Acute (-)-Epicatechin Consumption: Effects on Local Vasodilation Following Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Exercise Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment 1—Resistance Exercise and Vasodilation
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Protocol
2.1.3. Barbell Curl 1-RM Assessment
2.1.4. Venous Blood Sampling
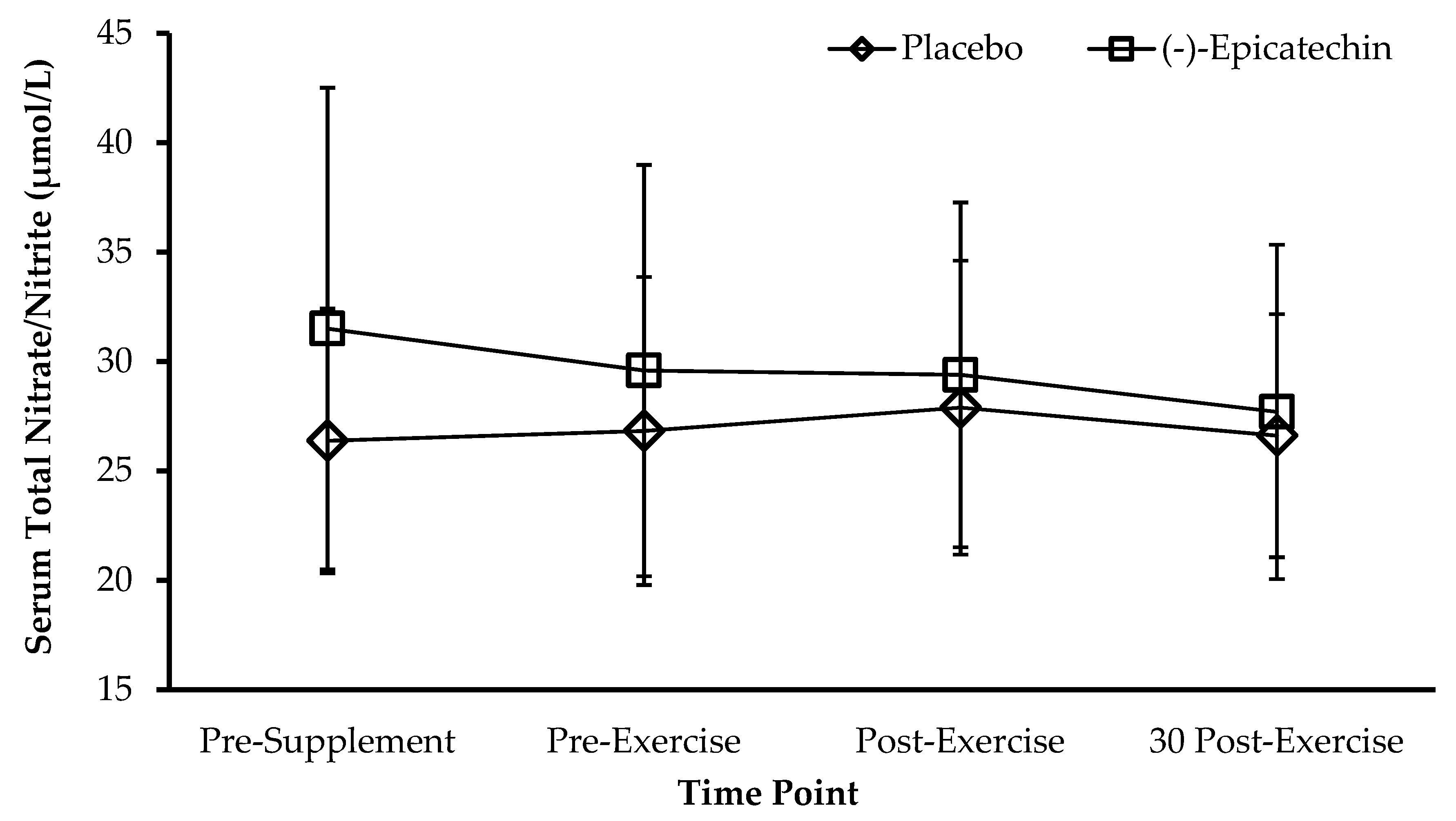
2.1.5. Total Serum Nitrate/Nitrite Measurement
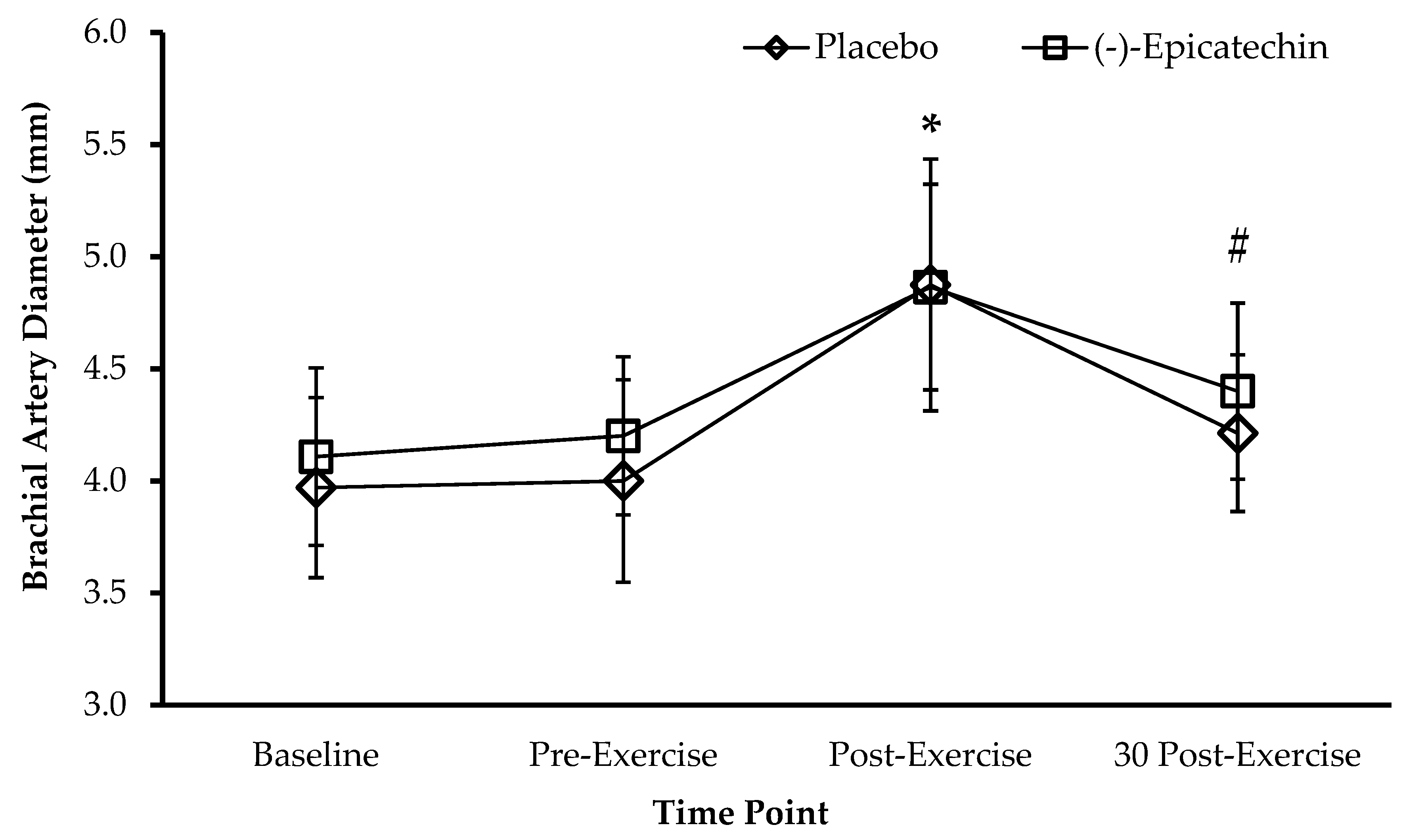
2.1.6. Brachial Artery Diameter Measurement
2.1.7. Statistical Analyses
2.2. Experiment 2—High-Intensity Exercise Performance
2.2.1. Participants
2.2.2. Protocol
2.2.3. 15.5 CrossFit® Open Workout
2.2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1—Resistance Exercise and Vasodilation
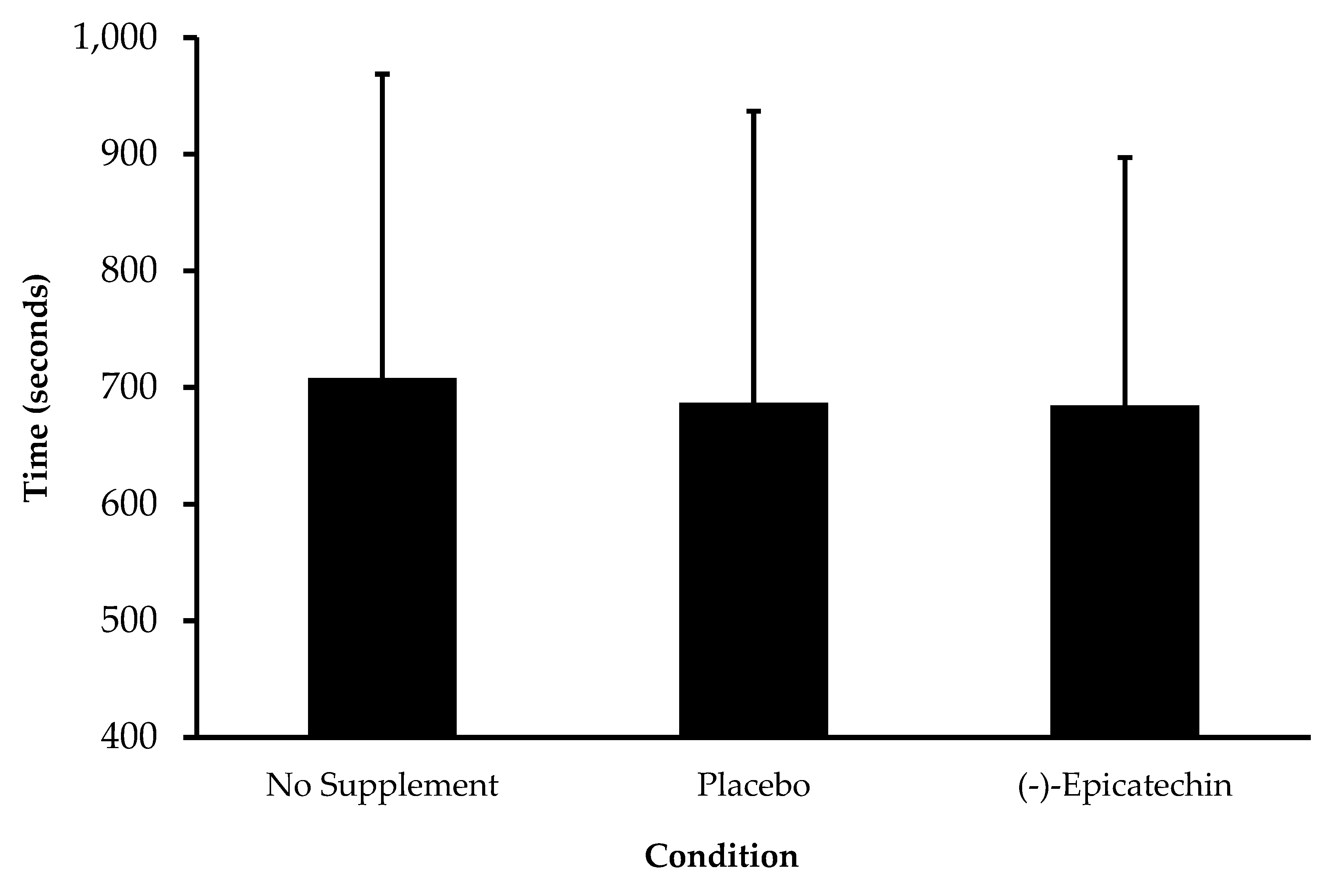
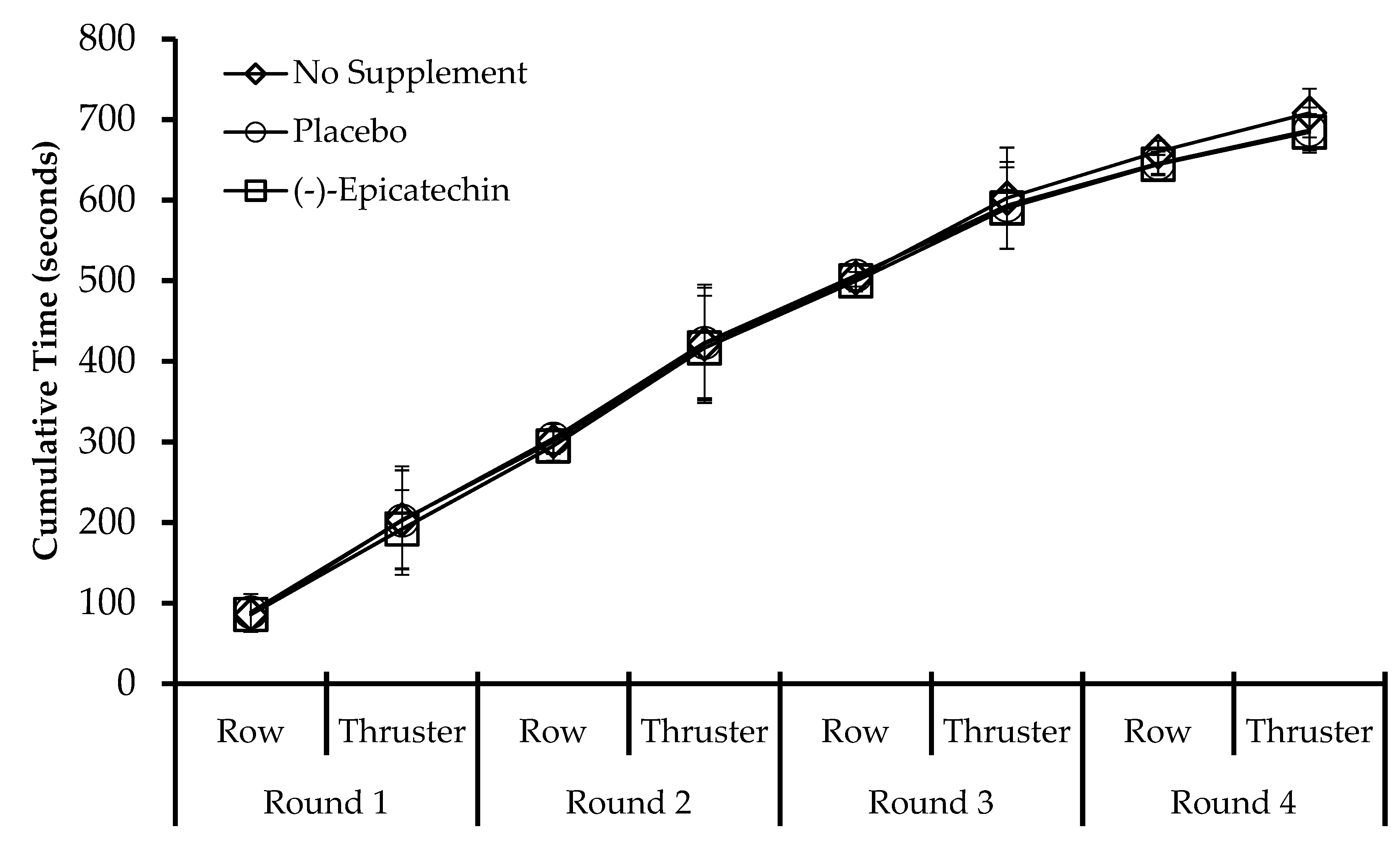
3.2. Experiment 2—High-Intensity Exercise Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andújar, I.; Recio, M.C.; Giner, R.M.; Ríos, J.L. Cocoa Polyphenols and Their Potential Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, H.; Heiss, C.; Balzer, J.; Kleinbongard, P.; Keen, C.L.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Sies, H.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Schmitz, H.H.; Kelm, M. (-)-Epicatechin mediates beneficial effects of flavanol-rich cocoa on vascular function in humans. PNAS 2006, 103, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, W.M.; Hodgson, J.M.; Proudfoot, J.M.; McKinley, A.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Croft, K.D. Pure dietary flavonoids quercetin and (−)-epicatechin augment nitric oxide products and reduce endothelin-1 acutely in healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, J.I.; Momma, T.Y.; Heiss, C.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Schroeter, H.; Keen, C.L. The stereochemical configuration of flavanols influences the level and metabolism of flavanols in humans and their biological activity in vivo. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2011, 50, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, C.F.; Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Shiva, S.; Ramírez-Sánchez, I.; Taub, P.R.; Su, Y.; Ceballos, G.; Dugar, S.; Schreiner, G.; Villarreal, F. Pharmacokinetic, partial pharmacodynamic and initial safety analysis of (-)-epicatechin in healthy volunteers. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprotosoaie, A.C.; Miron, A.; Trifan, A.; Luca, V.S.; Costache, I.-I. The Cardiovascular Effects of Cocoa Polyphenols—An Overview. Diseases 2016, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.A.; Blahnik, Z.J.; Prahadeeswaran, S.; McKinley-Barnard, S.K.; Holden, S.L.; Waldhelm, A. (-)-Epicatechin Supplementation Inhibits Aerobic Adaptations to Cycling Exercise in Humans. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G.; Ortiz-Vilchis, P.; Vacaseydel, C.M.; Rubio-Gayosso, I.; Meaney, E.; Villarreal, F.; Ramírez-Sánchez, I.; Ceballos, G. Acute effects of an oral supplement of (-)-epicatechin on postprandial fat and carbohydrate metabolism in normal and overweight subjects. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgrove, J.; Farrell, E.; Gleeson, M.; Williamson, G.; Cooper, K. Regular dark chocolate consumption’s reduction of oxidative stress and increase of free-fatty-acid mobilization in response to prolonged cycling. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellingwerff, T.; Godin, J.P.; Chou, C.J.; Grathwohl, D.; Ross, A.B.; Cooper, K.A.; Williamson, G.; Actis-Goretta, L. The effect of acute dark chocolate consumption on carbohydrate metabolism and performance during rest and exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 39, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroix, L.; Tonoli, C.; Soares, D.D.; Descat, A.; Drittij-Reijnders, M.-J.; Weseler, A.R.; Bast, A.; Stahl, W.; Heyman, E.; Meeusen, R. Acute cocoa Flavanols intake has minimal effects on exercise-induced oxidative stress and nitric oxide production in healthy cyclists: A randomized controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley-Barnard, S.; Andre, T.; Morita, M.; Willoughby, D.S. Combined L-citrulline and glutathione supplementation increases the concentration of markers indicative of nitric oxide synthesis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, H.; Motoyama, T.; Kugiyama, K.; Hirashima, O.; Ohgushi, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Ogawa, H.; Okumura, K.; Yasue, H. Menstrual cyclic variation of endothelium-dependent vasodilation of the brachial artery: Possible role of estrogen and nitric oxide. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1996, 108, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby, D.S.; Boucher, T.; Reid, J.; Skelton, G.; Clark, M. Effects of 7 days of arginine-alpha-ketoglutarate supplementation on blood flow, plasma L-arginine, nitric oxide metabolites, and asymmetric dimethyl arginine after resistance exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, J.K.; Macdonald, M.J.; Hughson, R.L. Time course of brachial artery diameter responses to rhythmic handgrip exercise in humans. Cardiovasc. Res. 1997, 35, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reebok CrossFit Games. Available online: https://games.crossfit.com/workouts/open/2015#workoutsTab5 (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Saarenhovi, M.; Salo, P.; Scheinin, M.; Lehto, J.; Lovró, Z.; Tiihonen, K.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Junnila, J.; Hasselwander, O.; Tarpila, A.; et al. The effect of an apple polyphenol extract rich in epicatechin and flavan-3-ol oligomers on brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilatory function in volunteers with elevated blood pressure. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, M.B.; Engler, M.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Malloy, M.J.; Browne, A.; Chiu, E.Y.; Kwak, H.-K.; Milbury, P.; Paul, S.M.; Blumberg, J.; et al. Flavonoid-rich dark chocolate improves endothelial function and increases plasma epicatechin concentrations in healthy adults. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.D.; Hughes, M.; Gerhard-Herman, M.; Hollenberg, N.K. Flavanol-rich cocoa induces nitric-oxide-dependent vasodilation in healthy humans. J. Hypertens 2003, 21, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorond, F.A.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Fisher, N.D.L. Cerebral blood flow response to flavanol-rich cocoa in healthy elderly humans. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kondo, T.; Kimata, A.; Ueyama, J.; Shirotori, A.; Okada, Y.; Sakui, D.; Nakashima, M.; Yamada, S. Lack of effect of aerobic physical exercise on endothelium-derived nitric oxide concentrations in healthy young subjects. Nagoya J. Med Sci. 2007, 69, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Maroun, M.J.; Mehta, S.; Turcotte, R.; Cosio, M.G.; Hussain, S.N. Effects of physical conditioning on endogenous nitric oxide output during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Yamada, M.; Kurakake, S.; Okamura, N.; Yamaya, K.; Liu, Q.; Kudoh, S.; Kowatari, K.; Nakaji, S.; Sugawara, K. Circulating cytokines and hormones with immunosuppressive but neutrophil-priming potentials rise after endurance exercise in humans. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2000, 81, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delp, M.D. Differential effects of training on the control of skeletal muscle perfusion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, N.A.; Theodore, A.P.; Funderburg, B.R.; Waldhelm, A.; McKinley-Barnard, S.K.; Hudson, G.M. Acute (-)-Epicatechin Consumption: Effects on Local Vasodilation Following Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Exercise Performance. Sports 2020, 8, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020022
Schwarz NA, Theodore AP, Funderburg BR, Waldhelm A, McKinley-Barnard SK, Hudson GM. Acute (-)-Epicatechin Consumption: Effects on Local Vasodilation Following Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Exercise Performance. Sports. 2020; 8(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Neil A., Andrew P. Theodore, Brandon R. Funderburg, Andy Waldhelm, Sarah K. McKinley-Barnard, and Geoffrey M. Hudson. 2020. "Acute (-)-Epicatechin Consumption: Effects on Local Vasodilation Following Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Exercise Performance" Sports 8, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020022
APA StyleSchwarz, N. A., Theodore, A. P., Funderburg, B. R., Waldhelm, A., McKinley-Barnard, S. K., & Hudson, G. M. (2020). Acute (-)-Epicatechin Consumption: Effects on Local Vasodilation Following Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Exercise Performance. Sports, 8(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020022





