Simple Summary
Wolbachia is an endosymbiotic bacterium that infects numerous insects and crustaceans. Its ability to alter the reproduction of hosts results in incompatibilities of differentially infected individuals. Therefore, Wolbachia has been applied to suppress agricultural and medical insect pests. The European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi, is mainly distributed throughout Europe and Western Asia, and is infected with at least five different Wolbachia strains. The strain wCer2 causes incompatibilities between infected males and uninfected females, making it a potential candidate to control R. cerasi. Thus, the prediction of its spread is of practical importance. Like mitochondria, Wolbachia is inherited from mother to offspring, causing associations between mitochondrial DNA and endosymbiont infection. Misassociations, however, can be the result of imperfect maternal transmission, the loss of Wolbachia, or its horizontal transmission from infected to uninfected individuals. These are important parameters influencing the spread of infection. Here, we studied Wolbachia-mitochondrial haplotype associations in R. cerasi in two transition zones in the Czech Republic and Hungary, where wCer2 is currently spreading. Our results suggest imperfect maternal transmission only in the early phases of wCer2 invasion and no evidence of horizontal transmission of wCer2 in R. cerasi.
Abstract
The endosymbiont Wolbachia can manipulate arthropod host reproduction by inducing cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI), which results in embryonic mortality when infected males mate with uninfected females. A CI-driven invasion of Wolbachia can result in a selective sweep of associated mitochondrial haplotype. The co-inheritance of Wolbachia and host mitochondrial DNA can therefore provide significant information on the dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia invasion. Therefore, transition zones (i.e., regions where a Wolbachia strain is currently spreading from infected to uninfected populations) represent an ideal area to investigate the relationship between Wolbachia and host mitochondrial haplotype. Here, we studied Wolbachia-mitochondrial haplotype associations in the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi, in two transition zones in the Czech Republic and Hungary, where the CI-inducing strain wCer2 is currently spreading. The wCer2-infection status of 881 individuals was compared with the two known R. cerasi mitochondrial haplotypes, HT1 and HT2. In accordance with previous studies, wCer2-uninfected individuals were associated with HT1, and wCer2-infected individuals were mainly associated with HT2. We found misassociations only within the transition zones, where HT2 flies were wCer2-uninfected, suggesting the occurrence of imperfect maternal transmission. We did not find any HT1 flies that were wCer2-infected, suggesting that Wolbachia was not acquired horizontally. Our study provides new insights into the dynamics of the early phase of a Wolbachia invasion.
1. Introduction
Wolbachia are a group of maternally inherited Alphaproteobacteria that infect a wide range of nematode and arthropod species [1,2]. These endosymbionts influence the reproduction of their hosts and enhance their own spread. The most common phenotype in insects is cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI), which results in embryonic death when the sperm of an infected male fertilizes the egg of an uninfected female (unidirectional CI) or a female infected with another incompatible strain (bidirectional CI) [3]. Wolbachia is currently being used as a novel tool to control insect pest species by repressing populations due to CI and by reducing the ability to replicate pathogens in insect vector species [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Analogous to the sterile insect technique (SIT), where laboratory-reared males are sterilized prior to field releases [4], the incompatible insect technique (IIT) is based on the release of Wolbachia-infected incompatible males, which will lead to the suppression of natural pest populations. Nevertheless, models based on attributes of the strain and its host are necessary to predict the spread of the endosymbiont in field populations (e.g., [10,11]).
Wolbachia’s ability to induce unidirectional CI renders infected female hosts a reproductive advantage compared to uninfected females because infected females produce viable offspring by mating with both infected and uninfected males, whereas uninfected females only produce viable offspring by mating with uninfected males [3]. Thus, the frequency-dependent reproductive advantage of infected females results in the spread of the CI-inducing Wolbachia strain. Furthermore, the maternal transmission of the endosymbiont causes selective sweeps of associated host mitochondrial haplotypes [12,13]. Associations between Wolbachia strain and mitochondrial haplotype of its host have been studied in numerous insect species (e.g., [14,15,16,17]), including several drosophilid and tephritid fruit fly systems [12,18,19,20,21]. From these studies, almost perfect associations have been shown to result from high levels of CI-induction and nearly complete maternal transmission of Wolbachia, even when small amounts of paternal and/or horizontal transmission are present [12]. Misassociations between Wolbachia strain and host mitochondrial haplotype, however, have been found and can result from factors such as imperfect maternal transmission, loss of Wolbachia infection, and intra- and interspecific horizontal transmission [18,22]. The relationship between Wolbachia and host mitochondrial haplotype in field populations can therefore provide insights into the dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia invasion [23].
The dynamics of Wolbachia and host mitochondrial haplotype are most pronounced and best studied in ongoing selective sweeps of Wolbachia strains through natural populations (e.g., [24,25]). Diffusion equations have been used to depict Wolbachia transition zones as traveling waves, characterized by transects consisting of high to low infection frequencies [10,24,25,26,27].
The European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Linnaeus, 1758), is particularly well suited for the study of Wolbachia spread. This tephritid fly infests cherries (Prunus spp.) and honeysuckle (Lonicera spp.) and is mainly distributed throughout Europe and western Asia [28,29]. Rhagoletis cerasi is infected with at least five different Wolbachia strains, wCer1-5, whose spread is traceable on small spatial scales due to the fly’s univoltine life cycle and poor dispersal [30,31,32,33]. The CI-induction of wCer2 best explains previously reported incompatibilities among European populations of R. cerasi [34] and was further shown to induce CI when transferred into Drosophila simulans [35] and Ceratitis capitata [36]. Although wCer4 also showed evidence of CI-induction when transferred into C. capitata [36], it is less clear as to what phenotypes it, and other wCer strains, cause in R. cerasi.
European-wide surveys of wCer2 and R. cerasi mitochondrial haplotypes revealed the presence of two mitochondrial haplotypes, HT1 and HT2, across various European populations [18,36]. In wCer2-fixed regions, all flies are HT2, while in uninfected regions, all flies are HT1 [18]. Misassociations between wCer2 and HT2 were only found in the vicinity of transition zones (i.e., the forefronts of wCer2 spread where both haplotypes and infection types can be found) [18,36]. These consist of both wCer2-infected flies associated with HT1 and wCer2-uninfected flies associated with HT2. The former is best explained by intraspecific horizontal transmission from wCer2-infected to uninfected R. cerasi individuals, while the latter can arise from imperfect maternal transmission of wCer2, wherein an infected female transmits to offspring its mitochondrial haplotype but not its infection type [18,23].
In Germany, wCer2 infection frequencies follow a clear pattern, spreading from the north and south into the central region, which is wCer2-uninfected. Further collections of R. cerasi over smaller spatial scales and over multiple years showed that in transition zones wCer2 does not follow a typical gradient from high to low infection frequencies. Instead, a scattered wCer2-infection pattern was found [18,36]. In contrast to these findings, wCer2 transition zones found in the Czech Republic and Hungary show wave-like smooth gradients from high to low infection frequencies [33]. In the Czech Republic, the transition from wCer2-fixed to wCer2-uninfected populations was described within a 46-km transect from south to north. The wCer2 transition zone in Hungary showed a gradual decrease from wCer2-fixed to low infection frequencies within a 72-km west to east transect [33].
In this study, we determined the mitochondrial haplotypes of R. cerasi field populations used in [33] and characterized the wCer2-mitochondrial haplotype associations in these two transition zones. As wCer2 is perfectly associated with HT2 in populations completely invaded by wCer2, misassociations are only found in transitional populations and can be considered transient [18], representing a window in time to study the dynamics of wCer2 and its associated mitochondrial haplotype in a natural setting. The wCer2 transition zones in the Czech Republic and Hungary are unique in that they represent clear invasion fronts with smooth infection gradients [33]. This allows the study of wCer2 spread dynamics and its associated haplotypes in natural field populations.
2. Materials and Methods
In total, 881 R. cerasi samples were collected in the Czech Republic (CZ) and Hungary (HU), whose wCer2 infection frequencies have been previously published [33]. Here, we determined the mitochondrial haplotypes of these R. cerasi samples and their associations with wCer2. Each population was sampled from a single cherry tree. In transition zone CZ, 545 individuals were collected from 19 populations (CZ-1 to CZ-19). In transition zone HU, 336 individuals were collected from 12 populations (HU-1 to HU-12) (Figure 1).
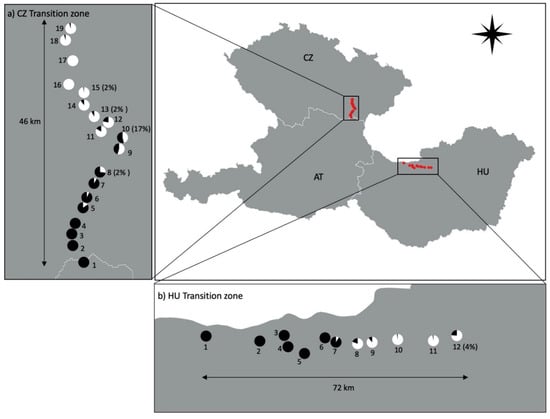
Figure 1.
The distribution of Rhagoletis cerasi mitochondrial haplotypes, HT1 and HT2, in two wCer2 transition zones within the Czech Republic (CZ), Hungary (HU) and Austria (AT). White and black pie-charts denote HT1 and HT2 frequencies, respectively. Percentages in parentheses indicate frequencies of misassociated HT1 flies infected with wCer2.
The mitochondrial haplotype of R. cerasi individuals was determined using PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism), as described by [17]. Briefly, a 546-bp fragment of the mitochondrial COI gene was amplified using the primers Pat and Dick [37]. The two mitochondrial haplotypes of R. cerasi are distinguished by a single nuclear polymorphism (SNP). RFLP-haplotype determination was performed by incubating 0.5 µL of the PCR product with 0.5 U of HaeIII (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) under 37 °C for 4 h and loaded on a 2% agarose gel. After incubation with HaeIII, haplotype HT2 is cut into a 342- and 204-bp fragment, while haplotype HT1 remains undigested (Supplementary Figure S1) [17].
The mitochondrial PCR products from a portion of samples from CZ populations, including individuals that showed Wolbachia-haplotype misassociations, were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Single strand sequencing of the COI fragment from samples showing the Wolbachia-haplotype misassociations was performed by Eurofins MWG Operon (Ebersberg, Germany). Sequence chromatograms were first inspected in ChromasLite version 2.1. (Technelysium, Brisbane, Australia), and subsequently edited in GeneRunner version 5.0. (www.generunner.net). Finally, the sequences were determined using the BLAST algorithm [38]. Information on individual haplotypes, the method used to determine the haplotypes, and Sanger sequences are found in Supplementary Table S1.
3. Results
In the majority of cases, wCer2-infected R. cerasi flies were associated with mitochondrial haplotype HT2, while wCer2-uninfected flies were associated with mitochondrial haplotype HT1. Out of the 881 flies analyzed, we found seven HT2 flies that were wCer2-uninfected and no HT1 flies that were wCer2-infected. Six of these misassociations were found within transitional populations, having both infected and uninfected individuals, whereas one individual of HT2 was found within a wCer2-uninfected population (CZ-15). In the Czech transition zone, around 1.1% of the individuals within transitional populations were wCer2-uninfected but linked with HT2. Similarly, around 0.8% of the individuals in Hungarian transitional populations were HT2 whilst being wCer2-uninfected (Figure 1).
In the Czech Republic, all flies from wCer2-fixed populations (i.e., CZ-1 to CZ-4) were assigned the mitochondrial haplotype HT2. The association of HT2 with wCer2 was perfect in populations with high wCer2 infection frequencies. To the contrary, misassociations were found in populations with low wCer2 infection frequencies. In total, five Wolbachia-haplotype misassociations were found: one in CZ-8, two in CZ-10, one in CZ-13, and one in CZ-15 (Figure 1).
In Hungary, all flies from wCer2-fixed populations (HU-1 to HU-6) were assigned the mitochondrial haplotype HT2. Two wCer2-uninfected flies were linked to HT2 and were found in HU-12 (Figure 1).
4. Discussion
The smooth gradient from high to low wCer2 infection frequencies within the Czech and Hungarian Wolbachia transition zones represent a hotspot to study the dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia spread. Here, we focused on the association between wCer2 infection and the R. cerasi mitochondrial haplotype to understand the dynamics of an ongoing selective sweep of Wolbachia. In contrast to the scattered wCer2 infection pattern previously studied in German transition zones [18,36], we can now identify in which part of the wave Wolbachia-mitochondrial haplotype misassociations are more likely to occur [33]. In accordance with the pattern observed in German wCer2 transition zones [18,36], we found wCer2-uninfected individuals associated with HT2 within populations with low wCer2 infection rates. The occurrence of wCer2-uninfected individuals associated with HT2 in wCer2-fixed populations was not found. Surprisingly, we detected HT2 even in one population that was not infected by wCer2 (CZ-15). This suggests that imperfect Wolbachia transmission or occasional losses of Wolbachia occur in the early phase of invasion in R. cerasi. Moreover, the absence of wCer2-infected HT1 flies suggests no evidence for intraspecific horizontal transmission, which contrasts previous findings in Germany [18,36].
The maternal transmission rate varies among host organisms and Wolbachia strains. Examples of high Wolbachia transmission rates include wRi of D. simulans, where transmission rates reach 95.2% [39], and in wAu of D. simulans the rate is estimated at 97.7% [25]. Similarly, we found that populations of R. cerasi show a high rate of maternal transmission through high Wolbachia-mitochondrial haplotype association rates, further supporting the presence of high CI induction. A perfect association between wCer2 and HT2 was found within populations outside the transition zone, highlighting the Wolbachia-driven selective sweep of HT2. However, within transitional populations with a low wCer2 infection frequency, we found wCer2-uninfected individuals associated with HT2. This indicates that imperfect maternal transmission and/or occasional loss of Wolbachia is occurring in the early phase of Wolbachia invasion. In transitional and wCer2-uninfected populations, females might be able to pass the misassociation to their offspring by mating with uninfected males. The likelihood of mating with uninfected males will decrease in populations with high wCer2 infection rates. Mating of wCer2 uninfected females with wCer2-infected males will result in embryonic mortality due to CI and will therefore be a dead end for individuals uninfected with wCer2 but associated with HT2 as wCer2 approaches fixation.
Wolbachia can be horizontally transferred from infected to uninfected individuals both within species [18] and between species [22,40]. Findings from German field populations of R. cerasi showed a substantial amount of wCer2-infected HT1 flies, an indication of intraspecific horizontal transmission [18,36]. In contrast, no wCer2-infected HT1 flies were found in this study. Currently, we can only speculate about the discrepancy of intraspecific horizontal transmission rates between wCer2 transition zones found in Germany and those found in the Czech Republic and Hungary. Schuler et al. [18] reported a higher incidence of wCer2-infected HT1 flies collected on honeysuckle as compared to flies collected from cherry. Since all flies analyzed in this study were collected from cherries, the host might play a crucial role. Different fruit sizes (honeysuckle being significantly smaller than cherries) might increase the likelihood of cannibalism by co-occurring larvae infesting the same fruit. Moreover, parasitoids may transfer wCer2 from infected to uninfected flies [41,42]. Since parasitation rates may vary between host forms with differentially sized host fruit [43,44,45], a lower parasitation rate in cherry-infesting flies might reflect the low number of intraspecific horizontal Wolbachia transfer in cherry flies.
Our results add on to a list of studies that highlight the problem of relying on only mitochondrial barcoding for demographic and population history inference in arthropod systems [13], as Wolbachia-driven selective sweeps of mitochondrial haplotypes will produce misleading results. Recent advances in genome sequencing [46] provide a great opportunity to reveal novel insights into the dynamics of this early-phase Wolbachia invasion on a genomic level. Based on the genome sequence data from [47], the genomic architecture of the CI trait in wCer2 [48] will help to reveal the genetic basis of CI in this naturally multiple-infected host and the interaction between different Wolbachia strains [49]. Finally, genome sequencing of the fruit fly within transitional populations will help to reveal if the invading Wolbachia strain leaves (transitional) footprints on the fly genome.
5. Conclusions
The wCer2 transition zones in the Czech Republic and Hungary present an excellent region to study the association of a spreading Wolbachia strain and its co-inherited mitochondrial haplotype. Here, we describe an almost strict association of wCer2 with mitochondrial haplotype HT2, with a few cases where HT2 flies were wCer2-uninfected. These misassociations indicate that imperfect maternal transmission occurs in early phases of Wolbachia invasion where they can further spread, but these misassociations are transient and will be eliminated as wCer2 approaches fixation. Future time-series studies on the co-inheritance of wCer2 and HT2 in these transition zones will provide a source of empirical data to test models describing the dynamics of Wolbachia-haplotype associations within an invasion front in natural populations.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4450/11/10/675/s1: Table S1: Method used for mitochondrial haplotype determination for each Rhagoletis cerasi individual accompanied by the Sanger sequence where applicable; Figure S1: Electrophoresis gel showing an example of HT1 and HT2 digestion with restriction enzyme HaeIII.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.S. and H.S.; formal analysis: V.B.; writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing: V.B., C.S., H.S., and M.S.; visualization: V.B.; project administration: C.S. and H.S.; funding acquisition: C.S. and H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF I2604-B25 and P31441).
Acknowledgments
We thank Ferenc Lakatos, Zoltan Kovacs, Josef Janoušek, and Petr Martinek for their help with sample collections and Susanne Krumböck for technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Weinert, L.A.; Araujo-Jnr, E.V.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Welch, J.J. The incidence of bacterial endosymbionts in terrestrial arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werren, J.H.; Windsor, D.M. Wolbachia infection frequencies in insects: Evidence of a global equilibrium? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werren, J.H.; Baldo, L.; Clark, M.E. Wolbachia: Master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolouli, K.; Colinet, H.; Renault, D.; Enriquez, T.; Mouton, L.; Gibert, P.; Sassu, F.; Cáceres, C.; Stauffer, C.; Pereira, R.; et al. Sterile insect technique and Wolbachia symbiosis as potential tools for the control of the invasive species Drosophila suzukii. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.; Parry, R.; Asgari, S. Effect of Wolbachia wAlbB on a positive-sense RNA negev-like virus: A novel virus persistently infecting Aedes albopictus mosquitoes and cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Walker, T.; O’Neill, S.L. Wolbachia and the biological control of mosquito-borne disease. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.L.; Barton, N.H.; Rasic, G.; Turley, A.P.; Montgomery, B.L.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Cook, P.E.; Ryan, P.A.; Ritchie, S.A.; Hoffmann, A.A.; et al. Local introduction and heterogeneous spatial spread of dengue-suppressing Wolbachia through an urban population of Aedes aegypti. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.; Moreira, L.A. Can Wolbachia be used to control Malaria? Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalou, S.; Riegler, M.; Theodarakopoulou, M.; Stauffer, C.; Savakis, C.; Bourtzis, K. Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility as a means for insect pest population control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15042–15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P. Spatially explicit models of Turelli-Hoffmann Wolbachia invasive wave fronts. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 215, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigatti, I.; McCormack, C.; Nedjati-Gilani, G.; Ferguson, N.M. Using Wolbachia for dengue control: Insights from modelling. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A.; McKechnie, S.W. Dynamics of cytoplasmic incompatibility and mtDNA variation in natural Drosophila simulans populations. Genetics 1992, 132, 713–723. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, G.D.D.; Jiggins, F.M. Problems with mitochondrial DNA as a marker in population, phylogeographic and phylogenetic studies: The effects of inherited symbionts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodandaramaiah, U.; Simonsen, T.J.; Bromilow, S.; Wahlberg, N.; Sperling, F. Deceptive single-locus taxonomy and phylogeography: Wolbachia-associated divergence in mitochondrial DNA is not reflected in morphology and nuclear markers in a butterfly species. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 5167–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.I.; Wilson, K. Male-killing Wolbachia and mitochondrial selective sweep in a migratory African insect. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, A.M.; Cook, J.M. Effects of a sex ratio-distorting endosymbiont on mtDNA variation in a global insect pest. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrdanz, R.L.; Levine, E. Wolbachia bacterial infections linked to mitochondrial DNA reproductive isolation among populations of northern corn rootworm (Coleoptera:Chrysomelidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2007, 100, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, H.; Köppler, K.; Daxböck-Horvath, S.; Rasool, B.; Krumböck, S.; Schwarz, D.; Hoffmeister, T.S.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Telschow, A.; et al. The hitchhiker’s guide to Europe: The infection dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia invasion and mitochondrial selective sweep in Rhagoletis cerasi. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenike, J.; Stahlhut, J.K.; Boelio, L.M.; Unckless, R.L. Association between Wolbachia and Spiroplasma within Drosophila neotestacea: An emerging symbiotic mutualism? Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Darsouei, R. Presence of the endosymbiont Wolbachia among some fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) from Iran: A multilocus sequence typing approach. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.; Martinez Montoya, H.; Lanzavecchia, S.B.; Conte, C.; Guillén, K.; Morán-Aceves, B.M.; Toledo, J.; Liedo, P.; Asimakis, E.D.; Doudoumis, V.; et al. Wolbachia pipientis associated with tephritid fruit fly pests: From basic research to applications. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, L.; Ayoub, N.A.; Hayashi, C.Y.; Russel, J.A.; Stahlhut, J.K.; Werren, J.H. Insight into the routes of Wolbachia invasion: High levels of horizontal transfer in the spider genus Agelenopsis revealed by Wolbachia strain and mitochondrial DNA diversity. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeap, H.L.; Rašić, G.; Endersby-Harshman, N.M.; Lee, S.F.; Arguni, E.; Le Nguyen, H.; Hoffmann, A.A. Mitochondrial DNA variants help monitor the dynamics of Wolbachia invasion into host populations. Heredity 2016, 116, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turelli, M.; Hoffmann, A.A. Rapid spread of an inherited incompatibility factor in California Drosophila. Nature 1991, 353, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriesner, P.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Lee, S.F.; Turelli, M.; Weeks, A.R. Rapid sequential spread of two Wolbachia variants in Drosophila simulans. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.H.; Kim, P.S. Modelling a Wolbachia invasion using a slow-fast dispersal reaction-diffusion approach. Bull. Math. Biol. 2013, 75, 1501–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Tang, M.; Yu, J. Wolbachia infection dynamics by reaction-diffusion equations. Sci. China Math. 2015, 58, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimiani, P. Mediterranean region. In Fruit Flies: Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control; Robinson, A.S., Hopper, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bakovic, V.; Schuler, H.; Schebeck, M.; Feder, J.L.; Stauffer, C.; Ragland, G.J. Host plant-related genomic differentiation in the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4648–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, M.; Stauffer, C. Wolbachia infections and superinfections in cytoplasmically incompatible populations of the European cherry fruit fly Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthofer, W.; Riegler, M.; Schneider, D.; Krammer, M.; Miller, W.J.; Stauffer, C. Hidden Wolbachia diversity in field populations of the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera, Tephritidae). Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3816–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustinos, A.A.; Asimakopoulou, A.K.; Moraiti, C.A.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P.; Papadopoulos, N.T.; Bourtzis, K. Microsatellite and Wolbachia analysis in Rhagoletis cerasi natural populations: Population structuring and multiple infections. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 1943–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakovic, V.; Schebeck, M.; Telschow, A.; Stauffer, C.; Schuler, H. Spatial spread of Wolbachia in Rhagoletis cerasi populations. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, e20180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boller, E.F.; Russ, K.; Vallo, V.; Bush, G.L. Incompatible races of European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera:Tephritidae), their origin and potential use in biological control. Entomol. Exp. App. 1976, 20, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, M.; Charlat, S.; Stauffer, C.; Mercot, H. Wolbachia transfer from a true fly into the real fruit fly: Investigating the outcomes of host/symbiont co-evolution. App. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schebeck, M.; Feldkirchner, L.; Stauffer, C.; Schuler, H. Dynamics of an ongoing Wolbachia spread in the European cherry fruit fly, Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects 2019, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Frati, F.; Beckenbach, A.; Crespi, B.; Liu, H.; Flook, P. Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene-sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain-reaction primers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1994, 87, 651–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, L.B.; Lipkowitz, J.R.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Turelli, M. A re-examination of Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility in California Drosophila simulans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, H.; Bertheau, C.; Egan, S.P.; Feder, J.L.; Riegler, M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Johannesen, J.; Kern, P.; Tuba, K.; et al. Evidence for a recent horizontal transmission and spatial spread of Wolbachia from endemic Rhagoletis cerasi (Diptera: Tephritidae) to invasive Rhagoletis cingulata in Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4101–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, H.; Kern, P.; Arthofer, W.; Vogt, H.; Fischer, M.; Stauffer, C.; Riegler, M. Wolbachia in parasitoids attacking native european and introduced eastern cherry fruit flies in Europe. Environ. Enthomol. 2016, 45, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Li, S.J.; Xue, X.; Yin, X.J.; Ren, S.X.; Jiggins, F.M.; Greeff, J.M.; Qiu, B.L. The intracellular bacterium Wolbachia uses parasitoid wasps as phoretic vectors for efficient horizontal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathrop, F.H.; Newton, R.C. The biology of Opius melleus Gahan, a parasite of the Blueberry Maggot. J. Agric. Res. 1933, 46, 143–160. [Google Scholar]
- Feder, J.F. The effect of parasitoids on sympatric host races of Rhagoletis pomonella (Diptera: Tephritidae). Ecology 1995, 76, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, K.; Smit, C.; Schilthuizen, M.; Beukeboom, L.W. Fitness benefits of the fruit fly Rhagoletis alternata on a non-native rose host. Oecologia 2016, 181, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.T.; Kim, J. Trends in next-generation sequencing and a new era for whole genome sequencing. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20, S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.L.; Schneider, D.I.; Klasson, L.; Janitz, C.; Miller, W.J.; Riegler, M. Parallel sequencing of Wolbachia wCer2 from donor and novel hosts reveals multiple incompatibility factors and genome stability after host transfers. Gen. Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shropshire, J.D.; Bordenstein, S.R. Two-By-One model of cytoplasmic incompatibility: Synthetic recapitulation by transgenic expression of cifA and cifB in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Klasson, L.; Näslund, K.; Bourtzis, K.; Andersson, S.G. Comparative genomics of Wolbachia and the bacterial species concept. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).