Abstract
As cellular materials are gaining more ground in the automotive, airplane, and railway industries, the demand for functionally graded metal foams has appeared. In the case of syntactic metal foams, by changing the distribution of the filler material, the properties of the foams can be precisely adjusted according to the desired area of application. Several kinds of graded aluminum matrix syntactic foams (GMSFs) were fabricated with lightweight expanded clay aggregate particles and ceramic hollow spheres as filler materials. Their mechanical properties were observed by modal analysis and compression tests, supplemented with an accurate density determination by computer tomography measurements. The compressive properties were set up on a large scale by adjusting the density by adding specific amounts of Al particles to the filler. Based on the modal analysis results, simple averaging the density of GMSFs produces an inaccurate result in mode shapes and material parameters, so the varying density distributions should be taken into account. By simply varying the distribution of the filler material, we can modify the effective material properties of metal foams to better fit industrial requirements.
1. Introduction
Depending on whether the pores are sealed or interconnected, we can divide metal foams into open-cell and closed-cell. Since high porosity is a defining characteristic of metal foams, the distribution of this porosity is also essential. For closed-cell metal foams and syntactic metal foams, the pore distribution and the filler distribution, respectively, within the material may be homogeneous or inhomogeneous. The latter are graded metal foams (GMFs) or functionally graded metal foams (FGMFs) [1]. The pore and filler distributions can be different in one or more directions [2,3,4,5,6] in the foams.
Several studies have been performed on the effects of pore size properties of aluminum, titanium, and magnesium alloy foams. It has been found that the relationship between compressive strength and porosity is entirely linear, in addition to the effect of pore size distribution on mechanical properties [7,8]. Furthermore, it is worth mentioning that both the foam structure and the pore morphology depend on the manufacturing process used in the production of the foams, which determines the foams’ mechanical properties [9,10].
The mechanism of adaptive bone transformation inspired the GMFs produced by Yi et al. [11]. The gradient pore density defined in the study was adjusted on the foam to further improve the energy absorption of the composite structure. Using their method, they designed the gradient of the density distribution of the foam, which was calculated by finite element (FE) analysis. During the production, aluminum foam samples of different densities were obtained by controlling the foaming time and the amount of TiH2 powder used. FE simulations showed that the energy absorption capacities of this type of foam, which is smaller on the outside and has a larger pore size on the inside, is up to 24% higher than that of samples with the same mass and uniform pore size [11]. Salehi et al. also investigated closed-cell FGMFs made of A356 alloy and zinc. Tubes were filled by single-layer and multilayer structures with different configurations. The results show that the deformation of the tubes filled with multilayer foam starts from the low-strength parts, and then propagates in the high-strength parts with a gradual increase in stress. These show overall superior crashworthiness to the uniform components [5].
Movahedi et al. investigated graded metallic syntactic foams (GMSFs) produced by the systematic spatial variation of two different types of fillers. The matrix material was ZA27 zinc–aluminum alloy, and the fillers were expanded perlite and activated carbon particles. The two filler distributions were varied in both the longitudinal and radial directions, and foams containing a random mixture of the identical particles were tested. Each sample was prepared by a one-step gravity infiltration casting process. The results show that the six-layer samples manufactured by alternating the two fillers along the longitudinal direction gave the highest plateau stress and energy absorption; radial and random GMFs exhibited superior initial strength; and increasing the number of layers enhanced the mechanical properties of the samples [3,4].
All studies showed that multilayer GMFs are very attractive for energy absorption and passive safety protection because of their ability to distribute the kinetic energy of a collision in a controlled manner, but other mechanical properties, such as the effective modulus of elasticity, are rarely investigated.
The effective modulus of elasticity of syntactic foams (the elastic modulus corresponding to the initial linear deformations of a theoretical homogeneous and isotropic body, replacing the syntactic foam) can be determined using experimental modal analysis. During measurements, column-shaped samples are suspended via a flexible rubber rope to achieve minimal disturbance and create a configuration allowing free vibrations. To determine the natural frequencies, impact tests are carried out using a micro modal hammer and a single accelerometer (provided by PCB Piezotronics). Based on visual inspection of the resultant frequency response functions and the half-power method, the first two natural frequencies and their corresponding modal damping ratios are acquired.
Using the Timoshenko beam theory [12,13], the natural frequencies of prismatic bars can be derived from their geometric and material properties. The same procedure can be applied backward to acquire estimates for the elastic and shear moduli based on the measured natural frequencies. Once the structural stiffness has been determined, metal foams may appear as structural materials in new applications.
On the other hand, the contact between the spherical shells and the matrix material of the metal foam affects the level of achieved damping. It can result in a significant increase due to micro-slip effects on these inner contact surfaces [14,15].
During our research, we investigated metal foams with AlSi10MnMg matrix material filled with ceramic hollow spheres (CHSs) and lightweight expanded clay aggregate particles (LECAPs) manufactured by pressure infiltration. The main contribution of this paper is in (i) the production of GMSFs with changing densities and (ii) the development of investigation techniques–on the basis of vibration analysis–to measure the effective mechanical properties of the produced GMSFs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
For the preparation of our samples, 99.5% pure aluminum particles (Al99.5) and AlSi10MnMg (Silafont®36) were used, whose characteristics are shown in Table 1. Aluminum is known for being an excellent matrix material, because it has low density, good casting properties, and does not require a lot of energy to melt. In addition, it has good resistance to corrosion and fire, which is also the advantage of the subsequent performance of the metal foams. AlSi10MnMg is a cast aluminum alloy with a low melting point and excellent fluidity. Due to its excellent castability, and because it is polishable, weldable, machinable, hardenable, and has good corrosion resistance, this alloy is used primarily in the automotive, food, construction, and military industries.

Table 1.
Material properties and chemical composition of Al99.5 and AlSi10MnMg (according to the manufacturer).
The filler materials lightweight expanded clay aggregate particles (LECAPs, obtained from Liapor GmbH & Co. KG, nominal diameter of 2 mm) or ceramic hollow spheres (CHSs, obtained from Hollomet GmbH, nominal diameter of 2.4 mm) were used. The chemical composition of the used LECAPs (according to the manufacturer) is 60 ± 5 wt.% SiO2, 17 ± 3 wt.% Al2O3, 14 ± 2 wt.% Fe2O3, and ~9 wt.% other oxides (CaO, MgO, Na2O, and K2O). The chemical composition of the used CHSs (according to the manufacturer) is 97–99 wt.% pure Al2O3.
2.2. Production
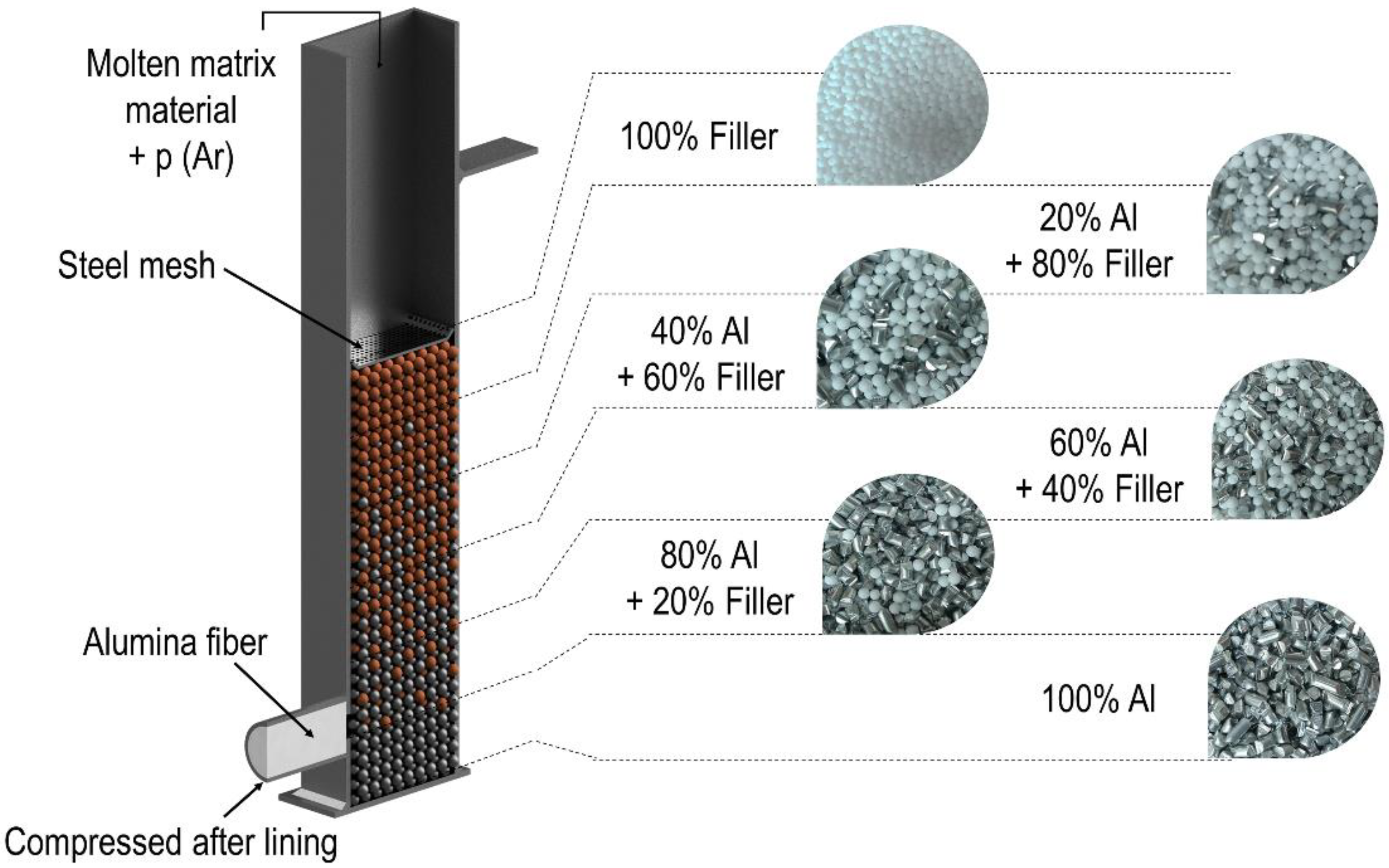
A low-pressure infiltration technique was used to produce the samples. In the production process, the aluminum particles were first mixed with the LECAPs in the appropriate volume ratio (Table 2). Then these mixtures were layered on top of each other in molds to form the gradient space filling of the reinforcing material (Figure 1). The density of aluminum is much higher than that of the LECAPs; therefore, these particles can move up during casting, thereby changing the carefully formed gradient space filling. A stainless steel mesh was inserted atop the mixture, which was wedged against the walls of the mold to prevent the movement of the filler material. After preheating the prepared molds for 30 min at 590 °C, the minimum 690 °C aluminum melt was poured onto the top of the mixture, and then pressed between the particles using argon gas at a pressure of 500 kPa. The infiltration time was 5 s. The air remaining under the melt exited the mold through a condensed tube at the bottom.

Table 2.
Marking of test samples according to volume ratio of filler material in each layer.
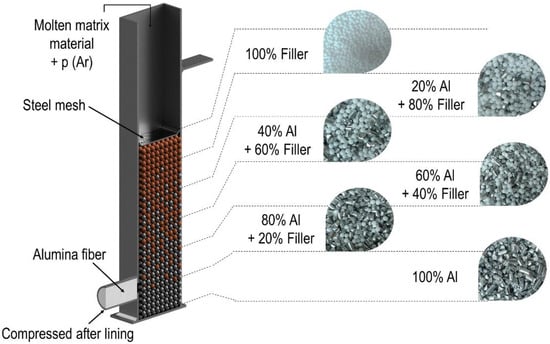
Figure 1.
The closed section was filled with an adequate amount of filler material to realize the different filling distributions (0-100 sample).
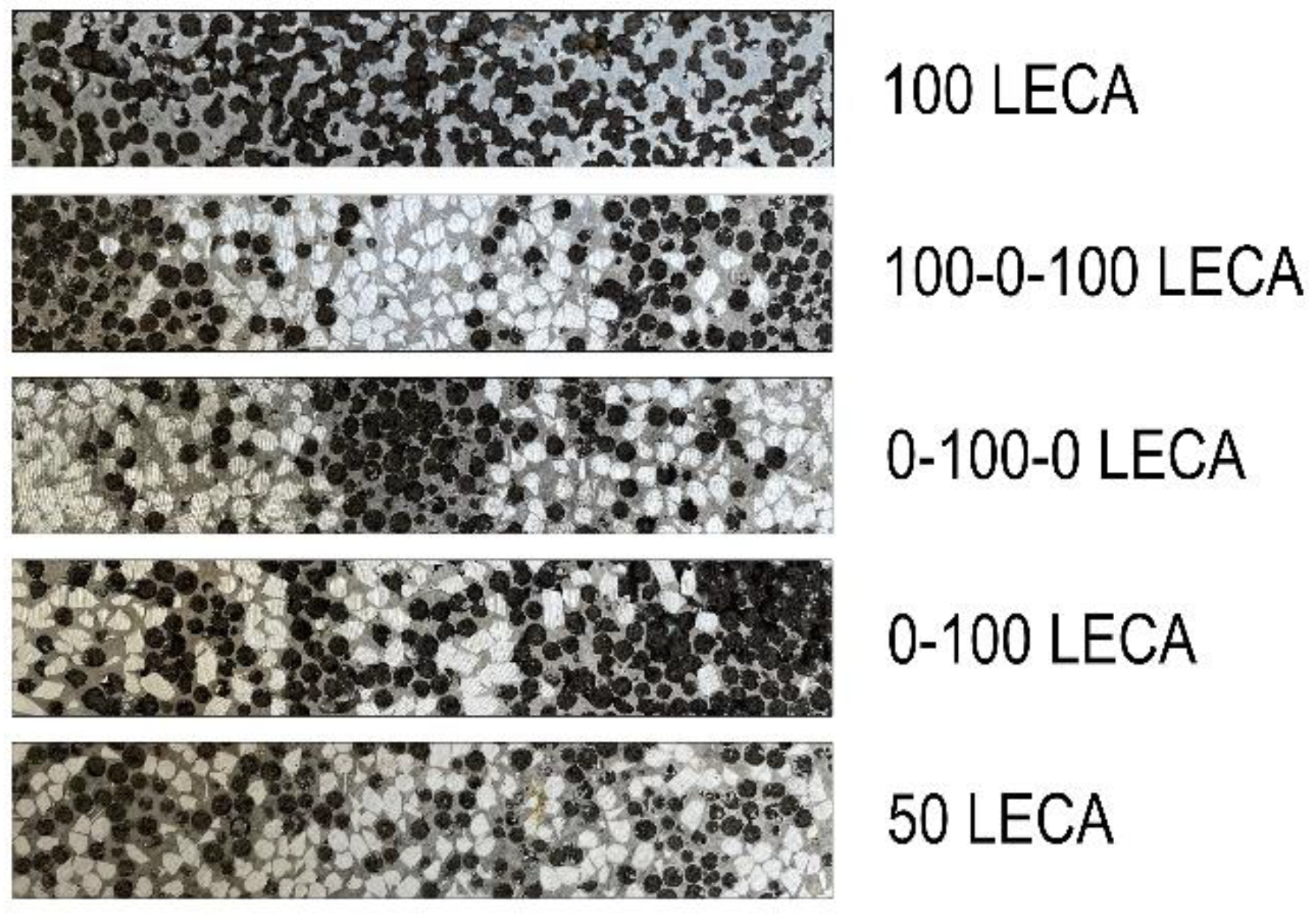
The layering of the sample was different in each case. Table 2 shows the volume ratio of the filler material in the mixture for each layer. The total volume of the sample was 210 cm3, evenly divided by the number of layers. From each block, five ~20 mm × 20 mm × 20 mm samples were machined for the compression test, and one ~15 mm × 25 mm × 110 mm sample was machined for the modal analysis. Figure 2 shows the photos of the samples for modal analysis with LECAPs as filler material.
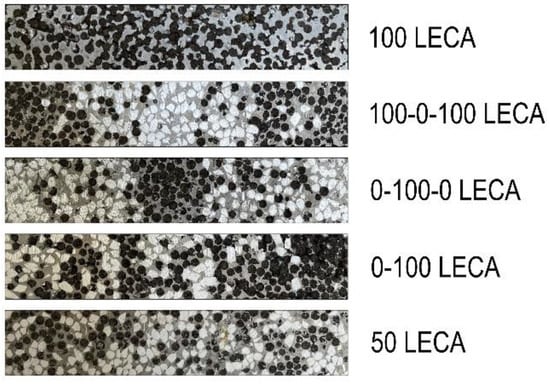
Figure 2.
Samples for modal analysis with different layering.
A heat treatment was applied to the sample to reach the T6 treatment state (according to the manufacturer’s recommendations). The first step was heating the sample at a rate of 300 °C∙h−1 to 535 °C, holding for 4 h, then cooling it rapidly in water. The second step was heating it at a rate of 150 °C∙h−1 to 150 °C, holding for 15 h, then rapidly cooling it in water. The experimental modal analysis was performed before and after the heat treatment.
2.3. Methods
The density of the samples was determined by a YXLON FF35 CT scanner (XYLON International, Hamburg, Germany) with Volume Graphics VGSTUDIO MAX 3.4 (Volume Graphics, Heidelberg, Germany) evaluation software. After automatic segmentation, the volume of each component was determined in a segment of a specific size (usually 10% of the sample’s length). Then using the density of each component, the whole density was calculated for the segment, which we refer to as calculated density. The graded samples were also cut to six (0-100 LECA) or seven (0-100-0 LECA and 100-0-100 LECA) layers, and each section’s mass was measured by a RADWAG PS 6100.R2.M precision balance (Radwag, Radom, Poland), and geometry by a caliper. Thus, the density was calculated, which we refer to as measured density.
A total of 16 samples were compressed from the 50 CHS, 50 LECA, 100 CHS, and 100 LECA grades (4 samples from each grade). Compression tests were carried out between two flat steel plates on an MTS810 universal hydraulic testing machine, equipped with a 250 kN load cell (both from MTS Systems, Eden Prairie, MN, USA). For lubrication, a 0.3 mm thick Kolofol Teflon foil was placed on the contact surfaces between the samples and the platens. Each sample was compressed with a 2 mm∙min−1 cross-head speed to at least 50% engineering strain value for comparability, based on ISO13314:2011 [16], since this method is the only standardized process to characterize the GMSFs’ compressive (and therefore, more important) properties. From the results, the following characteristic values were evaluated: compressive offset stress (σp0,2: the compressive stress at the plastic compressive strain of 0.2%), plateau stress (σpl: the arithmetic mean of the stresses between 10% and 40% engineering strain—the range was selected to have statistically better results) and energy absorption (W50%: area under the engineering stress—engineering strain curve up to 50% strain).
To safely and reliably implement GMFs as structural materials, determining their effective elastic and shear moduli is indispensable. Due to metal foams’ short linear deformation phase, destructive methods, such as compression and tensile tests, are inadequate for this task [16]. One of the most reliable methods to measure the elastic modulus of a material is the procedure based on the vibration theories. For example, experimental modal analysis is a valid alternative for simple geometries and fixture configurations, where the bending mode shapes and their corresponding natural frequencies can be derived analytically. Using these analytic calculations in reverse, material properties can be estimated from the measured natural frequencies.
To acquire these parameters for the produced syntactic metal foam samples, modal measurements were carried out in the form of impact tests, using a Brüel & Kjær 8021 micro modal hammer (Brüel & Kjær, Nærum, Denmark) and a PCB 352C23 accelerometer (PCB Piezotronics, Depew, NY, USA). For data acquisition and preprocessing, an NI 9234 and an NI cDAQ-9178 module (both from NI, Austin, TX, USA) were employed. Since determining the mode shapes was unnecessary for the calculations, exciting and measuring at only one point was sufficient. Approximately 15 mm × 25 mm × 110 mm rectangular prismatic beam samples were manufactured for these tests. The exact dimensions are listed in Table 3. To allow undisturbed free vibrations, the samples were suspended using an elastic rubber thread. In this configuration, the samples could be modeled as beam elements with two free ends. The analyses were performed in accordance with the applicable prescriptions of ASTM E1876-15 ‘Standard Test Method for Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus, and Poisson’s Ratio by Impulse Excitation of Vibration’.

Table 3.
Geometric properties of samples used in the experimental modal analysis.
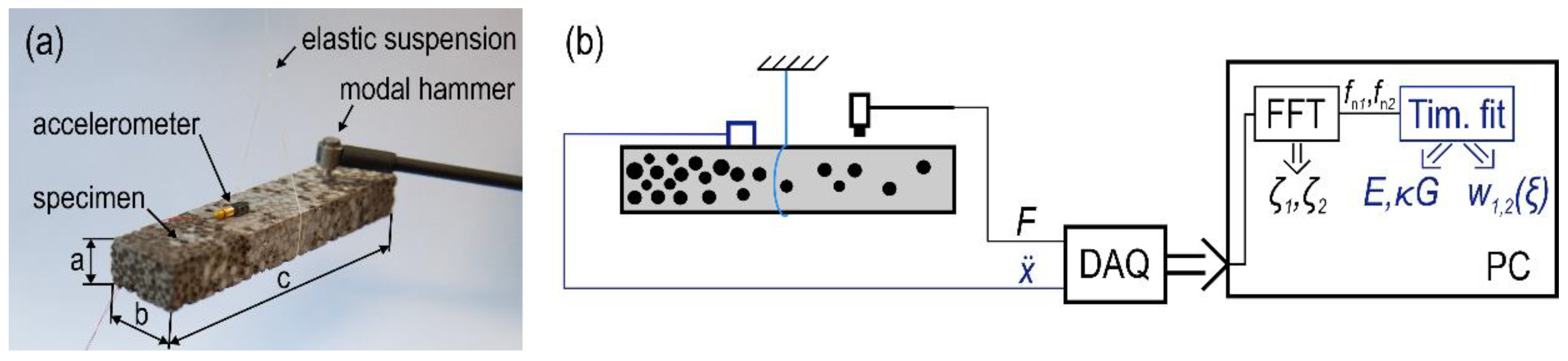
From the data collected during the impact tests, first from frequency response functions, then through visual inspection and the half-power method, natural frequencies and modal damping ratios were derived. These corresponded to the transversal bending modes of the beams and were evaluated concerning both cross-section principal axes, meaning the impulse tests and analytic/numeric calculations were repeated after rotating the samples by 90 degrees along their longest edge. The measurement configuration and the methodology of parameter extraction are illustrated in Figure 3.
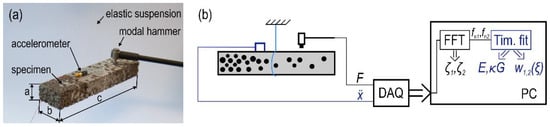
Figure 3.
Experimental modal analysis of syntactic metal foams. Panel (a) shows the measurement configuration, while panel (b) illustrates the process of material parameter extraction (where DAQ is for data acquisition device, and FFT is for Fast Fourier Transformation and Time. Fit is for time fitting).
Using the Euler–Bernoulli beam theory, and assuming uniform mass distribution, geometry, and material parameters, a rough estimate can be given for the effective elastic modulus based on the first natural frequency:
where is the sample’s density, and are the cross-section area and second moment of inertia, respectively, is the measured first angular natural frequency, and is the first non-zero root of the frequency equation corresponding to a free-free Euler–Bernoulli beam:
where is the length of the sample from Equation (2) .
A more accurate and robust estimate can be obtained using the Timoshenko beam theory [13], this time using the first two natural frequencies and estimating both the elastic and shear moduli simultaneously. Using the Timoshenko beam theory, the bending mode shapes of a free-free beam can be obtained by solving the following non-dimensionalized boundary value problem:
where is the dimensionless length coordinate, is the transversal displacement, and is the rotation angle of the cross sections. Furthermore, , , and , while is the shear modulus, and is the shear correction factor (usually for rectangular cross sections). The shearing part () of the expression can be more precisely determined on samples having changing density along their longitudinal axes (that is the why layered samples were measured).
As derived in [13] for uniform cantilever and pinned-pinned beams, a frequency equation can be formulated from the equation system of Equation (3) for the free-free Timoshenko beam:
Here
and
From Equation (4), and cannot be expressed explicitly; however, they can be obtained numerically via, e.g., the well-known Newton–Raphson method. Solving for two variables simultaneously requires two equality conditions, which can be formulated by substituting the first and then the second measured natural frequencies into when solving Equation (4).
If the density distribution is considered non-uniform, as with GMFs, the Equations (2) and (4) are no longer applicable. In this case, the boundary value problem the equation system of Equation (3) should be solved directly while considering to be a function of the length coordinate. There are analytical methods for acquiring approximate solutions to this problem [17]; however, it is more rewarding to solve the problem only numerically.
In this paper, Chebyshev polynomial-based spectral collocation [18] was employed for the numeric solution of the equation system of Equation (3). By discretizing the orbit onto a shifted and rescaled Chebyshev–Gauss–Lobatto grid , applying the boundary conditions, employing the spectral derivative matrix provided by the polynomial base, substituting in both measured natural frequencies, and constraining the norm of the solution mode shapes to 1, the sufficient number of equality constraints can be formulated to fully define the discretized version of the problem. The resulting system of equations can be solved for , , and the mode shapes and simultaneously by iterative means, via, e.g., the Newton–Raphson method.
Figure 3b illustrates that the above-described methodology was employed to fit mode shapes and material properties to the manufactured metal foam bars, based on their first two natural frequencies. The geometric and mass properties of these measurement samples are listed in Table 3, from which , , and either or depending on the current orientation of the beam.
3. Results and Discussion
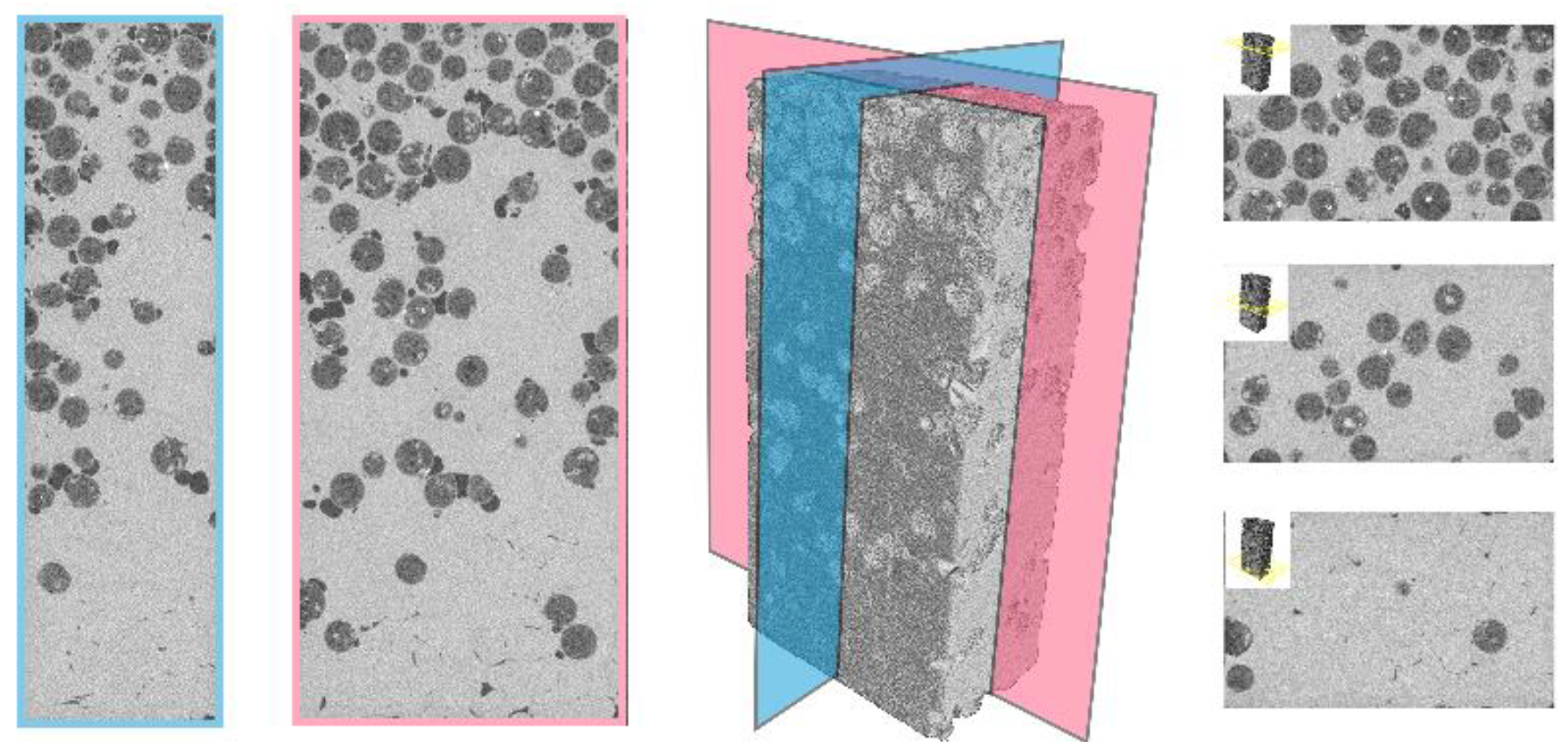
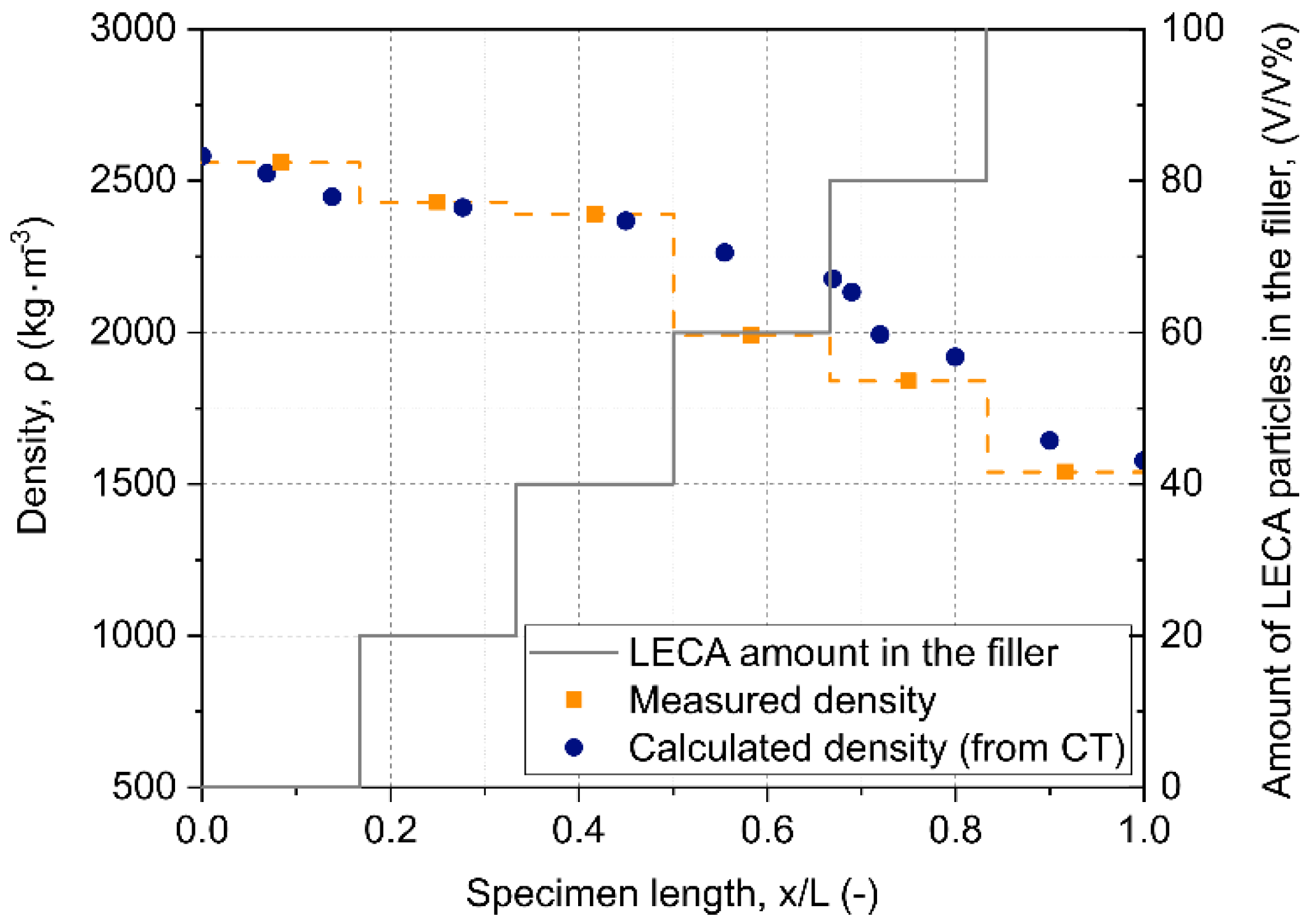
The density of the GMFs was determined by computer tomography (CT) scans, as can be seen in Figure 4. Comparing the calculated density from the CT scans and measured density gave relative values (Figure 5). The exact density distribution of the sample was needed for the fitting after the modal analysis, which can be seen later for a more detailed explanation.
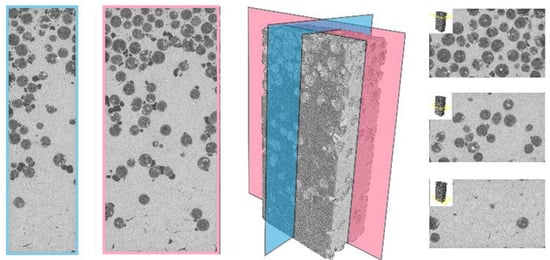
Figure 4.
CT scan layers of half of the 0-100-0 LECA sample.
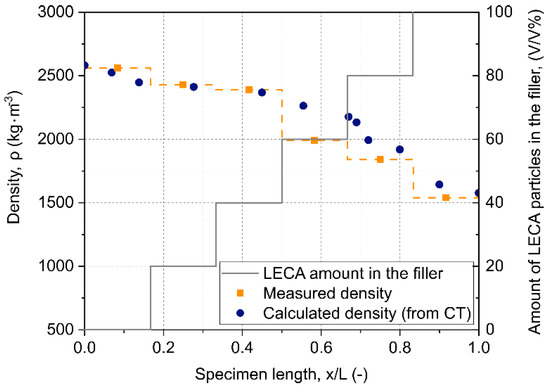
Figure 5.
Density and amount of LECA particles in the filler according to the length of the 0-100 LECA graded sample.
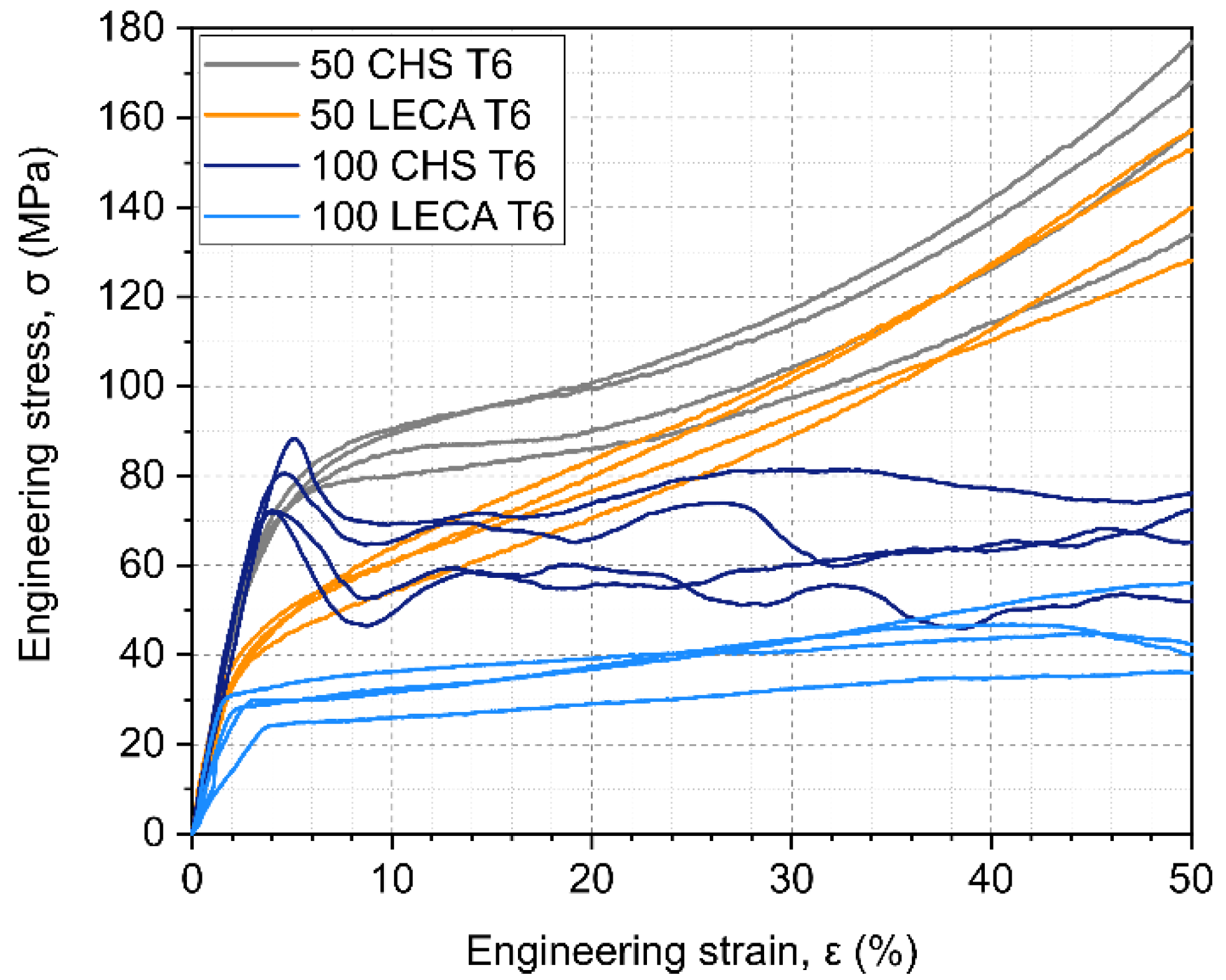
The engineering stress–engineering strain curves of the compressed foams until 50% strain are shown in Figure 6. The foams containing Al particles (50 CHS and 50 LECA) had higher slope curves (grey and orange) in the plateau region (10–40% strain) and showed a less foam-like stress–strain behavior in general compared to the random close-packed foams (100 CHS and 100 LECA). The produced foams maintained densities between 18–46% lower compared to bulk Al. The increase in density had a visible effect on the properties of CHS-filled foams, as their characteristic first compressive stress peak and plateau changed and became similar to the 50 LECA curves.
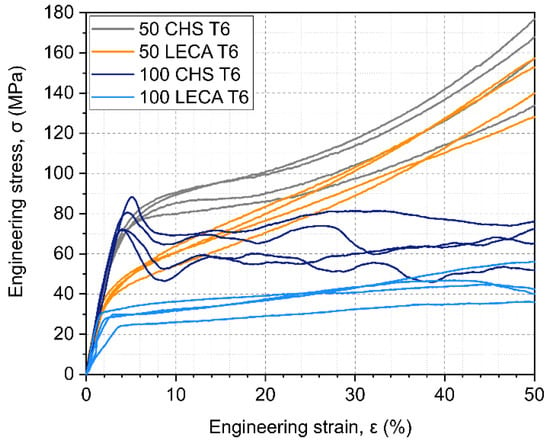
Figure 6.
Engineering stress–engineering strain curves of the samples.
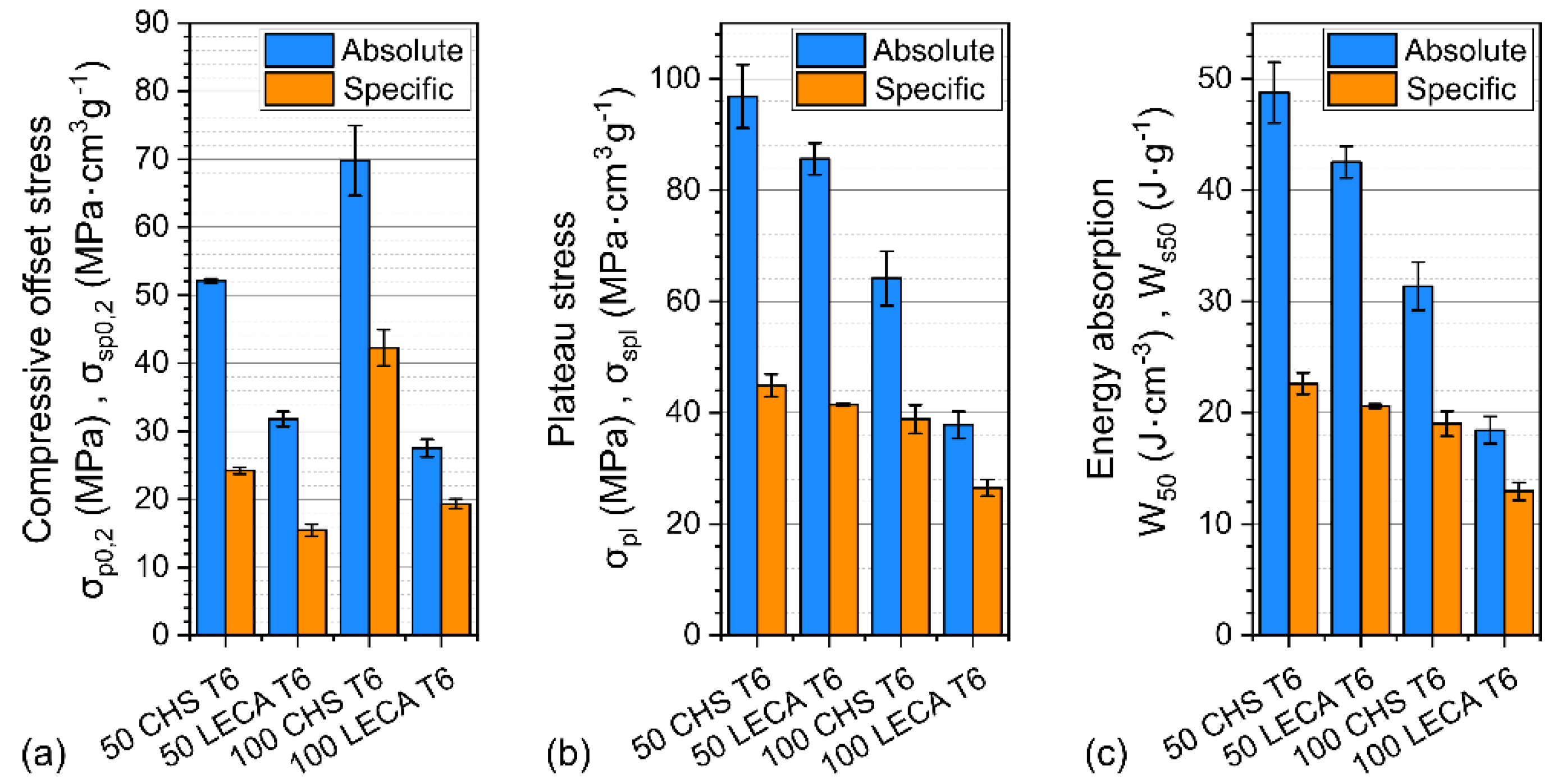
The evaluated results of the measurements are shown in Figure 7.
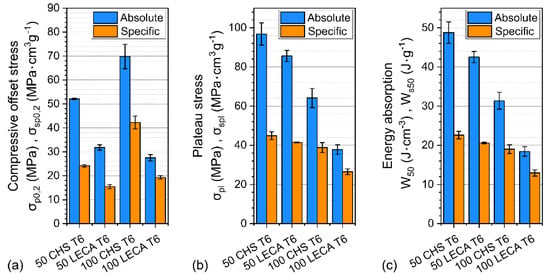
Figure 7.
The compressive offset stress (a), plateau stress (b), and energy absorption (c) values of the tested samples.
Both the 50 CHS and 100 CHS samples had significantly higher compressive offset stress (Figure 7a) values compared to the LECA-filled foams (>50%). The 100 CHS samples had the highest values, as these had a characteristic first compressive stress peak. This characteristic behavior disappeared with the adding of Al particles.
The highest plateau stress values (Figure 7b) occurred when the 50 CHS foams were compressed, followed by the 50 LECA foams. This shows that the plateau stress of 100 LECA foams could be significantly improved (~56%) by mixing with Al particles. The same mixing resulted in a ~34% improvement on the 100 CHS foams. The ~41% difference corresponding to the filler material could be decreased to ~12% with Al particle strengthening.
The energy absorption values (Figure 7c) had the same tendency as the plateau stress values in both absolute and specific systems.
An experimental modal analysis was employed to determine the effective elastic moduli of the manufactured GMF samples. Based on the visual inspection of the frequency response functions obtained through impact tests and the half-power method, the natural frequencies ( and damping ratios ( listed in Table 4 were obtained. Using the Timoshenko beam theory and the numerical methods discussed in the Methods section, the material parameters and were fitted to the measured natural frequencies.

Table 4.
Experimental modal analysis and material parameter fitting results. For varying density samples, values displayed in brackets denote the fitting results considering uniform density.
These values correspond to the measurement configuration where bending happens about the cross-section principal axis with the highest corresponding second moment of area (). The same measurements were repeated for the bending modes about the other principal axis. After the material parameter fitting, these produced approximately the same results, and thus their numerical values are not listed in this paper. The primary purpose of these repeated measurements was to validate the parameter fitting algorithm, and they fulfilled this purpose well.
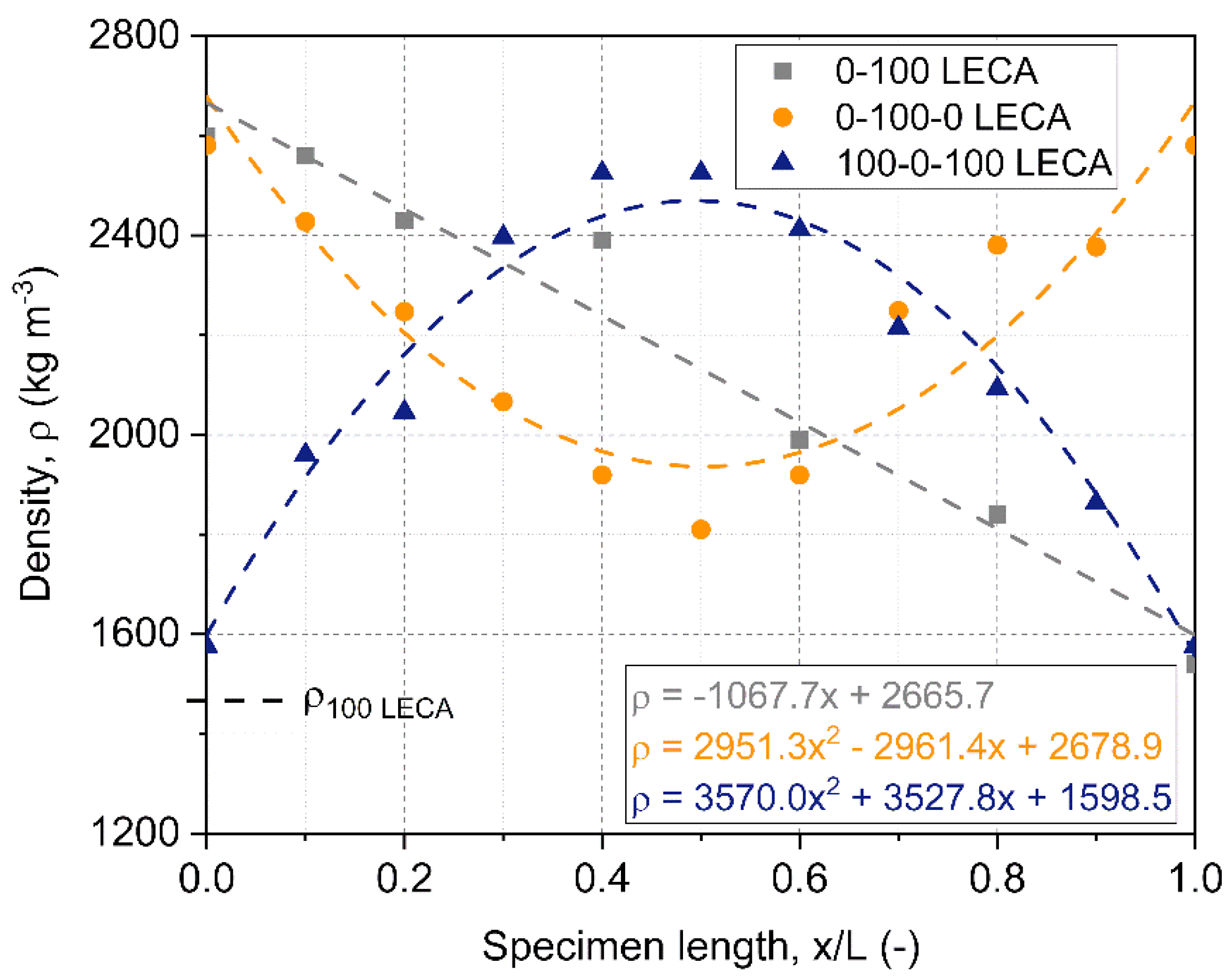
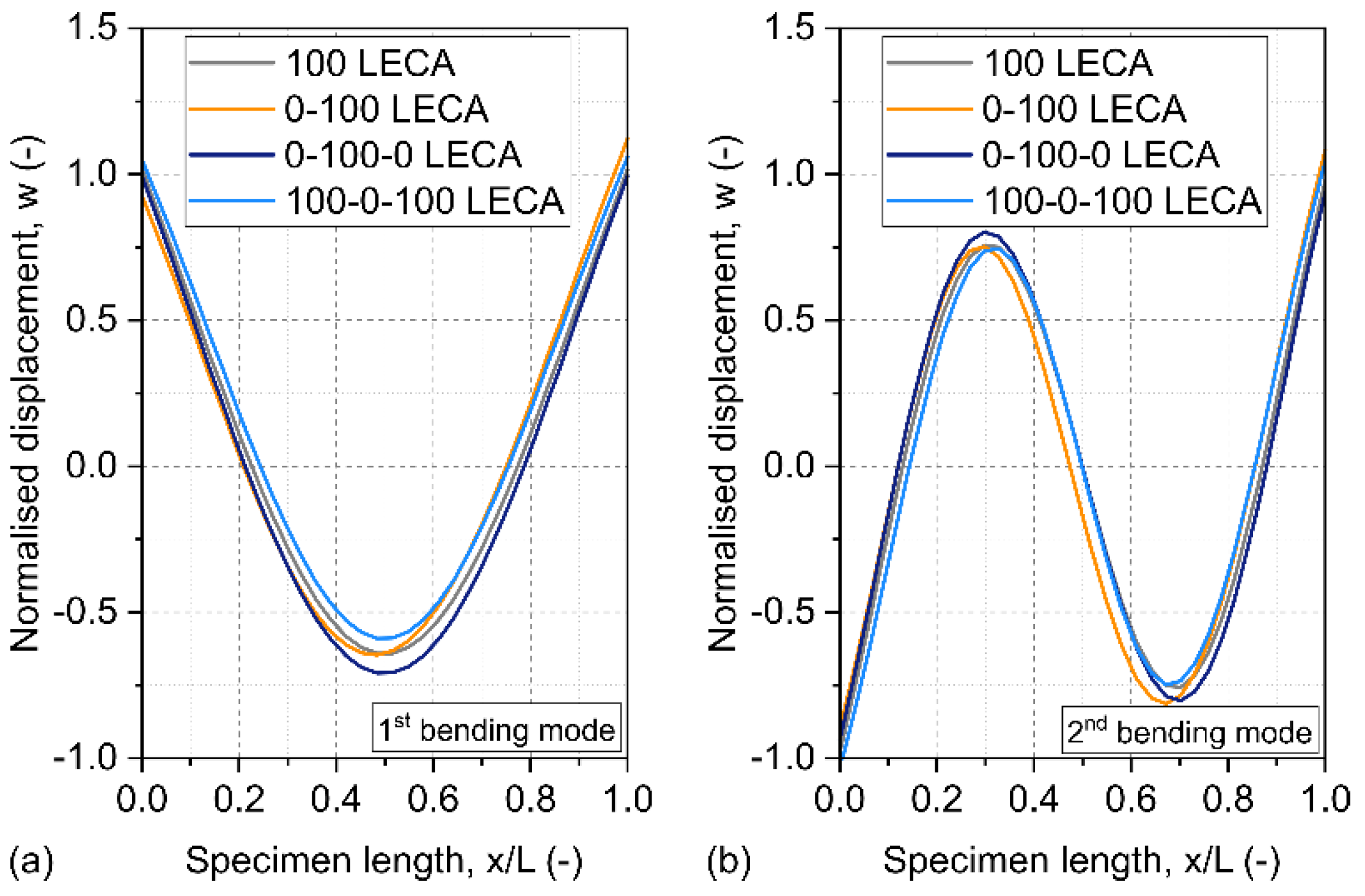
The and values listed in Table 4 were obtained using the spectral collocation method discussed in the Methods section. This method produced the exact same results as solving Equation (4) for samples with a uniform density distribution, but noticeably modified the fitted material parameters for samples with varying distributions of the filler materials (0-100 LECA, 0-100-0 LECA, and 100-0-100 LECA). Here the solutions of Equation (4), the values obtained considering uniform density, are indicated in brackets for comparison. The spectral collocation method produced lower effective elastic moduli values for the 0-100 LECA sample, in which the density distribution was linear, and for 100-0-100 LECA, which was most dense in the middle. For 100-0-100 LECA, which was least dense in its center, the correction resulted in an increase in the effective elastic modulus. If the edges are less dense, the sample can move more easily with a particular vibration pattern. In the parameter fitting scheme, the measured density distributions of graded samples were approximated by first and second order polynomials, as illustrated in Figure 8.
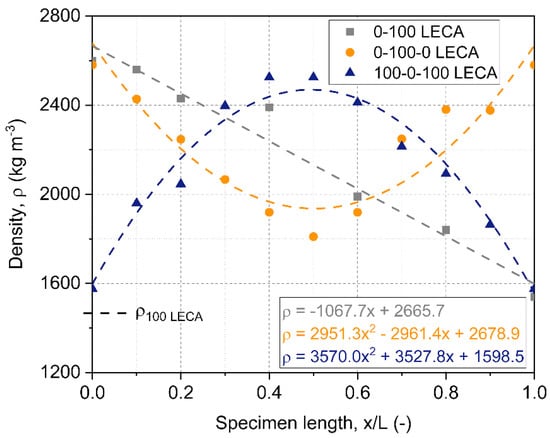
Figure 8.
Density and fitted curves for modal analysis in the case of graded samples (0-100 LECA, 0-100-0 LECA, and 100-0-100 LECA).
Considering these density functions, the resulting bending mode shapes are shown in Figure 9. There is a noticeable difference between these functions, with higher displacement values corresponding to cross sections with lower density values.
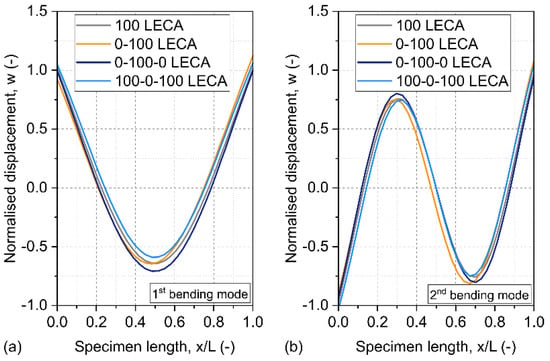
Figure 9.
Modal analysis results for different GMF samples. Panel (a) shows the measured and fitted density functions, while panel (b) illustrates the resulting first and second bending mode shapes.
The above-mentioned results are important and provide inevitable support for future, application-focused GMSF production methods. By the correct design of the density and the composition of the GMSFs, the mechanical properties could be tailored properly for the given application. For example, and in the practical point of view, the GMSFs for energy absorption could be tailored to have an energy absorption characteristic during the compression procedure itself.
4. Conclusions
In this research, 0.54–0.82 relative density GMFs were produced by a low-pressure infiltration method.
The compressive properties of both LECA- and CHS-filled aluminum matrix foams produced were set on a large scale by adjusting the density by adding specific amounts of Al particles.
An experimental modal analysis was employed to approximate the effective elastic moduli of the produced samples, based on the first two natural frequencies obtained from impact tests, and employing the Timoshenko beam theory. Modal damping was also measured and investigated, but the obtained results turned out to be meaningless due to high deviations, comparable in order of magnitude to the damping values themselves.
To fit material parameters to samples with non-uniform density distributions, spectral collocation was employed. Taking the varying density distributions into account produced clear differences in both the fitted material parameters and the mode shapes, proving simple averaging of the density to be inaccurate.
Based on this paper’s findings, it should be possible to artificially modify the effective material properties of metal foams to better fit industrial requirements by simply varying the distribution of the filler material. Further work should be devoted to this issue.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.N.O.; methodology, A.K., Z.I. and D.K.; validation, I.N.O.; formal analysis, Z.I.; investigation, A.K., Z.I., D.B.K. and D.K.; resources, I.N.O.; data curation, A.K., Z.I. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.K. and Z.I.; writing—review and editing, I.N.O.; visualization, Z.I., A.K. and D.B.K.; supervision, I.N.O.; project administration, D.K.; funding acquisition, I.N.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research reported in this paper is part of project No. BME-NVA-02, implemented with the support provided by the Ministry for Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the National Research, Development, and Innovation Fund, financed under the TKP2021 funding scheme. The research reported in this paper and carried out at BME was supported by the NRDI Fund (TKP2020 NC, Grant No. BME-NCS) based on the charter of bolster issued by the NRDI Office under the auspices of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology. This project was funded by the Hungarian NKFI FK 124361.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to institutional restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hangai, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Yamaguchi, R.; Utsunomiya, T.; Kitahara, S.; Kuwazuru, O.; Yoshikawa, N. Nondestructive observation of pore structure deformation behavior of functionally graded aluminum foam by X-ray computed tomography. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, X.-Y.; Wang, K.; He, S.-Y.; Liu, J.-G.; Zhao, W.; Gong, X.-L.; Yu, J. Fabrication of functionally radial graded metallic foam. Mater. Lett. 2020, 264, 127292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Conway, S.; Belova, I.V.; Murch, G.E.; Fiedler, T. Influence of particle arrangement on the compression of functionally graded metal syntactic foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, N.; Murch, G.E.; Belova, I.V.; Fiedler, T. Functionally graded metal syntactic foam: Fabrication and mechanical properties. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Mirbagheri, S.M.H.; Ramiani, A.J. Efficient energy absorption of functionally-graded metallic foam-filled tubes under impact loading. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Eng. Ed.) 2021, 31, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Compressive properties and failure mechanisms of gradient aluminum foams prepared by a powder metallurgy method. Metals 2021, 11, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Li, J.S.; Hu, R.; Kou, H.C.; Zhou, L. Mechanical properties of porous titanium with different distributions of pore size. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (Eng. Ed.) 2013, 23, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Petrudi, A.M. Optimization and experimental investigation of the ability of new material from aluminum casting on pumice particles to reduce shock wave. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2020, 64, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekoz, N.; Oktay, E. Mechanical properties of low alloy steel foams: Dependency on porosity and pore size. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 576, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.A.; Gábora, A.; Mankovits, T. Influence of the manufacturing parameters on the compressive properties of closed cell aluminum foams. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2020, 64, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Si-Yuan, H.; Jia-Gui, L.; Wei, Z.; Xiao-Lu, G.; Jin, Y. Density gradient tailoring of aluminum foam-filled tube. Compos. Struct. 2019, 220, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, S.P. LXVI. On the Correction for Shear of the Differential Equation for Transverse Vibrations of Prismatic Bars. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1921, 41, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, N.F.J.; van der Merwe, A.J. Natural frequencies and modes of a Timoshenko beam. Wave Motion 2006, 44, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertelli, P.; Esposito, S.; Mussi, V.; Goletti, M.; Monno, M. Effect of metal foam on vibration damping and its modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhart, J.; Baumeister, J.; Weber, M. Damping properties of aluminium foams. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 205, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kádár, C.; Szlancsik, A.; Dombóvári, Z.; Orbulov, I.N. Monitoring the failure states of a metal matrix syntactic foam by modal analysis. Mater. Lett. 2019, 257, 126733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, B.; McLaughlin, J.R. Asymptotic Formulas for the Eigenvalues of the Timoshenko Beam. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2001, 253, 341–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Trefethen, L.N. 6. Chebyshev Differentiation Matrices. In Spectral Methods in MATLAB; Society of Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).