Abstract
Porous NiTi shape memory alloys (SMAs) possess compatible mechanical properties with human bones and can effectively reduce the risk of stress shielding and stress concentration; therefore, they have been termed promising candidates for orthopedic implants. However, microstructure characteristics of porous NiTi SMAs during plastic deformation have rarely been investigated. The present study aims to specifically investigate microstructure characteristics and the corresponding underlying mechanisms of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs via a conventional sintering (CS) process with NaCl space holder during compressive deformation at room temperature. To realize the aforementioned target, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) are applied in the present study. The results show that the fabricated porous NiTi SMA is 51.8% for porosity, 181.65 μm for the average pore size, and 0.78 μm for the average grain size. Many Ni4Ti3 and NiTi2 phases are formed in the mixed matrix with dominant B2 (NiTi) and some B19′ (NiTi). Severe inhomogeneous deformation happens within compressed specimens, leading to the occurrence of tangled dislocation and shear bands. Microcracks occur within fabricated porous NiTi SMAs at a deformation degree of 9.2%; then, they extend quickly to form macrocracks, which finally results in the failure of regions between pores. The observed nanocrystallization and amorphization around microcrack tips within the 12.5%-deformed sample can be attributed to the relatively small grain size and the grain segmentation effect via statistically stored dislocation (SSD) and geometrically necessary dislocation (GND).
1. Introduction
Recently, porous NiTi shape memory alloys (SMAs) have become promising candidates for orthopedic implants because of their unique shape memory effect, outstanding superelasticity, and good biocompatibility and corrosion resistance [1,2,3,4]. Moreover, the introduction of controllable pore characteristics can effectively adjust the elastic modulus, stiffness, and strength of porous NiTi SMAs. Zhao et al. [5] reported that these fabricated porous NiTi SMAs with Menger sponges exhibit different porosity levels in the range of 25.93% to 95.64% and include three ranges of fractal pore sizes, which possess excellent superelastic recovery strain ratios even at high porosity levels. Li et al. [6] reported that the addition of NaCl space holder can increase the porosity of porous NiTi SMAs, as well as the average pore size and oxygen content. These fabricated NiTi SMAs with porosities of 14% and 22% exhibited compressive strengths >1600 MPa. These controllable pores make porous NiTi SMAs more mechanically compatible with human bones, and they can effectively reduce the risk of stress shielding and stress concentration [7,8].
By far, numerous powder metallurgy methodologies have been employed for the fabrication of porous NiTi SMAs, including conventional sintering (CS) [9,10], hot isostatic pressing (HIP) [11,12], self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) [13,14], microwave sintering [15,16], selective laser melting (SLM) [17,18], and metal injection molding (MIM) [19,20]. Unfortunately, these aforementioned studies mainly focus on tailoring the processing parameters to control the constituent phases, porosity ratios and sizes, and superelasticity behaviors of synthesized porous NiTi SMAs. Microstructure characteristics of porous NiTi SMAs beyond the threshold of superelasticity strain have rarely been investigated. Actually, a comprehensive understanding of this issue would be beneficial for broadening the further applications of porous NiTi SMAs in biomedical fields.
To achieve the above goal, a porous NiTi SMA with a composition of Ni:Ti = 50:50 (at.%) was prepared via the CS method under atmosphere protection in the present study. Afterward, uniaxial compression experiments beyond the threshold of superelasticity strain at room temperature and the corresponding characterization experiments were conducted to investigate the microstructure characteristics of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs during plastic deformation.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Porous NiTi SMA
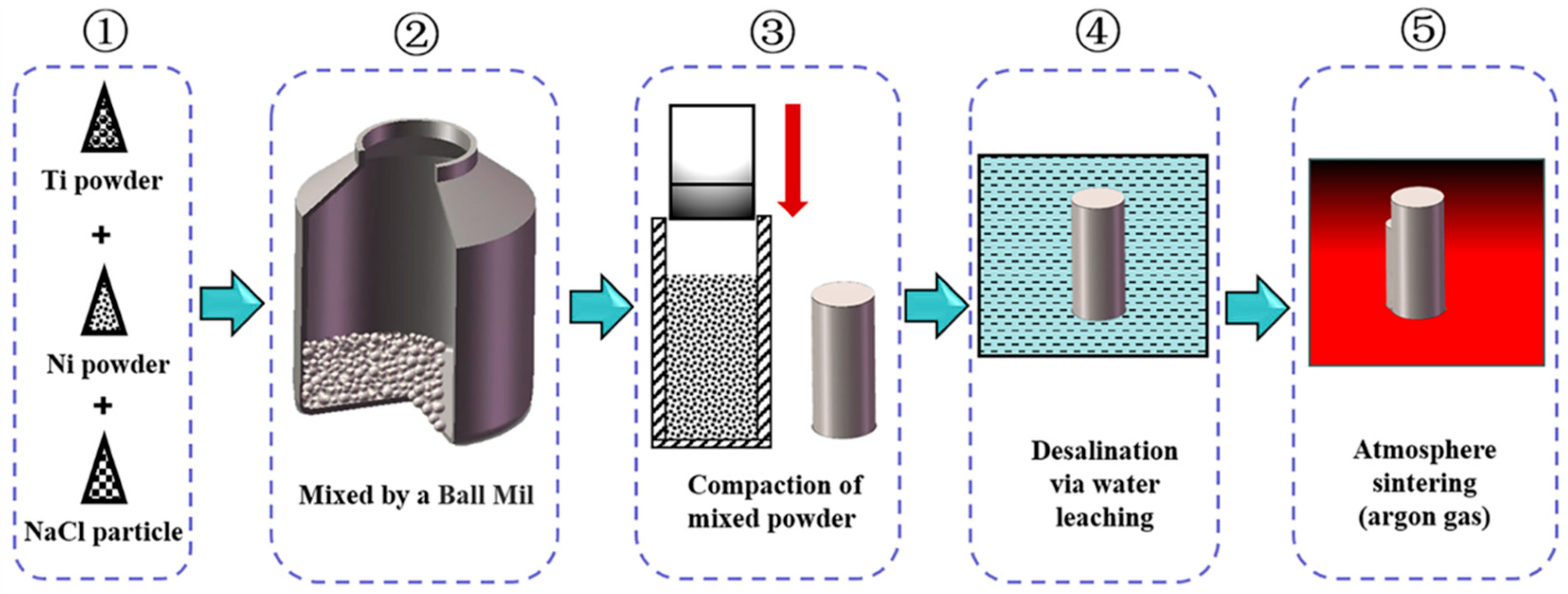
The raw materials used in the present study include the spherical carbonyl Ni powder, the irregular Ti powder, and the high-purity NaCl powder. Specifically, the carbonyl Ni powder has a mean particle size of ≤8 μm and a purity of ≥99.9%; the Ti powder has a mean particle size of ≤50 μm and a purity of ≥99.5%; and cubic NaCl powder has a mean particle size of ≤500 μm. Actually, the NaCl powder serves as the space holder material in the present study, which could provide sufficient stability to withstand pressure and temperature during the fabricating process [21]. The schematic diagram of the CS process is shown in Figure 1. Firstly, the equiatomic carbonyl Ni powder and Ti powder are applied and blended in a planetary ball mill (PM-400) at a constant speed of 200 r/min and 4 h. To maintain the homogeneity of the mixed powder and prevent oxidation of powders, the stainless steel balls are added with a powder-to-ball ratio of 2:1 by weight during the ball milling process with a protective argon gas atmosphere. Afterward, 50 wt.% NaCl powder is added and blended without balls at a protective argon gas atmosphere. The mill condition is 105 r/min and 0.5 h. These mixed powders are then cold-pressed into green samples (d 40 mm × 20 mm) under a uniaxial pressure of 800 MPa for 120 s. These fabricated green samples are further desalted by soaking in distilled water at 55 °C. The duration time is as long as 5 days for guaranteeing complete desalination. These desalinated samples are further sintered at a heating rate of 7 °C/min to 1000 °C and held for 4 h in a protective argon gas atmosphere. After sintering, cooling in a furnace under the protection of high-purity argon gas is performed in the present study at the rate of 7 °C/min to room temperature. No additional heat treatment is performed on these sintered samples.
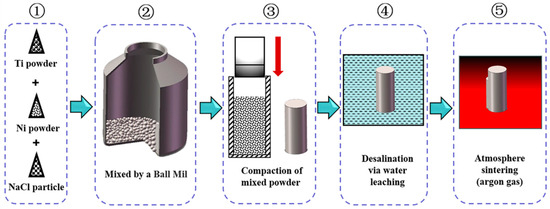
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the processing route for preparing porous NiTi SMA.
2.2. Experimental Characterization Procedures
Uniaxial compression experiments are performed in the present study on a CMT-5205GL microcomputer-controlled electro-hydraulic servo pressure testing machine at a chosen strain rate of 0.001 s−1. These compression specimens are cut from sintered samples with dimensions of d 8 mm × 12 mm via electrical discharge machining (EDM). The previously conducted loading–unloading experiments demonstrate that the threshold of superelasticity strain is about 8%, which is superior to the reported one (about 6%) in the work of Bram et al. [22]. The results of three repeated uniaxial compression experiments confirm that the fracture elongation of the fabricated porous NiTi SMA is about 16%. Therefore, in order to investigate the microstructure characteristics during plastic deformation, some compression specimens are deformed to a deformation degree of 9.2% and 12.5%, respectively.
The phase composition of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs is identified via X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Cu Kα radiation (PANalytical Empyrean Series 2, Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK) at a scanning speed of 2°/min and an operating voltage of 40 keV. The microstructure characteristics of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs during plastic deformation are investigated using a FEI NOVA 400 Zeiss Sigma field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI Corporation, Hillsboro, OR, USA), which is equipped with an electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) detector and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) detector. Samples for SEM characterization are prepared via mechanical grinding with #400, #800, and #2000 SiC papers. Samples for EBSD characterization are prepared by mechanical grinding first, followed by electrochemical polishing in electrolytes, including 80 vol.% ethanol and 20 vol.% sulfuric acid. These obtained data are post-processed using the Channel 5 analysis software. These observation areas are located in the central regions of specimens, which are parallel to the compression direction. Additionally, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) are applied in the present study on an FEI Tecnai G2 instrument to investigate the specific microstructure characteristics around microcrack regions. The TEM sample preparation method applied in the present study is similar to the reported one in the work of Yan et al. [23] for bulk NiTi SMA; therefore, they would not be declared here.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Characteristics of Fabricated Porous NiTi SMA Samples
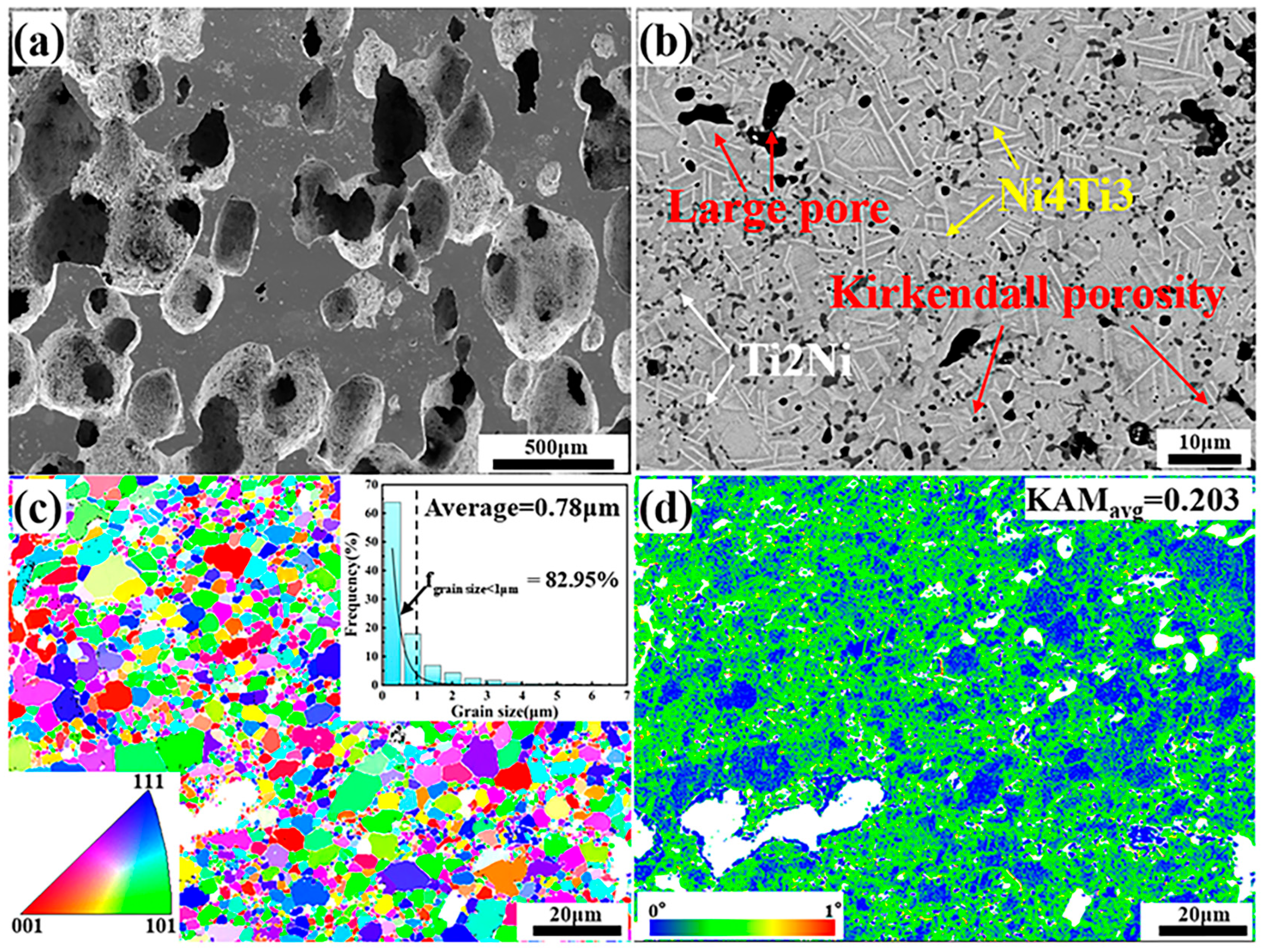
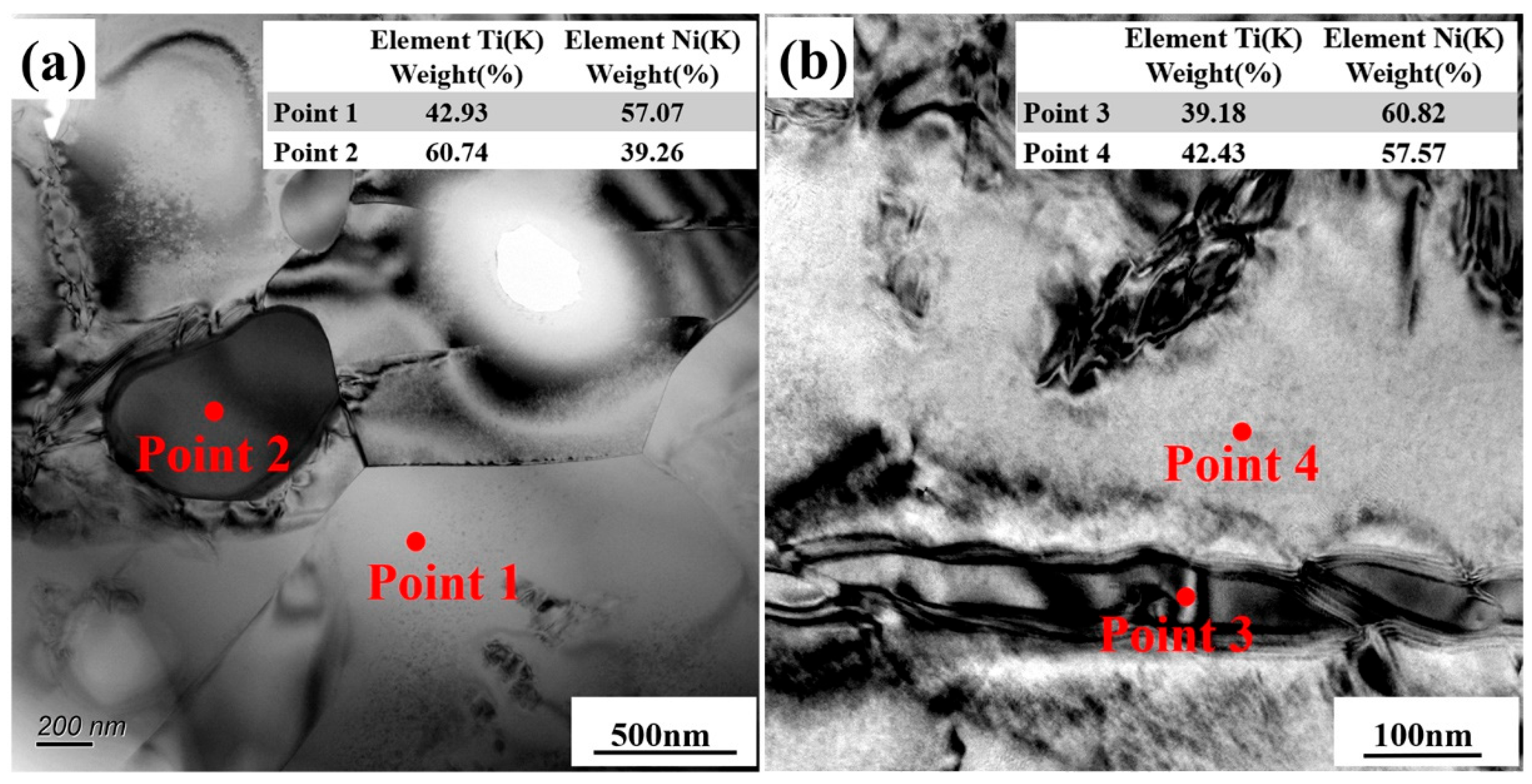
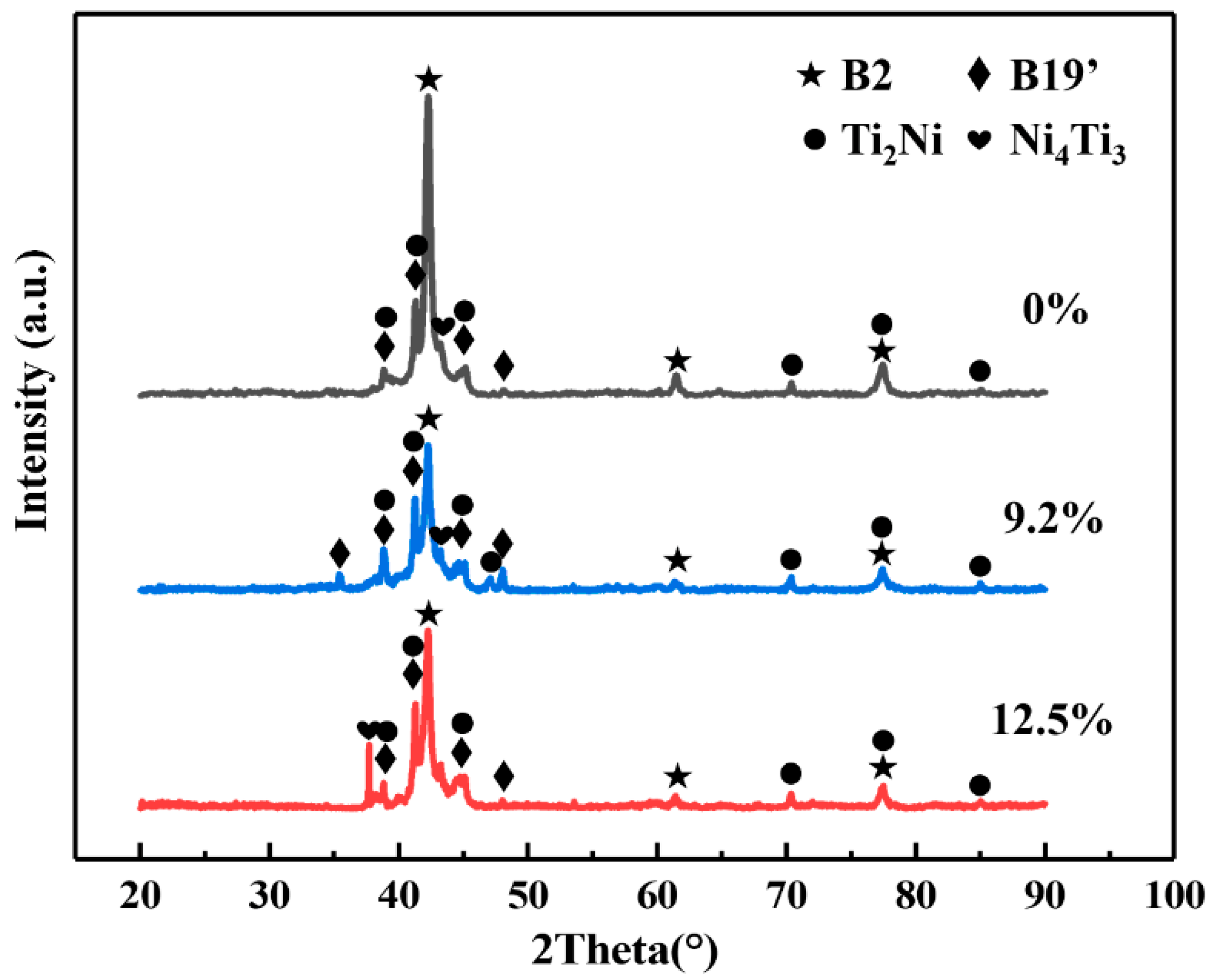
Figure 2 shows the microstructure characteristics of fabricated porous NiTi SMA samples via the CS method. Obviously, numerous pores with various sizes are randomly distributed in Figure 2a, and the corresponding porosity is determined to be about 51.8% via Archimedes’ principle. Besides, the average size of pores is determined to be 181.65 μm via the line-segment method. Except for these large pores deriving from these desalted NaCl powders, there also exist many small pores in Figure 2b, which is termed the Kirkendall porosity. The underlying mechanism leading to this phenomenon is that Ni atoms diffuse faster than Ti atoms during the sintering process, resulting in a quicker diffusion of Ni atoms into Ti atoms instead of a quick diffusion of Ti atoms into Ni atoms. This would cause unbalanced mass transfer, which is responsible for the formation of the Kirkendall porosity [24,25]. Besides, Figure 2b shows that there exist various secondary phases (the lath-like phases, which are larger and brighter, and the block-like phases, which are smaller and darker) in the NiTi matrix. Furthermore, TEM characterizations via bright field (BF) images on these secondary phases are shown in Figure 3, where analysis of their composition is inserted. Based on the relative atomic mass of Ni (58.69) and Ti (47.87), as for the matrix NiTi, the theory weight percents are calculated to be 55.08% for Ni and 44.92% for Ti. Similarly, with respect to the Ti2Ni phase, the theory weight percents are determined to be 38.0% for Ni and 62% for Ti. With regard to the Ni4Ti3 phase, the theory weight percentages are identified to be 62.05% for Ni and 37.95% for Ti. Obviously, Point 1 and Point 4 in Figure 3 refer to the NiTi matrix; meanwhile, Point 2 refers to the Ti2Ni phase, and Point 4 refers to the Ni4Ti3 phase. XRD patterns of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs in Figure 4 further confirm this issue, where peaks of B2 (NiTi), B19′ (NiTi), Ni4Ti3 and NiTi2 are measured. Zhu et al. [26] and Laeng et al. [27] both have reported that the formation of the NiTi2 phase is due to the solid-state diffusion reaction, which is more thermodynamically favorable than the formation of the NiTi matrix during the sintering process. Meanwhile, these intermediate phases (NiTi2) are brittle ones, and they are adverse to the superelasticity property of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs [22]. Figure 2c,d depict the results of EBSD measurement, including the inverse pole figure (IPF) map and the kernel average misorientation (KAM) map. Obviously, the grain color in Figure 2c is rather random, indicating that the grain orientation also distributes randomly. This observation is similar to the reported result in the work of Lu et al. [1]. The average grain size is determined to be 0.78 μm, and the average KAM value is calculated to be 0.203 in the present study. In general, KAM is positively related to the density of geometrically necessary dislocation (GND) [28,29]. The rather low KAM value in the present study demonstrates that the formation of thermal stress during fabricating porous NiTi SMAs via the CS process is limited, as well as the formation of dislocations [28].
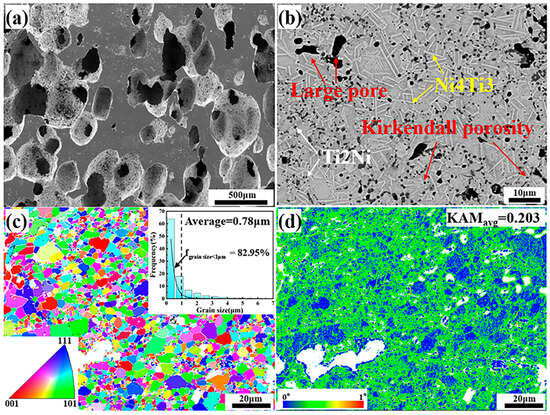
Figure 2.
Microstructure characteristics measured via SEM and EBSD techniques: (a) secondary-electron SEM with low magnification; (b) backscattered electron SEM with large magnification; (c) IPF map inserted with the statistical result of grain size; (d) KAM map inserted with the average KAM value.
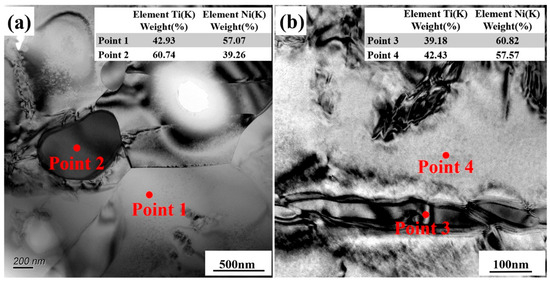
Figure 3.
Microstructure characteristics measured via TEM technique: (a,b) BF images inserted with the corresponding EDS analysis results.
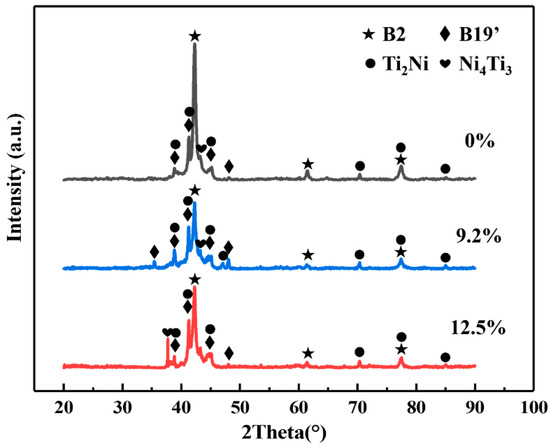
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of undeformed and deformed porous NiTi SMA samples during compressive deformation at room temperature.
3.2. Microstructure Characteristics of Deformed Porous NiTi SMA Samples
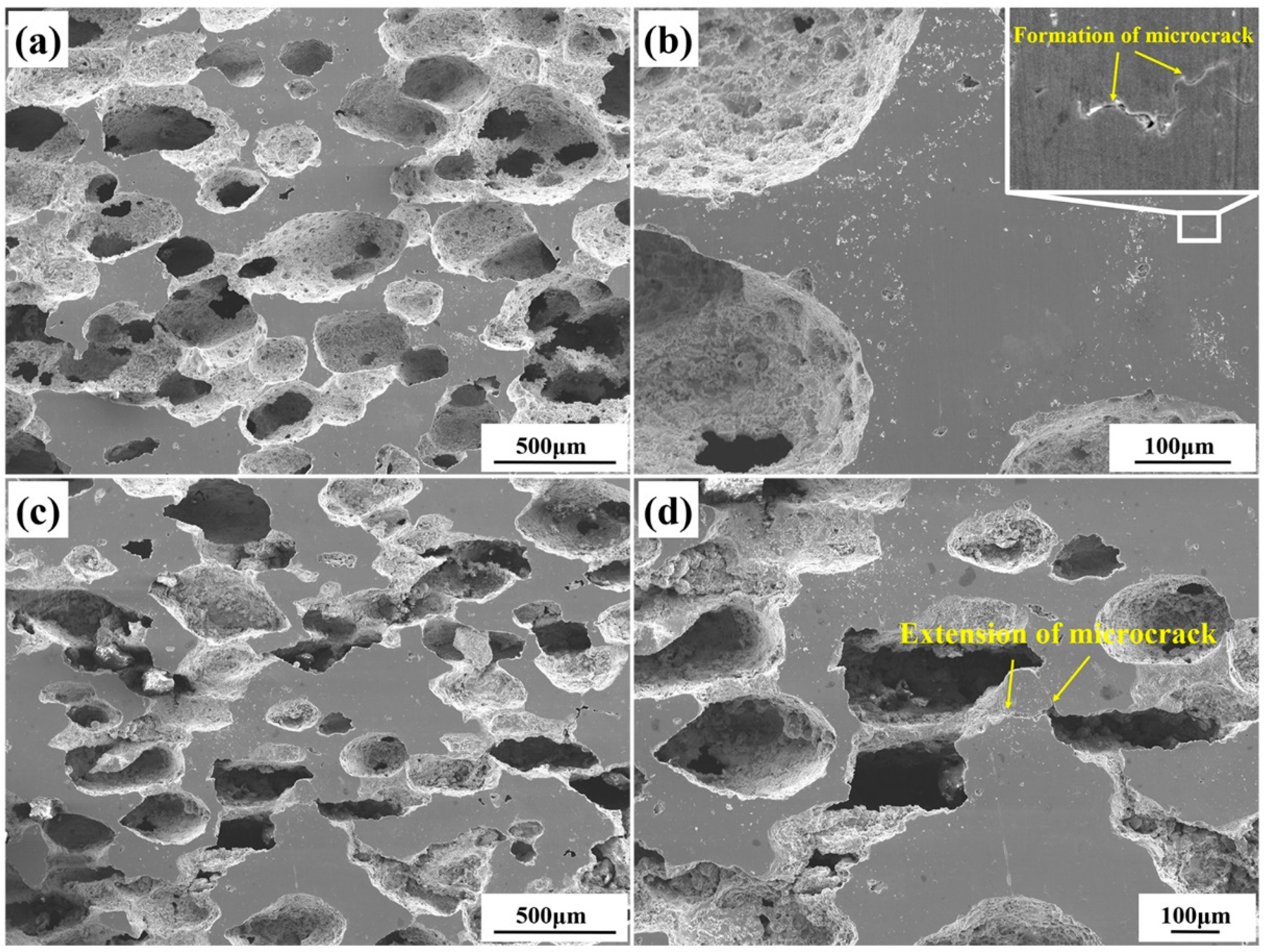
XRD patterns of 9.2%-deformed and 12.5%-deformed samples are shown in Figure 4. Obviously, peaks of B2 (NiTi), B19′(NiTi), Ni4Ti3, and NiTi2 are also included in deformed samples. However, intensities of peaks of B2 (NiTi) and B19′(NiTi) for deformed samples were changed in comparison with those in undeformed samples. This observation indicates the occurrence of stress-induced phase transformation during uniaxial compression of fabricated porous NiTi SMA sample at room temperature. Figure 5 shows the microstructure characteristics of deformed samples via SEM measurements. Microcracks occur within the 9.2%-deformed sample, as shown in Figure 5a,b. Mentz et al. [30] reported that these microcracks are preferentially initiated around these intermediate phases (Ni4Ti3 and Ti2Ni) and near the surface roughness of these formed pore microstructures. Mechanisms of its formation are as follows [22,25]: owing to the formed complex pore structure in fabricated porous NiTi SMAs, severe inhomogeneous deformation happens within the compressed specimen. Therefore, thin-walled regions would suffer from huge local strain and deform plastically, which contributes to the occurrence of buckling and/or microcracks. Meanwhile, stress-induced phase transformation would occur simultaneously within thick-walled regions. Figure 5c,d show that these existing microcracks extend quickly to form macrocracks preferentially near wall regions of 12.5%-deformed porous NiTi SMA sample. Clearly, the failure of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs starts locally, followed by a failure of neighboring regions [31].
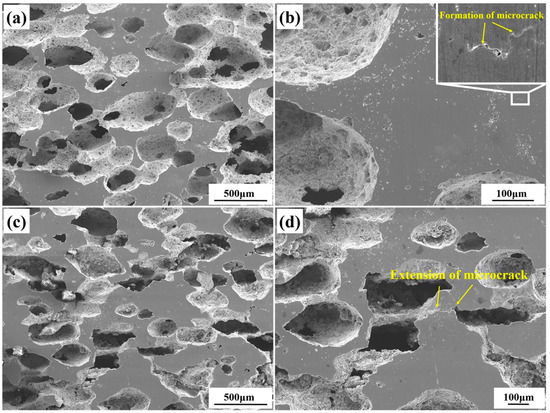
Figure 5.
SEM characterization results of deformed samples during compressive deformation: (a,b) at a deformation degree of 9.2%; (c,d) at a deformation degree of 12.5%.
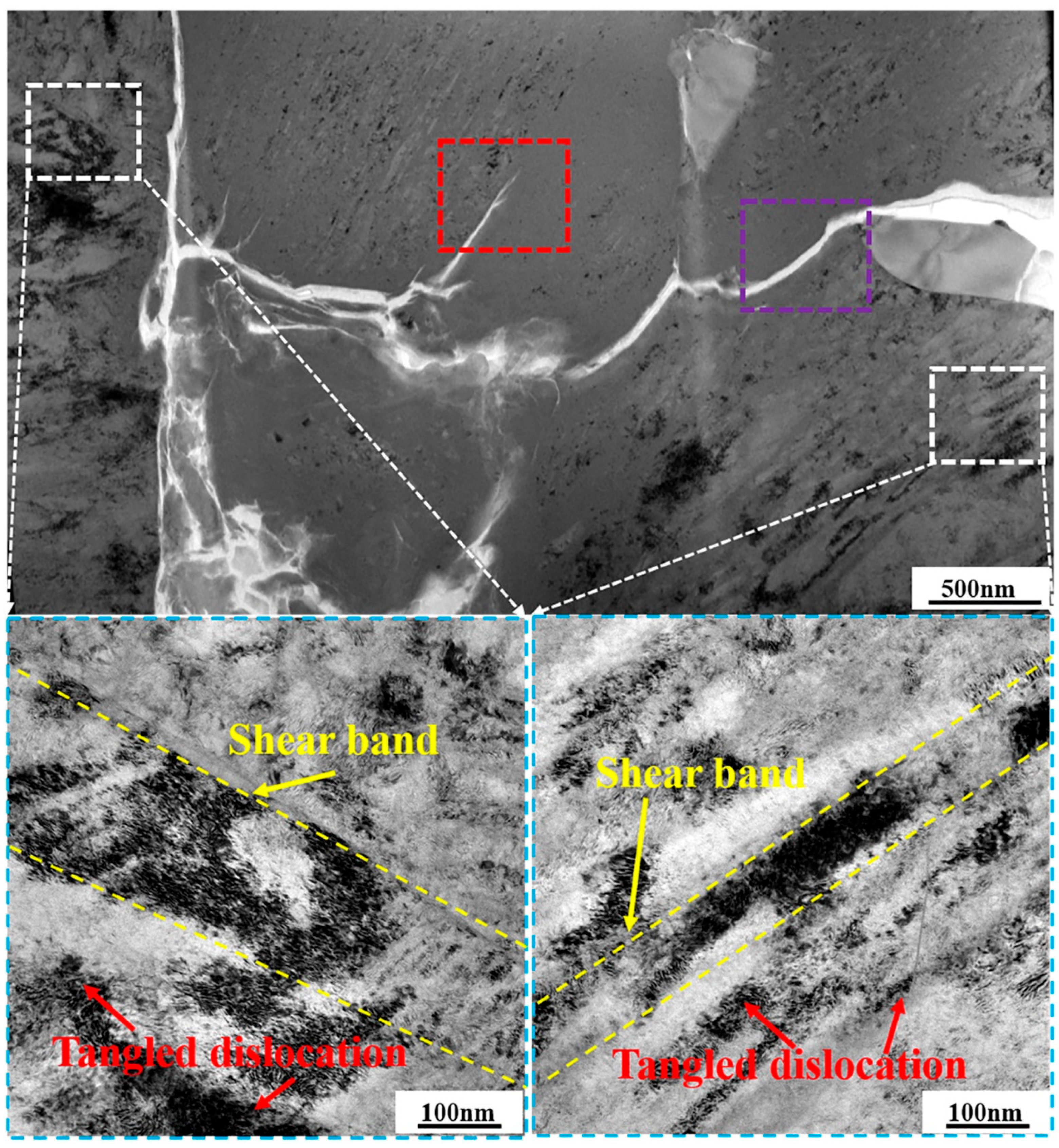
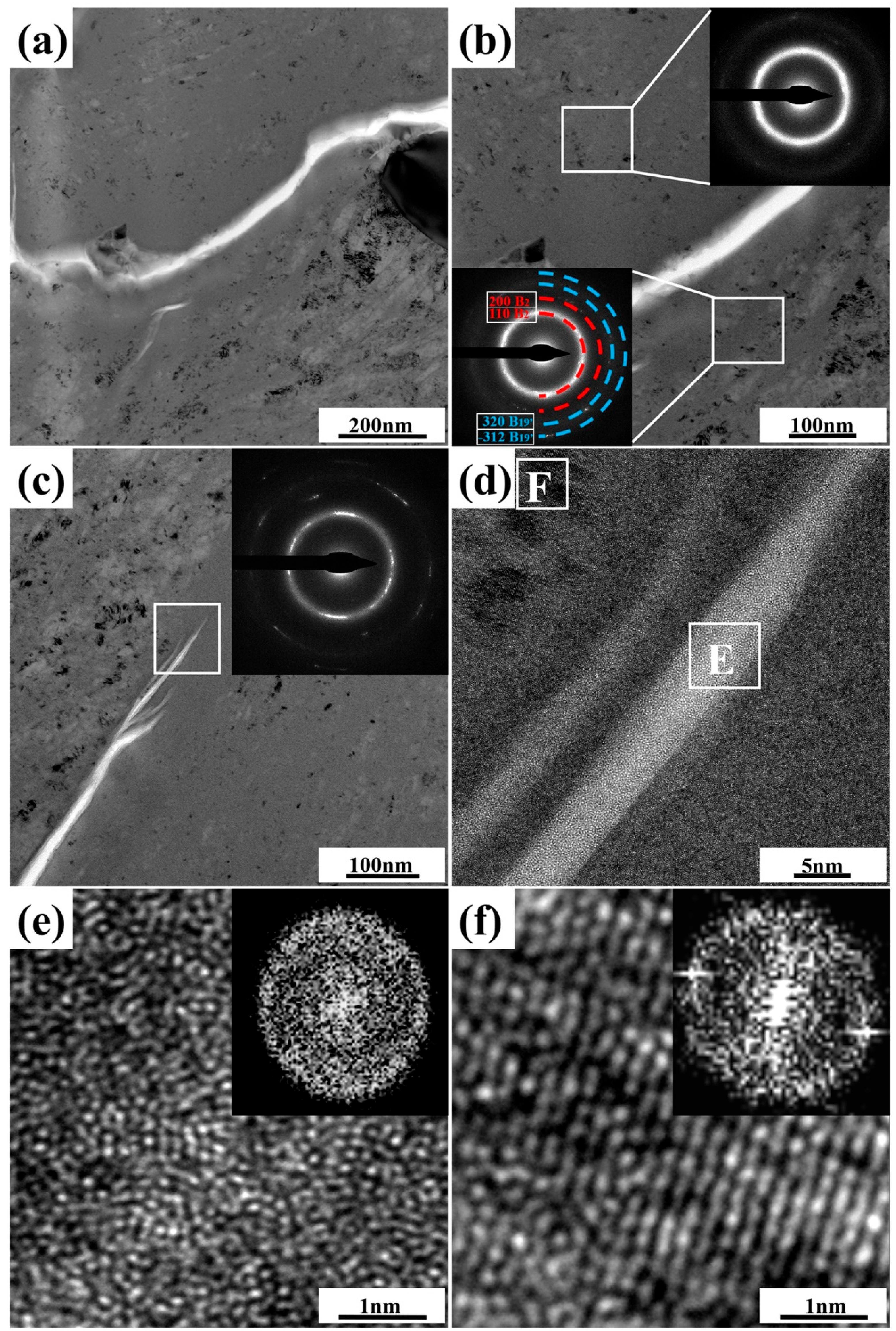
Further investigations on the specific microstructure characteristics around microcrack regions via TEM measurements are shown in Figure 6, where BF images are included. Regions highlighted by the white-dotted bordered rectangle refer to the porous NiTi SMA matrix. Clearly, tangled dislocation distributes unevenly in the matrix region of the 12.5%-deformed porous NiTi SMA sample, as well as the shear band. Both of them confirm the occurrence of severe inhomogeneous deformation [23]. As for the region of microcrack propagation, which is highlighted by the purple-dotted bordered rectangle in Figure 6, the inserted selected area electron diffraction patterns (SAEDPs) in Figure 7b depict the amorphous ring characteristics within the upper right area and the nanocrystalline grains with B2 (NiTi) and B19′ (NiTi) structures within the lower left area. With respect to the region at the microcrack tip, which is highlighted by the red-dotted bordered rectangle in Figure 6, BF images, HRTEM maps, and fast Fourier transformation (FFT) maps in Figure 7c–f demonstrate the occurrence of nanocrystallization near microcrack tip and the amorphization within microcrack tip. These specific TEM and HRTEM characterization results in Figure 7 confirm that severe deformation has occurred in the formed microcrack region. Mechanisms of its formation are as follows: firstly, the grain size of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs is relatively small, and the grain fraction with grain size lower than 1 μm is calculated to be 82.95% (Figure 2c when numerous dislocations and shear bands are activated to sustain plastic strain, grain would be effectively and easily divided via dislocation cells with the assistance of the statistically stored dislocations (SSDs) and the geometrically necessary dislocations (GNDs) [32]. This is responsible for the observed amorphous and nano-sized grains in Figure 7.
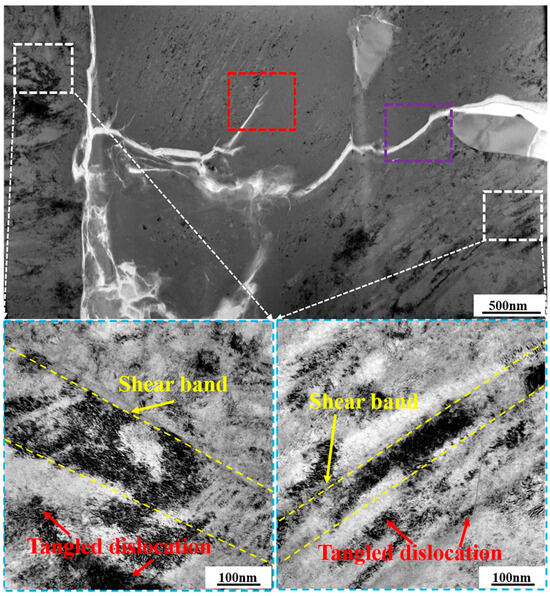
Figure 6.
BF images of selected regions near the formed crack within a 12.5%-deformed porous NiTi SMA sample (Regions highlighted by the white-dotted bordered rectangle refer to the porous NiTi SMA matrix. Region highlighted by the red-dotted bordered rectangle refers to the region at the microcrack tip. Region highlighted by the purple-dotted bordered rectangle refers to the region of microcrack propagation).
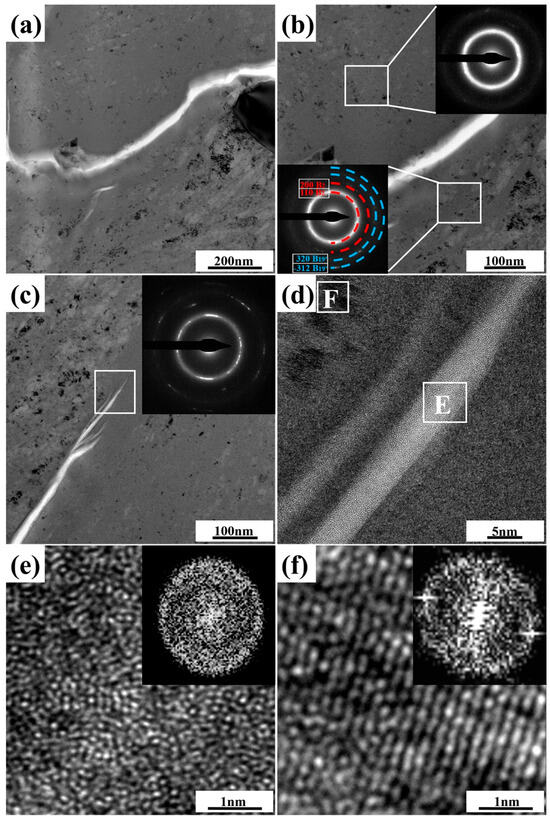
Figure 7.
Specific TEM and HRTEM characterization results of formed microcracks within 12.5%-deformed porous NiTi SMA sample: (a,b) BF images and the corresponding SAEDPs of the selected region highlighted by a purple-dotted bordered rectangle in Figure 6; (c–f) BF images, HRTEM maps, and FFT maps of the selected region highlighted by a red-dotted bordered rectangle in Figure 6.
4. Conclusions
Microstructure characteristics of fabricated porous NiTi SMAs via the CS process during compressive deformation at room temperature have been investigated in the present study by collectively using XRD, SEM, EBSD, TEM, and HRTEM techniques. The following conclusions can be drawn.
(1) The porous NiTi SMA with a porosity of 51.8% and an average size of pores 181.65 μm has been fabricated via CS process with a protective argon gas atmosphere. The sintering temperature is 1000 °C, and the holding time is 4 h. The composition includes a large amount of B2 (NiTi) matrix, a small amount of B19′ (NiTi) matrix, as well as Ni4Ti3 and NiTi2 phases.
(2) Microcracks occur within fabricated porous NiTi SMAs at a deformation degree of 9.2%, which is accompanied by the occurrence of stress-induced phase transformation from B2 (NiTi) to B19′ (NiTi). With increasing plastic deformation, these formed microcracks extend quickly to form macrocracks at a deformation degree of 12.5%, which leads to the failure of regions between pores.
(3) Tangled dislocation distributes unevenly in the matrix region of the 12.5%-deformed porous NiTi SMA sample, as well as the shear band. Both of them confirm the occurrence of severe inhomogeneous deformation. Owing to the relatively small grain size and the grain segmentation effect via GND and SSD, nanocrystallization and amorphization could be observed around microcrack tips.
Author Contributions
L.H.: Methodology: Writing—original draft, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. Z.S., X.C. and K.H.: Data curation, Investigation. M.T. and L.W.: Visualization, Formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Project for the Construction of the Chengdu Chongqing Double City Economic Circle (Grant No. KJCX2020045), the Postgraduate Research Innovation of Chongqing Province (Grant No. CYS21439), the Undergraduate Scientific Research Project of Chongqing University of Technology (Grant No. KLA22042), the 2022 Science and Technology Progress Plan of Chongqing Gear Box. Co LTD (Grant No. KY2022-04) and the Cultivation Plan of Scientific Research and Innovation Team of Chongqing University of Technology (Grant Nos. 2023TDZ010).
Data Availability Statement
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Lu, H.; Ma, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lupoi, R.; Yin, S.; Yang, C. Microstructure, shape memory properties, and in vitro biocompatibility of porous NiTi scaffolds fabricated via selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 6797–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Xu, J.-L.; Xiao, Q.-F.; Tong, Y.-X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.-P.; Luo, J.-M.; Liu, Y. Preparation and characterization of porous NiTi alloys synthesized by microwave sintering using Mg space holder. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, E.; Baigonakova, G.; Dubovikov, K.; Kokorev, O.; Yasenchuk, Y.; Vorozhtsov, A. In Vitro Bio-Testing Comparative Analysis of NiTi Porous Alloys Modified by Heat Treatment. Metals 2022, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, E.S.; Kozulin, A.A.; Yasenchuk, Y.F.; Vetrova, A.V.; Volinsky, A.A.; Zhang, Y. Numerical and experimental study of porous NiTi anisotropy under compression. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 3502–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Qing, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, M.; Geng, Y.; Liang, J.; Lu, B. Superelastic behaviors of additively manufactured porous NiTi shape memory alloys designed with Menger sponge-like fractal structures. Mater. Des. 2021, 200, 109448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Du, C.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, F.; He, H. High-strength porous NiTi shape memory alloys with stable cyclic recovery properties fabricated using elemental powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 886, 145682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Ruan, J. Low elastic modulus titanium–nickel scaffolds for bone implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, N.; Mirzaali, M.; Apachitei, I.; Zhou, J.; Zadpoor, A. Multi-material additive manufacturing technologies for Ti-, Mg-, and Fe-based biomaterials for bone substitution. Acta Biomater. 2020, 109, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Eggeler, G.; Zhang, X. High porosity and high-strength porous NiTi shape memory alloys with controllable pore characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.F.; Liu, J.B.; Wang, L.Q.; Ma, R.L.; Zhong, Y.S.; Lu, W.J.; Zhang, L.C. Superelastic behavior of in-situ eutectic-reaction manufactured high strength 3D porous NiTi-Nb scaffold. Scr. Mater. 2020, 181, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chung, C.; Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ho, J.; Chu, C.; Chan, Y.; Yeung, K.; Lu, W.; Cheung, K.; et al. Pore formation mechanism and characterization of porous NiTi shape memory alloys synthesized by capsule-free hot isostatic pressing. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3437–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chung, C.; Zhu, M. Microstructure and martensitic transformation behavior of porous NiTi shape memory alloy prepared by hot isostatic pressing processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 382, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, A.; Aghajani, H. Fabrication of porous NiTi biomedical alloy by SHS method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnina, N.; Rubanik, V., Jr.; Rubanik, V.; Kulak, M.; Belyaev, S.; Liulchak, P.; Chepela, D.; Kalganov, V. Influence of the Ar pressure on the structure of the NiTi foams produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Mater. Lett. 2021, 299, 130047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wong, C.; Chan, K.; Yue, T. Fabrication and characteristics of porous NiTi shape memory alloy synthesized by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6006–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bao, L.; Liu, A.; Jin, X.; Luo, J.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, Y. Effect of pore sizes on the microstructure and properties of the biomedical porous NiTi alloys prepared by microwave sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sun, Y.K.; Yang, C.; Sun, M.; Peng, H.; Shen, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, J. Compression and superelasticity behaviors of NiTi porous structures with tiny strut fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademzadeh, S.; Carmignato, S.; Parvin, N.; Zanini, F.; Bariani, P.F. Micro porosity analysis in additive manufactured NiTi parts using micro computed tomography and electron microscopy. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoxin, H.; Lixiang, Z.; Yunliang, F.; Yanhong, L. Fabrication of high porous NiTi shape memory alloy by metal injection molding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 206, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chang, K.; Ebel, T.; Nie, H.; Willumeit, R.; Pyczak, F. Sintering behavior and mechanical properties of a metal injection molded Ti–Nb binary alloy as biomaterial. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Dunand, D. Shape-memory NiTi foams produced by replication of NaCl space-holders. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bram, M.; Köhl, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stöver, D. Mechanical Properties of Highly Porous NiTi Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, J.; Sun, D.; Tang, M. Mechanical properties and fracture mechanisms of martensitic NiTi shape memory alloy based on various thermomechanical-processing microstructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Khosrovabadi, P.B.; Lindenhovius, J.; Kolster, B. TiNi shape memory alloys prepared by normal sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 150, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.H.; Goodall, R.; Davies, H.A.; Todd, I. Formation of microporous NiTi by transient liquid phase sintering of elemental powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, X.; Fu, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Cui, Z. Stress–strain behavior of porous NiTi alloys prepared by powders sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 408, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeng, J.; Xiu, Z.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Ru, H.; Liu, Y. Phase formation of Ni–Ti via solid state reaction. Phys. Scr. 2007, 129, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantleon, W. Resolving the geometrically necessary dislocation content by conventional electron backscattering diffraction. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qin, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. Effect of initial state on hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization of Ni-Fe based alloy GH984G for steam boiler applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 795, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentz, J.; Bram, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stöver, D. Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Powder Metallurgical NiTi Shape Memory Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoudas, D.C.; Vandygriff, E.L. Processing and Characterization of NiTi Porous SMA by Elevated Pressure Sintering. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2002, 13, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y. Multiscale investigation of inhomogeneous plastic deformation of NiTi shape memory alloy based on local canning compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 569, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).