Integrative Taxonomy of Polynema (Doriclytus) (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Oriental China: Three New Species and Five New Records Revealed by Morphological and Molecular Analyses †
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. Morphological Study and Imaging
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Processing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Identification and Delimitation
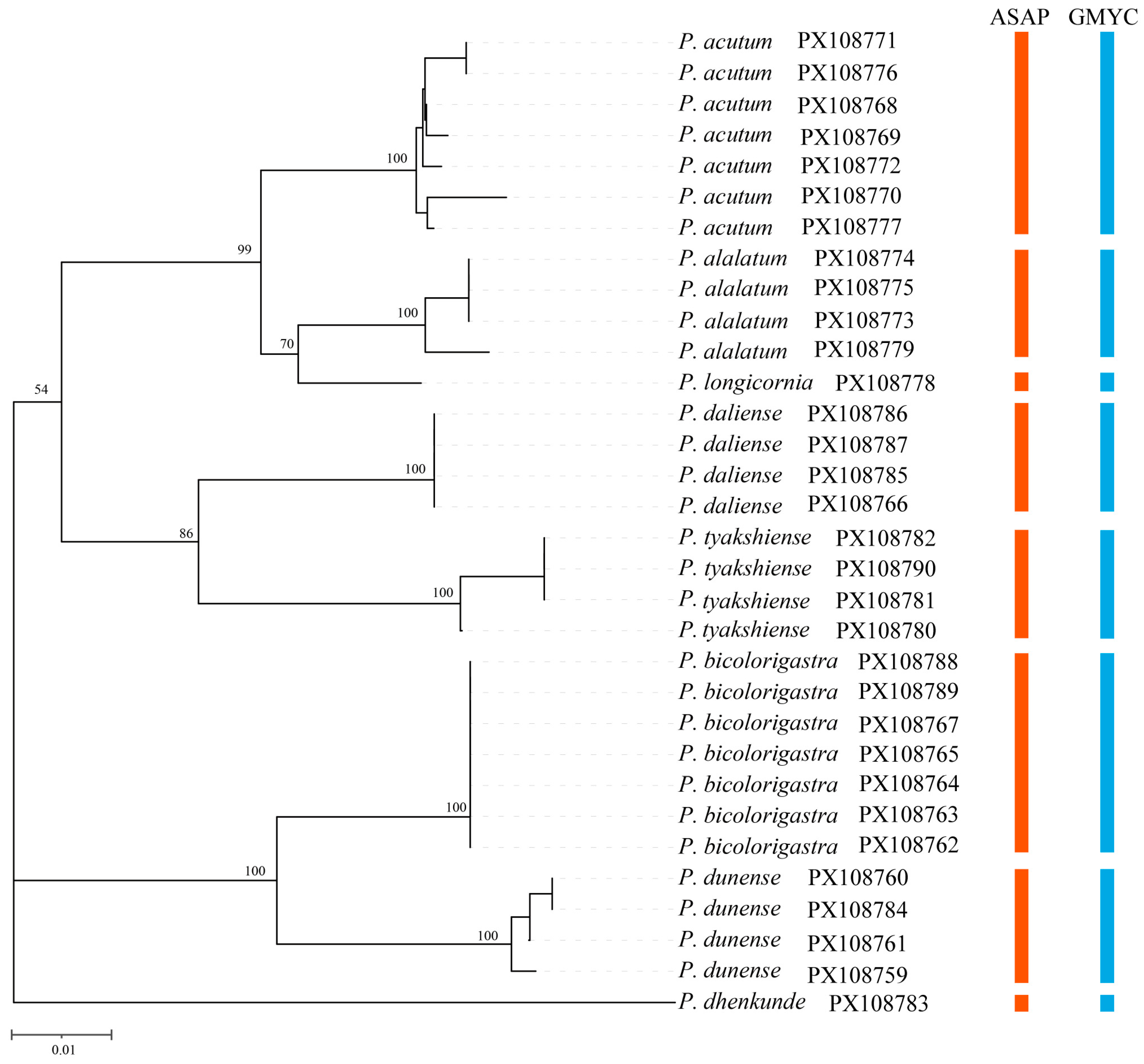
3.2. Taxonomic Treatment of Polynema (Doriclytus)
3.2.1. Key to Species of Polynema (Doriclytus) from the Oriental Region of China (Females)
- 1
- Antennal scape with cross ridges…………P. (Doriclytus) alalatum Rehmat & Anis
- -
- Antennal scape smooth………………...…………………………………………………2
- 2
- Scutellum with frenal foveae……………………..………………………………………3
- -
- Scutellum without frenal foveae…………………………………………………………4
- 3
- Scutellum with a row of foveae; clava relatively narrow and long, at least 3.8× as long as wide; F2 and F3 subequal in length, both the longest funiculars; ovipositor 0.6–0.7× length of metatibia…………………………….… P. (Doriclytus) dunense Hayat & Anis
- -
- Scutellum with bits of foveae; clava at most 3.6× as long as wide; F2 the longest funicular, F3 shorter than F2; ovipositor 0.8–1.2× length of metatibia……………………………….. …..P. (Doriclytus) bicolorigastra Rehmat & Anis
- 4
- Antenna with clava fusiform, apically acute; ovipositor markedly exserted beyond apex of gaster ………………………..P. (Doriclytus) acutum Wang & Aishan sp. nov.
- -
- Antenna with clava not acute; ovipositor exserted slightly beyond apex of gaster…...5
- 5
- Fore wing relatively narrow, 3.7–4.3× as long as wide; propodeum with a short, inconspicuous median carina……………..P. (Doriclytus) dhenkunde Mani & Saraswat
- -
- Fore wing relatively wide, at most 3.5 × as long as wide……………………………….6
- 6
- Propodeum with a complete median carina, extending to anterior margin of propodeum…………………………..P. (Doriclytus) longicornia Wang & Aishan sp. nov.
- -
- Propodeum with median carina incomplete, not extending to anterior margin of propodeum………………………….…………………………………………………………..7
- 7
- Posterior half of petiole with numerous transverse striations; ovipositor 1.2–1.5× as long as metatibia………………….. P. (Doriclytus) daliense Wang & Aishan sp. nov.
- -
- Posterior half of petiole smooth; ovipositor 0.9–1.0× length of metatibia…………………………………………P. (Doriclytus) tyakshiense Irfan & Anis
3.2.2. Polynema (Doriclytus) Foerster, 1847
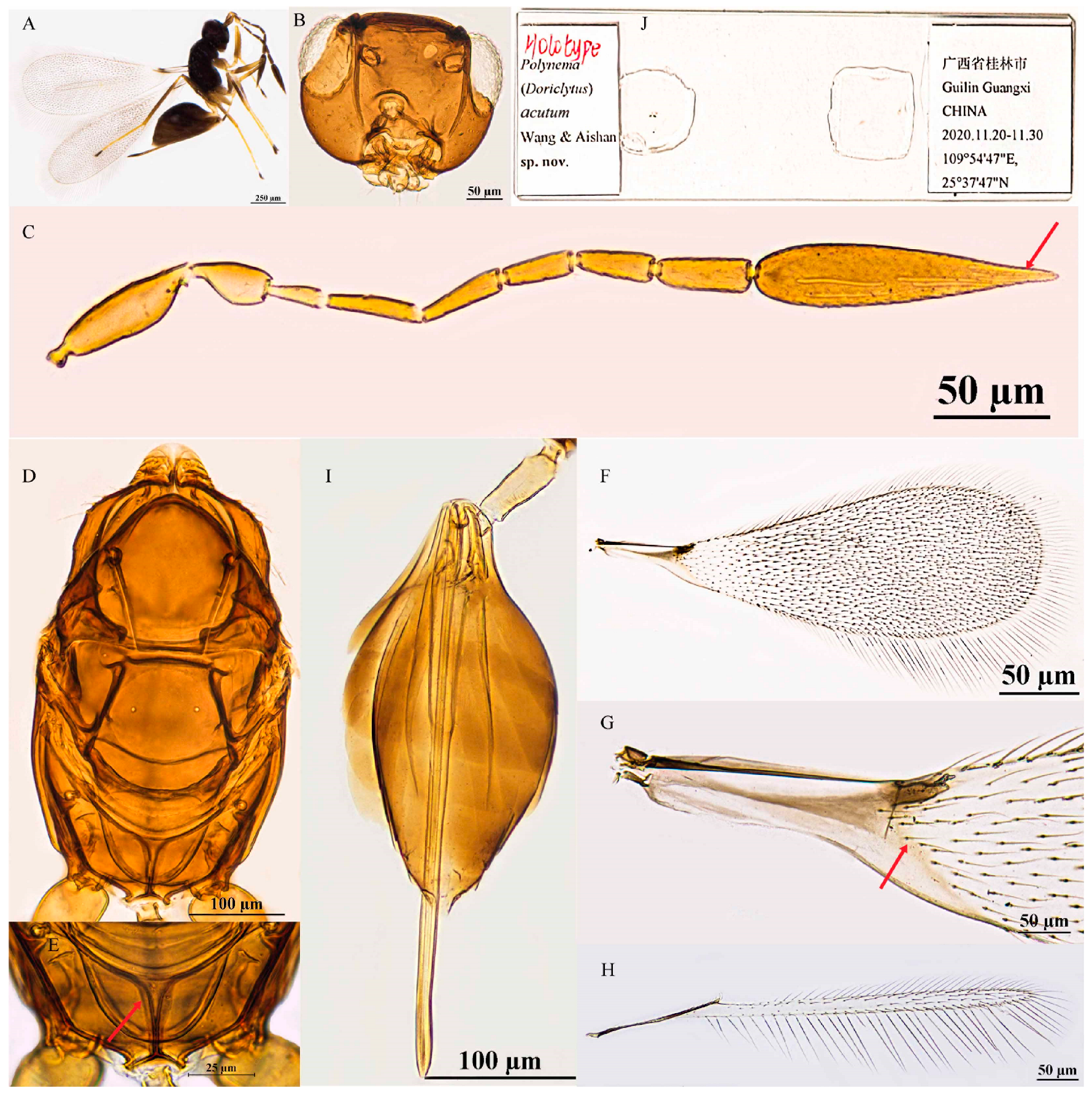
3.2.3. Polynema (Doriclytus) acutum Wang & Aishan, sp. nov.
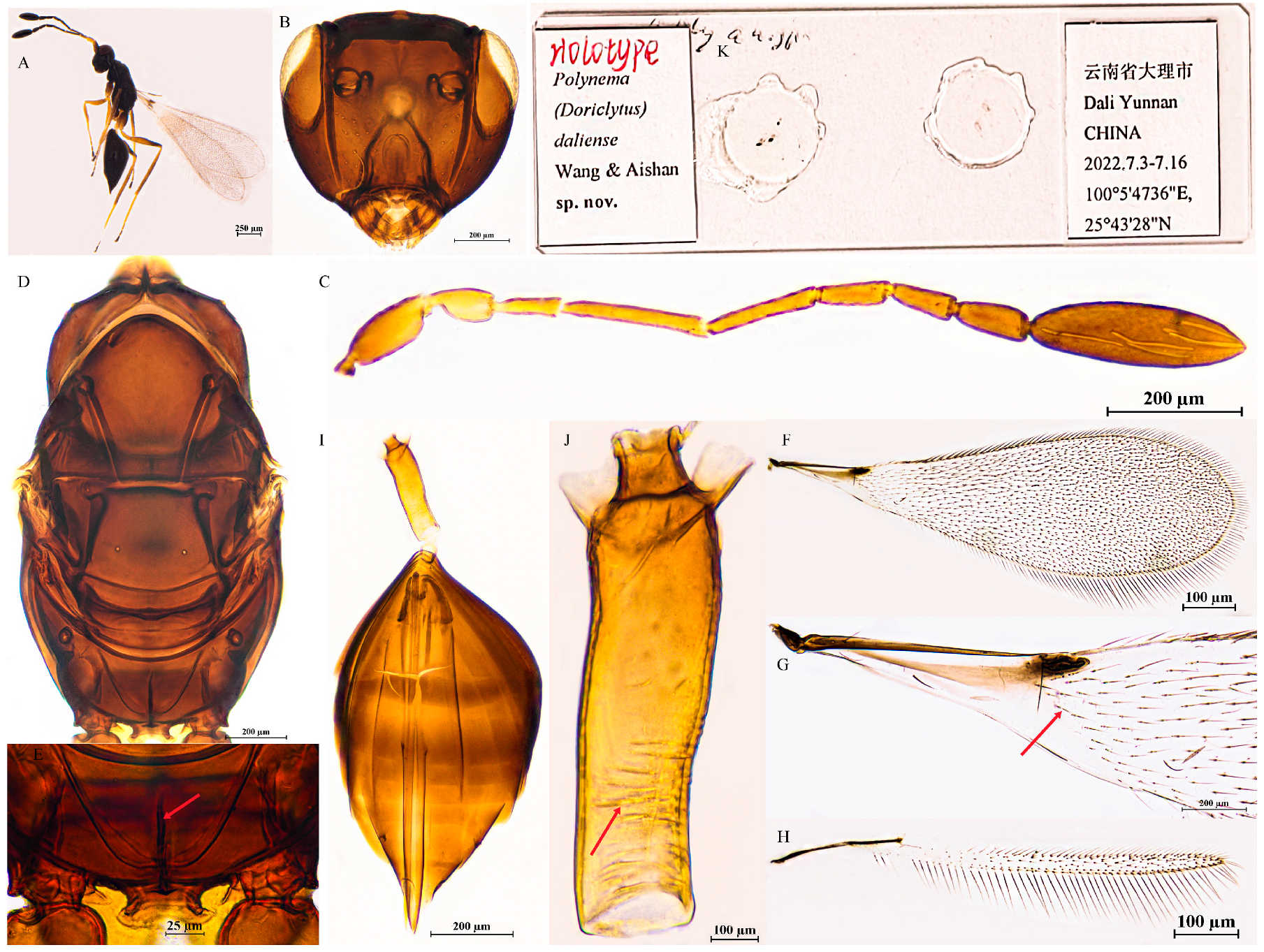
3.2.4. Polynema (Doriclytus) daliense Wang & Aishan, sp. nov.
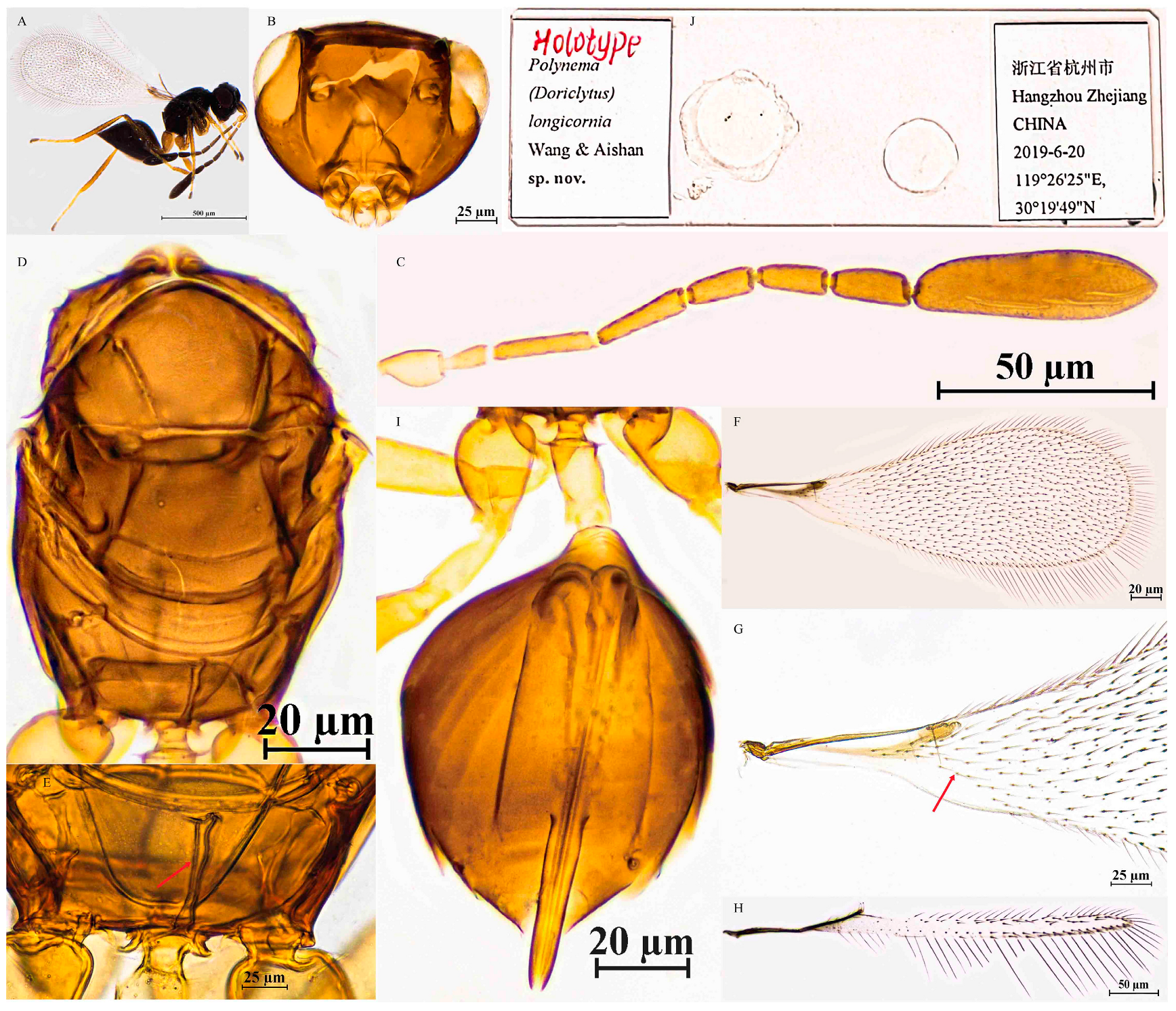
3.2.5. Polynema (Doriclytus) longicornia Wang & Aishan, sp. nov.
3.2.6. Polynema (Doriclytus) alalatum Rehmat & Anis, 2016
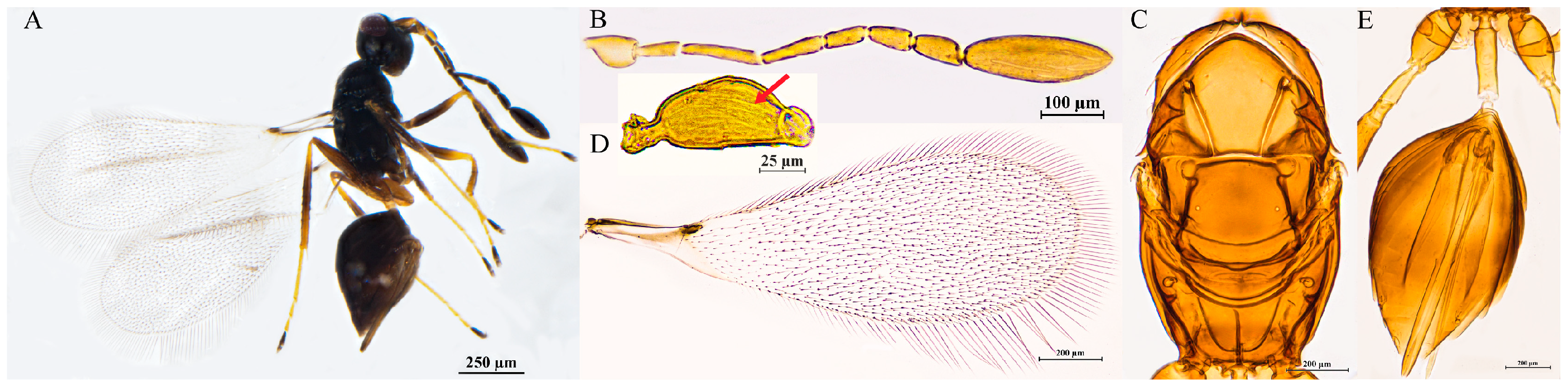
3.2.7. Polynema (Doriclytus) bicolorigastra Rehmat & Anis, 2016
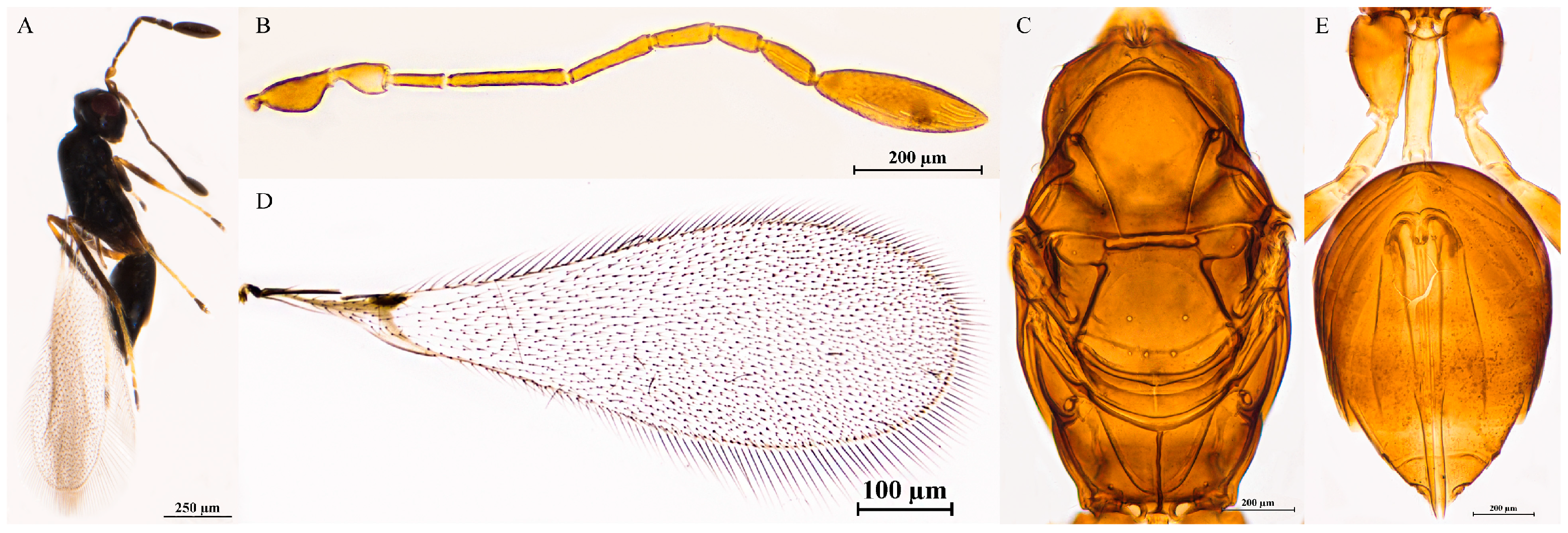
3.2.8. Polynema (Doriclytus) dhenkunde Mani & Saraswat, 1973

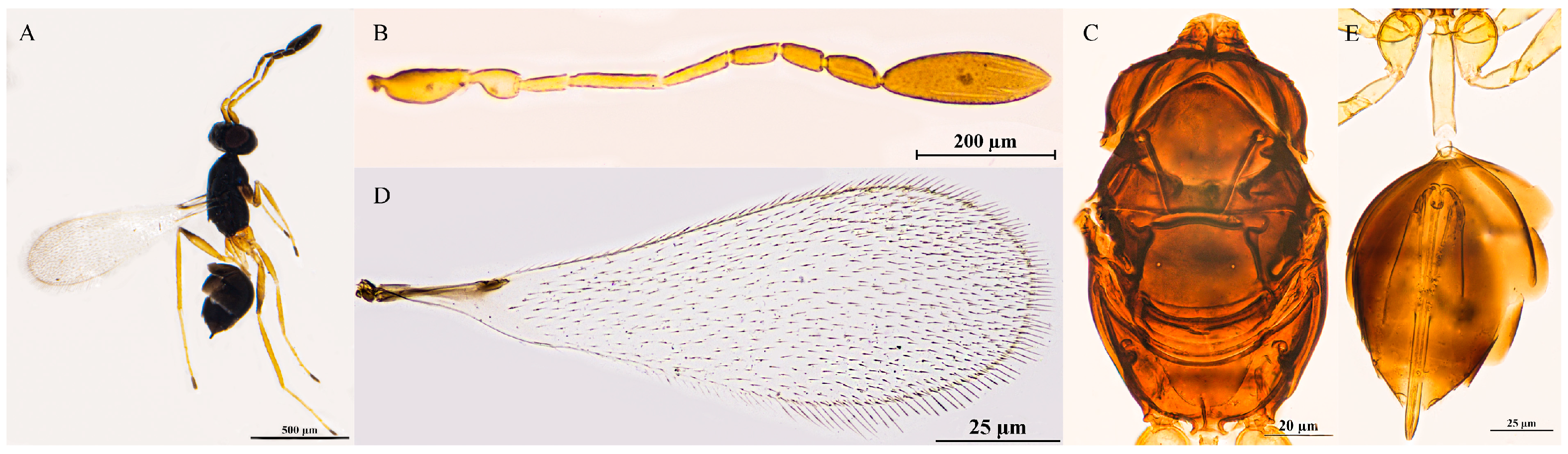
3.2.9. Polynema (Doriclytus) dunense Hayat & Anis, 1999
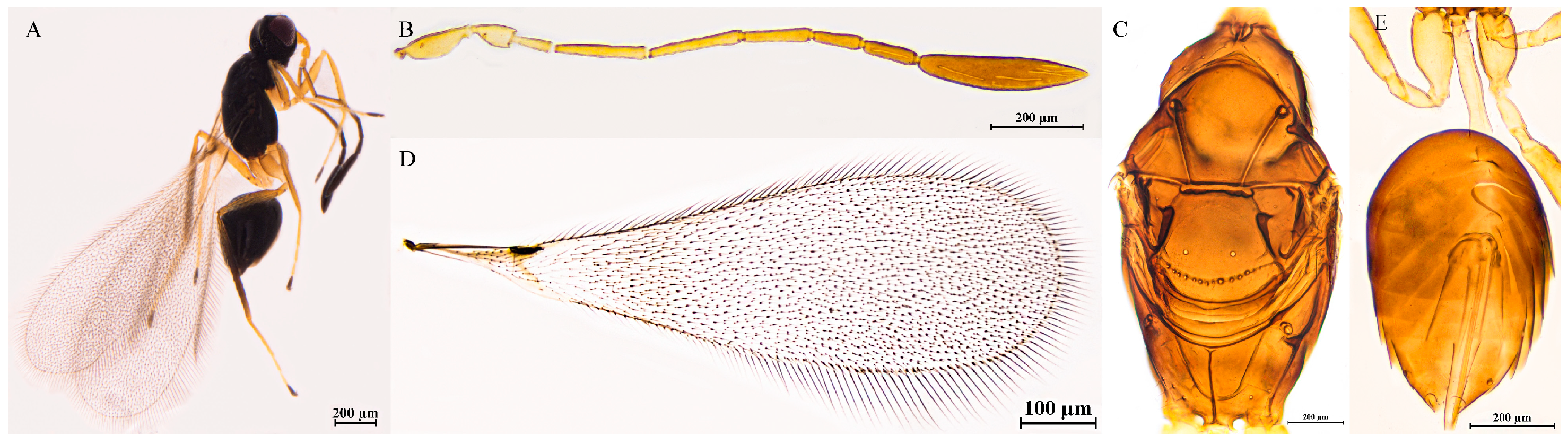
3.2.10. Polynema (Doriclytus) tyakshiense Irfan & Anis, 2023
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UCD Community. Universal Chalcidoidea Database Website. Available online: https://ucd.chalcid.org (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Aquino, D.A. Revisión del género Polynema Haliday sl (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) en Argentina y Paises Limítrofes. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata, Argentina, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Azab, S. The Mymaridae of Egypt (Chalcidoidea: Hymenoptera). Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. A Entomol. 2020, 13, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V.; Fidalgo, P. Definition of Doriclytus, stat. rev. as a subgenus of Polynema and redescription of its type species, P.(Doriclytus) vitripenne (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). Zootaxa 2006, 1362, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, A. Über der Familie der Mymariden. Linnea Entomol. 1847, 2, 195–233. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, P.T.; Zeya, S.B.; Khan, F.R.; Usman, S.U. Four new species of Polynema Haliday (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from the Al-Qassim region of Saudi Arabia. North-West. J. Zool. 2024, 20, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Anis, S.B. Description of a new species of Polynema (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Ladakh, India. Int. J. Entomol. Res. 2023, 8, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rehmat, T.; Anis, S.B. A review of Indian species of Polynema Haliday (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). J. Insect Syst. 2015, 2, 138–166. [Google Scholar]
- Schuppenhauer, M.M.; Triapitsyn, S.V. Contribution to the taxonomy of Polynema Haliday, 1833 and Stephanodes Enock, 1909 (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) of Sweden. Entomol. Tidskr. 2018, 139, 159–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sharen, G.; Aishan, Z.; Wang, J.L. Description of Doriclytus Foerster as a subgenus of Polynema Haliday from Xinjiang (Hy-menoptera:Mymaridae). Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2024, 33, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V. Taxonomic review of Polynema (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) in Australia and New Zealand, with descriptions of eight new species. Zootaxa 2021, 4915, zootaxa.4915.2.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V. Revised taxonomy of the common northern European fairyfly Polynema (Doriclytus) atratum Haliday, 1833 (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae), with fourteen new synonymies. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2021, 58, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V.; Koponen, M.; Vikberg, V.; Várkonyi, G. Taxonomy, annotated new records and a checklist of Mymaridae (Hymenoptera) of Finland, with description of a new species of Eustochus. Acta Entomol. Musei Natl. Pragae 2020, 60, 565–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugnes, F.; Bernardo, U.; Viggiani, G. An integrative approach to species discrimination in the Anagrus atomus group sensu stricto (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae), with a description of a new species. Syst. Biodivers. 2017, 15, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V.; Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Tretiakov, P.S.; Daane, K.M.; Wilson, H. Reassessment of molecular and morphological variation within the Anagrus atomus species complex (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae): Egg parasitoids of leafhoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) in Europe and North America. J. Nat. Hist. 2020, 54, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, Z.; Cao, H.X.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhu, C.D. Chinese species of the genus Pseudanaphes Noyes & Valentine (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) with description of a new species. Insects 2022, 14, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triapitsyn, S.V.; Aquino, D.A. Redescription of Polynemula, with description of a new species of Polynema (Doriclytus) from Argentina (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). Zootaxa 2008, 1818, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, K.A.; Murphy, N.P.; Sallam, N.; Donnellan, S.C.; Austin, A.D. Phylogenetics and genetic diversity of the Cotesia flavipes complex of parasitoid wasps (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), biological control agents of lepidopteran stemborers. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 63, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Hoeh, W.R.; Black, M.B.; Vrijenhoek, R.C. Conserved primers for PCR amplification of mitochondrial DNA from different invertebrate phyla. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In Nucleic Acids Symposium Series; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, C. Performance of criteria for selecting evolutionary models in phylogenetics: A comprehensive study based on simulated datasets. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Montoya, J.; Tao, Q.; Kumar, S. Using a GTR+ Γ substitution model for dating sequence divergence when stationarity and time-reversibility assumptions are violated. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, i884–i894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezard, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Splits: Species’ Limits by Threshold Statistics. Available online: http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/splits (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, M.S.; Dubey, O.P.; Kaul, B.K.; Saraswat, G.G. Memoirs of the School of Entomology: On Some Chalcidoidea from India; St. John’s College: Annapolis, MD, USA, 1973; pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao, B.R.; Hayat, M. Chalcidoidea (Insecta: Hymenoptera) of India and the adjacent countries. Part II. A catalogue of Chalcidoidea of India and the adjacent countries. Orient. Insects 1986, 20, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, M.S. The Fauna of India and Adjacent Countries, Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera). Part II; Zoological Survey of India: Calcutta, India, 1989; pp. 1381–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, M.; Anis, S.B. The Indian species of Polynema with notes on Stephanodes reduvioli (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). Orient. Insects 1999, 33, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.B.; Rehmat, T. An updated checklist of fairyflies (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Mymaridae) occurring in India. Colemania 2013, 36, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Triapitsyn, S.V. Notes and corrections on some records of Mymaridae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) from India. Biosystematica 2013, 7, 39–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Triapitsyn, S.V.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Aishan, Z. Integrative Taxonomy of Polynema (Doriclytus) (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Oriental China: Three New Species and Five New Records Revealed by Morphological and Molecular Analyses. Insects 2025, 16, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111166
Liu Y, Triapitsyn SV, Zhang D, Wang J, Aishan Z. Integrative Taxonomy of Polynema (Doriclytus) (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Oriental China: Three New Species and Five New Records Revealed by Morphological and Molecular Analyses. Insects. 2025; 16(11):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111166
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanyan, Serguei V. Triapitsyn, Dan Zhang, Jinling Wang, and Zhulidezi Aishan. 2025. "Integrative Taxonomy of Polynema (Doriclytus) (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Oriental China: Three New Species and Five New Records Revealed by Morphological and Molecular Analyses" Insects 16, no. 11: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111166
APA StyleLiu, Y., Triapitsyn, S. V., Zhang, D., Wang, J., & Aishan, Z. (2025). Integrative Taxonomy of Polynema (Doriclytus) (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) from Oriental China: Three New Species and Five New Records Revealed by Morphological and Molecular Analyses. Insects, 16(11), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16111166






