Abstract
The microstructure and soft magnetic properties under direct current (DC) mode and alternating current (AC) mode of FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) high-entropy alloys (HEAs) are investigated. All the studied HEAs show body-centered cubic (BCC) structures, and the [100] texture is formed in the x = 0.4 HEA. The iron (Fe) segregation at the grain boundaries is helpful in increasing the soft magnetic properties under DC. The FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA exhibits optimal DC and AC soft magnetic properties, primarily due to the formation of the texture along the easy magnetization axis. The x = 0.4 HEA shows the highest permeability (μi = 344 and μm = 1334) and the smallest coercivity (Hc = 51 A/m), remanence (Br = 132 mT), and hysteresis loss (Pu = 205 J/m3). In comparison to the x = 0.2 HEA and x = 0.6 HEA, the total loss (AC Ps) at 50 Hz of the x = 0.4 HEA is decreased by 15% and 18%, and it is reduced at 950 Hz by 13% and 7%. Our findings can provide a useful approach for developing novel HEAs with increased soft magnetic properties by tuning ferromagnetic elemental segregation and forming the texture along the easy magnetization axis.
1. Introduction
Soft magnetic materials (SMMs) have been widely used in motors, generators, transformers, and sensors [1,2]. The ever-growing demand for the sustainable conversion of electrical power and electrical machines requires advanced SMMs with high performance [3]. One approach to meet this requirement is to improve the magnetic properties of currently used SMMs (e.g., silicon steels, soft ferrites, and nanocrystalline magnetic materials) by optimizing their microstructure and using advanced processing techniques [4,5,6]. The other strategy is to develop novel soft magnetic alloys, such as multi-principal-element alloys or high-entropy alloys (HEAs). In comparison to conventional alloys, HEAs exhibit distinct compositional and microstructural features [7,8]. HEAs consist of more than four principal elements in equal or near-equal atomic proportions and usually form face-centered cubic (FCC) or body-centered cubic (BCC) solid solutions. Moreover, four core effects (i.e., the high-entropy effect, sluggish diffusion effect, lattice distortion effect, and cocktail effect) are present in HEAs, leading to excellent mechanical properties and good corrosion resistance [9,10,11,12,13]. In recent years, ferromagnetic HEAs have attracted more attention due to a combination of their good soft magnetic and mechanical properties [14,15].
Since soft magnetic properties are sensitive to the composition and microstructure of the HEAs, elemental alloying is an effective approach to improve the soft magnetic properties. The addition of metalloid Si has been successfully used to enhance the soft magnetic properties of silicon steels [4], and it is also employed in ferromagnetic HEAs. For example, Si-containing HEAs exhibit high saturation magnetization (Ms), such as the Fe2CoNi(AlSi)0.4 HEA (Ms = 155.2 emu/g), the (Co30Fe45Ni25)0.82(Al40Si60)0.18 HEA (Ms = 148.5 emu/g), and the FeCoNi(MnSi)0.1 HEA (Ms = 142.4 emu/g) [16,17,18], which is higher than that of permalloys (Ms = 80–120 emu/g), soft magnetic ferrites (Ms = 30–60 emu/g), and some soft amorphous and nanocrystalline materials (Ms = 90–130 emu/g) [6]. Moreover, the soft magnetic properties of Si-containing HEAs can be improved by optimizing their microstructure, adjusting phase constitutions, and using various methods of preparation [19,20,21]. Some Si-containing HEAs, such as the Fe40Co40Ni10Si10 HEA and the (Fe0.3Co0.5Ni0.2)95(Al1/3Si2/3)5 HEA, show both good soft magnetic performance and mechanical properties, indicating their prospective applications as novel SMMs [22,23].
Despite the significant progress in the study of the magnetic properties of ferromagnetic HEAs, further exploration of both DC and AC soft magnetic characteristics is essential for enhancing their performance in practical applications. Most studies focus on static or direct current (DC) soft magnetic properties, primarily evaluating Ms and coercivity (Hc). However, other important DC soft magnetic parameters, such as initial permeability (μi), maximum permeability (μm), remanence (Br), and hysteresis loss (Pu), are also critical for assessing soft magnetic properties [6]. Additionally, soft magnetic materials are widely used in alternating current (AC) applications, including motors, transformers, and generators. While some studies have explored the AC soft magnetic properties of ferromagnetic HEAs, further investigation is necessary. For example, Zhou et al. found that the total power loss of the (Co30Fe45Ni25)0.8(Al40Si60)0.2 HEA was smaller than that of Fe-Si alloys at frequencies above 200 Hz [17]. Wu et al. reported that magnetic field annealing could optimize the domain structure and improve the AC soft magnetic properties of the Co28Fe28Ni19Si13B12 HEA [24]. Li et al. showed that the presence of a Mn6Ni16Si7 phase deteriorated the AC magnetic properties of FeCoNi(MnSi)x (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) HEAs by increasing the total loss [25]. However, the underlying magnetic mechanism still needs to be studied. In this work, we investigate the microstructure, as well as the DC and AC soft magnetic properties, of FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs. The Ms, Hc, Br, Pu, μi, and μm are used to characterize DC soft magnetic properties, while the total loss (Ps), eddy loss (Pe), and hysteresis loss (AC Ph) are employed to describe AC soft magnetic properties. Notably, the FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA exhibits optimal DC and AC soft magnetic properties, primarily due to the formation of texture along the easy magnetization axis.
2. Materials and Methods
The ingots with a nominal composition of FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs were prepared by vacuum arc melting (Physcience Opto-electronics Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) the pure ingredients of Fe (99.980%), Co (99.999%), Ni (99.999%), Al (99.990%), and Si (99.999%) under an argon atmosphere. The Ti-getter was used to remove residual nitrogen and oxygen in the chamber. The alloy buttons were remelted four times to achieve chemical homogeneity. Sheet samples with dimensions of 90 mm in length, 10 mm in width, and 2 mm in thickness were prepared by sucking the molten alloys into a water-cooled copper mold. The saturation magnetization of the samples at room temperature was measured using a Lake Shore 7407 vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, Lake Shore Cryotronics, OH, USA). The DC soft magnetic properties at room temperature were measured using a hysteresis curve test system (FE-2100 SD, Hunan Forever Elegance Technology Co., Ltd., Hunan, Loudi City, China). The AC soft magnetic properties in the frequency range of 50–950 Hz with a fixed maximum magnetic flux density (Bm = 200 mT) were obtained using an AC hysteresis curve test system (FE-2100 M, Hunan Forever Elegance Technology Co., Ltd., Hunan, Loudi City, China). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns from 20° to 100° at a scanning rate of 1°/min were recorded using an X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (Empyrean, PANalytical Corporation, Almelo, Holland). The backscattered electron (BSE) images, elemental mappings, line scans, and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) images were observed using a Tescan mira3 scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and a Bruker e-FlashFS EBSD detector (Bruker Scientific Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China). The EBSD samples were prepared by electro-polishing in a solution of 90% ethanol + 10% HClO4 under a DC voltage of 30 V for 50 s, and the EBSD data were analyzed using the Esprit 2.1 software.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
It is found from the XRD patterns of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs in Figure 1a that all samples have BCC structures. The relative intensities (I) of the crystalline planes in the x = 0.2 HEA and x = 0.6 HEA follow I(110) > I(211) > I(200), while it fails in the x = 0.4 HEA. That is, I(200) > I(211) is observed in the x = 0.4 HEA, indicating the presence of texture along the <100> direction (marked with an arrow). This can be further confirmed by the inverse pole figure (IPF) map in Figure 1c and the pole figure in Figure 1e. However, no texture is observed in the x = 0.2 HEA and x = 0.6 HEA, as seen in Figure 1b,d. The cubic crystal symmetry and the schematic image of the measured direction of the sample are shown in Figure 1e,f. The easy magnetization axis of the alloys with BCC structures is in the [100] direction [6]. Hence, the texture along the easy magnetization axis is formed in the x = 0.4 HEA.
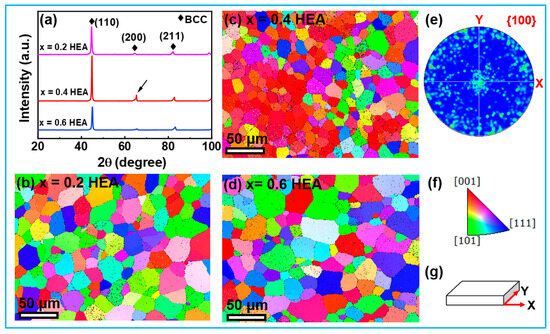
Figure 1.
(a) The XRD patterns and (b–d) Z-axis inverse pole figure (IPF) maps of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs; (e) the pole figure; (f) the cubic crystal symmetry; and (g) the schematic image of the measured direction of the sample.
Figure 2a–c show the grain boundary character distribution of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs. The low-angle boundaries (LABs) are defined as the misorientation angle between 2° and 5° (marked in yellow) and 6° and 15° (marked in blue). The high-angle boundaries (HABs) have a misorientation angle larger than 15° and are marked in pink. The HAB is dominant (>81%) in the studied HEAs. The kernel average misorientation (KAM) can be used to estimate the strain distribution [26]. Figure 2d,f show the KAM images of three HEAs. The colors from blue to red represent the increased concentration of the strain. It is found that blue is the main color in the KAM images, indicating that the concentration of the strain is not obvious in the studied HEAs.
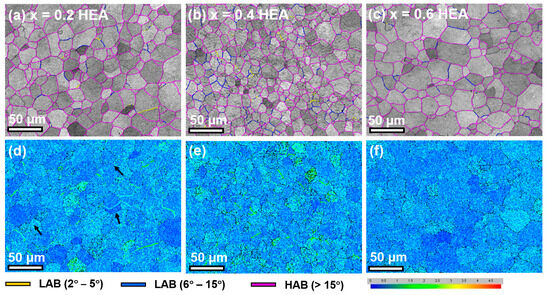
Figure 2.
The grain boundary character distribution and the kernel average misorientation (KAM) images of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs: (a,d) x = 0.2 HEA; (b,e) x = 0.4 HEA; and (c,f) x = 0.6 HEA.
Figure 3 shows the backscattered electron (BSE) images and elemental maps of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs. The red rectangle in Figure 3b represents the measured region of SEM mapping. Different contrasts at the grain boundary and grain core are observed, indicating that the compositional distribution is not uniform. The elemental maps of the x = 0.2 HEA in Figure 3a show that the grain boundary is Fe-rich and Si-rich (marked with an arrow). The enrichment of Si at the grain boundary is also observed in the x = 0.4 and x = 0.6 HEAs, as seen in Figure 3b,c. The yellow dashed line arrows in the BSE images in Figure 3 represent the measured region and direction of the line scans. The change in the elemental composition is observed in Figure 4, and the dashed line represents the location of the grain boundary (GB). The average compositions of elements at the GB and in the grain are listed in Table 1. In the x = 0.2 HEA, the average compositions of Fe and Si at the GB are 27.06 ± 0.70 at% and 4.96 ± 0.29 at%, which is higher than those of Fe (23.54 ± 0.72 at%) and Si (3.42 ± 0.27 at%) in the grain. In the x = 0.4 HEA, the average composition of Fe at the GB is 25.93 ± 0.58 at%, which is larger than that of Fe (23.82 ± 0.63 at%) in the grain. The addition of more Si (x = 0.6) decreases the segregation of Fe, leading to the close composition of Fe at the GB (26.54 ± 0.63 at%) and in the grain (25.63 ± 0.65 at%).
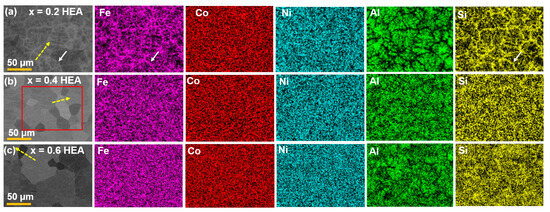
Figure 3.
The backscattered electron (BSE) images and elemental maps of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs: (a) x = 0.2 HEA; (b) x = 0.4 HEA; and (c) x = 0.6 HEA. The red rectangle in (b) is the measured region of SEM mapping. The yellow dashed line arrows in the BSE images represent the measured region and direction of the line scans.
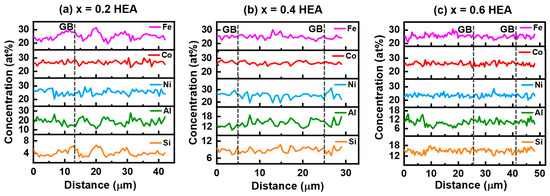
Figure 4.
The line scans of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs: (a) x = 0.2 HEA; (b) x = 0.4 HEA; and (c) x = 0.6 HEA. The dashed line represents the location of the grain boundary (GB).

Table 1.
The average elemental compositions in the line scans of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs.
3.2. Soft Magnetic Properties
The hysteresis loops at room temperature, shown in Figure 5a, demonstrate the soft magnetic behavior of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs. The addition of Si slightly reduces the Ms from 108 Am2/kg for the x = 0.2 HEA to 106 Am2/kg for the x = 0.4 HEA, and further to 101 Am2/kg for the x = 0.6 HEA. Key DC soft magnetic parameters, such as initial permeability (μi), maximum permeability (μm), coercivity (Hc), remanence (Br), and hysteresis loss (Pu), can be obtained from the measurement of the DC soft magnetic behavior. Figure 5b shows the variation in μi, μm, Br, Hc, and Pu with different levels of Si content (x). Both μi and μm increase, reaching a peak at x = 0.4, but drop sharply at x = 0.6. In contrast, the Br, Hc, and Pu show an opposite changing trend, reaching their lowest values at x = 0.4. The FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA exhibits optimal DC soft magnetic properties, with the highest permeability (μi = 344 and μm = 1334) and the smallest Hc (51A/m), Br (132 mT), and Pu (205 J/m3), as summarized in Table 2.
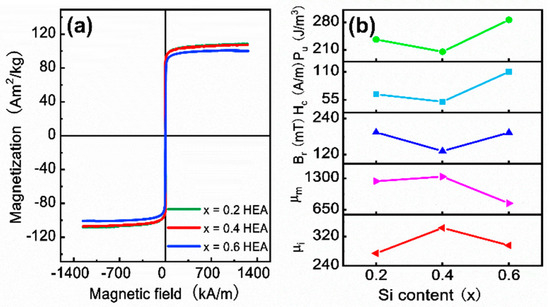
Figure 5.
(a) The hysteresis loops and (b) the soft magnetic properties as a function of the Si content (x) in the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs.

Table 2.
The DC and AC magnetic properties of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs.
The AC soft magnetic parameters include the coercivity (AC Hc), the total loss (AC Ps), the hysteresis loss (AC Ph), and the eddy loss (AC Pe). The detailed calculation of AC Ph and AC Pe can be referred to in our previous work [25]. With smaller values of the AC Hc, AC Ps, AC Ph, and AC Pe, we can achieve better AC soft magnetic properties. Figure 6a–d show the AC Hc, AC Ps, AC Ph, and AC Pe as functions of frequency, which ranges from 50 Hz to 950 Hz, with a constant Bm of 200 mT. All parameters decrease with the increase in the frequency. The x = 0.4 HEA exhibits the lowest AC Hc, AC Ps, AC Ph, and AC Pe, indicating that it has the optimal AC soft magnetic properties in the frequency range of 50–950 Hz.
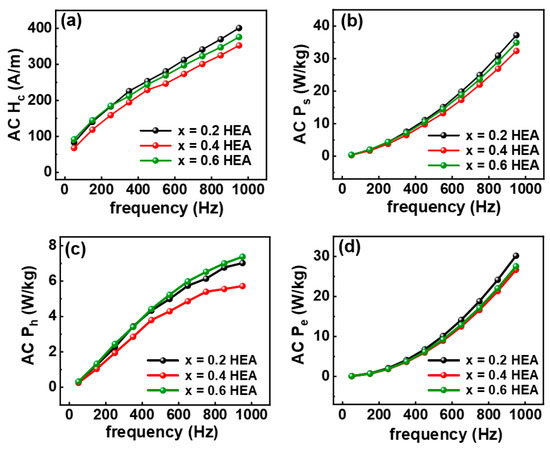
Figure 6.
The AC soft magnetic properties of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs in the frequency range of 50–950 Hz with a fixed magnetic flux density (Bm = 200 mT): (a) the coercivity (AC Hc); (b) the total loss (AC Ps); (c) the hysteresis loss (AC Ph); and (d) the eddy current loss (AC Pe).
Figure 7a,b show the AC Ps separated by the Ph and Pe at 50 Hz and 950 Hz. It is seen that the Ph is dominant in the Ps (>78%) at 50 Hz, while the Pe amounts to more than 80% of the Ps at 950 Hz. This indicates that the Ph is a main consideration to be avoided at a low frequency (50 Hz), whereas the Pe should be eliminated as much as possible at a relatively high frequency (950 Hz). Moreover, it is also found from Figure 7 that the FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA exhibits the smallest Ps (0.33 W/kg), Ph (0.24 W/kg), and Pe (0.08 W/kg) at 50 Hz and Ps (32.37 W/kg), Ph (5.72 W/kg), and Pe (26.25 W/kg) at 950 Hz among the studied HEAs. In comparison to the x = 0.2 HEA and x = 0.6 HEA, the Ps at 50 Hz of the x = 0.4 HEA is decreased by 15% and 18%, and it is reduced at 950 Hz by 13% and 7%.
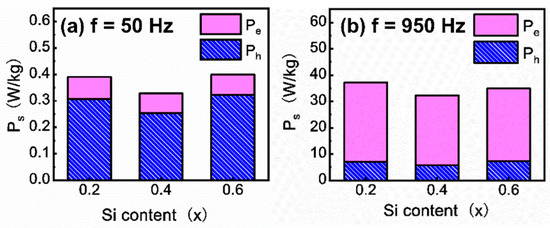
Figure 7.
The AC total loss (Ps) separated by the hysteresis loss (Ph) and the eddy current loss (Pe): (a) 50 Hz and (b) 950 Hz.
4. Discussion
It is reported that the strain concentration at the low-angle boundaries (LABs) with a misorientation angle between 2° and 5° leads to the deterioration of the soft magnetic properties [27]. In this work, a very small fraction of LAB (<3%) is observed in the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs, and no obvious strain concentration is present in the KAM images. This indicates that the LAB has a minor effect on the soft magnetic properties. The coercivity of polycrystalline magnetic materials is closely related to the grain size (D). The relationship of Hc ∝ 1/D occurs for a macroscopic grain size, indicating that low coercivity can be obtained from large grains [28]. In this work, the respective average grain sizes of the FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs are 26 μm, 18 μm, and 27 μm. The values of coercivity of the current HEAs are 66 A/m, 51 A/m, and 110 A/m. However, the change in the coercivity owing to the different grain sizes does not follow the 1/D law. Hence, other influencing factors on coercivity should be considered.
Elemental segregation is observed in the studied HEAs, which can affect their soft magnetic properties. Some reported work showed that the segregation of non-magnetic elements (such as Cu) at the grain boundaries of the HEAs could decrease their DC and AC soft magnetic properties [24,29,30]. However, the enrichment of Fe can improve the soft magnetic properties of the HEAs by enhancing the exchange coupling effect [31]. In the current work, the obvious Fe segregation at the grain boundary is observed in the FeCoNiAl0.8Si0.2 (x = 0.2) HEA, while the segregation decreases with the increase in Si content. The segregation of Fe in the x = 0.2 HEA leads to good DC soft magnetic properties. In comparison to the x = 0.6 HEA with slight Fe segregation, the μm of the x = 0.2 HEA is increased by 58%, and the Hc and Pu are decreased by 40% and 17%.
Elemental segregation is related to the density differences between the liquid and solid phases and the shrinkage that occurs during solidification [32]. The Si segregation at the grain boundary is observed in the current FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs. In the x = 2 HEA, the segregation of Si may result from the rejection of Si at the boundary in order to reduce the interfacial energy during solidification. The addition of more Si (x = 0.4) reduces the driving force for grain growth due to the adsorption of solute at the boundaries and further decreases the mobility of the boundaries, leading to the reduction in the grain size [33]. In the x = 0.6 HEA, the elemental segregation is decreased due to the back diffusion phenomenon, which can decrease the microsegregation [32]. This leads to the increase in the driving force for grain growth, resulting in grain coarsening. Hence, the x = 0.4 HEA shows the smallest average grain size of 18 μm, which is smaller than the 26 μm of the x = 0.2 HEA and the 27 μm of the x = 0.6 HEA.
The formation of texture is sensitive to the interfacial energy and thermal gradient during solidification [4,33]. The EBSD results in Figure 2 show that the x = 0.2 HEA has the smallest fraction of high-angle boundaries with 81.1% compared with 93.1% for the x = 0.2 HEA and 91.5% for the x = 0.6 HEA. This indicates that the x = 0.4 HEA has less interfacial energy during solidification, which increases the propensity of grain growth along the preferred thermal gradient. This may cause the formation of grains in the direction of easy growth (e.g., <100> direction for cubic materials) [33]. Hence, the texture is observed only in the x = 0.4 HEA. Moreover, the <100> direction is the easy magnetization axis for BCC crystals. That is, the texture along the easy magnetization axis is formed in the x = 0.4 HEA.
Some studies on silicon steels showed that the texture along the easy magnetization axis could effectively increase their permeability and reduce energy loss [34,35,36,37]. Hence, the FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA exhibits the optimal DC and AC soft magnetic properties due to the formation of the texture along the easy magnetization axis. Figure 8 shows the values of Ms and Hc of the currently studied HEA compared to those of other ferromagnetic HEAs [6,14,15,17]. The FeCoNiAl0.6Si0.4 (x = 0.4) HEA in this work is marked as a red pentagram. The Ms of the x = 0.4 HEA is larger than that of the Fe-Co-Ni-Al-Cu and Fe-Co-Ni-Al-Cu-Sn HEAs, and the Hc is lower than those of the ferromagnetic HEAs used for comparison.
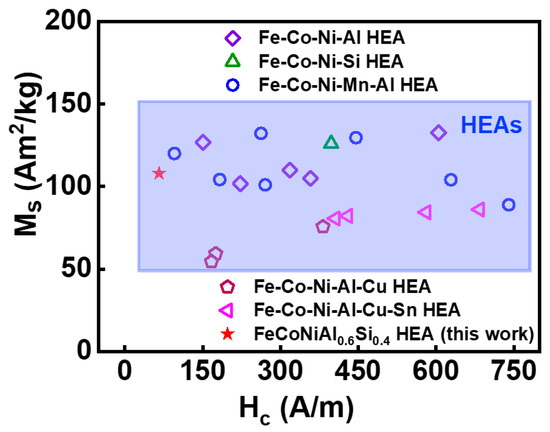
Figure 8.
The comparison of the soft magnetic properties between the currently studied HEA and ferromagnetic HEAs.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the correlations between the DC and AC soft magnetic properties and the microstructure of FeCoNiAl1−xSix (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) HEAs are investigated. The XRD and EBSD results show that all samples consist of a BCC phase, and the [100] texture is formed in the x = 0.4 HEA. It is found from the SEM-EDS analysis that elemental segregation is observed in the studied HEAs, which has a significant effect on their DC soft magnetic properties. The grain boundary is Fe-rich and Si-rich, while the grain is Al-rich. In the x = 0.2 HEA, the average composition of Fe at the grain boundary is 27.06 ± 0.70 at%, which is higher than the amount of Fe (23.54 ± 0.72 at%) in the grain. The addition of more Si can decrease the segregation of Fe at the grain boundary, leading to the deterioration of soft magnetic properties. The x = 0.4 HEA exhibits the optimum DC soft magnetic properties with the highest permeability (μi = 344 and μm = 1334) and the smallest Hc (51 A/m), Br (132 mT), and Pu (205 J/m3) among the currently studied HEAs. The x = 0.4 HEA also shows the best AC soft magnetic properties in the frequency range of 50–950 Hz. In comparison to the x = 0.2 HEA and x = 0.6 HEA, the total loss at 50 Hz of the x = 0.4 HEA is decreased by 15% and 18%, and it is reduced at 950 Hz by 13% and 7%. The x = 0.4 HEA exhibits the optimal DC and AC soft magnetic properties due to the presence of the texture along the easy magnetization axis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, funding acquisition, X.T.; data curation, visualization, formal analysis, J.L.; data curation, visualization, formal analysis, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.T. and H.X.; supervision, project administration, H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 51971125).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chang Liu and Mengxin Lv from Shanghai University for their assistance with the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ram, B.S.; Paul, A.K.; Kulkarni, S.V. Soft magnetic materials and their applications in transformers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 537, 168210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, M.; Narjes, G.; Hoffmann, J.; Wohlers, C.; Urbanek, S.; Heister, C.; Steinbrink, J.; Canders, W.R.; Ponick, B. Challenges and opportunities of very light high-performance electric drives for aviation. Energies 2018, 11, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, J.M.; Ferrara, E.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C. Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science 2018, 362, eaao0195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, Y.F.; Macziewski, C.; Cui, J. Review of Fe-6.5 wt% Si high silicon steel—A promising soft magnetic material for sub-kHz application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 481, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theisen, E. Development of new amorphous and nanocrystalline magnetic materials for use in energy-efficient devices. MRS Adv. 2017, 2, 3409–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Recent advances in tribology of high entropy alloys: A critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 136, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Yang, C.; Shu, D.; Sun, B.D. A review of irradiation-tolerant refractory high-entropy alloys. Metals 2023, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniri, S.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J.; Yuan, Y.K.; Zhou, J.H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, F.; Liao, Y.X.; Yao, Y.G.; Hu, L.B.; et al. Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium-and high-entropy nanoalloys. Nature 2023, 624, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.N.; Wang, S.S.; Jia, Y.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, R.G.; Cao, B.X.; Yu, S.Z.; Wei, J. Review on the tensile properties and strengthening mechanisms of additive manufactured CoCrFeNi-based high-entropy alloys. Metals 2024, 14, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirari, T.; Trabadelo, V. A review on wear, corrosion, and wear-corrosion synergy of high entropy alloys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.; Chaudhary, R.; Banerjee, R.; Ramanujan, R.V. Accelerated and conventional development of magnetic high entropy alloys. Mater. Today 2021, 49, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.W.; Hung, G.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jain, J.; Chang, K.P.; Chou, J.J.; Yang, W.C.; Liaw, P.K. Mechanical and magnetic properties of the high-entropy alloys for combinatorial approaches. Crystals 2020, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.X.; Wu, S.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.L.; Lu, Y.P. Novel Fe2CoNi(AlSi)x high-entropy alloys with attractive soft magnetic and mechanical properties. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2021, 127, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.X.; Sun, B.R.; Liu, G.Y.; Li, X.W.; Xin, S.W.; Liaw, P.K.; Shen, T.D. FeCoNiAlSi high entropy alloys with exceptional fundamental and application-oriented magnetism. Intermetallics 2020, 122, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Samal, S.; Kumar, V. Microstructural, magnetic, and geometrical thermodynamic investigation of FeCoNi(MnSi)x (0.0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0) high entropy alloys. Materialia 2021, 18, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.T.; Yang, X.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. Influence of Bridgman solidification on microstructures and magnetic behaviors of a non-equiatomic FeCoNiAlSi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2015, 67, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.Z.; Wei, R.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, T.; Wu, K.; Li, F.S.; Guan, S.K.; et al. Improvement of corrosion resistance and magnetic properties of FeCoNiAl0.2Si0.2 high entropy alloy via rapid-solidification. Intermetallics 2020, 122, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Liaw, P.K. High-entropy alloys with high saturation magnetization, electrical resistivity and malleability. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fan, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Wei, P.; Wang, W.; Qin, J.W.; Wei, R.; Wang, T.; et al. A novel Fe-Co-Ni-Si high entropy alloy with high yield strength, saturated magnetization and Curie temperature. Mater. Lett. 2020, 281, 128653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Zhou, K.X.; Gao, M.C.; Sun, B.R.; Shen, T.D. Compositional design of soft magnetic high entropy alloys by minimizing magnetostriction coefficient in (Fe0.3Co0.5Ni0.2)100−x(Al1/3Si2/3)x system. Metals 2019, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dai, Z.K.; Liu, R.R.; Zhou, H.T. Effects of heat treatment on the microstructures and magnetic properties of Co28Fe28Ni19Si13B12 high-entropy amorphous toroidal core. J. Alloy Compd. 2024, 981, 173713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, Y.; Pan, M.X.; Wang, C.X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Hou, X.L.; Tan, X.H.; Xu, H. Tailoring AC magnetic properties of FeCoNi(MnSi)x (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) high-entropy alloys by the addition of Mn and Si elements. J. Alloy Compd. 2019, 792, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.R.; Ström, V.; Efsing, P. Spatial correlation between local misorientations and nanoindentation hardness in nickel-base alloy 690. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Tang, Y.J.; Tan, Y.F.; Tan, X.H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H. Effect of grain boundary character distribution on soft magnetic property of face-centered cubic FeCoNiAl0.2 medium-entropy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2020, 159, 110028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Modern soft magnets: Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.J.; Sun, S.B.; Lv, M.X.; Zhu, J.X.; Tan, Y.F.; Tan, X.H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H. Effect of Ho addition on AC soft magnetic property, microstructure and magnetic domain of FeCoNi(CuAl)0.8Hox (x = 0–0.07) high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2021, 135, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.M.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiao, H.S.; Tan, X.H.; Xu, H. The AC soft magnetic properties of FeCoNixCuAl (1.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.75) high-entropy alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.; Zou, C.M.; Zhu, D.D.; Wang, X.H.; Wei, Z.J.; Wang, H.W.; Fang, N.; Chen, J.H. The evolution of microstructure, micromechanical and magnetic properties of FeCoNiAlSi alloys with peritectic structure processed by high-pressure solidification. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 920, 165958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, A.; Toda-Caraballo, I.; San-Martín, D.; Caballero, F.G. Influence of cast part size on macro-and microsegregation patterns in a high carbon high silicon steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3013–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, S.; Agrawal, P.; Agrawal, P.; Nene, S.S.; Mishra, R.S.; McWilliams, B.A.; Cho, K.C. Segregation engineering of grain boundaries of a metastable Fe-Mn-Co-Cr-Si high entropy alloy with laser-powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2021, 219, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, B.; Guo, Q.Y.; Wu, X.; Sui, H.; Xiang, L.; Luo, H.W. Characterizing changes in microstructures, mechanical and magnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel due to pulsed current. Mater. Charact. 2024, 211, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.T.; Xu, Y.B.; Zhao, L.Z.; Misra, R.D.K.; Tang, Y.C.; Liu, D.J.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, M.J.; Shen, M.X. Texture evolution in twin-roll strip cast non-oriented electrical steel with strong Cube and Goss texture. Acta Mater. 2020, 199, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Schneider, J.; Li, H.L.; Sun, Y.; Gao, F.; Lu, H.H.; Song, H.Y.; Li, L.; Geng, D.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; et al. Fabrication of high permeability non-oriented electrical steels by increasing < 0 0 1> recrystallization texture using compacted strip casting processes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 577–586. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lan, M.F.; Yuan, G.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Abnormal growth of {100} grains and strong Cube texture in strip cast Fe-Si electrical steel. Scripta Mater. 2018, 147, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).