Abstract
This study systematically optimizes the T6 heat treatment of a commercial EV31A magnesium alloy and evaluates the resulting microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. Optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to characterize the microstructure and phase constitution, while differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was employed to determine appropriate solution treatment parameters. Brinell hardness measurements and tensile tests at room temperature and 150 °C were carried out to quantify the mechanical response. The as-cast alloy consists of α-Mg equiaxed grains, bone-shaped Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases at grain boundaries, and minor intragranular lath-shaped Mg12Nd phases. After T6 treatment (520 °C/10 h solution treatment + 200 °C/16 h aging), the grain boundary eutectic phases partially dissolve and transform into Mg41(Nd,Gd)5, while intragranular nano-scale β′ precipitates and stable Zn2Zr3 particles form, achieving multi-scale synergistic strengthening. Compared to the as-cast condition, the T6-treated alloy exhibits room-temperature ultimate tensile strength and yield strength of 309 ± 40.5 MPa (31% increase) and 180 ± 14.2MPa (45% increase), respectively. At 150 °C, the strength reaches 241 ± 7.5 MPa (39% increase) and 154 ± 16.8 MPa (52% increase), while maintaining an elongation of 10.9± 0.7%, demonstrating an excellent strength–ductility balance.
1. Introduction
Magnesium alloys show promising application prospects in three key areas: rail vehicles, aircraft structures, and electronic enclosures. This potential is primarily attributed to their favorable physical properties, including low density, high specific strength, excellent mechanical energy absorption capacity, and reliable electromagnetic compatibility [1,2,3,4]. However, the widespread industrial adoption of traditional magnesium alloys is significantly constrained by their insufficient strength at room and elevated temperatures, poor ductility, and inadequate corrosion resistance [5,6]. To address these limitations, alloy composition design and subsequent heat treatment are regarded as core strategies for synergistically enhancing overall service performance. Rare earth microalloying has proven effective in simultaneously improving the strength and high-temperature performance of magnesium alloys [7]. These elements form thermally stable intermetallic compounds with high melting points that pin grain boundaries and suppress high-temperature slip. Concurrently, they refine eutectic structures, promote the formation of dispersed precipitates, and weaken the basal texture while activating non-basal slip systems, thereby achieving a synergistic improvement in both strength and ductility [8,9,10,11]. Currently, prominent rare earth magnesium alloy systems include Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr, Mg-RE-Zn-Zr, Mg-RE-Al, and Mg-Y-Zn-Zr series [12]. The EV31A alloy (also known as Elektron 21), belonging to the Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr system, is characterized by high strength and good heat resistance, enabling service in environments exceeding 150 °C. Having met the AMS 4429 standard, it is recognized as a highly promising material for aircraft transmission systems [13,14,15]. Additionally, EV31A magnesium alloy possesses good castability and age-hardening capability, which contribute to its enhanced room-temperature strength, elevated temperature strength, creep resistance, and corrosion resistance [16].
Although EV31A is a well-established alloy, its performance under more extreme operating conditions, particularly with respect to high-temperature stability and strength, has not been fully optimized. Many existing studies on EV31A have largely emphasized room-temperature properties, while this study addresses its high-temperature performance, with particular emphasis on tensile behavior at 150 °C, which is directly relevant to the targeted service temperature range of EV31A components. The optimization of T6 heat treatment for EV31A alloys has not been thoroughly explored, particularly in terms of achieving a balanced enhancement in both strength and ductility at elevated temperatures. Heat treatment, a fundamental thermomechanical processing technique, plays a pivotal role in bridging this gap by precisely controlling magnesium alloys’ microstructure and mechanical responses. Appropriate solution and aging treatments facilitate the dissolution of intermetallic compounds, optimize the distribution of secondary phases, and refine the morphology of precipitates, thereby significantly enhancing both mechanical properties and corrosion resistance [17]. Furthermore, in the EV31A alloy, the combined effect of light rare earth Nd and heavy rare earth Gd contributes to increased solid solubility and improved precipitation behavior, enabling the alloy to exhibit greater strengthening potential after heat treatment [18]. Fan R et al. [19] reported that isothermal aging at 200 °C for 72 h increased the hardness of a Mg-2Gd-2Y-2Nd-2Sm-1Ag-1Zn-0.5Zr alloy from 80 HV (solution-treated) to 118 HV, with corresponding tensile improvements. Similarly, WANG Y et al. [20] demonstrated that a Mg-4.2Zn-1.5RE-0.7Zr alloy achieved optimal tensile properties after aging at 325 °C for 10 h, with yield strength and ultimate tensile strength reaching 153.9 MPa and 247.0 MPa, representing increases of 48 MPa and 23 MPa, respectively, compared to the as-cast condition. Additionally, Zheng J et al. [21] systematically investigated the effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of a Mg-9.5Gd-4Y-2.2Zn-0.5Zr alloy, identifying the optimal T6 treatment as 520 °C for 24 h followed by 200 °C for 112 h. The alloy strength under this regime was significantly superior to both the as-cast condition and the state after solution treatment alone. These studies collectively highlight that well-designed heat treatment can significantly enhance the mechanical performance of rare-earth magnesium alloys.
While T6 heat treatment is well-established, a thorough investigation into the optimization of T6 parameters for EV31A alloy, particularly to achieve a better balance between strength and ductility at elevated temperatures, is still lacking in the literature. As demand for lightweight and heat-resistant components in advanced equipment continues to rise, the service capability of EV31A magnesium alloy under more severe operating conditions has attracted growing attention. A critical challenge lies in precisely tailoring its microstructure and precipitation behavior through heat treatment to achieve a more desirable balance of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. This study systematically investigates the microstructural evolution and its impact on mechanical properties in a commercial EV31A magnesium alloy under different heat treatment regimes. Specifically, this study establishes clear microstructure-property relationships by correlating the dissolution/transformation of RE-rich eutectic phases and precipitate formation with tensile properties and fracture behavior at both room and elevated temperatures. The objective is to optimize and identify the most suitable T6 heat treatment process for this alloy, providing a theoretical foundation and technical guidance for its engineering application in high-temperature lightweight structures.
2. Materials and Methods
The experimental alloy investigated in this work was an as-cast EV31A-type (near-EV31A) alloy cast in-house. Alloy preparation used pure Mg (99.95 wt%), Nd (99.5 wt%), Gd (99.5 wt%), Zn (99.5 wt%), and Mg-30Zr master alloy. The raw materials were melted in an electrical resistance furnace (Jilin Langjiang Technology Co., Ltd., Changchun, China)and subsequently refined under a protective flux atmosphere. The melt was then cast into ingots measuring φ80 mm × 3000 mm using a semi-continuous casting procedure. The alloy’s chemical composition was quantified using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Analytik Jena (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), and the measured values are presented in Table 1. The measured Gd content (1.76 wt%) is slightly above the nominal upper limit of the EV31A specification (1.7 wt%); therefore, the material is referred to as EV31A-type (near-EV31A) in terms of specification compliance, while “EV31A” is retained in the manuscript for consistency with the literature on Elektron 21/EV31A alloys.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the EV31A-type magnesium alloy used in this study (wt%).
For microstructural characterization (including optical microscopy, SEM/EDS, and XRD), cubic specimens measuring 10 × 10 × 10 mm were prepared. These specimens were mechanically ground using abrasive paper from 120# to 5000#, followed by polishing with a 1 μm diamond suspension. Prior to microscopic observation, the samples were lightly etched with a 4 vol.% nitric acid ethanol solution to reveal clear microstructural features. The microstructure of the alloys was examined using a 30XD-PC optical microscope (Shanghai Optical Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and an Apreo 2s scanning electron microscope (SEM, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.,Waltham, MA, USA). An Oxford energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) system coupled to the SEM was used to analyze elemental distribution and phase composition. Phase identification was performed using a D8 DISCOVER X-ray diffractometer (XRD, BRUKER, Karlsruhe, Germany).
For mechanical property evaluation, Brinell hardness (HBW) was measured using a THBS-62.5 microhardness tester (Beijing Time High Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) with a 1 mm tungsten carbide (hard metal) ball indenter under a load of 10 kg and a dwell time of 30 s. Five independent measurements were taken on each specimen, and the average value was reported to ensure reliability. Tensile tests were performed on a universal testing machine (Shanghai Tuofeng Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) using M10 × Φ5 rod-shaped specimens fabricated according to GB/T 228.1-2019 [22]. All tests were performed using at least three parallel specimens. Tensile testing was conducted at a crosshead speed of 2 mm/min, corresponding to an initial strain rate of approximately 1.0 × 10−3 s−1 (gauge length: 35 mm).
This study focuses on optimizing the T6 heat treatment for EV31A magnesium alloy, which involves evaluating the effects of the solution treatment stage and the complete solution-plus-aging (T6) regime on the microstructure and properties. Solution treatment was conducted in an SX2-4-10NP box-type resistance furnace (Shanghai Yiheng Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), while aging treatment was performed using a 101-0B electric blast drying oven (Shanghai Shangpu Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was performed using an STA509 synchronous thermal analyzer(NETZSCH-Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany) to analyze potential phase transformation characteristics, thereby providing a basis for determining the solution treatment temperature.
All specimens were cut from the same casting batch. The heat-treatment parameters and the corresponding tests performed for each specimen condition are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of specimen conditions, heat-treatment parameters and corresponding tests.
3. Results
3.1. As-Cast Microstructural Characteristics
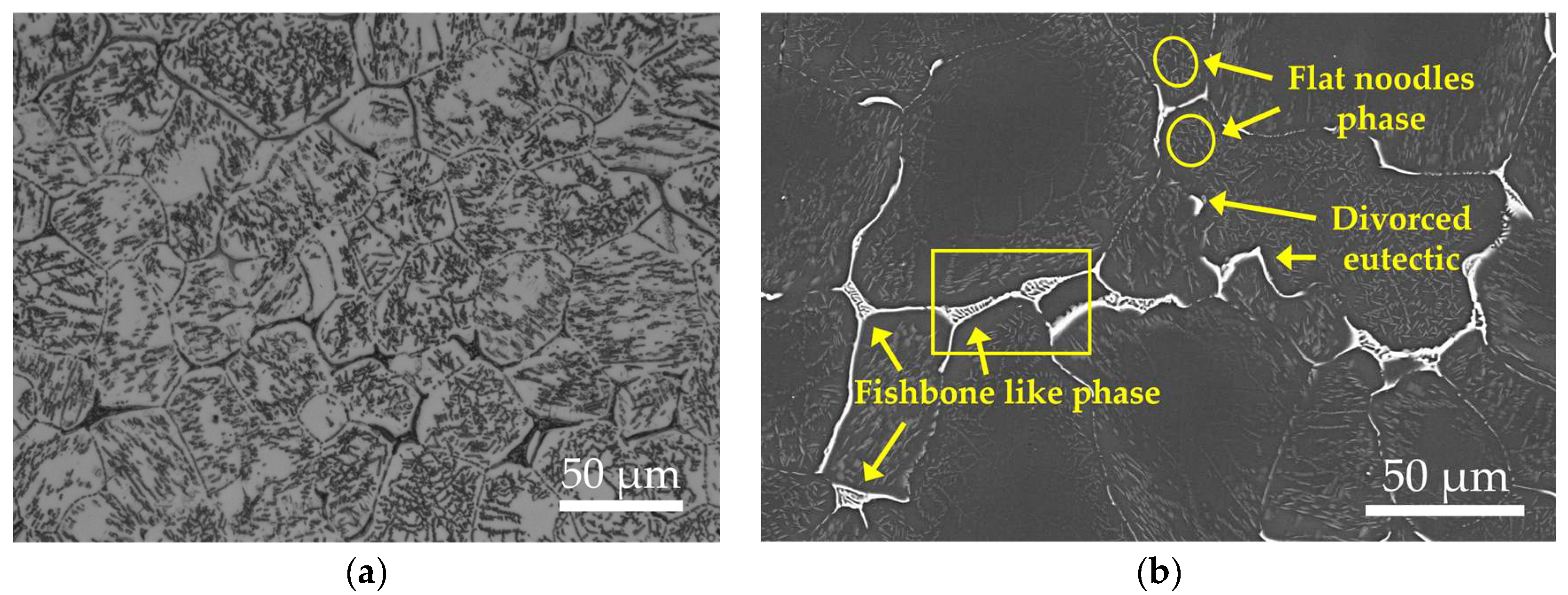
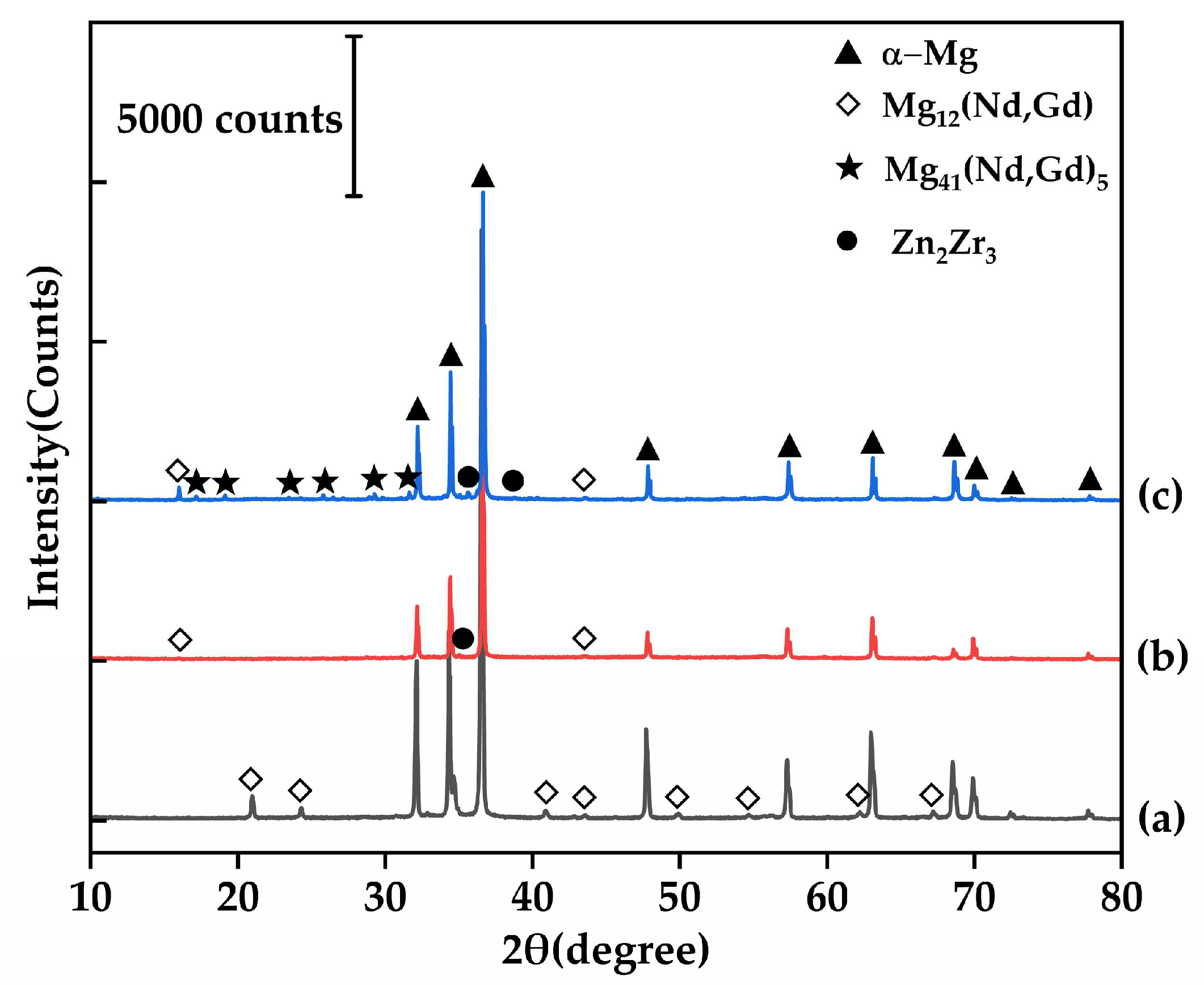
Figure 1 displays the as-cast microstructure of the EV31A magnesium alloy. Overall, the microstructure consists of an α-Mg matrix and non-equilibrium eutectic phases distributed along grain boundaries, exhibiting characteristics typical of cast Mg-RE alloys. The average grain size of the as-cast alloy, measured by the linear intercept method, is approximately 72.94 μm. XRD results (Figure 2a) indicate that, besides α-Mg, only diffraction peaks corresponding to Mg12(Nd,Gd) are detected, with no evident characteristic peaks of other rare-earth phases, suggesting that this phase is the sole major secondary phase in the as-cast alloy. The identity of secondary phases in the as-cast EV31A alloy remains controversial. Yang et al. [23] identified the microstructure as α-Mg with grain-boundary Mg3RE networks and intragranular Mg12Nd plates. In contrast, Su et al. [24] reported α-Mg with Mg12Nd eutectic phases at grain boundaries. Meanwhile, A. Kielbus et al. [25] attributed the predominant secondary phase to Mg12(Nd,Gd), where Gd substitutes for Nd in the Mg12Nd lattice—a stabilization enabled by their similar atomic radii.
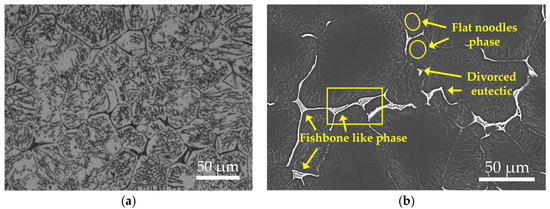
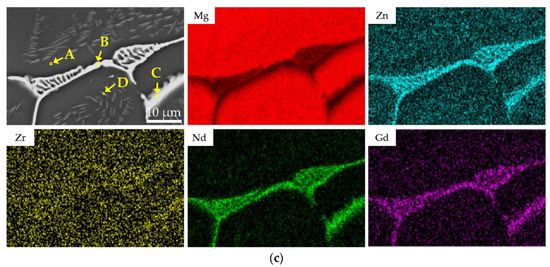
Figure 1.
Microstructure of as-cast EV31A magnesium alloy: (a) OM image; (b) SEM image; (c) EDS elemental mapping.
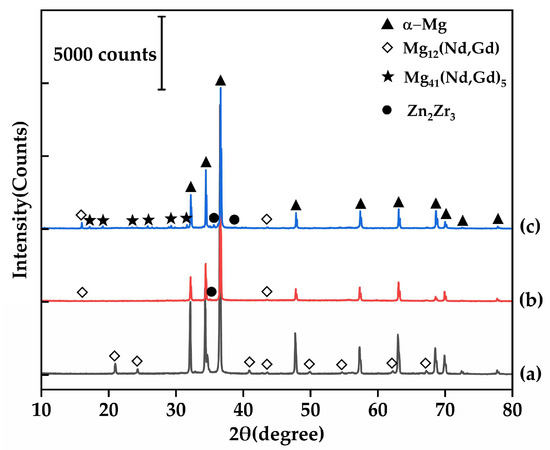
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the EV31A magnesium alloy: (a) as-cast; (b) 520 °C/10 h; (c) T6 condition.
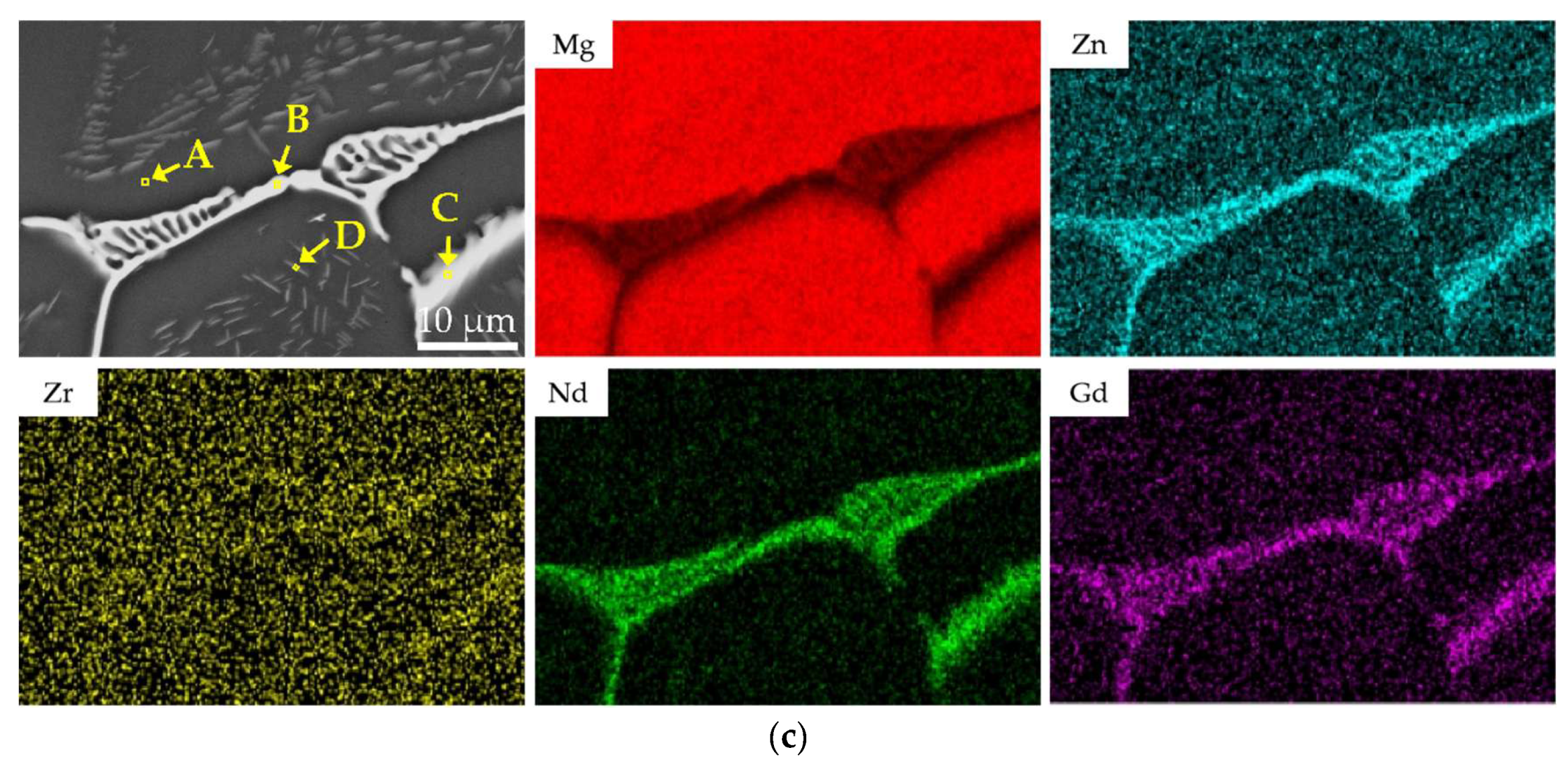
SEM results further reveal that the secondary phases in the as-cast alloy exist in two distinct morphologies: (1) a continuous or semi-continuous network of eutectic phases along grain boundaries, exhibiting lamellar bone-like structures and blocky divorced eutectic constituents; and (2) a small amount of lath- or needle-shaped precipitates within grains, formed by non-equilibrium eutectic reactions in solute-enriched regions during the final stages of solidification. The secondary phases distributed along grain boundaries and within grain interiors have a characteristic size on the order of 20–30 μm and occupy approximately 10.59 area.% of the as-cast microstructure. To further clarify the compositional characteristics of the secondary phases, SEM-EDS elemental mapping and point analysis were performed on the as-cast sample (Figure 1c and Table 3). It should be noted that the elemental maps reflect qualitative relative intensity distributions with contrast adjusted to highlight local enrichment; therefore, a weaker Mg contrast in RE-rich regions does not indicate the absence of Mg. The elemental mapping results indicate that the skeletal and network-like eutectic phases at grain boundaries are significantly enriched in Nd and Zn, while the Gd content is relatively low. This observation aligns with the lower overall Gd content compared to Nd in the EV31A alloy and the higher solid solubility of Gd in Mg. Notably, the intragranular lath-shaped precipitates dissolve completely after subsequent solution treatment, indicating significantly lower thermal stability compared to the grain boundary eutectic phases. Based on their morphology and dissolution behavior, it can be inferred that these lath-shaped phases correspond to the Mg12Nd phase reported in the literature [26].

Table 3.
EDS point analysis results (at.%) for the α-Mg matrix (A), grain-boundary eutectic phases (B, C), and intragranular needle-like precipitates (D) in the as-cast EV31A alloy (locations in Figure 1c).
The EDS point analysis results (Table 3) indicate that the matrix (Point A) is a typical α-Mg solid solution, while all secondary phases (Points B and C) are enriched with Nd and Gd elements. The Mg/RE atomic ratio at Point C is approximately 9.01:1 (87.78 at.% Mg:9.74 at.% RE), which is closer to the ideal stoichiometric ratio of Mg12RE. In comparison, Point B exhibits a higher degree of RE enrichment, with an Mg/RE atomic ratio of approximately 6.37:1 (83.23 at.% Mg:13.07 at.% RE). Additional EDS analysis on intragranular needle-like phases (Point D, Table 3) confirmed Nd enrichment (with minor Gd). Although the small needle size and matrix contribution preclude precise stoichiometric determination from the Mg/RE ratio, the compositional trend—combined with their morphology and complete dissolution during solution treatment—supports their identification as Mg12Nd-type precipitates. The compositional differences among the measured points primarily arise from the relatively large interaction volume of the electron beam during EDS point analysis, which inevitably incorporates signals from the surrounding α-Mg matrix. This leads to an overestimation of Mg content and an underestimation of RE content in the measurements. Furthermore, a solid solution of Zn was detected in all secondary phases (3.71 at.% at Point B and 2.43 at.% at Point C), consistent with the Nd/Zn co-segregation observed in the elemental mapping. Combined with the phase identification results from XRD, it is confirmed that the secondary phases in the as-cast microstructure are predominantly Mg12(Nd,Gd), in which some Nd lattice sites are substituted by Gd (an element with a similar atomic radius). A small amount of Zn is also detected in the matrix, while the subsequent precipitation heat treatment (solution treatment followed by aging) promotes the formation/increase in precipitates. This conclusion is highly consistent with the findings reported by A. Kielbus et al. [25] for the Elektron 21/EV31A alloy system.
The formation of the as-cast microstructure is closely related to the solidification characteristics of Mg-RE alloys. During solidification, the primary α-Mg phase forms first, causing rare earth elements to become progressively enriched in the remaining liquid. When the temperature drops to the eutectic transformation range of approximately 548 °C, the enriched Nd/Gd undergoes a eutectic reaction, forming continuous or semi-continuous grain boundary Mg-RE eutectic phases. Consequently, rare earth elements are predominantly distributed along grain boundaries rather than within the grain interiors [27]. Meanwhile, Zn continues to enrich in the late stages of solidification and ultimately dissolves into the Mg12(Nd,Gd) phase. Zr primarily exists in the form of heterogeneous nucleation sites, effectively promoting the nucleation of α-Mg and thereby refining the grains [28]. Brinell hardness tests show that the as-cast EV31A alloy has an average hardness of 56.26 HBW. This hardness is mainly due to the strengthening effect of RE-enriched eutectic phases at grain boundaries, combined with grain refinement caused by Zr.
In summary, the as-cast microstructure of the EV31A magnesium alloy can be described as α-Mg equiaxed grains + bone-shaped Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases along grain boundaries + a small amount of lath-shaped Mg12Nd precipitates within grains. This microstructural configuration reflects significant non-equilibrium solidification behavior and establishes the essential foundation for subsequent age-hardening during T6 treatment.
3.2. Microstructural Evolution After Solution Treatment
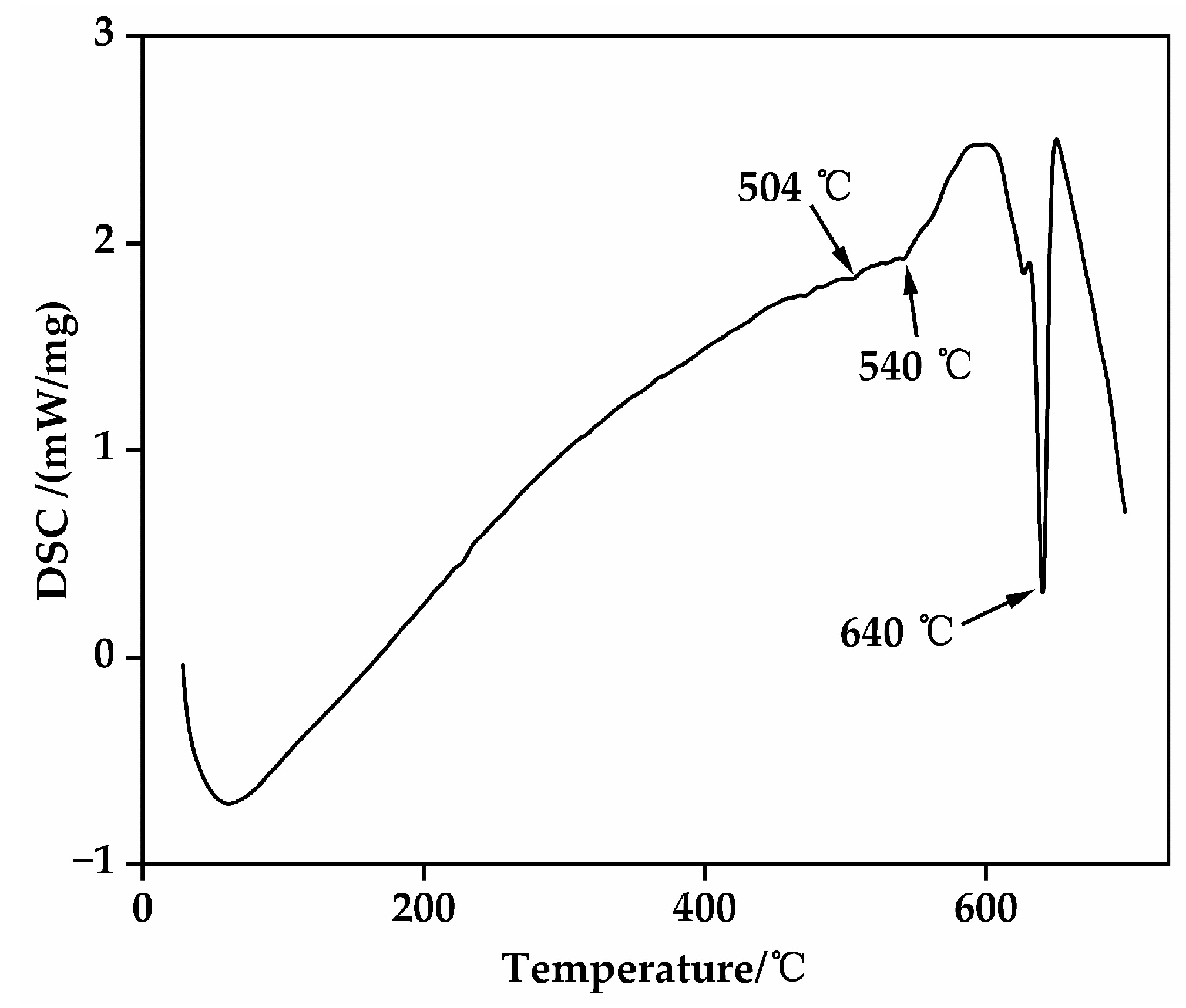
The primary objective of solution treatment is to facilitate the complete dissolution of the non-equilibrium Mg-RE intermetallic compounds, distributed along grain boundaries and within grains in the as-cast EV31A alloy, back into the α-Mg matrix. This process aims to form a supersaturated solid solution, thereby establishing a stable microstructural foundation for subsequent age-hardening precipitation [29]. To determine appropriate solution treatment temperatures, DSC analysis was performed on the as-cast alloy (Figure 3). The results reveal endothermic peaks near 504 °C and 540 °C, corresponding to the melting of low-melting-point secondary phases, and a peak at approximately 640 °C associated with the melting of the α-Mg matrix. Consequently, the solution temperature must be maintained below the melting points of these low-melting-point phases to avoid localized overheating. This study selected solution temperatures of 510 °C, 520 °C, and 530 °C, combined with holding times of 6 h, 10 h, and 14 h, to systematically investigate the dissolution behavior of secondary phases and grain evolution, thereby identifying the optimal solution treatment parameters (Table 2).
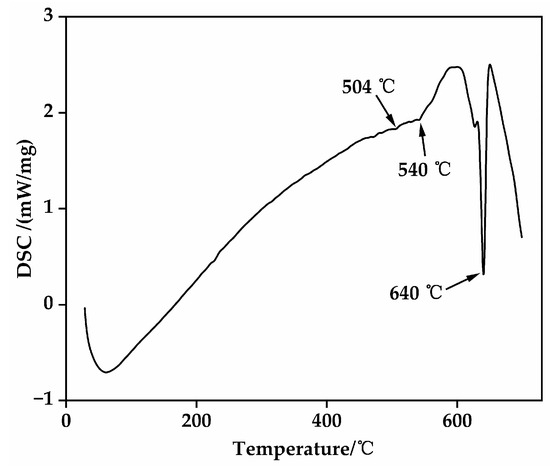
Figure 3.
DSC curve of the as-cast EV31A magnesium alloy.
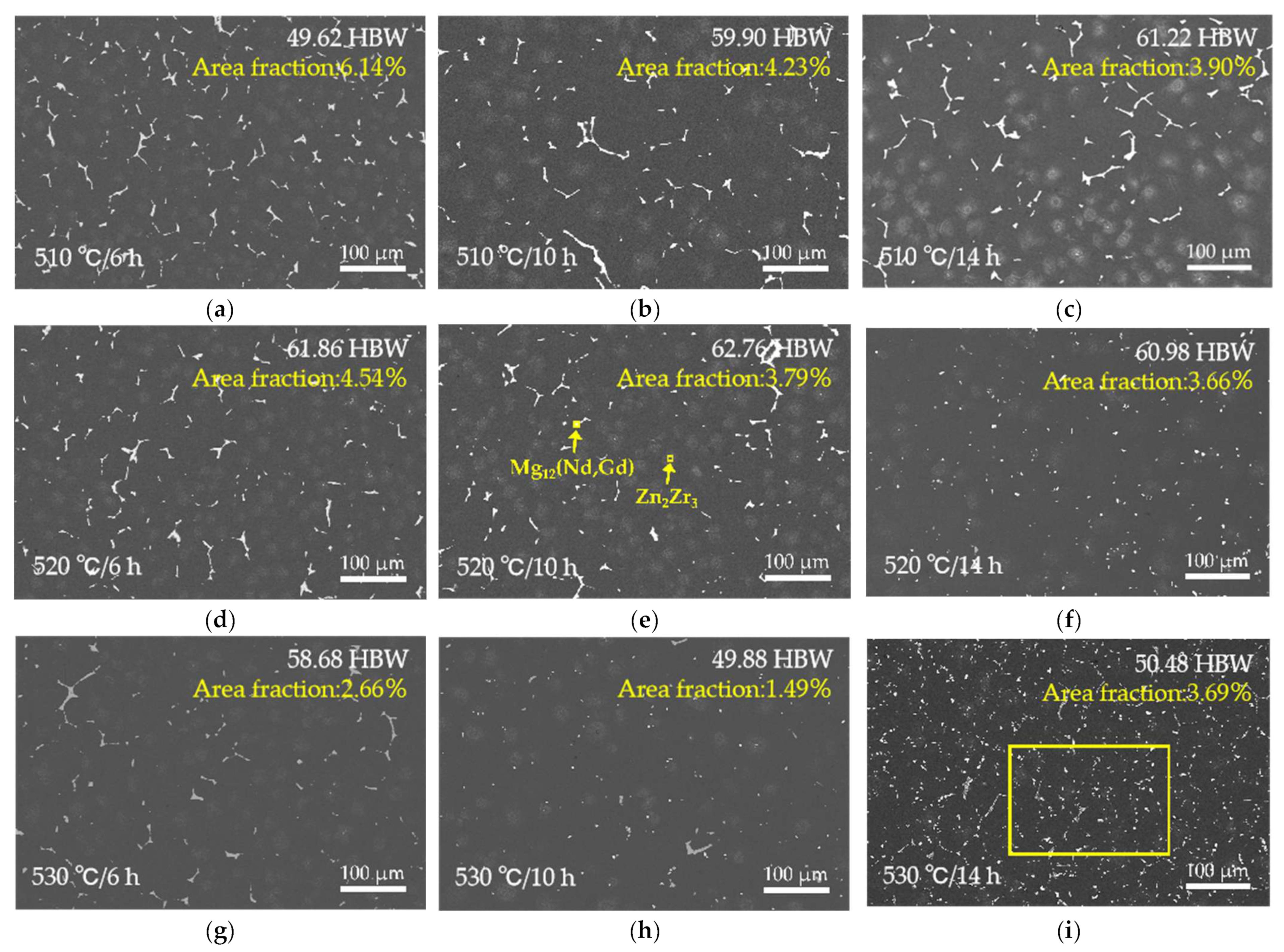
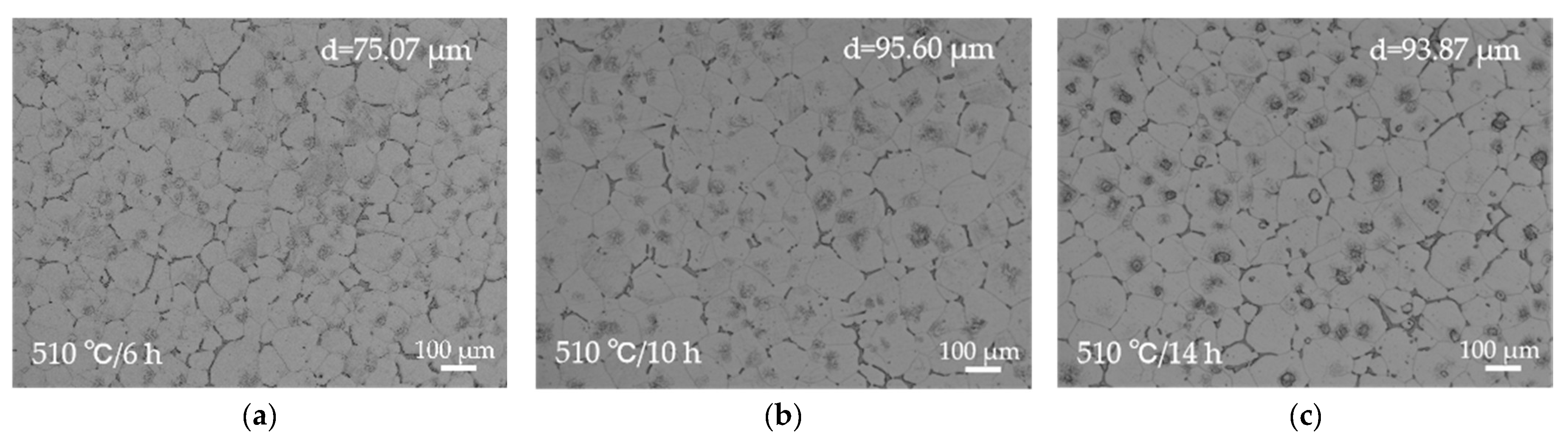
Figure 4 and Figure 5 illustrate the microstructural evolution of the EV31A alloy under different solution treatment conditions. All three temperature ranges exhibit typical dissolution characteristics of secondary phases, yet significant differences exist in the degree of dissolution, grain growth rate, and microstructural stability. At 510 °C (Figure 4a–c), the grain boundary Mg12RE eutectic phases remain prominently present. It should be noted that the bright (white-contrast) features observed in Figure 4 include two distinct types of phases. The coarse, blocky/skeletal bright constituents located mainly along grain boundaries and triple junctions correspond to residual Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases. In contrast, some finer bright particles/rods with a different contrast are Zr–Zn-rich phases (Zn2Zr3), which become more evident after solution treatment. Detailed compositional and crystallographic evidence confirming Zn2Zr3 is presented in Section 3.3 for the T6 condition. As the holding time extends from 6 h to 14 h, the area fraction of the eutectic phase decreases noticeably, yet it persists as continuous or blocky constituents, particularly at triple junctions. Although an exact volume fraction was not determined, a semi-quantitative assessment based on ImageJ (1.50b Version) analysis of multiple SEM micrographs indicates a clear and systematic decrease in the area fraction of grain-boundary eutectic phases after solution treatment. At this temperature, hardness increases from 49.62 to 61.22 HBW due to solid solution strengthening. However, grain size grows from 75.07 to 93.87 μm, and secondary phases remain incompletely dissolved, indicating that 510 °C is inadequate for forming a homogeneous supersaturated solid solution.
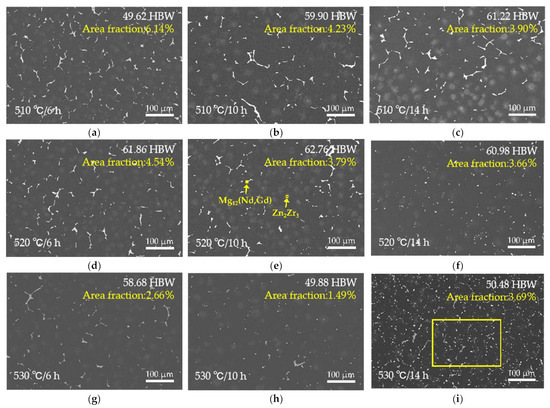
Figure 4.
SEM images of the solution-treated EV31A magnesium alloy: (a) 510 °C × 6 h; (b) 510 °C × 10 h; (c) 510 °C × 14 h; (d) 520 °C × 6 h; (e) 520 °C × 10 h; (f) 520 °C × 14 h; (g) 530 °C × 6 h; (h) 530 °C × 10 h; (i) 530 °C × 14 h. The corresponding Brinell hardness value and area fraction of secondary phases for each condition is inset in (a) through (i).
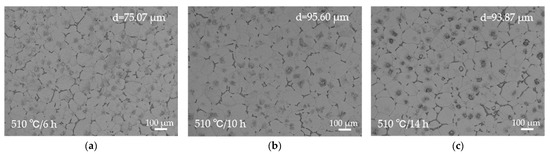
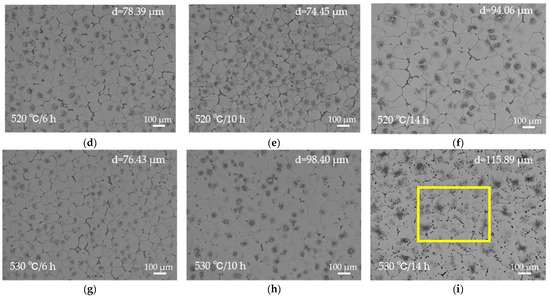
Figure 5.
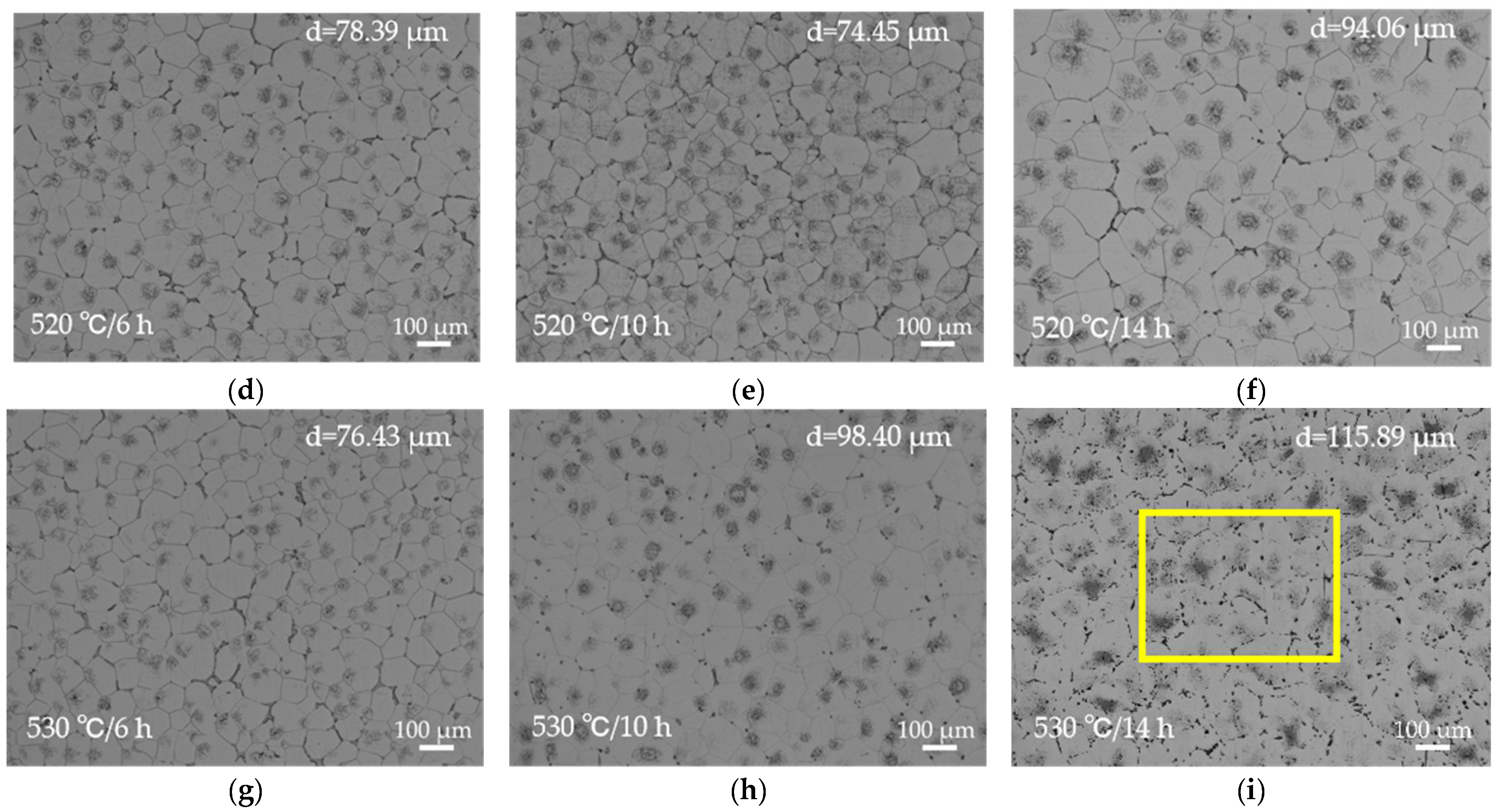
OM images of the solution-treated EV31A magnesium alloy: (a) 510 °C × 6 h; (b) 510 °C × 10 h; (c) 510 °C × 14 h; (d) 520 °C × 6 h; (e) 520 °C × 10 h; (f) 520 °C × 14 h; (g) 530 °C × 6 h; (h) 530 °C × 10 h; (i) 530 °C × 14 h. The corresponding average grain size each condition is inset in (a) through (i).
At 520 °C × 10 h, secondary phases dissolve adequately with minimal grain coarsening (grain size 74.45 μm). This condition yields the most homogeneous and structurally stable microstructure among all solution treatment parameters. Simultaneously, XRD results (Figure 2b) confirm that only a small amount of Mg12RE remains in the alloy under this condition, with a significant reduction in the intensity of its corresponding diffraction peaks, further demonstrating the essentially complete dissolution of secondary phases at 520 °C. All XRD patterns were collected under identical conditions and normalized to the α-Mg reference peak (~36.6°); the background-corrected peak-height ratio of Mg12(Nd,Gd) at ~21° decreases from 0.036717 (as-cast) to 0.001654 after solution treatment, supporting substantial dissolution of Mg12(Nd,Gd). When the holding time is extended to 14 h, the grain size rapidly increases to 94.06 μm and the hardness decreases to 60.98 HBW, indicating that prolonged holding induces grain coarsening and should be avoided in practice.
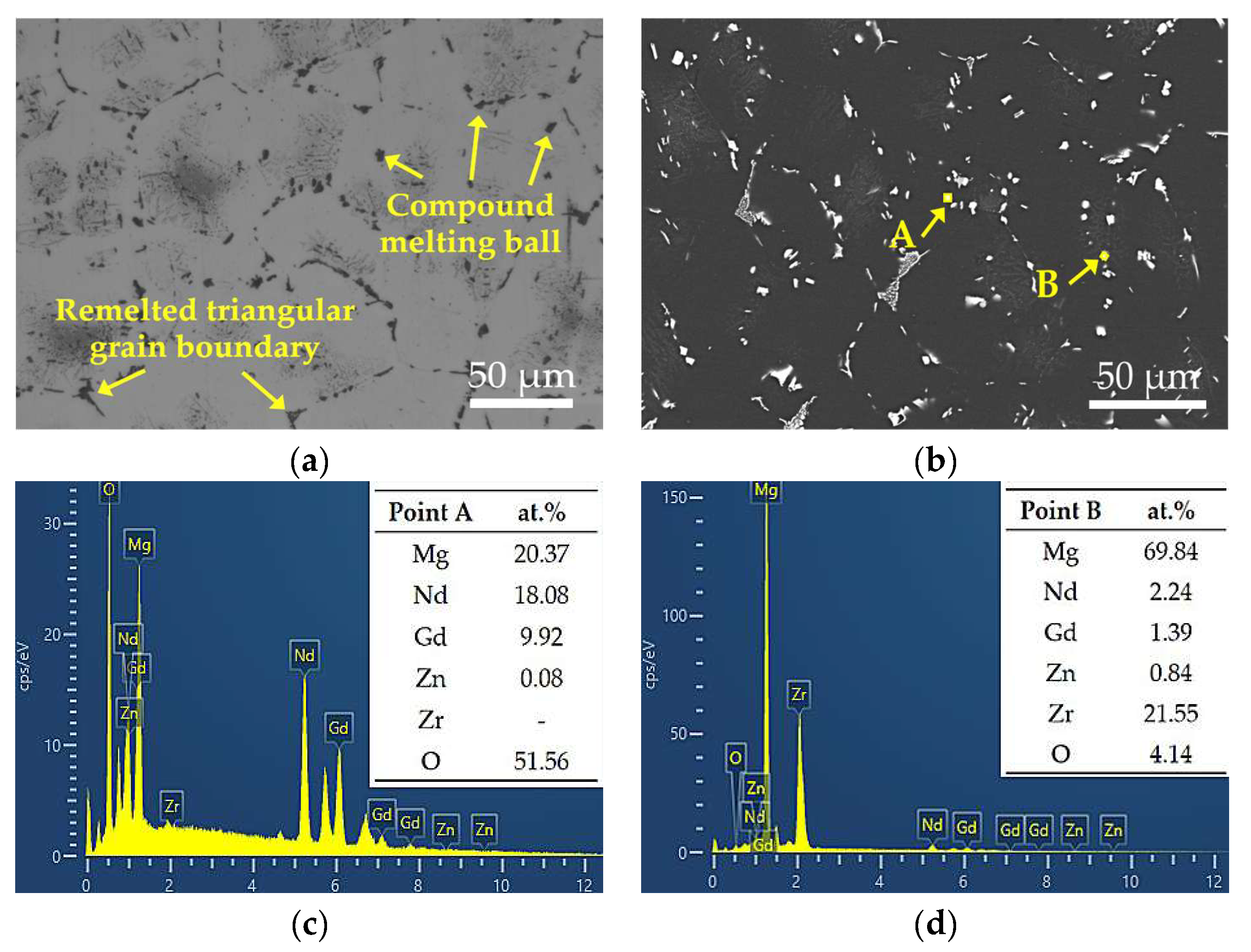
At 530 °C, secondary phases appear nearly fully dissolved upon initial observation, but microstructural stability is significantly compromised. The grain size increases rapidly from 76.43 μm to 115.89 μm, while the hardness drops from 58.68 HBW to approximately 50 HBW. Clear over-burning features are observed, including resolidified spherical phases at grain boundaries and the disappearance of triangular grain boundaries, as shown in Figure 6a. SEM-EDS analysis (Figure 6c,d) further confirms the formation of oxygen-enriched zones at grain boundaries under this temperature condition. Point A exhibits an oxygen content as high as 51.56 at.%, accompanied by high concentrations of Nd and Gd, indicating localized melting of low-melting-point secondary phases at grain boundaries and subsequent oxidation during cooling. This molten phase migrates and forms spherical oxidized regions during grain growth and coalescence, representing a typical microstructural characteristic of over-burning in magnesium alloys [30]. Such localized melting disrupts grain boundary continuity and significantly degrades both microstructural and mechanical stability.
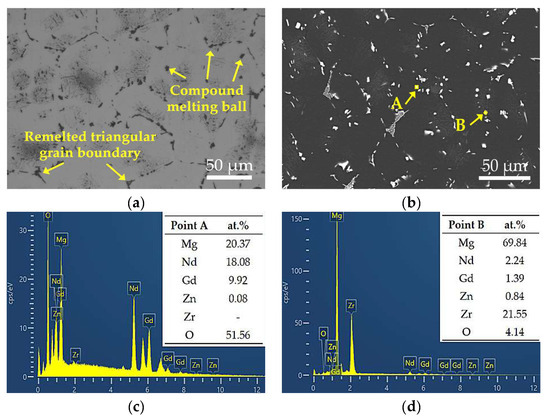
Figure 6.
Magnified views of the yellow rectangular areas (a,b) in Figure 4i and i with corresponding EDS results (c,d).
Therefore, based on a comprehensive evaluation of the secondary phase dissolution degree, grain growth tendency, hardness evolution, and susceptibility to over-burning, 520 °C for 10 h was identified as the optimal solution treatment regime. This parameter set effectively dissolves the non-equilibrium phases. It also avoids localized melting at grain boundaries and suppresses excessive grain growth. Consequently, it provides the most stable and homogeneous microstructural foundation for the subsequent T6 aging treatment.
3.3. Precipitation Behavior and Microstructural Evolution During Aging Treatment
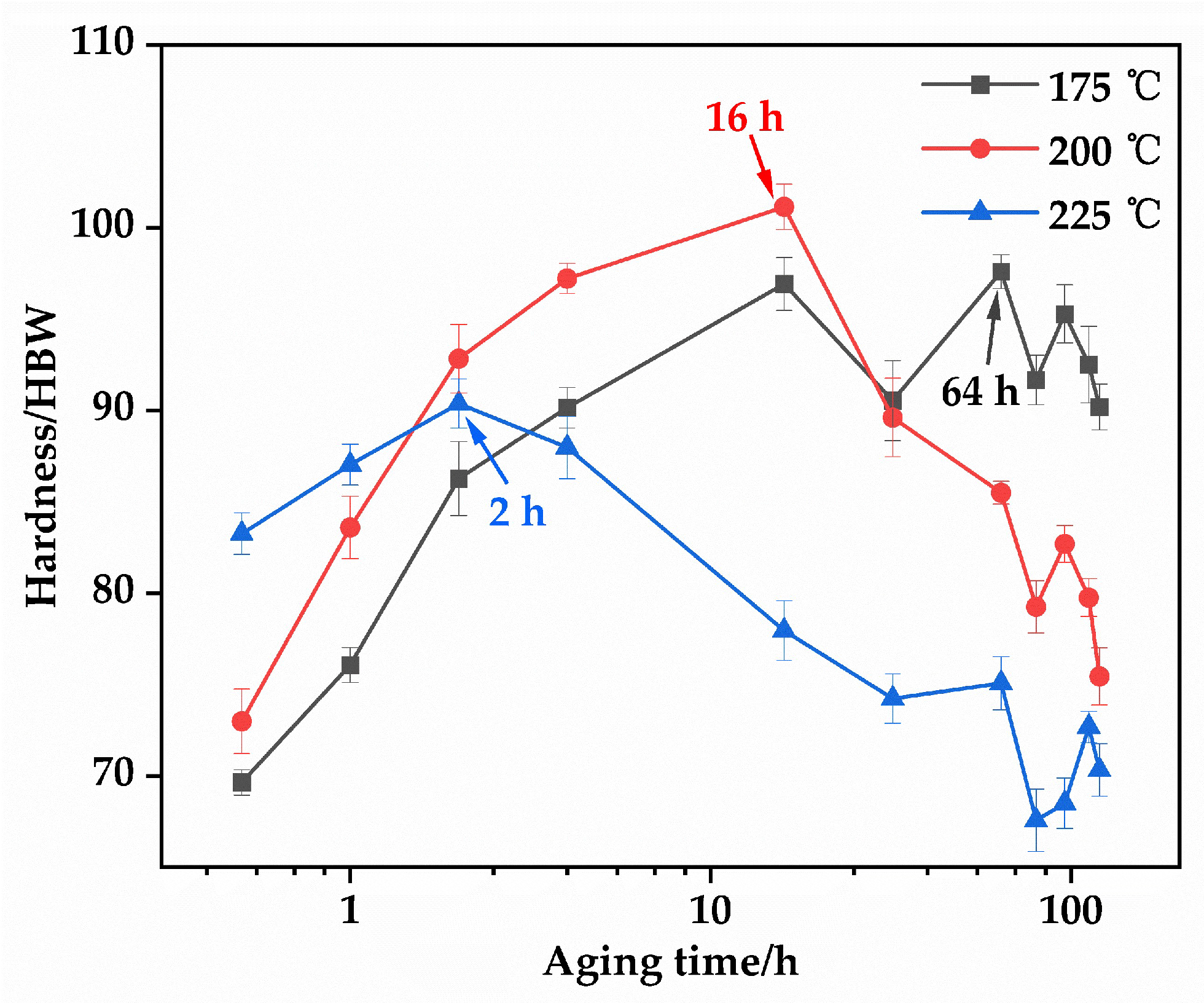
Figure 7 illustrates the age-hardening behavior of the EV31A magnesium alloy at 175 °C, 200 °C, and 225 °C. After the optimal solution treatment (520 °C × 10 h), the initial hardness of the alloy was 62.76 HBW. All three temperatures exhibit typical age-hardening characteristics: a rapid increase in hardness during the early stage, followed by a peak hardness plateau (PHP), and ultimately a decline in the over-aged stage [31]. At 225 °C, the alloy exhibits the fastest aging kinetics. The hardness increases to 83.26 HBW within 0.5 h and peaks at 90.38 HBW after 2 h. However, the peak hardness plateau (PHP) at this temperature is very narrow. After 14 h of aging (16 h total), the hardness drops rapidly to 77.96 HBW. This indicates that while elevated temperature accelerates the β″ → β′ → β transformation, it also readily induces over-aging. At 200 °C, the hardness increases steadily with aging time, reaching a peak value of 101.14 HBW after 16 h. This temperature condition shows a relatively wide peak hardness plateau (approximately 8–20 h). This indicates moderate precipitation kinetics and an optimal combination of the quantity and morphology of strengthening phases, resulting in stable strengthening within a practical aging duration. Further extension of aging time leads to a decrease in hardness, consistent with typical over-aging behavior. At the lower temperature of 175 °C, the precipitation kinetics are significantly slower. The hardening process is considerably prolonged, with peak hardness of 97.60 HBW achieved only after 64 h, but the low aging efficiency makes it impractical for industrial applications.
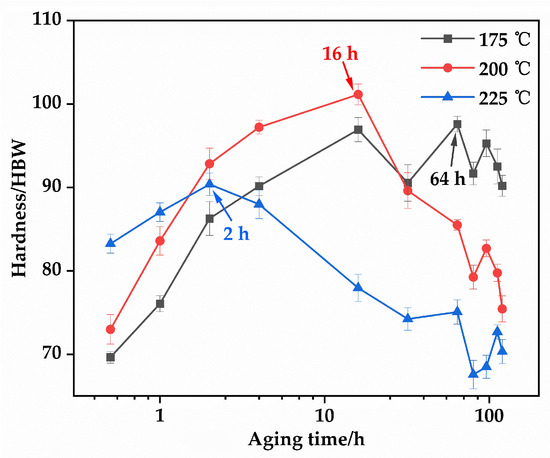
Figure 7.
Brinell hardness of the EV31A alloy as a function of aging time after aging at 175, 200, and 225 °C.
The aging condition of 200 °C for 16 h was selected based on three key criteria: peak hardness, width of the peak hardness plateau, and practical application efficiency. This treatment provides the highest strengthening effect and the most stable precipitate structure. Consequently, the optimal T6 treatment for the EV31A alloy is determined as follows: solution treatment at 520 °C for 10 h (water quenching) followed by aging at 200 °C for 16 h (air cooling). This regime ensures sufficient dissolution of secondary phases during the solution stage while promoting the formation of strengthening precipitates with optimal quantity and morphology during the aging stage, thereby achieving the highest hardness and the best overall mechanical properties.
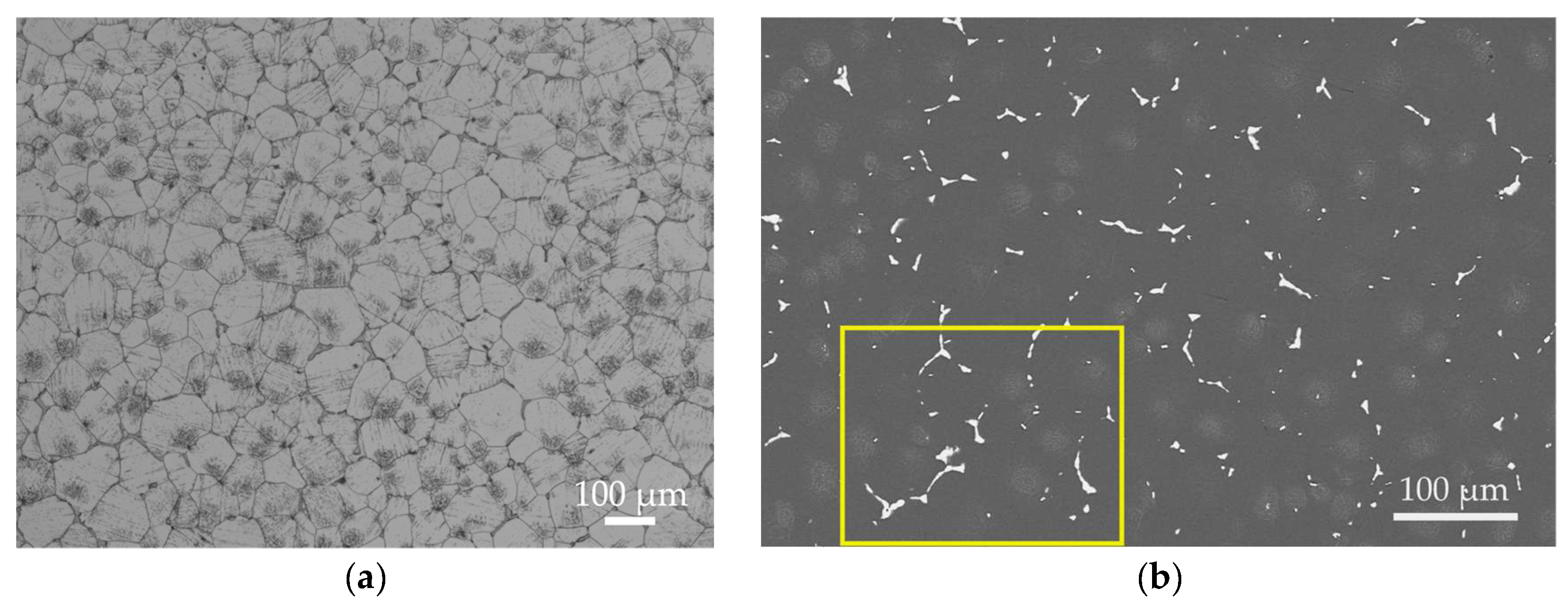
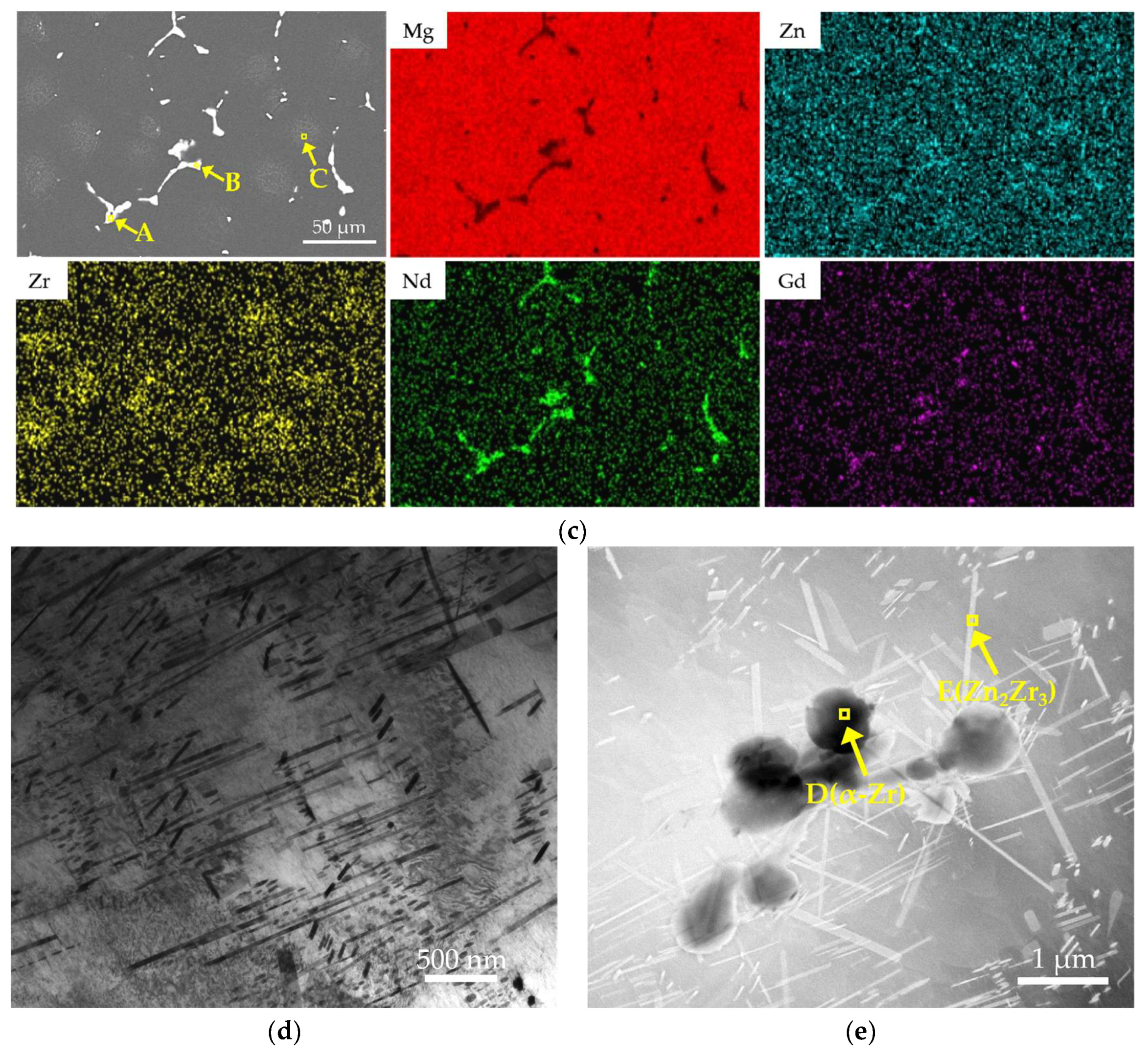
Figure 8 displays the microstructure of the alloy after the optimal T6 treatment. As shown in Figure 8a, the T6-treated microstructure still consists primarily of an α-Mg matrix and secondary phases discontinuously distributed along triple junctions. Figure 8c and Table 4 show that these grain boundary phases are enriched with rare earth elements. Their Mg-to-RE atomic ratio of approximately 8:1 aligns with the expected transformation of Mg12RE into Mg41RE5 during T6 treatment. Compared to the as-cast condition, the eutectic area at grain boundaries is significantly reduced after T6 treatment, indicating that the solution treatment dissolved most of the Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phase. However, a small amount of coarse phases persists due to their higher thermal stability, effectively pinning the grain boundaries and inhibiting grain growth. The XRD results (Figure 2c) further reveal that most diffraction peaks of Mg12(Nd,Gd) in the T6 condition have transformed into characteristic peaks of Mg41(Nd,Gd)5, confirming the phase transformation of the residual eutectic phases, although a small amount of Mg12(Nd,Gd) remains detectable. The background-corrected normalized peak-height ratio of Mg41(Nd,Gd)5 at ~29° increases to 0.013231 after T6 aging, while the Zn2Zr3-related peak near ~35.5° is below the detection limit in the as-cast condition and becomes evident after T6 aging (0.014058); noting that this region may be influenced by adjacent α-Mg peaks/background, the intensity comparison is discussed as a semi-quantitative trend. Figure 8d reveals a large number of fine, uniformly dispersed precipitates within the grains. With reference to the study by Gu et al. [32], these precipitates can be identified as predominantly β′ phase, which serves as the key strengthening phase responsible for the enhanced strength in the T6 condition.
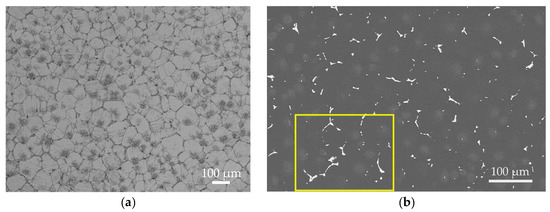
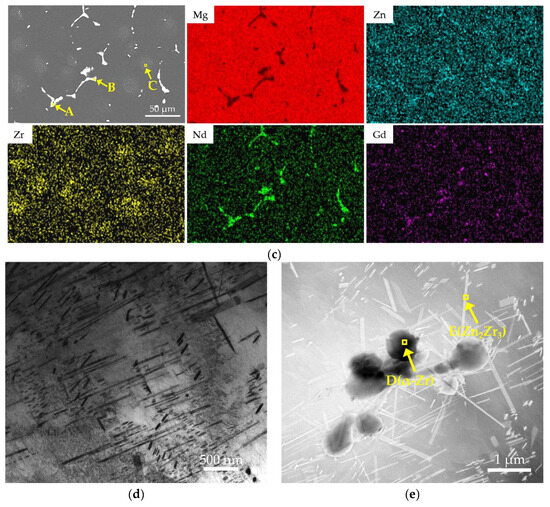
Figure 8.
Microstructure of the T6-treated EV31A magnesium alloy: (a) OM; (b) SEM; (c) EDS elemental mapping and the corresponding point analysis results at locations A, B, and C; (d) high-magnification TEM; (e) low-magnification TEM.

Table 4.
EDS point analysis results (at.%) at locations A–E in Figure 8c,e for the T6-treated EV31A alloy.
Furthermore, Figure 8a reveals agglomerated low-contrast regions (dark patches) of varying sizes within the grains. Combined with Figure 8c and Table 4, these regions consist of bright white particles rich in Zr and Zn, with an atomic ratio of approximately 1.7:1, closely matching the stoichiometry of Zn2Zr3. Since Zn2Zr3 was not detected in the as-cast microstructure, it can be inferred that this phase formed during the solution treatment through reactions between undissolved Zr particles and dissolved Zn. The formation of this phase is thermodynamically favored by the high affinity of Zr for Zn and its relatively low formation enthalpy.
This finding is highly consistent with the study by Liu et al. [26] on similar alloys. Using TEM and SAED analysis, they unequivocally confirmed that such bright white rod-shaped precipitates within grains and along grain boundaries are the Zn2Zr3 phase. Combined with the aforementioned evidence and the TEM results presented in Figure 8e and Table 4, this study confirms the presence of the Zn2Zr3 phase, which is also substantiated by XRD (Figure 2c). These stable Zn2Zr3 particles formed during the solution treatment process can serve as heterogeneous nucleation sites for the β′ phase, promoting the refinement and uniform distribution of precipitates. In summary, the T6 treatment achieves significant improvement in the strength of the EV31A alloy through the synergistic effect of three mechanisms: (1) the transformation and pinning effect of grain boundary Mg12RE to Mg41RE5, (2) dispersion strengthening by intragranular nano-sized β′ precipitates, and (3) the refinement of β′ precipitates via Zn2Zr3-assisted heterogeneous nucleation. This multi-scale strengthening approach enables the simultaneous enhancement of strength with acceptable ductility, resulting in optimized overall mechanical properties.
3.4. Analysis of Mechanical Properties and Fracture Behavior
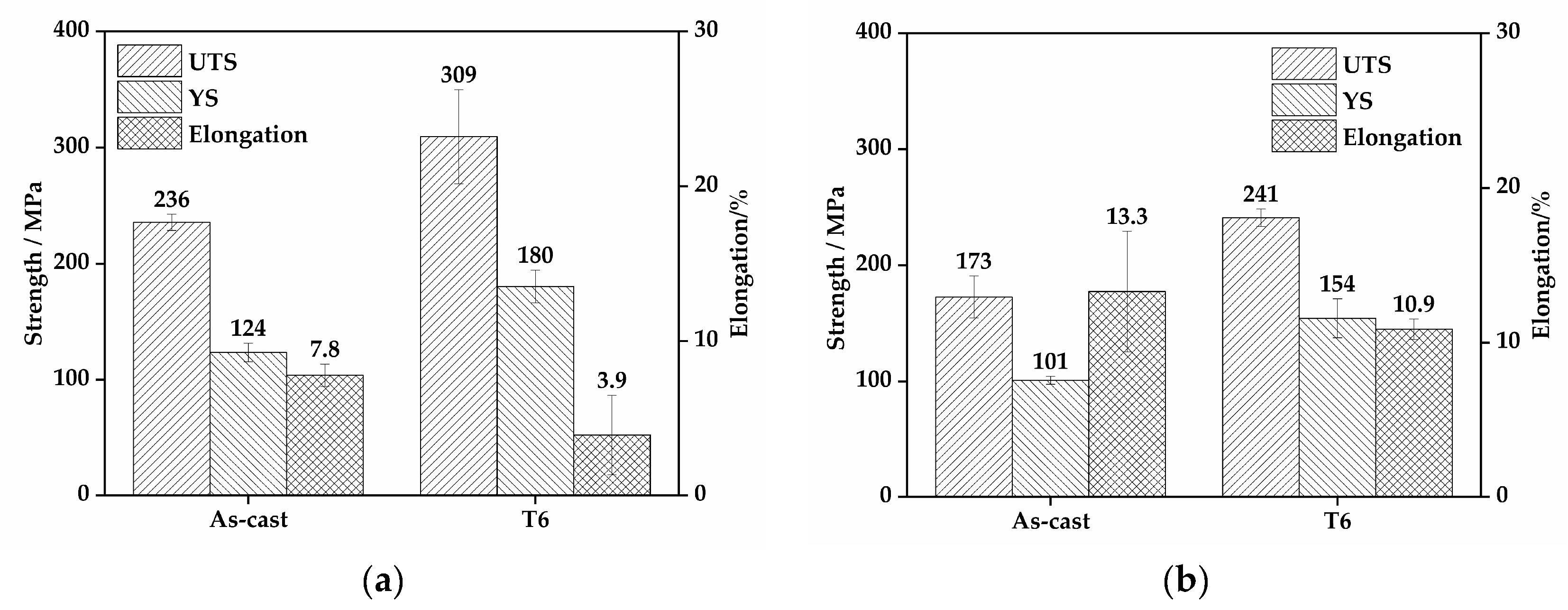
Figure 9 shows the mechanical properties of EV31A magnesium alloy at room and elevated temperatures. These properties are presented for both as-cast and T6 conditions, with corresponding data in Table 5. At room temperature, the as-cast alloy exhibits ultimate tensile strength (UTS), yield strength (YS), and elongation (EL) of 236 ± 7.0 MPa, 124 ± 8.0 MPa, and 7.8 ± 0.7%, respectively. After T6 treatment (520 °C × 10 h + 200 °C × 16 h), these properties are significantly enhanced to 309 ± 40.5 MPa and 180 ± 14.2 MPa, though the elongation decreases to 3.9 ± 2.6%. At the elevated temperature of 150 °C, the as-cast alloy shows UTS and YS of 173 ± 18.0 MPa and 101 ± 3.5 MPa, respectively, with the elongation increasing to 13.3 ± 3.9%. In contrast, the T6-treated alloy demonstrates strengths of 241 ± 7.5 MPa and 154 ± 16.8 MPa, while maintaining an elongation of 10.9 ± 0.7%. These findings demonstrate that T6 treatment significantly enhances alloy strength at both room temperature and 150 °C. Although ductility shows some reduction, the T6-conditioned alloy maintains satisfactory plasticity at elevated temperatures, achieving an excellent strength-ductility synergy.
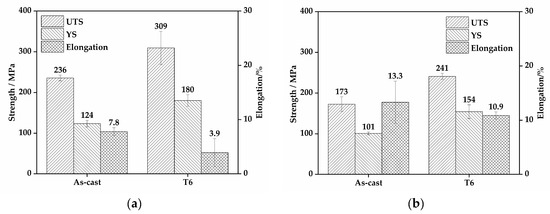
Figure 9.
Mechanical properties of the EV31A alloy: (a) room-temperature properties; (b) elevated-temperature (150 °C) properties.

Table 5.
Mechanical Properties of the Experimental Alloy at Different Test Temperatures.
The enhancement of mechanical properties is closely related to the microstructural evolution. In the as-cast condition, the coarse and continuous Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases readily induce stress concentration under external load and facilitate rapid crack propagation along grain boundaries, resulting in insufficient strength and brittle fracture. Solution treatment promotes the dissolution of most of these eutectic phases into the α-Mg matrix, accompanied by the complete dissolution of the intragranular lath-shaped Mg12Nd precipitates. This process yields a highly supersaturated solid solution and significantly homogenizes the microstructure through the elimination of continuous brittle phases at grain boundaries, thereby providing sufficient solute for the subsequent precipitation of fine strengthening phases. During subsequent aging at 200 °C, a high density of fine, homogeneously dispersed β′ nano-precipitates forms. These precipitates are the primary contributor to the remarkable strength improvement in the T6 condition. Concurrently, the presence of Mg41RE5 phases and the stable Zn2Zr3 particles formed during solution treatment further enhance dislocation pinning effects [33].
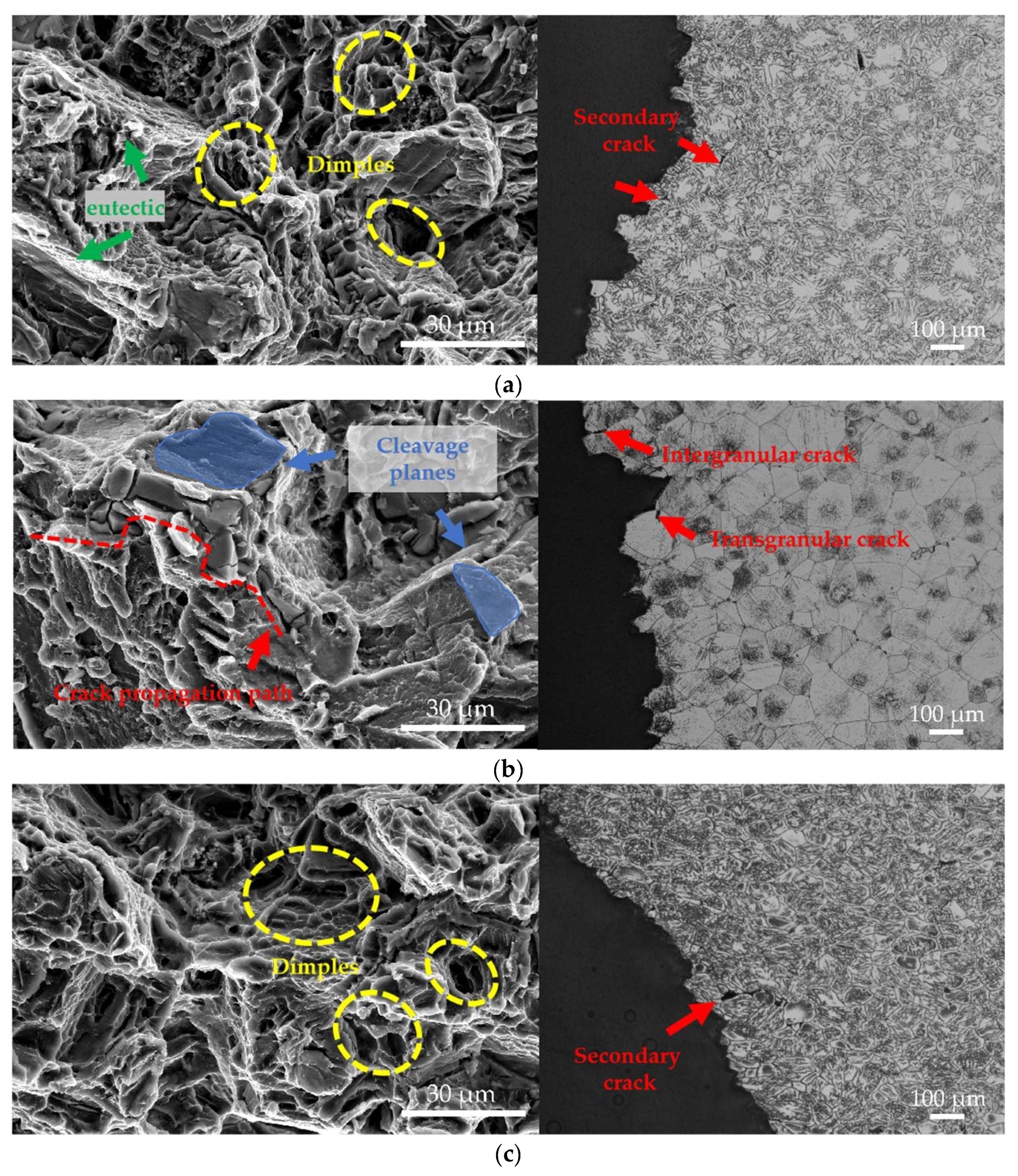
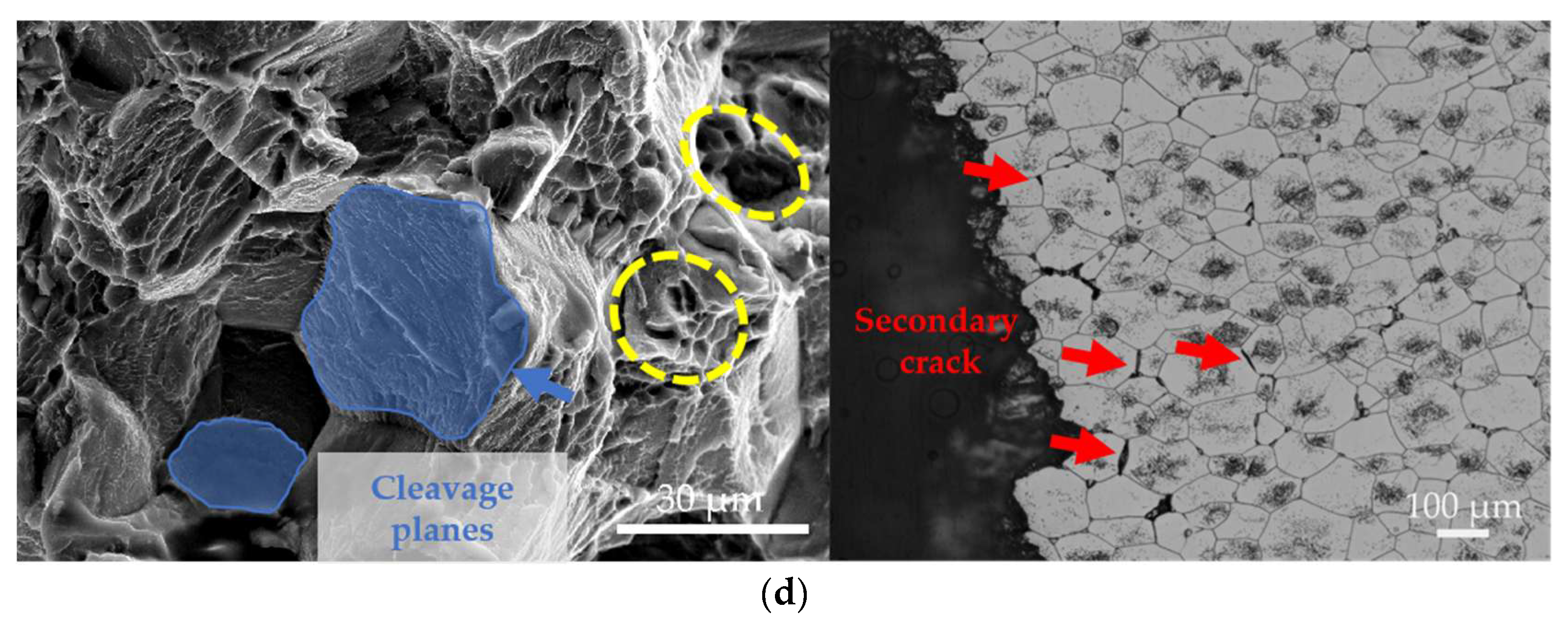
Figure 10 displays the tensile fracture morphologies and corresponding longitudinal section microstructures of the EV31A alloy under different conditions and temperatures. At room temperature, the fracture surface of the as-cast alloy exhibits mixed ductile-brittle characteristics. Cracks primarily initiate at the continuous Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases along grain boundaries and propagate rapidly through intergranular paths. Secondary microcracks distributed within the eutectic structure are also observed in the metallographic microstructure near the fracture surface. The high hardness and brittleness of the eutectic phases readily induce dislocation accumulation and stress concentration, serving as the dominant source of brittle fracture in the room-temperature as-cast condition. The presence of some dimples on the fracture surface indicates limited microvoid coalescence during the fracture process.
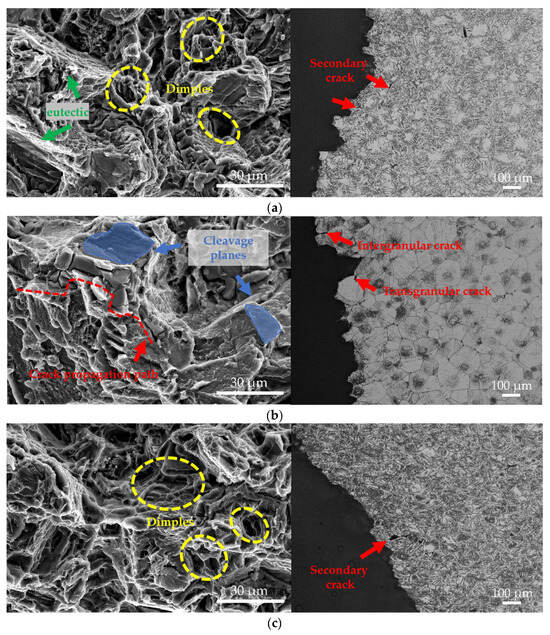
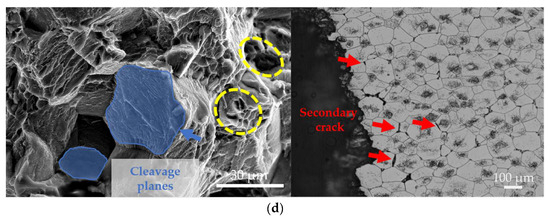
Figure 10.
SEM fractographs and OM microstructures of longitudinal sections near fractures of the experimental alloy: (a) as-cast alloy tested at room temperature; (b) T6-treated alloy tested at room temperature; (c) as-cast alloy tested at elevated temperature; (d) T6-treated alloy tested at elevated temperature.
The fracture surface of the T6-treated alloy at room temperature exhibits typical quasi-cleavage characteristics, consisting of large smooth cleavage facets, river patterns, and intergranular facets with scarce dimples. This fracture behavior primarily results from the significant obstruction of dislocation motion by β′ nano-precipitates, which causes local microcrack deflection and rapid propagation, leading to markedly reduced plasticity. Combined with metallographic observations showing coexistent intergranular and transgranular cracks, this further confirms the brittle fracture mode induced by precipitation strengthening.
When the test temperature increased to 150 °C, the tensile fracture surface of the as-cast alloy transitioned to characteristic ductile fracture features. It exhibited numerous deep, uniformly distributed dimples, some of which appeared elongated. The corresponding microstructure revealed significantly elongated grains, with the macroscopic fracture orientation inclined at approximately 45° to the tensile axis, consistent with ductile shear fracture characteristics. The thermal softening effect at elevated temperature promotes dislocation glide and coordinated grain deformation, resulting in the as-cast elongation reaching 13.3 ± 3.9%.
At 150 °C, the fracture surface of the T6-treated alloy is mainly characterized by dimples with localized quasi-cleavage facets. This indicates a persistent ductile-brittle mixed fracture mechanism. However, plasticity is significantly improved compared to room temperature due to thermal activation. The presence of coarse dimples and tear ridges on the fracture surface suggests a partial recovery of dislocation glide capability. Meanwhile, precipitates such as the β′ phase, Mg41RE5, and Zn2Zr3 remain stable at 150 °C without noticeable coarsening or dissolution. They continue to effectively restrain plastic deformation, resulting in the retention of some flat cleavage facets. Numerous intergranular secondary cracks are observed in the microstructure near the fracture surface. These cracks absorb additional energy during the propagation of the primary crack, thereby delaying fracture. Combined with the maintained stability of precipitates, this mechanism enables the T6-conditioned alloy to retain a considerable elongation of 10.9 ± 0.7% even at elevated temperature.
The fracture behavior of the EV31A magnesium alloy is significantly influenced by heat treatment and testing temperature. In the as-cast condition, the room-temperature fracture surface exhibits a mixed morphology of dimples and intergranular features, while at elevated temperatures, thermal softening transforms the fracture into a predominantly ductile mode characterized by deep dimples. For the T6-conditioned alloy, the strong pinning effect of nano-scale precipitates, such as the β′ phase, leads to a quasi-cleavage-dominated fracture at room temperature, resulting in reduced plasticity. However, at high temperature, thermal activation partially restores dislocation mobility, shifting the fracture mechanism to dimple dominance, while the precipitates remain effective in maintaining strength. Consequently, the T6-treated alloy achieves an excellent synergy of strength and ductility at 150 °C. In summary, the T6 treatment significantly enhances the strength of the EV31A alloy through multiple mechanisms. These include grain boundary purification and precipitation strengthening. The treatment also endows the alloy with superior comprehensive performance at elevated temperatures. This provides a critical material foundation for its application in lightweight engineering fields.
Although long-term thermal aging and creep tests at 150–200 °C were not performed in this study, the microstructural features observed after T6 treatment allow a qualitative assessment of the expected elevated-temperature stability. The thermally stable RE-rich grain-boundary phases are expected to assist grain-boundary pinning, while the precipitation-strengthened matrix and stable particles (e.g., Zn2Zr3) are expected to improve resistance to microstructural degradation and creep deformation at around 150 °C. At temperatures approaching 200 °C under prolonged exposure, precipitate coarsening/over-aging may gradually reduce the precipitation-strengthening contribution and thus strength. Future work will conduct systematic thermal-exposure and creep tests and explore over-aged (T7-type) treatments to quantitatively evaluate thermal stability and creep performance.
4. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the as-cast microstructural characteristics of EV31A magnesium alloy and the effects of solution and aging heat treatments on its microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. The main conclusions are as follows:
- 1.
- The as-cast EV31A alloy primarily consists of α-Mg equiaxed grains, bone-shaped Mg12(Nd,Gd) eutectic phases along grain boundaries, and a limited number of intragranular lath-shaped Mg12Nd phases. After the optimized T6 heat treatment (520 °C × 10 h solution treatment + 200 °C × 16 h aging), the grain boundary eutectic phases partially dissolve and transform into Mg41(Nd,Gd)5, while intragranular nano-scale β′ strengthening precipitates form with a dispersed distribution, accompanied by the formation of stable Zn2Zr3 particles;
- 2.
- The optimized T6 treatment significantly enhances the strength of the alloy. Compared to the as-cast condition, the T6-treated alloy exhibits 31% and 45% increases in ultimate tensile strength (to 309 ± 40.5 MPa) and yield strength (to 180 ± 14.2 MPa) at room temperature, respectively. At the elevated temperature of 150 °C, the ultimate tensile strength and yield strength are improved by 39% (to 241 ± 7.5 MPa) and 52% (to 154 ± 16.8 MPa), respectively, while maintaining an elongation of 10.9 ± 0.7%, achieving an excellent strength-ductility synergy;
- 3.
- The fracture mode of the EV31A alloy exhibits significant variations with heat treatment conditions and testing temperature. At room temperature, the as-cast alloy undergoes mixed ductile-brittle fracture, while the T6-treated alloy displays quasi-cleavage brittle fracture due to the strong pinning effect of β′ precipitates. At 150 °C, the as-cast alloy transitions to fully ductile fracture, whereas the T6-conditioned alloy demonstrates mixed ductile-brittle fracture dominated by dimples with localized quasi-cleavage features, where thermal activation at elevated temperature enhances its plasticity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and T.M.; methodology, X.Y., L.A., T.M. and D.L.; software, C.Y. and Y.L.; validation, H.L. and D.L.; formal analysis, C.Y.; investigation, H.L.; resources, X.Y. and T.M.; data curation, J.C. and L.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, T.M. and H.L.; visualization, J.C. and Y.L.; supervision, T.M.; project administration, T.M.; funding acquisition, X.Y. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (U21A20323, U24A20560); Kunlun Talent Program of Qinghai Province, Qinghai Provincial Science and Technology Project (2025ZY025).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Daogui Lai was employed by the company AECC South Industry Company Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ovri, H.; Markmann, J.; Barthel, J.; Kruth, M.; Dieringa, H.; Lilleodden, E.T. Mechanistic origin of the enhanced strength and ductility in Mg-rare earth alloys. Acta Mater. 2023, 244, 118550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Cao, F.; Zhang, L.; Atrens, A.; Chen, X.; Pan, F. Tailoring the corrosion behavior and mechanism of Mg-Gd-Zn alloys via Sc microalloying. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 5010–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Z.; Zha, M.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wang, S.-C.; Wang, C.; Jia, H.-L.; Wang, H.-Y. Alloying design and microstructural control strategies towards developing Mg alloys with enhanced ductility. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Shen, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, B.; Bai, W.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hong, L.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X. Enhanced Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of As-Extruded Mg-12Gd-2Zn-0.4Zr Alloy by Nd Additions. Metals 2025, 15, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-W.; Yang, H.-Y.; Dong, B.-X.; Liu, T.-S.; Liu, L.; Tian, Z.; Zhan, L.; Wang, C.-G.; Li, Z.-G.; Meng, J.; et al. The development of high-strength flame-retardant magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 36, 5797–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.M.R.; Ishtiaq, M.; Kang, H.-H.; Chaudry, U.M.; Jun, T.-S. A Critical Review on the Comparative Assessment of Rare-Earth and Non-Rare-Earth Alloying in Magnesium Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Influence of rare earth elements on microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of Mg-12Gd-3Y-0.5Zr magnesium alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 768, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; You, S.; Gan, W.; Karl, K.U.; Hort, N. Strengthening and ductilizing of magnesium alloying with heavy rare earth elements. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 188, 03021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ninlachart, J.; Raja, K.S. Effect of Light Illumination on the Corrosion Behavior of Mg-RE Alloy EV31A in Chloride-Alkaline Solutions. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2018, MA2018-01, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wen, S.; Huang, H.; Wei, W.; Nie, Z. Grain Refinement of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys by Sc and Zr. Metals 2023, 13, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Ding, W. The role of Gd on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-0.5Zr alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 175, 111076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekumalla, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Almajid, A.; Gupta, M. Mechanical Properties of Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloy Systems: A Review. Metals 2015, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbus, A.; Jarosz, R. Gating System Optimization for EV31A Magnesium Alloy Engine Body Sand Casting. Materials 2022, 15, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.-F. Precipitation and Hardening in Magnesium Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, V.; Ceschini, L.; Morri, A.; Apelian, D. Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Rare Earth-Rich Magnesium Alloy. Int. J. Met. 2017, 11, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M. Recent developments in high-strength Mg-RE-based alloys: Focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninlachart, J.; Raja, K.S. Threshold Chloride Concentration for Passivity Breakdown of Mg–Zn–Gd–Nd–Zr Alloy (EV31A) in Basic Solution. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2017, 30, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Guo, E. Strengthening of Mg Alloy with Multiple RE Elements with Ag and Zn Doping via Heat Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-D.; Wu, G.-H.; Liu, W.-C.; Pang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.-J. Influence of heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of gravity cast Mg–4.2Zn–1.5RE–0.7Zr magnesium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yan, Z.; Ji, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Y. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Mg-9.5Gd-4Y-2.2Zn-0.5Zr alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1-2019 ISO 6892-1: 2019 MOD; Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing-Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Yang, H.; Zander, D.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y.; Gavras, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Dieringa, H. Effects of heat treatment on the microstructural evolution and creep resistance of Elektron21 alloy and its nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 789, 139669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Huang, J.-F.; Du, X.-D.; An, R.-S.; Wang, F.; Lou, Y.-C. Influence of a low-frequency alternating magnetic field on hot tearing susceptibility of EV31 magnesium alloy. China Foundry 2021, 18, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, L.; Mounib, M.; Lefebvre, W.; Vorozhtsov, S.; Pavese, M.; Badini, C.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.M.; Jimenez, C.C.; Prado, M.T.P.; Dieringa, H. Microstructure, mechanical properties and creep of magnesium alloy Elektron21 reinforced with AlN nanoparticles by ultrasound-assisted stirring. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 659, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Yang, G.Y.; Luo, S.F.; Jie, W.Q. Microstructure evolution during heat treatment and mechanical properties of Mg–2.49Nd–1.82Gd–0.19Zn–0.4Zr cast alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, C.; Xie, H.; Jiang, B.; Dong, Z.; Jin, P.; Pan, F. Recent advances of high strength Mg-RE alloys: Alloy development, forming and application. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2919–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Liu, H.; Xiong, J.-P.; Li, J.-L.; Liu, Y. Enhanced Grain Refining Effect of Mg–Zr Master Alloy on Magnesium Alloys via a Synergistic Strategy Involving Heterogeneous Nucleation and Solute-Driven Growth Restriction. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2024, 37, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Shan, D.; Guo, B.; Jin, B.C. Mechanism of high-strength and ductility of Mg-RE alloy fabricated by low-temperature extrusion and aging treatment. Mater. Des. 2021, 199, 109384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Liang, X.; Tao, H.; Che, Y.; Zhao, M.-C. An investigation of the impacts of non-isothermal aging on the microstructures and corrosion of WE43 Mg alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 7605–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yan, K.; Zeng, G. Effects of Mg2Sn precipitation on the age-hardening and deformation behaviour of a Mg-Sn-Al-Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 867, 144714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Zeng, X.-Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.-X. Effect of double aging on mechanical properties and microstructure of EV31A alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 2606–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, C.; Xie, H.; Hu, H.; Dong, Z.; Tan, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, B. Effect of fine-tuning Zn/RE ratio on the precipitates and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1038, 182898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.