve a good implant tolerance by the bone, it is generally recognised that the Ca/P ratio in the surface layer should be close to 1.67, corresponding to the value in hydroxyapatites, the material which constitutes the mineral part of natural bone [7].
Plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) is an appropriate method with which to produce oxide layers on titanium alloys [8]. Carried out in electrolytes containing calcium and phosphorous compounds in appropriate forms (ions or fine dispersions), the PEO process can be employed for the formation of bioactive coatings. Therefore, β-Ti alloys treated by PEO in Ca- and P- containing electrolytes could find their application in implantology.
Various Ca- and P- containing salts are suitable electrolytes with which to obtain biocompatible PEO layers on different titanium alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V [9], Ti-15Mo [10], Ti-13Nb-13Zr [11]). It was demonstrated that Ca/P ratio in the PEO coatings depends on the electrolyte composition, the process duration, and the electrical regime of electrolysis. However, there is no evident dependence between the Ca and P concentration in the electrolyte and that in the coating. It is merely established that the higher the Ca/P ratio in the electrolyte, the higher the probability to form a hydroxyapatite layer, with a Ca/P ratio of 1.67.
In the present work, we firstly focus on the selection of an appropriate electrolyte for successful PEO anodization of Ti-15Mo. Then, the optimization of the PEO process parameters is carried out in order to reach maximum Ca/P ratio in the coating. The influence of the electrolyte nature and process parameters on some characteristics of the anodized layers is discussed. Finally, selected coatings were subjected to a biological test to evaluate their biocompatibility with osteoblasts. The results suggest that, despite a low Ca/P ratio in the coatings (about 1), they possess a relatively high rate of cell proliferation and, therefore, can be considered as a good candidate for biological applications.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Sample and Electrolyte Preparation
The material used for anodization experiments was Ti-15Mo ASTM F 2066 alloy (in wt %: C—0.1, H—0.015, Fe—0.1, O—0.2, H—0.015, N—0.05, O—0.2, Mo—14–16, Ti—balance), provided by PX Group (La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland). The disk-shaped samples with a diameter of 10 mm were cut from the bar and mechanically polished to remove cutting strides. Before anodization, the samples were cleaned in acetone and ethanol and rinsed with distilled water. After cleaning, the samples were chemically etched in a mixture of 48% HF and 70% HNO3 (volume ratio 1:3) during 60 s at room temperature.
The oxidation experiments were performed in different alkaline and acidic electrolytes. Alkaline electrolytes were prepared from mixtures of two Ca- and P-containing salts including slightly soluble calcium compounds. In this case, the 1N solution of Trilon B (Na2EDTA) was introduced at a quantity sufficient to keep the solution free of the precipitates [12]. The formation of a complex with calcium cations [CaY]2−, in which Y = [(OOC)·NCH2CH2N·(COO)2]4−, leads to the following results: (a) The solubility of calcium compounds increases and the probability of precipitation of Ca/P compounds from the electrolyte decreases; (b) The positively charged cations are converted to a negatively charged complex [CaY]2−, whose movement to the anode is facilitated. Calcium ions are binding to the stable complex only in an alkaline medium, while in a weakly acidic medium, low-stability complexes of Ca with EDTA are destroyed. To maintain pH = 13, 2N KOH solution was added to the electrolyte.
In addition, three acidic electrolytes were used in the PEO experiments. They contained soluble calcium salts, Ca(CH3COO)2·H2O, Ca(H2PO2)2·2H2O, and Ca(H2PO4)2·2H2O. In this case, the electrolytes were prepared by direct dissolution of the components in water, with the pH value set spontaneously.
2.2. PEO Process
Plasma anodizing was performed using a bipolar adjustable pulsed current power supply (OMA CERATRONIC®CER004-GIT01 from GIT, Paris, France) operated in the galvanostatic mode. This type of power source is known for its robustness and flexibility. Indeed, it offers a possibility to adjust independently and over a wide range several process parameters, such as the duration of each step in the waveform and the amplitudes of the positive (Ip) and negative (In) current. This enables one to tailor the properties of the anodized layers to a large extent, especially in the case of alloyed materials, such as Ti-15Mo.
In the first experimental campaign aimed at selecting a proper electrolyte for successful anodization of Ti-15Mo, the process parameters were fixed as follows: the negative-to-positive current ratio (R = In/Ip) was set at 50%, time of electrolysis was 10 min, and the frequency was 100 Hz. In these experiments, 8 alkaline and 3 acidic Ca- and P-containing electrolytes were used for anodization.
In the second campaign, the process parameters were varied in order to obtain a maximum Ca/P ratio in the oxidized layers. The samples were anodized using one electrolyte selected from the first campaign. Three series of samples were prepared, in which one of the following parameters was varied at a time. The negative-to-positive current ratio (R = In/Ip) varied between 10 and 90%; time of electrolysis (t) varied between 5 and 20 min, and frequency (F) varied between 100 to 900 Hz. Three samples were treated under each process condition in order to insure the reproducibility of the process. For the biological tests, 11 samples were produced using selected process parameters.
During all anodization experiments, the electrolyte was cooled down by cold water circulation. The temperature of the electrolyte did not exceed 20 °C. After anodization, the samples were rinsed with distilled water and dried in air.
2.3. Sample Characterisation
The anodized samples were characterized using the following methods.
Cross-section optical microscopy observations on cut and polished anodised samples were carried out for thickness measurement of the oxide layers using Leica Olympus optical microscope. In addition, surface and in-depth morphology observations were performed with scanning electron microscope (SEM, model JEOL JSM-6400).
Elemental (Ti, Mo, Ca, P) content of the anodised layer was determined by X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) using FISCHERSCOPE® X-RAY XDV®-SDD according to the standards DIN EN ISO 3497 and ASTM B 568. Oxygen content was not detected with XRF.
Phase analysis was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a DRON-3 diffractometer (CuKα radiation). The measurements were done using Bragg-Brentano theta-2theta geometry. The diffraction patterns were recorded within the range from 5° to 100° in 2theta. The obtained XRD patterns were compared with the JCPDS standards to identify the phase composition.
Finally, biological assays with osteoblast cells were performed on selected Ti-15Mo anodized layers in order to assess their biocompatibility. Biological assays were detailed previously [13,14]. Briefly, human osteoblasts like cells HOS (ATCC® CRL1543TM) (HOBs) were grown on several anodized samples. Resazurin colorimetric assays were used to monitor the proliferation kinetics of HOBs. Cell adhesion was also analysed at day 4 by using SEM. For each treatment, experiments were conducted up to 22 days. Commercially pure titanium (CP-4 Ti) samples prepared by a standard SLA (sand-blasted acid etched) procedure [15] were used for comparison.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. First Campaign: Selection of a Suitable Electrolyte for Ti-15Mo Anodization
To study the influence of electrolyte composition on the elemental content of the coating, eight series of alkaline electrolytes consisting of a mixture of two Ca- and P-containing salts were prepared. For all series, the concentration of each compound was varied to get different Ca/P ratios (Table 1).

Table 1.
Relationship between (Ca/P)sol and (Ca/P)coat for the anodized layers obtained on Ti-15Mo in different alkaline electrolytes.
The mass ratio of calcium and phosphorus in each solution (Ca/P)sol was calculated according to the concentration of the corresponding compounds as follows:
in which is the concentration of compounds (I and II) in solution (g·L−1); and are the number of Ca and P atoms in the corresponding compounds; and are the atomic mass of Ca and P atoms (g·at−1); and is the molar mass of corresponding compounds (g·mol−1).
These series of electrolytes were used for the PEO treatment of the Ti-15Mo alloy. The Ca/P ratio in the coatings is always lower than that in the solution, independently of the solution composition and its concentration. Moreover, the Ca/P ratios in the coatings are considerably lower than the target value of 1.67, which is considered necessary for successful biological applications. A logical way to increase this value would be to increase Ca/P ratio in the solution. However, the trials to perform anodization experiments in solutions with higher Ca/P ratios (2–4) failed because of the instability of concentrated solutions of Ca and P and the high amount of EDTA used for their preparation. Therefore, we decided to carry out further anodization experiments only in solutions with low Ca/P ratio, as presented in the Table 1.
The anodized layers obtained on Ti-15Mo alloys in these alkaline solutions were very heterogeneous in appearance and exhibited a very rough, powder-like aspect (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Photographs of the coatings obtained on Ti-15Mo in the electrolytes of series 1, 3, 4 (a); 2, 5 (b), and 6–8 (c).
Such an inhomogeneity could be explained by the fact that all used solutions are alkaline (pH = 13). It looks like this kind of electrolyte is not suitable for PEO treatment of Ti-15Mo alloys, as is the case with commercially pure Ti. It might be related to the complex nature of anodic layers formed on Ti-15Mo, which will be discussed later.
Simka et al. [16] suggested using acidic solutions containing H3PO4 and Ca(H2PO2)2 in case of PEO treatment of Ti-15Mo alloys. Following this suggestion and targeting a uniform appearance of the anodic layers, it was decided to use three acidic solutions, namely Ca(H2PO2)2·2H2O + Ca(H2PO4)2·2H2O with pH = 4.5 (series 9), Ca(H2PO4)2·2H2O + Ca(CH3COO)2·2H2O with pH = 4.33 (series 10), and Ca(H2PO2)2·2H2O + Ca(CH3COO)2·2H2O with pH = 3.44 (series 11). The main reason for choosing these combinations of compounds was their comparatively high solubility in water, which allowed using more concentrated solutions. Besides, in contrast to previous compositions, these solutions are relatively stable, despite the fact that both contain Ca salts. First experiments showed that, unlike alkaline electrolytes, these three acidic solutions are suitable for obtaining smooth and adherent coatings on the Ti-15Mo alloy (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Photographs of the anodized Ti-15Mo discs treated in the electrolytes of series 9 (a), 10 (b), and 11 (c).
Therefore, the subsequent PEO experiments were carried out with these three electrolytes. For each series, solutions of different concentrations were prepared with variable component contents to get different Ca/P ratios.
The relationships between Ca/P ratio in the coating, (Ca/P)coat and that in the solution, and (Ca/P)sol for the Ti-15Mo samples treated in these solutions are shown in Figure 3.
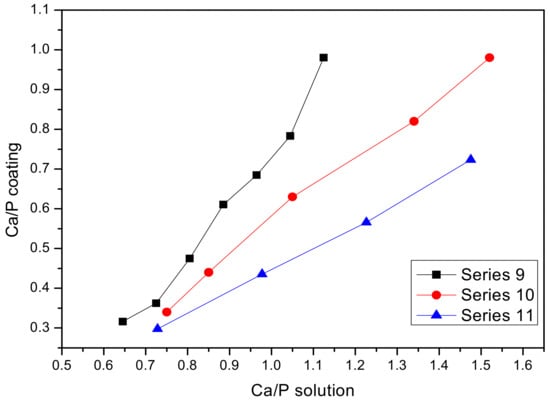
Figure 3.
Relationship between the Ca/P ratio in the coating and that in the solution (for the electrolytes of series 9, 10, and 11).
The Ca/P ratio in the coatings obtained in these electrolytes was quite low (between 0.72–0.99). The best (1:1) correspondence between Ca/P ratio in the electrolyte and in the coating was found for the samples treated in the electrolyte of series 9. The two other series (10 and 11) showed lower Ca/P ratio in the coating than in the solution. In addition, it was remarked that the anodized layers obtained in the solution 9 showed lower surface roughness and better homogeneity, as seen macroscopically.
In order to choose the most appropriate electrolyte for further PEO experiments, the cross-section and surface morphology of two layers having comparable value of Ca/P in the coating (about 1) were examined. Figure 4a shows optical cross-sections of the first sample with (Ca/P)coat = 0.98, obtained with the electrolyte of series 9. The second sample (Figure 4b) with (Ca/P)coat = 0.99 was anodized in the electrolyte of series 10 having (Ca/P)sol = 1.52.
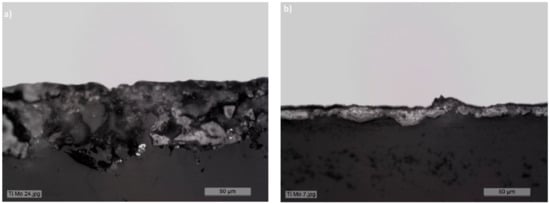
Figure 4.
Optical cross-sections of two Ti-15Mo oxidized layers obtained by PEO with the electrolyte of series 9, (Ca/P)sol = 1.12, and (Ca/P)coat = 0.98 (a); and electrolyte of series 10, (Ca/P)sol =1.52, and (Ca/P)coat = 0.99) (b).
The coating obtained in calcium hypophosphite solution (series 9) is much thicker (55–60 μm) than that obtained in calcium acetate solution (series 10), with a thickness of 15–20 μm.
The surface morphology of these two coatings, examined by SEM, is shown in Figure 5. The first coating (series 9) exhibits lower pore density, but the size of pores is generally higher than that of the second coating (series 10). The first coating also shows less developed surface morphology than the second one. The surface morphology of the second coating develops on two scales, with small grains (crystals) growing on a top of coarse features.
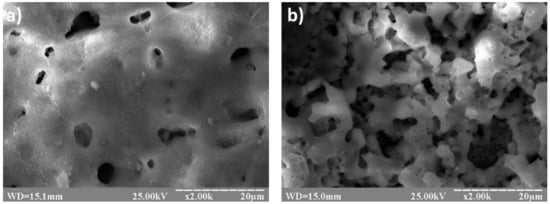
Figure 5.
Surface morphology of the two anodized layers, shown in Figure 4, obtained on Ti-15Mo in the electrolytes of series 9 (a) and series 10 (b).
In order to elucidate the phase composition of these two coatings, XRD measurements were carried out. Figure 6 shows the XRD patterns of the same two coatings obtained in an electrolyte of series 9 (a) and 10 (b).
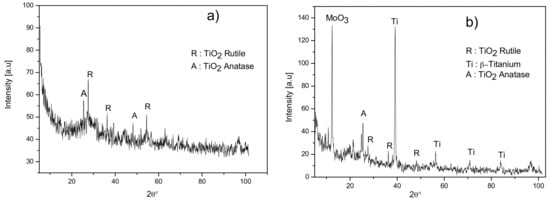
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of two layers obtained by anodization of Ti-15Mo in electrolytes of series 9 (a) and 10 (b).
The XRD spectra of the two coatings are very different. This is mainly due the difference in the coating thickness. The sample anodized in the electrolyte 9 is much thicker (55–60 μm) than that treated in the electrolyte 10 (15–20 μm). Taking into account the penetration depth of the X-rays, the XRD patterns of the second (thinner layer) are influenced more by the Ti-15Mo substrate material than the first (thicker) layer.
The XRD spectrum of the sample treated in the solution 9 (Figure 6a) exhibits broad and weak “halo-like” features in a low-angle region, typical for amorphous materials. Few peaks of low intensity can be identified as those belonging to TiO2 anatase and rutile phases. The presence of molybdenum oxides is not clearly evidenced by the XRD. Two peaks, at about 25.5° and 27°, which could correspond to the orthorhombic MoO3 phase, also correspond to TiO2 anatase and TiO2 rutile phases, respectively. The presence of Ca- and P-containing compounds is not revealed by XRD either, as no clear peaks corresponding to these phases are seen. As the presence of Ca and P has been detected by XRF analysis, we suggest that the Ca- and P-containing phases exist in an amorphous or nanocrystalline state.
The XRD spectrum of the sample treated in the solution 10 (Figure 6b) exhibits several peaks (at about 40°, 56° and 71°), which can be attributed to the cubic β-Ti phase (Ti-15Mo substrate material). In addition, titanium and molybdenum oxide phases are also clearly identified. The peak at 25.5° confirms the presence of TiO2-anatase, while the peak at 27° belongs to the TiO2-rutile phase. A strong peak observed at 12.7° corresponds to the orthorhombic α-MoO3 phase (JCPDS Card No.: 35-0609). Its unusually high intensity suggests that the MoO3 phase is highly textured with the (002) plane parallel to the crystal growth direction. The other peaks typical for the α-MoO3 phase (23.5°, 25.7°, 27.3°, 29.8°, 33.6°, 39.1°, 49.3°, 58.9°, and 64.5°) are not clearly seen. They could be hidden by the background or overlapped with the peaks coming from TiO2 phases, anatase (25.7°), or rutile (27.3°). The peak at 12.7° might also belong to the low-symmetry Mo18O52 phase (O/Mo = 2.89), which can be formed by a partial reduction of MoO3 phase during the anodization process. The peak at about 21° can belong to another molybdenum oxide, monoclinic Mo9O26 (JCPDS Card No.: 05-0442). However, it is difficult to identify other peaks corresponding to this oxide, as they are overlapped with the peaks coming from other above-mentioned phases.
The existence of different molybdenum oxides can be explained by the influence of sparks during the anodization process. Ti and Mo atoms can be eroded from the substrate and react with water vapour produced by the discharges according to the reactions shown below [17]:
Rapid cooling of the melted particles on the oxide-electrolyte interface results in the formation of non-thermodynamically stable compounds, such as Ti2O3, Mo9O26, or Mo18O52. These non-stoichiometric compounds can form as a result of the partial reduction TiO2 and MoO3 by hydrogen.
Finally, as in the case of the first sample, the presence of Ca- and P-salts in a polycrystalline state is not confirmed by XRD. It is very likely that these compounds occur in amorphous or nanocrystalline forms.
In conclusion, the samples treated in the solutions 9 and 10 show differences in surface morphology, coating thickness, and the nature of the oxides formed during anodization. While the thinner layer produced in the electrolyte of series 10 clearly shows the presence of molybdenum and titanium oxides, the thicker layer, obtained in the electrolyte 9, seems to be composed only of different TiO2 phases. It could be explained by the fact that the MoO3 phase is formed only during the initial stage of the anodic layer growth. Then, only TiO2 phases continue to grow in the anodic layer. That is probably why X-rays do not detect the presence of molybdenum oxide buried underneath the TiO2 thick layer.
To summarize the results of the first campaign, the electrolyte nature and its concentration strongly influence the quality (homogeneity, roughness) of the PEO anodized layers obtained in Ca- and P-containing electrolytes on Ti-15Mo. Generally speaking, the homogeneity of the layers depends mainly on the pH of the electrolyte. The use of alkaline electrolytes stabilized by EDTA is not recommended for successful PEO anodization of Ti-15Mo alloy. The layers obtained in the alkaline electrolytes are porous and inhomogeneous. Only acidic electrolytes allow one to obtain good quality adherent layers on Ti-15Mo.
The oxide stability on Ti-15Mo is superior in acidic media, decreasing significantly in neutral and alkaline media due to the formation of soluble surface species. Acidic electrolytes are less corrosive with respect to molybdenum due to the formation of a highly protective barrier oxide film. Molybdenum oxides undergo continuous dissolution in alkali media, and the dissolution rate depends on the alkali concentration. In alkaline solutions, the molybdenum species exist only as . Their small size and high mobility enhance the metal solubility in the electrolyte and inhibit the creation of a protective barrier layer. At pH values below 7, heptamolybdate ions are formed in the electrolytes by the condensation reaction. Their big size and low mobility allow one to reduce the metal solubility in the electrolyte and enhance the formation of a barrier layer [18].
Even though the acidic electrolytes are more suitable for Ti-15Mo anodization than the alkaline ones, a successful PEO application on this alloy remains a difficult task. The mechanism of the electrochemical processes at the surface/solution interface during Ti-15Mo anodization is very complex. During the first stage of the process, before the appearance of the sparks, the main anodic electrochemical reactions for titanium and molybdenum processes are
Due to the competition between the Ti and Mo oxidation process, a non-homogeneous coating is formed. It was shown [19] that under classical anodizing (without sparks), anodic films on Ti-15Mo alloy consist of an outer TiO2 layer and an inner layer composed of TiO2 and MoO3. The formation of the double-layer films results from faster migration of Ti4+ ions compared with that of Mo6+ ions. The poor homogeneity of the anodised layers obtained on Ti-15Mo by PEO can also be explained by the difference in the Pilling-Bedworth ratio for TiO2 (1.95), MoO2 (2.12), and MoO3 (3.29). Such a difference results in Ti oxides being more compact than Mo oxides. As a consequence, oxide layers on Ti-15Mo are non-homogeneous.
Besides, the molybdenum oxides, which can be formed during the oxidation process on Ti-15Mo (e.g., Mo18O52, Mo9O26, Mo8O23, Mo5O14, Mo17O47, η-Mo4O11, γ-Mo4O11, MoO2, and MoO3), possess metallic or semi-conductor conductivity. MoO3, the most expected oxide forming during PEO process, has an energy bandgap of 2.75–2.95 eV. This is lower than that of TiO2 (Eg = 3.5 eV) [20]. It is clear that formation of a dielectric oxide layer on Ti-15Mo alloy, with two oxides having different band-gaps, is more complex than in case of pure Ti.
According to our experience, the most homogeneous anodized layers were formed in the electrolyte of the series 9, composed of Ca(H2PO2)2·2H2O and Ca(H2PO4)2·2H2O with pH = 4.5. Nevertheless, the Ca/P values in the coating (0.98) reached with this electrolyte were comparable to those obtained with other acidic electrolytes used in this study. We showed that increasing the Ca/P ratio in the electrolyte led to higher Ca/P ratio in the coating. However, due to the limited solubility of the Ca- and P-containing compounds, the highest Ca/P ratio reached in the electrolyte 9 was 1.1, which resulted in the Ca/P in the coating of 0.98.
Taking into account the better visual aspect of the oxide layer formed in the electrolyte of the series 9, it was decided to conduct the second anodization campaign in this electrolyte and to fix its Ca/P ratio at 1.1.
3.2. Second Campaign: Selection of the PEO Process Parameters
The aim of the second anodization campaign was to attempt an increase of the Ca/P ratio in the coating by the variation of the process parameters such as time of electrolysis (t), negative-to-positive current ratio (R), and frequency (F). Three sets of samples were prepared (Table 2). In each set, only one parameter was varied, and all others were kept constant.

Table 2.
PEO process parameters used in the second anodization campaign.
Figure 7 shows the variation of Ca/P ratio in the coating as a function of electrolysis time (a), frequency (b), and negative-to-positive current ratio, R (c). In all cases, no clear influence of these parameters on the Ca/P ratio was observed. The Ca/P ratios fluctuated between 0.86–1.07.
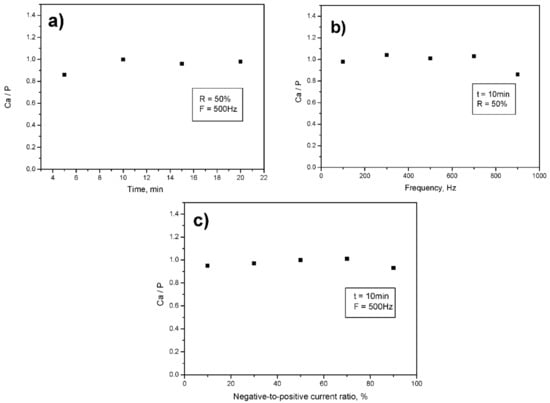
Figure 7.
Variation of Ca/P ratio in the coating as a function of electrolysis time (a); frequency (b) and negative-to-positive current ratio, R (c).
The Ca/P ratio in the coating does not vary significantly; nor does its elemental content. Elemental content in the coatings varies as follows: Ca 15–22 at. %., Ti 46–55 at. %, Mo 11–12 at. %, and P 17–21 at. %. Oxygen content could not be quantified with our XRF equipment. The elemental content is influenced by the process time, since the thicker the coating, the less is the signal coming from the substrate. Therefore, only Ca/P ratios can be compared for all the coatings.
In order to study the influence of process parameters on the coating surface morphology, SEM observation of the coatings has been carried out. Figure 8 shows SEM photographs of three layers deposited at different R-values (negative-to-positive current ratio). Their surface morphology does not differ significantly. It can be concluded that the negative-to-positive current ratio does not influences the surface morphology of the anodized layers, at least in the range studied. The same holds for the other process parameters, since similar surface morphology was observed for all other coatings shown in Table 2. It can be concluded that, like the Ca/P ratio, surface morphology is not significantly influenced by the process parameters (R-value, frequency, and electrolysis time).
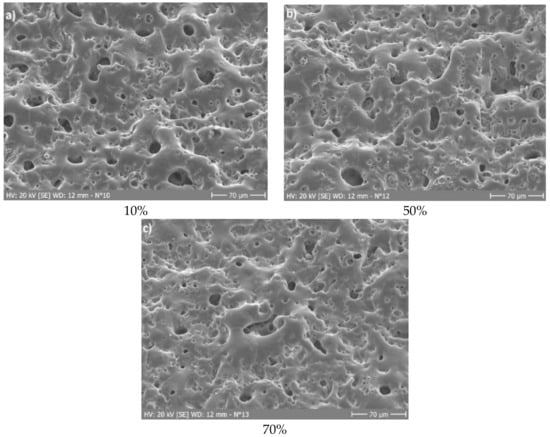
Figure 8.
Surface morphology of three anodized Ti-15Mo layers obtained at different R-values (negative-to-positive current ratio): (a) R = 10%, (b) R = 50%, and (c) R = 70%.
The coating crystallographic structure was not influenced by the process parameters either. The XRD patterns (not shown) indicate the presence of TiO2 phases (anatase and rutile). No peaks corresponding to crystalline Ca- and P-containing compounds, or to Mo oxide phases, were seen on the XRD patterns. It is likely that Ca- and P-containing compounds are present in the oxide layer in an amorphous or nanocrystalline forms.
The only coating property that is influenced by the process parameters is its thickness. It increases linearly with electrolysis time from 27 ± 6 µm (for the coating anodized during 5 min) to 115 ± 25 µm (for the coating anodized during 20 min).
In conclusion, the optimization of the process parameters did not result in a significant increase of the Ca/P ratio in the coating. The highest Ca/P ratio achieved in this campaign was close to 1.0.
3.3. Biocompatibility Tests
Surface biocompatibility was assessed in terms of cell proliferation and cell adhesion. Osteoblasts were seeded on Ti SLA (i.e., the reference standard) and PEO anodized Ti-15Mo samples. Proliferation was measured on days 4, 8, 15, and 22 (Figure 9). Cell proliferation on Ti SLA increased gradually from day 4 to day 15 to reach a plateau value (ca. 25% resazurin reduction). The proliferation rate on anodized Ti-15Mo sample was slightly delayed during the first week after seeding (1.3 fold decrease at day 8), but the values became equivalent during the second week until day 22. At day 4, the cell proportion on Ti SLA and anodized Ti-15Mo was equal (ca. 8% resazurin reduction), suggesting a similar cell affinity and adhesion for both surfaces. It was confirmed morphologically, with cells largely spread and emitting extensions on both Ti SLA and anodized Ti-15Mo (Figure 10). The microporosities served as anchorages, as shown for example in Figure 10d.
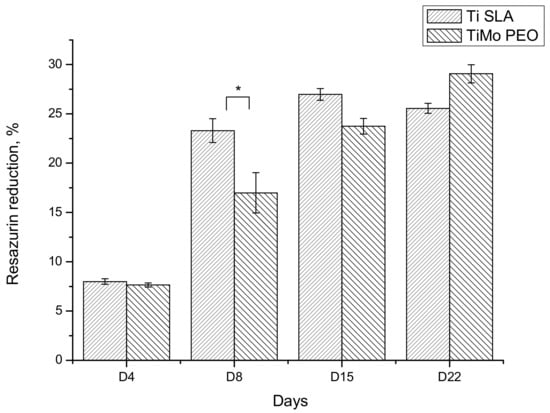
Figure 9.
Bioactivity of the selected anodized Ti-15Mo (TiMo PEO) as compared to microrough Ti (Ti SLA); Resazurin assay of osteoblast grown on both surfaces (mean ± SE, n = 6; * p < 0.05, student t-test between Ti SLA and TiMo PEO at the same day).
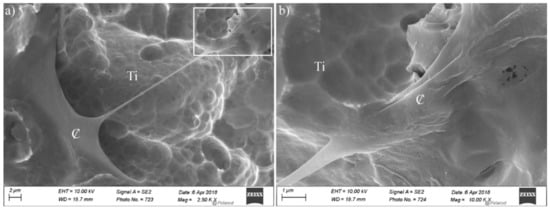

Figure 10.
Typical SEM micrographs of osteoblasts grown on Ti SLA (a,b) higher magnification) and anodized Ti-15Mo (c,d) higher magnification) at day 4 (white square: magnified zone; ₵: cell; Ti: uncovered Ti SLA; TiMo: anodized Ti-15Mo).
Generally, except for a little delay during the first week, the cell behavior on PEO-anodized Ti-15Mo was comparable to that on the reference standard Ti SLA. The cell adhesion was tight and homogenous on the surface, whether on flat zones or micropits, suggesting a high osteoblast affinity for this microstructure and chemistry. The Ca/P ratio may be optimized to catch up the delay in the start of proliferation during the first day after seeding. The results herein obtained led us to conclude that the surface structure and chemistry is highly biocompatible and fairly equivalent to the standards in terms of cell proliferation and adhesion. Further experiments are needed to study the mechanisms of adhesion, as well as the cell differentiation capability on PEO-anodized Ti-15Mo, before drawing definitive conclusions.
4. Conclusions
A wide range of Ca- and P-containing solutions was employed to incorporate Ca and P ions into the anodized layer formed on Ti-15Mo by the PEO process. Eight series of alkaline electrolytes containing Ca- and P-compounds with different concentrations have been used to perform anodization experiments, with the aim to obtain a high Ca/P ratio in the anodized layer (close to 1.67). The efficiency of the Ca and P incorporation in the coating was analysed by the Ca/P ratio in the anodized layer and compared to that in the electrolyte. For all electrolytes used in this study, the Ca/P ratio in the layer was lower than that in the electrolyte. The maximum Ca/P ratio, reached in the layer anodized in an alkaline electrolyte of series 7, was 1.38. However, this layer exhibits high phase heterogeneity, which can be explained by the complex nature of anodic layers formed on Ti-15Mo, especially at high pH. Therefore, we conclude that alkaline electrolytes are not suitable for the formation of good quality uniform anodic layers. Only acidic electrolytes are appropriate in the case of Ti-15Mo.
Three acidic electrolytes (series 9–11) containing two Ca- and P- containing compounds resulted in good quality PEO layers on Ti-15Mo. The best results, as judged from the coating appearance, were obtained using the electrolytes of the series 9. The use of this electrolyte results in almost 1:1 correspondence between Ca/P value in the coating and that in the electrolyte. The maximum Ca/P value reached using this electrolyte was 0.98. This value was much lower than the targeted value of 1.67.
Attempts at further optimization by varying the process time, frequency, and negative-to-positive current ratio did not result in the significant changes of the Ca/P ratio, crystallographic structure, and surface morphology of the anodized layers. Only layer thickness linearly increases with the process time. The maximum Ca/P achieved was about 1.0.
Despite the low Ca/P ratios in the anodized layers, they show a high rate of osteoblast proliferation, which is comparable to pure microrough Ti. Initial adhesion to PEO anodized Ti-15Mo surfaces seems to be very tight, similar to that on Ti. These are promising results; however, they need further optimization. However, the Ti-15Mo alloy anodized by PEO in Ca- and P-containing electrolytes may already be considered as a good candidate for biological applications.
Author Contributions
Investigation: L.S., T.J., C.C., O.K., O.G. and L.M. Project administration: O.B., P.-A.G. and S.D. Supervision: O.B., L.S. and S.D. Writing, review & editing: O.B., S.D. and L.S.
Funding
“This research was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SCOPES grant No. IZ73Z0_152399/1 “Theory and application of plasma electrolytic treatment of new generation titanium alloys for biomedical applications”) and the Haute Ecole Spécialisée de la Suisse Occidentale (HES-SO, Switzerland).”
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SCOPES grant No. IZ73Z0_152399/1. “Theory and application of plasma electrolytic treatment of new generation titanium alloys for biomedical applications”) and the Haute Ecole Spécialisée de la Suisse Occidentale (HES-SO, Switzerland). The authors thank to M. Pierre-Alain Montandon (Haute Ecole Arc Ingénierie, HES-SO) for sample preparation. Also, they would like to thank Olha Sereda and Saba Zabihzadeh (CSEM, Switzerland) for the interpretation of the XRD results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Özcan, M.; Hämmerle, C. Titanium as a reconstruction and implant material in dentistry: Advantages and pitfalls. Materials 2012, 5, 1528–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disegi, J.A. Titanium alloys for fracture fixation implants. Injury 2000, 31, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, H.J.; Qazi, J.I. Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y. New developments of Ti-based alloys for biomedical applications. Materials 2014, 7, 1709–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, N.T.C.; Guastaldi, A.C. Electrochemical behavior of Ti-Mo alloys applied as biomaterial. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babilas, D.; Słuzalska, K.; Krza̧kała, A.; Maciej, A.; Socha, R.P.; Dercz, G.; Tylko, G.; Michalska, J.; Osyczka, A.M.; Simka, W. Plasma electrolytic oxidation of a Ti-15Mo alloy in silicate solutions. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayon, M.T.; Lacout, J.L. Study of the Ca/P atomic ratio of the amorphous phase in plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 172, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Oliveira, F.; Boldrini, L.C.; Leite, P.E.; Falagan-Lotsch, P.; Linhares, A.B.R.; Zambuzzi, W.F.; Fragneaud, B.; Campos, A.P.C.; Gouvêa, C.P.; et al. Micro-arc oxidation as a tool to develop multifunctional calcium-rich surfaces for dental implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 54, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzakała, A.; Słuzalska, K.; Dercz, G.; Maciej, A.; Kazek, A.; Szade, J.; Winiarski, A.; Dudek, M.; Michalska, J.; Tylko, G.; et al. Characterisation of bioactive films on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 104, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Dercz, G.; Kalemba, I.; Suchanek, K.; Kukharenko, A.I.; Korotin, D.M.; Michalska, J.; Krzakala, A.; Piotrowski, J.; Kurmaev, E.Z.; et al. Surface characterisation of Ti-15Mo alloy modified by a PEO process in various suspensions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 39, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simka, W. Preliminary investigations on the anodic oxidation of Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy in a solution containing calcium and phosphorus. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9831–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauchiger, V.M.; Schlottig, F.; Gasser, B.; Textor, M. Anodic plasma-chemical treatment of CP titanium surfaces for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, O.; Journot, T.; Gay, P.A.; Matthey, J.; Csefalvay, C.; Kalinichenko, O.; Sereda, O.; Moussa, M.; Durual, S.; Snizhko, L. Synthesis by anodic-spark deposition of Ca- and P-containing films on pure titanium and their biological response. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.; Banakh, O.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Fontana, P.; Scherrer, S.; Cattani, M.; Wiskott, A.; Durual, S. TiNxOy coatings facilitate the initial adhesion of osteoblasts to create a suitable environment for their proliferation and the recruitment of endothelial cells. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durual, S.; Pernet, F.; Rieder, P.; Mekki, M.; Cattani-Lorente, M.; Wiskott, H.W.A. Titanium nitride oxide coating on rough titanium stimulates the proliferation of human primary osteoblasts. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2011, 22, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simka, W.; Krzakała, A.; Korotin, D.M.; Zhidkov, I.S.; Kurmaev, E.Z.; Cholakh, S.O.; Kuna, K.; Dercz, G.; Michalska, J.; Suchanek, K.; et al. Modification of a Ti-Mo alloy surface via plasma electrolytic oxidation in a solution containing calcium and phosphorus. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 96, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, G.; Nakasugi, Y.; Akiyama, T. Excitation temperature of a solution plasma during nanoparticle synthesis. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 83301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S.; Lee, C.W. Molybdenum, molybdenum oxides, and their electrochemistry. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1146–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habazaki, H.; Uozumi, M.; Konno, H.; Shimizu, K.; Nagata, S.; Asami, K.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E. Influence of molybdenum species on growth of anodic titania. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3837–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, M.; Rauls, E.; Schmidt, W.G. The electronic structure and optical response of rutile, anatase and brookite TiO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 195503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).