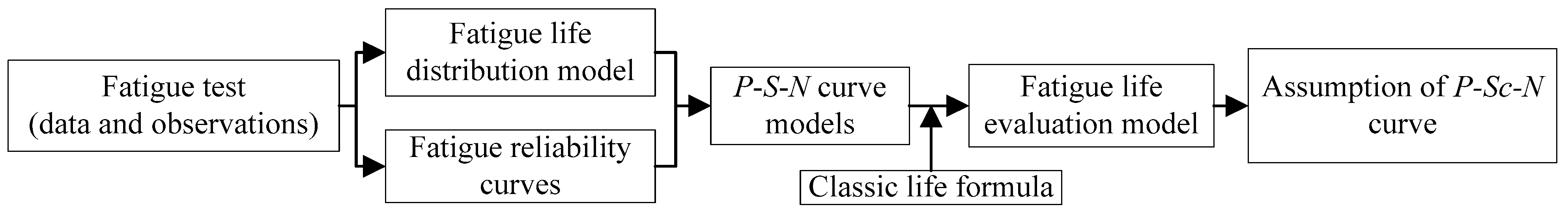
Fatigue Life Evaluation Considering Fatigue Reliability and Fatigue Crack for FV520B-I in VHCF Regime Based on Fracture Mechanics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods Fatigue Test
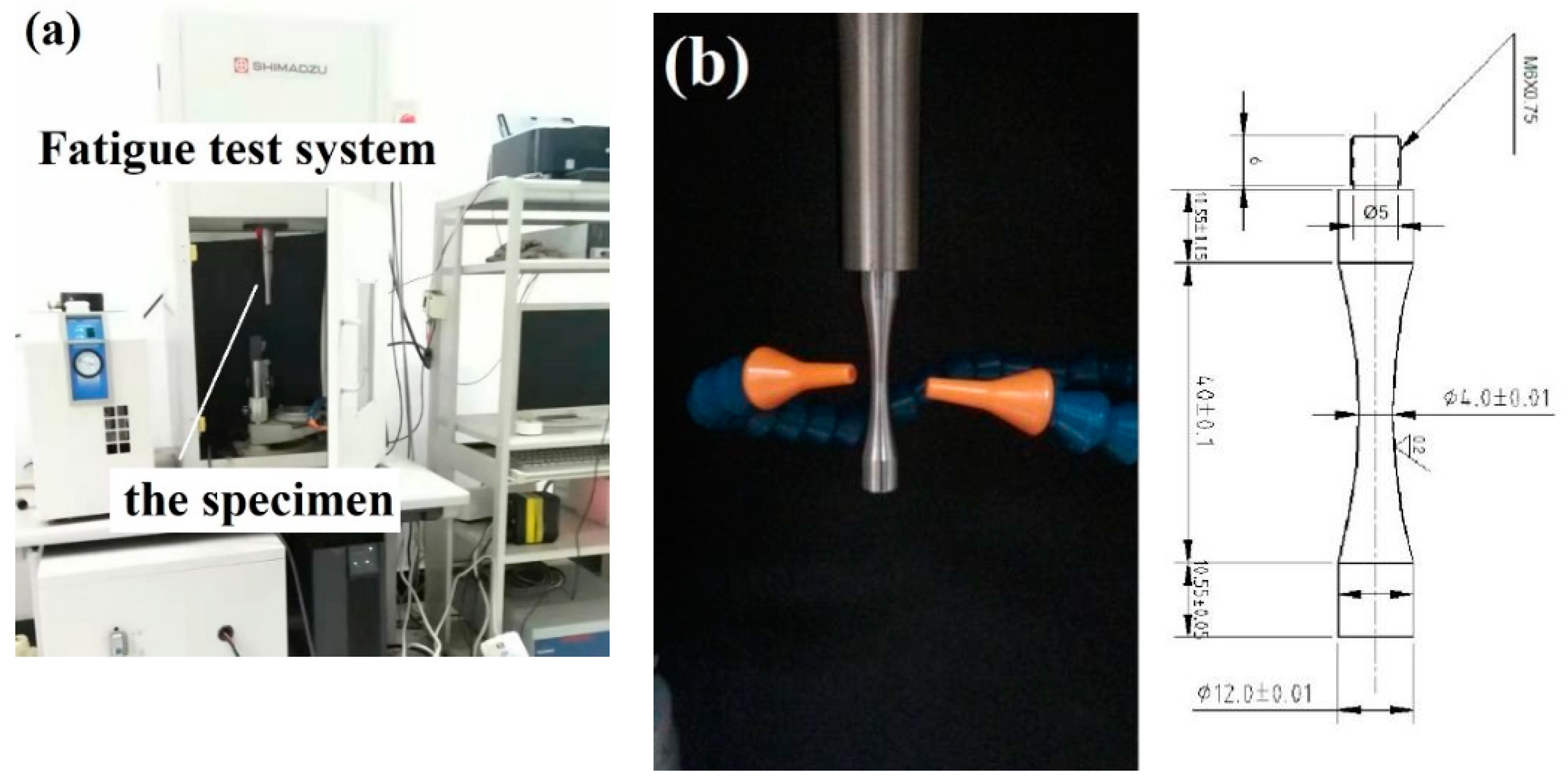
2.1. Test Method
2.2. Material and Specimen
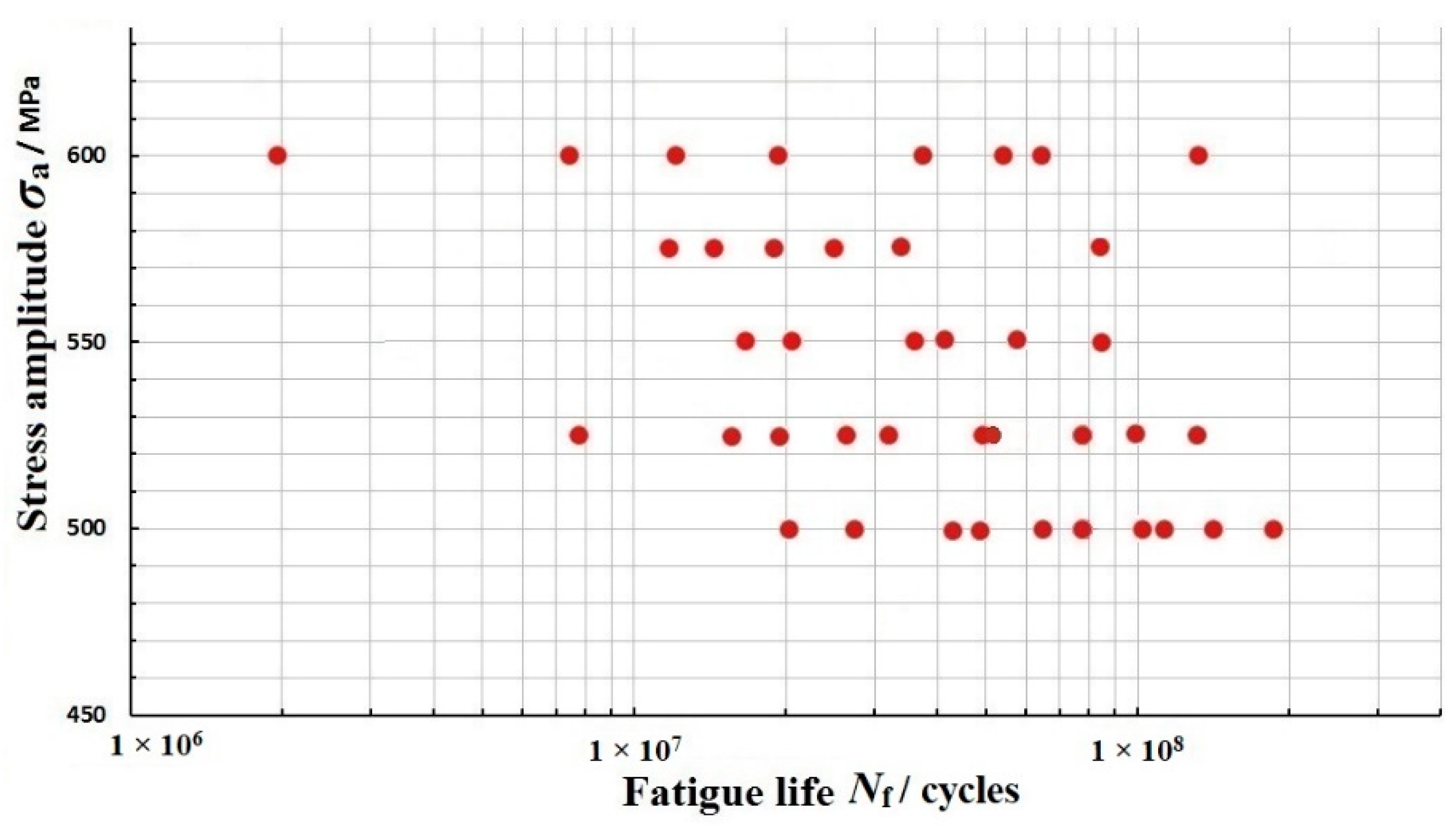
2.3. The Results and Observations
3. Fatigue Reliability of FV520B-I in the VHCF Regime
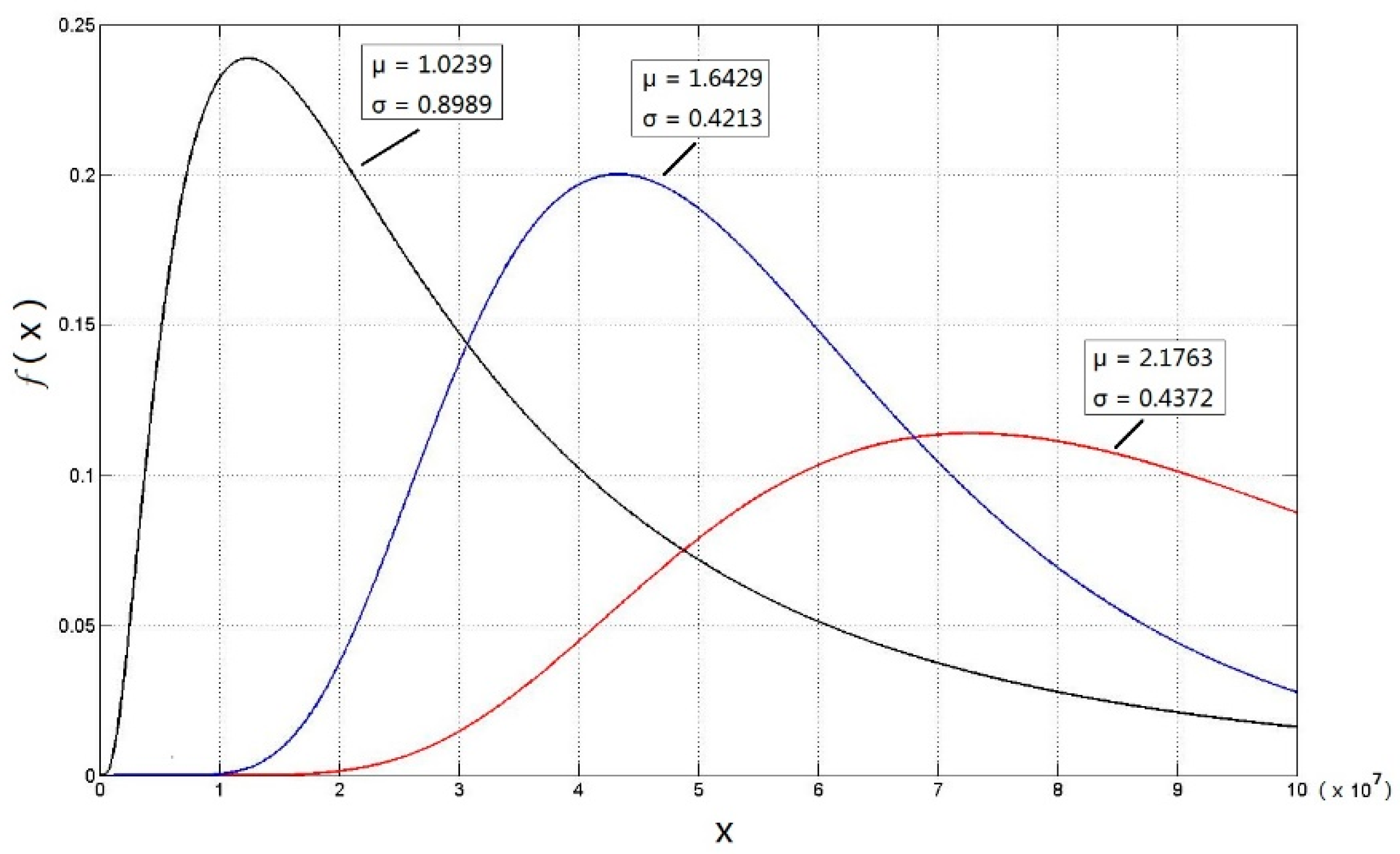
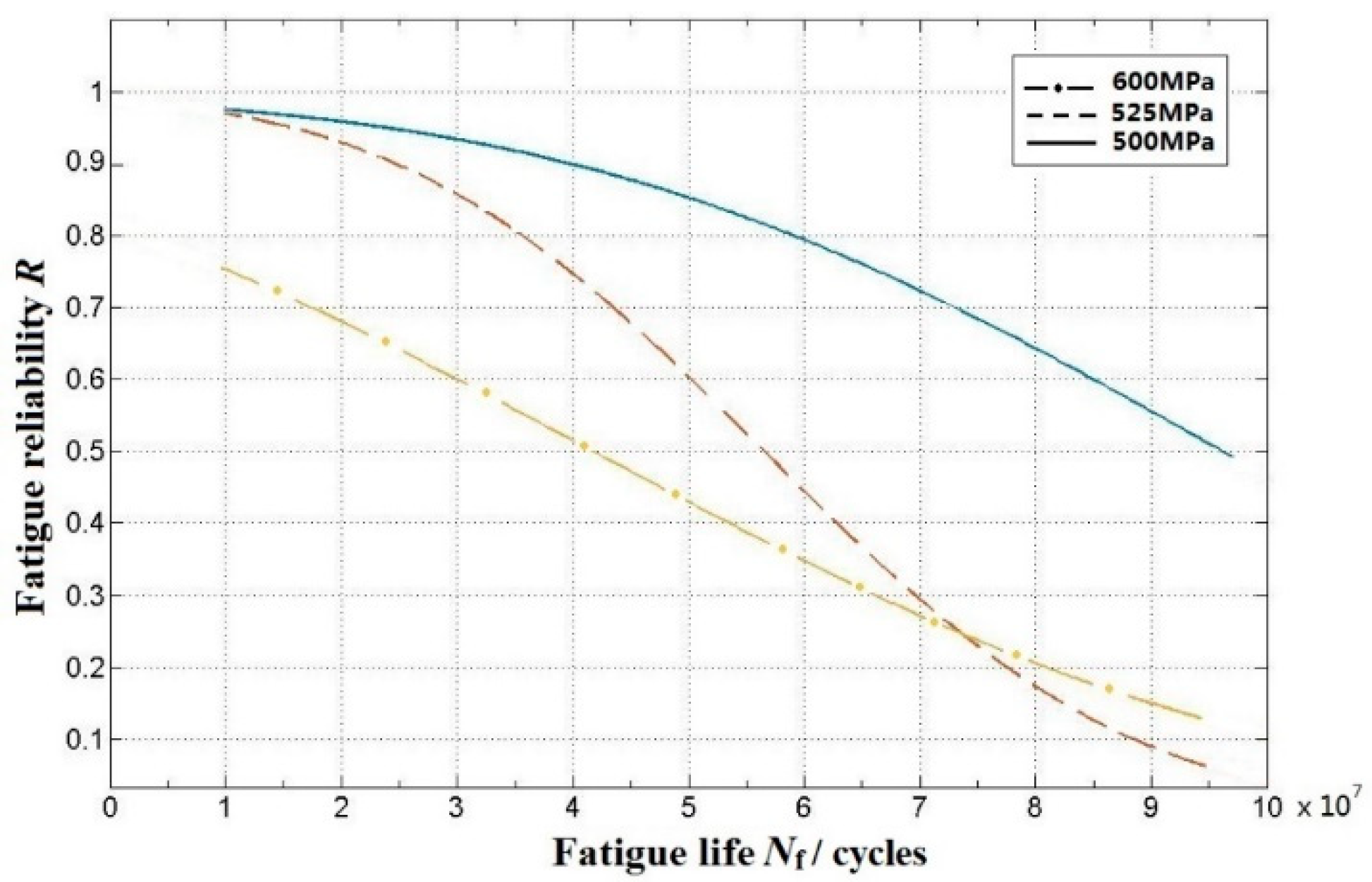
3.1. Very-High Cycle Fatigue Life Distribution of FV520B-I in the VHCF Regime
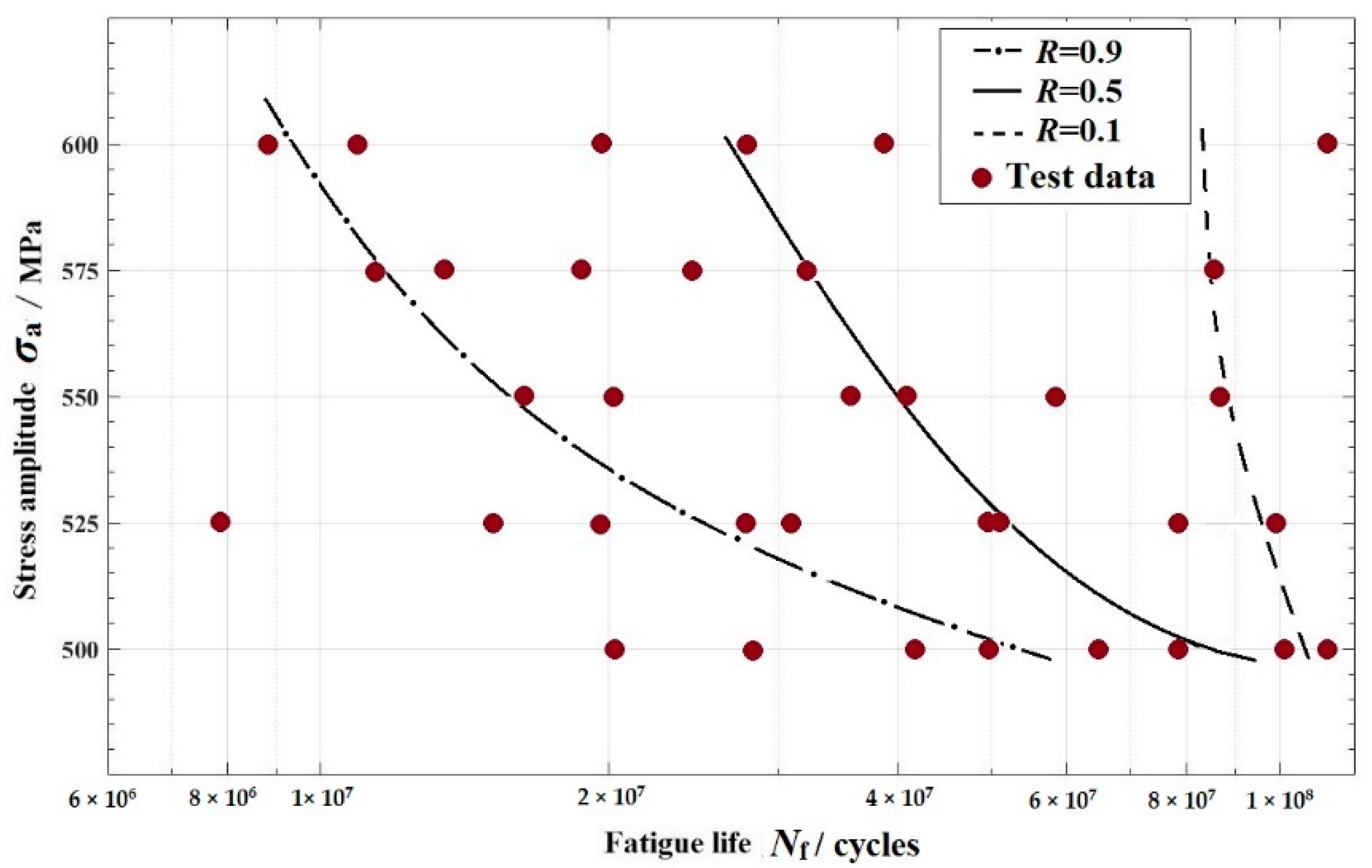
3.2. The P-S-N Curve Estimation
3.3. Discussion
4. The Fatigue Life Evaluation for FV520B-I
4.1. The Fatigue Life Evaluation Model Considering Reliability
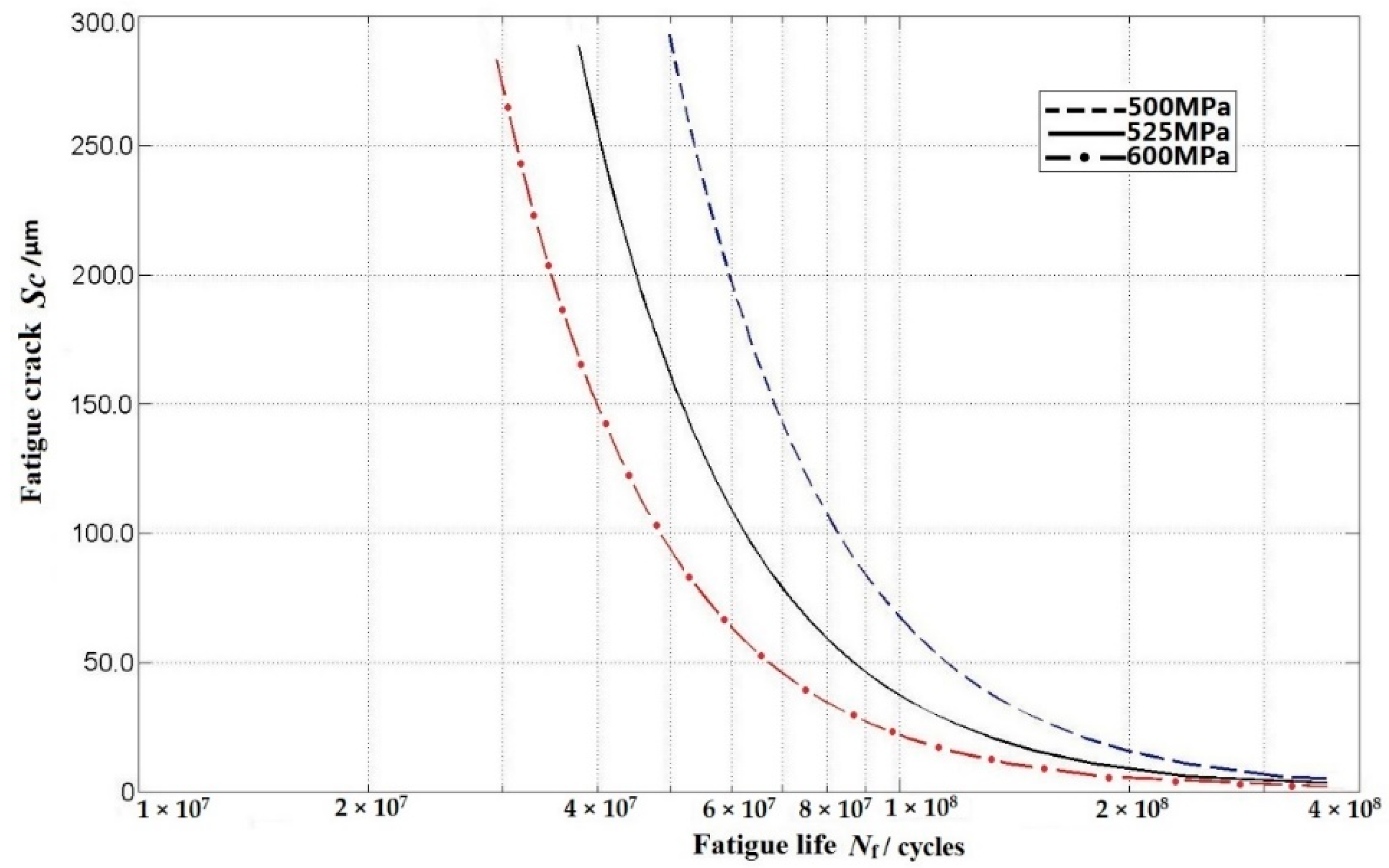
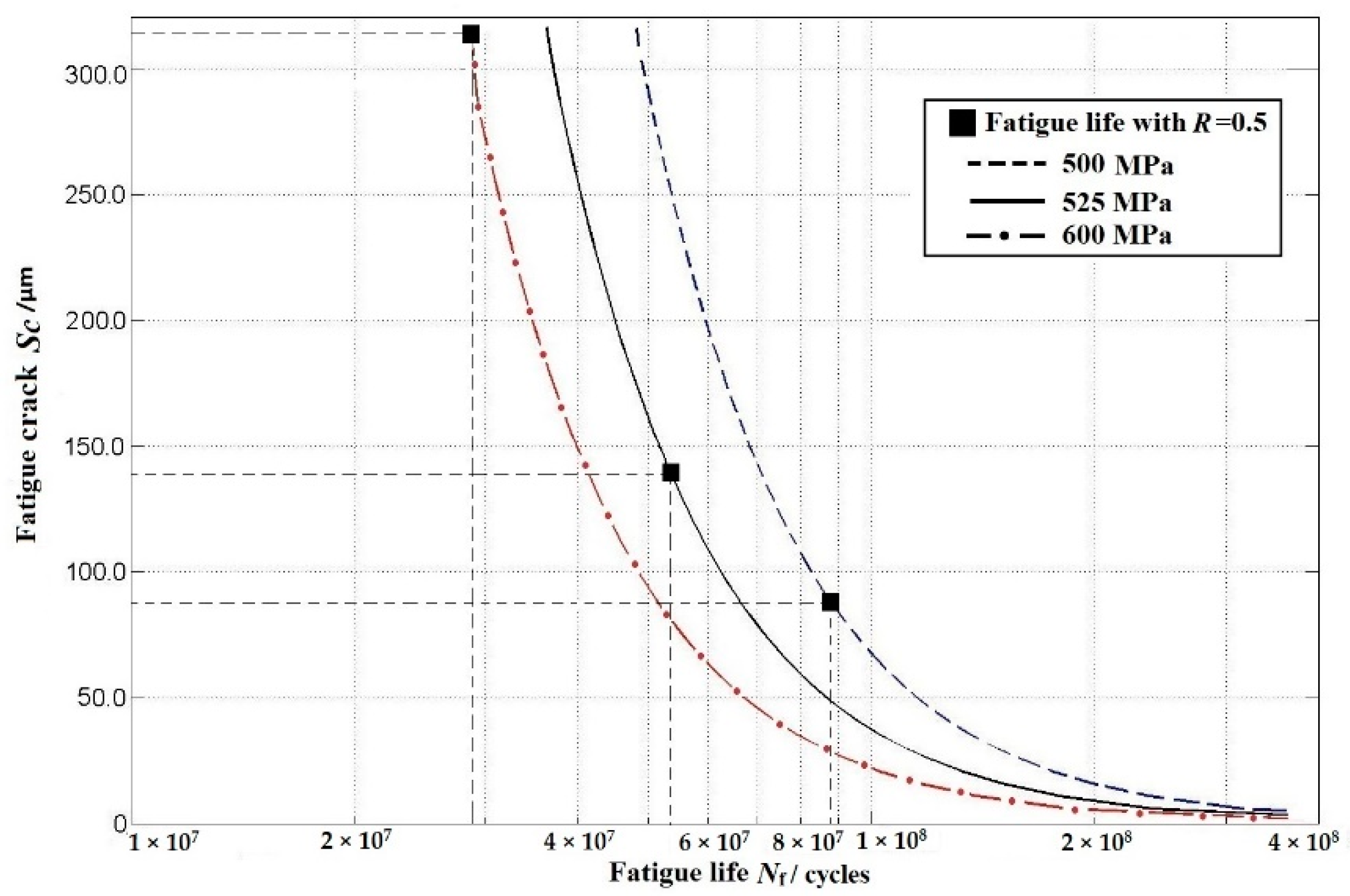
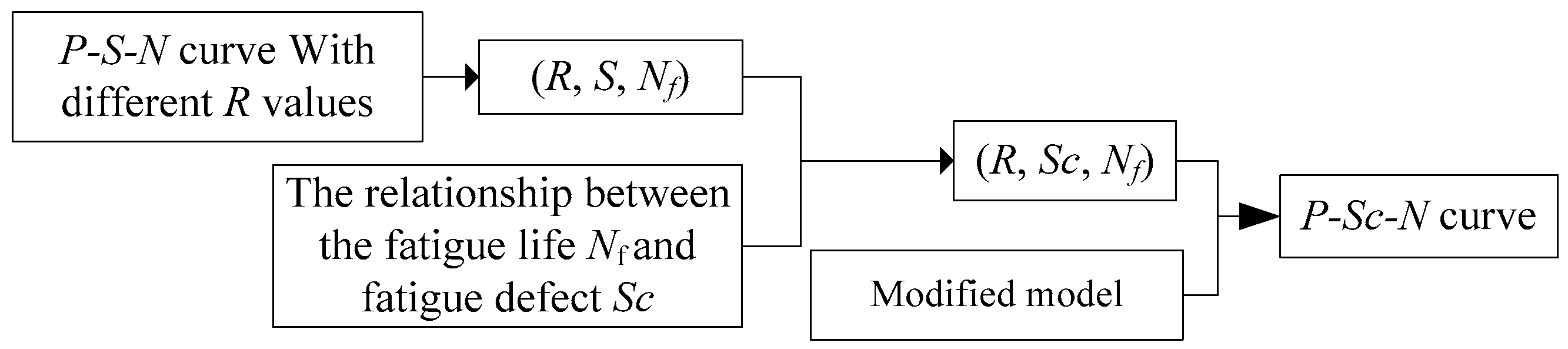
4.2. Further Assumption: The P-Sc-N Curve
4.3. Discussions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The ultrasonic fatigue test for FV520B-I was performed. Obvious evidence of very-high cycle fatigue failure in FV520B-I, including “fish-eye” and GBF regions, were detected on the fracture surface; these are constant with the reported results of the very-high cycle fatigue study.
- (2)
- A three-parameter model for FV520B-I was achieved. The unknown parameters related to FV520B-I were obtained, and the fatigue reliability of FV520B-I in the VHCF regime was modeled. The corresponding P-S-N curves with different fatigue reliability values were drawn, respectively. The determination of the three-parameter model and the P-S-N curve for FV520B-I make up for the lack of a fatigue reliability study of FV520B-I in the VHCF regime.
- (3)
- A new fatigue evaluation model for FV520B-I, considering fatigue reliability and fatigue crack, was developed based on the P-S-N curves. This new model was verified using the test data and the errors were in an acceptable range.
- (4)
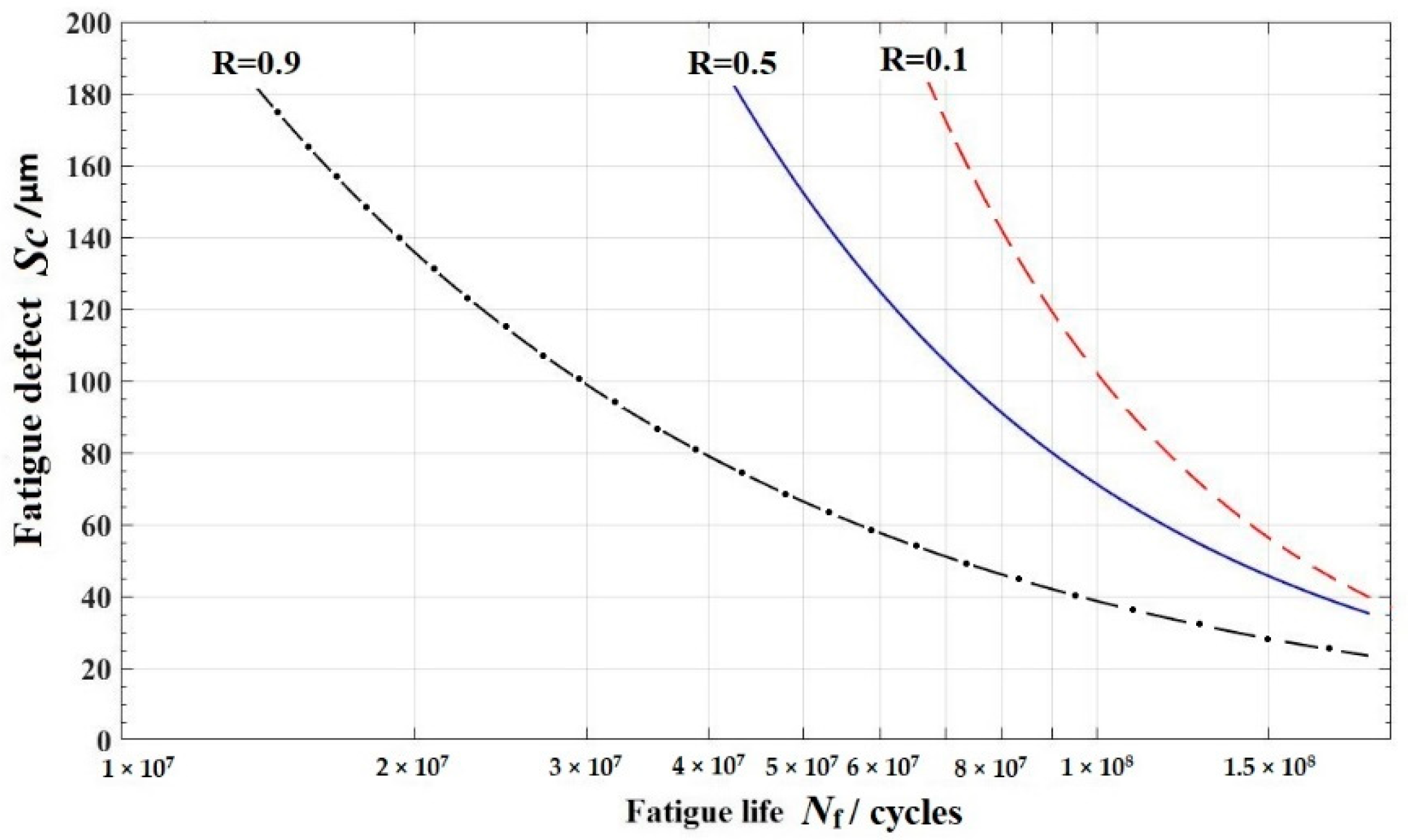
- A new relationship curve between fatigue reliability, fatigue crack and fatigue life N for FV520B-I in the VHCF regime was proposed: the P-Sc-N curve. The P-Sc-N curve model with different reliability values was developed with the combined application of the classic formula and test data. The corresponding P-S-N curves with different fatigue reliability values were drawn, respectively.
- (5)
- Using the P-Sc-N curve for FV520B-I, it was observed that there is a negative correlation between fatigue cracking and the reliability for FV520B-I. The new P-Sc-N curve is also useful for the decision-making process in re-manufacturing, based on the fatigue cracking information.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, Q.C.; Zhang, H.C. Study of fatigue crack critical threshold of remanufacturing cores and judgment of re-manufacturability based on fatigue crack. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. CHS 2017, 53, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.Q.; Wang, P.F.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.F. Fatigue behavior and mechanism of FV520B-I welding seams in a very high cycle regime. Int. J. Fatigue. 2016, 87, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Maekawa, Z. Fatigue Life Analysis of Particle Dispersed Composite Materials by Reliability Concept. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 1978, 27, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibull, W. Fatigue Testing and Analysis of Results; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, W. A Statistical function of the wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Smaga, M.; Boemke, A.; Daniel, T.; Skorupski, R.; Sorich, A.; Beck, T. Fatigue behavior of metastable austenitic stainless steels in LCF, HCF and VHCF regimes at ambient and elevated temperatures. Metals 2019, 9, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozumek, D.; Marciniak, Z.; Lesiuk, G.; Correia, J.A.; de Jesus, A.M. Experimental and numerical investigation of mixed mode I+ II and I+ III fatigue crack growth in S355J0 steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 113, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.S.; Liu, X.L.; Lei, Z.Q.; Sun, C.Q. The formation mechanism of characteristic region at crack initiation for very-high-cycle fatigue of high-strength steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 89, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirsching, P.H.; Wu, Y.T. Probabilistic and Statistical Methods of Fatigue Analysis and Design. Press. Vessel Pip. Technol. A Decade Prog. 1985, 793–819. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Wirsching, P.H. Advanced Reliability Method for Fatigue Analysis. J. Eng. Mech. 1984, 110, 536–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.S.; Wirsching, P.H. Fatigue crack initiation-propagation reliability model. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 1991, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martindale, S.G.; Wirsching, P.H. Reliability-based Progressive Fatigue Collapse. J. Struct. Eng. 1983, 109, 1792–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, L.Z.; Lin, H.Q.; Yang, Y.L. Research on Life of Sliding Rail and Idler Wheel and Reliability Under Constant Amplitude Load. Bearing 2016, 10, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.S.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.C.; Su, Y.N. The bending fatigue strength test based on the reliability of material 8822H. Locomot. Roll. Stock Technol. 2015, 3, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wurzel, G.; Alderliesten, R. Reliability modeling for rotorcraft component fatigue life prediction with assumed usage. Aeronaut. J. 2016, 1, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Paolino, D.S.; Tridello, A.; Chiandussi, G.; Rossetto, M. Effect of crack size on P-S-N curves in Very-High-Cycle Fatigue. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2017, 7, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.W.; Gao, S.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, H.C. Fatigue life assessment of centrifugal compressor impeller based on FEA. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 60, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, S.J.; Gao, S.B.; Hu, Y.W.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, H.C. Fatigue life assessment of the centrifugal compressor impeller with cracks based on the properties of FV520B. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 66, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, Q.C.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.M.; Lu, H.T. The fatigue failure analysis and fatigue life prediction model of FV520B-I as a function of surface roughness in HCF regime. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.L.; Sun, Q.C.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, P.S. Fatigue Life Prediction of FV520B with Internal Inclusions. Mater. Des. 2015, 69, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, Q.C.; Liu, S.J.; Shi, B.W.; Lu, H.T. Giga-fatigue life prediction of FV520B-I with surface roughness. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Shi, B.W.; Zhao, Q.C.; Sun, Q.C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.Y. Fatigue behavior and mechanism of FV520B-I owing to the effect of loading frequency on the fatigue property in HCF and VHCF regime. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2018, 63, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa, K.; Lu, L.; Ishihara, S. S-N curve characteristics and subsurface crack initiation behaviour in ultra-long life fatigue of a high carbon-chromium bearing steel. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. 2010, 24, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, K.; Lu, L. Very high-cycle fatigue behaviour of shot-peened high-carbon-chromium bearing steel. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. 2010, 25, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, K.; Morii, Y.; Nishino, S.; Lu, L. Subsurface crack initiation and propagation mechanism in high-strength steel in a very high cycle fatigue regime. Int. J. Fatigue 2006, 28, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y. Mechanism of fatigue failure in ultralong life regime and application to fatigue design. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. 2002, 15, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, Y.; Takada, M.; Toriyama, T. Super-longlife tension-compression fatigue properties of quenehed a tempered 0.46% Carbon steel. Int. J. Fatigue 1998, 16, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y. Metal Fatigue-Effects of Small Cracks and Nonmetallic Inclusions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 6–7, pp. 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Q. Models for fatigue life distribution. J. Mech. Strength 1991, 13, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.M.; Gao, Z.T. A method for fitting P-S-N curve. Acta Aeronaut. ET Astronaut. Sin. 1988, 9, 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Basquin, O.H. The Exponential Law of Endurance Tests. Am. Soc. Test. Mater. Proc. 1910, 10, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.; Pan, J. A maximum likelihood method for estimating P-S-N curves. Int. J. Fatigue 1997, 19, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Wang, J.N.; Gao, Q. A unified classical maximum likelihood approach for estimating P-S-N curves of three commonly used fatigue stress-life relations. Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 2001, 18, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Deng, H.L.; Zhang, X.H. A method to building probabilistic S-N curves for multiple failure modes in very high cycle fatigue. Eng. Mech. 2016, 33, 218–224. [Google Scholar]


| Chemical Composition | C | Si | Ni | Cu | S | Cr | Mo | Nb | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.02–0.07 | 0.15–0.7 | 5–6 | 1.3–1.8 | <0.025 | 13–14.5 | 1.3–1.8 | 0.25–0.45 | Bal |
| Mechanical Parameters | Elastic Modulus E (GP) | Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) | Yield Strength Rp0.2 (MPa) | Vickers Hardness HV | Elongation A (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FV520B-I | 194 | 1180 | 1029 | 380 | 16.07 |
| Stress Amplitude | 500 MPa | 525 MPa | 600 MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| location parameter μ | 2.1673 | 1.6429 | 1.0239 |
| proportional parameter σ | 0.4372 | 0.4213 | 0.8989 |
| Stress Amplitude σa/MPa | S1 | S2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| The fatigue reliability R | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Fatigue life Nf | 2.78 × 107 | 5.17 × 107 | 8.73 × 107 |
| S0,0.5 | α0.5 | C0.5 |
|---|---|---|
| 481.1823 | 0.6205 | 53.9676 |
| Stress Amplitude σa/MPa | 600 | 525 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue reliability R | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Fatigue life Nf | 2.78 × 107 | 5.17 × 107 | 8.73 × 107 |
| Fatigue crack Sc/μm | 322 | 139.4 | 90.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Fatigue Life Evaluation Considering Fatigue Reliability and Fatigue Crack for FV520B-I in VHCF Regime Based on Fracture Mechanics. Metals 2020, 10, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10030371
Wang J, Yang Y, Yu J, Wang J, Du F, Zhang Y. Fatigue Life Evaluation Considering Fatigue Reliability and Fatigue Crack for FV520B-I in VHCF Regime Based on Fracture Mechanics. Metals. 2020; 10(3):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10030371
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinlong, Yuxing Yang, Jing Yu, Jingsi Wang, Fengming Du, and Yuanliang Zhang. 2020. "Fatigue Life Evaluation Considering Fatigue Reliability and Fatigue Crack for FV520B-I in VHCF Regime Based on Fracture Mechanics" Metals 10, no. 3: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10030371
APA StyleWang, J., Yang, Y., Yu, J., Wang, J., Du, F., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Fatigue Life Evaluation Considering Fatigue Reliability and Fatigue Crack for FV520B-I in VHCF Regime Based on Fracture Mechanics. Metals, 10(3), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10030371





